Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is an old version of this entry, which may differ significantly from the current revision.
Subjects:
Primary Health Care
Dental radiography (X-ray) is the most used imaging modality by dentists to identify dental issues such as lesions, periapical pathosis, and dental restorations, and evaluate oral health.
- healthcare
- deep learning
- image processing
- medical imaging
1. Introduction
Dental radiography (X-ray) is the most used imaging modality by dentists to identify dental issues such as lesions [14,15,16,17,18,19,20], periapical pathosis [21], and dental restorations [22], and evaluate oral health [23,24,25,26,27]. The examples of imaging modalities employed by researchers for dental disease diagnosis are shown in Figure 2. Different imaging modalities have been explored and their differences are outlined in the following subsections.
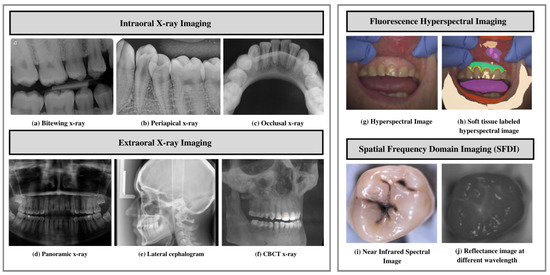
Figure 2. Imaging modalities. (a–c) Examples of different intraoral imaging. (d–f) Extraoral imaging modalities. (g–j) Near-infrared imaging. (a) Bitewing X-ray images. (b) Periapical X-rays. (c) Occlusal X-ray. (d) Panoramic X-ray. (e) Lateral cephalograms. (f) CBCT X-ray. (g,h) Fluorescence hyperspectral imaging. (i,j) Spatial frequency domain imaging.
2. X-ray Imaging Systems
To reinstate traditional photographic X-ray films, digital X-ray imaging is employed. X-ray images rely on sensors to produce enhanced images of oral structures [28]. In traditional dental disease diagnosis, the images are evaluated by dentists to identify issues such as tooth lesions and cavities, and devise treatments accordingly [29]. Dentists take several types of dental X-rays to record different mouth views. For example, for the detection of dental cavities, and to monitor mouth and teeth health, intraoral radiographs are used. In addition, dentists use extraoral radiographs to detect impacted teeth, monitor the development and growth of jaws, and identify potential problems in jaws, facial bones, and teeth.
2.1. Intraoral X-ray Imaging
Intraoral radiographs remain one of dentistry’s most widely used imaging modalities. These radiographs provide high spatial resolution images that can be used to identify dental and jawbone diseases [30]. Furthermore, these radiographs provide helpful information on bone structure and density. Paralleling and bisecting angles are two techniques to obtain an intraoral radiograph. The sensor is placed on the tooth in parallel planes, leveraging the parallel technique, exposing the radiation. The latter technique involves placing the receptor as close as possible to the tooth and exposing it to a central X-ray beam. The beam is directed perpendicularly to the imaginary line. This line allows bisecting the angle forming a long axis on the tooth and receptor plane [31]. The following are the types of intraoral radiographs used widely by dentists for dental diagnosis and treatment planning.
-
Bitewing X-ray provides a detailed account of maxillary and mandibular dental arches in a certain region of supporting bone. Bitewing radiographs aid in detecting tooth decay variations, finding dental decay, and identifying restorations.
-
Periapical X-ray portrays teeth in a full-dimensional view of one of either dental arches. The radiograph allows for detecting issues in a specific set of teeth and identifying root structure abnormalities, and detecting the surrounding bone structure.
-
Occlusal X-ray shows tooth positioning and their subsequent development in the dental arches of either the maxilla or mandible.
2.2. Extraoral X-ray Imaging
Extraoral imaging focuses on detecting dental issues in the jaw and skull. These are generally used to identify problems between the teeth, jaws, and temporomandibular joint.
-
On a single radiograph, a panoramic X-ray gives a two-dimensional view of the oral cavity including both the maxilla and mandible. These types of X-rays help identify impacted teeth and diagnose dental tumors [32].
-
Cone-beam computed tomography (CBCT) offers a substantial solution to the conventional radiography demerits. CBCT imaging is used. This type of imaging shows the interior body structures as (three-dimensional) 3-D images and enables identifying fractures and tumors in face bones. This imaging aids surgeons in avoiding after-surgery complications [35].
3. Near Infrared Imaging Systems
Near-infrared imaging is a nonionizing photo-optical method leveraged for caries detection. This imaging employs long wave radiation against tooth sides [36]. It penetrates objects deeper, thus acquiring good contrast between health and carious tissues [37,38]. This type of imaging offers certain advantages over conventional detection methods, including less radiation exposure. Furthermore, this method provides improved quality images using DIAGNOCAM [36] that transmit light through the alveolar process, including:
-
Fluorescence hyperspectral imaging system is a non-contact approach to dental tissue diagnostics. It helps degenerate raw data in a sizeable amount making it suitable for computer vision processing [39]. This imaging system combines spatial and spectral information, enabling dentists to obtain a precise optical characterization of dental issues, including dental plaque. The images are captured using a line scanning camera with 400–1000 nm spectral direction with a 5 nm sampling interval and spatial resolution of 22 μ�m. In addition, the hyperspectral imaging modality helps assess dental caries severity [40].
-
Spatial frequency domain imaging (SFDI) is a quantitative imaging technique [41] that enables the separation of components that are scattered and the optical absorption of a sample. This imaging modality relies on modulating project fringe patterns’ depth at varying frequencies and phases.
4. Spectral Ranges
There are different spectral bands that have been explored in dental applications.
-
Near-infrared, mid-infrared, and long-infrared: These spectral ranges provide valuable information about the chemical composition and molecular structure of dental tissues; this helps in the detection and characterization of dental lesions. Infrared is divided into three spectral regions, mainly near infrared ranging between 4000 and 14,000 cm−1, mid-infrared (MIR) ranging between 400 and 4000 cm−1, and far infrared, ranging between 25 and 400 cm−1 [42].
-
Radio frequency (RF) range: Non-ionizing radio frequency pulse with a range of frequencies is used in the presence of a controlled magnetic field for generating MRI [46]. The MRIs generated have found applications in implant dentistry, providing more precise information related to bone density, contour, and bone height [47].
5. Challenges in Automated Dental Disease Diagnosis
AI-based models have recently gained immense popularity for predicting, detecting, and diagnosing dental diseases. However, specific issues include limited data availability, accessibility, generality, lacking methodological standards, and practical issues revolving around the usefulness and standards in developing such solutions [11]. Therefore, the prime research focus remains on developing efficient and accurate systems to overcome these issues, and help dental practitioners plan treatment and prognosis. Disease classification has been researched extensively. However, certain challenges limit researchers from accomplishing similar levels of achievement in disease segmentation and treatment planning. A few of the open challenges include:
-
Limited Data Availability and Comprehensiveness: Due to data protection concerns, medical, especially dental, data is not readily accessible. Moreover, certain challenges including lack in terms of structure and relatively smaller size hinder applications of artificial intelligence techniques [11]. Thus, data availability affects the extent to which deep-learning-based approaches can be employed in this field.
-
Data Annotation: Medical data annotation requires specialized knowledge from healthcare professionals. Moreover, data labeling requires an adequate workforce and the process is cost intensive. In the absence of progressive flow and accurately annotated data, deep-learning algorithms cannot make correct interpretations and accurate predictions [48].
-
Limited Generalizability: Varying imaging characteristics lead to limited deep-learning model generalizability [49]. The underlying possible generalizability deficits must be elucidated to facilitate the development of improved modeling strategies.
-
Class Imbalance: The predominant occurrence of standard samples as compared to abnormal samples leads to class imbalance [50]. The imbalanced data lead to learning bias in the majority class.
-
External Validation: Lack of external validation leads to issues in the replication and transparency of AI-based models within dentistry. The community standards for model sharing, benchmarking, and reproducibility must be adhered to [51].
-
Interpretability: Lack in terms of interpretability and transparency makes it challenging to predict failures. Interpretability must be ensured to build a proper rapport between technology and humans, and generalize algorithms for specific tasks [8].
-
Expertise Gap: The ability to make accurate diagnoses and treatment plans relies on expertise derived from the extensive knowledge and practical experience. AI may not be able to fully replicate the nuanced decision-making that experienced clinicians possess. Bridging the gap between human expertise and AI capabilities poses a significant challenge in automated dental disease diagnosis.
-
Sensitivity and Specificity Limitations: Due to variations in image quality and anatomical structures, AI models may have limitations in achieving high sensitivity and specificity.
-
Image Interpretation Issues: The overlapping structures and presence of artifacts make interpreting dental images a daunting task. AI models should overcome these challenges to ensure accurate and reliable interpretation of dental images.
-
Variations in Pathology Presentation: Dental diseases manifest in different ways. These variations can be in terms of size, shape, or appearance. AI models are required to be able to take into account these variations accurately to provide accurate detection and classification of different pathologies.
This entry is adapted from the peer-reviewed paper 10.3390/diagnostics13132196
This entry is offline, you can click here to edit this entry!
