During restricted time windows of postnatal life, called critical periods, neural circuits are highly plastic and are shaped by environmental stimuli. In several mammalian brain areas, from the cerebral cortex to the hippocampus and amygdala, the closure of the critical period is dependent on the formation of perineuronal nets (PNNs). PNNs are condensed aggregates of an extracellular matrix (ECM) enwrapping the cell body, dendrites, and axon initial segments of several neurons in the adult central nervous system (CNS). They represent one form of an ECM in the CNS, together with the ECM that is loosely distributed in the parenchyma, the ECM that constitutes the basal lamina (which separates the CNS tissue from meningeal and vascular tissues), and the ECM that is located at the nodes of Ranvier.
- perineuronal net
- critical period
- Alzheimer’s disease
- drug addiction
1. Introduction
The PNN coating is interrupted by holes, in which synaptic boutons are contained (see Figure 1A,B for representative pictures of PNNs in the mouse cerebellar nuclei that enwrap GABAergic terminals).
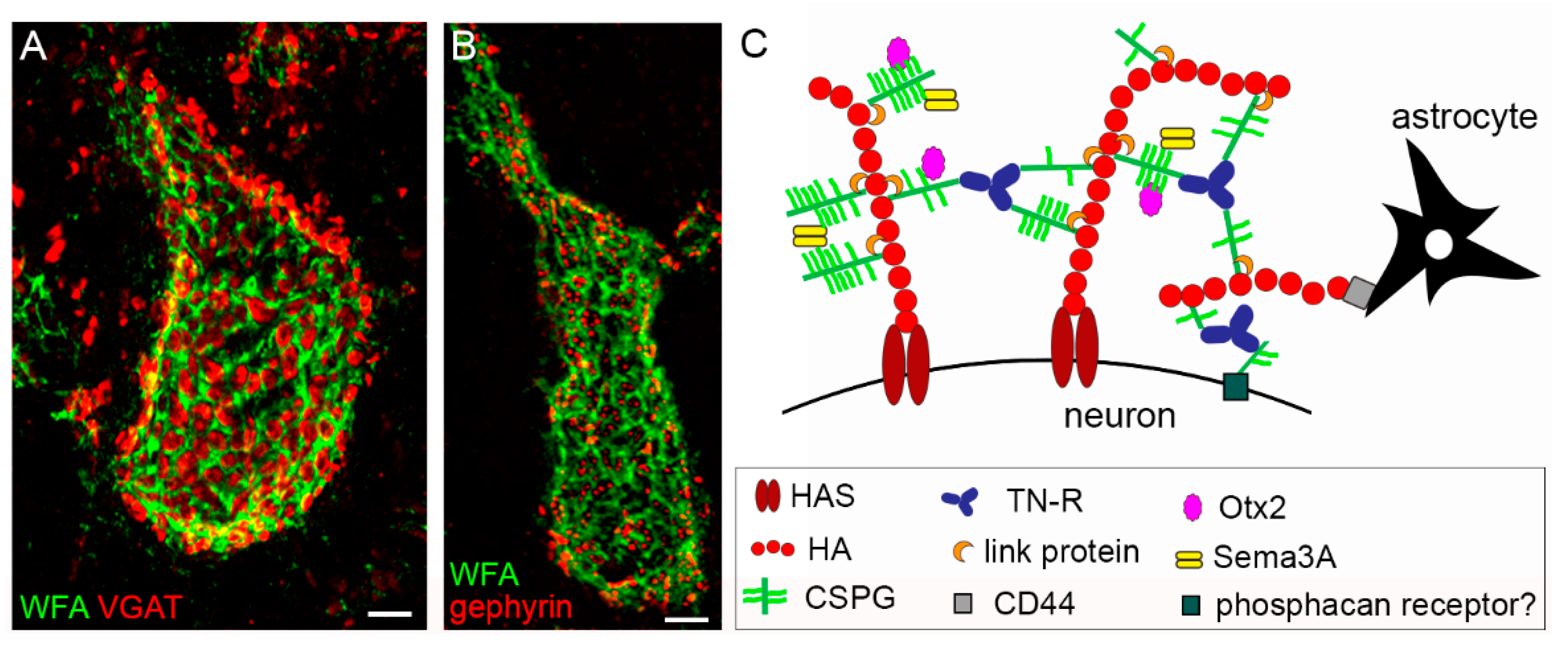
PNN embedded synapses can be viewed as a tetrapartite structure, comprising the presynaptic terminal, the postsynaptic element, astrocytic processes, and the PNN [1]. PNNs are found around distinct classes of inhibitory and excitatory neurons throughout the rostrocaudal axis of the CNS of vertebrates, from the cortex to the spinal cord. PNNs are particularly well developed in birds and mammals. In the latter class, PNNs have been described in several species, including mice, rats, guinea pigs, gerbils, cats, dogs, sheep, monkeys, and humans. Examples of PNN-bearing neurons in rodents are GABAergic parvalbumin (PV)+ neurons in the cortex, interneurons, and pyramidal neurons in the hippocampus; PV-positive and negative neurons in the striatum; excitatory neurons in the cerebellar nuclei; motoneurons and interneurons in the spinal cord [2][3][4][5][6][7][8][9][10][11][12][13][14][15][16][17]. Notably, species-dependent differences exist with respect to whether PNNs surround the inhibitory or excitatory neurons. Although in rodents, the majority of PNN-enwrapped neurons in the cortex are PV+ GABAergic neurons, in primates, a substantial number of pyramidal neurons in the motor and somatosensory cortex bear a PNN [6][18][19]. In the basolateral amygdala of rats, PNNs are found around PV+ and PV− neurons, while in mice, they are reported only around excitatory neurons [20][21]. The common denominator of all different types of PNN-bearing neurons seems to be their fast-spiking neuronal activity. Thus, PNNs are proposed to serve as extracellular reservoirs for physiologically relevant cations, such as Ca2+, K+, or Na+, contributing to fast and precise neuronal transmission [22]. Indeed, through ionic interactions, polyanionic components of PNNs are able to reversibly accumulate cationic molecules at physiological concentrations, potentially contributing to local molecular gradients of ions [23]. The “anionic shield” made by the PNN may also represent a protective mechanism against toxic species that are generated by metabolic or oxidative stress.
2. PNNs and Memory-Related Diseases
In the last decade, several studies focused on the relationship between PNNs and memory processes, as well as PNNs and various brain diseases, including schizophrenia, epilepsy, depression, multiple sclerosis, and Huntington’s disease [24][25][26][27][28]. Here, we address PNN changes and their roles in two widespread memory-related diseases, namely Alzheimer’s disease (AD), in which memory formation is compromised, and drug addiction, in which maladaptive memories are present.
2.1. PNNs in Alzheimer’s Disease
AD is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that affects the neocortex and hippocampus and is characterized by impaired learning and retrieval of memories. Two hallmarks of AD are extraneuronal deposition of the amyloid-beta protein in the form of plaques and intraneuronal aggregation of the microtubule-associated protein tau in the form of filaments [29][30]. Some studies document a partial loss of chondroitin sulfate-glycosaminoglycans (CS-GAGs)/CSPGs in the PNNs of patients and mouse models of AD, particularly in the cingulate, frontal, temporal, and entorhinal cortexes [26][31][32] and middle frontal gyrus [33] in humans, and in the hippocampus CA1, CA2, and CA3 [34], subiculum, and visual cortex [33] in mice. However, other studies report no alteration of PNNs in the brains of AD patients or mice in the human insular cortex and subcortical regions [35]; human primary sensory, secondary, and associative areas of the temporal and occipital lobe [36]; mouse parietal cortex [35]. A recent study pointed to an intriguing role of microglia activation, triggered by amyloid plaques, in mediating extensive PNN loss in a mouse model of AD [33]. While there are no studies reporting a PNN increase in human AD brains, mice characterized by amyloid-beta plaque production (APP/PS1 mice) show increased WFA labeling around hippocampal PV neurons and the upregulation of several ECM proteins in hippocampal synaptosome preparations at early stages (3 months of age), when amyloid-beta plaques are not yet observed, but when contextual fear memory is impaired and long-term potentiation (LTP) is reduced. These physiological and behavioral deficits are reversed when the ECM/PNNs are removed by chondroitinase ABC (ChABC), indicating that perisynaptic ECM accumulation may contribute to early memory and plasticity impairments in AD [37]. Interestingly, PNNs may protect neurons and synapses from amyloid toxicity, as shown in vitro [38], and from tau pathology [35][39]. Direct evidence for a role of PNN in neuroprotection is shown in the study by Suttkus et al. [40]. When exogenous tau protein is added to brain organotypic cultures, it is mainly internalized in neurons without a PNN. However, if the PNN is disrupted due to the lack of aggrecan, link protein 1, or tenascin-R, tau becomes internalized in PNN neurons as well. Membrane-associated heparan sulfate proteoglycans have been shown to induce the internalization of tau aggregates [41]. PNNs may bind tau aggregates (possibly through the large polyanionic molecule aggrecan), therefore inhibiting their interaction with the heparan sulfate proteoglycans and, as a consequence, their internalization.
In order to overcome the progressive loss of functional connections due to neurodegeneration in AD, new connections may help bypass nonfunctional neurons, leading to functional improvements. To help form new connections, the degradation of PNNs may be beneficial. In the study by Yang et al. [42], the digestion of PNNs in the perirhinal cortex of AD mice with neurodegenerative tauopathy, in which object memory decays rapidly, results in restoration of normal synaptic transmission and behavioral amelioration. The sulfation pattern of CS-GAGs affects CSPG binding properties and function, with 4-sulfated CS-GAGs being inhibitory to neurite growth. Interestingly, in tauopathy mice, the administration of antibodies blocking 4-sulfated CS-GAGs in the perirhinal cortex is sufficient to restore object memory [43].
Overall, there is some discrepancy between studies investigating PNN changes in AD human tissue, as well as in mouse models, with some studies reporting no changes and others reporting a PNN reduction. These differences in mice may depend on the mouse genetic background, and in humans, on the disease stage, the brain area investigated, the age of the patient, and technical issues. Moreover, AD mouse models do not always match with the human pathology, as PNN expression is increased in some mouse models of AD, whereas in human AD brains, PNNs are mostly decreased or unchanged. Given the important role of sulfation patterns in PNN functions, it would be interesting to address whether PNN sulfation in brain regions affected by AD is different from that of healthy subjects. PNN sulfation pattern can be a potential therapeutic target for improving AD symptoms.
PNNs are shown to have a neuroprotective role against tau pathology. However, beneficial effects on memory were obtained by acute PNN disruption in tauopathy mice [42]. Further studies are needed to elucidate the synaptic/anatomical changes underlying memory restoration, as well as long-term effects, following PNN manipulation in AD mice. Moreover, in view of developing therapeutic strategies, the dual role of PNNs in neuroprotection and the restriction of plasticity should be taken into account.
2.2. PNNs and Drug Addiction
Drug addiction is considered a chronic relapsing disorder, in which craving and relapse to drug seeking occur even after prolonged abstinence [44]. This is because addiction involves many of the same brain circuits that govern learning and memory. Exposure to environmental stimuli that have previously been associated with the effects of self-administered drugs is often a major contributor to relapse, as it evokes memories of the effects of the drug [44][45]. Given the role of PNNs in learning and memory processes, including associative memories, it is not surprising that PNNs are not only altered following drug consumption or during addiction but also play an active role in the consolidation of addiction memories [46][47]. Memories of drug-associated environmental cues are assessed using the conditioned place preference test, in which animals learn to associate the environment in which they received the drug with the internal positive state achieved while on the drug, and thus spend more time in the drug-paired compartment, even in the absence of the drug. In rats that received a ChABC injection in the prelimbic cortex or the anterior dorsal region of the lateral hypothalamus before conditioning, the development of a cocaine-conditioned place preference is attenuated, indicating that PNNs in those brain regions are important for memories of drug–environment associations [48][49]. Moreover, PNNs in the anterior dorsal region of the lateral hypothalamus are instrumental for the expression of the cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior [50]. Interestingly, when ChABC is injected into the prefrontal cortex after extinction, but before the reactivation of the cocaine memory, the preference for the cocaine-paired chamber is attenuated, suggesting that PNNs are also important for memory reconsolidation [48]. In accordance with the results shown by Gogolla et al. [51], in which the reinstatement of a fear memory is reduced after ChABC injection in the amygdala, PNN digestion in the amygdala enables extinction training to erase drug memories, attenuating the reinstatement of morphine-induced and cocaine-induced conditioned-place preference [52]. Together, these observations highlight a crucial role of PNNs in memory of drug-associated environments and suggest that targeting PNNs might be a therapeutic strategy to suppress these maladaptive memories and prevent relapse to drug use.
3. Conclusions
Although at the time of their first detection, PNNs did not receive much attention, being considered as mere staining artifacts, later they were recognized as an integral part of the brain maturation process, especially with the unexpected discovery of a link between PNNs and brain plasticity [53]. In the adult brain, PNNs turned out to be more dynamic than initially thought, and they took center stage in what is considered to be one of the great mysteries of neuroscience, namely, how memories are encoded in the brain [51][54][55].
To get a better understanding of PNN dynamics, however, the production of tools allowing for live PNN imaging would be required. This way, temporal changes in the structure and expression of PNNs in vivo, for instance, during learning and memory, might be unveiled. Furthermore, developing molecular tools (vectors, antibodies, peptides, antagonists, etc.) to specifically interfere with PNN components would be beneficial to further our understanding of PNN functions and, in view of designing therapeutic tools, to improve certain CNS conditions. Most studies have used ChABC to remove PNN-GAG chains and increase CNS plasticity. However, in the context of human therapy, this approach is not feasible, as multiple injections of the enzyme would be needed to target large volumes of the human brain and to ensure a long-term supply of it. The delivery of ChABC via viral vectors, which can ensure a cell-type-specific and continuous delivery of the enzyme, may be a promising strategy to overcome those issues [56][57][58][59]. The recent development of an immune-evasive and time-regulatable ChABC gene therapy system [60] is a further step in this direction. It has to be noted, though, that ChABC treatment affects PNNs, as well as diffuse and membrane-bound CS-GAGs, and is therefore not ideal when there is the need to specifically target PNNs. Even when targeting PNN-CSPGs, ChABC can be considered a crude intervention, as it affects all CS-GAGs and, in turn, CSPG-binding partners, which may play distinct roles in the control of plasticity. Therefore, targeting specific components of the PNN seems a better approach. Potentially interesting candidates in this respect are Sema3A and Otx2. Further studies are needed to unravel their precise role in physiological conditions, such as during learning and memory or the aging process, as well as in pathological conditions. In addition, given the crucial role played by specific sulfated CS-GAGs in PNN binding properties and the regulation of plasticity, memory, and aging, targeting the sulfation pattern of CS-GAGs may be another strategy to delicately manipulate PNNs.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms22052434
References
- Dityatev, A.; Schachner, M.; Sonderegger, P. The dual role of the extracellular matrix in synaptic plasticity and homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2010, 11, 735–746.
- Hockfield, S.; McKay, R.D.; Hendry, S.H.; Jones, E.G. A surface antigen that identifies ocular dominance columns in the visual cortex and laminar features of the lateral geniculate nucleus. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol. 1983, 48, 877–889.
- Seeger, G.; Brauer, K.; Härtig, W.; Brückner, G. Mapping of perineuronal nets in the rat brain stained by colloidal iron hydroxide histochemistry and lectin cytochemistry. Neuroscience 1994, 58, 371–388.
- Brückner, G.; Schütz, A.; Härtig, W.; Brauer, K.; Paulke, B.R.; Bigl, V. Projection of non-cholinergic basal forebrain neurons ensheathed with perineuronal nets to rat mesocortex. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 1994, 8, 11–18.
- Härtig, W.; Brückner, G.; Brauer, K.; Schmidt, C.; Bigl, V. Allocation of perineuronal nets and parvalbumin-, calbindin-D28k- and glutamic acid decarboxylase-immunoreactivity in the amygdala of the rhesus monkey. Brain Res. 1995, 698, 265–269.
- Hausen, D.; Brückner, G.; Drlicek, M.; Härtig, W.; Brauer, K.; Bigl, V. Pyramidal cells ensheathed by perineuronal nets in human motor and somatosensory cortex. Neuroreport 1996, 7, 1725–1729.
- Ojima, H.; Sakai, M.; Ohyama, J. Molecular heterogeneity of Vicia villosa-recognized perineuronal nets surrounding pyramidal and nonpyramidal neurons in the guinea pig cerebral cortex. Brain Res. 1998, 786, 274–280.
- Brückner, G.; Grosche, J.; Hartlage-Rübsamen, M.; Schmidt, S.; Schachner, M. Region and lamina-specific distribution of extracellular matrix proteoglycans, hyaluronan and tenascin-R in the mouse hippocampal formation. J. Chem. Neuroanat. 2003, 26, 37–50.
- Carulli, D.; Rhodes, K.E.; Brown, D.J.; Bonnert, T.P.; Pollack, S.J.; Oliver, K.; Strata, P.; Fawcett, J.W. Composition of perineuronal nets in the adult rat cerebellum and the cellular origin of their components. J. Comp. Neurol. 2006, 494, 559–577.
- Vidal, E.; Bolea, R.; Tortosa, R.; Costa, C.; Domènech, A.; Monleón, E.; Vargas, A.; Badiola, J.J.; Pumarola, M. Assessment of calcium-binding proteins (Parvalbumin and Calbindin D-28K) and perineuronal nets in normal and scrapie-affected adult sheep brains. J. Virol. Methods 2006, 136, 137–146.
- Galtrey, C.M.; Kwok, J.C.F.; Carulli, D.; Rhodes, K.E.; Fawcett, J.W. Distribution and synthesis of extracellular matrix proteoglycans, hyaluronan, link proteins and tenascin-R in the rat spinal cord. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 27, 1373–1390.
- Lee, H.; Leamey, C.A.; Sawatari, A. Perineuronal nets play a role in regulating striatal function in the mouse. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e32747.
- Yamada, J.; Jinno, S. Spatio-temporal differences in perineuronal net expression in the mouse hippocampus, with reference to parvalbumin. Neuroscience 2013, 253, 368–379.
- Carstens, K.E.; Phillips, M.L.; Pozzo-Miller, L.; Weinberg, R.J.; Dudek, S.M. Perineuronal nets suppress plasticity of excitatory synapses on CA2 pyramidal neurons. J. Neurosci. 2016, 36, 6312–6320.
- Fech, T.; Calderón-Garcidueñas, L.; Kulesza, R.J. Characterization of the superior olivary complex of Canis lupus domesticus. Hear. Res. 2017, 351, 130–140.
- Mirzadeh, Z.; Alonge, K.M.; Cabrales, E.; Herranz-Pérez, V.; Scarlett, J.M.; Brown, J.M.; Hassouna, R.; Matsen, M.E.; Nguyen, H.T.; Garcia-Verdugo, J.M.; et al. Perineuronal net formation during the critical period for neuronal maturation in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus. Nat. Metab. 2019, 1, 212–221.
- Marchand, A.; Schwartz, C. Perineuronal net expression in the brain of a hibernating mammal. Brain Struct. Funct. 2020, 225, 45–56.
- Härtig, W.; Brauer, K.; Bigl, V.; Brückner, G. Chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan-immunoreactivity of lectin-labeled perineuronal nets around parvalbumin-containing neurons. Brain Res. 1994, 635, 307–311.
- Alpár, A.; Gärtner, U.; Härtig, W.; Brückner, G. Distribution of pyramidal cells associated with perineuronal nets in the neocortex of rat. Brain Res. 2006, 1120, 13–22.
- Baker, K.D.; Gray, A.R.; Richardson, R. The development of perineuronal nets around parvalbumin GABAergic neurons in the medial prefrontal cortex and basolateral amygdala of rats. Behav. Neurosci. 2017, 131, 289–303.
- Morikawa, S.; Ikegaya, Y.; Narita, M.; Tamura, H. Activation of perineuronal net-expressing excitatory neurons during associative memory encoding and retrieval. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 46024.
- Härtig, W.; Derouiche, A.; Welt, K.; Brauer, K.; Grosche, J.; Mäder, M.; Reichenbach, A.; Brückner, G. Cortical neurons immunoreactive for the potassium channel Kv3.1b subunit are predominantly surrounded by perineuronal nets presumed as a buffering system for cations. Brain Res. 1999, 842, 15–29.
- Morawski, M.; Reinert, T.; Meyer-Klaucke, W.; Wagner, F.E.; Tröger, W.; Reinert, A.; Jäger, C.; Brückner, G.; Arendt, T. Ion exchanger in the brain: Quantitative analysis of perineuronally fixed anionic binding sites suggests diffusion barriers with ion sorting properties. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 16471.
- Crapser, J.D.; Ochaba, J.; Soni, N.; Reidling, J.C.; Thompson, L.M.; Green, K.N. Microglial depletion prevents extracellular matrix changes and striatal volume reduction in a model of Huntington’s disease. Brain 2020, 143, 266–288.
- Gray, E.; Thomas, T.L.; Betmouni, S.; Scolding, N.; Love, S. Elevated matrix metalloproteinase-9 and degradation of perineuronal nets in cerebrocortical multiple sclerosis plaques. J. Neuropathol. Exp. Neurol. 2008, 67, 888–899.
- Pantazopoulos, H.; Berretta, S. In sickness and in health: Perineuronal nets and synaptic plasticity in psychiatric disorders. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 9847696.
- Testa, D.; Prochiantz, A.; Di Nardo, A.A. Perineuronal nets in brain physiology and disease. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2019, 89, 125–135.
- Spijker, S.; Koskinen, M.K.; Riga, D. Incubation of depression: ECM assembly and parvalbumin interneurons after stress. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2020, 118, 65–79.
- Braak, H.; Braak, E. Neuropathological stageing of Alzheimer-related changes. Acta Neuropathol. 1991, 82, 239–259.
- Goedert, M.; Sisodia, S.S.; Price, D.L. Neurofibrillary tangles and β-amyloid deposits in Alzheimer’s disease. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 1991, 1, 441–447.
- Kobayashi, K.; Emson, P.C.; Mountjoy, C.Q. Vicia villosa lectin-positive neurones in human cerebral cortex. Loss in Alzheimer-type dementia. Brain Res. 1989, 498, 170–174.
- Baig, S.; Wilcock, G.K.; Love, S. Loss of perineuronal net N-acetylgalactosamine in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2005, 110, 393–401.
- Crapser, J.D.; Spangenberg, E.E.; Barahona, R.A.; Arreola, M.A.; Hohsfield, L.A.; Green, K.N. Microglia facilitate loss of perineuronal nets in the Alzheimer’s disease brain. EBioMedicine 2020, 58, 102919.
- Cattaud, V.; Bezzina, C.; Rey, C.C.; Lejards, C.; Dahan, L.; Verret, L. Early disruption of parvalbumin expression and perineuronal nets in the hippocampus of the Tg2576 mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease can be rescued by enriched environment. Neurobiol. Aging 2018, 72, 147–158.
- Morawski, M.; Brückner, G.; Jäger, C.; Seeger, G.; Arendt, T. Neurons associated with aggrecan-based perineuronal nets are protected against tau pathology in subcortical regions in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 1347–1363.
- Morawski, M.; Brückner, G.; Jäger, C.; Seeger, G.; Matthews, R.T.; Arendt, T. Involvement of perineuronal and perisynaptic extracellular matrix in Alzheimer’s disease neuropathology. Brain Pathol. 2012, 22, 547–561.
- Végh, M.J.; Heldring, C.M.; Kamphuis, W.; Hijazi, S.; Timmerman, A.J.; Li, K.W.; van Nierop, P.; Mansvelder, H.D.; Hol, E.M.; Smit, A.B.; et al. Reducing hippocampal extracellular matrix reverses early memory deficits in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2014, 2, 76.
- Miyata, S.; Nishimura, Y.; Nakashima, T. Perineuronal nets protect against amyloid β-protein neurotoxicity in cultured cortical neurons. Brain Res. 2007, 1150, 200–206.
- Brückner, G.; Hausen, D.; Härtig, W.; Drlicek, M.; Arendt, T.; Brauer, K. Cortical areas abundant in extracellular matrix chondroitin sulphate proteoglycans are less affected by cytoskeletal changes in Alzheimer’s disease. Neuroscience 1999, 92, 791–805.
- Suttkus, A.; Holzer, M.; Morawski, M.; Arendt, T. The neuronal extracellular matrix restricts distribution and internalization of aggregated Tau-protein. Neuroscience 2016, 313, 225–235.
- Holmes, B.B.; DeVos, S.L.; Kfoury, N.; Li, M.; Jacks, R.; Yanamandra, K.; Ouidja, M.O.; Brodsky, F.M.; Marasa, J.; Bagchi, D.P.; et al. Heparan sulfate proteoglycans mediate internalization and propagation of specific proteopathic seeds. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3138–E3147.
- Yang, S.; Cacquevel, M.; Saksida, L.M.; Bussey, T.J.; Schneider, B.L.; Aebischer, P.; Melani, R.; Pizzorusso, T.; Fawcett, J.W.; Spillantini, M.G. Perineuronal net digestion with chondroitinase restores memory in mice with tau pathology. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 265, 48–58.
- Yang, S.; Hilton, S.; Nuno Alves, J.; Saksida, L.M.; Bussey, T.; Matthews, R.T.; Kitagawa, H.; Spillantini, M.G.; Kwok, J.C.F.; Fawcett, J.W. Antibody recognizing 4-sulfated chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans restores memory in tauopathy-induced neurodegeneration. Neurobiol. Aging 2017, 59, 197–209.
- Gawin, F.H.; Kleber, H.D. Abstinence Symptomatology and Psychiatric Diagnosis in Cocaine Abusers: Clinical Observations. Arch. Gen. Psychiatry 1986, 43, 107–113.
- O’Brien, C.P.; Childress, A.R.; Ehrman, R.; Robbins, S.J. Conditioning factors in drug abuse: Can they explain compulsion? J. Psychopharmacol. 1998, 12, 15–22.
- Lasek, A.W.; Chen, H.; Chen, W.Y. Releasing Addiction Memories Trapped in Perineuronal Nets. Trends Genet. 2018, 34, 197–208.
- Slaker, M.; Blacktop, J.M.; Sorg, B.A. Caught in the net: Perineuronal nets and addiction. Neural Plast. 2016, 2016, 7538208.
- Slaker, M.; Churchill, L.; Todd, R.P.; Blacktop, J.M.; Zuloaga, D.G.; Raber, J.; Darling, R.A.; Brown, T.E.; Sorg, B.A. Removal of perineuronal nets in the medial prefrontal cortex impairs the acquisition and reconsolidation of a cocaine-induced conditioned place preference memory. J. Neurosci. 2015, 35, 4190–4202.
- Blacktop, J.M.; Todd, R.P.; Sorg, B.A. Role of perineuronal nets in the anterior dorsal lateral hypothalamic area in the acquisition of cocaine-induced conditioned place preference and self-administration. Neuropharmacology 2017, 118, 124–136.
- Blacktop, J.M.; Sorg, B.A. Perineuronal nets in the lateral hypothalamus area regulate cue-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking behavior. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 850–858.
- Gogolla, N.; Caroni, P.; Lüthi, A.; Herry, C. Perineuronal nets protect fear memories from erasure. Science 2009, 325, 1258–1261.
- Xue, Y.-X.; Xue, L.-F.; Liu, J.-F.; He, J.; Deng, J.-H.; Sun, S.-C.; Han, H.-B.; Luo, Y.-X.; Xu, L.-Z.; Wu, P.; et al. Depletion of Perineuronal Nets in the Amygdala to Enhance the Erasure of Drug Memories. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 6647–6658.
- Pizzorusso, T.; Medini, P.; Berardi, N.; Chierzi, S.; Fawcett, J.W.; Maffei, L. Reactivation of ocular dominance plasticity in the adult visual cortex. Science 2002, 298, 1248–1251.
- Tsien, R.Y. Very long-term memories may be stored in the pattern of holes in the perineuronal net. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 12456–12461.
- Duncan, J.A.; Foster, R.; Kwok, J.C.F. The potential of memory enhancement through modulation of perineuronal nets. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 176, 3611–3621.
- Carulli, D.; Broersen, R.; de Winter, F.; Muir, E.M.; Mešković, M.; de Waal, M.; de Vries, S.; Boele, H.-J.; Canto, C.B.; De Zeeuw, C.I.; et al. Cerebellar plasticity and associative memories are controlled by perineuronal nets. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2020, 117, 6855–6865.
- Zhao, R.R.; Muir, E.M.; Nuno Alves, J.; Rickman, H.; Allan, A.Y.; Kwok, J.C.F.; Roet, K.C.D.; Verhaagen, J.; Schneider, B.L.; Bensadoun, J.-C.; et al. Lentiviral vectors express chondroitinase ABC in cortical projections and promote sprouting of injured corticospinal axons. J. Neurosci. Methods 2011, 201, 228–238.
- Bartus, K.; James, N.D.; Didangelos, A.; Bosch, K.D.; Verhaagen, J.; Yáñez-Muñoz, R.J.; Rogers, J.H.; Schneider, B.L.; Muir, E.M.; Bradbury, E.J. Large-Scale Chondroitin Sulfate Proteoglycan Digestion with Chondroitinase Gene Therapy Leads to Reduced Pathology and Modulates Macrophage Phenotype following Spinal Cord Contusion Injury. J. Neurosci. 2014, 34, 4822–4836.
- James, N.D.; Shea, J.; Muir, E.M.; Verhaagen, J.; Schneider, B.L.; Bradbury, E.J. Chondroitinase gene therapy improves upper limb function following cervical contusion injury. Exp. Neurol. 2015, 271, 131–135.
- Burnside, E.R.; De Winter, F.; Didangelos, A.; James, N.D.; Andreica, E.-C.; Layard-Horsfall, H.; Muir, E.M.; Verhaagen, J.; Bradbury, E.J. Immune-evasive gene switch enables regulated delivery of chondroitinase after spinal cord injury. Brain 2018, 141, 2362–2381.
