The principle of hydrodynamic delivery was initially used to develop a method for delivering plasmids into mouse hepatocytes through tail vein injection and has since been expanded for use in delivering various biologically active materials to cells in different organs of several animal species. This review summarizes the fundamentals of hydrodynamic delivery and the progress made in its application, which offers tantalizing prospects for the development of a new generation of technologies with broader applications of hydrodynamic delivery.
- hydrodynamic injection
- systemic
- regional
- capillary
1. Introduction
2. Characteristics of Hydrodynamic Delivery
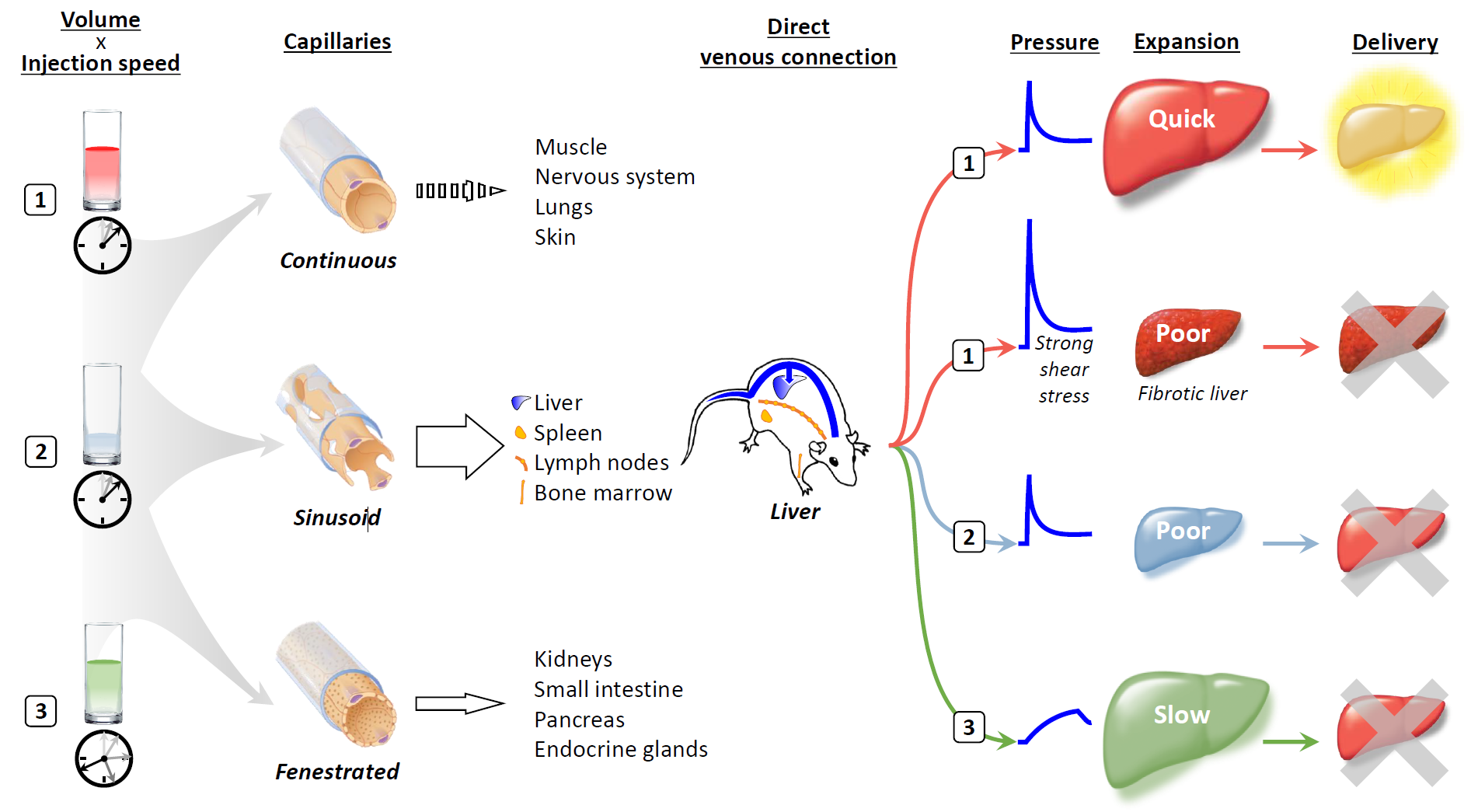
A single injection of less than 50 μg of plasmid DNA in saline through a mouse tail vein over a period of 5 s in a volume equal to 8 to 10% of the animal's body weight results in transgene expression in up to 40% of hepatocytes [1]. A key determinant of the efficiency of hydrodynamic delivery is the anatomical structure and expansion rate of the target organs after intravascular injection. A rapid influx of a large amount of solution into a capillary quickly extends the cell membrane and creates an invagination through which the solution enters the cell interior [3]. OurThe previous work, employing computed tomography and contrast medium, showed that the optimal expansion rate for the liver is 60%/5 s in mice [4].
Capillaries connect arteries and veins and can be divided into three classes based on differences in two components: the endothelium and the basement membrane [5] (Figure 1). Continuous capillaries consist of tightly connected endothelium and basement membrane without gaps, which prevent the leakage of water-soluble materials of 1 kDa or larger in size. Sinusoid capillaries provide large interendothelial gaps over 1 μm in size, in which there is incomplete shielding by the basement membrane, allowing molecules 100 kDa or larger in size to readily transude. The third type of capillary is the fenestrated capillary; in these capillaries, small fenestrae of 50–80 nm are present in the endothelium, which has a complete basement membrane. The organs that contain sinusoid capillaries are the most suitable targets for hydrodynamic delivery.
Among the organs that contain sinusoid capillaries, direct connections with the inferior vena cava and a unique system of the portal vein make the liver an ideal target for hydrodynamic delivery from the tail vein. A large volume of solution rapidly injected into the tail vein travels to the heart and induces cardiac congestion, followed by rapid retrograde flow into the hepatic veins, which directly transfers the hydrodynamic impact to the liver [4]. The specific infrastructure of the portal vein provides a natural flow and extra space, which counteracts the hydrodynamic retrograde flow that inhibits spillover of the injected solution into the portal vein and which can accommodate pushed-back preexisting blood and remove nucleases from sinusoids, respectively.
Although the rapid injection of a small volume of fluid can induce a high pressure comparable to that caused by injection of a volume corresponding to 8 to 10% of body weight if the injection speed is high enough, the delivery efficiency achieved is not equivalent to that obtained using authentic hydrodynamic delivery [1]. In a fibrotic liver, injection under the standard hydrodynamic conditions gives rise to much higher pressure and stronger shear stress than those reached using the same injection profile in a normal liver, but transgene expression is markedly lower [6,7][6][7]. Slow injection of a large volume over a longer period can cause the liver to expand to a size similar to that resulting from hydrodynamic delivery; however, gene delivery occurs with much lower efficiency [4].
The liver lobes are composed of hexagonal-shaped microscopic units called lobules, where the central structure is a terminal hepatic venule of the central vein. The peripheral vertices are bordered by portal tracts containing the portal vein, hepatic artery, and bile duct. Since the central vein and portal tracts consist of structures with higher rigidity, such as the basal membrane and vascular smooth muscle, the intervening parenchyma is more susceptible to physical stretch [8]. Rapid flow entering the liver from the central vein passes through the middle zone sinusoids and exits into the portal veins or vice versa. It is expected that a rapid flow exiting from a rigid inlet toward a rigid outlet would accumulate mostly at the front of the rigid outlet. In hydrodynamic delivery via the inferior vena cava or portal vein, transgene expression has been observed mainly at the end of the middle zone opposite the injection site [9].
To achieve effective hydrodynamic delivery, the physical impact of the injection must be transmitted to target cells through the solution's movement. If a physical impact that can quickly traverse the endothelium and basement membrane and cause organs to expand rapidly can be accomplished through local regional injection, hydrodynamic delivery may be a promising strategy not only for the liver but also for other organs.
3. Applications of Hydrodynamic Delivery
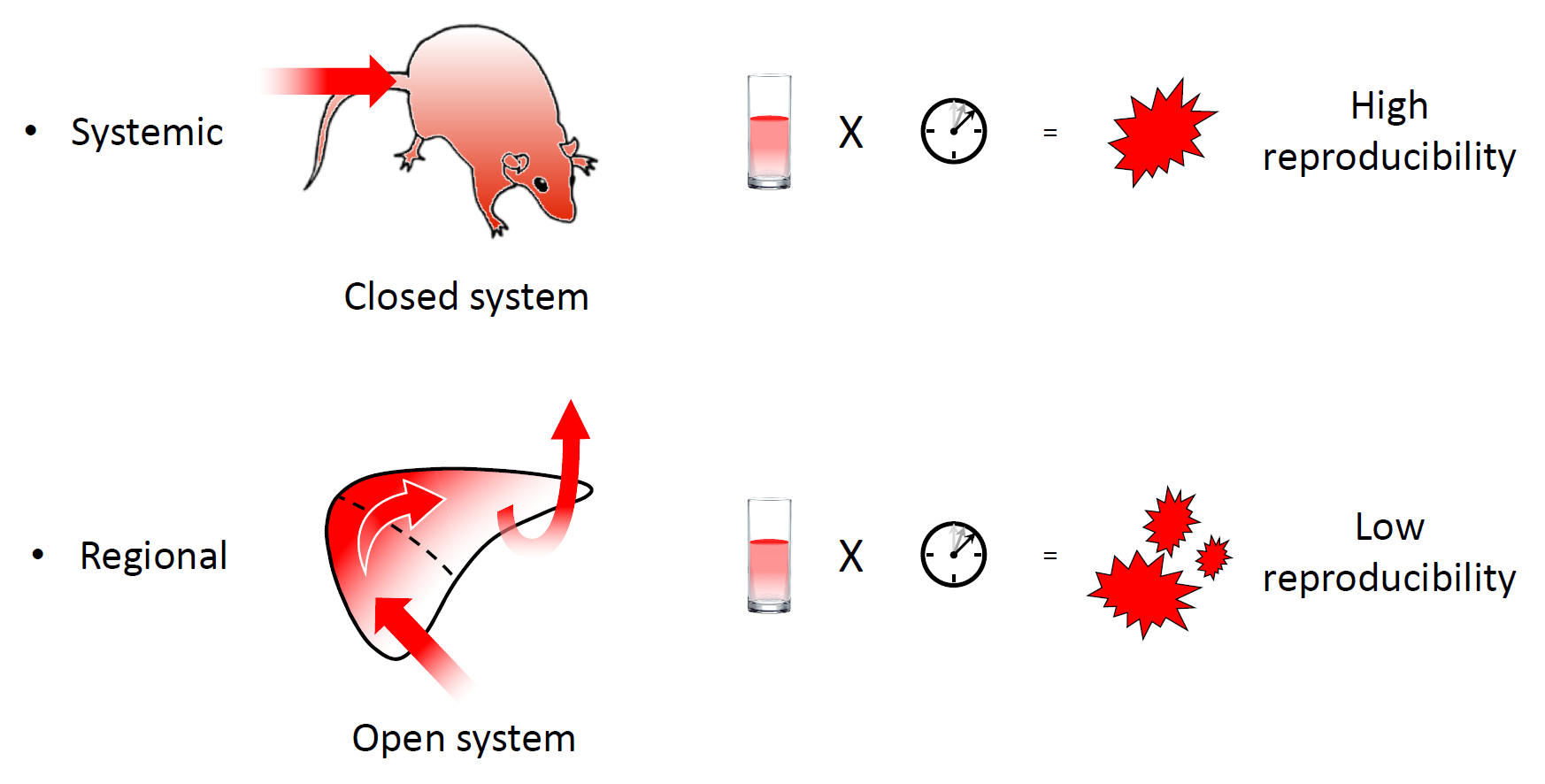
Human application is the ultimate goal of gene delivery system development. However, hydrodynamic impacts generated by systemic injection through the tail vein in mice can be temporarily overwhelming for the cardiovascular system. Therefore, when hydrodynamic delivery is applied in humans, hydrodynamic impacts must be limited around the target site. Although the insertion of an injecting device into a corresponding vasculature to target an organ or a part of an organ is an established technique in a clinical setting as interventional radiology, reproducing sufficient hydrodynamic impacts at a target region is challenging.
In hydrodynamic delivery of material injected into the tail vein, the injected solution never flows out of the body, making it a closed system (Figure 2). Under closed circulation, the hydrodynamic impact of the injection is reproducibly generated as a function of injection volume and speed. However, in regional hydrodynamic delivery, the solution is injected into an open system and can readily flow out of the target area through latent vascular connections [10]. Therefore, the hydrodynamic impact of regional hydrodynamic delivery cannot be reproducibly generated using fixed parameters of injection volume and speed. To achieve safety and reproducibility in the open system, a computer-controlled hydrodynamic delivery system called HydroJector has been developed, in which the injected solution is propelled by carbon dioxide gas [11] or by an electric motor [12] [12]. By compensating for leakage from the target area, the system controls the injection in a way that creates a reproducible intravascular pressure–time curve at the injection site.
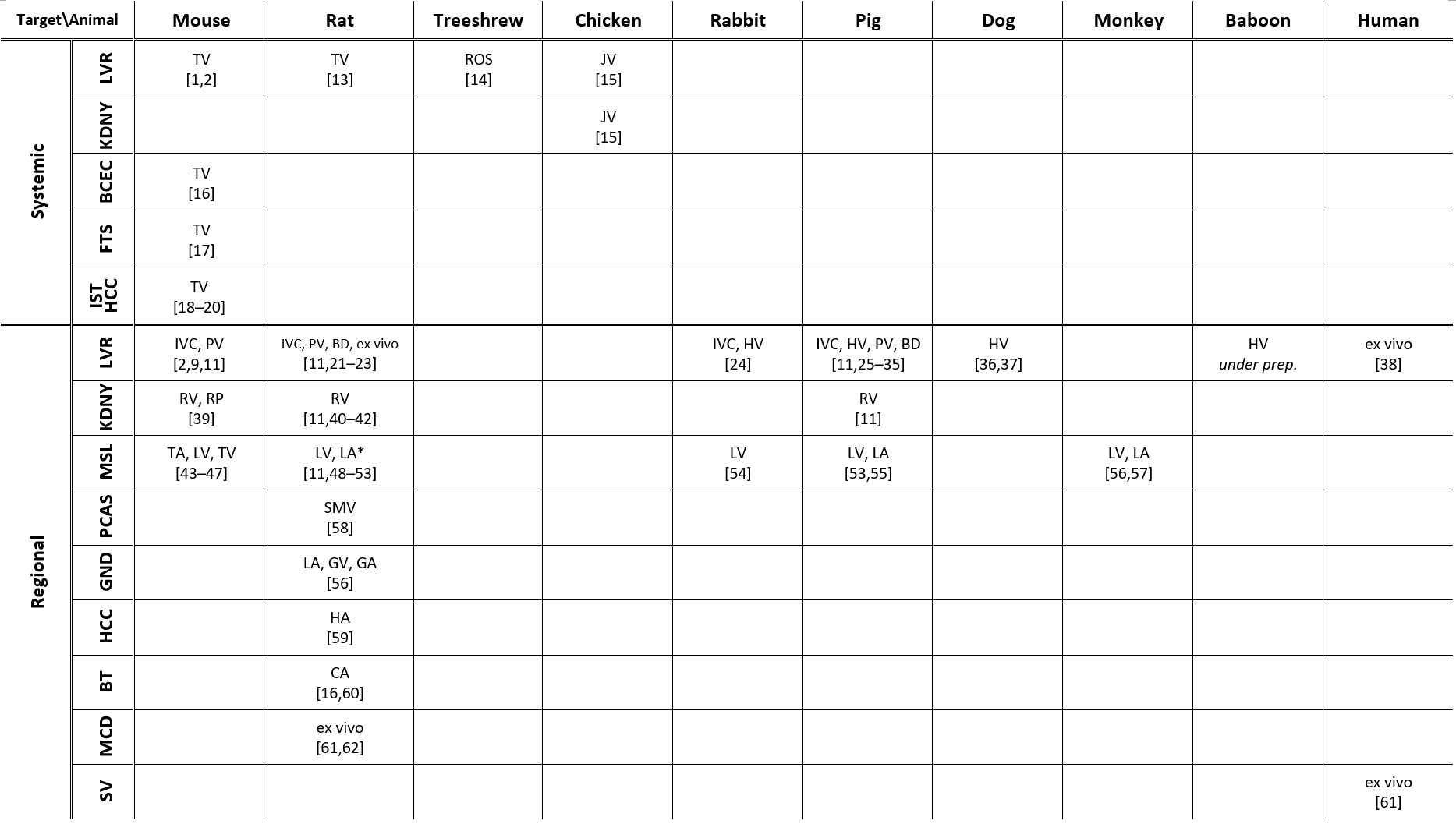
Recent studies on hydrodynamic delivery are reviewed from multiple perspectives, including the targeted animal species and routes of administration (Table 1), the types of diseases being treated (Table 2), and the delivery materials and strategies used (Table 3), particularly within the last five years.

| [ |
| 61 |
| ] |
| Infectious | Cancer | Hereditary | Liver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hepatitis B virus (HBV) [63][64][65][66] |
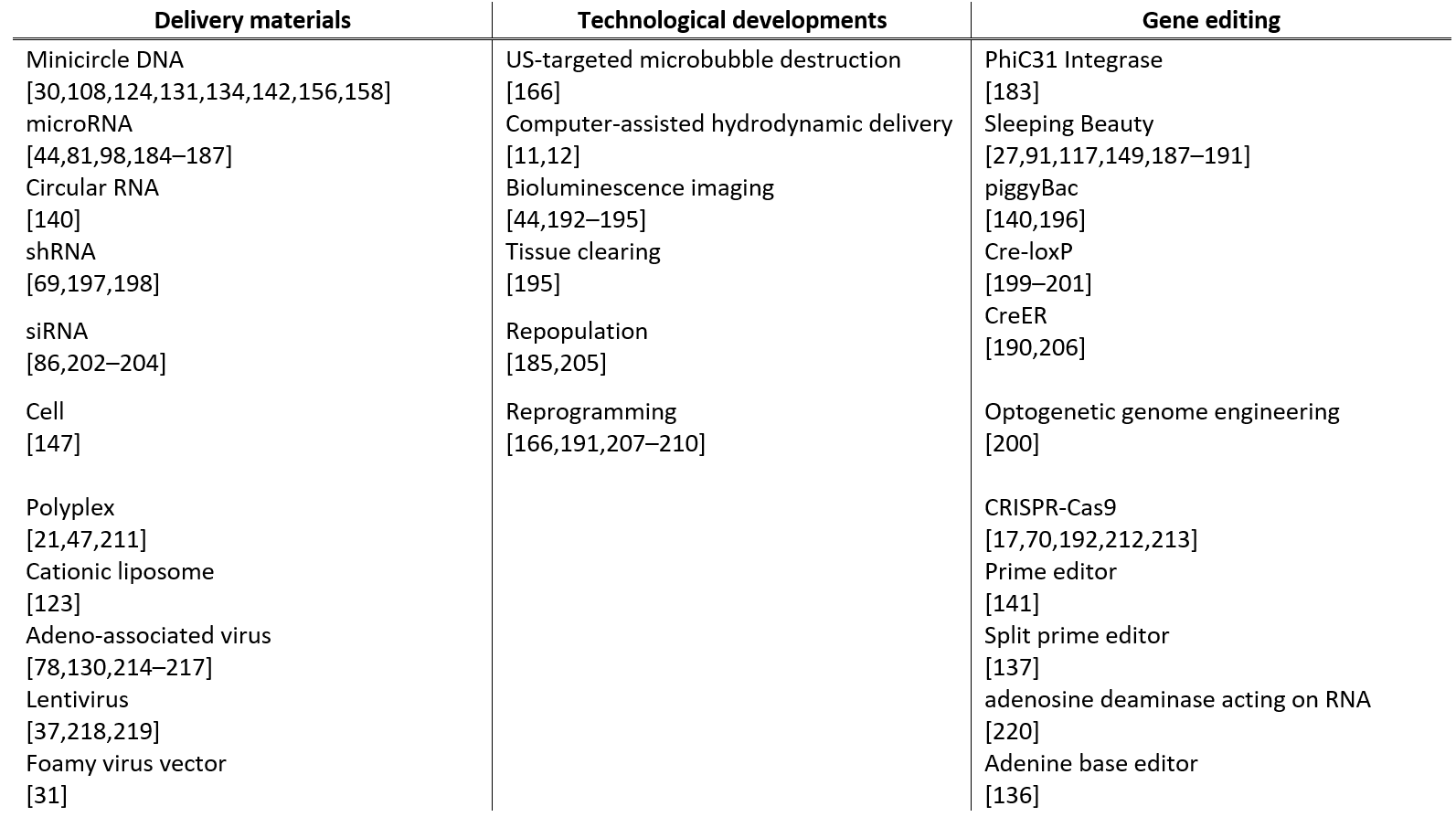
| Delivery Materials | Technological Developments | Gene Editing | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minicircle DNA [30][107][123][130][133][141][155][157]Hepatocellular carcinoma [59][67][68][69][70] |
Hemophilia A and B | US-targeted microbubble destruction [165] [71][72][73][74][75][76] |
Liver fibrosis [77][78][ |
PhiC31 Integrase [182]79][80][81][82] |
|||||||
| Hepatitis C virus [83][ | |||||||||||
| microRNA [44]84][81][85][97][86][183][87][184][88][[89][90] |
185][186]Hepatoblastoma [91][92][93] |
Computer-assisted hydrodynamic delivery [11][12]Pseudoxanthoma elasticum [94] |
Sleeping Beauty [27][91][116][148][186][Nonalcoholic fatty liver diseases [78][95][96][97][98] |
||||||||
| 187 | ] | [188][189][190] | Hepatitis D virus [99] |
Cholangiocellular carcinoma [100][101][ | |||||||
| Circular RNA [139]102][103] |
Bioluminescence imaging [44][191][192][193][194]von Willebrand disease [104][105][106 |
piggyBac [139][195]][107] |
Alcoholic liver injury [108][109] |
||||||||
| Influenza virus [110][111] |
|||||||||||
| shRNA [69][196][197]Colorectal cancer [18][19][112][113] |
Tissue clearing [194][114] |
Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura [115][116][117 |
Cre-loxP [198][199]][200][118] |
Portal hypertension [119] |
|||||||
| Enterovirus 71 [120] |
|||||||||||
| siRNA [86][201][202][203]Lung cancer [121] |
Repopulation [184][204]Mucopolysaccharidosis I and VII [122][123] |
CreER [189][205Fulminant hepatitis & regeneration [124][125][126] |
|||||||||
| Vaccination (HBV, Malaria, Influenza) [65][66][110][127][128][129] |
Brain tumor [60] |
165][190][206][207][Phenylketonuria [130] |
208][209Acute liver injury [131][132] |
||||||||
| ] | Malaria parasite [127][128] |
Lymphoma [133] |
Tyrosinemia [134][135][136] |
Others | |||||||
| Streptococcus [137] |
Melanoma [19][138][139] |
Leber congenital amaurosis [140] |
Atopic skin & cutaneous diseases [141][142][143][144] |
||||||||
| Sepsis [145] |
Metastasis (melanoma, breast cancer, RCC * (lungs, liver, kidneys)) [113][146][147] |
Sickle cell disease [148] |
Cardiovascular & ischemic diseases [149][150][151][152][153][154][155] | ||||||||
| Trypanosome [156] |
*, renal cell carcinoma | Cystathionine β-synthase deficiency [157] |
Kidney diseases & hyperparathyroidism [158][159][160][161] |
||||||||
| Fabry disease [162] |
Diabetes mellitus & obesity171][172][173][174] | ||||||||||
| ] | |||||||||||
| Cell [146] |
Reprogramming [ |
Optogenetic genome engineering [199] |
|||||||||
| Polyplex [22][47][210] |
CRISPR-Cas9 [17][70][191][211][212] |
||||||||||
| Cationic liposome [122] |
Prime editor [140] |
||||||||||
| Adeno-associated virus [78][129][213][214][215][216] |
Split prime editor [136] |
||||||||||
| Lentivirus [37][217][218] |
adenosine deaminase acting on RNA [163][164][165][166] |
||||||||||
| α-1 antitrypsin deficiency [167] |
Hypertriglyceridemia [168] |
||||||||||
| [ | 219 | Growth hormone deficiency [169] |
Inflammatory diseases [170][ |
Metachromatic leukodystrophy [175] |
Osteoporosis [176] |
||||||
| ] | |||||||||||
| Foamy virus vector [31] |
Adenine base editor [135] |
Short-chain acyl-CoA dehydrogen. def. [177] |
Transplantation & intoxication [23][178][179] |
||||||||
| Muscular dystrophy [180] |
Humanized immune system [142][181] |
||||||||||
| Target\Animal | Mouse | Rat | Treeshrew | Chicken | Rabbit | Pig | Dog | Monkey | Baboon | Human | |
| Systemic | LVR | TV [1][2] |
TV [13] |
ROS [14] |
JV [15] |
||||||
| KDNY | JV [15] |
||||||||||
| BCEC | TV [16] |
||||||||||
| FTS | TV [17] |
||||||||||
| IST HCC |
TV [18][19][20] |
||||||||||
| Regional | LVR | IVC, PV [2][9][11] |
IVC, PV, BD, ex vivo [11][21][22][23] |
IVC, HV [24] |
IVC, HV, PV, BD [11][25][26][27][28][29][30][31][32][33][34][35] |
HV [36][37] |
HV under prep. |
ex vivo [38] |
|||
| KDNY | RV, RP [39] |
RV [11][40][41][42] |
RV [11] |
||||||||
| MSL | TA, LV, TV [43][44][45][46][47] |
LV, LA * [11][48][49][50][51][52][53] |
LV [54] |
LV, LA [53][55] |
LV, LA [56][57] |
||||||
| PCAS | SMV [58] |
||||||||||
| GND | LA, GV, GA [56] |
||||||||||
| HCC | HA [59] |
||||||||||
| BT | CA [16][60] |
||||||||||
| MCD | ex vivo [61][62] |
||||||||||
| SV | |||||||||||
| ex vivo |
4. Conclusions
4. Conclusions
The comprehension of the mechanism behind hydrodynamic delivery allows uresearcher to overcome biological barriers, such as the capillary endothelium and cell membranes, and develop efficient methods for intracellular delivery of biologically active materials. The physical nature of hydrodynamic delivery allows for delivery of various types of materials, including gene coding sequences, RNAs, oligonucleotides, proteins, and mixtures of substances for genome editing. If the hydrodynamic impact of injection can be tightly controlled, hydrodynamic delivery could be feasible for clinical applications in humans. A computer-assisted hydrodynamic injection device has been developed, which could serve as a foundation for the development of next-generation hydrodynamic delivery devices. Regional hydrodynamic delivery could provide a platform for sophisticated gene therapy, allowing for site-directed editing, repopulation, and activation control of genes with minimal auxiliary effects.
[1]
References
- 1. Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamics-Based Transfection in Animals by Systemic Administration of Plasmid DNA. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 1258–1266, doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3300947.2. Zhang, G.; Budker, V.; Wolff, J.A. High Levels of Foreign Gene Expression in Hepatocytes after Tail Vein Injections of Naked Plasmid DNA. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 1735–1737, doi:10.1089/10430349950017734.3. Suda, T.; Gao, X.; Stolz, D.B.; Liu, D. Structural Impact of Hydrodynamic Injection on Mouse Liver. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 129–137, doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3302865.4. Kanefuji, T.; Yokoo, T.; Suda, T.; Abe, H.; Kamimura, K.; Liu, D. Hemodynamics of a Hydrodynamic Injection. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2014, 1, 14029, doi:10.1038/mtm.2014.29.5. Maynard, R.L.; Downes, N. Chapter 8 - Histology of the Vascular System. In Anatomy and Histology of the Laboratory Rat in Toxicology and Biomedical Research; Maynard, R.L., Downes, N., Eds.; Academic Press, 2019; pp. 91–95 ISBN 978-0-12-811837-5.6. Yeikilis, R.; Gal, S.; Kopeiko, N.; Paizi, M.; Pines, M.; Braet, F.; Spira, G. Hydrodynamics Based Transfection in Normal and Fibrotic Rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 6149–6155, doi:10.3748/wjg.v12.i38.6149.7. Kobayashi, Y.; Kamimura, K.; Abe, H.; Yokoo, T.; Ogawa, K.; Shinagawa-Kobayashi, Y.; Goto, R.; Inoue, R.; Ohtsuka, M.; Miura, H.; et al. Effects of Fibrotic Tissue on Liver-Targeted Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery. Mol. Ther. - Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e359, doi:10.1038/mtna.2016.63.8. Vg, B.; Vm, S.; T, B.; Mg, S.; G, Z.; Ja, W. Mechanism of Plasmid Delivery by Hydrodynamic Tail Vein Injection. II. Morphological Studies. J. Gene Med. 2006, 8, doi:10.1002/jgm.920.9. Suda, T.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamic Delivery. Adv. Genet. 2015, 89, 89–111, doi:10.1016/bs.adgen.2014.10.002.10. Yokoo, T.; Kanefuji, T.; Suda, T.; Kamimura, K.; Liu, D.; Terai, S. Site-Specific Impact of a Regional Hydrodynamic Injection: Computed Tomography Study during Hydrodynamic Injection Targeting the Swine Liver. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 334–343, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics7030334.11. Suda, T.; Suda, K.; Liu, D. Computer-Assisted Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2008, 16, 1098–1104, doi:10.1038/mt.2008.66.12. Yokoo, T.; Kamimura, K.; Suda, T.; Kanefuji, T.; Oda, M.; Zhang, G.; Liu, D.; Aoyagi, Y. Novel Electric Power-Driven Hydrodynamic Injection System for Gene Delivery: Safety and Efficacy of Human Factor IX Delivery in Rats. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 816–823, doi:10.1038/gt.2013.2.13. Kameda, S.; Maruyama, H.; Higuchi, N.; Nakamura, G.; Iino, N.; Nishikawa, Y.; Miyazaki, J.; Gejyo, F. Hydrodynamics-Based Transfer of PCR-Amplified DNA Fragments into Rat Liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 309, 929–936, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2003.08.087.14. Yan, S.; Fu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Duan, X.; Jia, S.; Peng, J.; Gao, B.; Du, J.; et al. High Levels of Gene Expression in the Hepatocytes of Adult Mice, Neonatal Mice and Tree Shrews via Retro-Orbital Sinus Hydrodynamic Injections of Naked Plasmid DNA. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2012, 161, 763–771, doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2012.05.018.15. Hen, G.; Bor, A.; Simchaev, V.; Druyan, S.; Yahav, S.; Miao, C.H.; Friedman-Einat, M. Expression of Foreign Genes in Chicks by Hydrodynamics-Based Naked Plasmid Transfer in Vivo. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2006, 30, 135–143, doi:10.1016/j.domaniend.2005.06.002.16. Hino, T.; Yokota, T.; Ito, S.; Nishina, K.; Kang, Y.-S.; Mori, S.; Hori, S.; Kanda, T.; Terasaki, T.; Mizusawa, H. In Vivo Delivery of Small Interfering RNA Targeting Brain Capillary Endothelial Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 340, 263–267, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2005.11.173.17. Nakamura, S.; Ando, N.; Watanabe, S.; Akasaka, E.; Ishihara, M.; Sato, M. Hydrodynamics-Based Transplacental Delivery as a Useful Noninvasive Tool for Manipulating Fetal Genome. Cells 2020, 9, E1744, doi:10.3390/cells9071744.18. Hamana, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Nishikawa, M.; Takakura, Y. Interferon-Inducible Mx Promoter-Driven, Long-Term Transgene Expression System of Interferon-β for Cancer Gene Therapy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2016, 27, 936–945, doi:10.1089/hum.2016.023.19. Ochoa, M.C.; Fioravanti, J.; Rodriguez, I.; Hervas-Stubbs, S.; Azpilikueta, A.; Mazzolini, G.; Gúrpide, A.; Prieto, J.; Pardo, J.; Berraondo, P.; et al. Antitumor Immunotherapeutic and Toxic Properties of an HDL-Conjugated Chimeric IL-15 Fusion Protein. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 139–149, doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-12-2660.20. Kamimura, K.; Yokoo, T.; Abe, H.; Sakai, N.; Nagoya, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohtsuka, M.; Miura, H.; Sakamaki, A.; Kamimura, H.; et al. Effect of Diphtheria Toxin-Based Gene Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 472, doi:10.3390/cancers12020472.21. Jiang, X.; Ren, Y.; Williford, J.-M.; Li, Z.; Mao, H.-Q. Liver-Targeted Gene Delivery through Retrograde Intrabiliary Infusion. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2013, 948, 275–284, doi:10.1007/978-1-62703-140-0_19.22. Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; Sawyer, G.J.; Collins, L.; Fabre, J.W. Regional Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery to the Rat Liver with Physiological Volumes of DNA Solution. J. Gene Med. 2004, 6, 693–703, doi:10.1002/jgm.595.23. Tsoulfas, G.; Takahashi, Y.; Liu, D.; Yagnik, G.; Wu, T.; Murase, N.; Geller, D.A. Hydrodynamic Plasmid DNA Gene Therapy Model in Liver Transplantation. J. Surg. Res. 2006, 135, 242–249, doi:10.1016/j.jss.2006.04.020.24. Eastman, S.J.; Baskin, K.M.; Hodges, B.L.; Chu, Q.; Gates, A.; Dreusicke, R.; Anderson, S.; Scheule, R.K. Development of Catheter-Based Procedures for Transducing the Isolated Rabbit Liver with Plasmid DNA. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 2065–2077, doi:10.1089/10430340260395910.25. Chan, T.; Grisch-Chan, H.M.; Schmierer, P.; Subotic, U.; Rimann, N.; Scherer, T.; Hetzel, U.; Bozza, M.; Harbottle, R.; Williams, J.A.; et al. Delivery of Non-Viral Naked DNA Vectors to Liver in Small Weaned Pigs by Hydrodynamic Retrograde Intrabiliary Injection. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2022, 24, 268–279, doi:10.1016/j.omtm.2022.01.006.26. Kamimura, K.; Suda, T.; Zhang, G.; Aoyagi, Y.; Liu, D. Parameters Affecting Image-Guided, Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery to Swine Liver. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2013, 2, e128, doi:10.1038/mtna.2013.52.27. Kumbhari, V.; Li, L.; Piontek, K.; Ishida, M.; Fu, R.; Khalil, B.; Garrett, C.M.; Liapi, E.; Kalloo, A.N.; Selaru, F.M. Successful Liver-Directed Gene Delivery by ERCP-Guided Hydrodynamic Injection (with Videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 88, 755-763.e5, doi:10.1016/j.gie.2018.06.022.28. Sendra, L.; Carreño, O.; Miguel, A.; Montalvá, E.; Herrero, M.J.; Orbis, F.; Noguera, I.; Barettino, D.; López-Andújar, R.; Aliño, S.F. Low RNA Translation Activit Limits the Efficacy of Hydrodynamic Gene Transfer to Pig Liver in Vivo. J. Gene Med. 2014, 16, 179–192, doi:10.1002/jgm.2777.29. Sendra, L.; Herrero, M.J.; Montalvá, E.M.; Noguera, I.; Orbis, F.; Díaz, A.; Fernández-Delgado, R.; López-Andújar, R.; Aliño, S.F. Efficacy of Interleukin 10 Gene Hydrofection in Pig Liver Vascular Isolated “in Vivo” by Surgical Procedure with Interest in Liver Transplantation. PloS One 2019, 14, e0224568, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0224568.30. Stoller, F.; Schlegel, A.; Viecelli, H.M.; Rüfenacht, V.; Cesarovic, N.; Viecelli, C.; Deplazes, S.; Bettschart, R.; Hurter, K.; Schmierer, P.; et al. Hepatocyte Transfection in Small Pigs After Weaning by Hydrodynamic Intraportal Injection of Naked DNA/Minicircle Vectors. Hum. Gene Ther. Methods 2015, 26, 181–192, doi:10.1089/hgtb.2014.140.31. Zacharoulis, D.; Rountas, C.; Katsimpoulas, M.; Morianos, J.; Chatziandreou, I.; Vassilopoulos, G. Efficient Liver Gene Transfer with Foamy Virus Vectors. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2013, 19, 214–220, doi:10.12659/MSMBR.883996.32. Kamimura, K.; Suda, T.; Xu, W.; Zhang, G.; Liu, D. Image-Guided, Lobe-Specific Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery to Swine Liver. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2009, 17, 491–499, doi:10.1038/mt.2008.294.33. Huang, Y.; Kruse, R.L.; Ding, H.; Itani, M.I.; Morrison, J.; Wang, Z.Z.; Selaru, F.M.; Kumbhari, V. Parameters of Biliary Hydrodynamic Injection during Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio-Pancreatography in Pigs for Applications in Gene Delivery. PloS One 2021, 16, e0249931, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0249931.34. Kruse, R.L.; Huang, Y.; Shum, T.; Bai, L.; Ding, H.; Wang, Z.Z.; Selaru, F.M.; Kumbhari, V. Endoscopic-Mediated, Biliary Hydrodynamic Injection Mediating Clinically Relevant Levels of Gene Delivery in Pig Liver. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 1119-1130.e4, doi:10.1016/j.gie.2021.06.016.35. Sendra, L.; Miguel, A.; Pérez-Enguix, D.; Herrero, M.J.; Montalvá, E.; García-Gimeno, M.A.; Noguera, I.; Díaz, A.; Pérez, J.; Sanz, P.; et al. Studying Closed Hydrodynamic Models of “In Vivo” DNA Perfusion in Pig Liver for Gene Therapy Translation to Humans. PloS One 2016, 11, e0163898, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0163898.36. Kamimura, K.; Kanefuji, T.; Yokoo, T.; Abe, H.; Suda, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Zhang, G.; Aoyagi, Y.; Liu, D. Safety Assessment of Liver-Targeted Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery in Dogs. PloS One 2014, 9, e107203, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0107203.37. Noda, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Matsui, H.; Matsunari, Y.; Sato, T.; Fukuoka, Y.; Hotta, A.; Okano, T.; Kichikawa, K.; Sugimoto, M.; et al. Development of Alternative Gene Transfer Techniques for Ex Vivo and in Vivo Gene Therapy in a Canine Model. Regen. Ther. 2021, 18, 347–354, doi:10.1016/j.reth.2021.08.009.38. Herrero, M.J.; Sabater, L.; Guenechea, G.; Sendra, L.; Montilla, A.I.; Abargues, R.; Navarro, V.; Aliño, S.F. DNA Delivery to “ex Vivo” Human Liver Segments. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 504–512, doi:10.1038/gt.2011.144.39. Woodard, L.E.; Welch, R.C.; Williams, F.M.; Luo, W.; Cheng, J.; Wilson, M.H. Hydrodynamic Renal Pelvis Injection for Non-Viral Expression of Proteins in the Kidney. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2018, doi:10.3791/56324.40. Corridon, P.R.; Rhodes, G.J.; Leonard, E.C.; Basile, D.P.; Gattone, V.H.; Bacallao, R.L.; Atkinson, S.J. A Method to Facilitate and Monitor Expression of Exogenous Genes in the Rat Kidney Using Plasmid and Viral Vectors. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2013, 304, F1217-1229, doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00070.2013.41. Maruyama, H.; Higuchi, N.; Kameda, S.; Nakamura, G.; Iguchi, S.; Miyazaki, J.-I.; Gejyo, F. Rat Kidney-Targeted Naked Plasmid DNA Transfer by Retrograde Injection into the Renal Vein. Mol. Biotechnol. 2004, 27, 23–31, doi:10.1385/mb:27:1:23.42. Woodard, L.E.; Cheng, J.; Welch, R.C.; Williams, F.M.; Luo, W.; Gewin, L.S.; Wilson, M.H. Kidney-Specific Transposon-Mediated Gene Transfer in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44904, doi:10.1038/srep44904.43. Girardin, C.; Maze, D.; Gonçalves, C.; Le Guen, Y.T.; Pluchon, K.; Pichon, C.; Montier, T.; Midoux, P. Selective Attachment of a Microtubule Interacting Peptide to Plasmid DNA via a Triplex Forming Oligonucleotide for Transfection Improvement. Gene Ther. 2022, doi:10.1038/s41434-022-00354-1.44. Guess, M.G.; Barthel, K.K.; Pugach, E.K.; Leinwand, L.A. Measuring MicroRNA Reporter Activity in Skeletal Muscle Using Hydrodynamic Limb Vein Injection of Plasmid DNA Combined with in Vivo Imaging. Skelet. Muscle 2013, 3, 19, doi:10.1186/2044-5040-3-19.45. Le Guen, Y.T.; Le Gall, T.; Midoux, P.; Guégan, P.; Braun, S.; Montier, T. Gene Transfer to Skeletal Muscle Using Hydrodynamic Limb Vein Injection: Current Applications, Hurdles and Possible Optimizations. J. Gene Med. 2020, 22, e3150, doi:10.1002/jgm.3150.46. Liang, K.W.; Nishikawa, M.; Liu, F.; Sun, B.; Ye, Q.; Huang, L. Restoration of Dystrophin Expression in Mdx Mice by Intravascular Injection of Naked DNA Containing Full-Length Dystrophin CDNA. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 901–908, doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3302239.47. Nagata, K.; Itaka, K.; Baba, M.; Uchida, S.; Ishii, T.; Kataoka, K. Muscle-Targeted Hydrodynamic Gene Introduction of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Using Polyplex Nanomicelle to Treat Peripheral Nerve Injury. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2014, 183, 27–34, doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2014.03.021.48. Yasuzaki, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Harashima, H. Validation of Mitochondrial Gene Delivery in Liver and Skeletal Muscle via Hydrodynamic Injection Using an Artificial Mitochondrial Reporter DNA Vector. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 4311–4320, doi:10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.5b00511.49. Yasuzaki, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Fukuda, Y.; Harashima, H. Condensation of Plasmid DNA Enhances Mitochondrial Association in Skeletal Muscle Following Hydrodynamic Limb Vein Injection. Pharm. Basel Switz. 2014, 7, 881–893, doi:10.3390/ph7080881.50. Yasuzaki, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Kanefuji, T.; Harashima, H. Localization of Exogenous DNA to Mitochondria in Skeletal Muscle Following Hydrodynamic Limb Vein Injection. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2013, 172, 805–811, doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2013.09.029.51. Sato, Y.; Ajiki, T.; Inoue, S.; Hakamata, Y.; Murakami, T.; Kaneko, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kobayashi, E. A Novel Gene Therapy to the Graft Organ by a Rapid Injection of Naked DNA I: Long-Lasting Gene Expression in a Rat Model of Limb Transplantation. Transplantation 2003, 76, 1294–1298, doi:10.1097/01.TP.0000098904.27401.4B.52. Budker, V.; Zhang, G.; Danko, I.; Williams, P.; Wolff, J. The Efficient Expression of Intravascularly Delivered DNA in Rat Muscle. Gene Ther. 1998, 5, 272–276, doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3300572.53. Danialou, G.; Comtois, A.S.; Matecki, S.; Nalbantoglu, J.; Karpati, G.; Gilbert, R.; Geoffroy, P.; Gilligan, S.; Tanguay, J.-F.; Petrof, B.J. Optimization of Regional Intraarterial Naked DNA-Mediated Transgene Delivery to Skeletal Muscles in a Large Animal Model. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2005, 11, 257–266, doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2004.09.016.54. Bates, M.K.; Zhang, G.; Sebestyén, M.G.; Neal, Z.C.; Wolff, J.A.; Herweijer, H. Genetic Immunization for Antibody Generation in Research Animals by Intravenous Delivery of Plasmid DNA. BioTechniques 2006, 40, 199–208, doi:10.2144/000112088.55. Kamimura, K.; Zhang, G.; Liu, D. Image-Guided, Intravascular Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery to Skeletal Muscle in Pigs. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2010, 18, 93–100, doi:10.1038/mt.2009.206.56. Zhang, G.; Budker, V.; Williams, P.; Subbotin, V.; Wolff, J.A. Efficient Expression of Naked Dna Delivered Intraarterially to Limb Muscles of Nonhuman Primates. Hum. Gene Ther. 2001, 12, 427–438, doi:10.1089/10430340150504046.57. Hagstrom, J.E.; Hegge, J.; Zhang, G.; Noble, M.; Budker, V.; Lewis, D.L.; Herweijer, H.; Wolff, J.A. A Facile Nonviral Method for Delivering Genes and SiRNAs to Skeletal Muscle of Mammalian Limbs. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2004, 10, 386–398, doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2004.05.004.58. Ogawa, K.; Kamimura, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Abe, H.; Yokoo, T.; Sakai, N.; Nagoya, T.; Sakamaki, A.; Abe, S.; Hayashi, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Pancreas-Targeted Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery in Rats. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 9, 80–88, doi:10.1016/j.omtn.2017.08.009.59. Tada, M.; Hatano, E.; Taura, K.; Nitta, T.; Koizumi, N.; Ikai, I.; Shimahara, Y. High Volume Hydrodynamic Injection of Plasmid DNA via the Hepatic Artery Results in a High Level of Gene Expression in Rat Hepatocellular Carcinoma Induced by Diethylnitrosamine. J. Gene Med. 2006, 8, 1018–1026, doi:10.1002/jgm.930.60. Barnett, F.H.; Scharer-Schuksz, M.; Wood, M.; Yu, X.; Wagner, T.E.; Friedlander, M. Intra-Arterial Delivery of Endostatin Gene to Brain Tumors Prolongs Survival and Alters Tumor Vessel Ultrastructure. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 1283–1289, doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3302287.61. Mann, M.J.; Gibbons, G.H.; Hutchinson, H.; Poston, R.S.; Hoyt, E.G.; Robbins, R.C.; Dzau, V.J. Pressure-Mediated Oligonucleotide Transfection of Rat and Human Cardiovascular Tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 1999, 96, 6411–6416, doi:10.1073/pnas.96.11.6411.62. Su, L.T.; Gopal, K.; Wang, Z.; Yin, X.; Nelson, A.; Kozyak, B.W.; Burkman, J.M.; Mitchell, M.A.; Low, D.W.; Bridges, C.R.; et al. Uniform Scale-Independent Gene Transfer to Striated Muscle after Transvenular Extravasation of Vector. Circulation 2005, 112, 1780–1788, doi:10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.105.534008.63. McCaffrey, A.P.; Nakai, H.; Pandey, K.; Huang, Z.; Salazar, F.H.; Xu, H.; Wieland, S.F.; Marion, P.L.; Kay, M.A. Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus in Mice by RNA Interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 639–644, doi:10.1038/nbt824.64. Yang, P.L.; Althage, A.; Chung, J.; Chisari, F.V. Hydrodynamic Injection of Viral DNA: A Mouse Model of Acute Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2002, 99, 13825–13830, doi:10.1073/pnas.202398599.65. Zhang, E.; Kosinska, A.D.; Ma, Z.; Dietze, K.K.; Xu, Y.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Dittmer, U.; et al. Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus Core Antigen-Based DNA and Protein Vaccines Induce Qualitatively Different Immune Responses That Affect T Cell Recall Responses and Antiviral Effects. Virology 2015, 475, 56–65, doi:10.1016/j.virol.2014.11.004.66. Huang, H.; Rückborn, M.; Le-Trilling, V.T.K.; Zhu, D.; Yang, S.; Zhou, W.; Yang, X.; Feng, X.; Lu, Y.; Lu, M.; et al. Prophylactic and Therapeutic HBV Vaccination by an HBs-Expressing Cytomegalovirus Vector Lacking an Interferon Antagonist in Mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 393–407, doi:10.1002/eji.202048780.67. Ho, C.; Wang, C.; Mattu, S.; Destefanis, G.; Ladu, S.; Delogu, S.; Armbruster, J.; Fan, L.; Lee, S.A.; Jiang, L.; et al. AKT (v-Akt Murine Thymoma Viral Oncogene Homolog 1) and N-Ras (Neuroblastoma Ras Viral Oncogene Homolog) Coactivation in the Mouse Liver Promotes Rapid Carcinogenesis by Way of MTOR (Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1), FOXM1 (Forkhead Box M1)/SKP2, and c-Myc Pathways. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 2012, 55, 833–845, doi:10.1002/hep.24736.68. Engelholm, L.H.; Riaz, A.; Serra, D.; Dagnæs-Hansen, F.; Johansen, J.V.; Santoni-Rugiu, E.; Hansen, S.H.; Niola, F.; Frödin, M. CRISPR/Cas9 Engineering of Adult Mouse Liver Demonstrates That the Dnajb1-Prkaca Gene Fusion Is Sufficient to Induce Tumors Resembling Fibrolamellar Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1662-1673.e10, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.09.008.69. Moon, H.; Ju, H.-L.; Chung, S.I.; Cho, K.J.; Eun, J.W.; Nam, S.W.; Han, K.-H.; Calvisi, D.F.; Ro, S.W. Transforming Growth Factor-β Promotes Liver Tumorigenesis in Mice via Up-Regulation of Snail. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1378-1391.e6, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2017.07.014.70. Gao, M.; Liu, D. CRISPR/Cas9-Based Pten Knock-out and Sleeping Beauty Transposon-Mediated Nras Knock-in Induces Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in Mice. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 505–512, doi:10.1080/15384047.2017.1323597.71. Miao, C.H.; Thompson, A.R.; Loeb, K.; Ye, X. Long-Term and Therapeutic-Level Hepatic Gene Expression of Human Factor IX after Naked Plasmid Transfer in Vivo. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2001, 3, 947–957, doi:10.1006/mthe.2001.0333.72. Balestra, D.; Scalet, D.; Pagani, F.; Rogalska, M.E.; Mari, R.; Bernardi, F.; Pinotti, M. An Exon-Specific U1snRNA Induces a Robust Factor IX Activity in Mice Expressing Multiple Human FIX Splicing Mutants. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e370, doi:10.1038/mtna.2016.77.73. Mashausi, D.S.; Roy, D.; Mangukiya, H.B.; Merugu, S.B.; Raza, G.; Yunus, F.-U.-N.; Liu, G.-S.; Negi, H.; Li, D. A High Efficient FVIII Variant Corrects Bleeding in Hemophilia A Mouse Model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, S0006-291X(22)00255-8, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2022.02.066.74. Fu, R.Y.; Chen, A.C.; Lyle, M.J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liu, C.L.; Miao, C.H. CD4+ T Cells Engineered with FVIII-CAR and Murine Foxp3 Suppress Anti-Factor VIII Immune Responses in Hemophilia a Mice. Cell. Immunol. 2020, 358, 104216, doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2020.104216.75. Huai, C.; Jia, C.; Sun, R.; Xu, P.; Min, T.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, C.; Chen, H.; Lu, D. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Somatic and Germline Gene Correction to Restore Hemostasis in Hemophilia B Mice. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 875–883, doi:10.1007/s00439-017-1801-z.76. Mohammed, B.M.; Cheng, Q.; Matafonov, A.; Monroe, D.M.; Meijers, J.C.M.; Gailani, D. Factor XI Promotes Hemostasis in Factor IX-Deficient Mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2018, 16, 2044–2049, doi:10.1111/jth.14243.77. Yang, K.-L.; Hung, K.-C.; Chang, W.-T.; Li, E.I.C. Establishment of an Early Liver Fibrosis Model by the Hydrodynamics-Based Transfer of TGF-Beta1 Gene. Comp. Hepatol. 2007, 6, 9, doi:10.1186/1476-5926-6-9.78. Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, L.; Tang, J.; Meng, Z.; Dai, L.; Gao, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Y.; et al. ANGPTL8 Accelerates Liver Fibrosis Mediated by HFD-Induced Inflammatory Activity via LILRB2/ERK Signaling Pathways. J. Adv. Res. 2022, S2090-1232(22)00174-6, doi:10.1016/j.jare.2022.08.006.79. Matsuda, M.; Tsurusaki, S.; Miyata, N.; Saijou, E.; Okochi, H.; Miyajima, A.; Tanaka, M. Oncostatin M Causes Liver Fibrosis by Regulating Cooperation between Hepatic Stellate Cells and Macrophages in Mice. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 2018, 67, 296–312, doi:10.1002/hep.29421.80. Guo, Q.; Chen, M.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, G.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y. Silencing P53 Inhibits Interleukin 10-Induced Activated Hepatic Stellate Cell Senescence and Fibrotic Degradation in Vivo. Exp. Biol. Med. Maywood NJ 2021, 246, 447–458, doi:10.1177/1535370220960391.81. Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.-S.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Li, C.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Liu, Z.-H.; Zhan, T.-Z.; Xu, J.; Xia, C.-M. MiR-130a-3p Alleviates Liver Fibrosis by Suppressing HSCs Activation and Skewing Macrophage to Ly6Clo Phenotype. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696069, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.696069.82. Abe, H.; Kamimura, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohtsuka, M.; Miura, H.; Ohashi, R.; Yokoo, T.; Kanefuji, T.; Suda, T.; Tsuchida, M.; et al. Effective Prevention of Liver Fibrosis by Liver-Targeted Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 in a Rat Liver Fibrosis Model. Mol. Ther. - Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e276, doi:10.1038/mtna.2015.49.83. McCaffrey, A.P.; Meuse, L.; Karimi, M.; Contag, C.H.; Kay, M.A. A Potent and Specific Morpholino Antisense Inhibitor of Hepatitis C Translation in Mice. Hepatology 2003, 38, 503–508, doi:10.1053/jhep.2003.50330.84. Zhu, W.; Wu, C.; Deng, W.; Pei, R.; Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; Qin, B.; Lu, M.; Chen, X. Inhibition of the HCV Core Protein on the Immune Response to HBV Surface Antigen and on HBV Gene Expression and Replication in Vivo. PloS One 2012, 7, e45146, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045146.85. Yu, W.; Grubor-Bauk, B.; Gargett, T.; Garrod, T.; Gowans, E.J. A Novel Challenge Model to Evaluate the Efficacy of Hepatitis C Virus Vaccines in Mice. Vaccine 2014, 32, 3409–3416, doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2014.04.014.86. Duan, L.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Li, P.; Hu, Q.; Chen, W. Target Delivery of Small Interfering RNAs with Vitamin E-Coupled Nanoparticles for Treating Hepatitis C. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24867, doi:10.1038/srep24867.87. Ahlén, G.; Sällberg, M.; Frelin, L. Methods for Monitoring Gene Gun-Induced HBV- and HCV-Specific Immune Responses in Mouse Models. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2013, 940, 239–267, doi:10.1007/978-1-62703-110-3_20.88. Nakai, M.; Oshiumi, H.; Funami, K.; Okamoto, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Seya, T.; Sakamoto, N. Interferon (IFN) and Cellular Immune Response Evoked in RNA-Pattern Sensing During Infection with Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). Sensors 2015, 15, 27160–27173, doi:10.3390/s151027160.89. Fu, Q.; Yan, S.; Wang, L.; Duan, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; An, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Hepatic NK Cell-Mediated Hypersensitivity to ConA-Induced Liver Injury in Mouse Liver Expressing Hepatitis C Virus Polyprotein. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 52178–52192, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.11052.90. Moyo, B.; Bloom, K.; Scott, T.; Ely, A.; Arbuthnot, P. Advances with Using CRISPR/Cas-Mediated Gene Editing to Treat Infections with Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus. Virus Res. 2018, 244, 311–320, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2017.01.003.91. Zhang, W.; Meyfeldt, J.; Wang, H.; Kulkarni, S.; Lu, J.; Mandel, J.A.; Marburger, B.; Liu, Y.; Gorka, J.E.; Ranganathan, S.; et al. β-Catenin Mutations as Determinants of Hepatoblastoma Phenotypes in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 17524–17542, doi:10.1074/jbc.RA119.009979.92. Smith, J.L.; Rodríguez, T.C.; Mou, H.; Kwan, S.-Y.; Pratt, H.; Zhang, X.-O.; Cao, Y.; Liang, S.; Ozata, D.M.; Yu, T.; et al. YAP1 Withdrawal in Hepatoblastoma Drives Therapeutic Differentiation of Tumor Cells to Functional Hepatocyte-Like Cells. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 2021, 73, 1011–1027, doi:10.1002/hep.31389.93. Wang, D.; Tian, J.; Yan, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Wu, D.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Guo, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Mitochondrial Fragmentation Is Crucial for C-Myc-Driven Hepatoblastoma-like Liver Tumors. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2022, 30, 1645–1660, doi:10.1016/j.ymthe.2022.01.032.94. Jin, L.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Shao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, L.; Uitto, J.; Wang, G. Genetic Heterogeneity of Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum: The Chinese Signature Profile of ABCC6 and ENPP1 Mutations. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1294–1302, doi:10.1038/jid.2015.10.95. Mohammed, B.M.; Cheng, Q.; Matafonov, A.; Monroe, D.M.; Meijers, J.C.M.; Gailani, D. Factor XI Promotes Hemostasis in Factor IX-Deficient Mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2018, 16, 2044–2049, doi:10.1111/jth.14243.96. Wang, H.; Chen, X. Hydrodynamic Injection for Developing NASH Model. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2022, 2455, 31–39, doi:10.1007/978-1-0716-2128-8_3.97. Cheng, Y.-W.; Chen, K.-W.; Kuo, H.-C.; Kuo, C.-H.; Lin, W.-H.; Chen, P.-J.; Yeh, S.-H. Specific Diacylglycerols Generated by Hepatic Lipogenesis Stimulate the Oncogenic Androgen Receptor Activity in Male Hepatocytes. Int. J. Obes. 2005 2019, 43, 2469–2479, doi:10.1038/s41366-019-0431-z.98. Chai, C.; Cox, B.; Yaish, D.; Gross, D.; Rosenberg, N.; Amblard, F.; Shemuelian, Z.; Gefen, M.; Korach, A.; Tirosh, O.; et al. Agonist of RORA Attenuates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Progression in Mice via Up-Regulation of MicroRNA 122. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 999-1014.e9, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2020.05.056.99. Yano, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Seko, Y.; Okishio, S.; Ishiba, H.; Tochiki, N.; Takahashi, A.; Kataoka, S.; Okuda, K.; Liu, Y.; et al. Hepatocyte-Specific Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Overexpression Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Liver Steatosis in Mice. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2022, 102, 281–289, doi:10.1038/s41374-021-00680-9.100. Chang, J.; Sigal, L.J.; Lerro, A.; Taylor, J. Replication of the Human Hepatitis Delta Virus Genome Is Initiated in Mouse Hepatocytes Following Intravenous Injection of Naked DNA or RNA Sequences. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 3469–3473, doi:10.1128/JVI.75.7.3469-3473.2001.101. Chen, X.; Calvisi, D.F. Hydrodynamic Transfection for Generation of Novel Mouse Models for Liver Cancer Research. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 912–923, doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.12.002.102. Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Peters, M.; Ding, N.; Ribback, S.; Utpatel, K.; Cigliano, A.; Dombrowski, F.; Xu, M.; Chen, X.; et al. Loss of Fbxw7 Synergizes with Activated Akt Signaling to Promote C-Myc Dependent Cholangiocarcinogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 742–752, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2019.05.027.103. Zhang, J.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Song, K.; Lee, S.; Han, C.; Wu, T. Epigenetic Silencing of 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase by Histone Methyltransferase EHMT2/G9a in Cholangiocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2022, 20, 350–360, doi:10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-21-0536.104. Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Cui, G.; Liang, B.; Chen, X.; Ko, S.; Affo, S.; Song, X.; Liao, Y.; Feng, J.; et al. β-Catenin Sustains and Is Required for YES-Associated Protein Oncogenic Activity in Cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 481–494, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.04.028.105. Navarrete, A.-M.; Casari, C.; Legendre, P.; Marx, I.; Hu, J.-R.; Lenting, P.J.; Christophe, O.D.; Denis, C.V. A Murine Model to Characterize the Antithrombotic Effect of Molecules Targeting Human von Willebrand Factor. Blood 2012, 120, 2723–2732, doi:10.1182/blood-2012-03-420042.106. Legendre, P.; Navarrete, A.-M.; Rayes, J.; Casari, C.; Boisseau, P.; Ternisien, C.; Caron, C.; Fressinaud, E.; Goudemand, J.; Veyradier, A.; et al. Mutations in the A3 Domain of von Willebrand Factor Inducing Combined Qualitative and Quantitative Defects in the Protein. Blood 2013, 121, 2135–2143, doi:10.1182/blood-2012-09-456038.107. Pruss, C.M.; Golder, M.; Bryant, A.; Hegadorn, C.; Haberichter, S.; Lillicrap, D. Use of a Mouse Model to Elucidate the Phenotypic Effects of the von Willebrand Factor Cleavage Mutants, Y1605A/M1606A and R1597W. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2012, 10, 940–950, doi:10.1111/j.1538-7836.2012.04675.x.108. Swystun, L.L.; Georgescu, I.; Mewburn, J.; Deforest, M.; Nesbitt, K.; Hebert, K.; Dwyer, C.; Brown, C.; Notley, C.; Lillicrap, D. Abnormal von Willebrand Factor Secretion, Factor VIII Stabilization and Thrombus Dynamics in Type 2N von Willebrand Disease Mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2017, 15, 1607–1619, doi:10.1111/jth.13749.109. Wang, Y.; Wu, T.; Hu, D.; Weng, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, P.-J.; Luo, X.; Wang, H.; Ning, Q. Intracellular Hepatitis B Virus Increases Hepatic Cholesterol Deposition in Alcoholic Fatty Liver via Hepatitis B Core Protein. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 58–68, doi:10.1194/jlr.M079533.110. Zhang, Y.-Y.; Li, S.-Q.; Song, Y.; Wang, P.; Song, X.-G.; Zhu, W.-F.; Wang, D.-M. Silencing the ADAM9 Gene through CRISPR/Cas9 Protects Mice from Alcohol-Induced Acute Liver Injury. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5110161, doi:10.1155/2022/5110161.111. Yamazaki, T.; Nagashima, M.; Ninomiya, D.; Ainai, A.; Fujimoto, A.; Ichimonji, I.; Takagi, H.; Morita, N.; Murotani, K.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Neutralizing Antibodies Induced by Gene-Based Hydrodynamic Injection Have a Therapeutic Effect in Lethal Influenza Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 47, doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.00047.112. Lin, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhao, K.; Kemper, T.; Yu, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; et al. Glucosamine Promotes Hepatitis B Virus Replication through Its Dual Effects in Suppressing Autophagic Degradation and Inhibiting MTORC1 Signaling. Autophagy 2020, 16, 548–561, doi:10.1080/15548627.2019.1632104.113. Ochoa, M.C.; Fioravanti, J.; Duitman, E.H.; Medina-Echeverz, J.; Palazon, A.; Arina, A.; Dubrot, J.; Alfaro, C.; Morales-Kastresana, A.; Murillo, O.; et al. Liver Gene Transfer of Interkeukin-15 Constructs That Become Part of Circulating High Density Lipoproteins for Immunotherapy. PloS One 2012, 7, e52370, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0052370.114. Cheng, L.; Du, X.; Wang, Z.; Ju, J.; Jia, M.; Huang, Q.; Xing, Q.; Xu, M.; Tan, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. Hyper-IL-15 Suppresses Metastatic and Autochthonous Liver Cancer by Promoting Tumour-Specific CD8+ T Cell Responses. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1297–1303, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2014.07.004.115. Miyakawa, N.; Nishikawa, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Ando, M.; Misaka, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Takakura, Y. Gene Delivery of Albumin Binding Peptide-Interferon-Gamma Fusion Protein with Improved Pharmacokinetic Properties and Sustained Biological Activity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 3110–3118, doi:10.1002/jps.23493.116. Desch, K.C.; Kretz, C.; Yee, A.; Gildersleeve, R.; Metzger, K.; Agrawal, N.; Cheng, J.; Ginsburg, D. Probing ADAMTS13 Substrate Specificity Using Phage Display. PloS One 2015, 10, e0122931, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0122931.117. Verhenne, S.; Vandeputte, N.; Pareyn, I.; Izsvák, Z.; Rottensteiner, H.; Deckmyn, H.; De Meyer, S.F.; Vanhoorelbeke, K. Long-Term Prevention of Congenital Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in ADAMTS13 Knockout Mice by Sleeping Beauty Transposon-Mediated Gene Therapy. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 836–844, doi:10.1161/ATVBAHA.116.308680.118. De Cock, E.; Hermans, C.; De Raeymaecker, J.; De Ceunynck, K.; De Maeyer, B.; Vandeputte, N.; Vandenbulcke, A.; Deckmyn, H.; Rottensteiner, H.; De Maeyer, M.; et al. The Novel ADAMTS13-p.D187H Mutation Impairs ADAMTS13 Activity and Secretion and Contributes to Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2015, 13, 283–292, doi:10.1111/jth.12804.119. Ostertag, E.M.; Bdeir, K.; Kacir, S.; Thiboutot, M.; Gulendran, G.; Yunk, L.; Hayes, V.M.; Motto, D.G.; Poncz, M.; Zheng, X.L.; et al. ADAMTS13 Autoantibodies Cloned from Patients with Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: 2. Pathogenicity in an Animal Model. Transfusion (Paris) 2016, 56, 1775–1785, doi:10.1111/trf.13583.120. Mookerjee, R.P.; Mehta, G.; Balasubramaniyan, V.; Mohamed, F.E.Z.; Davies, N.; Sharma, V.; Iwakiri, Y.; Jalan, R. Hepatic Dimethylarginine-Dimethylaminohydrolase1 Is Reduced in Cirrhosis and Is a Target for Therapy in Portal Hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 325–331, doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.024.121. Qin, B.; Yan, Q.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Dong, X. Enterovirus 71 Infection Impairs the Reproductive Capacity of Female Mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 403–409, doi:10.3892/etm.2017.4499.122. Sun, H.; Liu, D. IL-15/SIL-15Rα Gene Transfer Suppresses Lewis Lung Cancer Growth in the Lungs, Liver and Kidneys. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 54–60, doi:10.1038/cgt.2015.67.123. Schuh, R.S.; Poletto, É.; Pasqualim, G.; Tavares, A.M.V.; Meyer, F.S.; Gonzalez, E.A.; Giugliani, R.; Matte, U.; Teixeira, H.F.; Baldo, G. In Vivo Genome Editing of Mucopolysaccharidosis I Mice Using the CRISPR/Cas9 System. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2018, 288, 23–33, doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2018.08.031.124. Richard, M.; Arfi, A.; Seguin, J.; Gandolphe, C.; Scherman, D. Widespread Biochemical Correction of Murine Mucopolysaccharidosis Type VII Pathology by Liver Hydrodynamic Plasmid Delivery. Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 746–756, doi:10.1038/gt.2009.36.125. Huang, M.; Sun, R.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Simultaneous Knockdown of Multiple Ligands of Innate Receptor NKG2D Prevents Natural Killer Cell-Mediated Fulminant Hepatitis in Mice. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 2013, 57, 277–288, doi:10.1002/hep.25959.126. Saito, Y.; Kon, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Kurotaki, D.; Fukuda, N.; Kimura, C.; Kanayama, M.; Ito, K.; Diao, H.; et al. Osteopontin Small Interfering RNA Protects Mice from Fulminant Hepatitis. Hum. Gene Ther. 2007, 18, 1205–1214, doi:10.1089/hum.2007.069.127. Tsai, S.-M.; Wang, W.-P. Expression and Function of Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) 7 during Liver Regeneration. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 27, 641–652, doi:10.1159/000330073.128. Chen, L.; Keitany, G.J.; Peng, X.; Gibson, C.; Mohar, I.; Vignali, M.; Crispe, I.N.; Huang, F.; Wang, R. Identification of Pre-Erythrocytic Malaria Antigens That Target Hepatocytes for Killing in Vivo and Contribute to Protection Elicited by Whole-Parasite Vaccination. PloS One 2014, 9, e102225, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0102225.129. Rai, U.; Huang, J.; Mishra, S.; Li, X.; Shiratsuchi, T.; Tsuji, M. A New Method to Determine Antigen-Specific CD8+ T Cell Activity in Vivo by Hydrodynamic Injection. Biomolecules 2012, 2, 23–33, doi:10.3390/biom2010023.130. Yamazaki, T.; Chiba, J.; Akashi-Takamura, S. Neutralizing Anti-Hemagglutinin Monoclonal Antibodies Induced by Gene-Based Transfer Have Prophylactic and Therapeutic Effects on Influenza Virus Infection. Vaccines 2018, 6, E35, doi:10.3390/vaccines6030035.131. Viecelli, H.M.; Harbottle, R.P.; Wong, S.P.; Schlegel, A.; Chuah, M.K.; VandenDriessche, T.; Harding, C.O.; Thöny, B. Treatment of Phenylketonuria Using Minicircle-Based Naked-DNA Gene Transfer to Murine Liver. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 2014, 60, 1035–1043, doi:10.1002/hep.27104.132. Geng, J.; Wang, X.; Wei, H.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z. Efficient Attenuation of NK Cell-Mediated Liver Injury through Genetically Manipulating Multiple Immunogenes by Using a Liver-Directed Vector. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 1950 2013, 190, 4821–4829, doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1203129.133. Sun, Z.; Wang, Q.; Sun, L.; Wu, M.; Li, S.; Hua, H.; Sun, Y.; Ni, T.; Zhou, C.; Huang, S.; et al. Acetaminophen-Induced Reduction of NIMA-Related Kinase 7 Expression Exacerbates Acute Liver Injury. JHEP Rep. Innov. Hepatol. 2022, 4, 100545, doi:10.1016/j.jhepr.2022.100545.134. Pang, X.; Ma, F.; Zhang, P.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Zheng, G.; Hou, X.; Zhao, J.; He, C.; et al. Treatment of Human B-Cell Lymphomas Using Minicircle DNA Vector Expressing Anti-CD3/CD20 in a Mouse Model. Hum. Gene Ther. 2017, 28, 216–225, doi:10.1089/hum.2016.122.135. Yin, H.; Xue, W.; Chen, S.; Bogorad, R.L.; Benedetti, E.; Grompe, M.; Koteliansky, V.; Sharp, P.A.; Jacks, T.; Anderson, D.G. Genome Editing with Cas9 in Adult Mice Corrects a Disease Mutation and Phenotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 551–553, doi:10.1038/nbt.2884.136. Song, C.-Q.; Jiang, T.; Richter, M.; Rhym, L.H.; Koblan, L.W.; Zafra, M.P.; Schatoff, E.M.; Doman, J.L.; Cao, Y.; Dow, L.E.; et al. Adenine Base Editing in an Adult Mouse Model of Tyrosinaemia. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 125–130, doi:10.1038/s41551-019-0357-8.137. Liu, B.; Dong, X.; Cheng, H.; Zheng, C.; Chen, Z.; Rodríguez, T.C.; Liang, S.-Q.; Xue, W.; Sontheimer, E.J. A Split Prime Editor with Untethered Reverse Transcriptase and Circular RNA Template. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1388–1393, doi:10.1038/s41587-022-01255-9.138. Lu, S.-L.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Luo, Y.-H.; Kuo, C.-F.; Lin, W.-C.; Chang, Y.-T.; Wu, J.-J.; Chuang, W.-J.; Liu, C.-C.; Chao, L.; et al. Kallistatin Modulates Immune Cells and Confers Anti-Inflammatory Response to Protect Mice from Group A Streptococcal Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5366–5372, doi:10.1128/AAC.00322-13.139. Cueto, F.J.; Del Fresno, C.; Brandi, P.; Combes, A.J.; Hernández-García, E.; Sánchez-Paulete, A.R.; Enamorado, M.; Bromley, C.P.; Gomez, M.J.; Conde-Garrosa, R.; et al. DNGR-1 Limits Flt3L-Mediated Antitumor Immunity by Restraining Tumor-Infiltrating Type I Conventional Dendritic Cells. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002054, doi:10.1136/jitc-2020-002054.140. Mecozzi, N.; Nenci, A.; Vera, O.; Bok, I.; Falzone, A.; DeNicola, G.M.; Karreth, F.A. Genetic Tools for the Stable Overexpression of Circular RNAs. RNA Biol. 2022, 19, 353–363, doi:10.1080/15476286.2022.2043041.141. Jang, H.; Jo, D.H.; Cho, C.S.; Shin, J.H.; Seo, J.H.; Yu, G.; Gopalappa, R.; Kim, D.; Cho, S.-R.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Application of Prime Editing to the Correction of Mutations and Phenotypes in Adult Mice with Liver and Eye Diseases. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 181–194, doi:10.1038/s41551-021-00788-9.142. Leys, L.; Wang, Y.; Paulsboe, S.; Edelmayer, R.; Salte, K.; Wetter, J.; Namovic, M.; Phillips, L.; Dunstan, R.; Gauvin, D.; et al. Characterization of Psoriasiform Dermatitis Induced by Systemic Injection of Interleukin-23 Minicircles in Mice. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 482–497, doi:10.1111/1346-8138.14899.143. Mencarelli, A.; Gunawan, M.; Yong, K.S.M.; Bist, P.; Tan, W.W.S.; Tan, S.Y.; Liu, M.; Huang, E.K.; Fan, Y.; Chan, J.K.Y.; et al. A Humanized Mouse Model to Study Mast Cells Mediated Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 797–807, doi:10.1002/JLB.3MA1219-210RR.144. Noti, M.; Kim, B.S.; Siracusa, M.C.; Rak, G.D.; Kubo, M.; Moghaddam, A.E.; Sattentau, Q.A.; Comeau, M.R.; Spergel, J.M.; Artis, D. Exposure to Food Allergens through Inflamed Skin Promotes Intestinal Food Allergy through the Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin-Basophil Axis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1390–1399, 1399.e1-6, doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2014.01.021.145. Watcharanurak, K.; Nishikawa, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Kabashima, K.; Takahashi, R.; Takakura, Y. Regulation of Immunological Balance by Sustained Interferon-γ Gene Transfer for Acute Phase of Atopic Dermatitis in Mice. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 538–544, doi:10.1038/gt.2012.69.146. Wesche-Soldato, D.E.; Lomas-Neira, J.; Perl, M.; Chung, C.-S.; Ayala, A. Hydrodynamic Delivery of SiRNA in a Mouse Model of Sepsis. Methods Mol. Biol. Clifton NJ 2008, 442, 67–73, doi:10.1007/978-1-59745-191-8_5.147. Alhamhoom, Y.; Zhang, G.; Gao, M.; Cai, H.; Liu, D. In Vivo Growth and Responses to Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Different Environments. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 301–311.148. Li, J.; Yao, Q.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamic Cell Delivery for Simultaneous Establishment of Tumor Growth in Mouse Lung, Liver and Kidney. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 12, 737–741, doi:10.4161/cbt.12.8.16442.149. Vercellotti, G.M.; Khan, F.B.; Nguyen, J.; Chen, C.; Bruzzone, C.M.; Bechtel, H.; Brown, G.; Nath, K.A.; Steer, C.J.; Hebbel, R.P.; et al. H-Ferritin Ferroxidase Induces Cytoprotective Pathways and Inhibits Microvascular Stasis in Transgenic Sickle Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 79, doi:10.3389/fphar.2014.00079.150. Louet, E.R.; Glavan, M.; Orset, C.; Parcq, J.; Hanley, D.F.; Vivien, D. TPA-NMDAR Signaling Blockade Reduces the Incidence of Intracerebral Aneurysms. Transl. Stroke Res. 2022, doi:10.1007/s12975-022-01004-9.151. Zhang, G.; Marshall, A.L.; Thomas, A.L.; Kernan, K.A.; Su, Y.; LeBoeuf, R.C.; Dong, X.R.; Tchao, B.N.A. In Vivo Knockdown of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor Α1 Diminishes Aortic Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2011, 215, 34–42, doi:10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.07.057.152. Brampton, C.; Aherrahrou, Z.; Chen, L.-H.; Martin, L.; Bergen, A.A.B.; Gorgels, T.G.M.F.; Erdmann, J.; Erdfdi, J.; Schunkert, H.; Szabó, Z.; et al. The Level of Hepatic ABCC6 Expression Determines the Severity of Calcification after Cardiac Injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 159–170, doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2013.09.015.153. Chen, I.Y.; Paulmurugan, R.; Nielsen, C.H.; Wang, D.S.; Chow, V.; Robbins, R.C.; Gambhir, S.S. A Titratable Two-Step Transcriptional Amplification Strategy for Targeted Gene Therapy Based on Ligand-Induced Intramolecular Folding of a Mutant Human Estrogen Receptor. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2014, 16, 224–234, doi:10.1007/s11307-013-0673-4.154. Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yang, L.; Miyagishi, M.; Kasim, V. Prolyl Hydroxylase Domain-2 Silencing Induced by Hydrodynamic Limb Vein Injection Enhances Vascular Regeneration in Critical Limb Ischemia Mice through Activation of Multiple Genes. Curr. Gene Ther. 2015, 15, 313–325, doi:10.2174/156652321503150329003735.155. Wang, C.-H.; Liang, C.-L.; Huang, L.-T.; Liu, J.-K.; Hung, P.-H.; Sun, A.; Hung, K.-S. Single Intravenous Injection of Naked Plasmid DNA Encoding Erythropoietin Provides Neuroprotection in Hypoxia-Ischemia Rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 314, 1064–1071, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.01.005.156. Shin, Y.J.; Luo, K.; Quan, Y.; Ko, E.J.; Chung, B.H.; Lim, S.W.; Yang, C.W. Therapeutic Challenge of Minicircle Vector Encoding Klotho in Animal Model. Am. J. Nephrol. 2019, 49, 413–424, doi:10.1159/000499863.157. Thomson, R.; Molina-Portela, P.; Mott, H.; Carrington, M.; Raper, J. Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery of Baboon Trypanosome Lytic Factor Eliminates Both Animal and Human-Infective African Trypanosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009, 106, 19509–19514, doi:10.1073/pnas.0905669106.158. Lee, H.-O.; Gallego-Villar, L.; Grisch-Chan, H.M.; Häberle, J.; Thöny, B.; Kruger, W.D. Treatment of Cystathionine β-Synthase Deficiency in Mice Using a Minicircle-Based Naked DNA Vector. Hum. Gene Ther. 2019, 30, 1093–1100, doi:10.1089/hum.2019.014.159. Higuchi, N.; Maruyama, H.; Kuroda, T.; Kameda, S.; Iino, N.; Kawachi, H.; Nishikawa, Y.; Hanawa, H.; Tahara, H.; Miyazaki, J.; et al. Hydrodynamics-Based Delivery of the Viral Interleukin-10 Gene Suppresses Experimental Crescentic Glomerulonephritis in Wistar-Kyoto Rats. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 1297–1310, doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3301988.160. Bu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, W.; Chen, L.; Cao, H.; Fang, L.; Wen, P.; Tan, R.; Yang, J. Systemic Administration of Naked Plasmid Encoding HGF Attenuates Puromycin Aminonucleoside-Induced Damage of Murine Glomerular Podocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2011, 301, F784-792, doi:10.1152/ajprenal.00210.2011.161. Yokoi, H.; Mukoyama, M.; Nagae, T.; Mori, K.; Suganami, T.; Sawai, K.; Yoshioka, T.; Koshikawa, M.; Nishida, T.; Takigawa, M.; et al. Reduction in Connective Tissue Growth Factor by Antisense Treatment Ameliorates Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2004, 15, 1430–1440, doi:10.1097/01.asn.0000130565.69170.85.162. Lee, S.; Hong, S.W.; Choi, H.S.; Lee, L.Y.; Nam, C.; Rhee, Y.; Chung, U.; Lim, S.-K. Experimental Parathyroid Hormone Gene Therapy Using ØC31 Integrase. Endocr. J. 2008, 55, 1033–1041, doi:10.1507/endocrj.k08e-040.163. Nakamura, G.; Maruyama, H.; Ishii, S.; Shimotori, M.; Kameda, S.; Kono, T.; Miyazaki, J.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Gejyo, F. Naked Plasmid DNA-Based Alpha-Galactosidase A Gene Transfer Partially Reduces Systemic Accumulation of Globotriaosylceramide in Fabry Mice. Mol. Biotechnol. 2008, 38, 109–119, doi:10.1007/s12033-007-9008-5.164. Jiang, J.; Yamato, E.; Miyazaki, J. Long-Term Control of Food Intake and Body Weight by Hydrodynamics-Based Delivery of Plasmid DNA Encoding Leptin or CNTF. J. Gene Med. 2003, 5, 977–983, doi:10.1002/jgm.433.165. Fukushima, M.; Hattori, Y.; Tsukada, H.; Koga, K.; Kajiwara, E.; Kawano, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Kamata, K.; Maitani, Y. Adiponectin Gene Therapy of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice Using Hydrodynamic Injection. J. Gene Med. 2007, 9, 976–985, doi:10.1002/jgm.1104.166. Yang, X.-F.; Wang, H.-Y.; Lu, W.-L.; Ma, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.-R. Direct Reprogramming of Hepatocytes into Insulin-Producing Cells for Anti-Diabetic Treatment by Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction Enhanced Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 7275–7286.167. Peng, W.; Zhou, X.; Xu, T.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Liang, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Xiao, Y.; et al. BMP-7 Ameliorates Partial Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Restoring SnoN Protein Level via Smad1/5 Pathway in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 254, doi:10.1038/s41419-022-04529-x.168. G, Z.; Yk, S.; D, L. Long-Term Expression of Human Alpha1-Antitrypsin Gene in Mouse Liver Achieved by Intravenous Administration of Plasmid DNA Using a Hydrodynamics-Based Procedure. Gene Ther. 2000, 7, doi:10.1038/sj.gt.3301229.169. Sun, K.; Yang, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, L.; Qi, J. Leu452His Mutation in Lipoprotein Lipase Gene Transfer Associated with Hypertriglyceridemia in Mice in Vivo. PloS One 2013, 8, e75462, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0075462.170. Sondergaard, M.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Jensen, T.G. Normalization of Growth in Hypophysectomized Mice Using Hydrodynamic Transfer of the Human Growth Hormone Gene. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 285, E427-432, doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00573.2002.171. Elnaggar, R.; Hanawa, H.; Liu, H.; Yoshida, T.; Hayashi, M.; Watanabe, R.; Abe, S.; Toba, K.; Yoshida, K.; Chang, H.; et al. The Effect of Hydrodynamics-Based Delivery of an IL-13-Ig Fusion Gene for Experimental Autoimmune Myocarditis in Rats and Its Possible Mechanism. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 1995–2005, doi:10.1002/eji.200425776.172. Effect of Hydrodynamics-Based Gene Delivery of Plasmid DNA Encoding Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist-Ig for Treatment of Rat Autoimmune Myocarditis: Possible Mechanism for Lymphocytes and Noncardiac Cells - PubMed Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15795329/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).173. Shigekawa, M.; Hikita, H.; Kodama, T.; Shimizu, S.; Li, W.; Uemura, A.; Miyagi, T.; Hosui, A.; Kanto, T.; Hiramatsu, N.; et al. Pancreatic STAT3 Protects Mice against Caerulein-Induced Pancreatitis via PAP1 Induction. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 2105–2113, doi:10.1016/j.ajpath.2012.08.038.174. Shashidharamurthy, R.; Machiah, D.; Bozeman, E.N.; Srivatsan, S.; Patel, J.; Cho, A.; Jacob, J.; Selvaraj, P. Hydrodynamic Delivery of Plasmid DNA Encoding Human FcγR-Ig Dimers Blocks Immune-Complex Mediated Inflammation in Mice. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 877–885, doi:10.1038/gt.2011.175.175. Okumura, A.; Saito, T.; Otani, I.; Kojima, K.; Yamada, Y.; Ishida-Okawara, A.; Nakazato, K.; Asano, M.; Kanayama, K.; Iwakura, Y.; et al. Suppressive Role of Leukocyte Cell-Derived Chemotaxin 2 in Mouse Anti-Type II Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 413–421, doi:10.1002/art.23215.176. Takakusaki, Y.; Hisayasu, S.; Hirai, Y.; Shimada, T. Coexpression of Formylglycine-Generating Enzyme Is Essential for Synthesis and Secretion of Functional Arylsulfatase A in a Mouse Model of Metachromatic Leukodystrophy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2005, 16, 929–936, doi:10.1089/hum.2005.16.929.177. Liu, H.C.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, W.L.; Wang, H.L.; Jiao, G.J.; Chen, Y.Z. Role of Recombinant Plasmid PEGFP-N1-IGF-1 Transfection in Alleviating Osteoporosis in Ovariectomized Rats. J. Mol. Histol. 2013, 44, 535–544, doi:10.1007/s10735-013-9498-3.178. Holm, D.A.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Simonsen, H.; Gregersen, N.; Bolund, L.; Jensen, T.G.; Corydon, T.J. Expression of Short-Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase (SCAD) Proteins in the Liver of SCAD Deficient Mice after Hydrodynamic Gene Transfer. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2003, 78, 250–258, doi:10.1016/s1096-7192(03)00038-6.179. Miki, Y.; Maruyama, S.; Liu, D.; Kobayashi, T.; Sato, F.; Shimizu, H.; Kato, S.; Sato, W.; Morita, Y.; Yuzawa, Y.; et al. In Vivo Gene Transfer of Endo-Beta-Galactosidase C Removes AlphaGal Antigen on Erythrocytes and Endothelial Cells of the Organs. Xenotransplantation 2004, 11, 444–451, doi:10.1111/j.1399-3089.2004.00163.x.180. Fu, A.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Sun, M.J. Naked DNA Prevents Soman Intoxication. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 328, 901–905, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2004.12.194.181. Zhang, G.; Ludtke, J.J.; Thioudellet, C.; Kleinpeter, P.; Antoniou, M.; Herweijer, H.; Braun, S.; Wolff, J.A. Intraarterial Delivery of Naked Plasmid DNA Expressing Full-Length Mouse Dystrophin in the Mdx Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2004, 15, 770–782, doi:10.1089/1043034041648408.182. Ren, D.; Liu, W.; Ding, S.; Li, Y. Protocol for Generating Human Immune System Mice and Hydrodynamic Injection to Analyze Human Hematopoiesis in Vivo. STAR Protoc. 2022, 3, 101217, doi:10.1016/j.xpro.2022.101217.183. Umemoto, Y.; Kawakami, S.; Otani, Y.; Higuchi, Y.; Yamashita, F.; Hashida, M. Evaluation of Long-Term Gene Expression in Mouse Liver Using PhiC31 Integrase and Hydrodynamic Injection. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1182–1186, doi:10.1248/bpb.b12-00083.184. Li, Y.; Xie, J.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Wan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhu, Y. Inducible Interleukin 32 (IL-32) Exerts Extensive Antiviral Function via Selective Stimulation of Interferon Λ1 (IFN-Λ1). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 20927–20941, doi:10.1074/jbc.M112.440115.185. Zahm, A.M.; Wang, A.W.; Wang, Y.J.; Schug, J.; Wangensteen, K.J.; Kaestner, K.H. A High-Content Screen Identifies MicroRNAs That Regulate Liver Repopulation After Injury in Mice. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1044-1057.e17, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2019.11.025.186. Liu, N.; Chang, C.W.; Steer, C.J.; Wang, X.W.; Song, G. MicroRNA-15a/16-1 Prevents Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Disrupting the Communication Between Kupffer Cells and Regulatory T Cells. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 575–589, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.015.187. Liu, N.; Wang, X.; Steer, C.J.; Song, G. MicroRNA-206 Promotes the Recruitment of CD8+ T Cells by Driving M1 Polarisation of Kupffer Cells. Gut 2022, 71, 1642–1655, doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2021-324170.188. Molina, L.; Yang, H.; Adebayo Michael, A.O.; Oertel, M.; Bell, A.; Singh, S.; Chen, X.; Tao, J.; Monga, S.P.S. MTOR Inhibition Affects Yap1-β-Catenin-Induced Hepatoblastoma Growth and Development. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 1475–1490, doi:10.18632/oncotarget.26668.189. Ding, N.; Che, L.; Li, X.-L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.-J.; Fan, B.; Tao, J.-Y.; Chen, X.; Ji, J.-F. Oncogenic Potential of IDH1R132C Mutant in Cholangiocarcinoma Development in Mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2071–2080, doi:10.3748/wjg.v22.i6.2071.190. Hubner, E.K.; Lechler, C.; Rösner, T.N.; Kohnke-Ertel, B.; Schmid, R.M.; Ehmer, U. Constitutive and Inducible Systems for Genetic In Vivo Modification of Mouse Hepatocytes Using Hydrodynamic Tail Vein Injection. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2018, doi:10.3791/56613.191. Hu, S.; Molina, L.; Tao, J.; Liu, S.; Hassan, M.; Singh, S.; Poddar, M.; Bell, A.; Sia, D.; Oertel, M.; et al. NOTCH-YAP1/TEAD-DNMT1 Axis Drives Hepatocyte Reprogramming Into Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 449–465, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2022.05.007.192. Cao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, S.; He, M.; Wang, X.; Ma, P.; Yang, X.; Lv, L.; Zhan, L. Establishment of a Novel Mouse Hepatocellular Carcinoma Model for Dynamic Monitoring of Tumor Development by Bioluminescence Imaging. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 794101, doi:10.3389/fonc.2022.794101.193. Ju, H.-L.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Baek, S.; Chung, S.I.; Seong, J.; Han, K.-H.; Ro, S.W. Investigation of Oncogenic Cooperation in Simple Liver-Specific Transgenic Mouse Models Using Noninvasive in Vivo Imaging. PloS One 2013, 8, e59869, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0059869.194. Mezzanotte, L.; Blankevoort, V.; Löwik, C.W.G.M.; Kaijzel, E.L. A Novel Luciferase Fusion Protein for Highly Sensitive Optical Imaging: From Single-Cell Analysis to in Vivo Whole-Body Bioluminescence Imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5727–5734, doi:10.1007/s00216-014-7917-2.195. Fumoto, S.; Nishimura, K.; Nishida, K.; Kawakami, S. Three-Dimensional Imaging of the Intracellular Fate of Plasmid DNA and Transgene Expression: ZsGreen1 and Tissue Clearing Method CUBIC Are an Optimal Combination for Multicolor Deep Imaging in Murine Tissues. PloS One 2016, 11, e0148233, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0148233.196. Staber, J.M.; Pollpeter, M.J.; Arensdorf, A.; Sinn, P.L.; Rutkowski, D.T.; McCray, P.B. PiggyBac-Mediated Phenotypic Correction of Factor VIII Deficiency. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2014, 1, 14042, doi:10.1038/mtm.2014.42.197. Díaz-Rivera, A.; Meza-Ríos, A.; Chagoya de Sánchez, V.; Velasco-Loyden, G.; García-Benavides, L.; Jave-Suarez, L.F.; Monroy-Ramirez, H.C.; Santos-García, A.; Armendáriz-Borunda, J.; Sandoval-Rodríguez, A. Hydrodynamics-Based Liver Transfection Achieves Gene Silencing of CB1 Using Short Hairpin RNA Plasmid in Cirrhotic Rats. PloS One 2020, 15, e0228729, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0228729.198. Wang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, X.; Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; Ma, L.; et al. Sexual Dimorphism in Gut Microbiota Dictates Therapeutic Efficacy of Intravenous Immunoglobulin on Radiotherapy Complications. J. Adv. Res. 2022, S2090-1232(22)00128-X, doi:10.1016/j.jare.2022.06.002.199. Nakamura, S.; Maehara, T.; Watanabe, S.; Ishihara, M.; Sato, M. Improvement of Hydrodynamics-Based Gene Transfer of Nonviral DNA Targeted to Murine Hepatocytes. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 928790, doi:10.1155/2013/928790.200. Takao, T.; Hiraoka, Y.; Kawabe, K.; Yamada, D.; Ming, L.; Tanaka, K.; Sato, M.; Takarada, T. Establishment of a TTA-Dependent Photoactivatable Cre Recombinase Knock-in Mouse Model for Optogenetic Genome Engineering. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 526, 213–217, doi:10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.03.015.201. Kruse, R.L.; Legras, X.; Barzi, M. Cre/LoxP-HBV Plasmids Generating Recombinant Covalently Closed Circular DNA Genome upon Transfection. Virus Res. 2021, 292, 198224, doi:10.1016/j.virusres.2020.198224.202. Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Jiang, A.T.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Johnston, N.; Siu, K.S.; et al. Synergic Silencing of Costimulatory Molecules Prevents Cardiac Allograft Rejection. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 142, doi:10.1186/1479-5876-12-142.203. Li, L.; Shen, H.; Li, A.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, D.; Lu, M.; et al. Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Gene Expression and Replication by HBx Gene Silencing in a Hydrodynamic Injection Mouse Model with a New Clone of HBV Genotype B. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 214, doi:10.1186/1743-422X-10-214.204. Guo, J.; Fu, W.; Xiang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Xu, C.-R.; Li, L.; Kuang, D.; Ye, F. Notch1 Drives the Formation and Proliferation of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Curr. Med. Sci. 2019, 39, 929–937, doi:10.1007/s11596-019-2125-0.205. Johnson, C.G.; Chen, T.; Furey, N.; Hemmingsen, M.G.; Bissig, K.-D. Somatic Liver Knockout (SLiK): A Quick and Efficient Way to Generate Liver-Specific Knockout Mice Using Multiplex CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2020, 130, e117, doi:10.1002/cpmb.117.206. Hubner, E.K.; Lechler, C.; Kohnke-Ertel, B.; Zmoos, A.-F.; Sage, J.; Schmid, R.M.; Ehmer, U. An in Vivo Transfection System for Inducible Gene Expression and Gene Silencing in Murine Hepatocytes. J. Gene Med. 2017, 19, doi:10.1002/jgm.2940.207. Yang, X.-F.; Ren, L.-W.; Yang, L.; Deng, C.-Y.; Li, F.-R. In Vivo Direct Reprogramming of Liver Cells to Insulin Producing Cells by Virus-Free Overexpression of Defined Factors. Endocr. J. 2017, 64, 291–302, doi:10.1507/endocrj.EJ16-0463.208. Cim, A.; Sawyer, G.J.; Zhang, X.; Su, H.; Collins, L.; Jones, P.; Antoniou, M.; Reynes, J.-P.; Lipps, H.-J.; Fabre, J.W. In Vivo Studies on Non-Viral Transdifferentiation of Liver Cells towards Pancreatic β Cells. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 214, 277–288, doi:10.1530/JOE-12-0033.209. Yilmazer, A.; de Lázaro, I.; Bussy, C.; Kostarelos, K. In Vivo Reprogramming of Adult Somatic Cells to Pluripotency by Overexpression of Yamanaka Factors. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2013, e50837, doi:10.3791/50837.210. Yilmazer, A.; de Lázaro, I.; Bussy, C.; Kostarelos, K. In Vivo Cell Reprogramming towards Pluripotency by Virus-Free Overexpression of Defined Factors. PloS One 2013, 8, e54754, doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0054754.211. Matsui, A.; Uchida, S.; Ishii, T.; Itaka, K.; Kataoka, K. Messenger RNA-Based Therapeutics for the Treatment of Apoptosis-Associated Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15810, doi:10.1038/srep15810.212. Liang, W.-C.; Liang, P.-P.; Wong, C.-W.; Ng, T.-B.; Huang, J.-J.; Zhang, J.-F.; Waye, M.M.-Y.; Fu, W.-M. CRISPR/Cas9 Technology Targeting Fas Gene Protects Mice From Concanavalin-A Induced Fulminant Hepatic Failure. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 530–536, doi:10.1002/jcb.25722.213. Pankowicz, F.P.; Barzi, M.; Kim, K.H.; Legras, X.; Martins, C.S.; Wooton-Kee, C.R.; Lagor, W.R.; Marini, J.C.; Elsea, S.H.; Bissig-Choisat, B.; et al. Rapid Disruption of Genes Specifically in Livers of Mice Using Multiplex CRISPR/Cas9 Editing. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1967-1970.e6, doi:10.1053/j.gastro.2018.08.037.214. Mao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xi, W.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, J.; Xi, X. Long-Term Correction of Hemorrhagic Diathesis in Hemophilia A Mice by an AAV-Delivered Hybrid FVIII Composed of the Human Heavy Chain and the Rat Light Chain. Front. Med. 2022, 16, 584–595, doi:10.1007/s11684-021-0844-7.215. Zhang, W.; Mao, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Shao, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; et al. Evaluation of the Activity Levels of Rat FVIII and Human FVIII Delivered by Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors Both in Vitro and in Vivo. Blood Cells. Mol. Dis. 2018, 73, 47–54, doi:10.1016/j.bcmd.2018.09.004.216. Xu, Z.; Ye, J.; Zhang, A.; Xie, L.; Shen, Q.; Xue, J.; Chen, J. Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B with Liver-Specific Element Mediated by Rep-RBE Site-Specific Integration System. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 65, 153–159, doi:10.1097/FJC.0000000000000172.217. Lu, W.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Gu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Xue, J.; Dong, X.; Chen, J. Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B Mice with ScAAV8-LP1-HFIX. Front. Med. 2016, 10, 212–218, doi:10.1007/s11684-016-0438-y.218. Kim, S.M.; Choi, J.E.; Hur, W.; Kim, J.-H.; Hong, S.W.; Lee, E.B.; Lee, J.H.; Li, T.Z.; Sung, P.S.; Yoon, S.K. RAR-Related Orphan Receptor Gamma (ROR-γ) Mediates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Of Hepatocytes During Hepatic Fibrosis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 2026–2036, doi:10.1002/jcb.25776.219. Chuai, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Deng, Y.; Wen, B.; Tan, W. Lentiviral Backbone-Based Hepatitis B Virus Replicon-Mediated Transfer Favours the Establishment of Persistent Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Mice after Hydrodynamic Injection. Antiviral Res. 2014, 101, 68–74, doi:10.1016/j.antiviral.2013.10.019.220. Reautschnig, P.; Wahn, N.; Wettengel, J.; Schulz, A.E.; Latifi, N.; Vogel, P.; Kang, T.-W.; Pfeiffer, L.S.; Zarges, C.; Naumann, U.; et al. CLUSTER Guide RNAs Enable Precise and Efficient RNA Editing with Endogenous ADAR Enzymes in Vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 759–768, doi:10.1038/s41587-021-01105-0.Liu, F.; Song, Y.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamics-Based Transfection in Animals by Systemic Administration of Plasmid DNA. Gene Ther. 1999, 6, 1258–1266.
- Zhang, G.; Budker, V.; Wolff, J.A. High Levels of Foreign Gene Expression in Hepatocytes after Tail Vein Injections of Naked Plasmid DNA. Hum. Gene Ther. 1999, 10, 1735–1737.
- Suda, T.; Gao, X.; Stolz, D.B.; Liu, D. Structural Impact of Hydrodynamic Injection on Mouse Liver. Gene Ther. 2007, 14, 129–137.
- Kanefuji, T.; Yokoo, T.; Suda, T.; Abe, H.; Kamimura, K.; Liu, D. Hemodynamics of a Hydrodynamic Injection. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2014, 1, 14029.
- Maynard, R.L.; Downes, N. Chapter 8—Histology of the Vascular System. In Anatomy and Histology of the Laboratory Rat in Toxicology and Biomedical Research; Maynard, R.L., Downes, N., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 91–95. ISBN 978-0-12-811837-5.
- Yeikilis, R.; Gal, S.; Kopeiko, N.; Paizi, M.; Pines, M.; Braet, F.; Spira, G. Hydrodynamics Based Transfection in Normal and Fibrotic Rats. World J. Gastroenterol. 2006, 12, 6149–6155.
- Kobayashi, Y.; Kamimura, K.; Abe, H.; Yokoo, T.; Ogawa, K.; Shinagawa-Kobayashi, Y.; Goto, R.; Inoue, R.; Ohtsuka, M.; Miura, H.; et al. Effects of Fibrotic Tissue on Liver-Targeted Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e359.
- Budker, V.G.; Subbotin, V.M.; Budker, T.; Sebestyén, M.G.; Zhang, G.; Wolff, J.A. Mechanism of Plasmid Delivery by Hydrodynamic Tail Vein Injection. II. Morphological Studies. J. Gene Med. 2006, 8, 874–888.
- Suda, T.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamic Delivery. Adv. Genet. 2015, 89, 89–111.
- Yokoo, T.; Kanefuji, T.; Suda, T.; Kamimura, K.; Liu, D.; Terai, S. Site-Specific Impact of a Regional Hydrodynamic Injection: Computed Tomography Study during Hydrodynamic Injection Targeting the Swine Liver. Pharmaceutics 2015, 7, 334–343.
- Suda, T.; Suda, K.; Liu, D. Computer-Assisted Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2008, 16, 1098–1104.
- Yokoo, T.; Kamimura, K.; Suda, T.; Kanefuji, T.; Oda, M.; Zhang, G.; Liu, D.; Aoyagi, Y. Novel Electric Power-Driven Hydrodynamic Injection System for Gene Delivery: Safety and Efficacy of Human Factor IX Delivery in Rats. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 816–823.
- Kameda, S.; Maruyama, H.; Higuchi, N.; Nakamura, G.; Iino, N.; Nishikawa, Y.; Miyazaki, J.; Gejyo, F. Hydrodynamics-Based Transfer of PCR-Amplified DNA Fragments into Rat Liver. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2003, 309, 929–936.
- Yan, S.; Fu, Q.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, J.; Liu, Y.; Duan, X.; Jia, S.; Peng, J.; Gao, B.; Du, J.; et al. High Levels of Gene Expression in the Hepatocytes of Adult Mice, Neonatal Mice and Tree Shrews via Retro-Orbital Sinus Hydrodynamic Injections of Naked Plasmid DNA. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2012, 161, 763–771.
- Hen, G.; Bor, A.; Simchaev, V.; Druyan, S.; Yahav, S.; Miao, C.H.; Friedman-Einat, M. Expression of Foreign Genes in Chicks by Hydrodynamics-Based Naked Plasmid Transfer in Vivo. Domest. Anim. Endocrinol. 2006, 30, 135–143.
- Hino, T.; Yokota, T.; Ito, S.; Nishina, K.; Kang, Y.-S.; Mori, S.; Hori, S.; Kanda, T.; Terasaki, T.; Mizusawa, H. In Vivo Delivery of Small Interfering RNA Targeting Brain Capillary Endothelial Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2006, 340, 263–267.
- Nakamura, S.; Ando, N.; Watanabe, S.; Akasaka, E.; Ishihara, M.; Sato, M. Hydrodynamics-Based Transplacental Delivery as a Useful Noninvasive Tool for Manipulating Fetal Genome. Cells 2020, 9, 1744.
- Hamana, A.; Takahashi, Y.; Nishikawa, M.; Takakura, Y. Interferon-Inducible Mx Promoter-Driven, Long-Term Transgene Expression System of Interferon-β for Cancer Gene Therapy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2016, 27, 936–945.
- Ochoa, M.C.; Fioravanti, J.; Rodriguez, I.; Hervas-Stubbs, S.; Azpilikueta, A.; Mazzolini, G.; Gúrpide, A.; Prieto, J.; Pardo, J.; Berraondo, P.; et al. Antitumor Immunotherapeutic and Toxic Properties of an HDL-Conjugated Chimeric IL-15 Fusion Protein. Cancer Res. 2013, 73, 139–149.
- Kamimura, K.; Yokoo, T.; Abe, H.; Sakai, N.; Nagoya, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohtsuka, M.; Miura, H.; Sakamaki, A.; Kamimura, H.; et al. Effect of Diphtheria Toxin-Based Gene Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2020, 12, 472.
- Zhang, X.; Dong, X.; Sawyer, G.J.; Collins, L.; Fabre, J.W. Regional Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery to the Rat Liver with Physiological Volumes of DNA Solution. J. Gene Med. 2004, 6, 693–703.
- Jiang, X.; Ren, Y.; Williford, J.-M.; Li, Z.; Mao, H.-Q. Liver-Targeted Gene Delivery through Retrograde Intrabiliary Infusion. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 948, 275–284.
- Tsoulfas, G.; Takahashi, Y.; Liu, D.; Yagnik, G.; Wu, T.; Murase, N.; Geller, D.A. Hydrodynamic Plasmid DNA Gene Therapy Model in Liver Transplantation. J. Surg. Res. 2006, 135, 242–249.
- Eastman, S.J.; Baskin, K.M.; Hodges, B.L.; Chu, Q.; Gates, A.; Dreusicke, R.; Anderson, S.; Scheule, R.K. Development of Catheter-Based Procedures for Transducing the Isolated Rabbit Liver with Plasmid DNA. Hum. Gene Ther. 2002, 13, 2065–2077.
- Chan, T.; Grisch-Chan, H.M.; Schmierer, P.; Subotic, U.; Rimann, N.; Scherer, T.; Hetzel, U.; Bozza, M.; Harbottle, R.; Williams, J.A.; et al. Delivery of Non-Viral Naked DNA Vectors to Liver in Small Weaned Pigs by Hydrodynamic Retrograde Intrabiliary Injection. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2022, 24, 268–279.
- Kamimura, K.; Suda, T.; Zhang, G.; Aoyagi, Y.; Liu, D. Parameters Affecting Image-Guided, Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery to Swine Liver. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2013, 2, e128.
- Kumbhari, V.; Li, L.; Piontek, K.; Ishida, M.; Fu, R.; Khalil, B.; Garrett, C.M.; Liapi, E.; Kalloo, A.N.; Selaru, F.M. Successful Liver-Directed Gene Delivery by ERCP-Guided Hydrodynamic Injection (with Videos). Gastrointest. Endosc. 2018, 88, 755–763.e5.
- Sendra, L.; Carreño, O.; Miguel, A.; Montalvá, E.; Herrero, M.J.; Orbis, F.; Noguera, I.; Barettino, D.; López-Andújar, R.; Aliño, S.F. Low RNA Translation Activit Limits the Efficacy of Hydrodynamic Gene Transfer to Pig Liver in Vivo. J. Gene Med. 2014, 16, 179–192.
- Sendra, L.; Herrero, M.J.; Montalvá, E.M.; Noguera, I.; Orbis, F.; Díaz, A.; Fernández-Delgado, R.; López-Andújar, R.; Aliño, S.F. Efficacy of Interleukin 10 Gene Hydrofection in Pig Liver Vascular Isolated “in Vivo” by Surgical Procedure with Interest in Liver Transplantation. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0224568.
- Stoller, F.; Schlegel, A.; Viecelli, H.M.; Rüfenacht, V.; Cesarovic, N.; Viecelli, C.; Deplazes, S.; Bettschart, R.; Hurter, K.; Schmierer, P.; et al. Hepatocyte Transfection in Small Pigs After Weaning by Hydrodynamic Intraportal Injection of Naked DNA/Minicircle Vectors. Hum. Gene Ther. Methods 2015, 26, 181–192.
- Zacharoulis, D.; Rountas, C.; Katsimpoulas, M.; Morianos, J.; Chatziandreou, I.; Vassilopoulos, G. Efficient Liver Gene Transfer with Foamy Virus Vectors. Med. Sci. Monit. Basic Res. 2013, 19, 214–220.
- Kamimura, K.; Suda, T.; Xu, W.; Zhang, G.; Liu, D. Image-Guided, Lobe-Specific Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery to Swine Liver. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2009, 17, 491–499.
- Huang, Y.; Kruse, R.L.; Ding, H.; Itani, M.I.; Morrison, J.; Wang, Z.Z.; Selaru, F.M.; Kumbhari, V. Parameters of Biliary Hydrodynamic Injection during Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangio-Pancreatography in Pigs for Applications in Gene Delivery. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0249931.
- Kruse, R.L.; Huang, Y.; Shum, T.; Bai, L.; Ding, H.; Wang, Z.Z.; Selaru, F.M.; Kumbhari, V. Endoscopic-Mediated, Biliary Hydrodynamic Injection Mediating Clinically Relevant Levels of Gene Delivery in Pig Liver. Gastrointest. Endosc. 2021, 94, 1119–1130.e4.
- Sendra, L.; Miguel, A.; Pérez-Enguix, D.; Herrero, M.J.; Montalvá, E.; García-Gimeno, M.A.; Noguera, I.; Díaz, A.; Pérez, J.; Sanz, P.; et al. Studying Closed Hydrodynamic Models of “In Vivo” DNA Perfusion in Pig Liver for Gene Therapy Translation to Humans. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0163898.
- Kamimura, K.; Kanefuji, T.; Yokoo, T.; Abe, H.; Suda, T.; Kobayashi, Y.; Zhang, G.; Aoyagi, Y.; Liu, D. Safety Assessment of Liver-Targeted Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery in Dogs. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e107203.
- Noda, M.; Tatsumi, K.; Matsui, H.; Matsunari, Y.; Sato, T.; Fukuoka, Y.; Hotta, A.; Okano, T.; Kichikawa, K.; Sugimoto, M.; et al. Development of Alternative Gene Transfer Techniques for Ex Vivo and in Vivo Gene Therapy in a Canine Model. Regen. Ther. 2021, 18, 347–354.
- Herrero, M.J.; Sabater, L.; Guenechea, G.; Sendra, L.; Montilla, A.I.; Abargues, R.; Navarro, V.; Aliño, S.F. DNA Delivery to “ex Vivo” Human Liver Segments. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 504–512.
- Woodard, L.E.; Welch, R.C.; Williams, F.M.; Luo, W.; Cheng, J.; Wilson, M.H. Hydrodynamic Renal Pelvis Injection for Non-Viral Expression of Proteins in the Kidney. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2018, 8, 56324.
- Corridon, P.R.; Rhodes, G.J.; Leonard, E.C.; Basile, D.P.; Gattone, V.H.; Bacallao, R.L.; Atkinson, S.J. A Method to Facilitate and Monitor Expression of Exogenous Genes in the Rat Kidney Using Plasmid and Viral Vectors. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2013, 304, F1217–F1229.
- Maruyama, H.; Higuchi, N.; Kameda, S.; Nakamura, G.; Iguchi, S.; Miyazaki, J.-I.; Gejyo, F. Rat Kidney-Targeted Naked Plasmid DNA Transfer by Retrograde Injection into the Renal Vein. Mol. Biotechnol. 2004, 27, 23–31.
- Woodard, L.E.; Cheng, J.; Welch, R.C.; Williams, F.M.; Luo, W.; Gewin, L.S.; Wilson, M.H. Kidney-Specific Transposon-Mediated Gene Transfer in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 44904.
- Girardin, C.; Maze, D.; Gonçalves, C.; Le Guen, Y.T.; Pluchon, K.; Pichon, C.; Montier, T.; Midoux, P. Selective Attachment of a Microtubule Interacting Peptide to Plasmid DNA via a Triplex Forming Oligonucleotide for Transfection Improvement. Gene Ther. 2022; Online ahead of print.
- Guess, M.G.; Barthel, K.K.; Pugach, E.K.; Leinwand, L.A. Measuring MicroRNA Reporter Activity in Skeletal Muscle Using Hydrodynamic Limb Vein Injection of Plasmid DNA Combined with in Vivo Imaging. Skelet. Muscle 2013, 3, 19.
- Le Guen, Y.T.; Le Gall, T.; Midoux, P.; Guégan, P.; Braun, S.; Montier, T. Gene Transfer to Skeletal Muscle Using Hydrodynamic Limb Vein Injection: Current Applications, Hurdles and Possible Optimizations. J. Gene Med. 2020, 22, e3150.
- Liang, K.W.; Nishikawa, M.; Liu, F.; Sun, B.; Ye, Q.; Huang, L. Restoration of Dystrophin Expression in Mdx Mice by Intravascular Injection of Naked DNA Containing Full-Length Dystrophin CDNA. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 901–908.
- Nagata, K.; Itaka, K.; Baba, M.; Uchida, S.; Ishii, T.; Kataoka, K. Muscle-Targeted Hydrodynamic Gene Introduction of Insulin-like Growth Factor-1 Using Polyplex Nanomicelle to Treat Peripheral Nerve Injury. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2014, 183, 27–34.
- Yasuzaki, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Ishikawa, T.; Harashima, H. Validation of Mitochondrial Gene Delivery in Liver and Skeletal Muscle via Hydrodynamic Injection Using an Artificial Mitochondrial Reporter DNA Vector. Mol. Pharm. 2015, 12, 4311–4320.
- Yasuzaki, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Fukuda, Y.; Harashima, H. Condensation of Plasmid DNA Enhances Mitochondrial Association in Skeletal Muscle Following Hydrodynamic Limb Vein Injection. Pharmaceuticals 2014, 7, 881–893.
- Yasuzaki, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Kanefuji, T.; Harashima, H. Localization of Exogenous DNA to Mitochondria in Skeletal Muscle Following Hydrodynamic Limb Vein Injection. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2013, 172, 805–811.
- Sato, Y.; Ajiki, T.; Inoue, S.; Hakamata, Y.; Murakami, T.; Kaneko, T.; Takahashi, M.; Kobayashi, E. A Novel Gene Therapy to the Graft Organ by a Rapid Injection of Naked DNA I: Long-Lasting Gene Expression in a Rat Model of Limb Transplantation. Transplantation 2003, 76, 1294–1298.
- Budker, V.; Zhang, G.; Danko, I.; Williams, P.; Wolff, J. The Efficient Expression of Intravascularly Delivered DNA in Rat Muscle. Gene Ther. 1998, 5, 272–276.
- Danialou, G.; Comtois, A.S.; Matecki, S.; Nalbantoglu, J.; Karpati, G.; Gilbert, R.; Geoffroy, P.; Gilligan, S.; Tanguay, J.-F.; Petrof, B.J. Optimization of Regional Intraarterial Naked DNA-Mediated Transgene Delivery to Skeletal Muscles in a Large Animal Model. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2005, 11, 257–266.
- Bates, M.K.; Zhang, G.; Sebestyén, M.G.; Neal, Z.C.; Wolff, J.A.; Herweijer, H. Genetic Immunization for Antibody Generation in Research Animals by Intravenous Delivery of Plasmid DNA. BioTechniques 2006, 40, 199–208.
- Kamimura, K.; Zhang, G.; Liu, D. Image-Guided, Intravascular Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery to Skeletal Muscle in Pigs. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2010, 18, 93–100.
- Zhang, G.; Budker, V.; Williams, P.; Subbotin, V.; Wolff, J.A. Efficient Expression of Naked Dna Delivered Intraarterially to Limb Muscles of Nonhuman Primates. Hum. Gene Ther. 2001, 12, 427–438.
- Hagstrom, J.E.; Hegge, J.; Zhang, G.; Noble, M.; Budker, V.; Lewis, D.L.; Herweijer, H.; Wolff, J.A. A Facile Nonviral Method for Delivering Genes and SiRNAs to Skeletal Muscle of Mammalian Limbs. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2004, 10, 386–398.
- Ogawa, K.; Kamimura, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Abe, H.; Yokoo, T.; Sakai, N.; Nagoya, T.; Sakamaki, A.; Abe, S.; Hayashi, K.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of Pancreas-Targeted Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery in Rats. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2017, 9, 80–88.
- Tada, M.; Hatano, E.; Taura, K.; Nitta, T.; Koizumi, N.; Ikai, I.; Shimahara, Y. High Volume Hydrodynamic Injection of Plasmid DNA via the Hepatic Artery Results in a High Level of Gene Expression in Rat Hepatocellular Carcinoma Induced by Diethylnitrosamine. J. Gene Med. 2006, 8, 1018–1026.
- Barnett, F.H.; Scharer-Schuksz, M.; Wood, M.; Yu, X.; Wagner, T.E.; Friedlander, M. Intra-Arterial Delivery of Endostatin Gene to Brain Tumors Prolongs Survival and Alters Tumor Vessel Ultrastructure. Gene Ther. 2004, 11, 1283–1289.
- Mann, M.J.; Gibbons, G.H.; Hutchinson, H.; Poston, R.S.; Hoyt, E.G.; Robbins, R.C.; Dzau, V.J. Pressure-Mediated Oligonucleotide Transfection of Rat and Human Cardiovascular Tissues. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 6411–6416.
- Su, L.T.; Gopal, K.; Wang, Z.; Yin, X.; Nelson, A.; Kozyak, B.W.; Burkman, J.M.; Mitchell, M.A.; Low, D.W.; Bridges, C.R.; et al. Uniform Scale-Independent Gene Transfer to Striated Muscle after Transvenular Extravasation of Vector. Circulation 2005, 112, 1780–1788.
- McCaffrey, A.P.; Nakai, H.; Pandey, K.; Huang, Z.; Salazar, F.H.; Xu, H.; Wieland, S.F.; Marion, P.L.; Kay, M.A. Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus in Mice by RNA Interference. Nat. Biotechnol. 2003, 21, 639–644.
- Yang, P.L.; Althage, A.; Chung, J.; Chisari, F.V. Hydrodynamic Injection of Viral DNA: A Mouse Model of Acute Hepatitis B Virus Infection. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 13825–13830.
- Zhang, E.; Kosinska, A.D.; Ma, Z.; Dietze, K.K.; Xu, Y.; Meng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, B.; Dittmer, U.; et al. Woodchuck Hepatitis Virus Core Antigen-Based DNA and Protein Vaccines Induce Qualitatively Different Immune Responses That Affect T Cell Recall Responses and Antiviral Effects. Virology 2015, 475, 56–65.
- Huang, H.; Rückborn, M.; Le-Trilling, V.T.K.; Zhu, D.; Yang, S.; Zhou, W.; Yang, X.; Feng, X.; Lu, Y.; Lu, M.; et al. Prophylactic and Therapeutic HBV Vaccination by an HBs-Expressing Cytomegalovirus Vector Lacking an Interferon Antagonist in Mice. Eur. J. Immunol. 2021, 51, 393–407.
- Ho, C.; Wang, C.; Mattu, S.; Destefanis, G.; Ladu, S.; Delogu, S.; Armbruster, J.; Fan, L.; Lee, S.A.; Jiang, L.; et al. AKT (v-Akt Murine Thymoma Viral Oncogene Homolog 1) and N-Ras (Neuroblastoma Ras Viral Oncogene Homolog) Coactivation in the Mouse Liver Promotes Rapid Carcinogenesis by Way of MTOR (Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Complex 1), FOXM1 (Forkhead Box M1)/SKP2, and c-Myc Pathways. Hepatol. Baltim. Md. 2012, 55, 833–845.
- Engelholm, L.H.; Riaz, A.; Serra, D.; Dagnæs-Hansen, F.; Johansen, J.V.; Santoni-Rugiu, E.; Hansen, S.H.; Niola, F.; Frödin, M. CRISPR/Cas9 Engineering of Adult Mouse Liver Demonstrates That the Dnajb1-Prkaca Gene Fusion Is Sufficient to Induce Tumors Resembling Fibrolamellar Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1662–1673.e10.
- Moon, H.; Ju, H.-L.; Chung, S.I.; Cho, K.J.; Eun, J.W.; Nam, S.W.; Han, K.-H.; Calvisi, D.F.; Ro, S.W. Transforming Growth Factor-β Promotes Liver Tumorigenesis in Mice via Up-Regulation of Snail. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 1378–1391.e6.
- Gao, M.; Liu, D. CRISPR/Cas9-Based Pten Knock-out and Sleeping Beauty Transposon-Mediated Nras Knock-in Induces Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Hepatic Lipid Accumulation in Mice. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2017, 18, 505–512.
- Miao, C.H.; Thompson, A.R.; Loeb, K.; Ye, X. Long-Term and Therapeutic-Level Hepatic Gene Expression of Human Factor IX after Naked Plasmid Transfer in Vivo. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2001, 3, 947–957.
- Balestra, D.; Scalet, D.; Pagani, F.; Rogalska, M.E.; Mari, R.; Bernardi, F.; Pinotti, M. An Exon-Specific U1snRNA Induces a Robust Factor IX Activity in Mice Expressing Multiple Human FIX Splicing Mutants. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e370.
- Mashausi, D.S.; Roy, D.; Mangukiya, H.B.; Merugu, S.B.; Raza, G.; Yunus, F.-U.-N.; Liu, G.-S.; Negi, H.; Li, D. A High Efficient FVIII Variant Corrects Bleeding in Hemophilia A Mouse Model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 637, 358–364.
- Fu, R.Y.; Chen, A.C.; Lyle, M.J.; Chen, C.-Y.; Liu, C.L.; Miao, C.H. CD4+ T Cells Engineered with FVIII-CAR and Murine Foxp3 Suppress Anti-Factor VIII Immune Responses in Hemophilia a Mice. Cell. Immunol. 2020, 358, 104216.
- Huai, C.; Jia, C.; Sun, R.; Xu, P.; Min, T.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, C.; Chen, H.; Lu, D. CRISPR/Cas9-Mediated Somatic and Germline Gene Correction to Restore Hemostasis in Hemophilia B Mice. Hum. Genet. 2017, 136, 875–883.
- Mohammed, B.M.; Cheng, Q.; Matafonov, A.; Monroe, D.M.; Meijers, J.C.M.; Gailani, D. Factor XI Promotes Hemostasis in Factor IX-Deficient Mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2018, 16, 2044–2049.
- Yang, K.-L.; Hung, K.-C.; Chang, W.-T.; Li, E.I.C. Establishment of an Early Liver Fibrosis Model by the Hydrodynamics-Based Transfer of TGF-Beta1 Gene. Comp. Hepatol. 2007, 6, 9.
- Zhang, Z.; Yuan, Y.; Hu, L.; Tang, J.; Meng, Z.; Dai, L.; Gao, Y.; Ma, S.; Wang, X.; Yuan, Y.; et al. ANGPTL8 Accelerates Liver Fibrosis Mediated by HFD-Induced Inflammatory Activity via LILRB2/ERK Signaling Pathways. J. Adv. Res. 2022; Online ahead of print.
- Matsuda, M.; Tsurusaki, S.; Miyata, N.; Saijou, E.; Okochi, H.; Miyajima, A.; Tanaka, M. Oncostatin M Causes Liver Fibrosis by Regulating Cooperation between Hepatic Stellate Cells and Macrophages in Mice. Hepatol. Baltim. Md. 2018, 67, 296–312.
- Guo, Q.; Chen, M.; Chen, Q.; Xiao, G.; Chen, Z.; Wang, X.; Huang, Y. Silencing P53 Inhibits Interleukin 10-Induced Activated Hepatic Stellate Cell Senescence and Fibrotic Degradation in Vivo. Exp. Biol. Med. 2021, 246, 447–458.
- Liu, L.; Wang, P.; Wang, Y.-S.; Zhang, Y.-N.; Li, C.; Yang, Z.-Y.; Liu, Z.-H.; Zhan, T.-Z.; Xu, J.; Xia, C.-M. MiR-130a-3p Alleviates Liver Fibrosis by Suppressing HSCs Activation and Skewing Macrophage to Ly6Clo Phenotype. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 696069.
- Abe, H.; Kamimura, K.; Kobayashi, Y.; Ohtsuka, M.; Miura, H.; Ohashi, R.; Yokoo, T.; Kanefuji, T.; Suda, T.; Tsuchida, M.; et al. Effective Prevention of Liver Fibrosis by Liver-Targeted Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery of Matrix Metalloproteinase-13 in a Rat Liver Fibrosis Model. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 2016, 5, e276.
- McCaffrey, A.P.; Meuse, L.; Karimi, M.; Contag, C.H.; Kay, M.A. A Potent and Specific Morpholino Antisense Inhibitor of Hepatitis C Translation in Mice. Hepatology 2003, 38, 503–508.
- Zhu, W.; Wu, C.; Deng, W.; Pei, R.; Wang, Y.; Cao, L.; Qin, B.; Lu, M.; Chen, X. Inhibition of the HCV Core Protein on the Immune Response to HBV Surface Antigen and on HBV Gene Expression and Replication in Vivo. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e45146.
- Yu, W.; Grubor-Bauk, B.; Gargett, T.; Garrod, T.; Gowans, E.J. A Novel Challenge Model to Evaluate the Efficacy of Hepatitis C Virus Vaccines in Mice. Vaccine 2014, 32, 3409–3416.
- Duan, L.; Yan, Y.; Liu, J.; Wang, B.; Li, P.; Hu, Q.; Chen, W. Target Delivery of Small Interfering RNAs with Vitamin E-Coupled Nanoparticles for Treating Hepatitis C. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24867.
- Ahlén, G.; Sällberg, M.; Frelin, L. Methods for Monitoring Gene Gun-Induced HBV- and HCV-Specific Immune Responses in Mouse Models. Methods Mol. Biol. 2013, 940, 239–267.
- Nakai, M.; Oshiumi, H.; Funami, K.; Okamoto, M.; Matsumoto, M.; Seya, T.; Sakamoto, N. Interferon (IFN) and Cellular Immune Response Evoked in RNA-Pattern Sensing During Infection with Hepatitis C Virus (HCV). Sensors 2015, 15, 27160–27173.
- Fu, Q.; Yan, S.; Wang, L.; Duan, X.; Wang, L.; Wang, Y.; Wu, T.; Wang, X.; An, J.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Hepatic NK Cell-Mediated Hypersensitivity to ConA-Induced Liver Injury in Mouse Liver Expressing Hepatitis C Virus Polyprotein. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 52178–52192.
- Moyo, B.; Bloom, K.; Scott, T.; Ely, A.; Arbuthnot, P. Advances with Using CRISPR/Cas-Mediated Gene Editing to Treat Infections with Hepatitis B Virus and Hepatitis C Virus. Virus Res. 2018, 244, 311–320.
- Zhang, W.; Meyfeldt, J.; Wang, H.; Kulkarni, S.; Lu, J.; Mandel, J.A.; Marburger, B.; Liu, Y.; Gorka, J.E.; Ranganathan, S.; et al. β-Catenin Mutations as Determinants of Hepatoblastoma Phenotypes in Mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2019, 294, 17524–17542.
- Smith, J.L.; Rodríguez, T.C.; Mou, H.; Kwan, S.-Y.; Pratt, H.; Zhang, X.-O.; Cao, Y.; Liang, S.; Ozata, D.M.; Yu, T.; et al. YAP1 Withdrawal in Hepatoblastoma Drives Therapeutic Differentiation of Tumor Cells to Functional Hepatocyte-Like Cells. Hepatol. Baltim. Md. 2021, 73, 1011–1027.
- Wang, D.; Tian, J.; Yan, Z.; Yuan, Q.; Wu, D.; Liu, X.; Yang, S.; Guo, S.; Wang, J.; Yang, Y.; et al. Mitochondrial Fragmentation Is Crucial for C-Myc-Driven Hepatoblastoma-like Liver Tumors. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2022, 30, 1645–1660.
- Jin, L.; Jiang, Q.; Wu, Z.; Shao, C.; Zhou, Y.; Yang, L.; Uitto, J.; Wang, G. Genetic Heterogeneity of Pseudoxanthoma Elasticum: The Chinese Signature Profile of ABCC6 and ENPP1 Mutations. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 135, 1294–1302.
- Wang, H.; Chen, X. Hydrodynamic Injection for Developing NASH Model. Methods Mol. Biol. 2022, 2455, 31–39.
- Cheng, Y.-W.; Chen, K.-W.; Kuo, H.-C.; Kuo, C.-H.; Lin, W.-H.; Chen, P.-J.; Yeh, S.-H. Specific Diacylglycerols Generated by Hepatic Lipogenesis Stimulate the Oncogenic Androgen Receptor Activity in Male Hepatocytes. Int. J. Obes. 2019, 43, 2469–2479.
- Chai, C.; Cox, B.; Yaish, D.; Gross, D.; Rosenberg, N.; Amblard, F.; Shemuelian, Z.; Gefen, M.; Korach, A.; Tirosh, O.; et al. Agonist of RORA Attenuates Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Progression in Mice via Up-Regulation of MicroRNA 122. Gastroenterology 2020, 159, 999–1014.e9.
- Yano, K.; Yamaguchi, K.; Seko, Y.; Okishio, S.; Ishiba, H.; Tochiki, N.; Takahashi, A.; Kataoka, S.; Okuda, K.; Liu, Y.; et al. Hepatocyte-Specific Fibroblast Growth Factor 21 Overexpression Ameliorates High-Fat Diet-Induced Obesity and Liver Steatosis in Mice. Lab. Investig. J. Tech. Methods Pathol. 2022, 102, 281–289.
- Chang, J.; Sigal, L.J.; Lerro, A.; Taylor, J. Replication of the Human Hepatitis Delta Virus Genome Is Initiated in Mouse Hepatocytes Following Intravenous Injection of Naked DNA or RNA Sequences. J. Virol. 2001, 75, 3469–3473.
- Chen, X.; Calvisi, D.F. Hydrodynamic Transfection for Generation of Novel Mouse Models for Liver Cancer Research. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 912–923.
- Wang, J.; Wang, H.; Peters, M.; Ding, N.; Ribback, S.; Utpatel, K.; Cigliano, A.; Dombrowski, F.; Xu, M.; Chen, X.; et al. Loss of Fbxw7 Synergizes with Activated Akt Signaling to Promote C-Myc Dependent Cholangiocarcinogenesis. J. Hepatol. 2019, 71, 742–752.
- Zhang, J.; Chen, W.; Ma, W.; Song, K.; Lee, S.; Han, C.; Wu, T. Epigenetic Silencing of 15-Hydroxyprostaglandin Dehydrogenase by Histone Methyltransferase EHMT2/G9a in Cholangiocarcinoma. Mol. Cancer Res. MCR 2022, 20, 350–360.
- Zhang, Y.; Xu, H.; Cui, G.; Liang, B.; Chen, X.; Ko, S.; Affo, S.; Song, X.; Liao, Y.; Feng, J.; et al. β-Catenin Sustains and Is Required for YES-Associated Protein Oncogenic Activity in Cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 481–494.
- Navarrete, A.-M.; Casari, C.; Legendre, P.; Marx, I.; Hu, J.-R.; Lenting, P.J.; Christophe, O.D.; Denis, C.V. A Murine Model to Characterize the Antithrombotic Effect of Molecules Targeting Human von Willebrand Factor. Blood 2012, 120, 2723–2732.
- Legendre, P.; Navarrete, A.-M.; Rayes, J.; Casari, C.; Boisseau, P.; Ternisien, C.; Caron, C.; Fressinaud, E.; Goudemand, J.; Veyradier, A.; et al. Mutations in the A3 Domain of von Willebrand Factor Inducing Combined Qualitative and Quantitative Defects in the Protein. Blood 2013, 121, 2135–2143.
- Pruss, C.M.; Golder, M.; Bryant, A.; Hegadorn, C.; Haberichter, S.; Lillicrap, D. Use of a Mouse Model to Elucidate the Phenotypic Effects of the von Willebrand Factor Cleavage Mutants, Y1605A/M1606A and R1597W. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2012, 10, 940–950.
- Swystun, L.L.; Georgescu, I.; Mewburn, J.; Deforest, M.; Nesbitt, K.; Hebert, K.; Dwyer, C.; Brown, C.; Notley, C.; Lillicrap, D. Abnormal von Willebrand Factor Secretion, Factor VIII Stabilization and Thrombus Dynamics in Type 2N von Willebrand Disease Mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2017, 15, 1607–1619.
- Wang, Y.; Wu, T.; Hu, D.; Weng, X.; Wang, X.; Chen, P.-J.; Luo, X.; Wang, H.; Ning, Q. Intracellular Hepatitis B Virus Increases Hepatic Cholesterol Deposition in Alcoholic Fatty Liver via Hepatitis B Core Protein. J. Lipid Res. 2018, 59, 58–68.
- Zhang, Y.-Y.; Li, S.-Q.; Song, Y.; Wang, P.; Song, X.-G.; Zhu, W.-F.; Wang, D.-M. Silencing the ADAM9 Gene through CRISPR/Cas9 Protects Mice from Alcohol-Induced Acute Liver Injury. BioMed Res. Int. 2022, 2022, 5110161.
- Yamazaki, T.; Nagashima, M.; Ninomiya, D.; Ainai, A.; Fujimoto, A.; Ichimonji, I.; Takagi, H.; Morita, N.; Murotani, K.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. Neutralizing Antibodies Induced by Gene-Based Hydrodynamic Injection Have a Therapeutic Effect in Lethal Influenza Infection. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 47.
- Lin, Y.; Wu, C.; Wang, X.; Liu, S.; Zhao, K.; Kemper, T.; Yu, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, M.; et al. Glucosamine Promotes Hepatitis B Virus Replication through Its Dual Effects in Suppressing Autophagic Degradation and Inhibiting MTORC1 Signaling. Autophagy 2020, 16, 548–561.
- Ochoa, M.C.; Fioravanti, J.; Duitman, E.H.; Medina-Echeverz, J.; Palazon, A.; Arina, A.; Dubrot, J.; Alfaro, C.; Morales-Kastresana, A.; Murillo, O.; et al. Liver Gene Transfer of Interkeukin-15 Constructs That Become Part of Circulating High Density Lipoproteins for Immunotherapy. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e52370.
- Cheng, L.; Du, X.; Wang, Z.; Ju, J.; Jia, M.; Huang, Q.; Xing, Q.; Xu, M.; Tan, Y.; Liu, M.; et al. Hyper-IL-15 Suppresses Metastatic and Autochthonous Liver Cancer by Promoting Tumour-Specific CD8+ T Cell Responses. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 1297–1303.
- Miyakawa, N.; Nishikawa, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Ando, M.; Misaka, M.; Watanabe, Y.; Takakura, Y. Gene Delivery of Albumin Binding Peptide-Interferon-Gamma Fusion Protein with Improved Pharmacokinetic Properties and Sustained Biological Activity. J. Pharm. Sci. 2013, 102, 3110–3118.
- Desch, K.C.; Kretz, C.; Yee, A.; Gildersleeve, R.; Metzger, K.; Agrawal, N.; Cheng, J.; Ginsburg, D. Probing ADAMTS13 Substrate Specificity Using Phage Display. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0122931.
- Verhenne, S.; Vandeputte, N.; Pareyn, I.; Izsvák, Z.; Rottensteiner, H.; Deckmyn, H.; De Meyer, S.F.; Vanhoorelbeke, K. Long-Term Prevention of Congenital Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in ADAMTS13 Knockout Mice by Sleeping Beauty Transposon-Mediated Gene Therapy. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2017, 37, 836–844.
- De Cock, E.; Hermans, C.; De Raeymaecker, J.; De Ceunynck, K.; De Maeyer, B.; Vandeputte, N.; Vandenbulcke, A.; Deckmyn, H.; Rottensteiner, H.; De Maeyer, M.; et al. The Novel ADAMTS13-p.D187H Mutation Impairs ADAMTS13 Activity and Secretion and Contributes to Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura in Mice. J. Thromb. Haemost. JTH 2015, 13, 283–292.
- Ostertag, E.M.; Bdeir, K.; Kacir, S.; Thiboutot, M.; Gulendran, G.; Yunk, L.; Hayes, V.M.; Motto, D.G.; Poncz, M.; Zheng, X.L.; et al. ADAMTS13 Autoantibodies Cloned from Patients with Acquired Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura: 2. Pathogenicity in an Animal Model. Transfusion 2016, 56, 1775–1785.
- Mookerjee, R.P.; Mehta, G.; Balasubramaniyan, V.; Mohamed, F.E.Z.; Davies, N.; Sharma, V.; Iwakiri, Y.; Jalan, R. Hepatic Dimethylarginine-Dimethylaminohydrolase1 Is Reduced in Cirrhosis and Is a Target for Therapy in Portal Hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 325–331.
- Qin, B.; Yan, Q.; Chen, X.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J.; Dong, X. Enterovirus 71 Infection Impairs the Reproductive Capacity of Female Mice. Exp. Ther. Med. 2017, 14, 403–409.
- Sun, H.; Liu, D. IL-15/SIL-15Rα Gene Transfer Suppresses Lewis Lung Cancer Growth in the Lungs, Liver and Kidneys. Cancer Gene Ther. 2016, 23, 54–60.
- Schuh, R.S.; Poletto, É.; Pasqualim, G.; Tavares, A.M.V.; Meyer, F.S.; Gonzalez, E.A.; Giugliani, R.; Matte, U.; Teixeira, H.F.; Baldo, G. In Vivo Genome Editing of Mucopolysaccharidosis I Mice Using the CRISPR/Cas9 System. J. Control. Release Off. J. Control. Release Soc. 2018, 288, 23–33.
- Richard, M.; Arfi, A.; Seguin, J.; Gandolphe, C.; Scherman, D. Widespread Biochemical Correction of Murine Mucopolysaccharidosis Type VII Pathology by Liver Hydrodynamic Plasmid Delivery. Gene Ther. 2009, 16, 746–756.
- Huang, M.; Sun, R.; Wei, H.; Tian, Z. Simultaneous Knockdown of Multiple Ligands of Innate Receptor NKG2D Prevents Natural Killer Cell-Mediated Fulminant Hepatitis in Mice. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 2013, 57, 277–288.
- Saito, Y.; Kon, S.; Fujiwara, Y.; Nakayama, Y.; Kurotaki, D.; Fukuda, N.; Kimura, C.; Kanayama, M.; Ito, K.; Diao, H.; et al. Osteopontin Small Interfering RNA Protects Mice from Fulminant Hepatitis. Hum. Gene Ther. 2007, 18, 1205–1214.
- Tsai, S.-M.; Wang, W.-P. Expression and Function of Fibroblast Growth Factor (FGF) 7 during Liver Regeneration. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2011, 27, 641–652.
- Chen, L.; Keitany, G.J.; Peng, X.; Gibson, C.; Mohar, I.; Vignali, M.; Crispe, I.N.; Huang, F.; Wang, R. Identification of Pre-Erythrocytic Malaria Antigens That Target Hepatocytes for Killing in Vivo and Contribute to Protection Elicited by Whole-Parasite Vaccination. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e102225.
- Rai, U.; Huang, J.; Mishra, S.; Li, X.; Shiratsuchi, T.; Tsuji, M. A New Method to Determine Antigen-Specific CD8+ T Cell Activity in Vivo by Hydrodynamic Injection. Biomolecules 2012, 2, 23–33.
- Yamazaki, T.; Chiba, J.; Akashi-Takamura, S. Neutralizing Anti-Hemagglutinin Monoclonal Antibodies Induced by Gene-Based Transfer Have Prophylactic and Therapeutic Effects on Influenza Virus Infection. Vaccines 2018, 6, 35.
- Viecelli, H.M.; Harbottle, R.P.; Wong, S.P.; Schlegel, A.; Chuah, M.K.; VandenDriessche, T.; Harding, C.O.; Thöny, B. Treatment of Phenylketonuria Using Minicircle-Based Naked-DNA Gene Transfer to Murine Liver. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 2014, 60, 1035–1043.
- Geng, J.; Wang, X.; Wei, H.; Sun, R.; Tian, Z. Efficient Attenuation of NK Cell-Mediated Liver Injury through Genetically Manipulating Multiple Immunogenes by Using a Liver-Directed Vector. J. Immunol. Baltim. Md 2013, 190, 4821–4829.
- Sun, Z.; Wang, Q.; Sun, L.; Wu, M.; Li, S.; Hua, H.; Sun, Y.; Ni, T.; Zhou, C.; Huang, S.; et al. Acetaminophen-Induced Reduction of NIMA-Related Kinase 7 Expression Exacerbates Acute Liver Injury. JHEP Rep. Innov. Hepatol. 2022, 4, 100545.
- Pang, X.; Ma, F.; Zhang, P.; Zhong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Wang, T.; Zheng, G.; Hou, X.; Zhao, J.; He, C.; et al. Treatment of Human B-Cell Lymphomas Using Minicircle DNA Vector Expressing Anti-CD3/CD20 in a Mouse Model. Hum. Gene Ther. 2017, 28, 216–225.
- Yin, H.; Xue, W.; Chen, S.; Bogorad, R.L.; Benedetti, E.; Grompe, M.; Koteliansky, V.; Sharp, P.A.; Jacks, T.; Anderson, D.G. Genome Editing with Cas9 in Adult Mice Corrects a Disease Mutation and Phenotype. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 551–553.
- Song, C.-Q.; Jiang, T.; Richter, M.; Rhym, L.H.; Koblan, L.W.; Zafra, M.P.; Schatoff, E.M.; Doman, J.L.; Cao, Y.; Dow, L.E.; et al. Adenine Base Editing in an Adult Mouse Model of Tyrosinaemia. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 4, 125–130.
- Liu, B.; Dong, X.; Cheng, H.; Zheng, C.; Chen, Z.; Rodríguez, T.C.; Liang, S.-Q.; Xue, W.; Sontheimer, E.J. A Split Prime Editor with Untethered Reverse Transcriptase and Circular RNA Template. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1388–1393.
- Lu, S.-L.; Tsai, C.-Y.; Luo, Y.-H.; Kuo, C.-F.; Lin, W.-C.; Chang, Y.-T.; Wu, J.-J.; Chuang, W.-J.; Liu, C.-C.; Chao, L.; et al. Kallistatin Modulates Immune Cells and Confers Anti-Inflammatory Response to Protect Mice from Group A Streptococcal Infection. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2013, 57, 5366–5372.
- Cueto, F.J.; Del Fresno, C.; Brandi, P.; Combes, A.J.; Hernández-García, E.; Sánchez-Paulete, A.R.; Enamorado, M.; Bromley, C.P.; Gomez, M.J.; Conde-Garrosa, R.; et al. DNGR-1 Limits Flt3L-Mediated Antitumor Immunity by Restraining Tumor-Infiltrating Type I Conventional Dendritic Cells. J. Immunother. Cancer 2021, 9, e002054.
- Mecozzi, N.; Nenci, A.; Vera, O.; Bok, I.; Falzone, A.; DeNicola, G.M.; Karreth, F.A. Genetic Tools for the Stable Overexpression of Circular RNAs. RNA Biol. 2022, 19, 353–363.
- Jang, H.; Jo, D.H.; Cho, C.S.; Shin, J.H.; Seo, J.H.; Yu, G.; Gopalappa, R.; Kim, D.; Cho, S.-R.; Kim, J.H.; et al. Application of Prime Editing to the Correction of Mutations and Phenotypes in Adult Mice with Liver and Eye Diseases. Nat. Biomed. Eng. 2022, 6, 181–194.
- Leys, L.; Wang, Y.; Paulsboe, S.; Edelmayer, R.; Salte, K.; Wetter, J.; Namovic, M.; Phillips, L.; Dunstan, R.; Gauvin, D.; et al. Characterization of Psoriasiform Dermatitis Induced by Systemic Injection of Interleukin-23 Minicircles in Mice. J. Dermatol. 2019, 46, 482–497.
- Mencarelli, A.; Gunawan, M.; Yong, K.S.M.; Bist, P.; Tan, W.W.S.; Tan, S.Y.; Liu, M.; Huang, E.K.; Fan, Y.; Chan, J.K.Y.; et al. A Humanized Mouse Model to Study Mast Cells Mediated Cutaneous Adverse Drug Reactions. J. Leukoc. Biol. 2020, 107, 797–807.
- Noti, M.; Kim, B.S.; Siracusa, M.C.; Rak, G.D.; Kubo, M.; Moghaddam, A.E.; Sattentau, Q.A.; Comeau, M.R.; Spergel, J.M.; Artis, D. Exposure to Food Allergens through Inflamed Skin Promotes Intestinal Food Allergy through the Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin-Basophil Axis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 1390–1399.e1–e6.
- Watcharanurak, K.; Nishikawa, M.; Takahashi, Y.; Kabashima, K.; Takahashi, R.; Takakura, Y. Regulation of Immunological Balance by Sustained Interferon-γ Gene Transfer for Acute Phase of Atopic Dermatitis in Mice. Gene Ther. 2013, 20, 538–544.
- Wesche-Soldato, D.E.; Lomas-Neira, J.; Perl, M.; Chung, C.-S.; Ayala, A. Hydrodynamic Delivery of SiRNA in a Mouse Model of Sepsis. Methods Mol. Biol. 2008, 442, 67–73.
- Alhamhoom, Y.; Zhang, G.; Gao, M.; Cai, H.; Liu, D. In Vivo Growth and Responses to Treatment of Renal Cell Carcinoma in Different Environments. Am. J. Cancer Res. 2017, 7, 301–311.
- Li, J.; Yao, Q.; Liu, D. Hydrodynamic Cell Delivery for Simultaneous Establishment of Tumor Growth in Mouse Lung, Liver and Kidney. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2011, 12, 737–741.
- Vercellotti, G.M.; Khan, F.B.; Nguyen, J.; Chen, C.; Bruzzone, C.M.; Bechtel, H.; Brown, G.; Nath, K.A.; Steer, C.J.; Hebbel, R.P.; et al. H-Ferritin Ferroxidase Induces Cytoprotective Pathways and Inhibits Microvascular Stasis in Transgenic Sickle Mice. Front. Pharmacol. 2014, 5, 79.
- Louet, E.R.; Glavan, M.; Orset, C.; Parcq, J.; Hanley, D.F.; Vivien, D. TPA-NMDAR Signaling Blockade Reduces the Incidence of Intracerebral Aneurysms. Transl. Stroke Res. 2022, 13, 1005–1016.
- Zhang, G.; Marshall, A.L.; Thomas, A.L.; Kernan, K.A.; Su, Y.; LeBoeuf, R.C.; Dong, X.R.; Tchao, B.N.A. In Vivo Knockdown of Nicotinic Acetylcholine Receptor A1 Diminishes Aortic Atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2011, 215, 34–42.
- Brampton, C.; Aherrahrou, Z.; Chen, L.-H.; Martin, L.; Bergen, A.A.B.; Gorgels, T.G.M.F.; Erdmann, J.; Erdfdi, J.; Schunkert, H.; Szabó, Z.; et al. The Level of Hepatic ABCC6 Expression Determines the Severity of Calcification after Cardiac Injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2014, 184, 159–170.
- Chen, I.Y.; Paulmurugan, R.; Nielsen, C.H.; Wang, D.S.; Chow, V.; Robbins, R.C.; Gambhir, S.S. A Titratable Two-Step Transcriptional Amplification Strategy for Targeted Gene Therapy Based on Ligand-Induced Intramolecular Folding of a Mutant Human Estrogen Receptor. Mol. Imaging Biol. 2014, 16, 224–234.
- Wu, S.; Zhang, J.; Huang, C.; Jia, H.; Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Yang, L.; Miyagishi, M.; Kasim, V. Prolyl Hydroxylase Domain-2 Silencing Induced by Hydrodynamic Limb Vein Injection Enhances Vascular Regeneration in Critical Limb Ischemia Mice through Activation of Multiple Genes. Curr. Gene Ther. 2015, 15, 313–325.
- Wang, C.-H.; Liang, C.-L.; Huang, L.-T.; Liu, J.-K.; Hung, P.-H.; Sun, A.; Hung, K.-S. Single Intravenous Injection of Naked Plasmid DNA Encoding Erythropoietin Provides Neuroprotection in Hypoxia-Ischemia Rats. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2004, 314, 1064–1071.
- Shin, Y.J.; Luo, K.; Quan, Y.; Ko, E.J.; Chung, B.H.; Lim, S.W.; Yang, C.W. Therapeutic Challenge of Minicircle Vector Encoding Klotho in Animal Model. Am. J. Nephrol. 2019, 49, 413–424.
- Thomson, R.; Molina-Portela, P.; Mott, H.; Carrington, M.; Raper, J. Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery of Baboon Trypanosome Lytic Factor Eliminates Both Animal and Human-Infective African Trypanosomes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 19509–19514.
- Lee, H.-O.; Gallego-Villar, L.; Grisch-Chan, H.M.; Häberle, J.; Thöny, B.; Kruger, W.D. Treatment of Cystathionine β-Synthase Deficiency in Mice Using a Minicircle-Based Naked DNA Vector. Hum. Gene Ther. 2019, 30, 1093–1100.
- Higuchi, N.; Maruyama, H.; Kuroda, T.; Kameda, S.; Iino, N.; Kawachi, H.; Nishikawa, Y.; Hanawa, H.; Tahara, H.; Miyazaki, J.; et al. Hydrodynamics-Based Delivery of the Viral Interleukin-10 Gene Suppresses Experimental Crescentic Glomerulonephritis in Wistar-Kyoto Rats. Gene Ther. 2003, 10, 1297–1310.
- Bu, X.; Zhou, Y.; Zhang, H.; Qiu, W.; Chen, L.; Cao, H.; Fang, L.; Wen, P.; Tan, R.; Yang, J. Systemic Administration of Naked Plasmid Encoding HGF Attenuates Puromycin Aminonucleoside-Induced Damage of Murine Glomerular Podocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Renal Physiol. 2011, 301, F784–F792.
- Yokoi, H.; Mukoyama, M.; Nagae, T.; Mori, K.; Suganami, T.; Sawai, K.; Yoshioka, T.; Koshikawa, M.; Nishida, T.; Takigawa, M.; et al. Reduction in Connective Tissue Growth Factor by Antisense Treatment Ameliorates Renal Tubulointerstitial Fibrosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. JASN 2004, 15, 1430–1440.
- Lee, S.; Hong, S.W.; Choi, H.S.; Lee, L.Y.; Nam, C.; Rhee, Y.; Chung, U.; Lim, S.-K. Experimental Parathyroid Hormone Gene Therapy Using ØC31 Integrase. Endocr. J. 2008, 55, 1033–1041.
- Nakamura, G.; Maruyama, H.; Ishii, S.; Shimotori, M.; Kameda, S.; Kono, T.; Miyazaki, J.; Kulkarni, A.B.; Gejyo, F. Naked Plasmid DNA-Based Alpha-Galactosidase A Gene Transfer Partially Reduces Systemic Accumulation of Globotriaosylceramide in Fabry Mice. Mol. Biotechnol. 2008, 38, 109–119.
- Jiang, J.; Yamato, E.; Miyazaki, J. Long-Term Control of Food Intake and Body Weight by Hydrodynamics-Based Delivery of Plasmid DNA Encoding Leptin or CNTF. J. Gene Med. 2003, 5, 977–983.
- Fukushima, M.; Hattori, Y.; Tsukada, H.; Koga, K.; Kajiwara, E.; Kawano, K.; Kobayashi, T.; Kamata, K.; Maitani, Y. Adiponectin Gene Therapy of Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetic Mice Using Hydrodynamic Injection. J. Gene Med. 2007, 9, 976–985.
- Yang, X.-F.; Wang, H.-Y.; Lu, W.-L.; Ma, W.; Zhang, H.; Li, F.-R. Direct Reprogramming of Hepatocytes into Insulin-Producing Cells for Anti-Diabetic Treatment by Ultrasound-Targeted Microbubble Destruction Enhanced Hydrodynamic Gene Delivery. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2020, 12, 7275–7286.
- Peng, W.; Zhou, X.; Xu, T.; Mao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Liang, L.; Liu, L.; Liu, L.; Xiao, Y.; et al. BMP-7 Ameliorates Partial Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by Restoring SnoN Protein Level via Smad1/5 Pathway in Diabetic Kidney Disease. Cell Death Dis. 2022, 13, 254.
- Zhang, G.; Song, Y.K.; Liu, D. Long-Term Expression of Human Alpha1-Antitrypsin Gene in Mouse Liver Achieved by Intravenous Administration of Plasmid DNA Using a Hydrodynamics-Based Procedure. Gene Ther. 2000, 7, 1344–1349.
- Sun, K.; Yang, W.; Huang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Xiang, L.; Qi, J. Leu452His Mutation in Lipoprotein Lipase Gene Transfer Associated with Hypertriglyceridemia in Mice in Vivo. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e75462.
- Sondergaard, M.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Flyvbjerg, A.; Jensen, T.G. Normalization of Growth in Hypophysectomized Mice Using Hydrodynamic Transfer of the Human Growth Hormone Gene. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 2003, 285, E427–E432.
- Elnaggar, R.; Hanawa, H.; Liu, H.; Yoshida, T.; Hayashi, M.; Watanabe, R.; Abe, S.; Toba, K.; Yoshida, K.; Chang, H.; et al. The Effect of Hydrodynamics-Based Delivery of an IL-13-Ig Fusion Gene for Experimental Autoimmune Myocarditis in Rats and Its Possible Mechanism. Eur. J. Immunol. 2005, 35, 1995–2005.
- Effect of Hydrodynamics-Based Gene Delivery of Plasmid DNA Encoding Interleukin-1 Receptor Antagonist-Ig for Treatment of Rat Autoimmune Myocarditis: Possible Mechanism for Lymphocytes and Noncardiac Cells—PubMed. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/15795329/ (accessed on 20 December 2022).
- Shigekawa, M.; Hikita, H.; Kodama, T.; Shimizu, S.; Li, W.; Uemura, A.; Miyagi, T.; Hosui, A.; Kanto, T.; Hiramatsu, N.; et al. Pancreatic STAT3 Protects Mice against Caerulein-Induced Pancreatitis via PAP1 Induction. Am. J. Pathol. 2012, 181, 2105–2113.
- Shashidharamurthy, R.; Machiah, D.; Bozeman, E.N.; Srivatsan, S.; Patel, J.; Cho, A.; Jacob, J.; Selvaraj, P. Hydrodynamic Delivery of Plasmid DNA Encoding Human FcγR-Ig Dimers Blocks Immune-Complex Mediated Inflammation in Mice. Gene Ther. 2012, 19, 877–885.
- Okumura, A.; Saito, T.; Otani, I.; Kojima, K.; Yamada, Y.; Ishida-Okawara, A.; Nakazato, K.; Asano, M.; Kanayama, K.; Iwakura, Y.; et al. Suppressive Role of Leukocyte Cell-Derived Chemotaxin 2 in Mouse Anti-Type II Collagen Antibody-Induced Arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2008, 58, 413–421.
- Takakusaki, Y.; Hisayasu, S.; Hirai, Y.; Shimada, T. Coexpression of Formylglycine-Generating Enzyme Is Essential for Synthesis and Secretion of Functional Arylsulfatase A in a Mouse Model of Metachromatic Leukodystrophy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2005, 16, 929–936.
- Liu, H.C.; Zhao, H.; Chen, J.; Wu, W.L.; Wang, H.L.; Jiao, G.J.; Chen, Y.Z. Role of Recombinant Plasmid PEGFP-N1-IGF-1 Transfection in Alleviating Osteoporosis in Ovariectomized Rats. J. Mol. Histol. 2013, 44, 535–544.
- Holm, D.A.; Dagnaes-Hansen, F.; Simonsen, H.; Gregersen, N.; Bolund, L.; Jensen, T.G.; Corydon, T.J. Expression of Short-Chain Acyl-CoA Dehydrogenase (SCAD) Proteins in the Liver of SCAD Deficient Mice after Hydrodynamic Gene Transfer. Mol. Genet. Metab. 2003, 78, 250–258.
- Miki, Y.; Maruyama, S.; Liu, D.; Kobayashi, T.; Sato, F.; Shimizu, H.; Kato, S.; Sato, W.; Morita, Y.; Yuzawa, Y.; et al. In Vivo Gene Transfer of Endo-Beta-Galactosidase C Removes AlphaGal Antigen on Erythrocytes and Endothelial Cells of the Organs. Xenotransplantation 2004, 11, 444–451.
- Fu, A.L.; Wang, Y.X.; Sun, M.J. Naked DNA Prevents Soman Intoxication. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2005, 328, 901–905.
- Zhang, G.; Ludtke, J.J.; Thioudellet, C.; Kleinpeter, P.; Antoniou, M.; Herweijer, H.; Braun, S.; Wolff, J.A. Intraarterial Delivery of Naked Plasmid DNA Expressing Full-Length Mouse Dystrophin in the Mdx Mouse Model of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy. Hum. Gene Ther. 2004, 15, 770–782.
- Ren, D.; Liu, W.; Ding, S.; Li, Y. Protocol for Generating Human Immune System Mice and Hydrodynamic Injection to Analyze Human Hematopoiesis in Vivo. STAR Protoc. 2022, 3, 101217.
- Umemoto, Y.; Kawakami, S.; Otani, Y.; Higuchi, Y.; Yamashita, F.; Hashida, M. Evaluation of Long-Term Gene Expression in Mouse Liver Using PhiC31 Integrase and Hydrodynamic Injection. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2012, 35, 1182–1186.
- Li, Y.; Xie, J.; Xu, X.; Liu, L.; Wan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhu, C.; Zhu, Y. Inducible Interleukin 32 (IL-32) Exerts Extensive Antiviral Function via Selective Stimulation of Interferon Λ1 (IFN-Λ1). J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 20927–20941.
- Zahm, A.M.; Wang, A.W.; Wang, Y.J.; Schug, J.; Wangensteen, K.J.; Kaestner, K.H. A High-Content Screen Identifies MicroRNAs That Regulate Liver Repopulation After Injury in Mice. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1044–1057.e17.
- Liu, N.; Chang, C.W.; Steer, C.J.; Wang, X.W.; Song, G. MicroRNA-15a/16-1 Prevents Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Disrupting the Communication Between Kupffer Cells and Regulatory T Cells. Gastroenterology 2022, 162, 575–589.
- Liu, N.; Wang, X.; Steer, C.J.; Song, G. MicroRNA-206 Promotes the Recruitment of CD8+ T Cells by Driving M1 Polarisation of Kupffer Cells. Gut 2022, 71, 1642–1655.
- Molina, L.; Yang, H.; Adebayo Michael, A.O.; Oertel, M.; Bell, A.; Singh, S.; Chen, X.; Tao, J.; Monga, S.P.S. MTOR Inhibition Affects Yap1-β-Catenin-Induced Hepatoblastoma Growth and Development. Oncotarget 2019, 10, 1475–1490.
- Ding, N.; Che, L.; Li, X.-L.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, L.-J.; Fan, B.; Tao, J.-Y.; Chen, X.; Ji, J.-F. Oncogenic Potential of IDH1R132C Mutant in Cholangiocarcinoma Development in Mice. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 2071–2080.
- Hubner, E.K.; Lechler, C.; Rösner, T.N.; Kohnke-Ertel, B.; Schmid, R.M.; Ehmer, U. Constitutive and Inducible Systems for Genetic In Vivo Modification of Mouse Hepatocytes Using Hydrodynamic Tail Vein Injection. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2018, 132, e56613.
- Hu, S.; Molina, L.; Tao, J.; Liu, S.; Hassan, M.; Singh, S.; Poddar, M.; Bell, A.; Sia, D.; Oertel, M.; et al. NOTCH-YAP1/TEAD-DNMT1 Axis Drives Hepatocyte Reprogramming Into Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Gastroenterology 2022, 163, 449–465.
- Cao, X.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Sun, S.; He, M.; Wang, X.; Ma, P.; Yang, X.; Lv, L.; Zhan, L. Establishment of a Novel Mouse Hepatocellular Carcinoma Model for Dynamic Monitoring of Tumor Development by Bioluminescence Imaging. Front. Oncol. 2022, 12, 794101.
- Ju, H.-L.; Ahn, S.H.; Kim, D.Y.; Baek, S.; Chung, S.I.; Seong, J.; Han, K.-H.; Ro, S.W. Investigation of Oncogenic Cooperation in Simple Liver-Specific Transgenic Mouse Models Using Noninvasive in Vivo Imaging. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59869.
- Mezzanotte, L.; Blankevoort, V.; Löwik, C.W.G.M.; Kaijzel, E.L. A Novel Luciferase Fusion Protein for Highly Sensitive Optical Imaging: From Single-Cell Analysis to in Vivo Whole-Body Bioluminescence Imaging. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2014, 406, 5727–5734.
- Fumoto, S.; Nishimura, K.; Nishida, K.; Kawakami, S. Three-Dimensional Imaging of the Intracellular Fate of Plasmid DNA and Transgene Expression: ZsGreen1 and Tissue Clearing Method CUBIC Are an Optimal Combination for Multicolor Deep Imaging in Murine Tissues. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0148233.
- Staber, J.M.; Pollpeter, M.J.; Arensdorf, A.; Sinn, P.L.; Rutkowski, D.T.; McCray, P.B. PiggyBac-Mediated Phenotypic Correction of Factor VIII Deficiency. Mol. Ther. Methods Clin. Dev. 2014, 1, 14042.
- Díaz-Rivera, A.; Meza-Ríos, A.; Chagoya de Sánchez, V.; Velasco-Loyden, G.; García-Benavides, L.; Jave-Suarez, L.F.; Monroy-Ramirez, H.C.; Santos-García, A.; Armendáriz-Borunda, J.; Sandoval-Rodríguez, A. Hydrodynamics-Based Liver Transfection Achieves Gene Silencing of CB1 Using Short Hairpin RNA Plasmid in Cirrhotic Rats. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0228729.
- Wang, Z.; Xiao, H.; Dong, J.; Li, Y.; Wang, B.; Chen, Z.; Zeng, X.; Liu, J.; Dong, Y.; Ma, L.; et al. Sexual Dimorphism in Gut Microbiota Dictates Therapeutic Efficacy of Intravenous Immunoglobulin on Radiotherapy Complications. J. Adv. Res. 2022; in press.
- Nakamura, S.; Maehara, T.; Watanabe, S.; Ishihara, M.; Sato, M. Improvement of Hydrodynamics-Based Gene Transfer of Nonviral DNA Targeted to Murine Hepatocytes. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 928790.
- Takao, T.; Hiraoka, Y.; Kawabe, K.; Yamada, D.; Ming, L.; Tanaka, K.; Sato, M.; Takarada, T. Establishment of a TTA-Dependent Photoactivatable Cre Recombinase Knock-in Mouse Model for Optogenetic Genome Engineering. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 526, 213–217.
- Kruse, R.L.; Legras, X.; Barzi, M. Cre/LoxP-HBV Plasmids Generating Recombinant Covalently Closed Circular DNA Genome upon Transfection. Virus Res. 2021, 292, 198224.
- Guo, J.; Fu, W.; Xiang, M.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, K.; Xu, C.-R.; Li, L.; Kuang, D.; Ye, F. Notch1 Drives the Formation and Proliferation of Intrahepatic Cholangiocarcinoma. Curr. Med. Sci. 2019, 39, 929–937.
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, G.; Shi, J.; Zhang, X.; Zheng, X.; Jiang, A.T.; Zhang, Z.-X.; Johnston, N.; Siu, K.S.; et al. Synergic Silencing of Costimulatory Molecules Prevents Cardiac Allograft Rejection. J. Transl. Med. 2014, 12, 142.
- Li, L.; Shen, H.; Li, A.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, B.; Wang, J.; Zheng, X.; Wu, J.; Yang, D.; Lu, M.; et al. Inhibition of Hepatitis B Virus (HBV) Gene Expression and Replication by HBx Gene Silencing in a Hydrodynamic Injection Mouse Model with a New Clone of HBV Genotype B. Virol. J. 2013, 10, 214.
- Johnson, C.G.; Chen, T.; Furey, N.; Hemmingsen, M.G.; Bissig, K.-D. Somatic Liver Knockout (SLiK): A Quick and Efficient Way to Generate Liver-Specific Knockout Mice Using Multiplex CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing. Curr. Protoc. Mol. Biol. 2020, 130, e117.
- Hubner, E.K.; Lechler, C.; Kohnke-Ertel, B.; Zmoos, A.-F.; Sage, J.; Schmid, R.M.; Ehmer, U. An in Vivo Transfection System for Inducible Gene Expression and Gene Silencing in Murine Hepatocytes. J. Gene Med. 2017, 19, e2940.
- Yang, X.-F.; Ren, L.-W.; Yang, L.; Deng, C.-Y.; Li, F.-R. In Vivo Direct Reprogramming of Liver Cells to Insulin Producing Cells by Virus-Free Overexpression of Defined Factors. Endocr. J. 2017, 64, 291–302.
- Cim, A.; Sawyer, G.J.; Zhang, X.; Su, H.; Collins, L.; Jones, P.; Antoniou, M.; Reynes, J.-P.; Lipps, H.-J.; Fabre, J.W. In Vivo Studies on Non-Viral Transdifferentiation of Liver Cells towards Pancreatic β Cells. J. Endocrinol. 2012, 214, 277–288.
- Yilmazer, A.; de Lázaro, I.; Bussy, C.; Kostarelos, K. In Vivo Reprogramming of Adult Somatic Cells to Pluripotency by Overexpression of Yamanaka Factors. J. Vis. Exp. JoVE 2013, 17, e50837.
- Yilmazer, A.; de Lázaro, I.; Bussy, C.; Kostarelos, K. In Vivo Cell Reprogramming towards Pluripotency by Virus-Free Overexpression of Defined Factors. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e54754.
- Matsui, A.; Uchida, S.; Ishii, T.; Itaka, K.; Kataoka, K. Messenger RNA-Based Therapeutics for the Treatment of Apoptosis-Associated Diseases. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15810.
- Liang, W.-C.; Liang, P.-P.; Wong, C.-W.; Ng, T.-B.; Huang, J.-J.; Zhang, J.-F.; Waye, M.M.-Y.; Fu, W.-M. CRISPR/Cas9 Technology Targeting Fas Gene Protects Mice From Concanavalin-A Induced Fulminant Hepatic Failure. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 530–536.
- Pankowicz, F.P.; Barzi, M.; Kim, K.H.; Legras, X.; Martins, C.S.; Wooton-Kee, C.R.; Lagor, W.R.; Marini, J.C.; Elsea, S.H.; Bissig-Choisat, B.; et al. Rapid Disruption of Genes Specifically in Livers of Mice Using Multiplex CRISPR/Cas9 Editing. Gastroenterology 2018, 155, 1967–1970.e6.
- Mao, J.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, W.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Xi, W.; Wang, Q.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, J.; Xi, X. Long-Term Correction of Hemorrhagic Diathesis in Hemophilia A Mice by an AAV-Delivered Hybrid FVIII Composed of the Human Heavy Chain and the Rat Light Chain. Front. Med. 2022, 16, 584–595.
- Zhang, W.; Mao, J.; Shen, Y.; Zhang, G.; Shao, Y.; Ruan, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wu, W.; Wang, X.; Zhu, J.; et al. Evaluation of the Activity Levels of Rat FVIII and Human FVIII Delivered by Adeno-Associated Viral Vectors Both in Vitro and in Vivo. Blood Cells. Mol. Dis. 2018, 73, 47–54.
- Xu, Z.; Ye, J.; Zhang, A.; Xie, L.; Shen, Q.; Xue, J.; Chen, J. Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B with Liver-Specific Element Mediated by Rep-RBE Site-Specific Integration System. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2015, 65, 153–159.
- Lu, W.; Zhou, Q.; Yang, H.; Wang, H.; Gu, Y.; Shen, Q.; Xue, J.; Dong, X.; Chen, J. Gene Therapy for Hemophilia B Mice with ScAAV8-LP1-HFIX. Front. Med. 2016, 10, 212–218.
- Kim, S.M.; Choi, J.E.; Hur, W.; Kim, J.-H.; Hong, S.W.; Lee, E.B.; Lee, J.H.; Li, T.Z.; Sung, P.S.; Yoon, S.K. RAR-Related Orphan Receptor Gamma (ROR-γ) Mediates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Of Hepatocytes During Hepatic Fibrosis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 118, 2026–2036.
- Chuai, X.; Wang, W.; Chen, H.; Deng, Y.; Wen, B.; Tan, W. Lentiviral Backbone-Based Hepatitis B Virus Replicon-Mediated Transfer Favours the Establishment of Persistent Hepatitis B Virus Infection in Mice after Hydrodynamic Injection. Antiviral Res. 2014, 101, 68–74.
- Reautschnig, P.; Wahn, N.; Wettengel, J.; Schulz, A.E.; Latifi, N.; Vogel, P.; Kang, T.-W.; Pfeiffer, L.S.; Zarges, C.; Naumann, U.; et al. CLUSTER Guide RNAs Enable Precise and Efficient RNA Editing with Endogenous ADAR Enzymes in Vivo. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 759–768.
