Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Chemistry, Medicinal
Peroxynitrite (ONOO−) is a crucial reactive oxygen species that plays a vital role in cellular signal transduction and homeostatic regulation. Determining and visualizing peroxynitrite accurately in biological systems is important for understanding its roles in physiological and pathological activity.
- peroxynitrite
- fluorescent probes
- intracellular imaging
1. Introduction
Peroxynitrite (ONOO−) is a kind of reactive oxygen species (ROS) generated by the rapid reaction of nitric oxide (NO) and a superoxide anion free radical (O2·−) in the absence of enzyme catalysis, which has strong oxidation, nucleophilic, and nitration properties [1]. It occupies crucial roles in the transformations of other major reactive species. (Scheme 1) Its pKa value is 6.8 [2], and the half-life is approximately 1 s [3,4] at pH 7.4. ONOO− can react with a variety of bioactive substances (such as protein, nucleic acid, lipid, etc.) with very high reactivity. In addition to its oxidation, nucleophilic, and nitration properties, ONOO− can also be converted into higher activity secondary free radicals, including hydroxyl radicals (·OH), nitro radicals (·NO2), and carbonate radicals (CO3·−), which further react with biomolecules and ultimately lead to cell death.
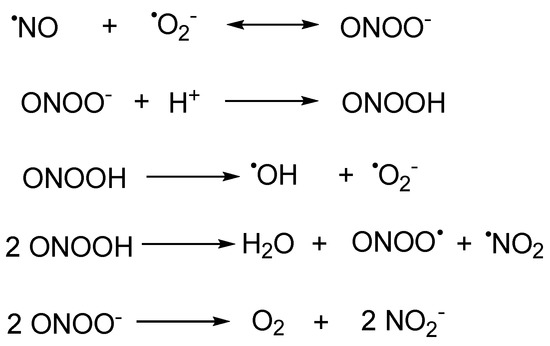
Scheme 1. The biogenesis of peroxynitrite and its transformations with other major reactive species.
Based on these properties, peroxynitrite exhibits two effects with different directions. In the living system, when the ONOO− remains at a level which is under normal physiological conditions, it serves as an indispensable physiological activator and signaling molecule. However, when the concentration of ONOO− elevates, the excess ONOO− will turn the redox state of the cell to a pro-oxidant state [5,6]. Eventually, serious inflammation and disease will be induced, for example, rheumatism, hepatic disease, neurodegenerative disease, cancer, and so on [7,8,9,10]. Therefore, it would be of great significance to develop a method which could accurately detect ONOO− and explore the physiological role of ONOO− in living systems.
In comparison to other ONOO− detection methods (positron emission computed tomography (PET), computed tomography (CT), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and genetically encoded indicators) [11], spectroscopic detections, especially fluorescent probes, possess advantages such as excellent temporal and spatial resolution, simple operation, high sensitivity and selectivity, and non-destructive and in situ real-time visualization of biological samples [12,13,14,15].
2. Fluorescent Probes
2.1. Xanthene as Fluorophore Core
Xanthene dyes can be categorized as fluorescein, rhodol, and rhodamine based on the type of the substituents on the 3- and 6-position [16]. They are well known because of their switchable fluorescent off–on flexibility. Xanthene dyes can produce fluorescence wavelengths above 510 nm, reaching far-red areas depending on the conjugative substituents. Thus, they are of widespread use in optical diagnostic research [17].
The triggers of ONOO−-responsive probes with xanthene as a fluorophore core were generally built on (1) oxidation of the hydrazide (Xan1–Xan15) [18,19,20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32], (2) oxidative cleavage of the substituents at the hydroxyl or amino group (Xan 16–Xan 28) [33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40,41,42,43,44,45], (3) oxidation of pyrylium (Xan 29–Xan 33) [46,47,48,49,50], and (4) oxidation of the hydrogenated xanthene (Xan 34–Xan 37) [51,52,53,54] and others (Xan 38–Xan 41) [55,56,57,58].
2.1.1. Hydrazide Oxidative Xanthene Probes
In 2002, Guo et al. reported a spiro form hydrazide rhodamine (Xan 1) [18] as the ONOO− fluorescent probe. The hydrazide probe was colorless and non-fluorescent. Upon treating with ONOO−, the spiro hydrazide group was oxidized, releasing a highly fluorescent rhodamine B. The response finished in as fast as 30 s. Meanwhile, the detection limit was only 24 nM. The response avoids interference from the 10−5 M Cu(II) ion. Thus, it represents the rapid, sensitive, and specific fluorescent detection of ONOO−.
Based on the recognized pattern and the easy structurally modification character of rhodamine, a series of related probes were developed, aiming to improve the performance of different aspects of the response (Figure 1). Longer emissive wavelengths (up to the NIR range) were obtained with more conjugate groups installed in Xan 2–5 [19,20,21,22], Xan 8 [25], and Xan 10 [27]. Dual-channel fluorescence was afforded when coumarins were introduced to the rhodamine ring (515/700 nm for Xan 5 and 631/669 nm for Xan 10), making the response produce more information. Ratiometric fluorescence was realized in Xan 6 [23] and Xan 7 [24] with the introduction of a 2-(2′-hydroxyphenyl)benzothiazole group and a 4-hydroxycarbazole group, respectively, in which the intensity of the original band disappeared with the generation of a new band with a longer wavelength. Large Stokes shift and excellent lysosome-targeting ability were achieved with the engineering of a fused tetrahydroquinoxaline ring, making Xan 9 [26] capable of detecting both peroxynitrite and lysosomal pH. Sodium-dependent multivitamin transporter (SMVT)-targeted ability was acquired by introducing the biotin group for Xan 9, making it possible to detect the peroxynitrite in head and neck cancer cells.
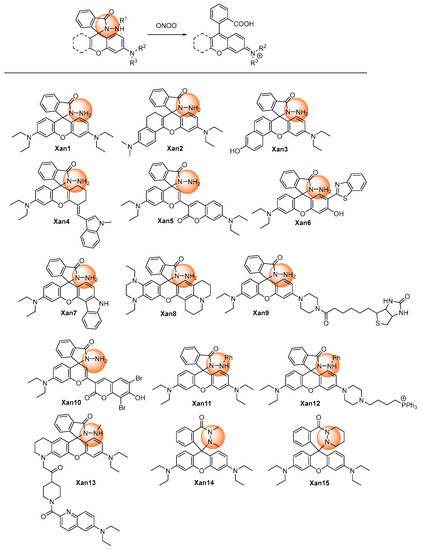
Figure 1. Chemical structures of the hydrazide oxidative xanthene probes.
If a phenyl group was introduced into the hydrazide (Xan 11–Xan 12) [28,29], the response time would prolong to 10 or more minutes, presumably due to the steric-hindrance-caused decreased reactivity. It should be noted that, with alkyl substituent groups in both nitrogens of the hydrazide, the cyclic hexahydropyridazin probes (Xan 14–Xan 15) [31,32] displayed a faster response rate than the alkyl-substituted (Xan 13) [30] or phenyl substituted hydrazide xanthene (Xan 11–Xan 12). The response was usually specific, without interferences from a lot of metal ions and other reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. [28,29,30,31,32]
Peroxynitrite generated from different cells, such as HeLa, RAW264.7, HepG2, HSC-2, and Cal-27, could be detected by hydrazide xanthenes. Meanwhile, these probes could detect peroxynitrite in zebrafish and mouse models. These outstanding performances made hydrazide xanthenes capable of revealing the important roles of peroxynitrite in many kinds of diseases, such as respiratory infectious diseases and inflammation in the future.
2.1.2. Oxidative Cleavage of the Recognition Groups to Release Xanthene Probes
Utilizing the oxidative ability of peroxynitrite, the recognition groups at the 2- or 6-hydroxyl or amino group of xanthenes derivative could be cleaved to release xanthenes with high fluorescence (Figure 2).
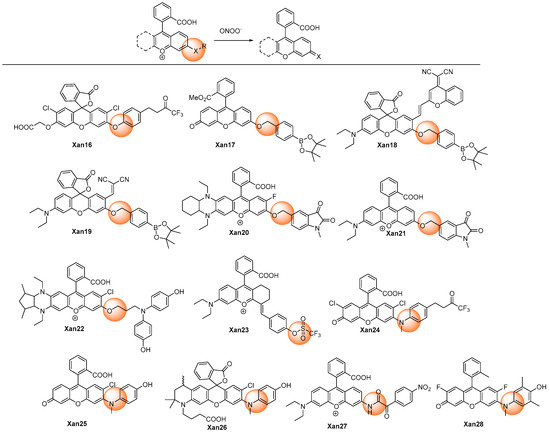
Figure 2. Chemical structures of the oxidative cleavage xanthene probes.
Yang et al. developed the HKGreen series of rhodamine probes (Xan 16 [33] and Xan 24 [41]) for detecting peroxynitrite with the employment of the trifluoromethyl ketone as the recognition group, which involved dioxirane rearrangement and oxidative O- or N-diarylation. The response was highly selective and sensitive, with high-fold fluorescent enhancement, though the response time was relatively long (>15 min).
While using the benzyl boronates moiety as a recognition group, Xan 17–19 [33,34,35] exhibited quite different responsive behaviors upon reactive species. Xan 17 [33] reacted not only to peroxynitrite but also with hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide, though with different second-order rate constants. However, Xan 18 [34] and Xan 19 [35] responded exclusively to peroxynitrite, even when hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide were at much higher concentrations. Nevertheless, all of them displayed obvious fluorescent enhancement and low detection limits, and thus they were all further employed for fluorescent imaging in biosystems involving diseases such as drug-introduced liver injury.
The 1-methylindoline-2,3-dione group can also be employed as the recognition moiety for the specific detection of peroxynitrite (Xan 20 [36] and Xan 21 [37]). The mechanism involving intramolecular cyclization of peroxynitrite with indoline-2,3-dione, rearrangement, and 1,6-elimination was proposed [36]. Leveraging the probes, the two-photon (TP) in vivo NIR imaging technique was applied to observe the peroxynitrite level in a mouse tumor, a tumor onset on the second day, a kidney injury of zebrafish, and the microvessels of mouse brains with strokes [37].
Xanthenes with the electron-donating groups substituted phenyl groups as recognition groups (Xan 16 [33], Xan 24 [41], Xan 25 [42], Xan 26 [43], and Xan 28 [45]) produced very high fluorescent enhancement, probably due to their better quenching effect.
2.1.3. Oxidation of Pyrylium
Yuan et al. discovered an aminophenyl-substituted pyrylium as a highly sensitive and selective scaffold towards peroxynitrite after the screening of nineteen dyes and then further modified it to a FRET probe (Xan 29) [46] with TP absorption. After the response, the pyrylium emission band at 651 nm disappeared, and a coumarin characteristic emission band at 473 nm was enhanced. Detailed response mechanisms involving nucleophilic addition, oxidation, elimination, and hydrolysis reactions on chromenylium fluorophore were proposed and verified by MS spectra. Although the destroyed-type response led to the decrease of the emission wavelength, the combination technique of the ratiometric measure and TP imaging made it possible to specifically and rapidly visualize the peroxynitrite in an inflamed mouse model. Furthermore, the detection limit was as low as 11.3 nM, which was at a super level among the peroxynitrite probes. Subsequently, similar structures were synthesized for different applications. Gong et al. reported esterified Xan 30 [47] with better membrane penetrability and mitochondria targeting ability, which could image the peroxynitrite in the acute liver injury model in living cells. Li et al. introduced a piperazine ring to respond to the pH and finally realized the fluorescent imaging of the cellular peroxynitrite level as well as the mitophagy behavior [48].
Yuan et al. performed an original structure–activity relationship study of the substituents at the recognition site. (Figure 3) They discovered that pyrylium involving aryl substituents with strong electron-withdrawing groups could improve the sensitivity; meanwhile, pyrylium involving aryl substituents with strong electron-donating groups could improve the selectivity. Hence, they designed a coumarin, which was a not strong electron-withdrawing and -donating group, substituted pyrylium (Xan 32) [49] to satisfy the high requirements of both selectivity and sensitivity, and the results showed that an outstanding detection sensitivity of 4.1 nM of the detection limit as well as a high 130-fold ratiometric emission signal were realized. Employing the probe, the changing content of peroxynitrite in the diseases model involving nonalcoholic fatty liver and drug-induced liver injury was successfully visualized to unfold the functionality of a related enzyme. Zhou et al. introduced a naphthimide fluorophore in the xanthene carboxylic position. After the response, both coumarin and naphthimide fluorescence were produced to output a multicolor signal. The probe Xan 33 was applied for the early detection and evaluation of arthritis [50].
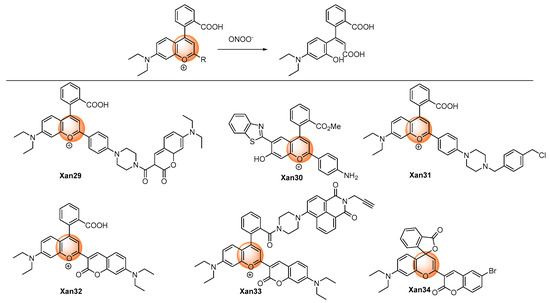
Figure 3. Chemical structures of the pyrylium oxidative xanthene probes.
However, a similar structure–activity relationship study conducted by Tang et al. produced totally different results and response mechanisms, in which electron-withdrawing groups were installed in the 6-position of coumarin moiety. They found that because of the installation of the electron-withdrawing groups in the 6-position of coumarin, Xan 34 produced 4-(2-carboxylphenyl)-7-diethylaminocoumarin (λem = 520 nm) and 3-hydroxy-6-bromocoumarin (non-fluorescent) as products after the response [51]; nevertheless, Xan 32 and Xan 33 produced 3-carboxyl-7-diethylaminocoumarin (λem = ~468 nm) and a ring-opening product of pyrylium (non-fluorescent). Furthermore, Xan 34 could also detect biothiols by the additional recognition site on coumarin.
2.1.4. Oxidation of Hydrogenated Xanthene
Peroxynitrite can oxidize t non-fluorescent hydrogenated xanthene to produce highly fluorescent aromatic products. (Figure 4) Gong et al. developed 9,10-dihydroacridine Xan 35 as the peroxynitrite detection probe. An over 100-fold fluorescence enhancement could be achieved after reacting with peroxynitrite. The probe was utilized to detect intracellular peroxynitrite [52]. Similar O-, Si-, and P- hydrogenated rhodamine systems were also reported. Xan 36–37 [53,54] displayed a very fast response speed (<20 s); for Xan 38 [55], the relatively low response speed was probably due to the low reactivity caused by the presence of the electron-withdrawing phosphonic group. Nevertheless, Xan 35–38 [52,53,54,55] all exhibited very low detection limits at the nanomolar level, and they were all applied to fluorescent imaging of cell endogenous peroxynitrite.
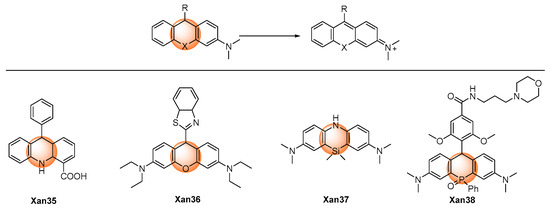
Figure 4. Chemical structures of the oxidative hydrogenated xanthene probes.
2.1.5. Others
Wu et al. described a Rhodol-based probe, Xan 39 [56], which introduced 1,1-dimethylhydrazone as a peroxynitrite recognition group. (Figure 5) The probe was non-fluorescent as a result of the rotational vibration of the C=N bond. Using the oxidative ability of peroxynitrite, the hydrazine was oxidatively cleaved into the corresponding aldehyde with significant fluorescence. The response exhibited a low detection limit (57 nM) with a short response time (<60 s). The probe was applied in the fluorescent imaging of exogenous and endogenous peroxynitrite in living cells.
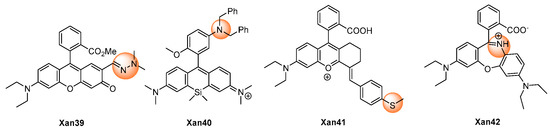
Figure 5. Chemical structures of the other xanthene probes.
Miao et al. reported Xan 40 [57] as a peroxynitrite off–on probe. The probe showed little fluorescence because of the photo-induced electron transfer (PeT) quenching effect of the 3-dibenzylaminophenyl group. Upon reaction with peroxynitrite, a benzyl group was removed and formed an N-oxide product, and the fluorescent was turned on.
Li et al. released the study on Xan 41 [58] as a peroxynitrite probe, in which the fluorescence was turned off by the intramolecular charge transfer (ICT) effect of the 4-methylthiophenyl group. After the response with peroxynitrite, the thiol ether was transformed into sulfoxide and discontinued the ICT effect, thus recovering the fluorescence and realizing the detection of the peroxynitrite concentration.
Zhang et al. reported a novel rhodamine probe Xan 42 with the dibenzo[1,4]oxazepine core as the responsive moiety [59]. Synthesized by the reaction of rhodamine with hydroxylamine, the probe was of little fluorescence at 672 nm. However, after the treatment with peroxynitrite, oxazines was generated with high fluorescence. The probe was used to monitor the peroxynitrite level in living cells.
2.2. Dicyano-Based Compounds as Fluorophore Core
Dicyano-based compounds are characteristic of their donor–π–acceptor structure, which endows them with large Stokes shifts and excellent photostability as a result of the ICT process. In addition, this sort of chromophore was generally easily synthesized and structurally modified. Thus, great attention has been attracted towards dicyano-based compounds to build probes with different functionalities [60].
The designing rule for dicyano-based peroxynitrite probes was a consensus, which was described in Figure 6. In general, the responsive groups, such as diphenylphosphonyl, benzyl boronates, and 4-hydroxyphenyl, were modified on the donor moiety to stop the ICT process. The response with peroxynitrite would break the links between the donor moiety and the response groups and release the dicyano-based chromophores with strong fluorescence.
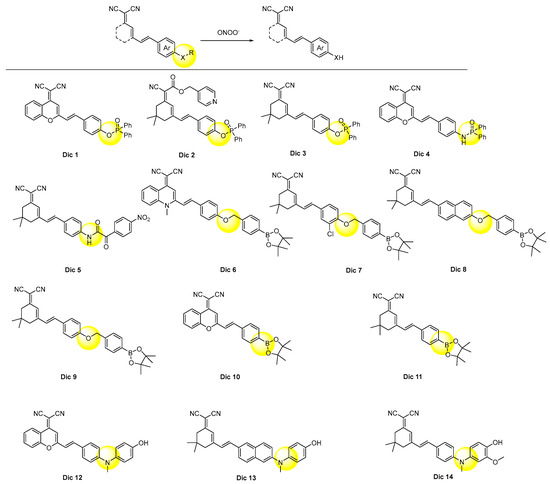
Figure 6. Chemical structures of the dicyano-based probes.
As summarized in Table 1, Dic 1–4 [61,62,63,64], with diphenylphosphonyl as a recognition group, took more than 10 min to respond, which was relatively longer than those of Dic 5–14 [65,66,67,68,69,70,71,72,73,74]. This was probably due to their high intrinsic structural stability. However, their detection selectivity and sensitivity were not reduced. Thus, they were employed for fluorescent imaging of the exogenous peroxynitrite in living cells. Among them, Dic 4 were further used to manifest the changing peroxynitrite concentration in the rat epilepsy model with the aid of two-photon fluorescent technology [64].
Dic 5 [65] with the 4-nitrophenyl oxoacetyl group as the responsive unit showed a much faster response rate (<2 s) than Dic 1–4, but its detection limit was at a similar level (81 nM). The probe was used for fluorescence imaging of the endogenous peroxynitrite in zebrafish and mice.
All of the benzyl boronates derived dicyano-based probes Dic 6–10 showed analogous response times to each other. Interestingly, Dic 6 [66] and Dic 10 [70] only displayed green-channel fluorescence, although they both have an extra conjugate phenyl ring compared Dic 7 [67] and Dic 9 [69], respectively. The boronate group of Dic 10–11 was oxidized to the hydroxyl group in situ by peroxynitrite, and the transformation generated the donor, thus forming the ICT process and producing fluorescence.
The response rates of the probes Dic 12–14 [72,73,74], which employed 4-hydroxylphenyl as a masking group, were all found to be ultrafast, which were 5, 25, and 1 s, respectively. This phenomenon was in accordance with those of Xan 25–26 [42,43] and Xan 28 [45], suggesting the great advantage of this mask group. Possessing the superior detecting sensitivity and selectivity, the probes Dic 12–14 were applied to visualize the peroxynitrite in different diseases, including inflammation, acute liver injury, and Parkinson’s disease [72,73,74].
2.3. Coumarin as Fluorophore Core
The research history of coumarin (also known as 1-benzopyran-2-one or 2H-chromen-2-one) was more than 200 years. Plenty of extensive investigations have been performed to modify the weak fluorescent parent coumarin to its derivatives with different desired photophysical properties, with a considerable amount of them now very active in the commercial market [75].
Inserting the electron-donors in the 7-position leads to a bathochromic shift to the emission wavelength; in addition, a donor–π–donor structure was formed, which facilitates the use of itself to design the ICT type probes by further introducing an electron-acceptor recognition group. (Figure 7) Xie et al. adopted this strategy and synthesized Cou 1 [76]. The 4-nitrophenyl oxoacetyl recognition group reacted with peroxynitrite rapidly and produced the deprotected product Cou 2 [77]. They used Cou 1, together with the two-photon fluorescent imaging technology, to visualize the peroxynitrite produced in the mitochondria in an anthracycline-induced cardiotoxicity mouse model. However, Li et al. reported that the deprotected product, Cou 2, also further reacted with peroxynitrite in 5 s in the concentration range of 0.064–0.64 μM, and the resulting nitration products were confirmed by ESI-MS analysis. The 3-position of coumarin could also be introduced with electron-donors to generate the donor–π–donor structure. Wei et al. developed Cou 3 as the peroxynitrite probe using the 4-nitrophenyl oxoacetyl group as a recognition moiety [78]. The fluorescence of Cou 3 was quenched but could be quickly recovered with eight-fold enhancement after the response with peroxynitrite. The probe was used to image exogenous peroxynitrite formation in living cells in a biosystem.
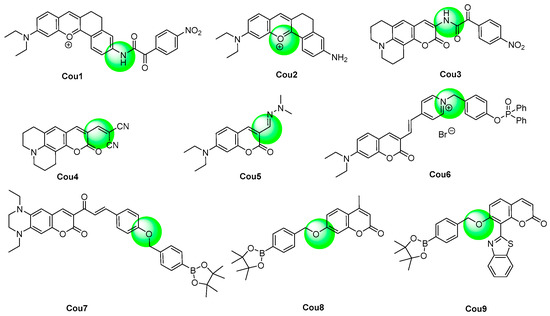
Figure 7. Chemical structures of the coumarin probes.
The electron effect of the substituents of the 3-position of 7-dialkylaminocoumarin derivatives decided their emission properties. The existence of an electron-acceptor can cause a strong ICT effect and fluorescence, and the stronger the electron-withdrawing ability the group owned, the longer the emission wavelength and stronger fluorescence the probes owned. If the electron-withdrawing ability changed, the fluorescent property would change accordingly. For example, the formyl group is a medium-ability electron-withdrawing group. If it was transformed into stronger electron-withdrawing groups, the emission wavelength of the product, Cou 4, would increase [79]. In reverse, after the response with peroxynitrite, the C=C bond of Cou 4 broke and generated the aldehyde product. The response was completed in a very short time with high selectivity and sensitivity to peroxynitrite. If the aldehyde group was reacted with hydrazine, the hydrazone product Cou 5 would emit only little fluorescence. However, after the reaction with peroxynitrite, the fluorescence would recover [80].
The ICT process is very strong in the quaternized pyridinium probe Cou 6 [81]. After the addition of peroxynitrite, the diphenyl phosphinate was eliminated, and the product owned a very weak ICT process. The fluorescence undergoes a hypochromatic shift from 643 nm to 538 nm, and the emission ration displays a 153-fold increase. The probe was applied to detect the peroxynitrite in living cells.
Parthiban et al. reported a coumarin–chalcone hybrid peroxynitrite probe Cou 7 containing a tetrahydroquinoxaline ring [82]. The probe displayed a large Stokes shift of 149 nm. The aryl boronate group was employed as the recognition group for peroxynitrite. The probe exhibited exceptional speed and sensitivity in detecting peroxynitrite. Palanisamy described another coumarin probe Cou 8 with a 7-position aryl boronate group as the response moiety, and the probe was applied to fluorescence imaging of peroxynitrite in a high-fat diet-induced obese mouse model [83].
Wang et al. reported a coumarin probe Cou 9-based 7-position benzyl borate as a recognition group. The probe exhibited weak ICT and weak fluorescence at 421 nm [84]. After the reaction with peroxnitrie, a strong ICT and FRET process was turned on and led to an incredible 1200-fold enhancement of the fluorescence. The probe was used for fluorescent imaging of the content of peroxnitrie in cancer cells.
2.4. N-Substituted Coumarin as Fluorophore Core
As analogues for coumarin dyes, 2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)phenylacrylonitrile derivatives exhibited longer emission wavelengths than the related coumarins. (Figure 8) In particular, 2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)acrylonitrile derivatives (NCou 1–3) [85,86,87] served as the precursors for iminocoumarin, and they exhibited aggregation-induced emission luminogens (AIEgens) in aqueous conditions. Upon the response with peroxynitrite, 2-(benzo[d]thiazol-2-yl)-3-(2-hydroxyphenyl)acrylonitrile would be generated, which would further transform into iminocoumarin in situ. The probes were applied for the fluorescent imaging of cell exogenous and endogenous peroxynitrite, though the response rate was usually relatively slow.
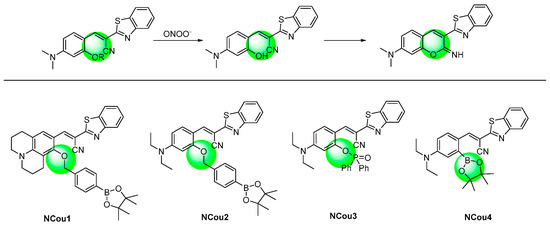
Figure 8. Chemical structures of the N-substituted coumarin probes and their responsive mechanism.
The hydroxyl group was also converted from the borate group. The probe NCou 4 exhibited high speed and sensitivity in detecting peroxynitrite [88]. The detection limit of the probe for peroxynitrite was 0.83 nM.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/ijms241612821
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
