Pharmacogenomics (PGx) is the knowledge of diverse drug responses and effects in people, based on their genomic profiles.
- pharmacogenomics
- NGS variants
1. Introduction: Pharmacogenomics and High Throughput Sequencing Methods
It has been reported for decades that different drugs show different responses and efficacy in diverse individuals or populations. Investigations proved that part of this diversity (20–30%) is because of genetic background and, more precisely, the inheritance of various alleles and variants in genes for drug-metabolizing and transporting (pharmacogenes) or drug target molecules [1]. Pharmacogenetics is the term for the knowledge of diverse drug responses and effects in people, based on their single genes on the genomic profiles. When a group of genes (multiple genes), or whole genome, and other influential genomic events, such as epigenetics will be addressed at once for such investigations, the phrase would be replaced by pharmacogenomics (PGx). Since the starting of employing high throughput sequencing methods, especially next generation sequencing (NGS) technologies, in addition to some comprehensive orthogonal tests, such as genome-wide single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) arrays in clinical investigations and practice, numerous genetic variants have been introduced in drug-related genes in the human body. Today, close to 100 variants in each people in more than 900 of such genes are mentioned in literature, and the number is increasing continuously [2][3]. There is no doubt that the NGS methods played a significant role in the identification of PGx variants in a clinical research setting and used in the prediction of the response to or adverse effects of drugs, which result in the calculation or estimation of appropriate drug dosage for patients. According to the patient’s responses, the drug outcome could be defined as efficient, inefficient, toxic, and resistant. All of these categories mostly arise from the interaction between the products of many genes in a cellular pathway or between the genes and environmental factors. Hence, genotype-specific therapy could bring huge benefits for drug safety and efficacy in patients in addition to time and cost reduction of treatment approaches for them [4]. The trends led to the practice of personalized therapy and precision medicine implementation in clinical centers. The explosion of examples in the field of pre-emptive and/or patient genotyping shows the true advantages of high throughput sequencing technologies in the PGx area [5][6][7][8]. However, despite the common belief between the physicians and general practitioners in the effects of the genetic landscape on diverse drug responses, if they asked that they order the PGx tests for their patients, less than 15% will answer positively. This is mostly because of the lack of clear guidelines and sufficient clinical evidence for many functional genetic variants (FGVs) in drug-related genes (FGVs or actionable genetic variants are those alterations in genome, with at least one report for introducing the effects on drug safety and/or efficacy in people. Moreover, the variants found in the research area with strong potential effects on drugs could be considered as FGVs during prescription. However, the latter needs clinical evidence to be influential on treatment decisions by physicians). Furthermore, the poor knowledge and background of PGx and the different related alleles and variants for many healthcare professionals may directly affect their desire to order the tests.
Yet, several rare and uncommon FGVs can be detected through the PGx tests in both clinical and research areas, especially when comprehensive and high capacity methods, such as NGS, have been utilized [9]. Moreover, it is necessary to distinguish the definition of FGVs and/or uncharacterized variants, such as variants with unknown clinical significance in two distinct genomic medicine areas, PGx, and medical genetics. Although the two concepts are usually mixed and many PGx variants are covered in the medical genetics zone, the first one mostly emphasizes those variants with an impact on pharmacological treatments, while the second group of variants is considered the genetic variations with pathogenicity effects in the human body. For a PGx variant, it might show an interaction with drug dosage modifications or not, but the functional and clinical consequences of a genetic variant may be unknown (does it have pathological consequences?) or well known (it has or not pathological consequences). However, both types of variants will be addressed as the same in NGS primary data analysis steps. To deal with the different genetic variants in PGx profiling of individuals, this review article reviews various NGS derived biomarkers and the possible approaches to use or consider them during the medicine prescription. Those PGx variants with no clear guidelines will be focused on more.
2. Different Types of Variants and Their Classifications in Clinical Pharmacogenomics
Both common and rare alleles are demonstrated as the functional biomarkers in PGx clinical practice. Low frequency and rare variants have been shown by 1–5% and lower than 1% minor allele frequency (MAF), respectively, in populations. Moreover, they proved to be very population-specific and the causative elements for diverse drug responses in alternative ethnic groups [10][11]. NGS methods revolutionized the detection of any type of variants in different aspects of genome analysis and profiling, as well as pharmacogenetics and genomic studies. Such investigations reported that most of the FGVs in the clinical PGx setting are Single Nucleotide Variations (SNVs). However, structural variants (SVs), such as Copy Number Variation (CNVs), small Insertion–Deletions (InDels), tandem-substitutions, and the deletion of entire exons are also identified as effective variants in drug responses [12][13]. In addition to wild-type alleles, the functional outcome for each of these variants may cause the individuals to fall into four main groups of responders including poor, intermediate, extensive, and ultra-rapid metabolizers.
Currently, core web-based resources for clinical PGx annotations include Pharmacogenomics Knowledge Base (PharmGKB), the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC), the Pharmacogenomics Research Network (PGRN), and Dutch Pharmacogenetics Working Group (DPWG). These are considered as reference databases that provide information about how human genetic variations affect response to medications. All of the confirmed data about clinically actionable gene-drug associations and genotype-phenotype relationships are sorted properly and available as a guide for personalized medicine implementation by healthcare professionals. However, other modules, such as PharmVar, FINDbase, SuperCYP, SEAPharm, etc. could also be applied when a specific type of gene or drug was on the desk. Nevertheless, according to PGx reference organizations (PharmGKB, CPIC-PGRN, and DPWG), all the diagnosed alleles and variants in a gene-drug interaction, based on the number of published studies and clinical evidence, will be classified in various types of level with clear explanations for each of them (Table 1). However, CPIC has also introduced a new categorization system for PGx level in more detail (Table 2). Generally, different levels of clinical relevance for PGx variants and/or gene-drug pairs will be assigned by the reference entities. All of them have their processes to assign the levels and prioritize approaches for providing the related guidelines. Meanwhile, some recommendations are related to each other (CPIC and PharmGKB) and the others go through it independently (DPWG). For example, the clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium (CPIC) allocates the levels for a variant in a gene-drug pair, based on three major criteria from PharmGKB clinical annotation levels of evidence and PGx level for Food and Drug Administration (FDA)-approved drug labels and also if it is nominated to CPIC for consideration. Only those gene/drug pairs that have been the subject of guidelines have had sufficient in-depth review of evidence to provide definitive CPIC level assignments. CPIC also use other considerations for assignment of CPIC level through some essential questions, containing the information of prescribing actionability, the severity of the clinical consequences for ignoring the genetic tests, already subjected gene to other CPIC guidelines, availability of genetic test for the gene, high-risk genetic variants, etc. [14][15]. PharmGKB also creates genotype-based summaries describing the phenotypic impact of the variant and provides the PGx levels from 1A to 4 in combination with four instructive labels as “Testing required”, “Testing recommended”, “Actionable PGx”, and “Informative PGx” via literature reviews while considering population size and statistical significance. The labels state different considerations for the drugs, based on gene/protein/chromosomal variants or phenotypes, and conclude the necessity of pre-emptive genetic testing for genotype/phenotype correlation assays and showing the potential changes in efficacy, dosage, metabolism, or toxicity [16][17]. Finally, the Dutch Pharmacogenetics working group (DPWG) uses the drug-gene interaction outcomes to providing the clinical relevance levels, where the AA is the lowest impact and F is the highest one. The impacts are categorized, based on adverse drug events, decreased therapeutic response, and other clinical effects, result in the allocation of specific scores from 1–7 derived from national cancer institute (NCI) common toxicity criteria and 0–4 level of evidence of gene–drug interaction in the literature [18].
Table 1. Different levels of clinical relevance for pharmacogenomics (PGx) variants in reference organizations.
| Reference Organization | PGx Level | Summary of Description | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| PharmGKB | 1A | Variants in this level are annotated and have a clear and endorsed guideline while showing a strong role in gene-drug interactions. | [19] |
| 1B | Annotated variant with strong evidence in the literature. Gene-drug association shows strong effects. | ||
| 2A | The annotated variant is in a VIP *, so functional significance is more likely. | ||
| 2B | Annotated variant but in moderate evidence of an association. There is no reliable replicated study in form of statistical significance or well-designed in size. | ||
| 3 | Annotated variant in a single study or multiple studies with no similar associations between the variant and the drug. | ||
| 4 | Annotated variant but in a case report and non-significant study or just in an in-vitro assay. | ||
| CPIC | A | Variants in this level oblige a change in related drug prescription. Strong clinical evidence and genotype-phenotype correlations exist. | [20] |
| B | Evidence is weak for the variant but still genotyping may be useful for alternative prescribing. | ||
| C | Different levels of evidence are mentioned in various publications for the variant. No prescribing actions are recommended. Mostly suitable for genes that are commonly included in clinical or DTC ** tests. | ||
| D | Weak evidence and conflicting data are introduced for the variant. Clinical actionability is unclear. No prescribing actions are recommended. | ||
| DPWG | AA | Variants with no significant clinical or kinetic effects. | [21] |
| A | Variants with minor clinical effects and kinetic effects. | ||
| B | Variants with mild clinical effects. | ||
| C | Variants with moderate clinical effects. | ||
| D | Variants with stronger clinical effects than level C. | ||
| E | Variants with severe clinical effects as the failure of lifesaving therapy or life-threatening complications. | ||
| F | Variants with most severe clinical effects, death is anticipated. | ||
| *** | |||
| 4 | There are good quality published studies for the variant/gene. | ||
| 3 | There are moderate quality published studies for the variant/gene. | ||
| 2 | Well documented case reports exist for the variant/gene. | ||
| 1 | Published incomplete case reports for the variant/gene. | ||
| 0 | Data on file. | ||
| . | No evidence. |
* VIP: very important pharmacogene, ** DTC: direct to consumer, *** Separate the two different levels definitions of the DPWG.
Table 2. Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC) new level of clinical relevance for gene/drug interactions.
| Cpic Level | Clinical Context | Level of Evidence | Strength of Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Genetic information should be used to change the prescribing of the affected drug. | The preponderance of the evidence is high or moderate in favor of changing prescribing. | At least one moderate or strong action (change in prescribing) is recommended. |
| A/B | Preliminary review indicates it is likely that the definitive CPIC level will be either A or B. | Full evidence review is needed to assess the level of evidence, but prescribing actionability is likely. | Full review by expert guideline group to assign strength of recommendation. |
| B | Genetic information could be used to change prescribing of the affected drug because alternative therapies/dosing are extremely likely to be as effective and as safe as non-genetically based dosing. | The preponderance of the evidence is weak with little conflicting data. | At least one optional action (change in prescribing) is recommended. |
| B/C | Preliminary review indicates it is likely that the definitive CPIC level will be either B or C. | Prescribing actionability based on genetics is not clear without further evidence review. | Full review by expert guideline group to assess the strength of recommendation. |
| C | There are published studies at varying levels of evidence, some with mechanistic rationale, but no prescribing actions are recommended because (a) dosing based on genetics makes no convincing difference; (b) alternatives are unclear, possibly less effective, more toxic, or otherwise impractical; or (c) few published studies or mostly weak evidence and clinical actions are unclear. Most important for genes that are subject to other CPIC guidelines or genes that are commonly included in clinical or DTC tests. | Evidence levels can vary. | No prescribing actions are recommended. |
| C/D | Preliminary review indicates it is likely that the definitive CPIC level will be either C or D. | Evidence levels can vary. | No prescribing actions are recommended. |
| D | There are few published studies, clinical actions are unclear, little mechanistic basis, mostly weak evidence, or substantial conflicting data. If the genes are not widely tested clinically, evaluations are not needed. Criteria for “widely tested” includes: 1) College of American Pathologists (CAP) proficiency testing is available; 2) gene is in disease-specific panels (e.g., pain, psychiatric, cancer, etc.); or 3) evidence exists for implementation of the gene into clinical practice (CPIC member feedback, publications, etc.). | Evidence levels can vary. | No prescribing actions are recommended. |
Adopted from cpicpgx.org/.
Regarding the abovementioned level of classification for the identified variants, the utilization of NGS platforms for clinical PGx tests brings various types of alleles, which after confirmation and validation processes could be categorized as functional/potential effective variants, fall into “five groups of (1) annotated variants with the clear guideline (i.e., rs1057910 in CYP2C9 and rs9923231 in VKORC1 genes for Warfarin). (2) Annotated variants with no clinical guideline (i.e., rs6166 in FSHR gene for urofollitropin). (3) Variants with annotation or guidelines for other drugs (i.e., rs9322335 in ESR1 gene for letrozole while the gene is studying and considered as the estrogen receptor and target molecule for Clomifene). (4) Non-pharmacogenetically annotated variants (i.e., different clinical related variants in AR gene as an important target molecule for infertility drugs). And (5) Variants of unknown significance (VUS). The next part will focus on different approaches for such variant interpretation and curation in clinical practice.
3. Approaches to Dealing with Diverse Pharmacogenomics Variants
To finding any clinical relevance for different groups of PGx variants from the sequencing platforms, standard algorithms, and procedures are introduced by the reference sources (Figure 1). These are the recommendations that indicate the approaches for decoding or predicting the variant functions and the related phenotypes as the diverse drug responses in individuals [22]. From the previous section, group 1 is considered as straightforward, actionable variants in gene-drug pairs with direct prescription recommendations for applying in routine clinical practice. Group 2 are the alleles, consisting of the most common types of identified variants during diagnostic procedures for PGx tests. As the PharmGKB included 19,028 variant annotations, most of the identified markers will fall into this group. Here, the number of clinical evidence in addition to statistical signification (i.e., number of patients in cohort studies) and types of the publications, if they are strong genome-wide association study, well designed replicated report, case report, non-significant study, or only an in-vitro study, would be the important factors for clinical consideration and decisions [23]. The other common scenario for the sequencing results of a pharmacogenetic screening test could be found in group 3, which are variants with the recommendations but not for the researchers/clinicians targeted drugs. Generally, if the related gene is introduced as a very important pharmacogene (VIP) in PGx databases, it is mostly well documented so the related cellular pathways must be analyzed thoroughly. Then the caution and consideration before dosage adjustment are suggested for more accurate implementation of personalized medicine in the clinic [24]. If there is a lack of such documents, more confirmation and validation assessments are necessary before any concerns for the patient’s prescription. Replicate tests in target drugs in such situations consist of various approaches, from looking for the same result in same/different ethnic groups to implementation of laboratory confirmation tests. However, alternative approaches have also been introduced for PGx findings validation, if replication studies for gene-drug interactions proved to be difficult and costly for some cases [25]. In the end, consulting with gene experts or experienced clinical pharmacologist in the gene–drug interaction field is necessary. So far, reference databases have explained the approaches to deal with variants in group one to three. However, many genetic variations may be classified in group 4, which is introduced as disease-associated biomarkers and placed into the different genomic databases, such as ClinVar, dbGaP, HapMap, gnomAD, COSMIC, etc. (as causative or pathogenic variants), but there is no PGx report for them. This is mostly happening during more comprehensive genomic profiling of individuals for decoding any PGx markers. In such a situation, the first step could be the evaluation of the gene, if it is introduced as drug related in literature and databases before. The positive result may follow the approaches for group 3 as well. If there is any, also clinical assays would help provide evidence in both groups 2 and 3 of variants during the clinical decision making.
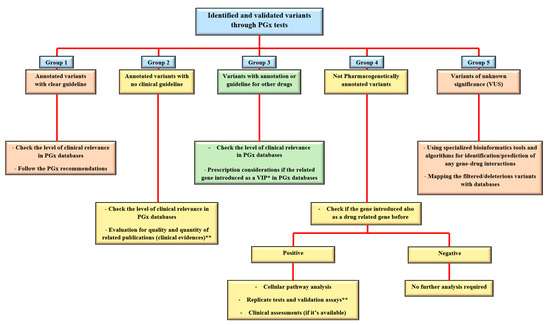
Figure 1. Approaches to deal with different types of PGx variants in clinical centers. After the identification and doing the confirmation tests on a PGx related variant, it could be categorized in one of the main five groups of annotated with PGx guideline, annotated without a guideline, informative for other drugs, not PGx annotated, or variants of unknown clinical significance (VUS). For the annotated variants, checking the level of clinical relevance (Table 1 of the current paper) is the first task to do. Bioinformatics tools are also supporting the analysis of not only VUS but also other types of variants in each group. Examples for groups 1–5 with explanations are provided in the main text. * VIP: very important pharmacogene. ** see the text for more details.
The last types of variants (group 5) are the novel and unreported variations in databases (ClinVar, HGMD, PharmGKB), but found in a PGx test mostly through comprehensive methods, such as whole exome or whole genome sequencing (WES and WGS), with no clue for their function in causing a particular phenotype. Moreover, incidental findings (IFs) are the group of known variations, but not related to specifically investigated phenotype, and accidentally revealed during a sequencing test. Both the VUS (novel variants) and IFs will be manageable with higher accuracy by the combined usage of highly specialized bioinformatics pipelines to find any possible interaction with drug responses in patients. IFs are mostly displayed as the annotated functional drug-related variants in pharmacogenes and potentially useful markers if the appropriate genomic analysis and accurate genotype–phenotype correlations are performed subsequently [26]. We will address this topic in detail in the following section.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/jcm10010034
References
- Sim, S.; Kacevska, M.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M. Pharmacogenomics of drug-metabolizing enzymes: A recent update on clinical implications and endogenous effects. Pharm. J. 2013, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozyra, M.; Ingelman-sundberg, M.; Lauschke, V.M. Rare genetic variants in cellular transporters, metabolic enzymes, and nuclear receptors can be important determinants of interindividual differences in drug response. Genet. Med. 2017, 19, 20–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schärfe, C.P.I.; Tremmel, R.; Schwab, M.; Kohlbacher, O.; Marks, D.S. Genetic variation in human drug-related genes. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabbani, B.; Nakaoka, H.; Akhondzadeh, S.; Tekin, M.; Mahdieh, N. Next generation sequencing: Implications in personalized medicine and pharmacogenomics. Mol. BioSyst. 2016, 12, 1818–1830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walczak, M.; Skrzypczak-Zielinska, M.; Plucinska, M.; Zakerska-Banaszak, O.; Marszalek, D.; Lykowska-Szuber, L.; Stawczyk-Eder, K.; Dobrowolska, A.; Slomski, R. Long-range PCR libraries and next generation sequencing for pharmacogenetic studies of patients treated with anti-TNF drugs. Pharm. J. 2019, 19, 358–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, M.; Niemi, M.; Hiratsuka, M.; Kumondai, M.; Ingelman-Sundberg, M.; Lauschke, V.M.; Rodríguez-Antona, C. Novel copy-number variations in pharmacogenes contribute to interindividual differences in drug pharmacokinetics. Genet. Med. 2018, 20, 622–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cousin, M.A.; Matey, E.T.; Blackburn, P.R.; Boczek, N.J.; McAllister, T.M.; Kruisselbrink, T.M.; Babovic-Vuksanovic, D.; Lazaridis, K.N.; Klee, E.W. Pharmacogenomic findings from clinical whole exome sequencing of diagnostic odyssey patients. Mol. Genet. Genome Med. 2017, 5, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, K.; Tremmel, R.; Winter, S.; Fehr, S.; Battke, F.; Scheurenbrand, T.; Schaeffeler, E.; Biskup, S.; Schwab, M.; Zanger, U.M. A New Panel-Based Next Generation Sequencing Method for ADME Genes Reveals Novel Associations of Common and Rare Variants With Expression in a Human Liver Cohort. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovelson, D.H.; Xue, Z.; Zawistowski, M.; Ehm, M.G.; Harris, E.C.; Stocker, S.L.; Gross, A.S.; Jang, I.-J.; Ieiri, I.; Lee, J.-E.; et al. Characterization of ADME gene variation in 21 populations by exome sequencing. Pharm. Genome 2017, 27, 89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega, V.E.; Meyers, D.A. Pharmacogenetics: Implications of race and ethnicity on defining genetic profiles for personalized medicine. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, E.; Park, T. Analysis of population-specific pharmacogenomic variants using next generation sequencing data. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 8416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizzi, C.; Peters, B.; Mitropoulou, C.; Mitropoulos, K.; Katsila, T.; Agarwal, M.R.; Van Schaik, R.H.; Drmanac, R.; Borg, J.; Patrinos, G.P. Personalized pharmacogenomics profiling using whole-genome sequencing. Pharmacogenomics 2014, 15, 1223–1234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lalioti, M.; Gerasimova, T.; Zattas, D.; Anastasakis, D.; Seli, E.; Sakkas, D. A Deleted Form of FSH Receptor, Found in Women Undergoing Infertility Treatment, Impairs the Function of the Normal Receptor When Co-Expressed In Vitro; Oxford University Press: Oxford, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Hoffman, J.M.; Dunnenberger, H.M.; Hicks, J.K.; Caudle, K.E.; Carrillo, M.W.; Freimuth, R.R.; Williams, M.S.; Klein, T.E.; Peterson, J.F. Developing knowledge resources to support precision medicine: Principles from the Clinical Pharmacogenetics Implementation Consortium (CPIC). J. Am. Med Inform. Assoc. 2016, 23, 796–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Relling, M.; Klein, T. CPIC: Clinical pharmacogenetics implementation consortium of the pharmacogenomics research network. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 89, 464–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbarino, J.M.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. PharmGKB: A worldwide resource for pharmacogenomic information. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. Syst. Biol. Med. 2018, 10, e1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tilleman, L.; Weymaere, J.; Heindryckx, B.; Deforce, D.; Van Nieuwerburgh, F. Contemporary pharmacogenetic assays in view of the PharmGKB database. Pharmacogenomics 2019, 20, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swen, J.J.; Nijenhuis, M.; De Boer, A.; Grandia, L.; Der Zee, A.M.-V.; Mulder, H.; Rongen, G.; Van Schaik, R.; Schalekamp, T.; Touw, D.; et al. Pharmacogenetics: From Bench to Byte—An Update of Guidelines. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2011, 89, 662–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- PharmGKB. Available online: https://www.pharmgkb.org/page/clinAnnLevels (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- CPIC. Available online: https://cpicpgx.org/genes-drugs (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- DPWG. Available online: https://www.pharmgkb.org/page/dpwg (accessed on 14 April 2020).
- Caudle, K.E.; Gammal, R.S.; Whirl-Carrillo, M.; Hoffman, J.M.; Relling, M.V.; Klein, T.E. Evidence and resources to implement pharmacogenetic knowledge for precision medicine. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 2016, 73, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Relling, M.V.; Evans, W.E. Pharmacogenomics in the clinic. Nature 2015, 526, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whirl-Carrillo, M.; McDonagh, E.M.; Hebert, J.; Gong, L.; Sangkuhl, K.; Thorn, C.; Altman, R.B.; Klein, T.E. Pharmacogenomics Knowledge for Personalized Medicine. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2012, 92, 414–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslibekyan, S.; Claas, S.A.; Arnett, D.K. To replicate or not to replicate: The case of pharmacogenetic studies: Establishing validity of pharmacogenomic findings: From replication to triangulation. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 2013, 6, 409–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.M.; Xu, K.; Mosbrook, E.; Links, A.; Guzman, J.; Adams, D.R.; Flynn, E.; Valkanas, E.; Toro, C.; Tifft, C.J.; et al. Pharmacogenomic incidental findings in 308 families: The NIH Undiagnosed Diseases Program experience. Genet. Med. 2016, 18, 1303–1307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
