Technological advancement is constantly evolving, and it is also developing in the mental health field. Various applications, often based on virtual reality, have been implemented to carry out psychological assessments and interventions, using innovative human–machine interaction systems. In this context, the LEAP Motion sensing technology has raised interest, since it allows for more natural interactions with digital contents, via an optical tracking of hand and finger movements.
- LEAP Motion
- hand movement
- virtual reality
- neurodevelopmental disorders
- neurocognitive disorders
- attention-deficit hyperactivity disorder
- dementia
- mild cognitive impairment
1. Introduction
Growing attention has been given to technology-based tools, and researchers are increasingly analyzing their potential to contribute to mental health services [1]. Recently, different technologies have been included in mental healthcare delivery, and this has promoted a reflection on innovative care models that can reach people who might not have access to services [2]. Studies in this field also shed light on the recently developed LEAP Motion technology. The LEAP Motion controller is a highly compact and affordable USB motion capture device with two cameras and three infrared LEDs (Figure 1—left side). Thanks to the illumination of the surrounding space, the device captures hand gestures at a one-meter distance with a mean accuracy of 0.7 mm [3]. A tracking algorithm allows us to estimate the position and orientation of hands and fingers that are directly visible in a three-dimensional virtual representation [4]. In this way, data coming from the LEAP Motion controller allow users to interact within a virtual environment in a touchless way, by using natural hand gestures as input commands [4] (Figure 1—right side).
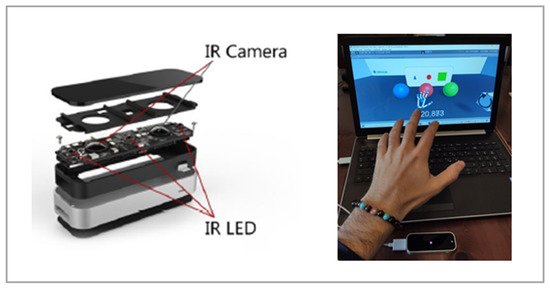
The LEAP Motion Software Development Kit recognizes simple movements such as swipe, tapping, grabbing, and circular gestures, making it possible to manipulate virtual objects by grasping and placing them [4]. It must be noted that the tracking quality can be altered by too strong or poor illumination of the room and that occluded parts of the hand cannot be traced by the device, even if it can estimate conventional movements [4].
Touchless interaction with small hand gestures could offer opportunities for people with disabilities [5]. Indeed, this kind of user interface is broadly used in gaming but also in assistive technologies, as they are able to identify movements of the body, thus valuable for people with impairments that prevent them from using touch interfaces [6].
Moreover, research also shows the benefits of gesture interaction in populations with developmental disorders, thanks to the possibility to promote motor skills as well as cognitive and social ones in monitored virtual environments that can reproduce real settings [7].
For these reasons, motion capture systems, such as Microsoft’s Kinect, have already demonstrated their usefulness in supporting physical rehabilitation [8,9] and intervention in clinical populations with specific needs [10,11]. However, such systems typically do not allow for the development of low-cost custom applications. The LEAP technology can overcome this limitation, by enabling immediate communication with freeware graphics engines. This has led researchers worldwide to develop a whole series of activities ex novo [12,13,14,15,16].
This technology is easily accessible by populations with different levels of technological expertise and could be used for gamified activities, which are appreciated, for instance, by children [17].
In general, playing, recreational programs [18,19], and virtual reality (VR) activities are often used by hospitals to support people in reducing their fear, distress, and the intensity of perceived pain in various medical procedures [20,21,22]. However, virtual gamified activities can not only be useful for distraction but also can offer a means to assess some psychological dimensions of users [23]. For instance, the use of virtual reality has recently been proposed to battle social isolation in institutionalized elderly people in residential structures, with positive effects regarding the reduction in loneliness [24].
With specific regard to the LEAP Motion technology, researchers have used it to project and implement interventions for neurodevelopmental and neurocognitive disorders that are of interest in this paper.
Neurodevelopmental disorders are a group of disorders characterized by the disorder onset in the developmental period. Indeed, the disorders often manifest before entering grade school, and they are defined by developmental deficits that cause impairments of personal, occupational, social, and academic functioning. Instead, the neurocognitive disorders include disorders characterized by core clinical deficits in cognitive functions. They are not developmental deficits but acquired, indeed, the cognition impairment is not present from birth or very early life, it rather constitutes a decline from a previous level of functioning [25].
Among neurodevelopmental disorders there are autism spectrum disorder and attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Autism spectrum disorder (ASD) is characterized by persistent deficits in social communication and interaction skills as well as repetitive and restricted behavior patterns, interests, and activities. Communication and interaction impairment are shown in different contexts including socio-emotional reciprocity, nonverbal communicative behaviors, and in developing, understanding, and maintaining relationships. Stereotypy can be found in motor movements, use of objects, and speech; inflexible adherence to routines and hyper- or hypo-reactivity to sensory input are other characteristics. The spectrum integrates four pervasive developmental disorders that were considered distinct diagnoses in the DSM-IV: Asperger’s disorder, autistic disorder, childhood disintegrative disorder, and pervasive developmental disorder are not otherwise specified. Prevalence in the U.S. and non-U.S. countries is around 1% of the population [25]. Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is characterized by persistent symptoms of inattention, impulsivity, and/or hyperactivity that interfere with functioning. Inattention may manifest in having difficulty sustaining focus, straying from activities, and being disorganized, for example. Impulsivity is defined by precipitous actions realized without forethought and potentially hurting the person. It may display in deciding without considering consequences and having socially intrusive behaviors. Hyperactivity is shown with excessive and inappropriate motor activity, resulting in extreme restlessness or also talkativeness. In the general population, attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder is more frequent in boys than in girls. ADHD seems to occur across cultures in about 5% of children and about 2.5% of adults [25].
Among neurocognitive disorders there are major and mild neurocognitive disorders. The major neurocognitive disorder is introduced in DSM-5 as an alternative term to dementia. It is characterized by a significant cognitive decline in one or more cognitive domains including complex attention, learning, language, memory, executive function, perceptual–motor, or social cognition. The cognitive deficits interfere with independence in everyday activities for which the person needs assistance, at least in complex instrumental ones. The maintenance of independent functioning distinguishes the mild and major neurocognitive disorders. Indeed, the mild neurocognitive disorder is characterized by a modest cognitive decline in the same cognitive domains, but cognitive impairment does not interfere with independent functioning in everyday activities [25]. Here, daily tasks become more laborious, and the person needs compensatory strategies [26]. Mild neurocognitive disorder represents a framework for the commonly used diagnosis of mild cognitive impairment (MCI) [26]. Estimates of prevalence for dementia—congruent with major neurocognitive disorder—are about 1–2% at 65 years and 30% by 85 years, while for mild cognitive impairment—congruent with mild neurocognitive disorder—are variable, from 2 to 10% at 65 years and 5 to 25% by 85 years [25].
2. Objectives of LEAP-Motion-Based Interventions
Psychological interventions performed so far with LEAP Motion have had different specific purposes, depending on the nature of the clinical condition considered. However, recurring objectives have typically included the evaluation and/or the enhancement of deficient areas.
Protocols for neurodevelopmental disorders have been aimed to promote, above all, psychomotor and psychosocial rehabilitation in contexts that stimulate learning. Concerning ADHD, interventions have targeted training of sustained and focalized attention, as well as hand–eye coordination [34,48]. This is because ADHD is characterized by an attention-deficit, often linked to fine motor impairments and visuo-spatial skills difficulties, which also have consequences on the learning process [34].
Similarly, ASD interventions have been focused on the improvement of fine motor skills and visual motor integration, fostering attention and motor control [14,37,38,39,40,41], as these functions have been found to be commonly problematic [37]. Learning difficulties have been supported too [35,36]. Additionally, socialization, communication, and independence have been encouraged by specific interventions [15,16,42], given the persistent deficits displayed.
Interventions for neurocognitive disorders typically have targeted cognitive screening, assessment of the impairment, and cognitive rehabilitation. In dementia, the core goals have concerned the evaluation of executive functions and the exercise of everyday activities associated with memory stimulation [44,45,47]. Likewise, in MCI, the cognitive performance has been assessed, and the action impairment has again been the focal point of intervention [23,43,46]. Indeed, declines in these domains are considered defining characteristics of this kind of disorder [49].
3. Protocols of LEAP-Motion-Based Interventions
Interactivity, immersivity, and multi-sensory stimulation are keywords in designing interventions for both neurodevelopmental and neurocognitive disorders. Indeed, LEAP Motion has been introduced in gamified virtual environments for engaging users to complete particular tasks, specifically implemented to assess or strengthen impaired functions. The following sections describe the protocols.
Protocols in neurodevelopmental disorders: ADHD and ASD.
Protocols in neurodevelopmental disorders have been based on the gamified manipulation of virtual objects and multisensory learning.
Hand–eye coordination and fine motor skills have been among the pivotal areas targeted in studies on ADHD. Garcia-Zapirain et al. [48] addressed them in a dual system for the rehabilitation of cognitive functions of children. Using an eye-tracker and LEAP Motion, participants could interact with an arithmetic gamified application and perform operations with numbers displayed on virtual flower’s petals. Users could introduce the correct solution using the eye gaze and the hands, by stretching the same number of fingers as the number of the result. The main outcomes showed that this hand–eye coordination exercise helped to improve users’ skills and attention, whereas the natural interaction devices proved to be engaging alternatives to handwriting or other kinds of interfaces. The underlying idea is that learning requires the interaction of different sensory modalities with activities that stimulate not only visual analysis and cognition, but also physical movements. This is also suggested by Capelo et al. [34] who used LEAP Motion in a multisensory virtual game, in which participants had to place different geometric figures (i.e., blocks, cubes, spheres) in color-matching containers. The authors found an increase in concentration and motivation levels, in a natural and entertaining interaction. Besides, the game promoted relaxation when children interacted with LEAP Motion because the device turned out to be easy to use.
Zhu et al. [38] implemented two similar LEAP-Motion-based games for children with ASD. In the first one, the task was to grasp and put some balls in boxes of the same color, while in the second one, users had to match fruits to some sticks. Despite the small sample size, the authors reported an improvement in fine motor skills and recognition, with the achievement of 100% accuracy in completing the task. Cai et al. [37] replicated the procedure and confirmed the aforementioned enhancements, underlining also a learning transfer of skills and rules. In particular, abilities such as looking at the hands and objects and moving the gaze with them were increased by the game. The author attributed this result to a probable combination of comprehension of the task rules together with the improvement of fine motor skills and recognition in interacting with LEAP Motion. As stated by the authors, this is one of the early attempts to investigate the effect of using gesture-based games for developing such skills in children with ASD.
Furthermore, even Tang et al. [39] considered LEAP Motion as a useful tool in order to train fine motor skills, especially because of its portability. In a first pilot study, they proposed a drawing game [39], whereas in a second study, they investigated an interaction with a domestic environment and in a zoo thanks to a word–image pairing task [39]. The results underlined high levels of sustained attention and showed that engagement with stimulating tasks, which was noticed with minimum training, made children practice specific movements, allowing them to develop motor control and learning towards more complex motor patterns. The authors also reported that parents and caregivers were involved, they noticed their child’s enduring attentiveness and commitment, and this could probably increase the possibility to extend the training at home, contributing to consolidating the learning.
Recently, Tang et al. [40] introduced LEAP Motion in a drum-playing game, observing that it can promote an entertaining learning approach. They also found that the acceptability of the application depended on the task being natural and that the children’s engagement was not influenced by the severity of the disorder.
Syahputra et al. [14] tried to train attention and focus relying on the abilities of children to move virtual objects, in particular collecting coins, while manipulating an item in four labyrinths of increasing difficulty. As a result, LEAP Motion was deemed able to exercise focusing in children.
Likewise, Rahmadiva et al. [41] addressed the focus of children with ASD and their social skills. They described multiple games, including a color-matching game with balls and boxes; a similar one, with fish and containers in a virtual underwater world; an activity of movement across virtual streets following signs and signals to meet virtual people; a game of item selection according to the gaze direction of a virtual character. The results indicated that participants were engaged and that LEAP Motion could be employed as a device in virtual settings for children with autism, even if its use as a means of rehabilitation requires practice.
To teach visual matching skills to students with ASD, Hu et al. [36] proposed an innovative LEAP-Motion-based computer-assisted instruction (CAI) approach. This was compared to a traditional teacher-implemented instruction (TII) approach in a task of daily item matching. Results showed that the innovative CAI was more effective in teaching the target skills to students with ASD, it showed to be more engaging, and some participants achieved a higher level of accuracy during the intervention with it. The authors concluded that it could promote their independence and learning. Hu and Han [35] investigated the same procedure and confirmed the aforementioned outcomes, underlining high task engagement and the maintenance of the acquired skills for three months. Nevertheless, Hu et al. [36] also observed some low accuracy issues because the hand-gesture recognition showed drops with young children’s small hands.
Other studies have been focused on social skills, developing collaborative virtual environments (CVE) with LEAP Motion for children with ASD. Zhao et al. [15,16] designed a series of collaborative games, aiming to foster socialization and communication. Specifically, they implemented a puzzle, a collection, and a delivery game, which required two users to spend an equal and coordinated effort, in order to match, move, and place virtual objects, usually across obstacles. To complete the task, they had to control a virtual tool with two handles, designed for a natural and more immersive experience. Results showed improvements in children’s engagement and motivation, as well as an increase in cooperation patterns and growing spontaneous communication.
Halabi et al. [42] included LEAP Motion and other devices in a virtual-reality-based system aiming to improve the social performance of children with ASD. They proposed a virtual school setting that involved the user in greetings and conversations with a teacher avatar. Usability studies showed that the system had a positive impact on communication skills.
4. Protocols in Neurocognitive Disorders: Dementia and MCI
5. Background for LEAP-Motion-Based Interventions
6. Technology Weaknesses and Future Challenges
Alongside positive impact outcomes, some technology weaknesses have been reported. Accuracy issues have been noted in LEAP Motion tacking ability; particularly, it has been found to be weaker when the hand is positioned perpendicularly to the device, and to be influenced by light [45]. Moreover, some studies reported negative feedback addressing LEAP Motion lacking sensitivity with younger children’s hands that were too small to be correctly detected [15,36]. This led to their exclusion from the study or to a sub-optimal fit to its usage.
Thence, future modifications would be needed to adjust its abilities in order to also fit with children’s characteristics, thus supporting not only a better game experience but also an improved validity in studies including it.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijerph18084006
