Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Gorana Jelic Mrcelic and Version 2 by Rita Xu.
Atlantic bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) is the most important tuna species in Mediterranean tuna fishery and a valuable commodity on the global fish market. Croatia is a pioneer in tuna farming in the Mediterranean and the only country that has the exclusive right to farm wild-caught juvenile tuna (8 to 30 kg).
- capture-based aquaculture
- Atlantic bluefin tuna
- fattening
- Thunnus thynnus
- farming
1. Introduction
Aquaculture is an important source of food, jobs, and income for millions of people. Since the 1960s, shortages of wild-caught fish and a growing demand for high-quality fish protein have spurred aquaculture production, and aquaculture continues to contribute to a 56% increase in the global aquatic food supply [1]. The European Green Deal, Farm-to-Fork Strategy, and strategic guidelines for more sustainable and competitive aquaculture in the EU highlight the importance of aquaculture to a sustainable food system and the importance of farmed fish as a low-carbon footprint source of protein [2]. As demand for fish protein continues to increase and many wild fish stocks are overexploited, aquaculture is playing an important role in feeding the world effectively, equitably, and sustainably and in providing a sustainable solution for rebuilding fish stocks [1][3][1,3]. Tuna is a valuable commodity on the global fish market because of its delicious taste and high market price. Tuna are larger, grow more slowly, mature later, and have a shorter spawning period than other warm-water predatory fish [4], making tuna vulnerable to exploitation [5]. Since the 1980s, increased demand for tuna and high market prices have led to unsustainable fisheries and reduced many tuna stocks in the wild [6]. Unlike the tuna steak and canned tuna industry, the tuna sushi-sashimi industry is highly selective and only a few tuna species are marketable on the sushi-sashimi market, including bluefin tuna (BFT): Atlantic bluefin tuna (ABFT) (Thunnus thynnus. Linnaeus, 1758), Pacific bluefin tuna (Thunnus orientalis, Temminck and Schlegel, 1844), and southern bluefin tuna (Thunnus maccoyii, Castelnau, 1872) [7][8][7,8]. In the Mediterranean, ABFT is the most important commercial tuna species in both fisheries and tuna aquaculture [6][9][6,9]. Due to its high fat content, ABFT fetches a high price on the Japanese market. Farming of ABFT started in 1996 in Spain and Croatia, and Italy, Malta, Spain, and Croatia are leading producers [10]. In the Mediterranean, ABFT rearing is actually the fattening of reproductively mature wild-caught tuna (over 30 kg) in cages for six to ten months, while Croatia has the exclusive right to farm wild-caught immature juvenile tuna (8 to 12 kg) for 1.5 years or even longer (farming). As ABFT farming and fattening rely on wild-caught ABFT for stocking and ABFT feeding requires a large amount of wild-caught small pelagic fish, the expansion of ABFT farming and fattening in the Mediterranean in the late 1990s increased pressure on wild fish populations as well as on the entire ecosystem [6][9][10][11][12][13][6,9,10,11,12,13].
2. ABTF Fishing in the Mediterranean
Until the 1950s, red lean tuna meat was popular for sushi-sashimi, but Japanese tastes changed and high-fat tuna species, including ABFT, became highly valued [7]. The development of the Japanese sushi-sashimi market in the 1980s made the ABFT fishery extremely profitable [14], especially in the Mediterranean Sea [5]. The increased demand for tuna and the high market price have led to unsustainable fishing (including illegal, unreported, and unregulated (IUU) fishing) and the depletion of tuna stocks [6]. In order to preserve tunas and tuna-like species in the Atlantic Ocean and adjacent seas, the International Commission for the Conservation of Atlantic Tunas (the Commission) establishes mandatory management measures to regulate fishing effort, fishing and farming capacity, Total Allowable Catch (TAC), the minimum size at landing, farming, and time-area closures [15]. There are currently 52 Contracting Parties to the International Convention for the Conservation of Atlantic Tunas [16]. The Commission manages the ABFT as the Eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean BFT stock (E-BFT) and Western BFT stock (W-BFT) with the 45°W meridian as the boundary [5]. W-BFT TAC has been in force since 1981, E-BFT TAC since 1998, while the minimum size limit for ABFT caught in the Atlantic of 6.4 kg (10 kg and 30 kg thereafter) has been in force since 1975 [17]. The 6.4 kg conservation measure was violated for decades in the East Atlantic and Mediterranean fisheries, resulting in the death of millions of fish [18]. The commercial ABFT fishery, including fishing gear, area, and season, has changed since 1996, when ABFT fattening and farming began in the Mediterranean [19]. In the period between 1995 and 2007, E-BFT catches in the Eastern Atlantic and Mediterranean were significantly underreported, and the actual annual catch was estimated to be between 50,000 t and 61,000 t [20]. Since 2008, reported catches have declined and stabilized at TACs levels [21]. In the period between 1991 and 2021 (Figure 1), reported E-BFT catches in the Mediterranean Sea fluctuated between 5790 t (2011) and 52559 t (2007). Reported catches in Croatia fluctuated between 374 t (2012) and 1360 t (1996, when ABFT farming was introduced in Croatia). In 1998, a TAC quota was introduced.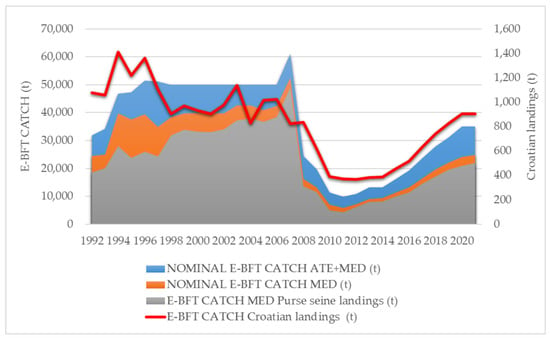
Figure 1. Nominal catch E-BFT data in live weight (total dead and alive landings and discards) in the East Atlantic and the Mediterranean (ATE+MED) and in the Mediterranean (MED); purse seine E-BFT catch landings in the Mediterranean (MED); and Croatian E-BFT catch landings in the period between 1992 and 2022.
ABFT Fishing in Croatia
As a European Union (EU) Member country, Croatian fishery is under the Common Fisheries Policy (CFP). The legal framework governing Croatian marine fisheries includes the Marine Fisheries Act (OG 56/10, 127/10, 55/11) and the Act on structural support and market organization in fisheries (OG 153/09, 127/10), as well as special regulations on E-BFT fishing (including purse seine fishing, recreational fishing for trophy tuna, etc.) [24]. The purse seine is the most important fishing gear in Croatian ABFT fishery and the Regulation on fishing opportunities and the allocation of the state quota in 2022 for fishing for bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) (OG 16/2022) set the quota for ABFT purse seine fishing at 833.46 t for 2022 [25]. Purse seine fishing for ABFT is allowed in the Eastern Atlantic and the Mediterranean from 26 May to 1 July, while for fish farmed in the Adriatic Sea, the season may be open from 26 May to 15 July in the Adriatic Sea (FAO fishing area 37.2.1) [22]. The minimum size for ABFT caught in the Adriatic Sea for farming purposes was set at 8 kg or 75 cm fork length based on historical data on the size composition of Croatian ABFT catches. Purse seine tuna fishing in the Croatian Adriatic began in 1929, when only one purse seiner was registered, but by 1954 there were 36 boats [26]. Commercial tuna fishing in Croatia has developed significantly since World War II. The first phase of development, which lasted from 1947 to 1964, ended with the disappearance of traps. In the second phase, the Croatian ABFT fishery has been dominated by purse seine fishing since 1965 [27].3. ABFT Fattening/Farming in the Mediterranean
3.1. History
The commercial rearing of BFT began in Canada in the late 1960s by a Japanese farm and then spread to Spain in 1979 and throughout the Mediterranean region in the 1990s [19]. ABFT rearing operations are classified as [28][30]:- -
-
fattening, when mature fish (30 kg or more) are reared for a short period of time (3 to 7 months) to achieve a high percentage of fat in the muscle;
- -
-
farming, when juvenile fish (8 to 30 kg body weight) are reared for an extended period (up to 2 years) to increase body weight and achieve the minimum size for the Japanese market.
3.2. Rearing Technology
In the Mediterranean, ABFT farming and fattening includes catching wild tuna with purse seines, overfeeding tuna with small pelagic fish in floating rearing cages, and exporting it for the sushi-sashimi market in Japan [6][9][10][13][6,9,10,13]. In ABFT fattening, mature tunas (30 kg or more) caught by purse seiners are transferred into circular (30 to 50 m diameter, 20 m deep) or hexagonal (22 m side length) transport cages and towed by a tugboat at a speed of 1 to 1.5 knots to the rearing site [13][14][13,14]. In the western Mediterranean, tuna have been shown to spawn inside transport cages [29][31]. At the rearing site, fish are placed in circular ring-shaped (50 to 120 m in diameter and 15 to 35 m deep) floating deep-sea net cages with a mesh size of 25 cm for rearing [30][32]. During the rearing period (of an average six months), fish are fed ad libitum with baitfish one to three times per day [9]. The reported stocking density ranges from 2 to 6.2 kg/m3 [31][33], and mortality ranges from 3.7 to 15.8% in most Mediterranean farms [13]. In ABFT farming, immature tuna (from 8 to 30 kg) caught by Croatian and Italian purse seiners in the Adriatic Sea [19] are reared for up to three years [32][34] until they reach a harvest size between 30 and 50 kg [33][35]. Ref. [34][36] reported that 2-year-old, 10-kg ABFT juveniles grow to 45–90 kg during a rearing period of 18 to 30 months. ABFT juveniles are kept in circular floating net cages (30 to 60 m in diameter and 13 to 21 m deep) [9][13][9,13]. Tuna is fed fresh or frozen small pelagic fish ad libitum one to six times daily, and the daily feed consumption is about 5% of the biomass in a temperature range of 18 °C to 24 °C [11]. Reported stocking densities range from 1 to 2 kg/m3 [31][33] and mortality ranges from 3% to 5% [11].3.3. Technical Requirements for Farming Facilities for Bluefin Tuna (FFBs)
Tuna is a large pelagic fish that needs to swim constantly and has a high oxygen demand. Therefore, tuna must be reared in large, robust cages in exposed oligotrophic coastal waters at least 50 m deep or offshore, with currents greater than 10 cm/s, salinity between 36 and 39 ‰, and dissolved oxygen levels greater than 90% (Croatian Regulation on Criteria for the Establishment of Marine Aquaculture Areas, OG 106/18). If FFB is appropriately sited and managed, the potential negative impacts of FFB on the environment are usually small-scale and temporary.3.4. Harvesting and Processing
The harvest season is usually December, when prices are high due to the many Japanese festivities [8]. The price of tuna correlates with the quality of the meat, and the quality of the meat is highly dependent on feeding, but also on the slaughter, processing (bleeding and cooling), storage, and shipping of the tuna [10]. To prevent metabolic products from accumulating in the muscle, which impart a bad taste to the meat, tuna must be killed, bled, and cooled quickly [35][37]. The shotgun method (the tuna is shot in the head from outside the water) is good for killing a large number of tunas in a short time. In the speargun method (the tuna is shot in the head by divers with a speargun), the tuna can be picked out and death occurs immediately, but it takes more time [13]. Further processing includes pithing, which involves using a metal rod to induce brain death, bleeding, which removes metabolic products and allows rapid cooling, the removal of internal organs, and placement in a slurry of ice and seawater for rapid cooling [10].3.5. Market
The tuna price depends on the size of the tuna (the bigger the better), the fat content (the fatter the better), the colour and texture of the meat, the absence/presence of metabolites in the meat, and the condition (fresh/frozen) of the meat [13]. All cultured ABFT are sold on the Japanese sushi-sashimi market [7][10][7,10], but unfortunately the majority of reared ABFT is graded as low to medium quality [6]. The development of ABFT aquaculture in the Mediterranean has increased the supply of ABFT, which has led to a drop in tuna prices. The sushi-sashimi market has also changed, from an exclusive Japanese market to a global market, which has also affected the price of tuna [7]. In the 1980s, the price of ABFT on the Tsukiji market ranged from US$ 100 to US$ 300/kg [7]. ABFT can be sold fresh or frozen. Since 2002, most of the ABFT aquaculture production has been exported frozen as a whole to Japanese freezer ships (so-called free on board, where the tuna is loaded on board and all other costs are supported by the buyer), which has resulted in lower costs and also lower tuna prices [13]. The fresh ABFT is transported to Japan by air [6]. In 2015, the price of fresh lower grade ABFT (headed and gutted) ranged from € 8 to € 17/kg and the price of higher grade ABFT (sashimi) ranged from € 35 to € 80/kg [6]. In 2022, the price of ABFT from Spain ranged from €18 to €37/kg [36][38]. Croatian farmed tuna is sold mainly on the Japanese sushi-sashimi market and generally has a lower quality and a lower price than large farmed tuna [19], although according to [9], the fat content of farmed juveniles can be very high, which could lead to higher prices on the Japanese market. In 2016, farmed ABFT from Croatia (ToroCro Maguro, Sashimigrade) won the Superior Taste Award [37][39]. The award-winning Croatian tuna is an example of how rearing tuna from the juvenile stage onwards can be very profitable even with small tuna sizes due to the high fat content.3.6. ABFT Fattening/Farming Legislation
In 1993, ICCAT launched the Bluefin Statistical Document Program (BFSD Program) for frozen tuna and in 1994 for fresh tuna. In 1999, ICCAT decided to use a special import form for reared BFT, but in fact reared tuna has been labelled since 1996 [19]. According to ICCAT Recommendation 06-07 on Bluefin Tuna Farming, farms have been required to report the size of each harvest operation since 2008. The same applies to the Regional Observer Program (ROP) [15]. The Recommendation 21-08 by ICCAT requires the establishment and maintenance of a record of facilities approved to farm BFT caught in the Convention Area (Farming Facilities for Bluefin Tuna, FFBs). Currently, the ICCAT Record of BFT Farming Facilities contains 69 FFBs in the Mediterranean Sea (ICCAT List of BFT Farming Facilities, 2022). In Croatia, Regulation on marking of breeding installations, monitoring of operations on breeding grounds, and traceability during the breeding of bluefin tuna (Thunnus thynnus) (OG 63/2022) was adopted in June 2022, based on the provisions of the Croatian Law on Aquaculture (OG 130/2017, 111/2018; 144/2020) [24].3.7. ABFT Aquaculture Production
Data on ABFT farm capacity is readily available in the ICCAT Record of ABFT farms. In 2022, there were 69 ABFT farms with a maximum potential capacity of 71,440 t: Italy, 18, 17,700 t; Malta, 8, 13,800 t; Croatia, 4, 7092 t; Morocco, 4, 6600 t; Turkey, 6, 6440 t; Spain, 11, 6002 t; Tunisia, 6, 5000 t; Cyprus, 3, 3000 t; Greece, 2, 2100 t; Egypt, 1, 1800 t; Libya, 3, 1800 t; Albania, 1, 500 t; and Portugal, 2, 500 t [16]. According to [37][39], in 2017 there were 54 ABFT farming companies with 62 farms and a maximum potential capacity of 54,000 t, mostly distributed in clusters (Cartagena in Spain, Naples in Italy, and Zadar in Croatia) While the maximum potential capacity is readily available in the ICCAT Record of ABFT farms, the situation is different for the reported data on ABFT aquaculture production. The total Mediterranean ABFT aquaculture production is difficult to estimate because cage input figures (biomass and ABFT size) are only rough estimates and farmers keep output figures confidential [9]. ABFT aquaculture production data have been irregular and there are contradictions in the FAO database (FishstatJ), the EU EUROSTAT database, and national databases [8][13][19][38][39][40][8,13,19,40,41,42]. Ref. [38][40] found that less than one-third of Mediterranean ABFT aquaculture production was reported in the FAO database (28,450 t vs. 10,000 t) in 2006. However, the data on ABFT aquaculture production in FishstatJ have been updated for the years starting from 2004, except for the data on ABFT aquaculture production in Libya and Morocco, which are not yet available. Figure 2. shows the data on Mediterranean ABFT aquaculture production (t) in FishstatJ, EU ABFT aquaculture production (t) in EUROSTAT, and Croatian ABFT aquaculture production (t) in the CMA database in the period between 1996 and 2000 [11][15][23][41][42][11,15,23,43,44].In 1996, the first year of ABFT farming production in the Mediterranean, ABFT aquaculture totalled 77 t, and 39 t in Croatia (Figure 2). Croatian ABFT aquaculture reached a peak of 6700 t in 2006, while Mediterranean ABFT aquaculture production has been steadily growing, reaching a peak of 34,385 t in 2020. Croatian ABFT production was 3323 t in 2020 and 4372 t in 2021. Croatian farming contributes about 10% to the ABFT aquaculture production in the Mediterranean region/sea. According to [40][42], EUROSTAT data on ABFT aquaculture production were not available for Cyprus, Greece, and Italy, and data for these countries are still missing (Greece from 2008, Cyprus from 2009, and Italy from 2012). The lack of data for Italy is a major shortcoming considering that Italy has the highest potential capacity among all Mediterranean countries (17,700 t in 2022). The figures in FishstatJ are low for Italy (from a minimum of 61 t in 2001 to a maximum of 2577 t in 2007) until 2011 and missing from 2012. Reported figures for Greece and Cyprus are missing in EUROSTAT from 2019. As in the Mediterranean region as a whole, data on ABFT aquaculture production in Croatia were not harmonized in the FAO database (FishstatJ), in the EUROSTAT database, and in the national database, so the data in FishstatJ and EUROSTAT differ until 2004 (minimum 0 t in 1996 and 1997 and maximum 782 t in 2003). The quality of the statistics contained in the FAO database depends mainly on the accuracy and reliability of the data provided by countries. Although FAO member countries should provide statistics to the government on a regular basis, this is not always the case, either due to erroneous reporting (inconsistencies between data compiled by different institutions), political reasons, or sometimes due to communication problems (e.g., change of responsible official, etc.) [43][45]. There is also a tendency for most ICCAT member states to under-report their catches to ICCAT and FAO in order to support their national finishing fleets. When they under-report landings, they also under-report catch-based aquaculture production levels to maintain consistency in reporting figures [37][39].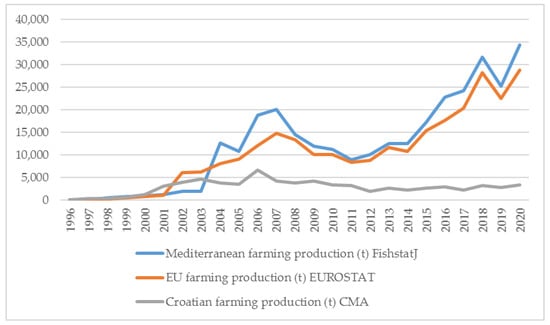 Figure 2. Growth/fluctuation of the Mediterranean ABFT aquaculture production (t) based on data available in FishstatJ, EU ABFT aquaculture production (t) in EUROSTAT, and Croatian ABFT aquaculture production (t) in CMA database in the period between 1996 and 2000.
Figure 2. Growth/fluctuation of the Mediterranean ABFT aquaculture production (t) based on data available in FishstatJ, EU ABFT aquaculture production (t) in EUROSTAT, and Croatian ABFT aquaculture production (t) in CMA database in the period between 1996 and 2000.
