5-Hydroxytryptamine (5-HT), or serotonin, plays a crucial role as a neuromodulator and/or neurotransmitter of several nervous system functions. Its actions are complex, and depend on multiple factors, including the type of effector or receptor activated. Briefly, 5-HT can activate: (i) metabotropic (G-protein-coupled) receptors to promote inhibition (5-HT1, 5-HT5) or activation (5-HT4, 5-HT6, 5-HT7) of adenylate cyclase, as well as activation (5-HT2) of phospholipase C; and (ii) ionotropic receptor (5-HT3), a ligand-gated Na+/K+ channel.
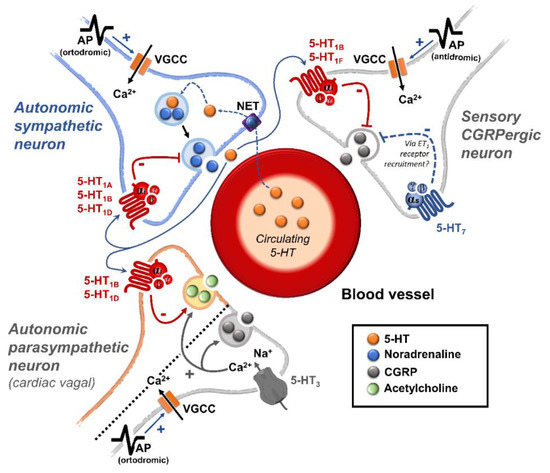
Regarding blood pressure regulation (and beyond the intricacy of central 5-HT effects), this monoamine also exerts direct postjunctional (on vascular smooth muscle and endothelium) or indirect prejunctional (on autonomic and sensory perivascular nerves) effects. At the prejunctional level, 5-HT can facilitate or preclude the release of autonomic (e.g., noradrenaline and acetylcholine) or sensory (e.g., calcitonin gene-related peptide) neurotransmitters facilitating hypertensive or hypotensive effects. Hence, we cannot formulate a specific impact of 5-HT on blood pressure level, since an increase or decrease in neurotransmitter release would be favoured, depending on the type of prejunctional receptor involved.
This review summarizes and discusses the current knowledge on the prejunctional mechanisms involved in blood pressure regulation by 5-HT and its impact on some vascular-related diseases.
- 5-hydroxytryptamine
- serotonin
- CGRP
- blood pressure
- hypertension
1. A Summary on 5-HT Receptors
| 5-HT Receptor |
Receptor Subtype | Agonists | Antagonists | Some Functions | Canonical Transduction System |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5-HT1 | 5-HT1A | 8-OH-DPAT | WAY 100635 | Central hypotension | G-protein coupled receptor (Gi)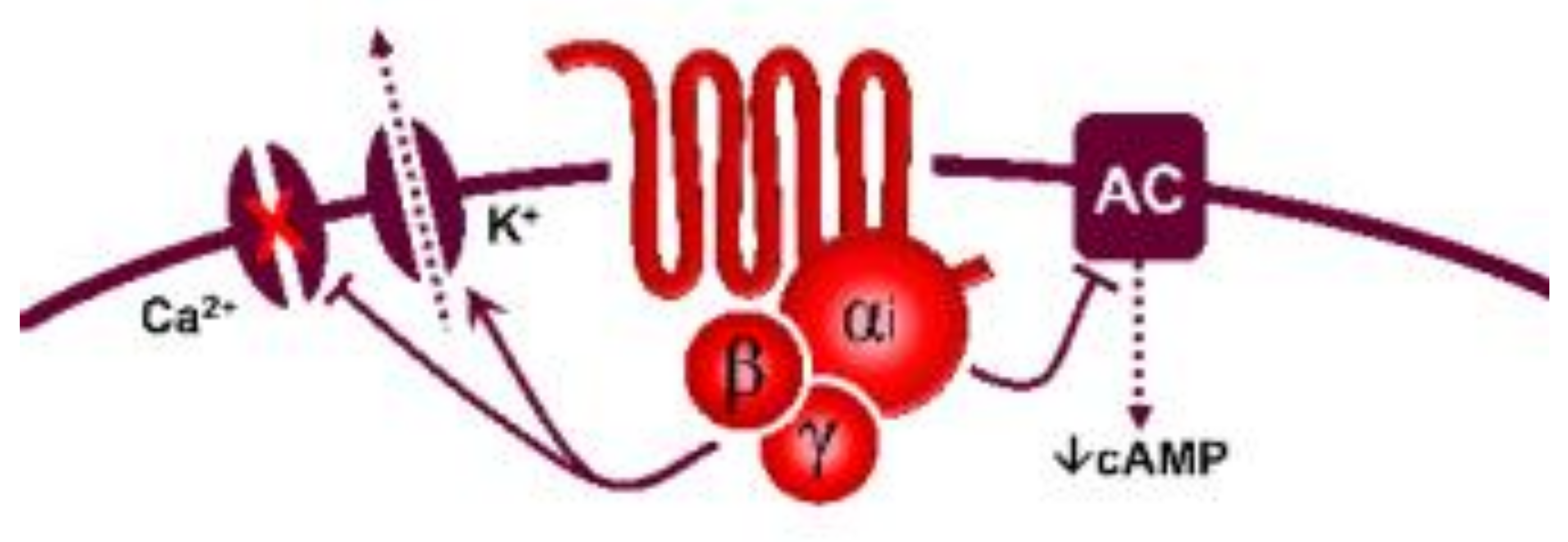 |
| 5-HT1B | Sumatriptan CP-93,129 (rodents) |
SB224289 | Vasoconstriction, sympatho-inhibition | ||
| 5-HT1D | PNU-109291 PNU-142633 |
BRL15572 | Autoreceptor, sympatho-inhibition | ||
| 5-HT1e * | 5-HT >> 5-CT LY334370 | Methiothepin (non-selective) |
Unknown | ||
| 5-HTF | LY344864, lasmiditan, LY334370 | Methysergide (non-selective) |
(−) Trigeminal system | ||
| 5-HT5 | 5-HT5A | 5-HT, ergotamine | SB699551 | Cardiac sympatho-inhibition in rats | |
| 5-HT5b * | 5-CT (non-selective) | Unknown | Unknown | ||
| 5-HT4 | - | Renzapride, BIMU8, ML10302, SC53116 | GR 113808 SB204070 | (+) Neuronal activity, vasodilatation, tachycardiain pigs and humans |
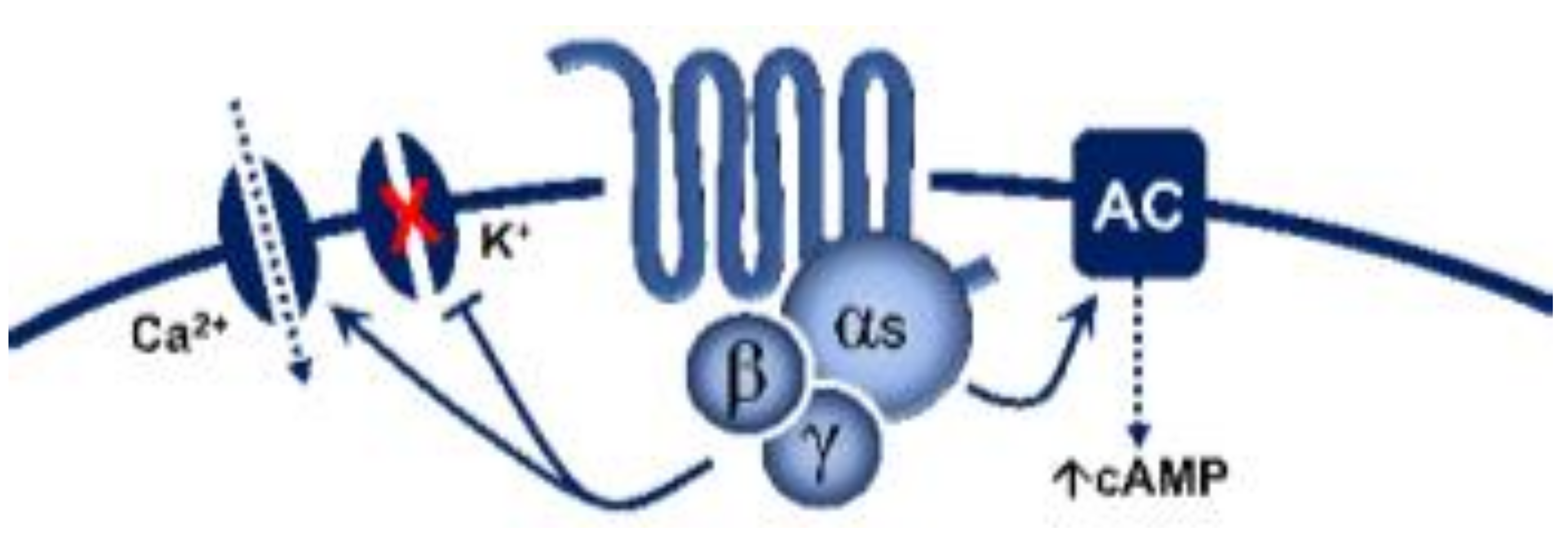 G-protein coupled receptor (Gs) |
| 5-HT6 | - | 5-MeO-T ≥ 5-HT SB357134 SB271046 |
Ro 630563 | Memory, not involved in cardiovascular regulation |
|
| 5-HT7 | - | 5-CT>>5-HT AS-19 |
SB269970 SB258719 | Circadian rhythm, vasodila- tation, tachycardia in cats |
|
| 5-HT2 | 5-HT2A | DOI, DOB α-methyl-5-HT |
MDL100907 Ketanserin |
Vasoconstriction, plateletaggregation | 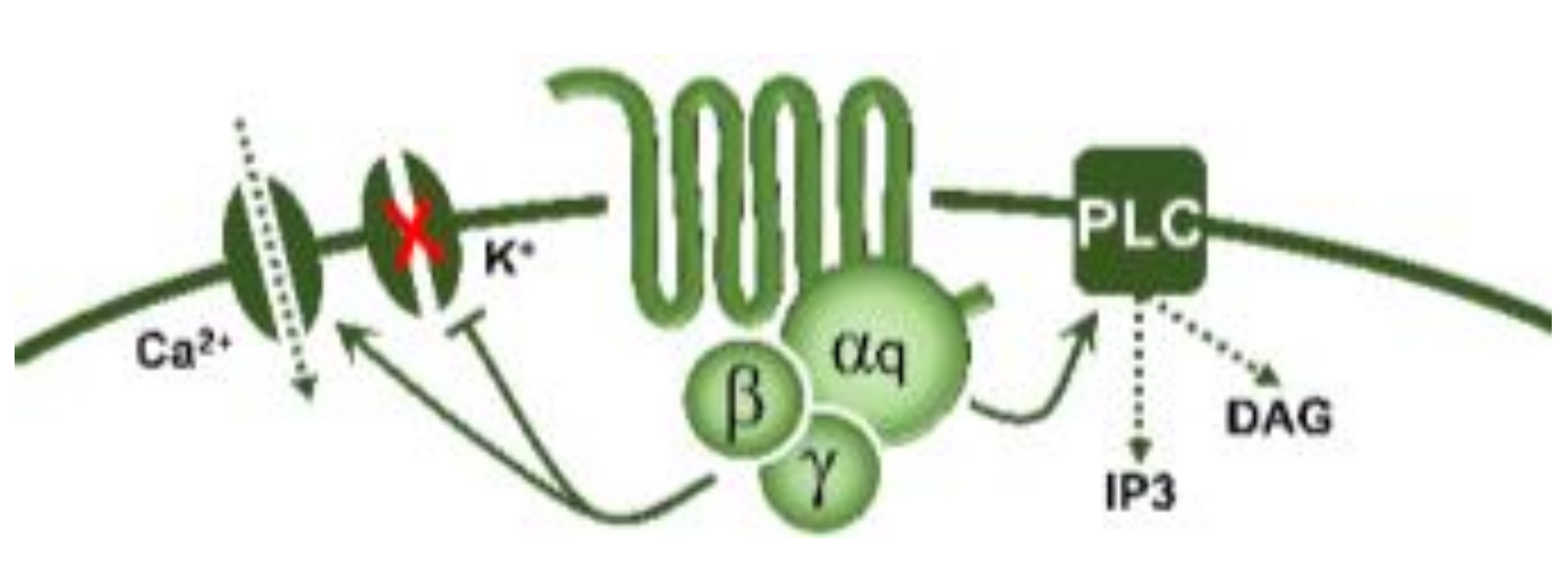 G-protein coupled receptor (Gq) |
| 5-HT2B | DOI, BW723C86 α-methyl-5-HT |
SB204741 RS-127445 |
Vasoconstriction, release of NO | ||
| 5-HT2C | DOI, Ro 60-0175 α-methyl-5-HT |
SB242084 RS-102221 |
CSF production | ||
| 5-HT3 | Pentameric ion channel ** | Phenylbiguanide 2-methyl-5-HT |
Tropisetron Granisetron MDL-72222 |
(+) Neuronal activity, reflex bradycardia |
Ligand-gated ion channel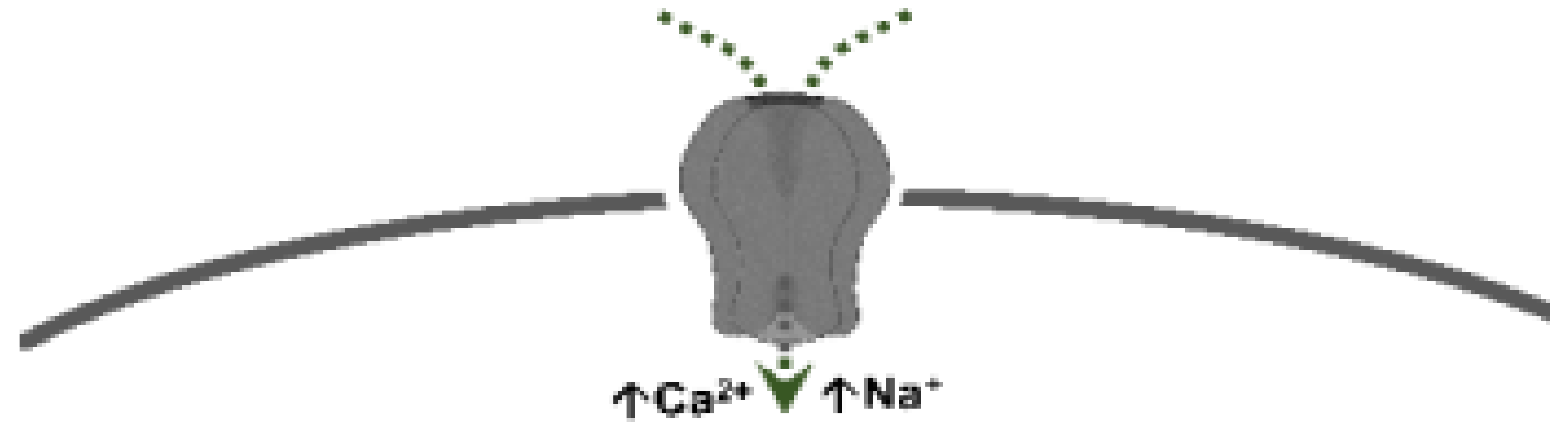 |
2. An Overview of the Effects of 5-HT on the Cardiovascular System
3. The Specific Interactions of 5-HT at Peripheral and Central Levels to Induce Cardiovascular Effects
3.1. Sensory Afferents
3.2. Sympathetic Ganglia
3.3. Cardiac Effects of 5-HT
3.3.1. Bradycardia
3.3.2. Tachycardia
3.4. Vascular and Blood Pressure Effects of 5-HT
3.4.1. Initial Transient Vasodepressor Effect
3.4.2. Vasopressor Effect
3.4.3. Late Long-Lasting Vasodepressor Effect
3.5. Receptor-Independent Actions of 5-HT
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/biomedicines11071864
