The environment and the human genome are closely entangled and many genetic variations that occur in human populations are the result of adaptive selection to ancestral environmental (mainly dietary) conditions. However, the selected mutations may become maladaptive when environmental conditions change, thus becoming candidates for diseases. Hereditary hemochromatosis (HH) is a potentially lethal disease leading to iron accumulation mostly due to mutations in the HFE gene. Indeed, homozygosity for the C282Y HFE mutation is associated with the primary iron overload phenotype. However, both penetrance of the C282Y variant and the clinical manifestation of the disease are extremely variable, suggesting that other genetic, epigenetic and environmental factors play a role in the development of HH, as well as, and in its progression to end-stage liver diseases. Alcohol consumption and dietary habits may impact on the phenotypic expression of HFE-related hemochromatosis. Indeed, dietary components and bioactive molecules can affect iron status both directly by modulating its absorption during digestion and indirectly by the epigenetic modification of genes involved in its uptake, storage and recycling. Thus, the premise of this review is to discuss how environmental pressures led to the selection of HFE mutations and whether nutritional and lifestyle interventions may exert beneficial effects on HH outcomes and comorbidities.
- Hereditary hemochromatosis
- HFE
- iron metabolism
- polyphenols
- vitamins
- miRNAs
- insulin signaling
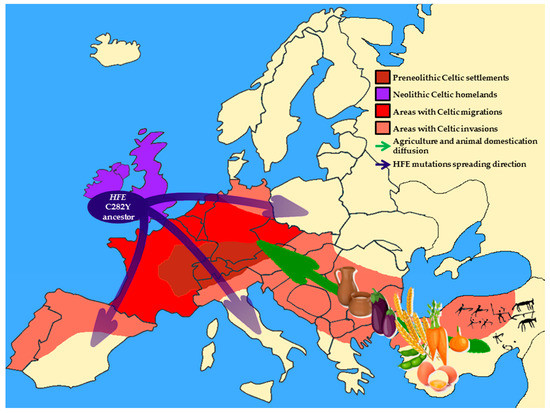
From the Environment to Genome: When Diet and Lifestyle May Change Our Genes
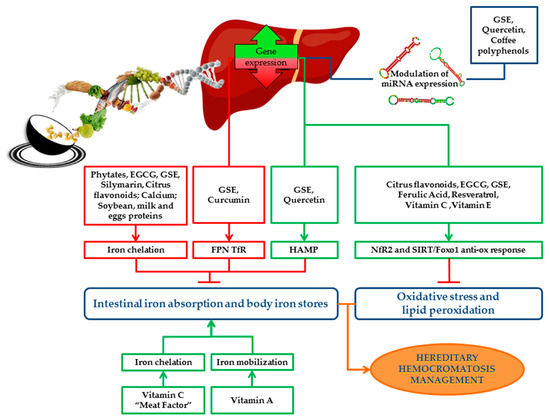
Going Back to Genome: How to Change the Environment to Treat the Disease
Alcohol Consumption
Dietary Iron Sources: Heme and Non-Heme Dietary Iron
Insulin Resistance and Iron Homeostasis
Role of Bioactive Compounds in Iron Metabolism
Dietary Inhibitors of Iron Absorption: Phytates, Polyphenols, Calcium and Milk Soybean and Egg Proteins
Phytates
Polyphenols
Calcium
Proteins
Dietary Enhancer of Iron Absorption: Vitamins and “Meat Factor”
Vitamins
Muscle Tissues from Meat, Fish and Poultry: The “Meat Factor” Effect
Prevention of Detrimental Effects of Iron-Induced Oxidative Stress: Antioxidants
Vitamin E
Phenolic Antioxidants: Flavonoids, Ferulic acid and Resveratrol
| Molecules | Source | Action on Iron Absorption | Mechanism of Action | Evidence in HH Patients or Animal Models | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vitamin C | Mineral | Antioxidant/enhancer | Redox/chelation | Reduction of iron stores | [48] |
| Phytates | Plants | Inhibition | Chelation | Improvement of iron-induced oxidative stress and liver injury in animal models | [80] |
| Polyphenols | Plants | Inhibition | Chelation | Reduction of iron absorption and of the frequency of phlebotomies | [94] [99] |
| Calcium | Mineral | Inhibition | Reducing iron uptake | Not investigated | |
| Soybean, milk and egg proteins | Animal | Inhibition | Unknown | Reduction of serum ferritin | [114] |
| Vitamin A | Mineral | Enhancer | Hepcidin-dependent upregulation of hepatic Hamp and duodenal Fpn | Vitamin A deficiency reported in HH | [119] [120] |
| Vitamin E | Mineral | Antioxidant | Scavenge ROS protecting membranes from lipid peroxidation | Vitamin E deficiency reported in HH | [160] [161] [162] [163] [164] [165] [166] [167] [168] |
| “Meat factor” | Animal | Enhancer | Chelation | Not investigated | |
| Orange/bergamot flavonoid-rich extracts | Plants | Antioxidant | Chelation of iron and reduction of ROS | Not investigated | [169] |
| EGCG | Plants | Antioxidant/inhibitor | Chelation, reduction of basolateral iron export and activation of Nrf2 in Caco-2 and in human mesenchymal stem cells | Not investigated | [170][171][172] |
| GSE | Plants | Antioxidant/inhibitor | Chelation, reduction of basolateral iron export in Caco-2 | Not investigated | [173] |
| Curcumin | Plants | Antioxidant | Reduction of iron content of liver, spleen and bone marrow; activation TfR-1 and IRP, repression of hepatic ferritin and hepcidin synthesis | Not investigated | [174] |
| Ferulic acid | Plants | Antioxidant | Reduction of liver damage by increasing hepatic antioxidants and mitochondrial membrane potential | Not investigated | [175][176] |
| Resveratrol | Plants | Antioxidant | Upregulation of SIRT1 expression and activation of FOXO1-dependent anti-oxidant response | Not investigated | [177][178] |
Epigenetic Modifiers of HFE: miRNAs-Nutrients Interaction in the Modulation of HH Phenotype
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms21103505
References
- Antonello Pietrangelo; Hereditary Hemochromatosis: Pathogenesis, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Gastroenterology 2010, 139, 393-408.e2, 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.06.013.
- Tomas Ganz; Systemic Iron Homeostasis. Physiological Reviews 2013, 93, 1721-1741, 10.1152/physrev.00008.2013.
- Brissot, P.; Pietrangelo, A.; Adams, P.C.; de Graaff, B.; McLaren, C.E.; Loreal, O.; Haemochromatosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2018, 4, 18016, 10.1038/nrdp.2018.16.
- Luisa Salter-Cid; Anders Brunmark; Yuanhao Li; Didier Leturcq; Per A. Peterson; Michael R. Jackson; Young Yang; Transferrin receptor is negatively modulated by the hemochromatosis protein HFE: Implications for cellular iron homeostasis. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1999, 96, 5434-5439, 10.1073/pnas.96.10.5434.
- Alberto Piperno; Sara Pelucchi; Raffaella Mariani; Inherited iron overload disorders.. Translational Gastroenterology and Hepatology 2020, 5, 25-25, 10.21037/tgh.2019.11.15.
- Robert E. Fleming; Robert S. Britton; Iron Imports. VI. HFE and regulation of intestinal iron absorption. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 2006, 290, G590-G594, 10.1152/ajpgi.00486.2005.
- John N. Feder; Andreas Gnirke; W. Thomas; Z. Tsuchihashi; D.A. Ruddy; A. Basava; F. Dormishian; R. Domingo; M.C. Ellis; A. Fullan; et al. A novel MHC class I–like gene is mutated in patients with hereditary haemochromatosis. Nature Genetics 1996, 13, 399-408, 10.1038/ng0896-399.
- P Holmström; J Marmur; G Eggertsen; M Gåfvels; Per Stal; Mild iron overload in patients carrying the HFE S65C gene mutation: a retrospective study in patients with suspected iron overload and healthy controls. Gut 2002, 51, 723-730, 10.1136/gut.51.5.723.
- Catherine Mura; Gérald Le Gac; Odile Raguénès; Anne-Yvonne Mercier; Alain Le Guen; Claude Férec; Relation between HFE Mutations and Mild Iron-Overload Expression. Molecular Genetics and Metabolism 2000, 69, 295-301, 10.1006/mgme.2000.2981.
- Carles De Diego; Maria José Murga; Pedro Martínez-Castro; Frequency ofHFEH63D, S65C, and C282Y Mutations in Patients with Iron Overload and Controls from Toledo, Spain. Genetic Testing 2004, 8, 263-267, 10.1089/gte.2004.8.263.
- Adams, P.C.; Reboussin, D.M.; Barton, J.C.; McLaren, C.E.; Eckfeldt, J.H.; McLaren, G.D.; Dawkins, F.W.; Acton, R.T.; Harris, E.L.; Gordeuk, V.R; et al. Hemochromatosis and iron-overload screening in a racially diverse population. New England Journal of Medicine 2005, 352, 1769-1778, 10.1056/NEJMoa041534.
- Merryweather-Clarke, A.T.; Pointon, J.J.; Jouanolle, A.M.; Rochette, J.; Robson, K.J.; Geography of HFE C282Y and H63D mutations. . Genet. Test. 2000, 4, 183-198, 10.1089/10906570050114902.
- Raha-Chowdhury, R.G.J. . Localization, allelic heterogeneity, and origins of the hemochromatosis gene. In Hemochromatosis: Genetics, Pathophysiology, Diagnosis and Treatment;; Barton, J.C.E.C., Ed, Eds.; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, 2000; pp. 75-95.
- Distante, S.; Robson, K.J.; Graham-Campbell, J.; Arnaiz-Villena, A.; Brissot, P.; Worwood, M.; The origin and spread of the HFE-C282Y haemochromatosis mutation.. Hum. Genet. 2004, 115, 269–279, 10.1007/s00439-004-1152-4.
- Remko S. Kuipers; Martine F. Luxwolda; D. A. Janneke Dijck-Brouwer; S. Boyd Eaton; Michael A. Crawford; Loren Cordain; Frits A. J. Muskiet; Estimated macronutrient and fatty acid intakes from an East African Paleolithic diet. British Journal of Nutrition 2010, 104, 1666-1687, 10.1017/s0007114510002679.
- Loren Cordain; S B Eaton; J Brand Miller; N Mann; K Hill; The paradoxical nature of hunter-gatherer diets: meat-based, yet non-atherogenic. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2002, 56, S42-S52, 10.1038/sj.ejcn.1601353.
- Richard F. Hurrell; Influence of Vegetable Protein Sources on Trace Element and Mineral Bioavailability. The Journal of Nutrition 2003, 133, 2973S-2977S, 10.1093/jn/133.9.2973s.
- Naugler, C; Hemochromatosis: A Neolithic adaptation to cereal grain diets.. Med. Hypotheses 2008, 70, 691-692, 10.1016/j.mehy.2007.06.020.
- Pennington, J.A.; Wilson, D.B.; Young, B.E.; Johnson, R.D.; Vanderveen, J.E.; Mineral content of market samples of fluid whole milk.. J. Am. Diet. Assoc 1987, 87, 1036-1042, .
- Ekhard E. Ziegler; Consumption of cow's milk as a cause of iron deficiency in infants and toddlers. Nutrition Reviews 2011, 69, S37-S42, 10.1111/j.1753-4887.2011.00431.x.
- Jean-Pierre Bocquet-Appel; When the World's Population Took Off: The Springboard of the Neolithic Demographic Transition. Science 2011, 333, 560-561, 10.1126/science.1208880.
- Samuli Helle; Jon E. Brommer; Jenni E. Pettay; Virpi Lummaa; Matti Enbuske; Jukka Jokela; Evolutionary demography of agricultural expansion in preindustrial northern Finland. Proceedings of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2014, 281, 20141559-20141559, 10.1098/rspb.2014.1559.
- Srdjan Denic; Mukesh M. Agarwal; Nutritional iron deficiency: an evolutionary perspective. Nutrition 2007, 23, 603-614, 10.1016/j.nut.2007.05.002.
- M. A. V. Bokhoven; C. T. B. M. V. Deursen; D. W. Swinkels; Diagnosis and management of hereditary haemochromatosis. BMJ 2011, 342, c7251-c7251, 10.1136/bmj.c7251.
- Beutler, E.; Felitti, V.J.; Koziol, J.A.; Ho, N.J.; Gelbart, T.; Penetrance of 845G--> A (C282Y) HFE hereditary haemochromatosis mutation in the USA.. Lancet 2002, 359, 211-218, 10.1016/S0140-6736(02)07447-0.
- Katrina J. Allen; Lyle Gurrin; Clare C. Constantine; Nicholas J. Osborne; Martin B. Delatycki; Amanda Nicoll; Christine E. McLaren; Melanie Bahlo; Amy Nisselle; Chris Vulpe; et al. Iron-Overload–Related Disease inHFEHereditary Hemochromatosis. New England Journal of Medicine 2008, 358, 221-230, 10.1056/nejmoa073286.
- Linda M. Fletcher; Jeannette L. Dixon; David M. Purdie; Lawrie W. Powell; Darrell H.G. Crawford; Excess alcohol greatly increases the prevalence of cirrhosis in hereditary hemochromatosis. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 281-289, 10.1053/gast.2002.30992.
- Daniel F. Wallace; V. Nathan Subramaniam; Co-factors in liver disease: The role of HFE-related hereditary hemochromatosis and iron. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - General Subjects 2009, 1790, 663-670, 10.1016/j.bbagen.2008.09.002.
- Virginie Scotet; Marie-Christine Mérour; Anne-Yvonne Mercier; Brigitte Chanu; Thérèse Le Faou; Odile Raguénes; Gérald Le Gac; Catherine Mura; Jean-Baptiste Nousbaum; C. Férec; et al. Hereditary hemochromatosis: effect of excessive alcohol consumption on disease expression in patients homozygous for the C282Y mutation.. American Journal of Epidemiology 2003, 158, 129-134, 10.1093/aje/kwg123.
- Loreal, O.; Deugnier, Y.; Moirand, R.; Lauvin, L.; Guyader, D.; Jouanolle, H.; Turlin, B.; Lescoat, G.; Brissot, P.; . Liver fibrosis in genetic hemochromatosis. Respective roles of iron and non-iron-related factors in 127 homozygous patients. . J. Hepatol. 1992, 16, 122–127, 10.1016/s0168-8278(05)80104-7.
- P C Adams; S Agnew; Alcoholism in hereditary hemochromatosis revisited: Prevalence and clinical consequences among homozygous siblings. Hepatology 1996, 23, 724-727, 10.1002/hep.510230411.
- Duygu Dee Harrison-Findik; Denise Schafer; Elizabeth Klein; Nikolai A. Timchenko; Hasan Kulaksiz; Dahn Clemens; Evelyn Fein; Billy Andriopoulos; Kostas Pantopoulos; John Gollan; et al. Alcohol Metabolism-mediated Oxidative Stress Down-regulates Hepcidin Transcription and Leads to Increased Duodenal Iron Transporter Expression. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2006, 281, 22974-22982, 10.1074/jbc.m602098200.
- Duane, P.; Raja, K.B.; Simpson, R.J.; Peters, T.J.; Intestinal iron absorption in chronic alcoholics. . Alcohol Alcohol. 1992, 27, 539-544, .
- Yutaka Kohgo; Katsuya Ikuta; Takaaki Ohtake; Yoshihiro Torimoto; Junji Kato; Iron overload and cofactors with special reference to alcohol, hepatitis C virus infection and steatosis/insulin resistance. World Journal of Gastroenterology 2007, 13, 4699-4706, 10.3748/wjg.v13.i35.4699.
- Bridle, K.; Cheung, T.K.; Murphy, T.; Walters, M.; Anderson, G.; Crawford, D.G.; Fletcher, L.M.; Hepcidin is down-regulated in alcoholic liver injury: Implications for the pathogenesis of alcoholic liver disease.. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2006, 30, 106–112, 10.1111/j.1530-0277.2006.00002.x.
- Duygu Dee Harrison-Findik; Elizabeth Klein; Callie Crist; John Evans; Nikolai Timchenko; John Gollan; Iron-mediated regulation of liver hepcidin expression in rats and mice is abolished by alcohol. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1979-1985, 10.1002/hep.21895.
- Michael Zimmermann; Nourredine Chaouki; Richard F Hurrell; Iron deficiency due to consumption of a habitual diet low in bioavailable iron: a longitudinal cohort study in Moroccan children. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2005, 81, 115-121, 10.1093/ajcn/81.1.115.
- Michael Zimmermann; Richard Hurrell; Nutritional iron deficiency. The Lancet 2007, 370, 511-520, 10.1016/s0140-6736(07)61235-5.
- Nancy Andrews; Disorders of Iron Metabolism. New England Journal of Medicine 1999, 341, 1986-1995, 10.1056/nejm199912233412607.
- Roy, C.N.; Enns, C.A.; Iron homeostasis: New tales from the crypt. . Blood 2000, 96, 4020–4027, .
- Charles E. Carpenter; Arthur W. Mahoney; Contributions of heme and nonheme iron to human nutrition. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 1992, 31, 333-367, 10.1080/10408399209527576.
- Diego Moretti; Gerrigje M Van Doorn; Rine W Swinkels; Alida Melse-Boonstra; Relevance of dietary iron intake and bioavailability in the management of HFE hemochromatosis: a systematic review. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2013, 98, 468-479, 10.3945/ajcn.112.048264.
- W. R. Bezwoda; P. B. Disler; S. R. Lynch; R. W. Charlton; J. D. Torrance; D. Derman; T. H. Bothwell; R. B. Walker; F. Mayet; Patterns of Food Iron Absorption in Iron-Deficient White and Indian Subjects and in Venesected Haemochromatotic Patients. British Journal of Haematology 1976, 33, 425-436, 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1976.tb03560.x.
- Bezwoda, W.R.; Bothwell, T.H.; Derman, D.P.; MacPhail, A.P.; Torrance, J.D.; Charlton, R.W.; Effect of diet on the rate of iron accumulation in idiopathic haemochromatosis. . S. Afr. Med. J. 1981, 59, 219–222., .
- V R Gordeuk; Laura Lovato; James C Barton; Mara Vitolins; Gordon McLaren; Ronald T Acton; Emily L. Harris; Mark Speechley; John H Eckfeldt; Sharmin Diaz; et al. Dietary Iron Intake and Serum Ferritin Concentration in 213 Patients Homozygous for the HFE C282Y Hemochromatosis Mutation. Canadian Journal of Gastroenterology 2012, 26, 345-349, 10.1155/2012/676824.
- D C. Greenwood; Janet E. Cade; J A. Moreton; B O??hara; Victoria Burley; Juliette Randerson-Moor; K Kukalizch; D Thompson; M Worwood; D. Timothy Bishop; et al. HFE Genotype Modifies the Influence of Heme Iron Intake on Iron Status. Epidemiology 2005, 16, 802-805, 10.1097/01.ede.0000181306.85583.ea.
- Peeters, P.H.; Grobbee, D.E.; Roest, M.; Voorbij, H.A.; van der Schouw, Y.T.; HFE genotypes and dietary heme iron: No evidence of strong gene-nutrient interaction on serum ferritin concentrations in middle-aged women. . Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. NMCD 2006, 16, 60–68, 10.1016/j.numecd.2005.07.008.
- Elizabeth A. Milward; Surinder K. Baines; Matthew Knuiman; Helen C. Bartholomew; Mark L. Divitini; David G. Ravine; David Bruce; John K. Olynyk; Noncitrus Fruits as Novel Dietary Environmental Modifiers of Iron Stores in People With or Without HFE Gene Mutations. Mayo Clinic Proceedings 2008, 83, 543-549, 10.4065/83.5.543.
- Silvia Fargion; Michela Mattioli; Anna Ludovica Fracanzani; Maurizio Sampietro; Dario Tavazzi; Paolo Fociani; Emanuela Taioli; Luca Valenti; Gemino Fiorelli; Hyperferritinemia, iron overload, and multiple metabolic alterations identify patients at risk for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. The American Journal of Gastroenterology 2001, 96, 2448-2455, 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2001.04052.x.
- José-Manuel Fernández-Real; Wifredo Ricart-Engel; Enric Arroyo; Rafael Balançá; Roser Casamitjana-Abella; Dolores Cabrero; Miquel Fernández-Castañer; Joan Soler; Serum ferritin as a component of the insulin resistance syndrome.. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 62-68, 10.2337/diacare.21.1.62.
- John D. Ryan; Andrew E. Armitage; Jeremy F. Cobbold; Rajarshi Banerjee; Oscar Borsani; Paola Dongiovanni; Stefan Neubauer; Reza Morovat; Lai Mun Wang; Sant-Rayn Pasricha; et al. Hepatic iron is the major determinant of serum ferritin in NAFLD patients. Liver International 2017, 38, 164-173, 10.1111/liv.13513.
- Giulio Marchesini; Mara Brizi; Giampaolo Bianchi; Sara Tomassetti; Elisabetta Bugianesi; Marco Lenzi; Arthur J. McCullough; Stefania Natale; Gabriele Forlani; Nazario Melchionda; et al. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: a feature of the metabolic syndrome.. Diabetes 2001, 50, 1844-1850, 10.2337/diabetes.50.8.1844.
- Luca Valenti; P Dongiovanni; Anna Ludovica Fracanzani; G Santorelli; E Fatta; C Bertelli; E Taioli; G Fiorelli; Silvia Fargion; Increased susceptibility to nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in heterozygotes for the mutation responsible for hereditary hemochromatosis.. Digestive and Liver Disease 2003, 35, 172-178, 10.1016/s1590-8658(03)00025-2.
- Paola Dongiovanni; Massimiliano Ruscica; Raffaela Rametta; Stefania Recalcati; Liliana Steffani; Stefano Gatti; Domenico Girelli; Gaetano Cairo; Paolo Magni; Silvia Fargion; et al. Dietary Iron Overload Induces Visceral Adipose Tissue Insulin Resistance. The American Journal of Pathology 2013, 182, 2254-2263, 10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.02.019.
- Larry W. Oberley; Free radicals and diabetes. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 1988, 5, 113-124, 10.1016/0891-5849(88)90036-6.
- Paola Dongiovanni; Claudia Lanti; Stefano Gatti; Raffaela Rametta; Stefania Recalcati; Marco Maggioni; Anna Ludovica Fracanzani; Patrizia Riso; Gaetano Cairo; Silvia Fargion; et al. High Fat Diet Subverts Hepatocellular Iron Uptake Determining Dysmetabolic Iron Overload. PLOS ONE 2015, 10, e0116855, 10.1371/journal.pone.0116855.
- Witte, D.L.; Crosby, W.H.; Edwards, C.Q.; Fairbanks, V.F.; Mitros, F.A.; Practice guideline development task force of the College of American Pathologists. Hereditary hemochromatosis. . Clin. Chim. Acta Int. J. Clin. Chem. 1996, 245, 139–200, 10.1016/0009-8981(95)06212-2.
- Tomi-Pekka Tuomainen; Kristiina Nyyssönen; Riitita Salonen; Arja Tervahauta; Heikki Korpela; Timo A. Lakka; George A Kaplan; Jukka T. Salonen; Body Iron Stores Are Associated With Serum Insulin and Blood Glucose Concentrations: Population study in 1,013 eastern Finnish men. Diabetes Care 1997, 20, 426-428, 10.2337/diacare.20.3.426.
- Jukka T. Salonen; Tomi-Pekka Tuomainen; Kristiina Nyyssönen; Hanna-Maaria Lakka; Kari Punnonen; Relation between iron stores and non-insulin dependent diabetes in men: case-control study. BMJ 1998, 317, 727-730, 10.1136/bmj.317.7160.727.
- E S Ford; M. E. Cogswell; Diabetes and serum ferritin concentration among U.S. adults.. Diabetes Care 1999, 22, 1978-1983, 10.2337/diacare.22.12.1978.
- Forouhi, N.G.; Harding, A.H.; Allison, M.; Sandhu, M.S.; Welch, A.; Luben, R.; Bingham, S.; Khaw, K.T.; Wareham, N.J.; Elevated serum ferritin levels predict new-onset type 2 diabetes: Results from the EPIC-Norfolk prospective study. . Diabetologia 2007, 50, 949–956, 10.1007/s00125-007-0604-5.
- Luca Valenti; Anna Ludovica Fracanzani; Elisabetta Bugianesi; Paola Dongiovanni; Enrico Galmozzi; Ester Vanni; Elena Canavesi; Ezio Lattuada; Giancarlo Roviaro; Giulio Marchesini; et al. HFE Genotype, Parenchymal Iron Accumulation, and Liver Fibrosis in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 905-912, 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.11.013.
- Miguel Arredondo; Marcela Fuentes; Denisse Jorquera; Valeria Candia; Elena Carrasco; Elba Leiva; Veronica Mujica; Eva Hertrampf; Francisco Pérez; Cross-Talk Between Body Iron Stores and Diabetes: Iron Stores are Associated with Activity and Microsatellite Polymorphism of the Heme Oxygenase and Type 2 Diabetes. Biological Trace Element Research 2010, 143, 625-636, 10.1007/s12011-010-8895-7.
- Raffaela Rametta; Anna Ludovica Fracanzani; Silvia Fargion; Paola Dongiovanni; Dysmetabolic Hyperferritinemia and Dysmetabolic Iron Overload Syndrome (DIOS): Two Related Conditions or Different Entities?. Current Pharmaceutical Design 2020, 26, 1025-1035, 10.2174/1381612826666200131103018.
- C. Niederau; M. Berger; W. Stremmel; A. Starke; G. Strohmeyer; R. Ebert; E. Siegel; W. Creutzfeldt; Hyperinsulinaemia in non-cirrhotic haemochromatosis: impaired hepatic insulin degradation?. Diabetologia 1984, 26, 441-444, 10.1007/bf00262217.
- Silvia Fargion; P. Dongiovanni; A. Guzzo; S. Colombo; L. Valenti; A. L. Fracanzani; Iron and insulin resistance. Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics 2005, 22, 61-63, 10.1111/j.1365-2036.2005.02599.x.
- Luca Valenti; Anna Ludovica Fracanzani; Paola Dongiovanni; Elisabetta Bugianesi; Giulio Marchesini; Paola Manzini; Ester Vanni; Silvia Fargion; Iron Depletion by Phlebotomy Improves Insulin Resistance in Patients With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Hyperferritinemia: Evidence from a Case-Control Study. The American Journal of Gastroenterology 2007, 102, 1251-1258, 10.1111/j.1572-0241.2007.01192.x.
- Facchini, F.S.; Effect of phlebotomy on plasma glucose and insulin concentrations. . Diabetes Care 1998,, 21, 2190, .
- Luca Valenti; Paola Dongiovanni; Anna Ludovica Fracanzani; Silvia Fargion; Bloodletting ameliorates insulin sensitivity and secretion in parallel to reducing liver iron in carriers of HFE gene mutations: response to Equitani et al.. Diabetes Care 2008, 31, e18-e18, 10.2337/dc07-2181.
- Francesco Equitani; José-Manuel Fernández-Real; Giacomo Menichella; Maurizio Koch; Menotti Calvani; Valerio Nobili; Geltrude Mingrone; Melania Manco; Bloodletting Ameliorates Insulin Sensitivity and Secretion in Parallel to Reducing Liver Iron in Carriers of HFE Gene Mutations. Diabetes Care 2007, 31, 3-8, 10.2337/dc07-0939.
- 76. Dongiovanni, P.; Valenti, L.; Ludovica Fracanzani, A.; Gatti, S.; Cairo, G.; Fargion, S.; Iron depletion by deferoxamine up-regulates glucose uptake and insulin signaling in hepatoma cells and in rat liver. . Am. J. Pathol. 2008, 172, 738–747, 10.2353/ajpath.2008.070097.
- G. L. Semenza; Regulation of Metabolism by Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1. Cold Spring Harbor Symposia on Quantitative Biology 2011, 76, 347-353, 10.1101/sqb.2011.76.010678.
- Chiara Macchi; Liliana Steffani; Roberto Oleari; Antonella Lettieri; Luca Valenti; Paola Dongiovanni; A Romero-Ruiz; Manuel Tena-Sempere; Anna Cariboni; Paolo Magni; et al. Iron overload induces hypogonadism in male mice via extrahypothalamic mechanisms. Molecular and Cellular Endocrinology 2017, 454, 135-145, 10.1016/j.mce.2017.06.019.
- Antonello Pietrangelo; Hemochromatosis: An endocrine liver disease. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1291-1301, 10.1002/hep.21886.
- Dongiovanni, P.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Fargion, S.; Valenti, L.; . Iron in fatty liver and in the metabolic syndrome: A promising therapeutic target.. J. Hepatol. 2011, 55, 920–932, 10.1016/j.jhep.2011.05.008.
- Raffaela Rametta; Paola Dongiovanni; Serena Pelusi; Paolo Francione; Federica Iuculano; Vittorio Borroni; Erika Fatta; Annalisa Castagna; Domenico Girelli; Silvia Fargion; et al. Hepcidin resistance in dysmetabolic iron overload. Liver International 2016, 36, 1540-1548, 10.1111/liv.13124.
- David D. Kitts; Bioactive substances in food: identification and potential uses. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 1994, 72, 423-434, 10.1139/y94-062.
- Hurrell, R.; Egli, I.; Iron bioavailability and dietary reference values. . Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 91, 1461S–1467S, 10.3945/ajcn.2010.28674F.
- Christina N. Kontoghiorghe; Annita Kolnagou; George J. Kontoghiorghes; Phytochelators Intended for Clinical Use in Iron Overload, Other Diseases of Iron Imbalance and Free Radical Pathology. Molecules 2015, 20, 20841-20872, 10.3390/molecules201119725.
- Anwesha Bhowmik; Durbadal Ojha; Debayan Goswami; Rashmi Das; Nidhi S. Chandra; Tapan K. Chatterjee; Amit Chakravarty; Sudipa Chakravarty; Debprasad Chattopadhyay; Inositol hexa phosphoric acid (phytic acid), a nutraceuticals, attenuates iron-induced oxidative stress and alleviates liver injury in iron overloaded mice. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 2017, 87, 443-450, 10.1016/j.biopha.2016.12.125.
- Ulrich Schlemmer; Wenche Frølich; Rafel M. Prieto; Félix Grases; Phytate in foods and significance for humans: Food sources, intake, processing, bioavailability, protective role and analysis. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 2009, 53, S330-S375, 10.1002/mnfr.200900099.
- 86. Cosgrove, D.J. . Inositol Phosphates; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 1980; pp. 1.
- Mats Brune; Lena Rossander-Hultén; Leif Hallberg; Ann Gleerup; Ann-Sofie Sandberg; Iron Absorption from Bread in Humans: Inhibiting Effects of Cereal Fiber, Phytate and Inositol Phosphates with Different Numbers of Phosphate Groups. The Journal of Nutrition 1992, 122, 442-449, 10.1093/jn/122.3.442.
- L Hallberg; M Brune; L Rossander; Iron absorption in man: ascorbic acid and dose-dependent inhibition by phytate. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1989, 49, 140-144, 10.1093/ajcn/49.1.140.
- R F Hurrell; M A Juillerat; M B Reddy; S R Lynch; S A Dassenko; J D Cook; Soy protein, phytate, and iron absorption in humans. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1992, 56, 573-578, 10.1093/ajcn/56.3.573.
- Véronique Cheynier; Gilles Comte; Kevin M. Davies; Vincenzo Lattanzio; Stefan Martens; Plant phenolics: Recent advances on their biosynthesis, genetics, and ecophysiology. Plant Physiology and Biochemistry 2013, 72, 1-20, 10.1016/j.plaphy.2013.05.009.
- Brune, M.; Rossander, L.; Hallberg, L.; Iron absorption and phenolic compounds: Importance of different phenolic structures. . Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1989, 43, 547–557, .
- Watson, R.R.; Preedy, V.R.; Zibadi, S. . Polyphenols in Human Health and Disease; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014.: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2014; pp. 1.
- Tuntawiroon, M.; Sritongkul, N.; Brune, M.; Rossander-Hulten, L.; Pleehachinda, R.; Suwanik, R.; Hallberg, L.; Dose-dependent inhibitory effect of phenolic compounds in foods on nonheme-iron absorption in men. . Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1991, 53, 554–557, 10.1093/ajcn/53.2.554..
- D J Fleming; P F Jacques; G E Dallal; Katherine L. Tucker; P W Wilson; R J Wood; Dietary determinants of iron stores in a free-living elderly population: The Framingham Heart Study.. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1998, 67, 722-733, 10.1093/ajcn/67.4.722.
- Hurrell, R.F.; Reddy, M.; Cook, J.D.; . Inhibition of non-haem iron absorption in man by polyphenolic-containing beverages.. Br. J. Nutr. 1999, 81, 289–295, .
- P B Disler; S R Lynch; R W Charlton; J D Torrance; T H Bothwell; R B Walker; F Mayet; The effect of tea on iron absorption.. Gut 1975, 16, 193-200, 10.1136/gut.16.3.193.
- L Rossander; L Hallberg; E Björn-Rasmussen; Absorption of iron from breakfast meals. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1979, 32, 2484-2489, 10.1093/ajcn/32.12.2484.
- Kaltwasser, J.P.; Werner, E.; Schalk, K.; Hansen, C.; Gottschalk, R.; Seidl, C.; Clinical trial on the effect of regular tea drinking on iron accumulation in genetic haemochromatosis.. Gut 1998, 43, 699-704, 10.1136/gut.43.5.699.
- S. Samman; BrittMarie Sandström; Maja Bjørndal Toft; K. Bukhave; Mikael Jensen; Sven S Sørensen; Marianne Hansen; Green tea or rosemary extract added to foods reduces nonheme-iron absorption.. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2001, 73, 607-612, 10.1093/ajcn/73.3.607.
- Marija Lesjak; Rukshana Hoque; Sara Balesaria; Vernon Skinner; Edward S. Debnam; Surjit K. S. Srai; Paul A. Sharp; Quercetin Inhibits Intestinal Iron Absorption and Ferroportin Transporter Expression In Vivo and In Vitro. PLOS ONE 2014, 9, e102900, 10.1371/journal.pone.0102900.
- Marija Lesjak; Sara Balesaria; Vernon Skinner; Edward S. Debnam; Surjit Kaila S. Srai; Quercetin inhibits intestinal non-haem iron absorption by regulating iron metabolism genes in the tissues.. European Journal of Nutrition 2018, 58, 743-753, 10.1007/s00394-018-1680-7.
- Zohreh Sajadi Hezaveh; Azita Azarkeivan; Leila Janani; Sharieh Hosseini; Farzad Shidfar; The effect of quercetin on iron overload and inflammation in β-thalassemia major patients: A double-blind randomized clinical trial.. Complementary Therapies in Medicine 2019, 46, 24-28, 10.1016/j.ctim.2019.02.017.
- Hutchinson, C.; Bomford, A.; Geissler, C.A.; The iron-chelating potential of silybin in patients with hereditary haemochromatosis.. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 2010, 64, 1239–1241, 10.1038/ejcn.2010.136.
- Wu, T.-H.; Grape Seed Proanthocyanidin Extract Chelates Iron and Attenuates the Toxic Effects of 6-Hydroxydopamine: Implications for Parkinson’s Disease. . J. Food Biochem. 2010 2010, 34, 1, 10.1111/j.1745-4514.2009.00276.x..
- Hervé Lobbes; Cécile Gladine; Andrzej Mazur; Bruno Pereira; Christian Dualé; Jean-Michel Cardot; Marc Ruivard; Effect of procyanidin on dietary iron absorption in hereditary hemochromatosis and in dysmetabolic iron overload syndrome: A crossover double-blind randomized controlled trial. Clinical Nutrition 2020, 39, 97-103, 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.02.012.
- J D Cook; S A Dassenko; P Whittaker; Calcium supplementation: effect on iron absorption. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1991, 53, 106-111, 10.1093/ajcn/53.1.106.
- Hallberg, L.; Rossander-Hulten, L.; Brune, M.; Gleerup, A.; . Calcium and iron absorption: Mechanism of action and nutritional importance. . Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 1992, 46, 317–327, .
- Zamzam K (Fariba) Roughead; Carol A Zito; J R Hunt; Inhibitory effects of dietary calcium on the initial uptake and subsequent retention of heme and nonheme iron in humans: comparisons using an intestinal lavage method. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2005, 82, 589-597, 10.1093/ajcn.82.3.589.
- Barton, J.C.; Conrad, M.E.; Parmley, R.T.; Calcium inhibition of inorganic iron absorption in rats. . Gastroenterology 1983, 84, 90–101, .
- Ben Thompson; Paul A. Sharp; Ruan Elliott; Susan Fairweather-Tait; Inhibitory Effect of Calcium on Non-heme Iron Absorption May Be Related to Translocation of DMT-1 at the Apical Membrane of Enterocytes. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2010, 58, 8414-8417, 10.1021/jf101388z.
- B Dawson-Hughes; F H Seligson; V A Hughes; Effects of calcium carbonate and hydroxyapatite on zinc and iron retention in postmenopausal women. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1986, 44, 83-88, 10.1093/ajcn/44.1.83.
- Sean R Lynch; The effect of calcium on iron absorption. Nutrition Research Reviews 2000, 13, 141-158, 10.1079/095442200108729043.
- S. M. Robinson; Keith M. Godfrey; Jonathan Denne; Vanessa Cox; The determinants of iron status in early pregnancy.. British Journal of Nutrition 1998, 79, 249-255, 10.1079/bjn19980042.
- J D Cook; E R Monsen; Food iron absorption in human subjects. III. Comparison of the effect of animal proteins on nonheme iron absorption. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1976, 29, 859-867, 10.1093/ajcn/29.8.859.
- R F Hurrell; S R Lynch; T P Trinidad; S A Dassenko; J D Cook; Iron absorption in humans as influenced by bovine milk proteins. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1989, 49, 546-552, 10.1093/ajcn/49.3.546.
- R F Hurrell; S R Lynch; T P Trinidad; S A Dassenko; J D Cook; Iron absorption in humans: bovine serum albumin compared with beef muscle and egg white. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1988, 47, 102-107, 10.1093/ajcn/47.1.102.
- Palle Pedersen; Nils Milman; Extrinsic factors modifying expressivity of the HFE variant C282Y, H63D, S65C phenotypes in 1,294 Danish men. Blut Zeitschrift für die gesamte Blutforschung 2009, 88, 957-965, 10.1007/s00277-009-0714-x.
- S R Lynch; S A Dassenko; J D Cook; M A Juillerat; R F Hurrell; Inhibitory effect of a soybean-protein–related moiety on iron absorption in humans. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1994, 60, 567-572, 10.1093/ajcn/60.4.567.
- Marı́a Nieves Garcı́a-Casal; Miguel Layrisse; Liseti Solano; Marı́a Adela Barón; Franklin Arguello; Daisy Llovera; José Ramı́rez; Irene Leets; Eleonora Tropper; María Nieves García-Casal; et al. Vitamin A and β-Carotene Can Improve Nonheme Iron Absorption from Rice, Wheat and Corn by Humans. The Journal of Nutrition 1998, 128, 646-650, 10.1093/jn/128.3.646.
- M W Bloem; M Wedel; E J Van Agtmaal; A J Speek; S Saowakontha; W H Schreurs; Vitamin A intervention: short-term effects of a single, oral, massive dose on iron metabolism. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1990, 51, 76-79, 10.1093/ajcn/51.1.76.
- R E Hodges; H E Sauberlich; J E Canham; D L Wallace; R B Rucker; L A Mejía; M Mohanram; Hematopoietic studies in vitamin A deficiency. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1978, 31, 876-885, 10.1093/ajcn/31.5.876.
- Dreyfuss, M.L.; Stoltzfus, R.J.; Shrestha, J.B.; Pradhan, E.K.; LeClerq, S.C.; Khatry, S.K.; Shrestha, S.R.; Katz, J.; Albonico, M.; West, K.P., Jr.; et al. Hookworms, malaria and vitamin A deficiency contribute to anemia and iron deficiency among pregnant women in the plains of Nepal. . J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 2527–2536, 10.1093/jn/130.10.2527..
- P. Brissot; A. Le Treut; G. Dien; M. Cottencin; M. Simon; M. Bourel; Hypovitaminemia A in Idiopathic Hemochromatosis and Hepatic Cirrhosis. Digestion 1978, 17, 469-478, 10.1159/000198153.
- G.D. Kom; E. Schwedhelm; P. Nielsen; R.H. Böger; Increased urinary excretion of 8-iso-prostaglandin F2α in patients with HFE-related hemochromatosis: A case-control study. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 2006, 40, 1194-1200, 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.11.004.
- Gardner, R.; Hodges, R.; Rucker, R. . Fate of erythrocyte iron in vitamin A deficient rats. In Federation Proceedings; FASEB: Bethesda, MD, USA, 1979; pp. Volume 38.
- L A Mejía; R E Hodges; R B Rucker; Clinical signs of anemia in vitamin A-deficient rats. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1979, 32, 1439-1444, 10.1093/ajcn/32.7.1439.
- K. W. Sijtsma; G. J. Van Den Berg; A. G. Lemmens; C. E. West; A. C. Beynen; Iron status in rats fed on diets containing marginal amounts of vitamin A. British Journal of Nutrition 1993, 70, 777-785, 10.1079/bjn19930173.
- Annet J. C. Roodenburg; Clive E. West; Shiguang Yu; Anton C. Beynen; Comparison between time-dependent changes in iron metabolism of rats as induced by marginal deficiency of either vitamin A or iron. British Journal of Nutrition 1994, 71, 687-699, 10.1079/bjn19940176.
- Marta Citelli; Luciana Linhares Bittencourt; Simone Vargas Da Silva; Anna Paola Trindade Rocha Pierucci; Cristiana Pedrosa; Vitamin A Modulates the Expression of Genes Involved in Iron Bioavailability. Biological Trace Element Research 2012, 149, 64-70, 10.1007/s12011-012-9397-6.
- Oksana Katz; Ram Reifen; Aaron Lerner; β-Carotene can reverse dysregulation of iron protein in an in vitro model of inflammation. Immunologic Research 2014, 61, 70-78, 10.1007/s12026-014-8570-8.
- Sean R. Lynch; James D. Cook; INTERACTION OF VITAMIN C AND IRON. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1980, 355, 32-44, 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb21325.x.
- Krishna Pillay Madhavan Nair; Ginnela N.V. Brahmam; Madhari S. Radhika; Roy Choudhury Dripta; Punjal Ravinder; Nagalla Balakrishna; Zhensheng Chen; Keli Hawthorne; Steven A. Abrams; Inclusion of guava enhances non-heme iron bioavailability but not fractional zinc absorption from a rice-based meal in adolescents.. The Journal of Nutrition 2013, 143, 852-8, 10.3945/jn.112.171702.
- Hallberg, L.; Rossander, L.; Effect of different drinks on the absorption of non-heme iron from composite meals. . Hum. Nutr. Appl. Nutr. 1982, 36, 116–123, .
- Hallberg, L.; Brune, M.; Rossander, L.; Effect of ascorbic acid on iron absorption from different types of meals. Studies with ascorbic-acid-rich foods and synthetic ascorbic acid given in different amounts with different meals.. Hum. Nutr. Appl. Nutr. 1986, 40, 97–113, .
- Margarita Diaz; Jorge L Rosado; Lindsay H Allen; Steve Abrams; Olga P García; The efficacy of a local ascorbic acid–rich food in improving iron absorption from Mexican diets: a field study using stable isotopes. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2003, 78, 436-440, 10.1093/ajcn/78.3.436.
- Prashanth Thankachan; Thomas Walczyk; Sumithra Muthayya; Anura V Kurpad; Richard F Hurrell; Iron absorption in young Indian women: the interaction of iron status with the influence of tea and ascorbic acid. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2008, 87, 881-886, 10.1093/ajcn/87.4.881.
- J D Cook; E R Monsen; Vitamin C, the common cold, and iron absorption. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1977, 30, 235-241, 10.1093/ajcn/30.2.235.
- D Siegenberg; R D Baynes; T H Bothwell; B J Macfarlane; R D Lamparelli; N G Car; P MacPhail; U Schmidt; A Tal; F Mayet; et al. Ascorbic acid prevents the dose-dependent inhibitory effects of polyphenols and phytates on nonheme-iron absorption. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1991, 53, 537-541, 10.1093/ajcn/53.2.537.
- A Stekel; M Olivares; F Pizarro; P Chadud; I Lopez; M Amar; Absorption of fortification iron from milk formulas in infants. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1986, 43, 917-922, 10.1093/ajcn/43.6.917.
- Ballot, D.; Baynes, R.D.; Bothwell, T.H.; Gillooly, M.; MacFarlane, B.J.; MacPhail, A.P.; Lyons, G.; Derman, D.P.; Bezwoda, W.R.; Torrance, J.D.; et al. The effects of fruit juices and fruits on the absorption of iron from a rice meal. . Br. J. Nutr. 1987, 57, 331–343, 10.1079/bjn19870041.
- M. Gillooly; T. H. Bothwell; J. D. Torrance; A. P. MacPhail; D. P. Derman; W. R. Bezwoda; W. Mills; R. W. Charlton; Fatima Mayet; The effects of organic acids, phytates and polyphenols on the absorption of iron from vegetables. British Journal of Nutrition 1983, 49, 331-342, 10.1079/bjn19830042.
- Seshadri, S.; Shah, A.; Bhade, S.; Haematologic response of anaemic preschool children to ascorbic acid supplementation.. Hum. Nutr. Appl. Nutr. 1985, 39, 151–154, .
- Mao, X.; Yao, G.; Effect of vitamin C supplementations on iron deficiency anemia in Chinese children.. Biomed. Environ. Sci. Bes 1992, 5, 125–129, .
- Kathryn L. Beck; Cathryn A. Conlon; Rozanne Kruger; Jane Coad; Welma Stonehouse; Gold kiwifruit consumed with an iron-fortified breakfast cereal meal improves iron status in women with low iron stores: a 16-week randomised controlled trial. British Journal of Nutrition 2010, 105, 101-109, 10.1017/s0007114510003144.
- J R Hunt; S K Gallagher; L K Johnson; Effect of ascorbic acid on apparent iron absorption by women with low iron stores. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1994, 59, 1381-1385, 10.1093/ajcn/59.6.1381.
- Olga P García; Margarita Diaz; Jorge L Rosado; L H Allen; Ascorbic acid from lime juice does not improve the iron status of iron-deficient women in rural Mexico. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2003, 78, 267-273, 10.1093/ajcn/78.2.267.
- L Hallberg; L Rossander; Improvement of iron nutrition in developing countries: comparison of adding meat, soy protein, ascorbic acid, citric acid, and ferrous sulphate on iron absorption from a simple Latin American-type of meal. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1984, 39, 577-583, 10.1093/ajcn/39.4.577.
- Jacklyn Jackson; Rebecca Haslam; Mark McEvoy; Lesley MacDonald-Wicks; Amanda J. Patterson; Is Higher Consumption of Animal Flesh Foods Associated with Better Iron Status among Adults in Developed Countries? A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2016, 8, 89, 10.3390/nu8020089.
- Miguel Layrisse; Carlos Martínez-Torres; Marcel Roche; Effect of Interaction of Various Foods on Iron Absorption. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1968, 21, 1175-1183, 10.1093/ajcn/21.10.1175.
- Sean R. Lynch; Richard F. Hurrell; Sandra A. Dassenko; James D. Cook; The Effect of Dietary Proteins on Iron Bioavailability in Man. Plant Promoters and Transcription Factors 1989, 249, 117-132, 10.1007/978-1-4684-9111-1_8.
- Bjorn-Rasmussen, E.; Hallberg, L.; Effect of animal proteins on the absorption of food iron in man. . Nutr. Metab. 1979, 23, 192–202, 10.1159/000176256.
- Zhang, D.; Carpenter, C.E.; Mahoney, A.W.; A mechanistic hypothesis for meat enhancement of nonheme iron absorption: Stimulation of gastric secretions and iron chelation. . Nutr. Res. 1990, 10, 929–935, .
- Richard F. Hurrell; Manju B. Reddy; Marcel Juillerat; James D. Cook; Meat Protein Fractions Enhance Nonheme Iron Absorption in Humans. The Journal of Nutrition 2006, 136, 2808-2812, 10.1093/jn/136.11.2808.
- S Storcksdieck Genannt Bonsmann; Genannt Bonsmann; R. F. Hurrell; Stefan Storcksdieck Genannt Bonsmann; Iron-Binding Properties, Amino Acid Composition, and Structure of Muscle Tissue Peptides from in vitro Digestion of Different Meat Sources. Journal of Food Science 2007, 72, S019-S029, 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2006.00229.x.
- Charlotte N. Armah; Paul Sharp; Fred A. Mellon; Sandra Pariagh; Elizabeth K. Lund; J R Dainty; Birgit Teucher; Susan Fairweather-Tait; L-α-Glycerophosphocholine Contributes to Meat's Enhancement of Nonheme Iron Absorption. The Journal of Nutrition 2008, 138, 873-877, 10.1093/jn/138.5.873.
- Etsuo Niki; Maret G. Traber; A History of Vitamin E. Annals of Nutrition and Metabolism 2012, 61, 207-212, 10.1159/000343106.
- Fatemeh Khadangi; Angelo Azzi; Vitamin E – The Next 100 Years. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 411-415, 10.1002/iub.1990.
- Lisa Schmölz; Marc Birringer; Stefan Lorkowski; Maria Wallert; Complexity of vitamin E metabolism. World Journal of Biological Chemistry 2016, 7, 14-43, 10.4331/wjbc.v7.i1.14.
- Bruce R. Bacon; Robert S. Britton; The pathology of hepatic iron overload: A free radical-Mediated Process?. Hepatology 1990, 11, 127-137, 10.1002/hep.1840110122.
- Bruce R. Bacon; John F. Healey; Gary M. Brittenham; C.H. Park; Jodi Nunnari; Anthony S. Tavill; Herbert L. Bonkovsky; Hepatic microsomal function in rats with chronic dietary iron overload. Gastroenterology 1986, 90, 1844-1853, 10.1016/0016-5085(86)90251-9.
- Bruce R. Bacon; Chanho H. Park; Gary M. Brittenham; Rosemary O-Neill; Anthony S. Tavill; Hepatic mitochondrial oxidative metabolism in rats with chronic dietary iron overload. Hepatology 1985, 5, 789-797, 10.1002/hep.1840050514.
- B M Myers; F G Prendergast; R Holman; S M Kuntz; N F LaRusso; Alterations in the structure, physicochemical properties, and pH of hepatocyte lysosomes in experimental iron overload.. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1991, 88, 1207-1215, 10.1172/jci115423.
- J. M. C. Gutteridge; D. A. Rowley; E. Griffiths; B. Halliwell; Low-molecular-weight iron complexes and oxygen radical reactions in idiopathic haemochromatosis. Clinical Science 1985, 68, 463-467, 10.1042/cs0680463.
- E Cadenas; M Ginsberg; U Rabe; H Sies; Evaluation of α-tocopherol antioxidant activity in microsomal lipid peroxidation as detected by low-level chemiluminescence. Biochemical Journal 1984, 223, 755-759, 10.1042/bj2230755.
- Graham W. Burton; Anne Joyce; Keith U. Ingold; Is vitamin E the only lipid-soluble, chain-breaking antioxidant in human blood plasma and erythrocyte membranes?. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics 1983, 221, 281-290, 10.1016/0003-9861(83)90145-5.
- Helmut Sies; Michael E. Murphy; Role of tocopherols in the protection of biological systems against oxidative damage. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology 1991, 8, 211, 10.1016/1011-1344(91)80061-l.
- B. Halliwell; JohnM.C. Gutteridge; LIPID PEROXIDATION, OXYGEN RADICALS, CELL DAMAGE, AND ANTIOXIDANT THERAPY. The Lancet 1984, 323, 1396-1397, 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91886-5.
- A J Dabbagh; T Mannion; S M Lynch; B Frei; The effect of iron overload on rat plasma and liver oxidant status in vivo. Biochemical Journal 1994, 300, 799-803, 10.1042/bj3000799.
- Ian S Young; Tom G. Trouton; Jonathan J. Torney; Dorothy McMaster; Michael E. Callender; Elisabeth R. Trimble; Antioxidant status and lipid peroxidation in hereditary haemochromatosis. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 1994, 16, 393-397, 10.1016/0891-5849(94)90041-8.
- von Herbay, A.; de Groot, H.; Hegi, U.; Stremmel, W.; Strohmeyer, G.; Sies, H.; Low vitamin E content in plasma of patients with alcoholic liver disease, hemochromatosis and Wilson's disease.. J. Hepatol. 1994, 20, 41–46, .
- K. E. Brown; J. E. Poulos; L. Li; A. M. Soweid; G. A. Ramm; R. O'neill; R. S. Britton; B. R. Bacon; Effect of vitamin E supplementation on hepatic fibrogenesis in chronic dietary iron overload. American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology 1997, 272, G116-G123, 10.1152/ajpgi.1997.272.1.g116.
- Whittaker, P.; Wamer, W.G.; Chanderbhan, R.F.; Dunkel, V.C.; Effects of alpha-tocopherol and beta-carotene on hepatic lipid peroxidation and blood lipids in rats with dietary iron overload. . Nutr. Cancer. 1996, 25, 119–128, 10.1080/01635589609514434.
- Nadia Ferlazzo; Giuseppa Visalli; Santa Cirmi; Giovanni Enrico Lombardo; Pasqualina Laganà; Angela Di Pietro; Michele Navarra; Natural iron chelators: Protective role in A549 cells of flavonoids-rich extracts of Citrus juices in Fe 3+ -induced oxidative stress. Environmental Toxicology and Pharmacology 2016, 43, 248-256, 10.1016/j.etap.2016.03.005.
- Joo-Hyun Shin; Hyo-Jin Jeon; Jihye Park; Mi-Sook Chang; Epigallocatechin-3-gallate prevents oxidative stress-induced cellular senescence in human mesenchymal stem cells via Nrf2.. International Journal of Molecular Medicine 2016, 38, 1075-82, 10.3892/ijmm.2016.2694.
- Helmut Sies; Dean P. Jones; Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents.. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology 2020, 21, 1-21, 10.1038/s41580-020-0230-3.
- Ma, Q.; Kim, E.Y.; Lindsay, E.A.; Han, O.; Bioactive dietary polyphenols inhibit heme iron absorption in a dose-dependent manner in human intestinal Caco-2 cells. . J. Food Sci. 2011, 76, H143–H150, 10.1111/j.1750-3841.2011.02184.x.
- Qiang Niu; Lati Mu; Shugang Li; Shangzhi Xu; Ruling Ma; Shuxia Guo; Proanthocyanidin Protects Human Embryo Hepatocytes from Fluoride-Induced Oxidative Stress by Regulating Iron Metabolism. Biological Trace Element Research 2015, 169, 174-179, 10.1007/s12011-015-0409-1.
- Jiao, Y.; Wilkinson, J.T.; Di, X.; Wang, W.; Hatcher, H.; Kock, N.D.; D’Agostino, R., Jr.; Knovich, M.A.; Torti, F.M.; Torti, S.V.; et al. Curcumin, a cancer chemopreventive and chemotherapeutic agent, is a biologically active iron chelator.. Blood 2009, 113, 462–469, 10.1182/blood-2008-05-155952.
- Naresh Kumar; Vikas Pruthi; Potential applications of ferulic acid from natural sources.. Biotechnology Reports 2014, 4, 86-93, 10.1016/j.btre.2014.09.002.
- Yang Qiao; Huan He; Zeyu Zhang; Zhangping Liao; Dong Yin; Dan Liu; Bo Yi; Ming He; Long-Term Sodium Ferulate Supplementation Scavenges Oxygen Radicals and Reverses Liver Damage Induced by Iron Overloading. Molecules 2016, 21, 1219, 10.3390/molecules21091219.
- Calamini, B.; Ratia, K.; Malkowski, M.G.; Cuendet, M.; Pezzuto, J.M.; Santarsiero, B.D.; Mesecar, A.D.; Pleiotropic mechanisms facilitated by resveratrol and its metabolites. . Biochem. J. 2010, 429, 273–282, 10.1042/BJ20091857.
- Subhash K. Das; Jessica Desaulniers; Jason R. B. Dyck; Zamaneh Kassiri; Gavin Y Oudit; Resveratrol mediates therapeutic hepatic effects in acquired and genetic murine models of iron-overload. Liver International 2015, 36, 246-257, 10.1111/liv.12893.
- Marica Meroni; Miriam Longo; Veronica Erconi; Luca Valenti; Stefano Gatti; Anna Ludovica Fracanzani; Paola Dongiovanni; mir-101-3p Downregulation Promotes Fibrogenesis by Facilitating Hepatic Stellate Cell Transdifferentiation During Insulin Resistance.. Nutrients 2019, 11, 2597, 10.3390/nu11112597.
- Bartel, D.P.; Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. . Cell 2004, 116, 281–297, 10.1016/s0092-8674(04)00045-5.
- Chiranjib Chakraborty; Ashish Ranjan Sharma; Garima Sharma; C. George Priya Doss; Sang-Soo Lee; Therapeutic miRNA and siRNA: Moving from Bench to Clinic as Next Generation Medicine. Molecular Therapy - Nucleic Acids 2017, 8, 132-143, 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.06.005.
- Paola Dongiovanni; Marica Meroni; Miriam Longo; Silvia Fargion; Anna Ludovica Fracanzani; miRNA Signature in NAFLD: A Turning Point for a Non-Invasive Diagnosis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2018, 19, 3966, 10.3390/ijms19123966.
- Céline Tiffon; The Impact of Nutrition and Environmental Epigenetics on Human Health and Disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2018, 19, 3425, 10.3390/ijms19113425.
- Eric Huntzinger; Elisa Izaurralde; Gene silencing by microRNAs: contributions of translational repression and mRNA decay. Nature Reviews Microbiology 2011, 12, 99-110, 10.1038/nrg2936.
- Friedman, R.C.; Farh, K.K.; Burge, C.B.; Bartel, D.P.; Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs.. Genome Res. 2009, 19, 92–105, 10.1101/gr.082701.108.
- Mirco Castoldi; Martina U. Muckenthaler; Regulation of iron homeostasis by microRNAs. Cellular and Molecular Life Sciences 2012, 69, 3945-3952, 10.1007/s00018-012-1031-4.
- Michael Faller; Michio Matsunaga; Sheng Yin; Joseph A. Loo; Feng Guo; Heme is involved in microRNA processing. Nature Structural & Molecular Biology 2006, 14, 23-29, 10.1038/nsmb1182.
- Dale G. Schaar; Daniel J. Medina; Dirk F. Moore; Roger K. Strair; Yi Ting; miR-320 targets transferrin receptor 1 (CD71) and inhibits cell proliferation. Experimental Hematology 2009, 37, 245-255, 10.1016/j.exphem.2008.10.002.
- Yalin Liao; Xiaogu Du; Bo Lönnerdal; miR-214 Regulates Lactoferrin Expression and Pro-Apoptotic Function in Mammary Epithelial Cells. The Journal of Nutrition 2010, 140, 1552-1556, 10.3945/jn.110.124289.
- Liao, Y.; Lonnerdal, B.; miR-584 mediates post-transcriptional expression of lactoferrin receptor in Caco-2 cells and in mouse small intestine during the perinatal period.. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2010, 42, 1363–1369, 10.1016/j.biocel.2009.07.019.
- Svitlana I. Shpyleva; Volodymyr Tryndyak; Olga Kovalchuk; Athena Starlard-Davenport; Vasyl’ F. Chekhun; Frederick A. Beland; Igor P. Pogribny; Role of ferritin alterations in human breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer Research and Treatment 2010, 126, 63-71, 10.1007/s10549-010-0849-4.
- Castoldi, M.; Vujic Spasic, M.; Altamura, S.; Elmen, J.; Lindow, M.; Kiss, J.; Stolte, J.; Sparla, R.; D'Alessandro, L.A.; Klingmuller, U.; et al. The liver-specific microRNA miR-122 controls systemic iron homeostasis in mice.. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 1386–1396, 10.1172/jci44883.
- Masuko Kobori; Saeko Masumoto; Yukari Akimoto; Hideaki Oike; Chronic dietary intake of quercetin alleviates hepatic fat accumulation associated with consumption of a Western-style diet in C57/BL6J mice. Molecular Nutrition & Food Research 2010, 55, 530-540, 10.1002/mnfr.201000392.
- Takatoshi Murase; Koichi Misawa; Yoshihiko Minegishi; Masafumi Aoki; Hideo Ominami; Yasuto Suzuki; Yusuke Shibuya; Tadashi Hase; Coffee polyphenols suppress diet-induced body fat accumulation by downregulating SREBP-1c and related molecules in C57BL/6J mice. American Journal of Physiology-Endocrinology and Metabolism 2011, 300, E122-E133, 10.1152/ajpendo.00441.2010.
