1. Introduction
In recent decades, regenerative medicine and tissue engineering have emerged with the purpose of rebuilding or repairing tissues and organs damaged by diseases, traumas or aging. In this context, a growing body of studies has been focused on stem-cell-based treatments for numerous human pathologies, including bone and cartilage disorders [
1,
2]. Stem cells are unspecialized cells capable of self-renewal and differentiation into various types of functional cells. There are different types of stem cells, such as embryonic stem cells, fetal stem cells, induced pluripotent stem cells and adult stem cells. The first three types are extensively studied for their marked proliferative potential and for their ability to differentiate into multiple cell lines; however, their use for clinical treatments is limited by considerable safety, ethical and regulatory issues [
3]. For these reasons, much attention has been focused on adult stem or stromal cells that, although featuring lower differentiation capabilities, are more suitable for treatments in humans [
4]. Adult stem cells are located in specialized niches of most tissues, where they continuously produce tissue-specific differentiated elements as well as other daughter stem cells that ensure a constant pool [
5]. Hematopoietic stem cells in the bone marrow were the first population to be identified [
6]. A few years later, a second population with different characteristics was discovered [
7]. Defined as “bone marrow stromal cells” (BMSCs), they are a heterogeneous population of cells able to differentiate into mesodermal elements [
8] and are thus considered mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs). Among these cells, marrow adipogenic lineage precursors seem to play important regulatory roles in bone remodeling, hematopoiesis regulation and marrow vasculature maintenance [
9]. Under appropriate conditions, MSCs can differentiate not only into cells of the mesodermal lineage but also into elements of ectodermal or endodermal origin [
10,
11]. Other than bone marrow, MSCs can be isolated from numerous other tissues, such as the umbilical cord, dental pulp, skin, salivary glands [
12,
13] and from adipose tissue [
14,
15,
16]. Comparative studies were carried out investigating the immunophenotype, proliferative potential, multilineage differentiation and immunomodulatory capacity of MSCs from different tissues (bone marrow, adipose tissue, the placenta and umbilical cord blood). On the basis of the gene expression profiles of stemness-related genes and lineage differentiation stage-related genes, it was found that no significant differences were observed in terms of the growth rate, colony-forming efficiency and immunophenotype. It was also found that BMSCs and ASCs shared both in vitro trilineage differentiation potential and gene expression profiles and represent the optimal stem cell source for tissue engineering and regenerative medicine [
17]. In particular, adipose-derived MSCs (ASCs) will be considered in this review, as they have been widely studied for their numerous advantages. Unlike BMSCs, which require general anesthesia because of the painful harvesting procedure, ASCs can be obtained in large quantities with less invasive methods, and moreover, they feature even more proliferative activity and are more easily available for autologous administration [
18,
19].
2. Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (ASCs)
ASCs are commonly isolated from the stromal vascular fraction (SVF) of adipose tissue, which is diffusely located in the human body at either the subcutaneous or visceral level. Depending on the anatomical region from which the adipose sample is taken, some differences have been reported. For example, a greater number of cells can be isolated from the adipose tissue of the arm, whereas cells with excellent plasticity can be obtained from the groin area [
20]. Many studies have been carried out on adipose tissue contained in the lipoaspirate that is available after liposuction and would be otherwise discarded. Although the harvesting procedure is generally accurate, contaminations may occur. Specifically, microorganisms (bacteria, viruses and fungi) can infect samples during the various preparation steps so that infections in the host tissues and immune reactions might be generated after implantation [
21]. For this reason, microbiological control is fundamental at each stage to ensure the absence of contamination and the safety of the final product. Once isolated, ASCs can be expanded and identified by their plastic adherence, colony forming capacity and rapid proliferation. They show a fibroblast-like morphology and are positive for typical MSC markers (CD44, CD73, CD90 and CD105) but not for typical hematopoietic markers (CD14, CD34 and CD45). According to their MSC nature, they are able to differentiate toward osteogenic, adipogenic, myogenic and chondrogenic lineages [
22,
23,
24,
25]. However, with specific treatment, ASCs can also differentiate not only into other cells of mesodermal derivation [
26,
27,
28] but also into cells originating from endodermal or ectodermal embryonic layers, such as neural cells [
29]. This can usually be obtained by supplementing the growth medium with bioactive molecules, although satisfactory results can be achieved by using conditioned media from other cell cultures [
30,
31,
32,
33,
34,
35]. It is important to underline that ASCs have a low immunological reactivity, thanks to the absence or low expression of immunogenic surface antigens (CD40, CD40L, CD80 and CD86) and major histocompatibility complex II. This low immunological reactivity also makes them suitable for allogeneic use [
20]. In addition, ASCs are able to modulate T and B cell activity and exert anti-inflammatory effects [
36]. Finally, ASC beneficial effects can also be due to their paracrine production of numerous cytokines and growth factors, such as vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and insulin-like growth factor 1 (IGF-1) [
37,
38]. As a result, the use of an ASC-conditioned medium is also investigated for potential cell-free therapeutic applications [
39].
2.1. ASC Osteogenic Differentiation
The osteogenic induction of ASCs is usually obtained in about 21 days by replacing the basal growth medium with osteogenic media containing dexamethasone, β-glycerophosphate and ascorbic acid [
40]. To verify the osteogenic phenotype, specific histological staining is commonly used (Von Kossa or Alizarin Red), which reveals calcium deposits and the mineralized matrix [
1]. During differentiation, ASCs produce a mineralized extracellular matrix (ECM) with an increased expression of bone markers, such as runt-related transcription factor 2 (RUNX2; a marker of osteoblast differentiation), osteonectin and osteocalcin, as well as an increased synthesis of alkaline phosphatase (ALP) and collagen type I [
41,
42]. A better degree of osteogenic differentiation has recently been obtained using ASCs transfected with osteo-specific genes, such as the insertion of encoding bone morphogenetic protein (BMP)-2 and Runx2 genes [
43]. Controversial results were reported by comparing ASC and BMSC osteogenic potential. According to Brennan et al. [
44], BMSCs show better osteogenesis, whereas ASCs feature enhanced angiogenesis. In contrast, in another comparative study, it was found that ASCs showed a higher proliferation rate and an increased ability to differentiate into osteocytes and chondrocytes, as evaluated using Alizarin Red and Alcian Blue staining, respectively [
18]. In particular, these properties were more pronounced for cells expressing CD271, a neurotrophin receptor that is a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily. However, the differences might be simply due to different experimental procedures.
2.2. ASC Chondrogenic Differentiation
Various protocols have been adopted to obtain ASC chondrogenic differentiation, normally requiring 21–28 days [
45]. Widely used differentiation media usually contain high glucose levels, fetal calf or bovine serum, penicillin and streptomycin, ascorbate-2-phosphate, dexamethasone, transforming growth factor beta (TGF-β1 or TGF-β3), insulin, transferrin, selenium, sodium pyruvate and L-glutamine. Additional supplements and growth factors can be included, such as BMP-2, 4 or 6, sex-determining region Y box 9 (SOX 9) and basic FGF [
46,
47,
48]. The chondrogenic phenotype can be evaluated using various tests, including histological staining using Alcian blue, toluidine blue or safranin O, detecting the presence of proteoglycan in the cartilage-like matrix. In addition, real-time PCR, Western blot analysis, ELISA, RNA microarray analysis and immunohistochemistry reveal the expression of chondrocyte-specific genes or proteins, such as different collagen types, keratin sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, aggrecan, decorin and biglycan [
41,
49]. In monolayer cultures, ASCs hardly maintain a chondrogenic phenotype, showing a decrease in collagen type II expression, while collagen type X production increases. A three-dimensional (3D) culture of chondrocyte-like ASCs overcomes this issue. In a study by Musumeci et al. [
50], ASCs treated with a specific chondrogenic medium for 28 days showed a high expression of collagen type I and II, as well as lubricin, a key molecule in cartilage wear prevention. This glycoprotein, which assures joint lubrication and synovial homeostasis, may represent an additional differentiation biomarker.
3. ASC-Based Repair Strategies
Different approaches have been explored for the treatment of cartilage and bone tissue disorders: the transplantation of uncultured ASCs; the transplantation of ASCs expanded in vitro; the transplantation of ASCs after their osteogenic or chondrogenic differentiation; and variously treated ASCs in combination with scaffolds (Figure 1).
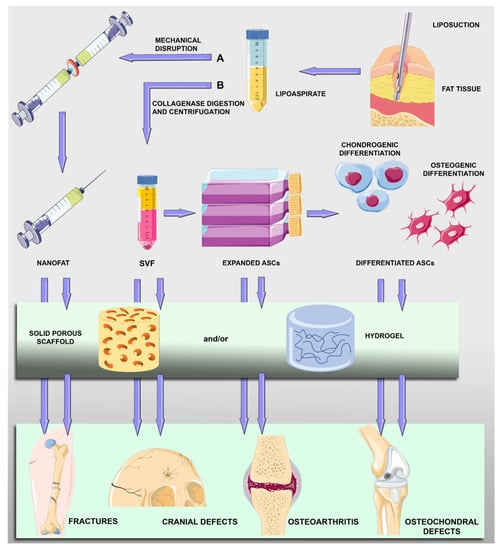
Figure 1. Schematic drawing showing main steps of harvesting and treatments of adipose-derived mesenchymal stromal cells (ASCs) for bone and cartilage repair. After liposuction procedures, fat tissue in the lipoaspirate can be mechanically disrupted (A) to obtain micro fat particles (nanofat) containing ASCs and other cell types (lymphocytes, pericytes, vascular endothelial cells and vascular smooth muscle cells). Lipoaspirate can be digested and centrifuged (B) to obtain a pellet (stromal vascular fraction, SVF) containing ASCs that can be expanded and undergo osteogenic or chondrogenic differentiation. Nanofat particles, SVF cells, expanded ASCs or predifferentiated ASCs can be directly implanted or included in scaffold-assisted treatments.
For cell-based applications, freshly isolated ASCs present in adipose SVF are preferred in some instances, not only to shorten the interval from harvesting to the transplant procedure but also to avoid restrictions and risks related to cell culturing, such as the possibility of contamination, tumorigenesis or unexpected cell differentiation. A collagenase enzyme is normally added to the adipose tissue, producing a mixture that, after filtration and centrifugation, can be separated into a superficial adipocyte fraction and precipitated cellular components. To overcome restrictions associated with the enzymatic procedure, alternative methods to obtain an SVF-like compound have been developed. Although with a lower cell yield, SVF cells featuring virtually the same regenerative potential can be obtained using mechanical disruption of the adipose tissue giving rise to micro fat particles that are also called nanofat [
51,
52]. Nanofat grafting is widely used in plastic surgery [
53] and for bone and cartilage repair, often combined with platelet-rich plasma (PRP) [
16]. After centrifugation, ASCs contained in the SVF can be successively expanded for further uses. Based on cell–cell and cell–matrix interactions, 3D cultures of ASCs would offer a favorable context for their multilineage vascular and osteogenic differentiation, providing in the resulting spheroids an in vitro model of the interactive elements [
54]. This strategy is particularly advantageous to improve the thickness of a scaffold-free implant.
Figure 1 illustrates the main steps of ASC treatment for bone and cartilage repair.
Scaffold-Assisted Strategies
Scaffold-based approaches have been widely investigated as cell implantation alone often raises substantial issues related to postimplantation cell fate, cellular loss and dispersion. A variety of scaffolds have been designed, improving not only the correct positioning of stem cells but also their attachment, viability, proliferation, migration and differentiation [
55,
56,
57]. Scaffolds can be subdivided into different categories (i.e., metallic or nonmetallic, natural or synthetic), and many of them are available for applications to skeletal and other tissues. Due to their properties, metallic implants using titanium and titanium dioxide are particularly suitable for bone defects. On the other hand, many more nonmetallic scaffolds have been designed, each of them characterized by different advantages and disadvantages. Examples of these scaffolds include the acellular matrix, coralline scaffolds, natural or synthetic polymers and hybrid scaffolds [
20,
58,
59]. Ideal scaffolds should be degradable and biocompatible and mimic as closely as possible the physiological microenvironment of the target tissue. In addition, they can be loaded not only with stem cells but also with bioactive molecules, such as growth factors and anti-inflammatory or antibacterial agents [
60]. Optimal pore size is a crucial characteristic of a scaffold and largely depends on the type of tissue for which the scaffold is planned [
61]. For example, smaller pore sizes are suitable for the formation of fibrous tissues, while larger pore sizes are more appropriate for the formation of bone tissue. Too wide pores hamper cell attachment and the stiffness of the scaffold, whereas too small pores reduce cell viability and migration, nutrient diffusion and waste removal. After the initial adhesion and tissue formation at the external surfaces, stem cells should be able to penetrate inside the scaffold giving rise to an inward gradient of tissue formation [
62]. The newly formed tissue would hopefully restore the proper shape and function.
Natural ECMs can be advantageously prepared in the form of hydrogels [
58], which are considered a promising cell-supporting alternative material [
63]. Hydrogels are characterized by a 3D polymeric network that, retaining a large amount of water, more closely resembles soft tissues, thus providing a wider range of scaffold applications. Hydrogels possess good biocompatibility, tunable swelling and mechanical properties and a biodegradation rate that is more predictable and adjustable than other scaffolds. The most used natural biomaterials include collagen, gelatin, hyaluronic acid, chitosan and alginate, noncollagenous proteins and proteoglycans [
64,
65].
For in vivo experiments, rodents are mostly investigated, but larger animals (goats, dogs or minipigs) are also often chosen because a large animal requires implantation procedures that are more similar to those for human treatments, thus improving the translational potential.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/biomedicines11071781