While viewed as the “guardian of the genome”, the importance of the tumor suppressor p53 protein has increasingly gained ever more recognition in modulating additional modes of action related to cell death. Slowly but surely, its importance has evolved from a mutated genetic locus heavily implicated in a wide array of cancer types to modulating lysosomal-mediated cell death either directly or indirectly through the transcriptional regulation of the key signal transduction pathway intermediates involved in this. Taken with its ability to directly modulate mitochondrial outer-membrane permeabilization (and cell death) collectively highlights the complex role that this protein undertakes at the molecular level
- p53
- cathepsin
- cancer
- apoptosis
- lysosomal membrane permeabilization
- MOMP
- miRNA
- intrinsic apoptosis
- extrinsic apoptosis
- lysosome
1. Introduction
As a nuclear transcription factor discovered as far back as 1979, the functional role of the tumor suppressor protein TP53 (p53) has evolved centrally in the regulation of DNA repair, cell cycle, and apoptosis [1][2]. Through such studies, p53 has revealed itself to be justifiably labelled as the “guardian of the genome” [3]. Mechanistically, this originates from its ability to be activated upon cellular stress and orchestrate the cell’s DNA damage response and, in doing so, helping to maintain genome integrity [4]. Consequently, the mutation of the functional p53 gene can give rise to the accumulation of a variety of cancer types [5] through its deregulated modulation of cellular senescence and apoptotic death signaling pathways [6]. Over the years, this aspect of p53 activity has unveiled a number of interesting phenomena that determine cell fate under normal conditions and throughout disease onset or progression. Moreover, through the identification and characterization of a number of TP53 somatic mutations and its isoform proteins, our understanding of the molecular events that give rise to deregulated p53 activity with such serious and physiologically relevant effects has vastly improved [7][8].
At the molecular level, monomeric-p53 is composed of 393 amino acids and is active as a homo-tetramer protein [9][10], which can be post-translationally modified in a variety of ways that modulate its activity [11][12][13][14]. One key regulatory step that keeps nuclear p53 in its inactive state is through minimizing its protein stability [15][16] through its poly-ubiquitination (and proteasomal degradation) by MDM2 in a negative auto-regulatory feedback manner [17]. Moreover, mono-ubiquitination can also behave as a signal for p53 to be cytoplasmically [18][19] or mitochondrially translocated [20], where it can undergo de-ubiquitination by herpesvirus-associated ubiquitin-specific protease (HAUSP) upon its arrival [21]. Another post-translational modification of p53 is protein acetylation (at Lysine-120), and this form of acetylated p53 is found at the mitochondrial outer membrane after DNA damage induction and displaces Mcl-1 from BAK [22] and positively regulates apoptosis. Simultaneously, the activation of p53 can also occur through DNA damage-induced phosphorylation (by HIPK2, for example) at Serine-46 as an important event for mitochondrial localization [23][24], and can cause the direct induction of Mitochondrial Outer Membrane Permeabilization (MOMP, [25][26]). Phosphorylation can also have the effect of stabilizing nuclear p53 levels [14], permitting it to modulate target gene expression, as seen with the cell cycle regulator p21 [27], either directly or with the aid of co-activators [28] (Figure 1).
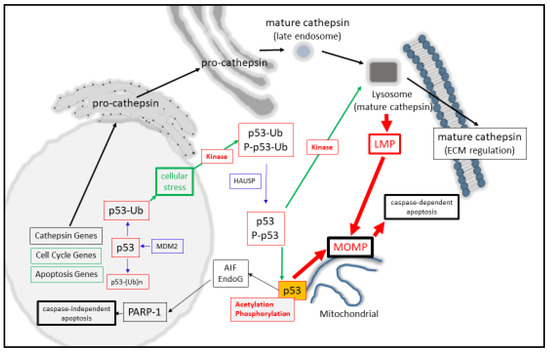
Figure 1. p53 regulates lysosomal- and mitochondrial-mediated apoptosis.
2. p53 Transcription and Functionality: An Update
Genetically, the p53 protein is encoded by 10 exons through a mature mRNA transcript spanning 2512 bp, which can translate from a number of translation start sites or with a number of alternatively spliced variants of the p53 pre-mRNA, giving rise to a number of isoform proteins [29][30]. The importance of the p53 protein has gained considerable momentum following the discovery that the p53 gene is found to be mutated (through deletions and point mutations) in over 50% of cancer types [2][31], which can give rise to the onset of disease [32]. Alternatively (and paradoxically), p53 over-expression can therefore be found in a high number of cancer types, albeit in its mutated form in most instances [2][33][34]. Based on the growing numbers of such mutated gene products, they can be classified as “contact” or “structural” mutations (based on alterations in their DNA-binding ability), such as the contact mutants R248W, R273C, and R73C [33] and the structural mutants R175H [35][36], R282W, [37], and Y220C [38]. Both groups give rise to loss of function. Conversely, a number of mutations can give rise to a gain of function through their ability to permit the aggregation of the p53 protein while enhancing their regulatory interactions with other transcription factors [39][40].
In offering greater context, paralleled progress has also been made in the key area of defining p53-mediated miRNA regulation (or vice versa). For example, p53 can regulate the processing and maturation of miRNA [41], while p53 itself can also be regulated by miRNA [41] or indirectly through MDM2-specific modulation by miRNA expression [42]. In keeping with p53-mediated transcription, another interesting research area of growth has been the area of defining (with greater clarity) the p53 consensus sites (and their structural requirements) present upstream of its target genes [43][44]. Herein, a number of excellent studies have emerged, which have given rise to the characterization of the p53 DNA-binding consensus sequence and what significance the structure of the DNA harboring this sequence can offer in p53-DNA recognition. Of equal importance has been the discovery that the p53 gene can also bind the p63 and p73 consensus sequences and suppress gene expression [45][46]. While such findings do offer a number of important findings insofar as the role that the p53 protein may play in regulating cell death (either indirectly or directly), it also diversifies the role that p53 may play in the regulation of genes once thought to be regulated exclusively by transcription factors p63 and p73 alone.
3. p53 As a Co-Regulator of Mitochondrial and Lysosomal Mediated Cell Death
Synonymous with activating LMP, a broad spectrum of agents such as reactive oxygen species, DNA damaging agents, heavy metals, ischemia, and inflammation can also result in the activation of p53 [47]. The contributing factors that have helped to resolve the importance of p53 for inducing death have arisen from the question of how effectively cells die in a p53-dependent manner. Here, p53-mediated death can be arrived at through the up-regulated expression of BAX [48], APAF-1 [49][50], NOXA [51], PUMA [52][53], BIM [54][55], Bcl-2 suppression [56], Bcl-xL [57][58][59], and Mcl-1 suppression [60][61]. Consequently, MOMP [25]can be directly induced by activated P-p53 [23], through activating BAX or BAK [25][62][63], or through displacing anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins from their pro-apoptotic counterparts [25][62][64]. However, a second contributing mechanism for this may also be involved through the actions of p53 mediating LMP directly as the initiating step of lysosomal-mediated cell death through MOMP induction (Figure 1). Such a suggestion comes from p53 directly inducing LMP in myeloid leukemia cells [65] and TNF-α-treated fibrosarcoma cells [66]. Herein, LMP activation strongly depends upon the localization of phosphor-Ser15-p53 to the lysosomal membrane [66], which could destabilize the lysosome and induce apoptosis in a lysosomal-mitochondrial linked pathway [65].
Based collectively on p53 and cathepsin being synonymous in their roles in destabilizing the lysosome, it appears that both of them therefore may have significant input into how effectively lysosomes are predisposed to LMP or LL. While high levels of cytoplasmic p53 may cause LMP, during low levels of p53 LMP inducibility may possibly be compensated for by the relatively high level of expression of cathepsin proteases. Clearly, such a mechanism requires there to be some regulatory relationship between the cathepsin proteases and p53 at the transcriptional, translational, or post-translational level.
4. p53 Activation and Cathepsin Protein Expression
As central factors that are heavily involved in mediating LMP, clearly one question that arises from our viewpoint is whether there is a direct regulatory relationship between the p53 and cathepsin proteins. To date, vital information addressing this has been arrived at through the analysis of p53 and cathepsin protein or mRNA expression levels in p53-positive or -negative cells, or through their evaluation as co-expressed diagnostic or prognostic markers, either in tissue samples or from serum [67]. Here, of central importance may be the p53 consensus binding sequence PuPuPuC(A/T)(A/T)GPyPyPy, which can be present in duplicate and separated by a 13 bp spacer and has the core consensus sequence C(A/T)(A/T)G. Through a deletion analysis of this sequence, p53 can bind the full site, half site, and 1.5 sites [10][68], and activate them all in reporter gene assays [68][69][70][71].
Being mindful of the aforementioned, a number of excellent studies have reported a very strong correlation between p53 expression and the regulation of some cathepsin genes. For example, Wu et al. (1998) demonstrated cathepsin D was expressed in a p53-dependent manner in U1752, Pa1, and ML1 leukemia cells following Adriamycin stimulation. Additionally, p53 could bind two p53 consensus sites within the cathepsin D promoter in vitro and direct luciferase-reporter gene activation in cells. Enhanced cathepsin D expression also offered cells a greater resistance to death following Etopiside treatments [72].
More recently, the anti-tumor effects of WIN55-212-2 in glioblastoma cell lines were evaluated and a positive relationship observed between DNA-damage induced mut-p53 and cathepsin D protein levels [73].
In the instance of cathepsin L, Katara et al. (2010) identified p53 as a positive binding factor to the cathepsin L promoter and mut-p53 reported to positively regulate cathepsin L expression in glioblastoma cells [74]. In a similar cellular context, the cathepin L expression was positively correlated with the mut-p53 expression in glioblastoma U251 cells treated with Ionizing Radiation (IR) and the inhibition of which (through cathepsin L inhibition) sensitized cells to IR-induced apoptosis [75]. In confirmation of such findings, mut-p53 also enhanced cathepsin L expression upon IR-induced EMT of NSCLC cells [76]. Lastly, cathepsins B and D activity could be enhanced in the rat hippocampus during IR therapy for 12 h, which correlated with enhanced WT-p53 proteins levels and which could be reversed upon treatment of cells with Pifithrin-α [77]. Supportingly, Xin et al. (2019) reported that cathepsin S and K mRNA expression was induced in line with p53 protein expression during chronic oxidative stress conditions in mouse aortic tissues [68].
Based on these collective findings, clearly p53 has some direct input into cathepsins D, L (and likely B) transcriptional and/or protein regulation. Herein, while some studies have explored the role of WT-p53, others had focused on mut-p53, and which generally emphasize a growing connection between p53 and cathepsin expression with EMT, oxidative stress, and chemotherapeutic resistance or sensitivity (Table 1).
Table 1. Wild Type (WT-) or mutant (mut-) p53 with cathepsin protein expression levels can be positively correlated in a variety of cancer cell lines and types.
| p53 Expression | Cathepsin | Cells | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| WT-p53 increased | D | Lung, Ovarian, Leukemia cells | [72] |
| mut-p53 increased | L | Glioblastoma | [74] |
| WT-p53 increased | B | Rat hippocampus | [77] |
| mut-p53 increased | L | Glioblastoma | [75] |
| WT-p53 increased | S, K | Mouse Aorta | [78] |
| WT-p53 increased | D | Glioblastoma Cell lines | [73] |
| mut-p53 increased | L | Non-small cell lung cancer | [76] |
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/cancers12113476
References
- Vogelstein, B.; Lane, D.; Levine, A.J. Surfing the p53 network. Nat. Cell Biol. 2000, 408, 307–310.
- Fischer, M. Census and evaluation of p53 target genes. Oncogene 2017, 36, 3943–3956.
- Lane, D.P. Cancer. p53, guardian of the genome. Nature 1992, 358, 15–16.
- Williams, A.B.; Schumacher, B. p53 in the DNA-damage-repair process. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, 026070.
- Nguyen, T.-A.T.; Menendez, D.; A Resnick, M.; Anderson, C.W. Mutant TP53 posttranslational modifications: Challenges and opportunities. Hum. Mutat. 2014, 35, 738–755.
- Mijit, M.; Caracciolo, V.; Melillo, A.; Amicarelli, F.; Giordano, A. Role of p53 in the regulation of cellular senescence. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 420.
- Molchadsky, A.; Rotter, V. p53 and its mutants on the slippery road from stemness to carcinogenesis. Carcinogenesis 2017, 38, 347–358.
- Hainaut, P.; Pfeifer, G.P. SomaticTP53Mutations in the era of genome sequencing. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2016, 6, 026179.
- Gencel-Augusto, J.; Lozano, G. p53 tetramerization: At the center of the dominant-negative effect of mutant p53. Genes Dev. 2020, 34, 1128–1146.
- McLure, K.G. How p53 binds DNA as a tetramer. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 3342–3350.
- Jimenez, G.S.; Khan, S.H.; Stommel, J.M.; Wahl, G.M. p53 regulation by post-translational modification and nuclear retention in response to diverse stresses. Oncogene 1999, 18, 7656–7665.
- Meek, D.W.; Anderson, C.W. Posttranslational modification of p53: Cooperative integrators of function. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2009, 1, 000950.
- Bode, A.M.; Dong, Z. Post-translational modification of p53 in tumorigenesis. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2004, 4, 793–805.
- Liu, Y.; Tavana, O.; Gu, W. p53 modifications: Exquisite decorations of the powerful guardian. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 564–577.
- Wu, L.; Levine, A.J. Differential regulation of the p21/WAF-1 and mdm2 genes after high-dose UV irradiation: p53-dependent and p53-independent regulation of the mdm2 gene. Mol. Med. 1997, 3, 441–451.
- Levine, A.J. p53, the cellular gatekeeper for growth and division. Cell 1997, 88, 323–331.
- Nag, S.; Qin, J.; Srivenugopal, K.S.; Wang, M.; Zhang, R. The MDM2-p53 pathway revisited. J. Biomed. Res. 2013, 27, 254–271.
- Lohrum, M.A.E.; Woods, D.B.; Ludwig, R.L.; Balint, E.; Vousden, K.H. C-terminal ubiquitination of p53 contributes to nuclear export. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2001, 21, 8521–8532.
- Li, M.; Brooks, C.L.; Wu-Baer, F.; Chen, D.; Baer, R.; Gu, W. Mono-versus polyubiquitination: Differential control of p53 fate by Mdm2. Science 2003, 302, 1972–1975.
- Marchenko, N.D.; Wolff, S.; Erster, S.; Becker, K.; Moll, U.M. Monoubiquitylation promotes mitochondrial p53 translocation. EMBO J. 2007, 26, 923–934.
- Li, M.; Chen, D.; Shiloh, A.; Luo, J.; Nikolaev, A.Y.; Qin, J.; Gu, W. Deubiquitination of p53 by HAUSP is an important pathway for p53 stabilization. Nature 2002, 416, 648–653.
- Sykes, S.M.; Stanek, T.J.; Frank, A.; Murphy, M.E.; McMahon, S.B. Acetylation of the DNA binding domain regulates transcription-independent apoptosis by p53. J. Biol. Chem. 2009, 284, 20197–20205.
- Sorrentino, G.; Mioni, M.; Giorgi, C.; Ruggeri, N.; Pinton, P.; Moll, U.; Mantovani, F.; Del Sal, G. The prolyl-isomerase Pin1 activates the mitochondrial death program of p53. Cell Death Differ. 2012, 20, 198–208.
- Mancini, F.; Di Conza, G.; Pellegrino, M.; Rinaldo, C.; Prodosmo, A.; Giglio, S.; D’Agnano, I.; Florenzano, F.; Felicioni, L.; Buttitta, F.; et al. MDM4 (MDMX) localizes at the mitochondria and facilitates the p53-mediated intrinsic-apoptotic pathway. EMBO J. 2009, 28, 1926–1939.
- Chipuk, J.E.; Kuwana, T.; Bouchier-Hayes, L.; Droin, N.M.; Newmeyer, D.D.; A Schuler, M.; Green, D.R. Direct activation of bax by p53 mediates mitochondrial membrane permeabilization and apoptosis. Science 2004, 303, 1010–1014.
- Mancini, F.; Moretti, F. Mitochondrial MDM4 (MDMX): An unpredicted role in the p53-mediated intrinsic apoptotic pathway. Cell Cycle 2009, 8, 3854–3859.
- El-Deiry, W.S.; Tokino, T.; Velculescu, V.E.; Levy, D.B.; Parsons, R.; Trent, J.M.; Lin, D.; Mercer, W.E.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B.; et al. WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 1993, 75, 817–825.
- Beckerman, R.; Prives, C. Transcriptional regulation by p53. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, 000935.
- Fujita, K. p53 isoforms in cellular senescence-and ageing-associated biological and physiological functions. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6023.
- Anbarasan, T.; Bourdon, J.C. The emerging landscape of p53 isoforms in physiology, cancer and degenerative diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6257.
- Olivier, M.; Hollstein, M.; Hainaut, P. TP53 mutations in human cancers: Origins, consequences, and clinical use. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2010, 2, a001008.
- Miller, J.J.; Gaiddon, C.; Storr, T. A balancing act: Using small molecules for therapeutic intervention of the p53 pathway in cancer. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2020, 49, 6995–7014.
- Baugh, E.H.; Ke, H.; Levine, A.J.; A Bonneau, R.; Chan, C.S. Why are there hotspot mutations in the TP53 gene in human cancers? Cell Death Differ. 2018, 25, 154–160.
- Freed-Pastor, W.A.; Prives, C. Mutant p53: One name, many proteins. Genes Dev. 2012, 26, 1268–1286.
- Loh, S.N. The missing Zinc: p53 misfolding and cancer. Metallomics 2010, 2, 442–449.
- Bullock, A.N.; Henckel, J.; Dedecker, B.S.; Johnson, C.M.; Nikolova, P.V.; Proctor, M.R.; Lane, D.P.; Fersht, A.R. Thermodynamic stability of wild-type and mutant p53 core domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1997, 94, 14338–14342.
- Cho, Y.; Gorina, S.; Jeffrey, P.D.; Pavletich, N.P. Crystal structure of a p53 tumor suppressor-DNA complex: Understanding tumorigenic mutations. Science 1994, 265, 346–355.
- Wilcken, R.; Liu, X.; Zimmermann, M.O.; Rutherford, T.J.; Fersht, A.R.; Joerger, A.C.; Boeckler, F.M. Halogen-enriched fragment libraries as leads for drug rescue of mutant p53. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2012, 134, 6810–6818.
- Silva, J.L.; Cino, E.A.; Soares, I.N.; Ferreira, V.F.; De Oliveira, G.A.P. Targeting the prion-like aggregation of mutant p53 to combat cancer. Accounts Chem. Res. 2017, 51, 181–190.
- Navalkar, A.; Ghosh, S.; Pandey, S.; Paul, A.; Datta, D.; Maji, S.K. Prion-like p53 amyloids in cancer. Biochemistry 2020, 59, 146–155.
- Liu, J.; Zhang, C.; Zhao, Y.; Feng, Z. MicroRNA control of p53. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 7–14.
- Sargolzaei, J.; Etemadi, T.; Alyasin, A. The P53/microRNA network: A potential tumor suppressor with a role in anticancer therapy. Pharmacol. Res. 2020, 160, 105179.
- Cai, B.H.; Chao, C.F.; Huang, H.C.; Lee, H.Y.; Kannagi, R.; Chen, J.Y. Roles of p53 family structure and function in non-canonical response element binding and activation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 3681.
- Brazda, V.; Fojta, M. The rich world of p53 DNA binding targets: The role of DNA structure. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 5605.
- Liu, K.; Ling, S.; Lin, W.C. TopBP1 mediates mutant p53 gain of function through NF-Y and p63/p73. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2011, 31, 4464–4481.
- Stindt, M.H.; Muller, P.A.J.; Ludwig, R.L.; Kehrloesser, S.; Dotsch, V.; Vousden, K.H. Functional interplay between MDM2, p63/p73 and mutant p53. Oncogene 2014, 34, 4300–4310.
- Kurz, T.; Terman, A.; Gustafsson, B.; Brunk, U.T. Lysosomes and oxidative stress in aging and apoptosis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2008, 1780, 1291–1303.
- Toshiyuki, M.; Reed, J.C. Tumor suppressor p53 is a direct transcriptional activator of the human bax gene. Cell 1995, 80, 293–299.
- Fortin, A.; Cregan, S.P.; Maclaurin, J.G.; Kushwaha, N.; Hickman, E.S.; Thompson, C.S.; Hakim, A.; Albert, P.R.; Cecconi, F.; Helin, K.; et al. APAF1 is a key transcriptional target for p53 in the regulation of neuronal cell death. J. Cell Biol. 2001, 155, 207–216.
- Moroni, M.C.; Hickman, E.S.; Denchi, E.L.; Caprara, G.; Colli, E.; Cecconi, F.; Müller, H.; Helin, K. Apaf-1 is a transcriptional target for E2F and p53. Nat. Cell Biol. 2001, 3, 552–558.
- Oda, E.; Ohki, R.; Murasawa, H.; Nemoto, J.; Shibue, T.; Yamashita, T.; Tokino, T.; Taniguchi, T.; Tanaka, N. Noxa, a BH3-only member of the Bcl-2 family and candidate mediator of p53-induced apoptosis. Science 2000, 288, 1053–1058.
- Nakano, K.; Vousden, K.H. PUMA, a novel proapoptotic gene, is induced by p53. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 683–694.
- Yu, J.; Zhang, L.; Hwang, P.M.; Kinzler, K.W.; Vogelstein, B. PUMA induces the rapid apoptosis of colorectal cancer cells. Mol. Cell 2001, 7, 673–682.
- Happo, L.; Cragg, M.S.; Phipson, B.; Haga, J.M.; Jansen, E.S.; Herold, M.J.; Dewson, G.; Michalak, E.M.; Vandenberg, C.J.; Smyth, G.K.; et al. Maximal killing of lymphoma cells by DNA damage–inducing therapy requires not only the p53 targets Puma and Noxa, but also Bim. Blood 2010, 116, 5256–5267.
- Lieschke, E.; Wang, Z.; Kelly, G.L.; Strasser, A. Discussion of some ‘knowns’ and some ‘unknowns’ about the tumour suppressor p53. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 212–223.
- Budhram-Mahadeo, V.; Morris, P.J.; Smith, M.D.; Midgley, C.A.; Boxer, L.M.; Latchman, D.S. p53 suppresses the activation of the Bcl-2 promoter by the Brn-3a POU family transcription factor. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 15237–15244.
- Miyashita, T.; Krajewski, S.; Krajewska, M.; Wang, H.G.; Lin, H.K.; A Liebermann, D.; Hoffman, B.; Reed, J.C. Tumor suppressor p53 is a regulator of bcl-2 and bax gene expression in vitro and in vivo. Oncogene 1994, 9, 1799–1805.
- Sugars, K.L.; Budhram-Mahadeo, V.; Packham, G.; Latchman, D.S. A minimal Bcl-x promoter is activated by Brn-3a and repressed by p53. Nucleic Acids Res. 2001, 29, 4530–4540.
- Pietrzak, M.; Puzianowska-Kuznicka, M. p53-dependent repression of the human MCL-1 gene encoding an anti-apoptotic member of the BCL-2 family: The role of Sp1 and of basic transcription factor binding sites in the MCL-1 promoter. Biol. Chem. 2008, 389, 383–393.
- Tagscherer, K.E.; Fassl, A.; Sinkovic, T.; Combs, S.E.; Roth, W. p53-dependent regulation of Mcl-1 contributes to synergistic cell death by ionizing radiation and the Bcl-2/Bcl-XL inhibitor ABT-737. Apoptosis 2012, 17, 187–199.
- Liu, J.; Chen, G.; Feng, L.; Zhang, W.; Pelicano, H.; Wang, F.; Ogasawara, M.A.; Lu, W.; Amin, H.M.; Croce, C.M.; et al. Loss of p53 and altered miR15-a/16-1short right arrowMCL-1 pathway in CLL: Insights from TCL1-Tg:p53(-/-) mouse model and primary human leukemia cells. Leukemia 2014, 28, 118–128.
- Mihara, M.; Erster, S.; Zaika, A.; Petrenko, O.; Chittenden, T.; Pancoska, P.; Moll, U.M. p53 has a direct apoptogenic role at the mitochondria. Mol. Cell 2003, 11, 577–590.
- Pietsch, E.C.; Perchiniak, E.; Canutescu, A.A.; Wang, G.; Dunbrack, R.L.; Murphy, M.E. Oligomerization of BAK by p53 Utilizes Conserved Residues of the p53 DNA Binding Domain. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 21294–21304.
- Leu, J.I.; Dumont, P.; Hafey, M.; Murphy, M.E.; George, D.L. Mitochondrial p53 activates Bak and causes disruption of a Bak-Mcl1 complex. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2004, 6, 443–450.
- Yuan, X.M.; Li, W.; Dalen, H.; Lotem, J.; Kama, R.; Sachs, L.; Brunk, U.T. Lysosomal destabilization in p53-induced apoptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 6286–6291.
- Li, N.; Zheng, Y.; Chen, W.; Wang, C.; Liu, X.; He, W.; Xu, H.; Cao, X. Adaptor protein LAPF recruits phosphorylated p53 to lysosomes and triggers lysosomal destabilization in apoptosis. Cancer Res. 2007, 67, 11176–11185.
- Higashiyama, M.; Doi, O.; Kodama, K.; Yokouchi, H.; Kasugai, T.; Ishiguro, S. Influence of cathepsin D expression in lung adenocarcinoma on prognosis: Possible importance of its expression in tumor cells and stromal cells, and its intracellular polarization in tumor cells. J. Surg. Oncol. 1997, 65, 10–19.
- Sloman, A.; D’Amico, F.; A Yousem, S. Immunohistochemical markers of prolonged survival in small cell carcinoma of the lung. An immunohistochemical study. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 1996, 120, 465–472.
- Ahrendt, S.A.; Chow, J.T.; Xu, L.-H.; Yang, S.C.; Eisenberger, C.F.; Esteller, M.; Herman, J.G.; Wu, L.; Decker, P.A.; Jen, J.; et al. Molecular detection of tumor cells in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid from patients with early stage lung cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1999, 91, 332–339.
- Lazaris, A.C.; Lendari, I.; Kavantzas, N.; Kandiloros, D.; Adamopoulos, G.; Davaris, P. Correlation of tumor markers p53, bcl-2 and cathepsin-D with clinicopathologic features and disease-free survival in laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Pathol. Int. 2000, 50, 717–724.
- Charpin, C.; Bonnier, P.; Khouzami, A.; Vacheret, H.; Andrac, L.; Lavaut, M.N.; Allasia, C.; Piana, L. Inflammatory breast carcinoma: An immunohistochemical study using monoclonal anti-pHER-2/neu, pS2, cathepsin, ER and PR. Anticancer. Res. 1992, 12, 591–597.
- Aziz, S.; Pervez, S.; Khan, S.; Siddiqui, T.; Kayani, N.; Israr, M.; Rahbar, M. Case control study of novel prognostic markers and disease outcome in pregnancy/lactation-associated breast carcinoma. Pathol. Res. Pract. 2003, 199, 15–21.
- Ioachim, E.; Tsanou, E.; Briasoulis, E.; Batsis, C.; Karavasilis, V.; Charchanti, A.; Pavlidis, N.; Agnantis, N.J. Clinicopathological study of the expression of hsp27, pS2, cathepsin D and metallothionein in primary invasive breast cancer. Breast 2003, 12, 111–119.
- Kanno, Y.; Takane, Y.; Izawa, T.; Nakahama, T.; Inouye, Y. The inhibitory effect of aryl hydrocarbon receptor repressor (AhRR) on the growth of human breast cancer MCF-7 Cells. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2006, 29, 1254–1257.
- Lösch, A.; Schindl, M.; Kohlberger, P.; Lahodny, J.; Breitenecker, G.; Horvat, R.; Birner, P. Cathepsin D in ovarian cancer: Prognostic value and correlation with p53 expression and microvessel density. Gynecol. Oncol. 2004, 92, 545–552.
- Shin, I.Y.; Sung, N.Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Kwon, T.S.; Si, Y.; Lee, Y.S.; Oh, S.T.; Lee, I.K. The expression of multiple proteins as prognostic factors in colorectal cancer: Cathepsin D, p53, COX-2, epidermal growth factor receptor, C-erbB-2, and Ki-67. Gut Liver 2014, 8, 13–23.
- Sun, T.; Jiang, D.; Zhang, L.; Su, Q.; Mao, W.; Jiang, C. Expression profile of cathepsins indicates the potential of cathepsins B and D as prognostic factors in breast cancer patients. Oncol. Lett. 2016, 11, 575–583.
- Guerra, E.; Cimadamore, A.; Simeone, P.; Vacca, G.; Lattanzio, R.; Botti, G.; Gatta, V.; D’Aurora, M.; Simionati, B.; Piantelli, M.; et al. p53, cathepsin D, Bcl-2 are joint prognostic indicators of breast cancer metastatic spreading. BMC Cancer 2016, 16, 649.
