In line with consumer preferences and due to the effects of global climate change, new trends have emerged in wine fermentation and wine technology. Consumers are looking for wines with less ethanol and fruitier aromas, but also with a good balance in terms of acidity and mouthfeel. Nonconventional yeasts contain a wide range of different genera of non-Saccharomyces. If in the past they were considered spoilage yeasts, now they are used to enhance the aroma profile of wine or to modulate wine composition.
1. Acids Present in Grapes and Wines and Their Perceived Taste
Organic acids, next to sugars, are the most abundant solids present in grape juice. They are a significant constituent of juice and wine. Responsible for the sour/acid taste, they also influence wine stability, color, and pH. The quality and quantity of organic acids in conjunction with the sugars has a significant effect on the mouthfeel quality of wines [
1].
Acid composition and concentration within the grape-must or wine are influenced by many factors, such as grape variety, soil composition, and climatic conditions. Accumulation of grape acids, namely tartaric acid, usually occurs at the beginning of grape berry development and is, to a large extent, completed at the beginning of ripening [
2].
Amerine [
3] reported that in berries, tartaric, malic, citric, ascorbic, phosphoric, and tannic acids were present, and soon after, Stafford [
4] confirmed the occurrence of all but ascorbic and tannic acids in grapevine leaves, and included oxalic acid, in the form of idioblast crystals of calcium oxalate. Kliewer [
5] identified 23 acids in berries, although most of these were found only in trace amounts. Nowadays we know that, by far, the predominant acids are tartaric and malic, which together may account for over 90% of the total acidity in the berry, existing at crudely a 1:1 to 1:3 ratio of tartaric to malic acid [
6], both contributing to the pH of the juice, must, and wine during vinification and subsequent aging (
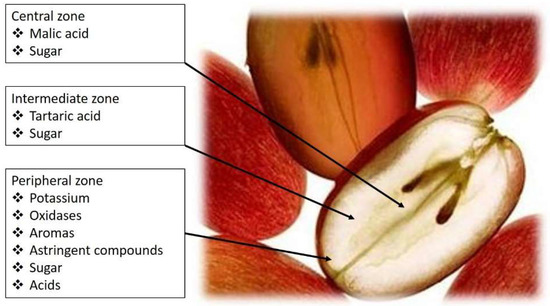
Figure 1) [
7].
Figure 1. Grape-berry flavor zones and distribution of tartaric and malic acids.
Tartaric and malic acids are diprotic, with two dissociable protons per molecule. It is the first proton dissociation, with pKa values of around 2.98 (tartaric) and 3.46 (malic) that are meaningful properties in a winemaking context. At a typical wine pH (3.4), tartaric acid will be three times as acidic as malic acid [
7].
The bitartrate and bimalate monoanions have important sensory roles to play in wine taste. Malic acid presents a harsh metallic taste (Table 1), sometimes correlated with the taste of green-apples, while the taste attributed to tartaric acid is frequently referred to as being ‘mineral’ or citrus-like. To compensate malic acid ‘lost’ in the late stages of berry ripening, the addition of tartaric acid at crush, or thereafter, can be performed, providing, in this way, control of must/wine pH. However, tartaric acid, unlike malic acid, is not a metabolic substrate for lactic acid bacteria or even yeasts.
Table 1. Organic acids present in grapes and wines and major acids’ sensory descriptors [
8].
(1) Present in wine made with grapes infected with Botrytis cinerea.
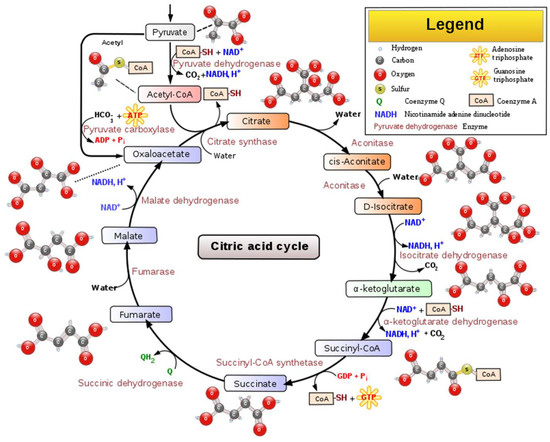
Citric acid, that presents a pleasant citrus-like taste (
Table 1), has many uses in wine production. Citric acid is a weak organic acid that presents antimicrobial activity against molds and bacteria. It can create a relationship with antioxidants by chelating metal ions, thus helping in browning prevention. Citric acid occurs in the metabolism of almost every organism because it is an important intermediate in the tricarboxylic acid cycle (TCA cycle) [
9],
Figure 2.
Figure 2. Schematic representation of the main steps, intermediated compounds, and enzymes of the TCA cycle [
10].
During the winemaking process, it is advisable to monitor the concentration of organic acids in order to ensure the quality of the wine, and a distinction is made between acids directly produced in grapes (tartaric, malic, and citric) and those originating during the fermentation—alcoholic and malolactic—succinic, lactic, and acetic acids, among others [
11],
Table 1.
Acetic acid, in quantities higher than 0.8–0.90 gL
−1 [
11], is immediately recognizable due to the vinegar smell an acrid taste, causing the wine to be considered spoiled. The maximum acceptable limit for volatile acidity in most wines is 1.2 gL
−1 of acetic acid [
12]. Acetic acid can appear on the grapes or the grape-must due to the presence of yeasts like
Hansenula spp. and
Brettanomyces spp., filamentous fungi (
Aspergillus niger,
Aspergillus tenuis,
Cladosporium herbarum,
Penicillium spp., and
Rhizopus arrhizus), and bacteria (LAB-like indigenous
Lactobacilli, and acetic acid bacteria). During alcoholic fermentation, acetic acid usually is formed in small quantities (0.2–0.5 gL
−1 acetic acid) as a byproduct of
S.
cerevisiae metabolism. If the amounts are higher, some contamination spoilage yeasts and bacteria can be present:
Candida krusei,
Candida stellate,
Hansaniaspora uvarum/
Kloeckera apiculate,
Pichia anomala,
Saccharomycodes ludwigii,
Acetobacter pasteurianus, and
Acetobacter liquefaciens; after malolactic fermentation, heterofermentative species of
Oenococcus and
Lactobacillus also have the potential to produce acetic acid through the metabolism of residual sugar [
13].
Succinic acid, with a sour, salty, and bitter taste, is the major acid produced by yeast during fermentation. This acid is resistant to microbial metabolism under fermentative conditions. During a period from 1991 to 2003, Coulter and coworkers [
14] studied 93 red and 45 white Australian wines and found that the concentration of succinic acid in red wines reached from “none” (detection limit of 0.1 gL
−1) to 2.6 gL
−1, with a mean value of 1.2 gL
−1, while the concentration in white wines was between 0.1 gL
−1 to 1.6 gL
−1, with a mean value of 0.6 gL
−1. Thus, succinic acid plays an important role in wine acidity [
14].
Lactic acid, that usually is perceived as sour and spicy, is mainly produced by lactic acid bacteria during malolactic fermentation. However, small amounts can also be synthesized by yeast.
Today, the range of wines on the market is huge. On the other hand, wine companies tend to develop a style. Last year’s tendency was to attribute “medals” to balanced flavor profile wines with bordering notes of vegetal-green, chemical, earthy, or sulfur characters, aromas of fruit and oak, hot/full mouthfeel (generally related to the alcohol content), low bitterness, and high sweetness [
15]. Consumers and winemakers, giving more importance to flavors and sweetness, tend to “despise” acidity, even if it is one of the most important components of the wine. So, it is important for the wine industry to be able to modulate wine acidity, having in mind the concept of “healthy” and “biological”, without the addition of enological products.
2. Wine Biological Acidity Modulation by Bacteria via Malolactic Fermentation
Physicochemical deacidification of wines is time-consuming, requires labor, capital input, and may reduce wine quality [
16]. Biological deacidification of wine with malolactic bacteria (MLB), most often strains of
Oenococcus oeni, previously known as
Leuconostoc oenos [
17], is the traditional method used for removing excess wine acidity. However, one important thing must be taken into account; of wine’s total acidity, biological deacidification only affects the malic acid portion, it does not reduce tartaric acid.
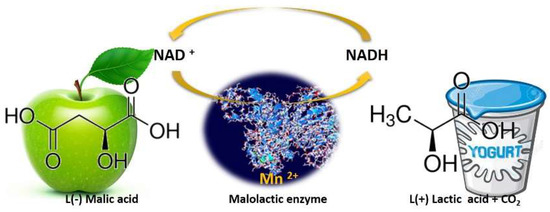
While during alcoholic fermentation, wine yeast strains convert the grape sugars into ethanol and other flavors/mouthfeel compounds, after sugar depletion and the decline of yeasts population, LAB proliferates by utilizing the remaining sugars and thereafter performs malolactic fermentation (MLF). Despite its name “malolactic fermentation”, this biological process is not a fermentation, but an enzymatic reaction in which malic acid (
l (−) malic acid) is decarboxylated to lactic acid (
l (+) lactic acid) and CO
2,
Figure 3, [
18,
19]. This process also reduces the potential carbon source for spoilage microorganisms and leads to wine microbial stabilization [
20].
Figure 3. Schematic representation of malolactic enzyme action. Malolactic bacteria convert sharp green-apple-like malic acid into softer, much less tart lactic acid, releasing CO2 along the way.
During MLF, the metabolism of
O. oeni can improve the wine’s sensory characteristics by producing a myriad of secondary metabolites [
21]. However, the success of MLF is influenced by oenological parameters, such as temperature, pH, alcohol content, SO
2 concentration [
22], and yeast inhibitory metabolites, such as medium chain fatty acids [
23] or peptic fractions [
24].
Several working groups are focused on alternative LAB, such as
Lactobacillus plantarum, to perform MLF in wine [
25,
26].
Lactobacillus plantarum can survive under winemaking stress conditions, and during the fermentation process they are also able to produce a huge number of secondary metabolites important for the wine’s aroma and flavor, including β-glucosidases, esterases, phenolic acid decarboxylases, and citrate lyases [
27,
28,
29] once they contain genes encoding important enzymes that are active under winemaking conditions [
30,
31]; and can even improve red wine’s color and solve problems associated with wine filtration due to tannase activities [
29].
More specific studies have found that depending on the stress conditions in the wine, the gene coding for the malolactic enzyme works differently for
O. oeni [
32] and
L. plantarum [
33]. Miller et al. [
33] found that the expression of mle (malolactic enzyme)
L. plantarum gene presented an increased expression in the middle of MLF and was inducible by the presence of malic acid and low pH wine values, decreasing, nevertheless, in the presence of ethanol. Later, Iorizzo and coworkers [
34] reported that some strains of
L. plantarum were able to grow at pH values ranging from 3.2 to 3.5 and in the presence of 13% (
v/
v) ethanol. Several strains of
L. plantarum were also found to be able to tolerate the presence of sulfite and in the concentrations used in winemaking [
35].
Moreover,
L. plantarum strains produce high concentrations of lactic acid, which may contribute to “biological acidification” in low acidity wines, and thus improving wine mouthfeel [
36].
3. Wines Biological Acidity Modulation by Nonconventional Yeasts
The malolactic fermentation process is not free from collateral effects (production of off-flavors, wine quality loss, and human health issues due to the production of biogenic amines). Benito et al. [
37] developed a new red winemaking methodology by combining the use of two non-
Saccharomyces yeast strains as an alternative to the traditional MLF. According to the authors, malic acid is consumed by
Schizosaccharomyces pombe, while
Lachancea thermotolerans produces lactic acid in order to increase the acidity of wines produced from low acidity musts. The main fermentative properties of interesting non-
Saccharomyces yeasts reported as advantageous for fermented beverages and that can modulate wine acidity are described in
Table 2.
Table 2. Percentage of ethanol formed during fermentation, sugars fermented, main volatile compounds formed and effect on wine acidity of seven non-Saccharomyces yeasts.
(i) The musts were obtained from botrytized Semillon grapes with initial sugar concentrations of 360 gL−1 [43]. (ii) Variable according to strain. (iii) Some Zygosaccharomyces are fructophilic. Z. rouxii and Z. bailii possess genes (FFZ) that encode specific fructose facilitators and proteins [49]. (iv) In white grape juice, not added with SO2, with 231 gL−1 sugar content [48]. (v) Z. bailii is known to consume acetic acid [50]. (vi) In microvinifications with chemically defined grape juice with similar nitrogen and acidic fraction composition to Patagonian Pinot noir juice (gL−1: glucose 100 gL−1, fructose 100 gL−1, potassium tartrate 5 gL−1, l-malic acid 3 gL−1, citric acid 0.2 gL−1, easily assimilable nitrogen 0.208 gL−1 and pH 3.5) [51]. (vii) Pichia kudriavzevii presents the ability to produce ethanol from xylose. Xylose is a sugar found in wood, meaning this can used as an alternative for ethanol production, which is particularly useful in the biofuel industry [52]. (viii) A decrease up to 0.7% (v/v) of ethanol when S. cerevisiae was inoculated with a delay of 48 h with respect to the inoculation of Starmerella bacillaris [53]. (xix) S. bacillaris show fructophilic, cryotellerant, and osmophylic characters of interest for the winemakers [55]. (x) Sauvignon blanc wines fermented by mixed cultures (S. bacillaris and S. cerevisiae) contained significantly higher levels of thiols [57].
Schizosaccharomyces pombe, Lachancea thermotolerans, and Torulaspora delbrueckii are presently produced at the industrial level by biotechnological companies [38]. Torulaspora delbrueckii is commercialized in the form of a pure culture, selected for its properties to increase aromatic complexity, mouthfeel, low production of volatile acidity, and high resistance to initial osmotic shock and it is highly recommended for the fermentation of late harvest wines in sequential culture with S. cerevisiae.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/fermentation5010027