Intraocular pressure (IOP) is an important measurement that needs to be taken during ophthalmic examinations, especially in ocular hypertension subjects, glaucoma patients, and patients with risk factors for developing glaucoma. The gold standard technique in measuring IOP is still Goldmann applanation tonometry (GAT); however, this procedure requires local anesthetics, can be difficult in patients with scarce compliance, surgical patients, and children, and is influenced by several corneal parameters. Numerous tonometers have been proposed in the past to address the problems related to GAT. The reseauthors reviewrch describes the various devices currently in use for the measurement of intraocular pressure (IOP), highlighting the main advantages and limits of the various tools. The continuous monitoring of IOP, which is still under evaluation, will be an important step for a more complete and reliable management of patients affected by glaucoma.
- intraocular pressure (IOP)
- tonometry
- Goldmann applanation tonometer (GAT)
1. Introduction
2. Indentation Tonometry
The prototype of the indentation tonometers is the Schiøtz tonometer that was introduced many years ago [4][1] and is no longer currently used (Figure 1).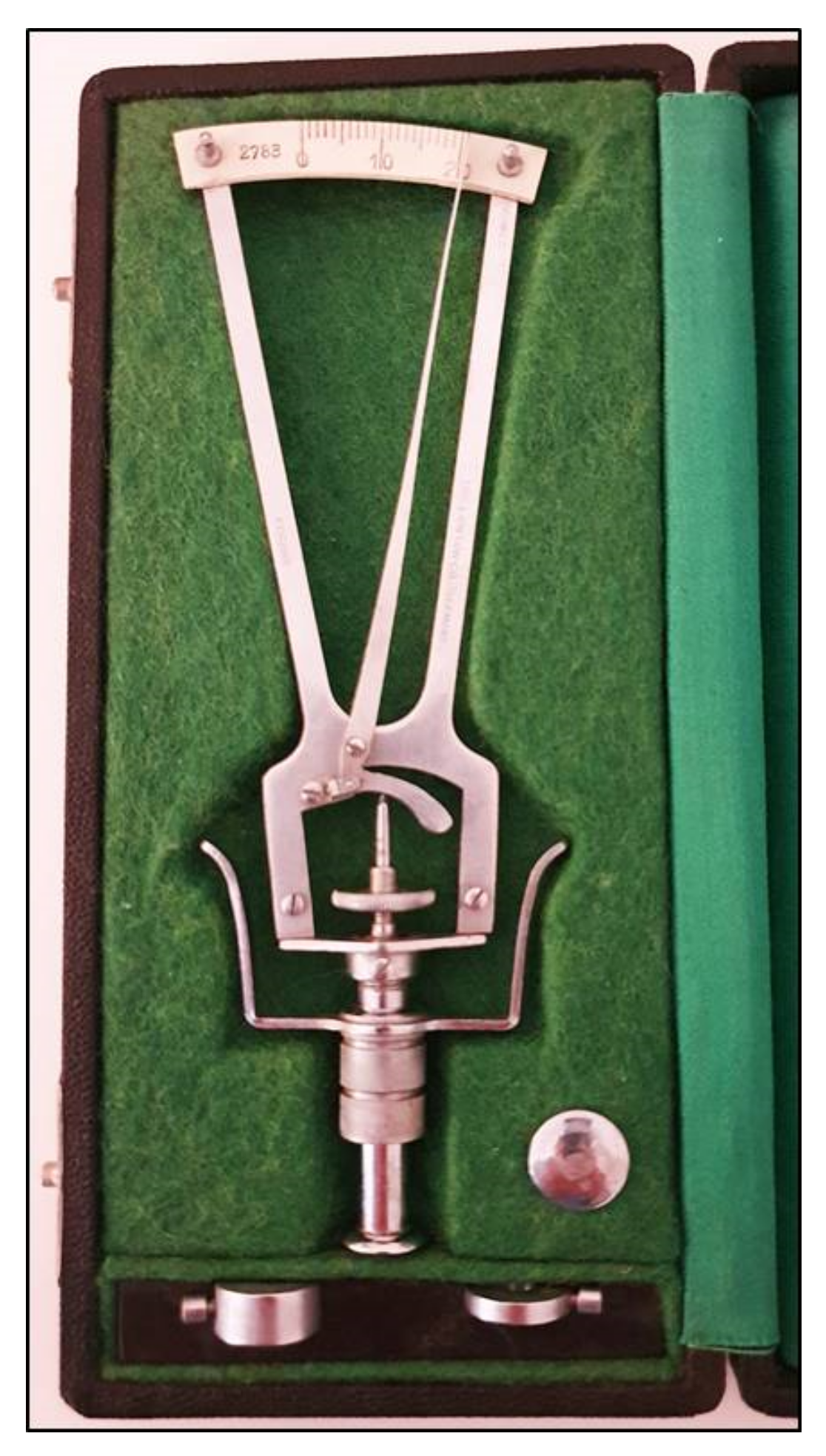
3. Applanation Tonometry
Applanation tonometers are currently considered the most reliable instruments for an accurate IOP measurement. Such tonometers use the Imbert–Fick law: P = F/S, in which P is pressure, S represents the surface of the flattened area, and F is the force needed to flatten a fixed corneal area. Apart from the tonometer by Maklakoff and several other instruments that are no longer currently in use, in which the force is provided by the weight of the tonometer itself, applanation tonometry is based on the area of flattened cornea that is calculated and converted in mmHg [2][6]. In almost all instruments of this type, the F value is varied to get the proper corneal applanation for a predetermined area. The Goldmann applanation tonometer (GAT) was first invented in 1948 by Hans Goldmann [9][7] and is still considered the gold standard to date. The tonometer needs to be positioned on a slit lamp. A truncated cone, with a 7.35 mm2 surface area and a dimeter of 3.06 mm, illuminated by a blue light, is pushed on the center of the anaesthetized cornea. A doubling prism embedded in the cone divides the circular meniscus on the surface of the flattened cornea e into two arcs, which need to be aligned in order to obtain a precise and standardized applanation (Figure 2).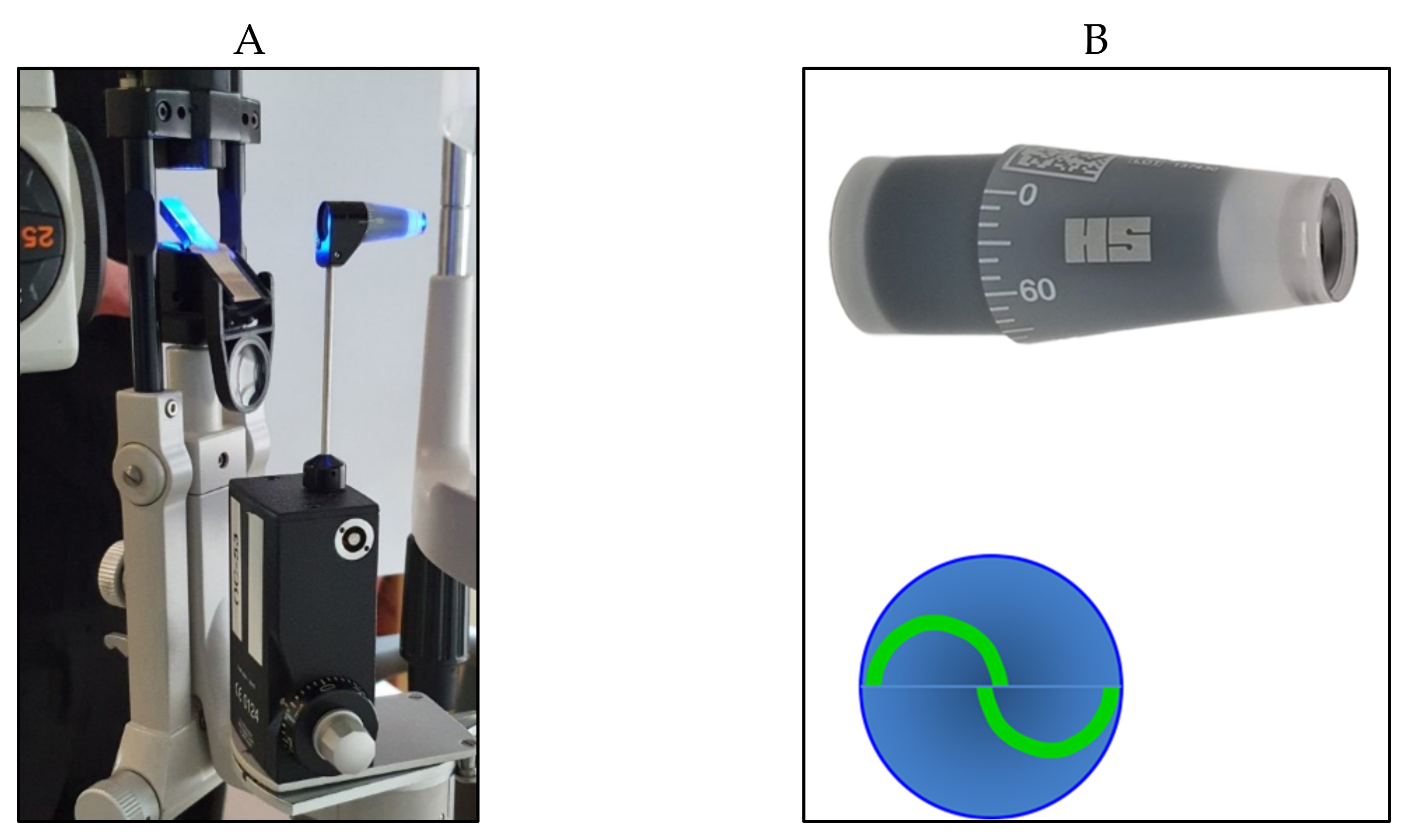
4. Non-Contact Tonometry (Air-Puff Tonometry)
5. Pneumotonometry
Pneumotonometers are devices based on the applanation principle, which use a different technology [69,70][23][24]: the tonometer probe consists of a hollow central tube flanked by a side exhaust, and the sensor is air pressure, which is dependent on the resistance of the exhaust. During the cornea applanation, the pressure within the central tubes increases to match the force generated by the IOP. A pneumatic electronic transducer converts the air pressure to a tracer on a strip of paper (Figure 95).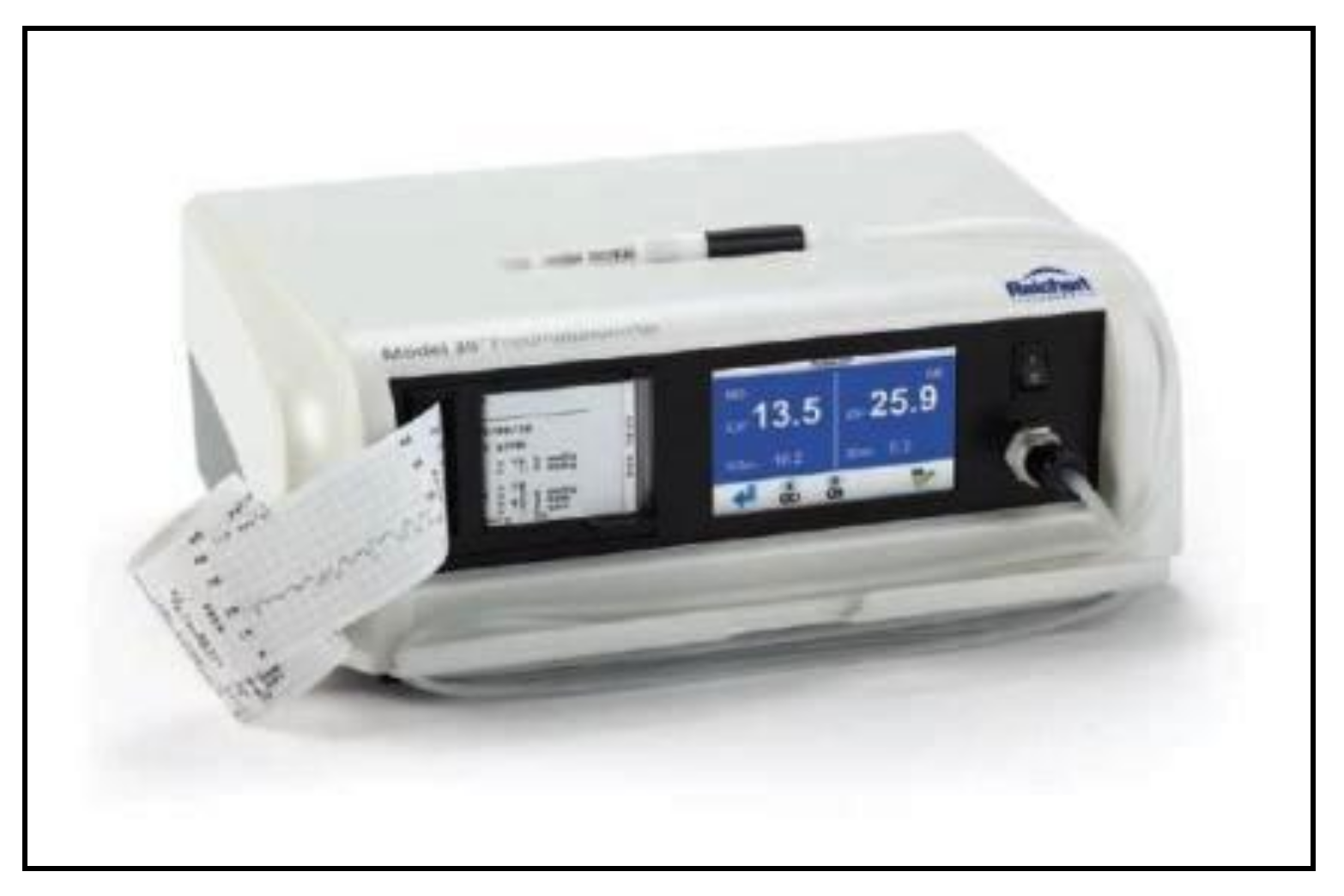
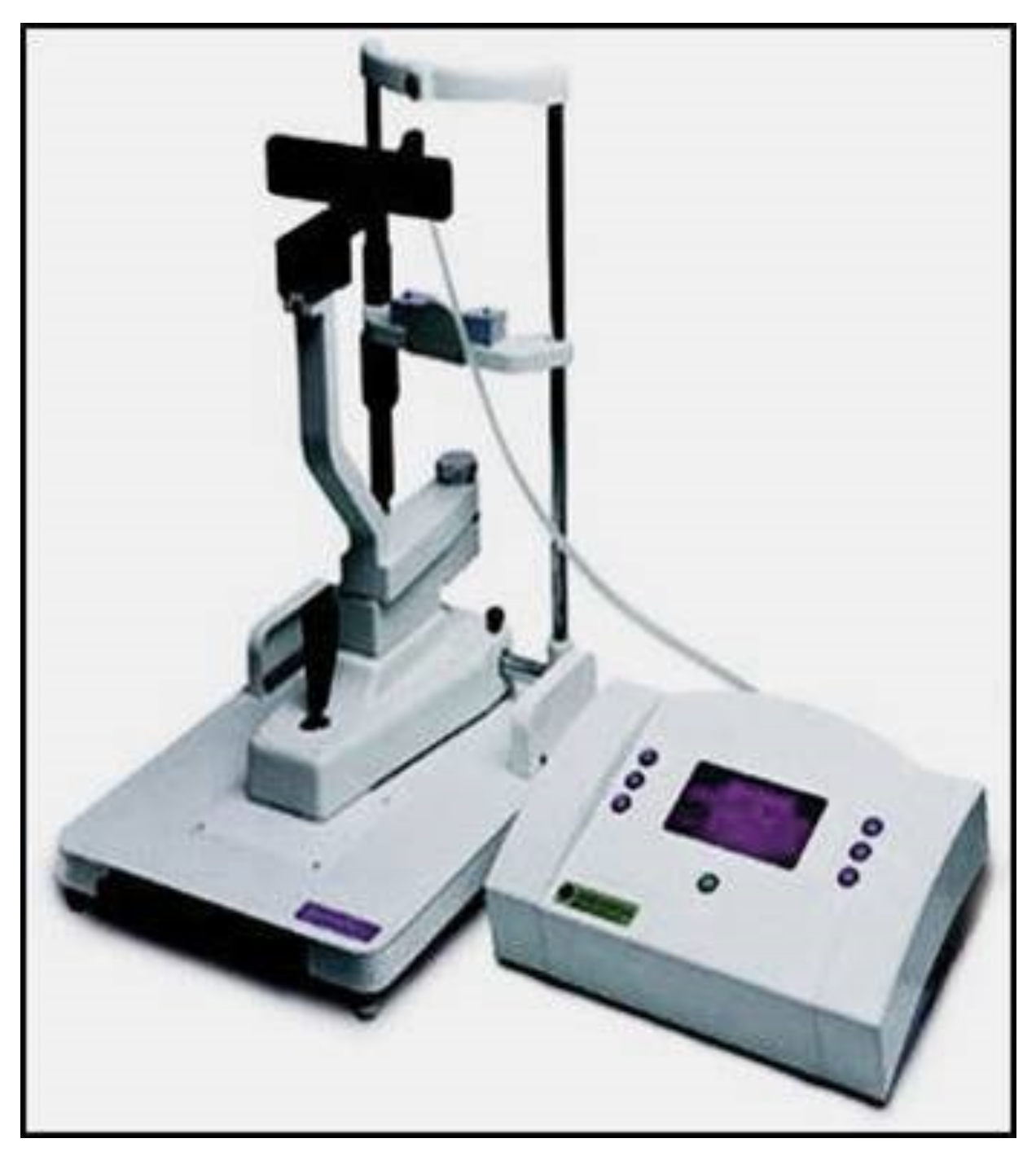

6. Rebound Tonometry
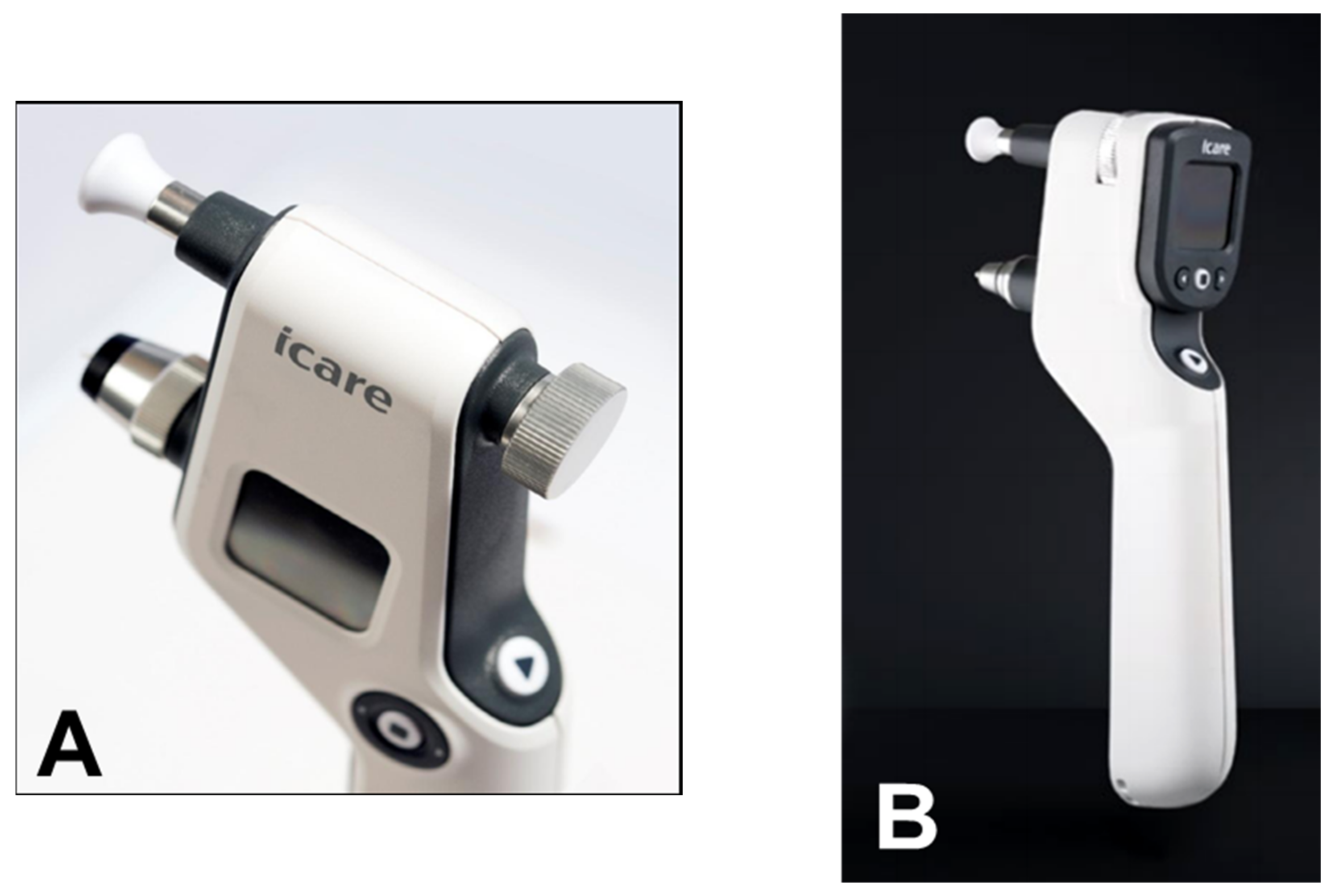
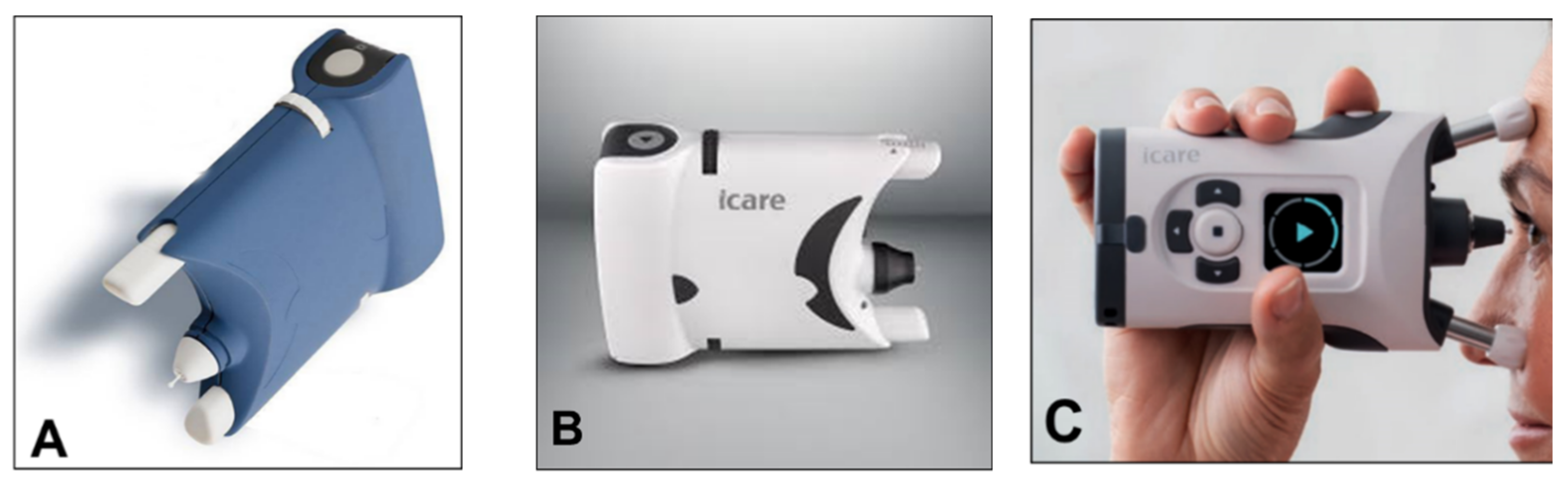
From a clinical point of view, the iCare rebound tonometer, introduced in 2000 by Kontiola [81][35], is currently one of the most interesting and widespread instruments used in practice (Figure 117).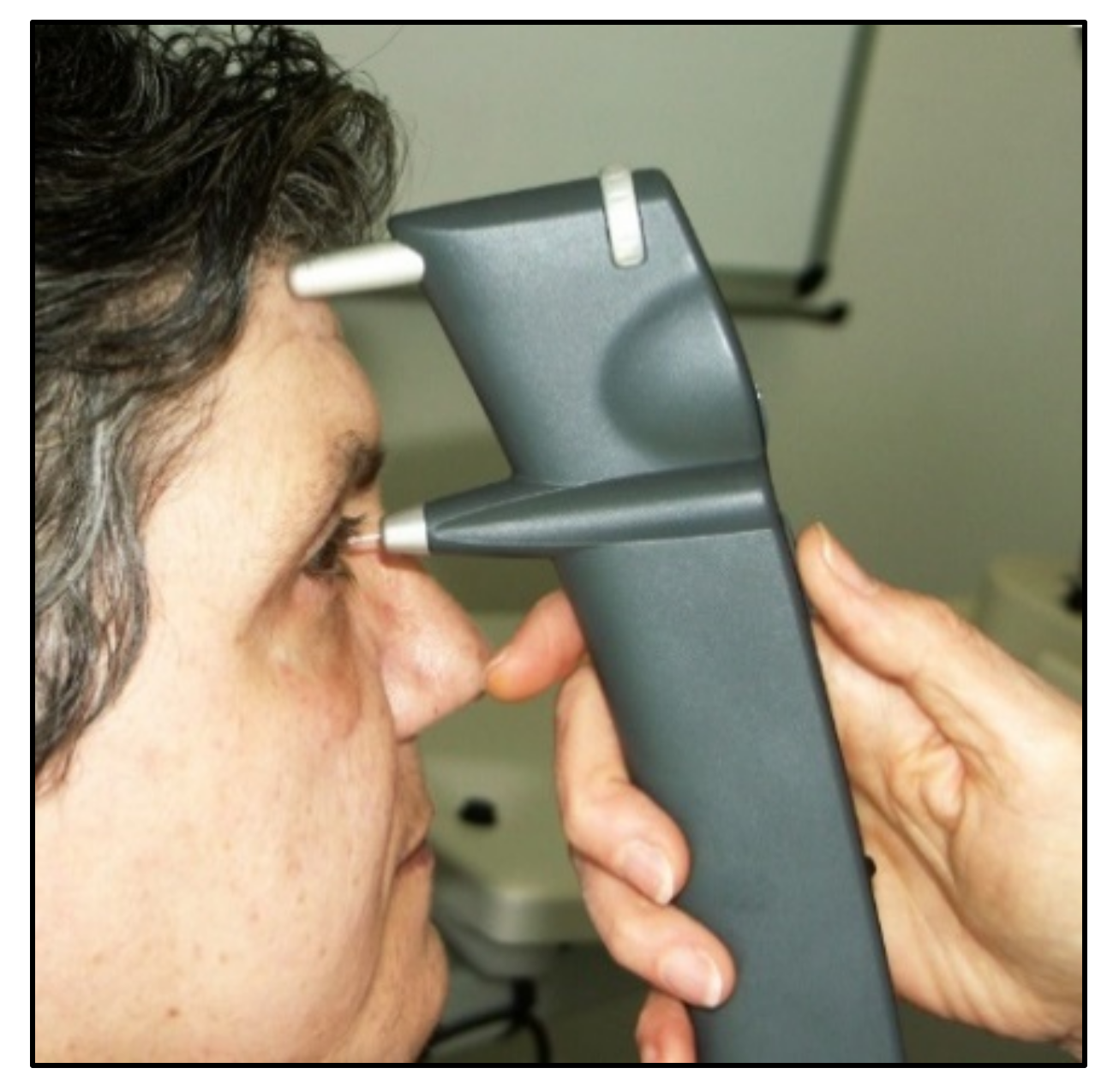
7. Dynamic Contour Tonometry
The Dynamic Contour Tonometer (PASCAL, DCT) (SMT Swiss Microtechnology AG, Port, Switzerland) is a relatively new device developed by Kaufmann et al. in 2003 [105][48] and implemented by Kanngiesser et al. in 2005 [106][49]. The DCT, which is not based on the applanation principle, calculates the IOP using the Pascal principle, according to which the pressure change is applied to all parts of a fluid in a contained enclosed space. The tonometer is positioned on the slit-lamp, requires the use of anesthetic drops (no fluorescein) and is automatically calibrated. It uses a concave contour tip that is equipped with a tiny sensor in the center of the contact surface (Figure 151).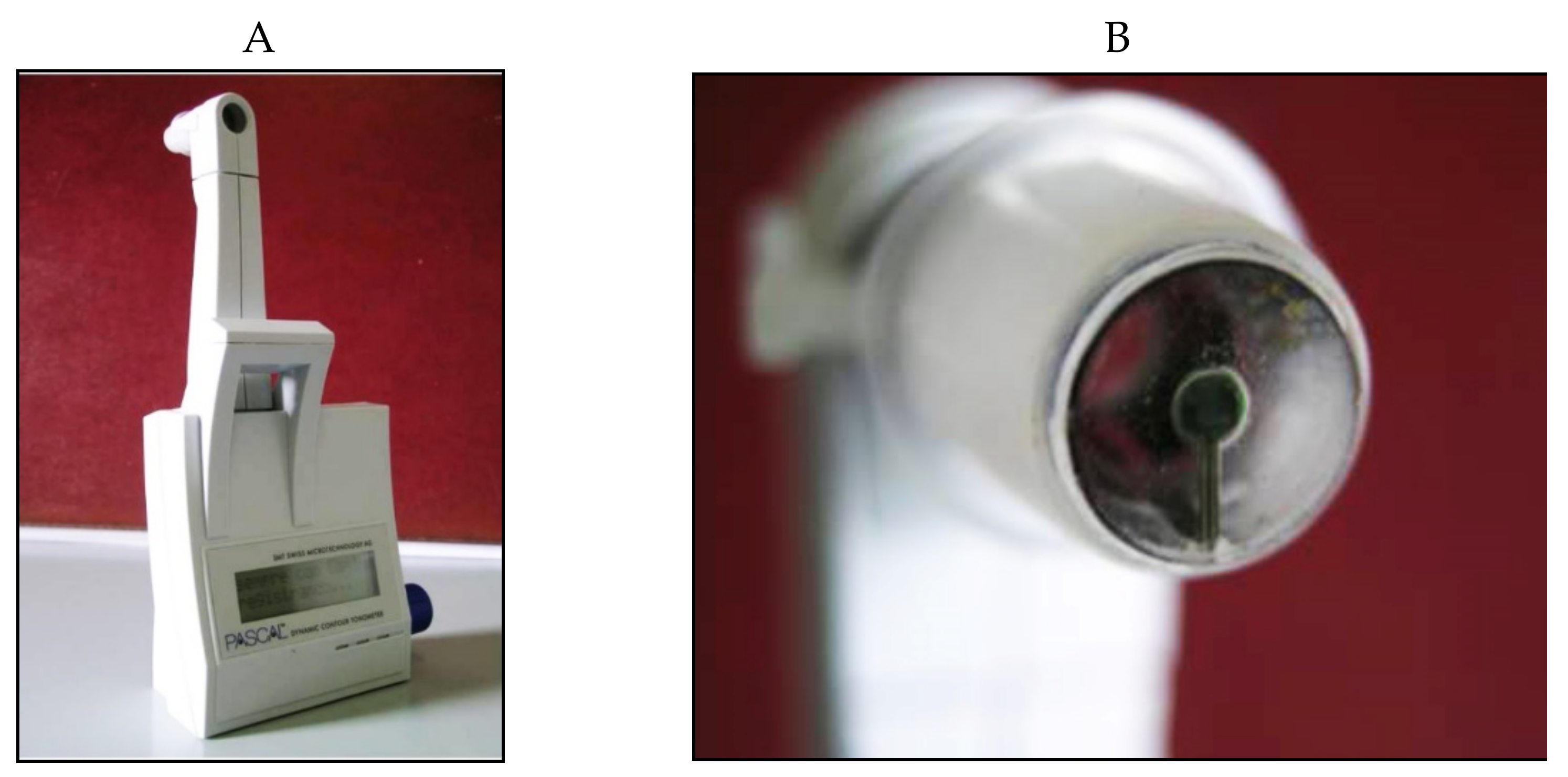
8. Applanation Resonance Tonometry
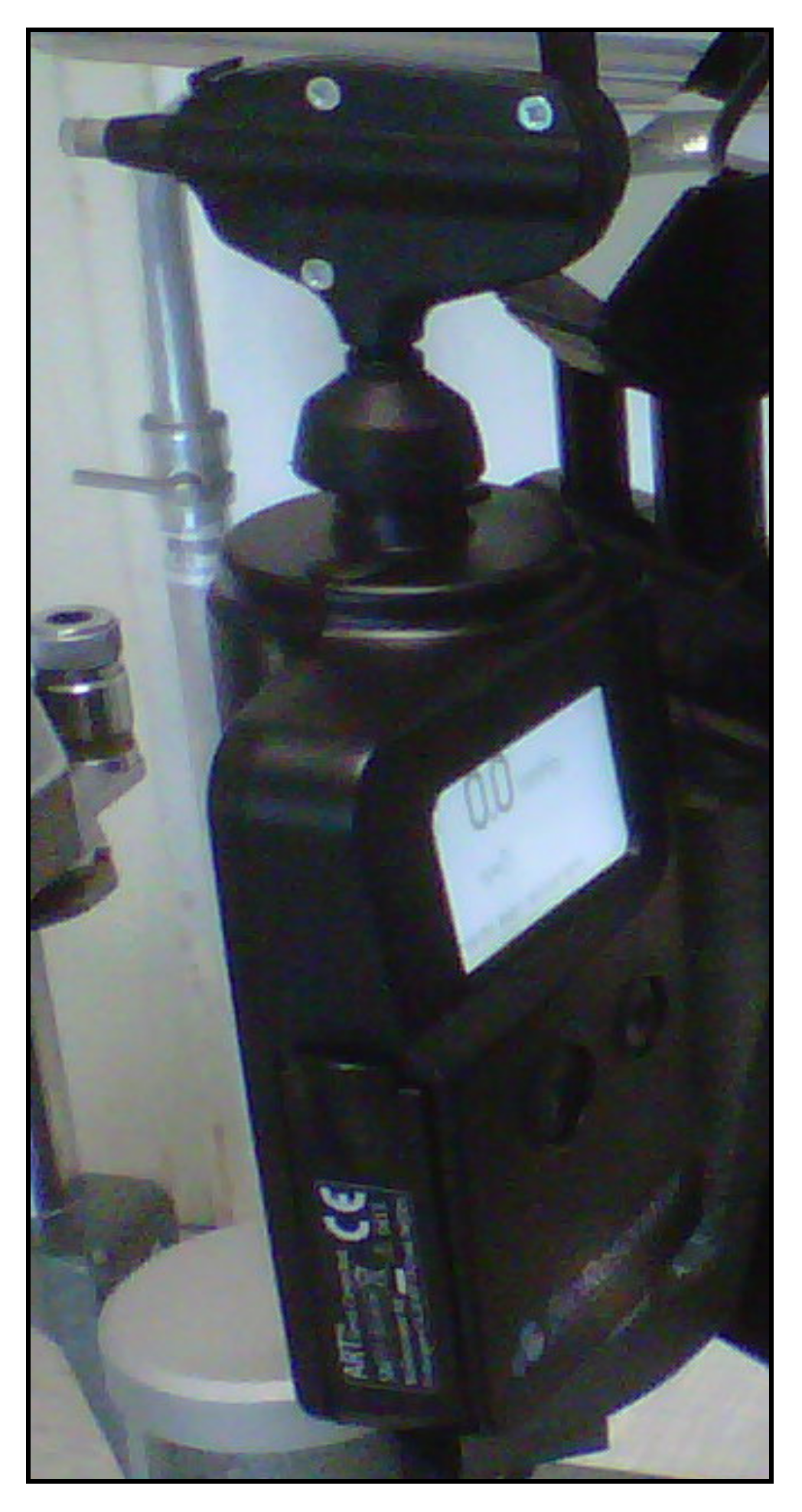

9. Continuous IOP Monitoring
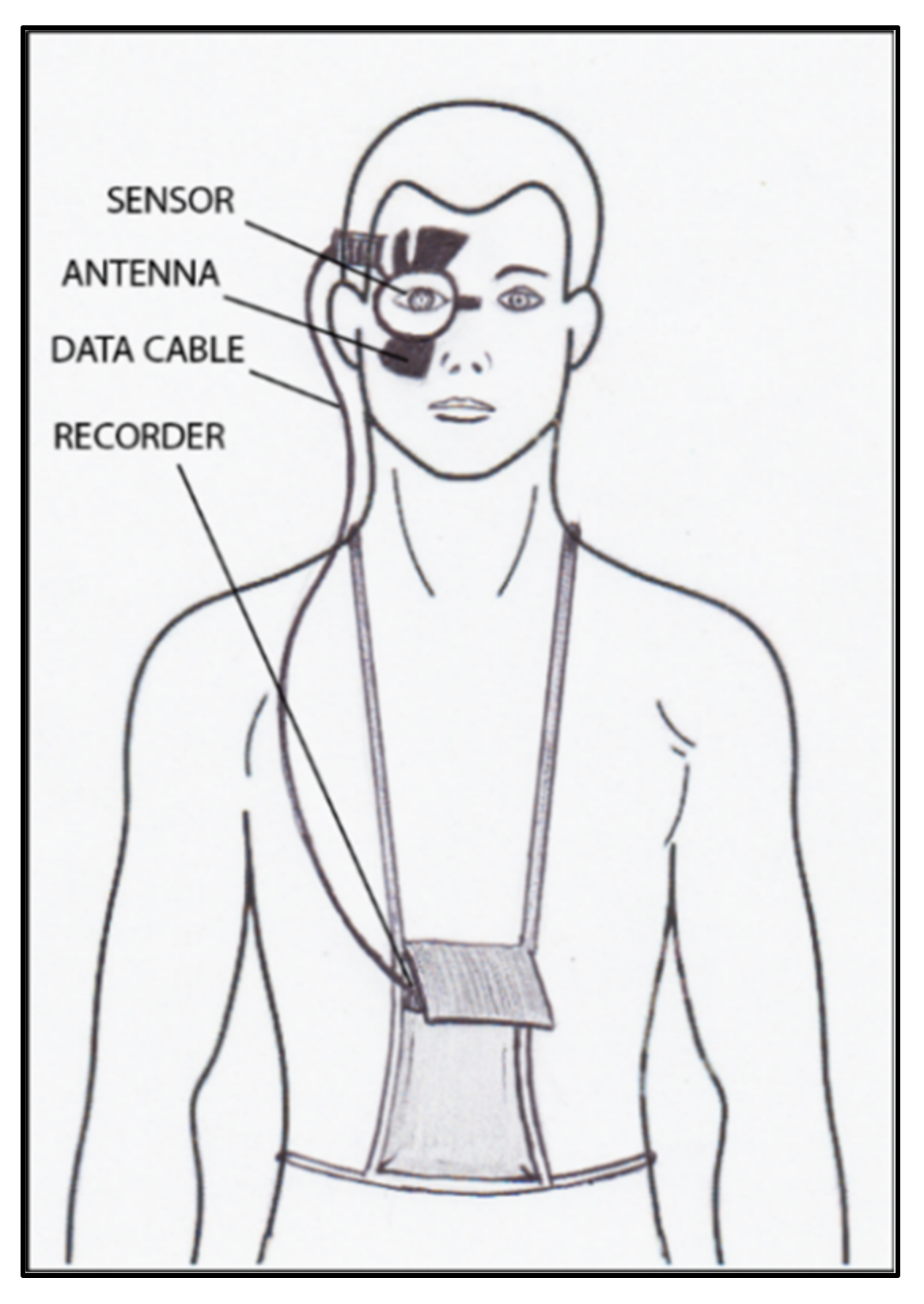
All the aforementioned devices can be usefully employed for taking spot IOP measurements during office time. This can be acceptable in a screening setting, but, unfortunately, undetected elevated IOP spikes tend to occur during the night in many glaucomatous patients [127][55]. IOP readings during clinical office hours fail to detect these peaks in more than 50% of cases with a significant underestimation of IOP [128,129,130,131][56][57][58][59]. Hughes et al. reported that data obtained with continuous monitoring in IOP using a 24 h device had an influence in therapeutic decisions in 79.3% of enrolled subjects [132][60]. Keeping these data in mind, it can be inferred that our current standards in clinics with regard to taking IOP measurements may not suffice and thus need to be modified [133][61]. An important step towards a more precise management of patients affected by ocular hypertension and chronic glaucoma would be the possibility of continuously monitoring IOP values not only during the day but also in the night, as occurs with the 24 h blood pressure Holter. This information could be particularly useful in the so-called normal tension glaucoma patients, which show significant damage progression despite an apparently normalized IOP. In these cases, an elevated IOP can sometimes be found during the night, especially early in the morning, outside office hours [134,135][62][63]. A number of devices, most of them only experimental, have been proposed for this purpose over the past 20 years [136,137,138][64][65][66]. Some of them need to be surgically inserted into the eye, either during a cataract extraction procedure, usually embedded in an intraocular lens [139,140[67][68][69],141], or positioned in the anterior chamber [142[70][71],143], or in the suprachoroidal space [144][72]. A non-invasive continuous IOP measurement is also possible using special contact lenses with different types of miniaturized sensors and a wireless power transmission of data to a recorder. The contact lens sensor Sensimed Triggerfish (Triggerfish CLS, Sensimed AG, Lausanne, Switzerland) is a miniaturized electromechanical system with a microprocessor embedded in a disposable silicon contact lens, which transmits a signal to an external wireless antenna located in the periocular surface (Figure 17 and Figure 18). The data are then transferred to a portable recorder, for a total of 288 data sets in 24 h. This device can measure small modifications in the curvature of the cornea believed to be due to variations of IOP [145,146,147,148,149][73][74][75][76][77].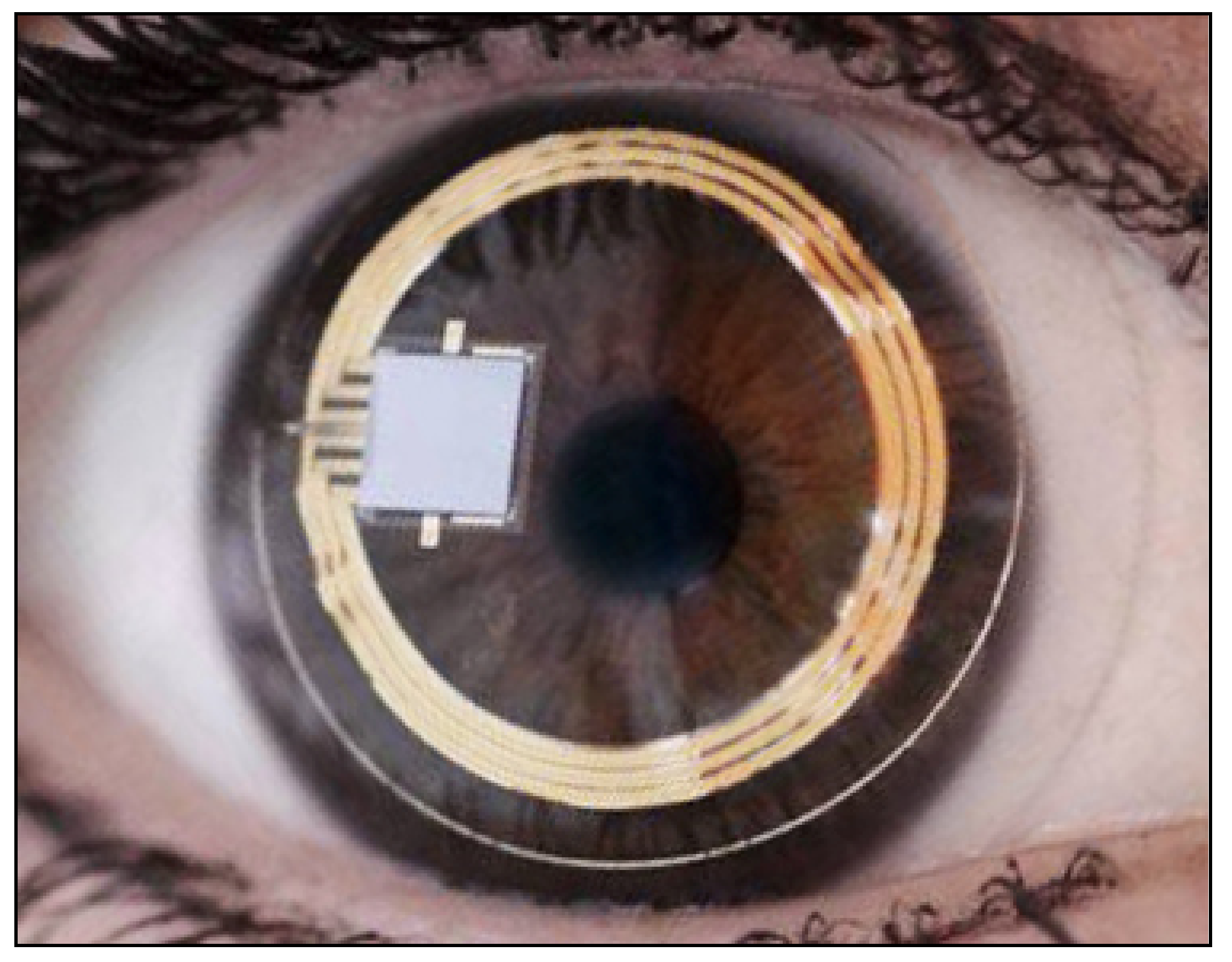
References
- Albert, D.M.; Keeler, R. The Pressure: Before and after Schiøtz. Ophthalmol. Glaucoma 2020, 3, 409–413.
- Kyari, F.; Nolan, W.; Gilbert, C. Ophthalmologists’ practice patterns and challenges in achieving optimal management for glaucoma in Nigeria: Results from a nationwide survey. BMJ Open. 2016, 6, e012230.
- Nagarajan, S.; Velayutham, V.; Ezhumalai, G. Comparative evaluation of applanation and indentation tonometers in a community ophthalmology setting in Southern India. Saudi. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 30, 83–87.
- Lasseck, J.; Jehle, T.; Feltgen, N.; Lagrèze, W.A. Comparison of intraocular tonometry using three different non-invasive tonometers in children. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2008, 246, 1463–1466.
- Ohana, O.; Varssano, D.; Shemesh, G. Comparison of intraocular pressure measurements using Goldmann tonometer, I-care pro, Tonopen XL, and Schiotz tonometer in patients after Descemet stripping endothelial keratoplasty. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 65, 579–583.
- Stamper, R.L. A History of Intraocular Pressure and Its Measurement. Optom. Vis. Sci. 2011, 88, E16–E28.
- Goldmann, H.; Schmidt, T. Über Applanationstonometrie. Acta. Ophthalmol. 1957, 134, 221–242.
- Grolman, B. A new tonometer system. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1972, 49, 646–660.
- Hansen, M.K. Clinical comparison of the XPERT non-contact tonometer and the conventional Goldmann applanation tonometer. Acta. Ophtahlmol. Scand. 1995, 73, 176–180.
- Vincent, S.; Vincent, R.A.; Shields, D.; Lee, G.A. Comparison of intraocular pressure measurement between rebound, non-contact and Goldmann applanation tonometry in treated glaucoma patients. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2011, 40, e163–e170.
- Demirci, G.; Erdur, S.K.; Tanriverdi, C.; Gulkilik, G.; Ozsutçu, M. Comparison of rebound tonometry and non-contact airpuff tonometry to Goldmann applanation tonometry. Ther. Adv. Ophthalmol. 2019, 11.
- Stock, R.A.; Ströher, C.; Sampaio, R.R.; Mergener, R.A.; Bonamigo, E.L. A Comparative Study between the Goldmann Applanation Tonometer and the Non-Contact Air-Puff Tonometer (Huvitz HNT 7000) in Normal Eyes. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2021, 15, 445–451.
- Gazzard, G.; Jayaram, H.; Roldan, A.M.; Friedman, D.S. When gold standards change: Time to move on from Goldmann tonometry? Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 1–2.
- Luce, D.A. Determining in vivo biomechanical properties of the cornea with an ocular response analyzer. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 2005, 31, 156–162.
- Salvetat, M.L.; Zeppieri, M.; Tosoni, C.; Felletti, M.; Grasso, L.; Brusini, P. Corneal Deformation Parameters Provided by the Corvis-ST Pachy-Tonometer in Healthy Subjects and Glaucoma Patients. J. Glaucoma 2015, 24, 568–574.
- Lopes, B.T.; Roberts, C.J.; Elsheikh, A.; Vinciguerra, R.; Vinciguerra, P.; Reisdorf, S.; Berger, S.; Koprowski, R.; Ambrósio, R. Repeatability and Reproducibility of Intraocular Pressure and Dynamic Corneal Response Parameters Assessed by the Corvis ST. J. Ophthalmol. 2017, 2017, 8515742.
- Serbecic, N.; Beutelspacher, S.; Markovic, L.; Roy, A.S.; Shetty, R. Repeatability and reproducibility of corneal biomechanical parameters derived from Corvis ST. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 30, 1287–1294.
- Reznicek, L.; Muth, D.; Kampik, A.; Neubauer, A.S.; Hirneiss, C. Evaluation of a novel Scheimpflug-based non-contact tonometer in healthy subjects and patients with ocular hypertension and glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2013, 97, 1410–1414.
- Luebke, J.; Bryniok, L.; Neuburger, M.; Jordan, J.F.; Boehringer, D.; Reinhard, T.; Wecker, T.; Anton, A. Intraocular pressure measurement with Corvis ST in comparison with applanation tonometry and Tomey non-contact tonometry. Int. Ophthalmol. 2019, 39, 2517–2521.
- Nakao, Y.; Kiuchi, Y.; Okumichi, H. Evaluation of biomechanically corrected intraocular pressure using Corvis ST and comparison of the Corvis ST, noncontact tonometer, and Goldmann applanation tonometer in patients with glaucoma. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0238395.
- Bao, F.; Huang, W.; Zhu, R.; Lu, N.; Wang, Y.; Li, H.; Wu, S.; Lin, H.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; et al. Effectiveness of the Goldmann Applanation Tonometer, the Dynamic Contour Tonometer, the Ocular Response Analyzer and the Corvis ST in Measuring Intraocular Pressure following FS-LASIK. Curr. Eye Res. 2019, 45, 144–152.
- Yang, K.; Xu, L.; Fan, Q.; Gu, Y.; Song, P.; Zhang, B.; Zhao, D.; Pang, C.; Ren, S. Evaluation of new Corvis ST parameters in normal, Post-LASIK, Post-LASIK keratectasia and keratoconus eyes. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 5676.
- Durham, D.G.; Bigliano, R.P.; Masino, J.A. Pneumatic applanation tonometer. Trans. Am. Acad. Ophthalmol. Otolaryngol. Am. Acad. Ophthalmol. Otolaryngol. 1965, 69, 1029–1047.
- West, C.E.; Capella, J.A.; Kaufman, H.E. Measurement of Intraocular Pressure with a Pneumatic Applanation Tonometer. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1972, 74, 505–509.
- Guildford, J.; O’day, D.M. Applanation Pneumotonometry in Screening for Glaucoma. South. Med. J. 1985, 78, 1081–1083.
- Abbasoglu Özlem, E.; Bowman, R.; Cavanagh, H.; McCulley, J.P. Reliability of intraocular pressure measurements after myopic excimer photorefractive keratectomy. Ophthalmology 1998, 105, 2193–2196.
- Zadok, D.; Tran, D.B.; Twa, M.; Carpenter, M.; Schanzlin, D.J. Pneumotonometry versus Goldmann tonometry after laser in situ keratomileusis for myopia. J. Cataract. Refract. Surg. 1999, 25, 1344–1348.
- Langham, M.E. Discussion on pneumatic applanation tonometer. Tr. Am. Acad. Ophth. Otolaryng. 1965, 69, 1042.
- Langham, M.E.; McCarthy, E. A Rapid Pneumatic Applanation Tonometer. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1968, 79, 389–399.
- Silver, D.M.; Farrell, R.A. Validity of pulsatile ocular blood flow measurements. Surv. Ophthalmol. 1994, 38, S72–S80.
- Esgin, H.; Alimgil, M.; Erda, S. Clinical comparison of the ocular blood flow tonograph and the Goldmann applanation tonometer. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 1998, 8, 162–166.
- Gunvant, P.; Baskaran, M.; Vijaya, L.; Joseph, I.S.; Watkins, R.J.; Nallapothula, M.; Broadway, D.C.; O’Leary, D.J. Effect of corneal parameters on measurements using the pulsatile ocular blood flow tonograph and Goldmann applanation tonometer. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 88, 518–522.
- Bhan, A.; Bhargava, J.; Vernon, S.A.; Armstrong, S.; Bhan, K.; Tong, L.; Sung, V. Repeatability of ocular blood flow pneumotonometry. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 1551–1554.
- Spraul, C.W.; Lang, G.E.; Ronzani, M.; Högel, J.; Lang, G.K. Reproducibility of measurements with a new slit lamp-mounted ocular blood flow tonograph. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 1998, 236, 274–279.
- Kontiola, A.I. A new induction-based impact method for measuring intraocular pressure. Acta. Ophthalmol. Scand. 2000, 78, 142–145.
- Brusini, P.; Salvetat, M.L.; Zeppieri, M.; Tosoni, C.; Parisi, L. Comparison of ICare Tonometer with Goldmann Applanation Tonometer in Glaucoma Patients. J. Glaucoma 2006, 15, 213–217.
- Kageyama, M.; Hirooka, K.; Baba, T.; Shiraga, F. Comparison of ICare Rebound Tonometer with Noncontact Tonometer in Healthy Children. J. Glaucoma 2011, 20, 63–66.
- Salvetat, M.L.; Zeppieri, M.; Miani, F.; Tosoni, C.; Parisi, L.; Brusini, P. Comparison of iCare tonometer and Goldmann applanation tonometry in normal corneas and in eyes with automated lamellar and penetrating keratoplasty. Eye 2011, 25, 642–650.
- Realini, T.; McMillan, B.; Gross, R.L.; Devience, E.; Balasubramani, G.K. Assessing the Reliability of Intraocular Pressure Measurements Using Rebound Tonometry. J. Glaucoma 2021, 30, 629–633.
- Rosentreter, A.; Athanasopoulos, A.; Schild, A.M.; Lappas, A.; Cursiefen, C.; Dietlein, T.S. Rebound, Applanation, and Dynamic Contour Tonometry in Pathologic Corneas. Cornea 2013, 32, 313–318.
- Badakere, S.V.; Chary, R.; Choudhari, N.S.; Rao, H.L.; Garudadri, C.; Senthil, S. Agreement of Intraocular Pressure Measurement of Icare ic200 with Goldmann Applanation Tonometer in Adult Eyes with Normal Cornea. Ophthalmol. Glaucoma 2021, 4, 89–94.
- Ve, R.S.; Jose, J.; Pai, H.V.; Biswas, S.; Parimi, V.; Poojary, P.; Nagarajan, T. Agreement and repeatability of Icare ic100 tonometer. Indian J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 68, 2122–2125.
- Halkiadakis, I.; Stratos, A.; Stergiopoulos, G.; Patsea, E.; Skouriotis, S.; Mitropoulos, P.; Papaconstantinou, D.; Georgopoulos, G. Evaluation of the Icare-ONE rebound tonometer as a self-measuring intraocular pressure device in normal subjects. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2012, 250, 1207–1211.
- Rosenfeld, E.; Barequet, D.; Mimouni, M.; Fischer, N.; Kurtz, S. Role of home monitoring with iCare ONE rebound tonometer in glaucoma patients management. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 14, 405–408.
- Cvenkel, B.; Velkovska, M.A.; Jordanova, V.D. Self-measurement with Icare HOME tonometer, patients’ feasibility and acceptability. Eur. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 30, 258–263.
- Quérat, L.; Chen, E. Clinical Use of iC are Home® tonometer. Acta. Ophthalmol. 2020, 98, e131–e132.
- Gao, F.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Q.; Pan, Y. Comparison of the iCare rebound tonometer and the Goldmann applanation tonometer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 13, 1912–1916.
- Kaufmann, C.; Bachmann, L.M.; Thiel, M.A. Intraocular Pressure Measurements Using Dynamic Contour Tonometry after Laser In Situ Keratomileusis. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 3790–3794.
- Kanngiesser, H.E.; Kniestedt, C.; Robert, Y.C.A. Dynamic Contour Tonometry. J. Glaucoma 2005, 14, 344–350.
- Eklund, A.; Hallberg, P.; Linden, C.; Lindahl, O.A. An Applanation Resonator Sensor for Measuring Intraocular Pressure Using Combined Continuous Force and Area Measurement. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 3017–3024.
- Jóhannesson, G.; Hallberg, P.; Eklund, A.; Lindén, C. Introduction and clinical evaluation of servo-controlled applanation resonance tonometry. Acta. Ophthalmol. 2011, 90, 677–682.
- Hallberg, P.; Eklund, A.; Bäcklund, T.; Lindén, C. Clinical Evaluation of Applanation Resonance Tonometry. J. Glaucoma 2007, 16, 88–93.
- Salvetat, M.L.; Zeppieri, M.; Tosoni, C.; Brusini, P. Repeatability and accuracy of applanation resonance tonometry in healthy subjects and patients with glaucoma. Acta. Ophthalmol. 2013, 92, e66–e73.
- Ottobelli, L.; Fogagnolo, P.; Frezzotti, P.; De Cillà, S.; Vallenzasca, E.; Digiuni, M.; Paderni, R.; Motolese, I.; Bagaglia, S.A.; Motolese, E.; et al. Repeatability and reproducibility of applanation resonance tonometry: A cross-sectional study. BMC Ophthalmol. 2015, 15, 36.
- Liu, J.H.; Kripke, D.F.; Hoffman, R.E.; Twa, M.; Loving, R.T.; Rex, K.M.; Gupta, N.; Weinreb, R.N. Nocturnal elevation of intraocular pressure in young adults. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1998, 39, 2707–2712.
- Konstas, A.G.P.; Mantziris, D.A.; Stewart, W.C. Diurnal Intraocular Pressure in Untreated Exfoliation and Primary Open-angle Glaucoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1997, 115, 182–185.
- Asrani, S.; Zeimer, R.; Wilensky, J.; Gieser, D.; Vitale, S.; Lindenmuth, K. Large Diurnal Fluctuations in Intraocular Pressure Are an Independent Risk Factor in Patients With Glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2000, 9, 134–142.
- Tan, S.; Baig, N.; Hansapinyo, L.; Jhanji, V.; Wei, S.; Tham, C.Y.C. Comparison of self-measured diurnal intraocular pressure profiles using rebound tonometry between primary angle closure glaucoma and primary open angle glaucoma patients. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0173905.
- Barkana, Y.; Anis, S.; Liebmann, J.; Tello, C.; Ritch, R. Clinical Utility of Intraocular Pressure Monitoring Outside of Normal Office Hours in Patients With Glaucoma. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2006, 124, 793–797.
- Hughes, E.; Spry, P.; Diamond, J. 24-Hour Monitoring of Intraocular Pressure in Glaucoma Management: A Retrospective Review. J. Glaucoma 2003, 12, 232–236.
- Konstas, A.G.P.; Quaranta, L.; Bozkurt, B.; Katsanos, A.; Feijoo, J.G.; Rossetti, L.; Shaarawy, T.; Pfeiffer, N.; Miglior, S. 24-h Efficacy of Glaucoma Treatment Options. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 481–517.
- Ho, C.H.; Wong, J.K.W. Role of 24-Hour Intraocular Pressure Monitoring in Glaucoma Management. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 2019, 3632197–3632213.
- Mcmonnies, C.W. The importance of and potential for continuous monitoring of intraocular pressure. Clin. Exp. Optom. 2017, 100, 203–207.
- Ittoop, S.M.; SooHoo, J.R.; Seibold, L.K.; Mansouri, K.; Kahook, M.Y. Systematic Review of Current Devices for 24-h Intraocular Pressure Monitoring. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 1679–1690.
- Molaei, A.; Karamzadeh, V.; Safi, S.; Esfandiari, H.; Dargahi, J.; Khosravi, M. Upcoming methods and specifications of continuous intraocular pressure monitoring systems for glaucoma. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2018, 13, 66–71.
- Dick, H.B.; Schultz, T.; Gerste, R.D. Miniaturization in Glaucoma Monitoring and Treatment: A Review of New Technologies That Require a Minimal Surgical Approach. Ophthalmol. Ther. 2019, 8, 19–30.
- Lee, J.O.; Park, H.; Du, J.; Balakrishna, A.; Chen, O.; Sretavan, D.; Choo, H. A microscale optical implant for continuous in vivo monitoring of intraocular pressure. Microsyst. Nanoeng. 2017, 3, 17057.
- Koutsonas, A.; Walter, P.; Roessler, G.; Plange, N. Implantation of a Novel Telemetric Intraocular Pressure Sensor in Patients with Glaucoma (ARGOS Study): 1-Year Results. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2015, 56, 1063–1069.
- Choritz, L.; Mansouri, K.; Bosch, J.V.D.; Weigel, M.; Dick, H.B.; Wagner, M.; Thieme, H.; Rüfer, F.; Szurmann, P.; Wehner, W.; et al. Telemetric Measurement of Intraocular Pressure via an Implantable Pressure Sensor—12-Month Results from the ARGOS-02 Trial. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 209, 187–196.
- Chen, P.-J.; Rodger, D.; Humayun, M.S.; Tai, Y.-C. Unpowered spiral-tube parylene pressure sensor for intraocular pressure sensing. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2006, 127, 276–282.
- Demeng, L.; Niansong, M.; Zhaofeng, Z. An ultralow power wireless intraocular pressure monitoring system. J. Semicond. 2014, 35, 105014.
- Mariacher, S.; Ebner, M.; Januschowski, K.; Hurst, J.; Schnichels, S.; Szurman, P. Investigation of a novel implantable suprachoroidal pressure transducer for telemetric intraocular pressure monitoring. Exp. Eye Res. 2016, 151, 54–60.
- Leonardi, M.; Leuenberger, P.; Bertrand, D.; Bertsch, A.; Renaud, P. First Steps toward Noninvasive Intraocular Pressure Monitoring with a Sensing Contact Lens. Investig. Opthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2004, 45, 3113–3117.
- Hediger, A.; Kniestedt, C.; Zweifel, S.; Knecht, P.; Funk, J.; Kanngiesser, H. Kontinuierliche Augeninnendruckmessung. Der. Ophthalmol. 2009, 106, 1111–1115.
- Twa, M.; Roberts, C.J.; Karol, H.J.; Mahmoud, A.M.; Weber, P.A.; Small, R.H. Evaluation of a Contact Lens-Embedded Sensor for Intraocular Pressure Measurement. J. Glaucoma 2010, 19, 382–390.
- Mansouri, K.; Shaarawy, T. Continuous intraocular pressure monitoring with a wireless ocular telemetry sensor: Initial clinical experience in patients with open angle glaucoma. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2011, 95, 627–629.
- Mansouri, K.; Weinreb, R.N.; Liu, J.H.K. Efficacy of a Contact Lens Sensor for Monitoring 24-H Intraocular Pressure Related Patterns. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0125530.
- Mansouri, K.; Medeiros, F.A.; Tafreshi, A.; Weinreb, R.N. Error in PubMed in: Global Burden of Visual Impairment and Blindness. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2012, 130, 1559.
- Lorenz, K.; Korb, C.; Herzog, N.; Vetter, J.M.; Elflein, H.; Keilani, M.M.; Pfeiffer, N. Tolerability of 24-Hour Intraocular Pressure Monitoring of a Pressure-sensitive Contact Lens. J. Glaucoma 2013, 22, 311–316.
- Dunbar, G.E.; Shen, B.Y.; Aref, A.A. The Sensimed Triggerfish contact lens sensor: Efficacy, safety, and patient perspectives. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2017, 11, 875–882.
- Mottet, B.; Aptel, F.; Romanet, J.-P.; Hubanova, R.; Pépin, J.-L.; Chiquet, C. 24-Hour Intraocular Pressure Rhythm in Young Healthy Subjects Evaluated With Continuous Monitoring Using a Contact Lens Sensor. JAMA Ophthalmol. 2013, 131, 1507–1516.
- Holló, G.; Kóthy, P.; Vargha, P. Evaluation of Continuous 24-Hour Intraocular Pressure Monitoring for Assessment of Prostaglandin-induced Pressure Reduction in Glaucoma. J. Glaucoma 2014, 23, e6–e12.
- Mansouri, K. The Road Ahead to Continuous 24-Hour Intraocular Pressure Monitoring in Glaucoma. J. Ophthalmic Vis. Res. 2014, 9, 260–268.
- Tojo, N.; Hayashi, A.; Otsuka, M. Correlation between 24-h continuous intraocular pressure measurement with a contact lens sensor and visual field progression. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2020, 258, 175–182.
- Tojo, N.; Hayashi, A.; Otsuka, M.; Miyakoshi, A. Fluctuations of the Intraocular Pressure in Pseudoexfoliation Syndrome and Normal Eyes Measured by a Contact Lens Sensor. J. Glaucoma 2016, 25, e463–e468.
- Pajic, B.; Pajic-Eggspuchler, B.; Haefliger, I. Continuous IOP Fluctuation Recording in Normal Tension Glaucoma Patients. Curr. Eye Res. 2011, 36, 1129–1138.
- Agnifili, L.; Mastropasqua, R.; Frezzotti, P.; Fasanella, V.; Motolese, I.; Pedrotti, E.; Di Iorio, A.; Mattei, P.A.; Motolese, E.; Mastropasqua, L. Circadian intraocular pressure patterns in healthy subjects, primary open angle and normal tension glaucoma patients with a contact lens sensor. Acta. Ophthalmol. 2014, 93, e14–e21.
- Tojo, N.; Abe, S.; Ishida, M.; Yagou, T.; Hayashi, A. The Fluctuation of Intraocular Pressure Measured by a Contact Lens Sensor in Normal-Tension Glaucoma Patients and Nonglaucoma Subjects. J. Glaucoma 2017, 26, 195–200.
- Kim, Y.W.; Kim, J.-S.; Lee, S.Y.; Ha, A.; Lee, J.; Park, Y.J.; Kim, Y.K.; Jeoung, J.W.; Park, K.H. Twenty-four–Hour Intraocular Pressure–Related Patterns from Contact Lens Sensors in Normal-Tension Glaucoma and Healthy Eyes. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, 1487–1497.
- Kim, Y.W.; Kim, M.J.; Park, K.H.; Jeoung, J.W.; Kim, S.H.; Jang, C.I.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, S.; Kang, J.Y. Preliminary study on implantable inductive-type sensor for continuous monitoring of intraocular pressure. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2015, 43, 830–837.
- Mansouri, K.; Rao, H.L.; Weinreb, R.N. Short-Term and Long-Term Variability of Intraocular Pressure Measured with an Intraocular Telemetry Sensor in Patients with Glaucoma. Ophthalmology 2021, 128, 227–233.
- Xu, S.C.; Gauthier, A.C.; Liu, J. The Application of a Contact Lens Sensor in Detecting 24-Hour Intraocular Pressure-Related Patterns. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 2016, 4727423.
- Kouhani, M.H.M.; Wu, J.; Tavakoli, A.; Weber, A.J.; Li, W. Wireless, passive strain sensor in a doughnut-shaped contact lens for continuous non-invasive self-monitoring of intraocular pressure. Lab. Chip. 2020, 20, 332–342.
- Xu, J.; Cui, T.; Hirtz, T.; Qiao, Y.; Li, X.; Zhong, F.; Han, X.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, S.; Ren, T.-L. Highly Transparent and Sensitive Graphene Sensors for Continuous and Non-invasive Intraocular Pressure Monitoring. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 2020, 12, 18375–18384.
- Maeng, B.; Chang, H.-K.; Park, J. Photonic crystal-based smart contact lens for continuous intraocular pressure monitoring. Lab. Chip. 2020, 20, 1740–1750.
- Wasilewicz, R.; Varidel, T.; Simon-Zoula, S.; Schlund, M.; Cerboni, S.; Mansouri, K. First-in-human continuous 24-hour measurement of intraocular pressure and ocular pulsation using a novel contact lens sensor. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2020, 104, 1519–1523.
- Agaoglu, S.; Diep, P.; Martini, M.; Kt, S.; Baday, M.; Araci, I.E. Ultra-sensitive microfluidic wearable strain sensor for intraocular pressure monitoring. Lab. Chip. 2018, 18, 3471–3483.
- Campigotto, A.; Leahy, S.; Zhao, G.; Campbell, R.J.; Lai, Y. Non-invasive Intraocular pressure monitoring with contact lens. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 104, 1324–1328.
- Fan, Y.; Tu, H.; Zhao, H.; Wei, F.; Yang, Y.; Ren, T. A wearable contact lens sensor for noninvasive in-situ monitoring of intraocular pressure. Nanotechnology 2021, 32, 095106.
- Dou, Z.; Tang, J.; Liu, Z.; Sun, Q.; Wang, Y.; Li, Y.; Yuan, M.; Wu, H.; Wang, Y.; Pei, W.; et al. Wearable Contact Lens Sensor for Non-invasive Continuous Monitoring of Intraocular Pressure. Micromachines 2021, 12, 108.
- Gillmann, K.; Wasilewicz, R.; Hoskens, K.; Simon-Zoula, S.; Mansouri, K. Continuous 24-hour measurement of intraocular pressure in millimeters of mercury (mmHg) using a novel contact lens sensor: Comparison with pneumatonometry. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0248211.
