Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Camila Xu and Version 1 by Li Zhao.
Vaccination plays an important role in the prevention of infection and subsequent severe COVID-19 among the general population. Compared to the general population, patients with malignancy are more likely to develop a less proficient immune response upon vaccination. This is mainly caused by disease-associated or therapy-led immune deficiency. Therefore, patients with cancer are usually prioritized for vaccinations but excluded from registration in clinical trials.
- COVID-19
- SARS-CoV-2 variants
- vaccines
- cancer
1. Introduction
The emergence of a novel species of coronavirus in 2019, named severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) by WHO [1], caused a worldwide pandemic with disastrous impacts to public health worldwide. The mortality rate for the disease is higher in patients with certain comorbidities, including cancer [2,3,4][2][3][4]. Even though patients with malignant disease overlap risk factors with the general population, such as advanced age, malignancy itself may contribute as an independent risk factor [5,6,7][5][6][7]. The risk of severe COVID-19 is obviously higher in patients <65 years of age with malignant disease [6,8][6][8]. It is considered that malignancy is associated with a significant increase in case fatality for both hematologic and solid malignancies [9]. Mortality rates among patients with active cancers are significantly higher, affected by their compromised immunity [8]. Additionally, mortality rates can also be influenced indirectly. Disruptions to the healthcare system caused by the pandemic can result in cancer treatment delays, frequent treatment modifications, and reduced screening, which impacts cancer-specific survival [10,11][10][11]. The incidence of long-term COVID-19 sequelae also affects up to 15% of cancer patients and adversely affects the survival rate and tumor prognosis after COVID-19 recovery [11]. However, it is also important to note that mortality rates in these studies were usually derived from inpatient data, so the specific rates might be overestimated.
Vaccination plays an important role in the prevention of infection and subsequent severe COVID-19 among the general population (Figure 1). As cancer patients face a higher risk of mortality from COVID-19, effective preventative efforts are especially important in this population, with vaccination being one of the most effective methods. It has already been proved that vaccination is a safe and powerful tool to protect this population against other infectious diseases [12,13,14][12][13][14]. Previous research also indicates that patients with cancer benefit from additional vaccine doses [15], which is in line with the current concept of prime–boost vaccination. However, insufficient data were collected to directly ascertain the efficacy and safety of vaccines that are currently available for COVID-19 patients with cancer. Compared to the general population, patients with malignancy are more likely to develop a less proficient immune response upon vaccination. This is mainly caused by disease-associated or therapy-led immune deficiency. Therefore, patients with cancer are usually prioritized for vaccinations but excluded from registration in clinical trials [16,17][16][17]. This means that vaccine efficacy in this population has had to be indirectly deduced from an immunological or antibody-response perspective [18,19,20][18][19][20].
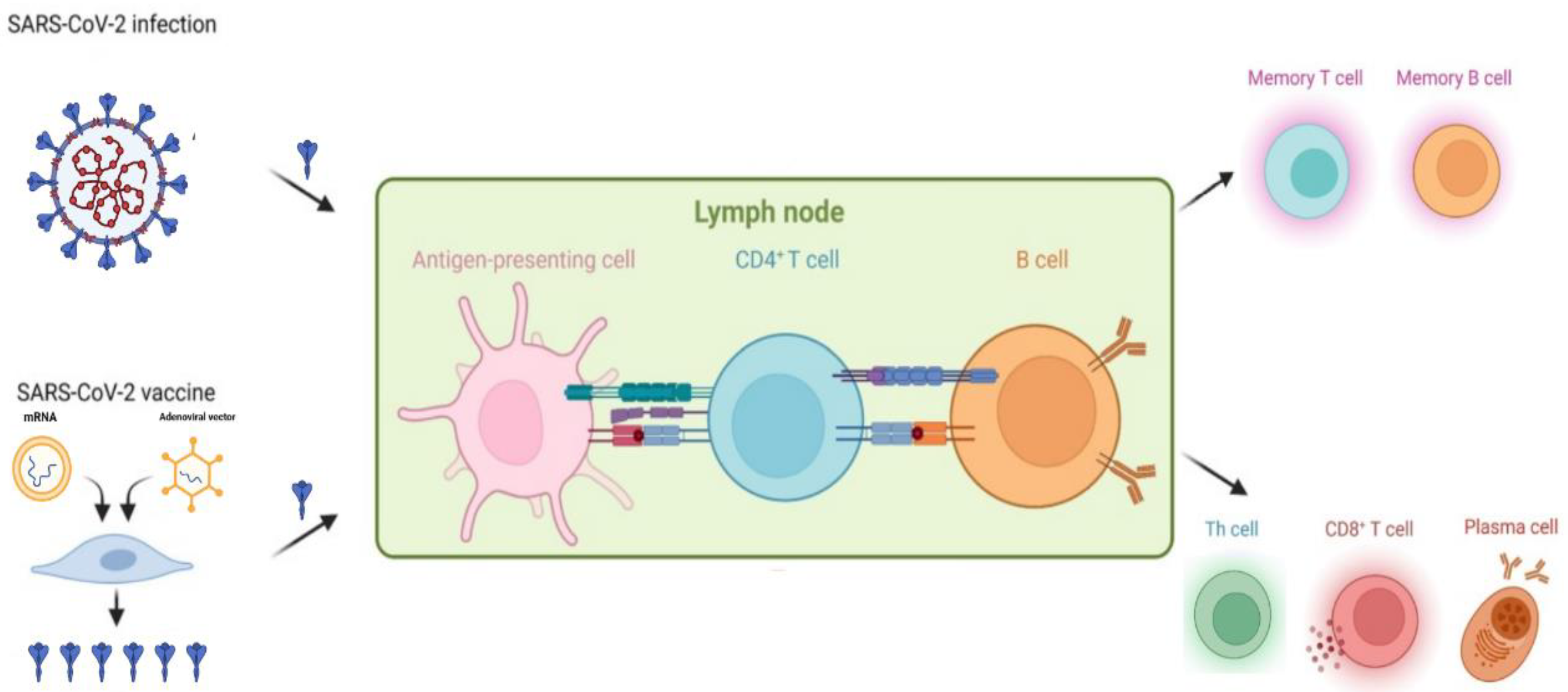
Figure 1.
Infection- or vaccination-induced immune protection against SARS-CoV-2.
2. Vaccine Effectiveness in Patients with Malignant Disease
Clinical vaccine efficacy, which is usually defined as the prevention of symptomatic COVID-19, is generally less proficient in patients with malignant disease [20,21,22,23,24,25,26,27,28,29][20][21][22][23][24][25][26][27][28][29]. The evaluation of vaccine-induced immune response in cancer patients is mainly focused on assessing the humoral immunity response. Humoral immunity response is primarily evaluated by establishing seroconversion rates and mean anti-body titers of antibodies that are spike-reactive or RBD-reactive [30,31,32,33][30][31][32][33]. Cellular immunity, mainly addressed by T cell response, is relatively limited and often provided along with humoral immunity.
According to a large US Veterans study including cancer patients who received mRNA vaccines, the overall vaccine effectiveness (VE) in patients with cancer was about 58%, which is lower compared to the general population [29]. The high risk of VE reduction against COVID-19 experienced by cancer patients has also been observed in several other studies [18,20,21,27,31,34,35][18][20][21][27][31][34][35]. A UK prospective cohort study of 6.9 million vaccinated participants identified hematological cancer (HR 1.86), respiratory tract cancer (HR 1.35), receiving chemotherapy (HR 3.63–4.3), and receiving bone marrow or solid organ transplantation within the past 6 months (HR 2.5) as risk factors for COVID-19-related death, despite receiving two doses of vaccination [36]. Fortunately, some research also indicates that in long-term follow ups, certain cancer survivors can develop higher VE, closer to the rates of the general population [29,37][29][37].
2.1. Humoral Immunity: Serology and Neutralizing Antibodies
2.1.1. Effectiveness of Vaccination on Humoral Immunity
Humoral immunity is mostly evaluated through the rates of seroconversion and mean antibody titers. According to a prospective observational study of the mRNA vaccine BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech), after receiving one does of the vaccine, the proportion of participants with positive anti-S IgG titers were 38% and <20% in patients with solid tumors and hematological malignancies, respectively, compared with 94% in the control cohort [20]. Consistent with the general population, neutralizing responses to variants of concern (VOCs) decrease progressively in patients with cancer [18,38][18][38]. In a predictive model study, neutralization titers against some SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern were reduced compared with the vaccine strain [39]. This might be the reason why, in patients with hematological malignancies, only 31% patients had detectable titers with activity against the Delta variant after two vaccine doses, compared to 56% against the previous Wuhan strain [18].
2.1.2. Risk Factors for Poor Humoral Immune Response to Vaccination
Solid Cancer
The presence of seroconversion can be detected in most patients (>90%) with solid tumors, which is comparable with the general population [18,34,40][18][34][40]. However, the specific conversion rate tends to be lower, as it is impacted by impaired immunogenicity [20,25,35][20][25][35]. A meta-analysis reported that 297 patients with cancer who have completed their vaccine regiment had a lower seroconversion rate compared with the 140-participant control group (RR 0.95; 95% CI 0.92–0.99) [26].
The cancer population and the general population share common risk factors for reduced seroconversion: age, sex, and the type of vaccine [18,30,34][18][30][34] (adenovirus-vectored vaccines are less effective compared to mRNA vaccines). The CAPTURE study compared the use of BNT162b2 (mRNA) and AZD1222 (adenovirus-vectored) in patients with malignant disease. In comparison with the AZD1222 cohort, an exceptionally higher proportion of the BNT162b2 cohort developed neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) against the VOCs, along with significantly higher median nAb titers [18]. Similar results have been reported by Astha et al. [34]. Thus, it might be important to prioritize mRNA vaccines for cancer patients wherever possible.
Specific cancer therapies can impair vaccine-induced immunogenicity. Chemotherapy: patients who received chemotherapy within 3 months prior to the first vaccination dose were estimated to have a vaccine effectiveness of 57% (95% CI, –23% to 90%) starting 14 days after the second dose vs 76% (95% CI, 50% to 91%) for those receiving endocrine therapy and 85% (95% CI, 29% to 100%) for those who had not received systemic therapy for at least 6 months prior [29]. Several other studies also identified chemotherapy as a risk factor for lower seroconversion and neutralizing responses [23,30,31,35,41,42,43,44][23][30][31][35][41][42][43][44]. Notably, seroconversion may not be affected by the timing of vaccination of ongoing chemotherapy cycles [31,34][31][34]. Therefore, centers do not have to reschedule chemotherapy plans for vaccination. However, to avoid acute adverse effects, vaccines should still not be administered with chemotherapy on the same day. Immune checkpoint inhibitors: the evidence is mixed on the impact of inhibitors on vaccination. In a recent study, 7% (9/131) of the patients treated with immunotherapy were classified as suboptimal responders or non-responders, while the extent of seroconversion is generally high [40]. A study of breast cancer patients receiving CDK4/6 inhibitors reported no significant decrement in response to the first dose of COVID-19 vaccines. However, another study showed significantly lower titer after vaccination in patients receiving CDK4/6 inhibitor therapy [34]. This is in line with the result of another study, where up to day 30 after the second dose, ovarian cancer patients receiving PARP inhibitors had significantly lower nAbs in comparison to matched healthy volunteers [45]. Steroids: a study reported chronic steroid as an independent risk factor for reduced seroconversion in solid cancer therapy [46].
Hematological Malignancies
An exceptionally lower seroconversion rate has been observed in patients with hematologic malignancies compared to those with solid tumors after complete immunization (65% vs. 94%; p < 0.0001) [26]. This is in line with another study that compares seropositive rate after vaccination in this population against the comparison group (75% vs. 99%; p < 0.001) [41]. However, vaccination responses are similar to the general population in long-term hematological malignancy patients, including patients that received very immunosuppressive therapies [29,37][29][37]. Patient-specific risk factors include sex [47[47][48][49],48,49], age [47[47][48][49][50][51],48,49,50,51], and type of vaccine [19,52][19][52]. A superiority in VE of mRNA vaccines has also been observed in patients with Hematological Malignancies [18]. Additionally, interestingly, within the mRNA vaccines, mRNA-1273 is more effective than BNT162b2 [28,50][28][50]. Another risk factor is progressive disease [50,53,54,55][50][53][54][55] (and other factors that result in the disorder of the immune system, such as reduced levels of uninvolved immunoglobulins or lymphopenia) [41,48,50,55,56,57,58][41][48][50][55][56][57][58]. Patients with different types of hematological malignancies may also respond differently to the same COVID-19 vaccine. A study shows that among patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL), non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL), multiple myeloma (MM), chronic myeloid leukemia (CML), myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPN), and myelodysplastic syndromes (MDS), patients with CLL, NHL, and MM had the lowest seropositivity rates [35]. Therefore, it might be important to run subgroup analyzes in future research. Specific therapies can also impair vaccine-induced immunogenicity. Antibody responses were substantially reduced in patients receiving anti-CD20 antibody therapies [27[27][31][41][47][48][51][54][58][59][60][61][62][63][64][65][66][67],31,41,47,48,51,54,58,59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67], BTK inhibitors [41,48,51,54[41][48][51][54][56][59][61][62][65],56,59,61,62,65], BCL inhibitors (such as venetoclax) [41,48[41][48][51][61][62][63][64][65],51,61,62,63,64,65], BCMA-targeted therapies [57,62[57][62][68][69],68,69], anti-CD38 antibody therapies [57,62,67[57][62][67][68][69][70],68,69,70], and JAK inhibitors [41,59][41][59]. Over 50% of patients exhibited less seropositive responses compared to control groups, especially in patients undergoing active treatment. Depletion of normal B cells is the main reason for negative seroconversion-receiving anti-CD20 antibody therapies, BTK inhibitors, or BCL inhibitors. Treatment with B cell–directed therapies may reduce the production of vaccination-induced antibodies in patients with hematological malignancy because of B cell depletion and/or disruption of the B cell-receptor signaling pathway. A duration of time before vaccination from the last B cell–directed treatment may result in improved antibody titers [64]. Additionally, steroids, especially active steroid therapy, seems to have a negative effect on humoral response [47,49,50,71][47][49][50][71]. Compared to specific therapies mentioned above, the negative effect seems to be milder, probably dosage-dependent, influencing <50% of patients with hematological malignancy. However, the negative effect of TKIs is rarely seen [41,59][41][59]. Encouragingly, it seems that deficient humoral immunity can be improved through the treatment of the primary disease, according to a study in which 79.2% of patients reached a positive serological response after receiving effective treatment. [48]. This is in line with the observation of long-term hematological malignancy patients, whose VE are comparable with the general population, including patients that received very immunosuppressive therapies [29,37][29][37].
2.2. Cellular Immunity: T Cell Responses
2.2.1. Effectiveness of Vaccination on Cellular Immunity
The effectiveness of vaccination on cellular immunity can be measured by flow cytometric analysis of cellular activation-induced markers [72], IFN-γ release [18,40[18][40][54],54], or combined IFN-γ and IL-2 release [20,66][20][66]. Waned T cell response could be detected more clearly with IFN-γ release or cellular activation-induced markers [18,32][18][32]. Cellular immunity is often weaker in cancer patients compared to the general population. Only 46–79% T cell responses are detected in solid tumor patients according to studies above. However, several studies still show comparable responses between the cancer population (both solid cancer and hematological patients) and the general population [18,32,33,54,72][18][32][33][54][72]. Additionally, strong T cell responses can be elicited after stimulation with SARS-CoV-2-derived peptides [34,73,74,75,76][34][73][74][75][76]. In contrast to humoral immunity, cellular immunity may correlate better with long-lasting immune memory and protection from severe disease [77]. T cell response is less affected by mutations, and epitopes are more broadly conserved [78]. Therefore, T cell responses are more robust in patients with hematological malignancies; they can be detected in 34% to 75% of patients in whom serological response is negative (although 34% of seronegative individuals had CD4 responses with mainly IL-2-only monofunctional cells) [18,54,58,68][18][54][58][68].
2.2.2. Risk Factors for Poor Cellular Immune Response to Vaccination
Criteria for T cell positivity alters among studies. Some studies use the presence of activation markers on virus-specific T cells, while others have quantified cellular cytokine secretion. Therefore, the establishing of risk factors for poor cellular immune responses to vaccination is more challenging than for humoral immunity.
Solid Cancer
Limited data are available on the risk factors of cellular immunity in solid cancer. In a study including cancer patients receiving BNT162b2 mRNA, chemotherapy or steroids within 15 days of vaccination were associated with reduced T cell responses to vaccination [33]. Other studies also reported reduced T cell responses but did not specify treatment [20,72][20][72]. Interestingly, T cells are detectable in the absence of antibody responses in patients receiving chemotherapy or immune checkpoint inhibitors [40].
Hematological Malignancies
Compared to the humoral response to vaccination, specific therapies (especially B cell-depleting therapies as anti-CD20 antibody therapies) seem to have a weaker impact on T cell responses [18,47,58,66][18][47][58][66]. CD8+ responses have been detected in hematologic cancer patients that received B cell-depleting therapies, even in the absence of humoral responses [79,80][79][80]. HSCT and allogeneic-HCT: recipients of HSCT and allogeneic-HCT have a much weaker T cell response; while serological response is detectable, T cell responses seem to occur in only 20–30% of patients [81,82][81][82]. Moreover, T cell performance might be influenced by the specific type of the disease. CML patients may achieve a polyfunctional T cell rate of 12/15 (80%) [83], while 80% and 60% of MPN patients showed a polyfunctional response of CD4 and CD8 T cells, respectively [84]. However, seronegative MM patients had significantly reduced CD4 T cell responses compared to those of healthy controls. Spike stimulation increases IL-2 levels in patients with hematological malignancies, but the IFN-γ and tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α) remain lower, which indicates a reduced magnitude of protection by T cell response [68]. Other studies using receptor-binding domain (RBD) as stimulation still elicited weaker immunogenicity responses in patients with MM vs healthy controls (34.2% vs. 71.4%). Moreover, in other hematological patients, low-RBD-specific T cell responses can also be seen [20,33][20][33]. This probably means that instead of disease-specific immunosuppression, cellular immunity is linked to the failure to generate a durable immune response to novel antigens. Humoral and cellular responses were often found to be discordant in patients with cancer. Thus, the disharmony of the humoral and cellular immune system is a possible cause of poor vaccine response.
2.3. Prime–Boost Vaccination: Solution for Waning Immunity and VOCs
Vaccine efficacy reduces over time due to the waning of humoral immunity and the emergence of novel VOCs. In line with reports from the general population, neutralizing responses to VOCs decrease progressively in patients with malignant disease [18,38][18][38]. However, the combination effect of VOCs and malignancy can lead to drastically reduced VE, which is more likely be seen in patients with hematological malignancies [39]. It has been reported the VE against the Delta variant was only 31%, compared to the previous 56% VE against the previous Wuhan strain [18]. Encouragingly, booster vaccination, as a solution for waning immunity and VOCs, is well tolerated in cancer patients [32]. Several studies have shown the poor immune effect of a single-dose vaccination, and that it can be significantly boosted through a second dose, with seropositivity boosted up to 75% and 95% after the second dose [22,25,30,31,32,34,35,44,46,54,60,72,85,86,87,88][22][25][30][31][32][34][35][44][46][54][60][72][85][86][87][88]. Therefore, booster doses for malignancy patients were urgently rolled out to compete with the waning humoral immunity. Increased performance of humoral immunity, measured by antibody titers, in patients with cancer have been observed, and neutralizing antibodies (nAbs) have also shown threefold increases compared with pre-booster doses [27,32,52,89,90,91,92,93][27][32][52][89][90][91][92][93].
Receiving treatment does not appear to be a contraindication for booster vaccination, as it increases the antibody response in patients with solid tumors, even in those receiving active treatment (intravenous anticancer medication) [94]. Furthermore, booster vaccination induced seroconversion in previously seronegative patients; up to 56% patients showed a humoral response after the second vaccine dose [76].
In certain circumstances, a positive immune response might not be achieved with two doses, especially to avoid response decrement due to novel VOCs. A third dose might be necessary. The percentage of patients with detectable neutralizing responses to VOCs can be broadened following booster vaccination; participants who had low neutralizing titers after two vaccine doses received a third booster dose and enhanced the neutralization against numerous VOCs [95]. Neutralizing responses against Omicron in patients with solid cancer increased from 47.8% to 88.9% after a third-dose vaccination [86]. Enhanced immunogenicity was observed after a third mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in solid cancer patients who previously received the heterologous CoronaVac/ChAdOx1(inactivated vaccine) regimens [96]. In another study, nAbs in patients with solid cancer increased from 37% to 90% after the third dose against Omicron [53]. Hematological patients could also benefit from this process. In the same research, neutralizing antibodies against Omicron are rarely detected after two vaccine doses. However, approximately 50% have detectable neutralizing antibodies after a third dose [53]. Notably, booster vaccination might be especially important to patients with hematological malignancies, as they have a higher risk of not seroconverting after vaccination, especially in those with B cell malignancies receiving B cell-depleting therapies (CD20-targeted therapies or BTK inhibitors) [61,76,97][61][76][97].
Interestingly, the effect of prime–boost vaccination might be influenced by the vaccine combination or the sequence of injection. It seems that heterologous vaccination is superior to homologous vaccination, at least in those vaccinated with adenovirus-vectored vaccines as the first dose [98]. However, the conclusion was drawn from a small observational study. Thus, it may be too early to preclude any meaningful conclusions, not to mention the most effective vaccine combination.
References
- Gorbalenya, A.E.; Baker, S.C.; Baric, R.S.; de Groot, R.J.; Drosten, C.; Gulyaeva, A.A.; Haagmans, B.L.; Lauber, C.; Leontovich, A.M.; Neuman, B.W.; et al. The species Severe acute respiratory syndrome-related coronavirus: Classifying 2019-nCoV and naming it SARS-CoV-2. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 536–544.
- Kuderer, N.M.; Choueiri, T.K.; Shah, D.P.; Shyr, Y.; Rubinstein, S.M.; Rivera, D.R.; Shete, S.; Hsu, C.Y.; Desai, A.; de Lima Lopes, G., Jr.; et al. Clinical impact of COVID-19 on patients with cancer (CCC19): A cohort study. Lancet 2020, 395, 1907–1918.
- Bakouny, Z.; Hawley, J.E.; Choueiri, T.K.; Peters, S.; Rini, B.I.; Warner, J.L.; Painter, C.A. COVID-19 and Cancer: Current Challenges and Perspectives. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 629–646.
- Williamson, E.J.; Walker, A.J.; Bhaskaran, K.; Bacon, S.; Bates, C.; Morton, C.E.; Curtis, H.J.; Mehrkar, A.; Evans, D.; Inglesby, P.; et al. Factors associated with COVID-19-related death using OpenSAFELY. Nature 2020, 584, 430–436.
- Ramaswamy, A.; Nayak, L.; Roy Moulik, N.; Sengar, M.; Chinnaswamy, G.; Jobanputra, K.; Shah, M.J.; Kapoor, A.; Joshi, A.; Kumar, A.; et al. COVID-19 in cancer patients on active systemic therapy—Outcomes from LMIC scenario with an emphasis on need for active treatment. Cancer Med. 2020, 9, 8747–8753.
- Rüthrich, M.M.; Giessen-Jung, C.; Borgmann, S.; Classen, A.Y.; Dolff, S.; Grüner, B.; Hanses, F.; Isberner, N.; Köhler, P.; Lanznaster, J.; et al. COVID-19 in cancer patients: Clinical characteristics and outcome-an analysis of the LEOSS registry. Ann. Hematol. 2021, 100, 383–393.
- Pagano, L.; Salmanton-García, J.; Marchesi, F.; Busca, A.; Corradini, P.; Hoenigl, M.; Klimko, N.; Koehler, P.; Pagliuca, A.; Passamonti, F.; et al. COVID-19 infection in adult patients with hematological malignancies: A European Hematology Association Survey (EPICOVIDEHA). J. Hematol. Oncol. 2021, 14, 168.
- Venkatesulu, B.P.; Chandrasekar, V.T.; Girdhar, P.; Advani, P.; Sharma, A.; Elumalai, T.; Hsieh, C.E.; Elghazawy, H.I.; Verma, V.; Krishnan, S. A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Cancer Patients Affected by a Novel Coronavirus. JNCI Cancer Spectr. 2021, 5, pkaa102.
- Mehta, V.; Goel, S.; Kabarriti, R.; Cole, D.; Goldfinger, M.; Acuna-Villaorduna, A.; Pradhan, K.; Thota, R.; Reissman, S.; Sparano, J.A.; et al. Case Fatality Rate of Cancer Patients with COVID-19 in a New York Hospital System. Cancer Discov. 2020, 10, 935–941.
- Hartman, H.E.; Sun, Y.; Devasia, T.P.; Chase, E.C.; Jairath, N.K.; Dess, R.T.; Jackson, W.C.; Morris, E.; Li, P.; Hochstedler, K.A.; et al. Integrated Survival Estimates for Cancer Treatment Delay Among Adults With Cancer During the COVID-19 Pandemic. JAMA Oncol. 2020, 6, 1881–1889.
- Pinato, D.J.; Tabernero, J.; Bower, M.; Scotti, L.; Patel, M.; Colomba, E.; Dolly, S.; Loizidou, A.; Chester, J.; Mukherjee, U.; et al. Prevalence and impact of COVID-19 sequelae on treatment and survival of patients with cancer who recovered from SARS-CoV-2 infection: Evidence from the OnCovid retrospective, multicentre registry study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1669–1680.
- Bastidas, A.; de la Serna, J.; El Idrissi, M.; Oostvogels, L.; Quittet, P.; López-Jiménez, J.; Vural, F.; Pohlreich, D.; Zuckerman, T.; Issa, N.C.; et al. Effect of Recombinant Zoster Vaccine on Incidence of Herpes Zoster After Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation: A Randomized Clinical Trial. Jama 2019, 322, 123–133.
- Winston, D.J.; Mullane, K.M.; Cornely, O.A.; Boeckh, M.J.; Brown, J.W.; Pergam, S.A.; Trociukas, I.; Žák, P.; Craig, M.D.; Papanicolaou, G.A.; et al. Inactivated varicella zoster vaccine in autologous haemopoietic stem-cell transplant recipients: An international, multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 2018, 391, 2116–2127.
- Lopez-Olivo, M.A.; Valerio, V.; Karpes Matusevich, A.R.; Brizio, M.; Kwok, M.; Geng, Y.; Suarez-Almazor, M.E.; Colmegna, I. Safety and Efficacy of Influenza Vaccination in Patients Receiving Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1195.
- de Lavallade, H.; Garland, P.; Sekine, T.; Hoschler, K.; Marin, D.; Stringaris, K.; Loucaides, E.; Howe, K.; Szydlo, R.; Kanfer, E.; et al. Repeated vaccination is required to optimize seroprotection against H1N1 in the immunocompromised host. Haematologica 2011, 96, 307–314.
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Pérez Marc, G.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA Covid-19 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615.
- Baden, L.R.; El Sahly, H.M.; Essink, B.; Kotloff, K.; Frey, S.; Novak, R.; Diemert, D.; Spector, S.A.; Rouphael, N.; Creech, C.B.; et al. Efficacy and Safety of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 403–416.
- Fendler, A.; Shepherd, S.T.C.; Au, L.; Wilkinson, K.A.; Wu, M.; Byrne, F.; Cerrone, M.; Schmitt, A.M.; Joharatnam-Hogan, N.; Shum, B.; et al. Adaptive immunity and neutralizing antibodies against SARS-CoV-2 variants of concern following vaccination in patients with cancer: The CAPTURE study. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 1305–1320.
- Lim, S.H.; Campbell, N.; Johnson, M.; Joseph-Pietras, D.; Collins, G.P.; O’Callaghan, A.; Fox, C.P.; Ahearne, M.; Johnson, P.W.M.; Goldblatt, D.; et al. Antibody responses after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in patients with lymphoma. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e542–e544.
- Monin, L.; Laing, A.G.; Muñoz-Ruiz, M.; McKenzie, D.R.; Del Molino Del Barrio, I.; Alaguthurai, T.; Domingo-Vila, C.; Hayday, T.S.; Graham, C.; Seow, J.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of one versus two doses of the COVID-19 vaccine BNT162b2 for patients with cancer: Interim analysis of a prospective observational study. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 765–778.
- Linardou, H.; Spanakis, N.; Koliou, G.A.; Christopoulou, A.; Karageorgopoulou, S.; Alevra, N.; Vagionas, A.; Tsoukalas, N.; Sgourou, S.; Fountzilas, E.; et al. Responses to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccination in Patients with Cancer (ReCOVer Study): A Prospective Cohort Study of the Hellenic Cooperative Oncology Group. Cancers 2021, 13, 4621.
- Shmueli, E.S.; Itay, A.; Margalit, O.; Berger, R.; Halperin, S.; Jurkowicz, M.; Levin, E.G.; Levy, I.; Olmer, L.; Regev-Yochay, G.; et al. Efficacy and safety of BNT162b2 vaccination in patients with solid cancer receiving anticancer therapy—A single centre prospective study. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 157, 124–131.
- Agbarya, A.; Sarel, I.; Ziv-Baran, T.; Agranat, S.; Schwartz, O.; Shai, A.; Nordheimer, S.; Fenig, S.; Shechtman, Y.; Kozlener, E.; et al. Efficacy of the mRNA-Based BNT162b2 COVID-19 Vaccine in Patients with Solid Malignancies Treated with Anti-Neoplastic Drugs. Cancers 2021, 13, 4191.
- Ligumsky, H.; Safadi, E.; Etan, T.; Vaknin, N.; Waller, M.; Croll, A.; Nikolaevski-Berlin, A.; Greenberg, I.; Halperin, T.; Wasserman, A.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine Among Actively Treated Cancer Patients. JNCI J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2022, 114, 203–209.
- Barrière, J.; Chamorey, E.; Adjtoutah, Z.; Castelnau, O.; Mahamat, A.; Marco, S.; Petit, E.; Leysalle, A.; Raimondi, V.; Carles, M. Impaired immunogenicity of BNT162b2 anti-SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients treated for solid tumors. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1053–1055.
- Becerril-Gaitan, A.; Vaca-Cartagena, B.F.; Ferrigno, A.S.; Mesa-Chavez, F.; Barrientos-Gutiérrez, T.; Tagliamento, M.; Lambertini, M.; Villarreal-Garza, C. Immunogenicity and risk of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) infection after Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccination in patients with cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 160, 243–260.
- Mair, M.J.; Berger, J.M.; Berghoff, A.S.; Starzer, A.M.; Ortmayr, G.; Puhr, H.C.; Steindl, A.; Perkmann, T.; Haslacher, H.; Strassl, R.; et al. Humoral Immune Response in Hematooncological Patients and Health Care Workers Who Received SARS-CoV-2 Vaccinations. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 106–113.
- Embi, P.J.; Levy, M.E.; Naleway, A.L.; Patel, P.; Gaglani, M.; Natarajan, K.; Dascomb, K.; Ong, T.C.; Klein, N.P.; Liao, I.C.; et al. Effectiveness of 2-Dose Vaccination with mRNA COVID-19 Vaccines Against COVID-19-Associated Hospitalizations Among Immunocompromised Adults—Nine States, January–September 2021. MMWR. Morb. Mortal. Wkly. Rep. 2021, 70, 1553–1559.
- Wu, J.T.; La, J.; Branch-Elliman, W.; Huhmann, L.B.; Han, S.S.; Parmigiani, G.; Tuck, D.P.; Brophy, M.T.; Do, N.V.; Lin, A.Y.; et al. Association of COVID-19 Vaccination With SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Patients With Cancer: A US Nationwide Veterans Affairs Study. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 281–286.
- Cavanna, L.; Citterio, C.; Biasini, C.; Madaro, S.; Bacchetta, N.; Lis, A.; Cremona, G.; Muroni, M.; Bernuzzi, P.; Lo Cascio, G.; et al. COVID-19 vaccines in adult cancer patients with solid tumours undergoing active treatment: Seropositivity and safety. A prospective observational study in Italy. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 157, 441–449.
- Peeters, M.; Verbruggen, L.; Teuwen, L.; Vanhoutte, G.; Vande Kerckhove, S.; Peeters, B.; Raats, S.; Van der Massen, I.; De Keersmaecker, S.; Debie, Y.; et al. Reduced humoral immune response after BNT162b2 coronavirus disease 2019 messenger RNA vaccination in cancer patients under antineoplastic treatment. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100274.
- Shroff, R.T.; Chalasani, P.; Wei, R.; Pennington, D.; Quirk, G.; Schoenle, M.V.; Peyton, K.L.; Uhrlaub, J.L.; Ripperger, T.J.; Jergović, M.; et al. Immune responses to two and three doses of the BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine in adults with solid tumors. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 2002–2011.
- McKenzie, D.R.; Muñoz-Ruiz, M.; Monin, L.; Alaguthurai, T.; Lechmere, T.; Abdul-Jawad, S.; Graham, C.; Pollock, E.; Graham, R.; Sychowska, K.; et al. Humoral and cellular immunity to delayed second dose of SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 mRNA vaccination in patients with cancer. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1445–1447.
- Thakkar, A.; Gonzalez-Lugo, J.D.; Goradia, N.; Gali, R.; Shapiro, L.C.; Pradhan, K.; Rahman, S.; Kim, S.Y.; Ko, B.; Sica, R.A.; et al. Seroconversion rates following COVID-19 vaccination among patients with cancer. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1081–1090.
- Massarweh, A.; Eliakim-Raz, N.; Stemmer, A.; Levy-Barda, A.; Yust-Katz, S.; Zer, A.; Benouaich-Amiel, A.; Ben-Zvi, H.; Moskovits, N.; Brenner, B.; et al. Evaluation of Seropositivity Following BNT162b2 Messenger RNA Vaccination for SARS-CoV-2 in Patients Undergoing Treatment for Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1133–1140.
- Hippisley-Cox, J.; Coupland, C.A.; Mehta, N.; Keogh, R.H.; Diaz-Ordaz, K.; Khunti, K.; Lyons, R.A.; Kee, F.; Sheikh, A.; Rahman, S.; et al. Risk prediction of COVID-19 related death and hospital admission in adults after covid-19 vaccination: National prospective cohort study. BMJ 2021, 374, n2244.
- Matkowska-Kocjan, A.; Owoc-Lempach, J.; Chruszcz, J.; Kuźnik, E.; Szenborn, F.; Jurczenko, L.; Wójcik, M.; Banyś, D.; Szenborn, L.; Ussowicz, M. The COVID-19 mRNA BNT163b2 Vaccine Was Well Tolerated and Highly Immunogenic in Young Adults in Long Follow-Up after Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1209.
- Wall, E.C.; Wu, M.; Harvey, R.; Kelly, G.; Warchal, S.; Sawyer, C.; Daniels, R.; Adams, L.; Hobson, P.; Hatipoglu, E.; et al. AZD1222-induced neutralising antibody activity against SARS-CoV-2 Delta VOC. Lancet 2021, 398, 207–209.
- Khoury, D.S.; Cromer, D.; Reynaldi, A.; Schlub, T.E.; Wheatley, A.K.; Juno, J.A.; Subbarao, K.; Kent, S.J.; Triccas, J.A.; Davenport, M.P. Neutralizing antibody levels are highly predictive of immune protection from symptomatic SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1205–1211.
- Oosting, S.F.; van der Veldt, A.A.M.; GeurtsvanKessel, C.H.; Fehrmann, R.S.N.; van Binnendijk, R.S.; Dingemans, A.C.; Smit, E.F.; Hiltermann, T.J.N.; den Hartog, G.; Jalving, M.; et al. mRNA-1273 COVID-19 vaccination in patients receiving chemotherapy, immunotherapy, or chemoimmunotherapy for solid tumours: A prospective, multicentre, non-inferiority trial. Lancet Oncol. 2021, 22, 1681–1691.
- Herzog Tzarfati, K.; Gutwein, O.; Apel, A.; Rahimi-Levene, N.; Sadovnik, M.; Harel, L.; Benveniste-Levkovitz, P.; Bar Chaim, A.; Koren-Michowitz, M. BNT162b2 COVID-19 vaccine is significantly less effective in patients with hematologic malignancies. Am. J. Hematol. 2021, 96, 1195–1203.
- Buttiron Webber, T.; Provinciali, N.; Musso, M.; Ugolini, M.; Boitano, M.; Clavarezza, M.; D’Amico, M.; Defferrari, C.; Gozza, A.; Briata, I.M.; et al. Predictors of poor seroconversion and adverse events to SARS-CoV-2 mRNA BNT162b2 vaccine in cancer patients on active treatment. Eur. J. Cancer 2021, 159, 105–112.
- Grinshpun, A.; Rottenberg, Y.; Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Djian, E.; Wolf, D.G.; Kadouri, L. Serologic response to COVID-19 infection and/or vaccine in cancer patients on active treatment. ESMO Open 2021, 6, 100283.
- Goshen-Lago, T.; Waldhorn, I.; Holland, R.; Szwarcwort-Cohen, M.; Reiner-Benaim, A.; Shachor-Meyouhas, Y.; Hussein, K.; Fahoum, L.; Baruch, M.; Peer, A.; et al. Serologic Status and Toxic Effects of the SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 Vaccine in Patients Undergoing Treatment for Cancer. JAMA Oncol. 2021, 7, 1507–1513.
- Liontos, M.; Terpos, E.; Markellos, C.; Zagouri, F.; Briasoulis, A.; Katsiana, I.; Skafida, E.; Fiste, O.; Kunadis, E.; Andrikopoulou, A.; et al. Immunological Response to COVID-19 Vaccination in Ovarian Cancer Patients Receiving PARP Inhibitors. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1148.
- Di Noia, V.; Pimpinelli, F.; Renna, D.; Barberi, V.; Maccallini, M.T.; Gariazzo, L.; Pontone, M.; Monti, A.; Campo, F.; Taraborelli, E.; et al. Immunogenicity and Safety of COVID-19 Vaccine BNT162b2 for Patients with Solid Cancer: A Large Cohort Prospective Study from a Single Institution. Clin. Cancer Res. 2021, 27, 6815–6823.
- Malard, F.; Gaugler, B.; Gozlan, J.; Bouquet, L.; Fofana, D.; Siblany, L.; Eshagh, D.; Adotevi, O.; Laheurte, C.; Ricard, L.; et al. Weak immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 vaccine in patients with hematologic malignancies. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 142.
- Herishanu, Y.; Avivi, I.; Aharon, A.; Shefer, G.; Levi, S.; Bronstein, Y.; Morales, M.; Ziv, T.; Shorer Arbel, Y.; Scarfò, L.; et al. Efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 2021, 137, 3165–3173.
- Chan, W.Y.; Howells, L.; Wilson, W.; Sanchez, E.; Ainley, L.; Chavda, S.J.; Dowling, E.; Correia, N.; Lecat, C.S.Y.; McMillan, A.; et al. Serological response to the BNT162b2 mRNA or ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 COVID-19 vaccine after first and second doses in patients with plasma cell disorders: Influence of host and disease factors. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, e21–e26.
- Stampfer, S.D.; Goldwater, M.S.; Jew, S.; Bujarski, S.; Regidor, B.; Daniely, D.; Chen, H.; Xu, N.; Li, M.; Green, T.; et al. Response to mRNA vaccination for COVID-19 among patients with multiple myeloma. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3534–3541.
- Roeker, L.E.; Knorr, D.A.; Thompson, M.C.; Nivar, M.; Lebowitz, S.; Peters, N.; Deonarine, I., Jr.; Momotaj, S.; Sharan, S.; Chanlatte, V.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine efficacy in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2703–2705.
- Naranbhai, V.; Pernat, C.A.; Gavralidis, A.; St Denis, K.J.; Lam, E.C.; Spring, L.M.; Isakoff, S.J.; Farmer, J.R.; Zubiri, L.; Hobbs, G.S.; et al. Immunogenicity and Reactogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 Vaccines in Patients With Cancer: The CANVAX Cohort Study. J. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 40, 12–23.
- Fendler, A.; Shepherd, S.T.C.; Au, L.; Wu, M.; Harvey, R.; Schmitt, A.M.; Tippu, Z.; Shum, B.; Farag, S.; Rogiers, A.; et al. Omicron neutralising antibodies after third COVID-19 vaccine dose in patients with cancer. Lancet 2022, 399, 905–907.
- Ehmsen, S.; Asmussen, A.; Jeppesen, S.S.; Nilsson, A.C.; Østerlev, S.; Vestergaard, H.; Justesen, U.S.; Johansen, I.S.; Frederiksen, H.; Ditzel, H.J. Antibody and T cell immune responses following mRNA COVID-19 vaccination in patients with cancer. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1034–1036.
- Bird, S.; Panopoulou, A.; Shea, R.L.; Tsui, M.; Saso, R.; Sud, A.; West, S.; Smith, K.; Barwood, J.; Kaczmarek, E.; et al. Response to first vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in patients with multiple myeloma. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e389–e392.
- Parry, H.; McIlroy, G.; Bruton, R.; Ali, M.; Stephens, C.; Damery, S.; Otter, A.; McSkeane, T.; Rolfe, H.; Faustini, S.; et al. Antibody responses after first and second Covid-19 vaccination in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 136.
- Terpos, E.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Briasoulis, A.; Gumeni, S.; Malandrakis, P.; Fotiou, D.; Papanagnou, E.D.; Migkou, M.; Theodorakakou, F.; et al. The neutralizing antibody response post COVID-19 vaccination in patients with myeloma is highly dependent on the type of anti-myeloma treatment. Blood Cancer J. 2021, 11, 138.
- Marasco, V.; Carniti, C.; Guidetti, A.; Farina, L.; Magni, M.; Miceli, R.; Calabretta, L.; Verderio, P.; Ljevar, S.; Serpenti, F.; et al. T-cell immune response after mRNA SARS-CoV-2 vaccines is frequently detected also in the absence of seroconversion in patients with lymphoid malignancies. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 548–558.
- Maneikis, K.; Šablauskas, K.; Ringelevičiūtė, U.; Vaitekėnaitė, V.; Čekauskienė, R.; Kryžauskaitė, L.; Naumovas, D.; Banys, V.; Pečeliūnas, V.; Beinortas, T.; et al. Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 COVID-19 mRNA vaccine and early clinical outcomes in patients with haematological malignancies in Lithuania: A national prospective cohort study. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e583–e592.
- Addeo, A.; Shah, P.K.; Bordry, N.; Hudson, R.D.; Albracht, B.; Di Marco, M.; Kaklamani, V.; Dietrich, P.Y.; Taylor, B.S.; Simand, P.F.; et al. Immunogenicity of SARS-CoV-2 messenger RNA vaccines in patients with cancer. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1091–1098.
- Greenberger, L.M.; Saltzman, L.A.; Senefeld, J.W.; Johnson, P.W.; DeGennaro, L.J.; Nichols, G.L. Antibody response to SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with hematologic malignancies. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1031–1033.
- Chung, D.J.; Shah, G.L.; Devlin, S.M.; Ramanathan, L.V.; Doddi, S.; Pessin, M.S.; Hoover, E.; Marcello, L.T.; Young, J.C.; Boutemine, S.R.; et al. Disease- and Therapy-Specific Impact on Humoral Immune Responses to COVID-19 Vaccination in Hematologic Malignancies. Blood Cancer Discov. 2021, 2, 568–576.
- Crombie, J.L.; Sherman, A.C.; Cheng, C.A.; Ryan, C.E.; Zon, R.; Desjardins, M.; Baker, P.; McDonough, M.; Izaguirre, N.; Bausk, B.; et al. Activity of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in patients with lymphoid malignancies. Blood Adv. 2021, 5, 3062–3065.
- Ghione, P.; Gu, J.J.; Attwood, K.; Torka, P.; Goel, S.; Sundaram, S.; Mavis, C.; Johnson, M.; Thomas, R.; McWhite, K.; et al. Impaired humoral responses to COVID-19 vaccination in patients with lymphoma receiving B-cell-directed therapies. Blood 2021, 138, 811–814.
- Tadmor, T.; Benjamini, O.; Braester, A.; Rahav, G.; Rokach, L. Antibody persistence 100 days following the second dose of BNT162b mRNA Covid19 vaccine in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2727–2730.
- Mellinghoff, S.C.; Robrecht, S.; Mayer, L.; Weskamm, L.M.; Dahlke, C.; Gruell, H.; Vanshylla, K.; Schlösser, H.A.; Thelen, M.; Fink, A.M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 specific cellular response following COVID-19 vaccination in patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Leukemia 2022, 36, 562–565.
- Marchesi, F.; Pimpinelli, F.; Sperandio, E.; Papa, E.; Falcucci, P.; Pontone, M.; di Martino, S.; de Latouliere, L.; Orlandi, G.; Morrone, A.; et al. The 12-week kinetics of anti-SARS-CoV-2 antibodies in different haematological cancers after vaccination with BNT162b2. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 362–367.
- Aleman, A.; Upadhyaya, B.; Tuballes, K.; Kappes, K.; Gleason, C.R.; Beach, K.; Agte, S.; Srivastava, K.; Van Oekelen, O.; Barcessat, V.; et al. Variable cellular responses to SARS-CoV-2 in fully vaccinated patients with multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1442–1444.
- Van Oekelen, O.; Gleason, C.R.; Agte, S.; Srivastava, K.; Beach, K.F.; Aleman, A.; Kappes, K.; Mouhieddine, T.H.; Wang, B.; Chari, A.; et al. Highly variable SARS-CoV-2 spike antibody responses to two doses of COVID-19 RNA vaccination in patients with multiple myeloma. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1028–1030.
- Terpos, E.; Trougakos, I.P.; Gavriatopoulou, M.; Papassotiriou, I.; Sklirou, A.D.; Ntanasis-Stathopoulos, I.; Papanagnou, E.D.; Fotiou, D.; Kastritis, E.; Dimopoulos, M.A. Low neutralizing antibody responses against SARS-CoV-2 in older patients with myeloma after the first BNT162b2 vaccine dose. Blood 2021, 137, 3674–3676.
- Piñana, J.L.; López-Corral, L.; Martino, R.; Montoro, J.; Vazquez, L.; Pérez, A.; Martin-Martin, G.; Facal-Malvar, A.; Ferrer, E.; Pascual, M.J.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-reactive antibody detection after SARS-CoV-2 vaccination in hematopoietic stem cell transplant recipients: Prospective survey from the Spanish Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Cell Therapy Group. Am. J. Hematol. 2022, 97, 30–42.
- Mairhofer, M.; Kausche, L.; Kaltenbrunner, S.; Ghanem, R.; Stegemann, M.; Klein, K.; Pammer, M.; Rauscher, I.; Salzer, H.J.F.; Doppler, S.; et al. Humoral and cellular immune responses in SARS-CoV-2 mRNA-vaccinated patients with cancer. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1171–1172.
- Wang, P.; Nair, M.S.; Liu, L.; Iketani, S.; Luo, Y.; Guo, Y.; Wang, M.; Yu, J.; Zhang, B.; Kwong, P.D.; et al. Antibody resistance of SARS-CoV-2 variants B.1.351 and B.1.1.7. Nature 2021, 593, 130–135.
- Solís Arce, J.S.; Warren, S.S.; Meriggi, N.F.; Scacco, A.; McMurry, N.; Voors, M.; Syunyaev, G.; Malik, A.A.; Aboutajdine, S.; Adeojo, O.; et al. COVID-19 vaccine acceptance and hesitancy in low- and middle-income countries. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1385–1394.
- Gupta, A.; Gonzalez-Rojas, Y.; Juarez, E.; Crespo Casal, M.; Moya, J.; Falci, D.R.; Sarkis, E.; Solis, J.; Zheng, H.; Scott, N.; et al. Early Treatment for Covid-19 with SARS-CoV-2 Neutralizing Antibody Sotrovimab. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 385, 1941–1950.
- Shapiro, L.C.; Thakkar, A.; Campbell, S.T.; Forest, S.K.; Pradhan, K.; Gonzalez-Lugo, J.D.; Quinn, R.; Bhagat, T.D.; Choudhary, G.S.; McCort, M.; et al. Efficacy of booster doses in augmenting waning immune responses to COVID-19 vaccine in patients with cancer. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 3–5.
- Le Bert, N.; Tan, A.T.; Kunasegaran, K.; Tham, C.Y.L.; Hafezi, M.; Chia, A.; Chng, M.H.Y.; Lin, M.; Tan, N.; Linster, M.; et al. SARS-CoV-2-specific T cell immunity in cases of COVID-19 and SARS, and uninfected controls. Nature 2020, 584, 457–462.
- Tarke, A.; Sidney, J.; Methot, N.; Yu, E.D.; Zhang, Y.; Dan, J.M.; Goodwin, B.; Rubiro, P.; Sutherland, A.; Wang, E.; et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 variants on the total CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cell reactivity in infected or vaccinated individuals. Cell Rep. Med. 2021, 2, 100355.
- Bange, E.M.; Han, N.A.; Wileyto, P.; Kim, J.Y.; Gouma, S.; Robinson, J.; Greenplate, A.R.; Hwee, M.A.; Porterfield, F.; Owoyemi, O.; et al. CD8(+) T cells contribute to survival in patients with COVID-19 and hematologic cancer. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 1280–1289.
- Fendler, A.; Au, L.; Shepherd, S.T.C.; Byrne, F.; Cerrone, M.; Boos, L.A.; Rzeniewicz, K.; Gordon, W.; Shum, B.; Gerard, C.L.; et al. Functional antibody and T cell immunity following SARS-CoV-2 infection, including by variants of concern, in patients with cancer: The CAPTURE study. Nat. Cancer 2021, 2, 1321–1337.
- Lindemann, M.; Klisanin, V.; Thümmler, L.; Fisenkci, N.; Tsachakis-Mück, N.; Ditschkowski, M.; Schwarzkopf, S.; Klump, H.; Reinhardt, H.C.; Horn, P.A.; et al. Humoral and Cellular Vaccination Responses against SARS-CoV-2 in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplant Recipients. Vaccines 2021, 9, 1075.
- Ram, R.; Hagin, D.; Kikozashvilli, N.; Freund, T.; Amit, O.; Bar-On, Y.; Beyar-Katz, O.; Shefer, G.; Moshiashvili, M.M.; Karni, C.; et al. Safety and Immunogenicity of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccine in Patients after Allogeneic HCT or CD19-based CART therapy-A Single-Center Prospective Cohort Study. Transplant. Cell. Ther. 2021, 27, 788–794.
- Harrington, P.; Doores, K.J.; Radia, D.; O’Reilly, A.; Lam, H.P.J.; Seow, J.; Graham, C.; Lechmere, T.; McLornan, D.; Dillon, R.; et al. Single dose of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine against severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) induces neutralising antibody and polyfunctional T-cell responses in patients with chronic myeloid leukaemia. Br. J. Haematol. 2021, 194, 999–1006.
- Harrington, P.; de Lavallade, H.; Doores, K.J.; O’Reilly, A.; Seow, J.; Graham, C.; Lechmere, T.; Radia, D.; Dillon, R.; Shanmugharaj, Y.; et al. Single dose of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine against SARS-CoV-2 induces high frequency of neutralising antibody and polyfunctional T-cell responses in patients with myeloproliferative neoplasms. Leukemia 2021, 35, 3573–3577.
- Nelli, F.; Fabbri, A.; Onorato, A.; Giannarelli, D.; Silvestri, M.A.; Giron Berrios, J.R.; Virtuoso, A.; Marrucci, E.; Signorelli, C.; Chilelli, M.G.; et al. Effects of active cancer treatment on safety and immunogenicity of COVID-19 mRNA-BNT162b2 vaccine: Preliminary results from the prospective observational Vax-On study. Ann. Oncol. 2022, 33, 107–108.
- Gounant, V.; Ferré, V.M.; Soussi, G.; Charpentier, C.; Flament, H.; Fidouh, N.; Collin, G.; Namour, C.; Assoun, S.; Bizot, A.; et al. Efficacy of Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus-2 Vaccine in Patients With Thoracic Cancer: A Prospective Study Supporting a Third Dose in Patients With Minimal Serologic Response After Two Vaccine Doses. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2022, 17, 239–251.
- Palich, R.; Veyri, M.; Vozy, A.; Marot, S.; Gligorov, J.; Benderra, M.A.; Maingon, P.; Morand-Joubert, L.; Adjoutah, Z.; Marcelin, A.G.; et al. High seroconversion rate but low antibody titers after two injections of BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) vaccine in patients treated with chemotherapy for solid cancers. Ann. Oncol. 2021, 32, 1294–1295.
- Figueiredo, J.C.; Merin, N.M.; Hamid, O.; Choi, S.Y.; Lemos, T.; Cozen, W.; Nguyen, N.; Finster, L.J.; Foley, J.; Darrah, J.; et al. Longitudinal SARS-CoV-2 mRNA Vaccine-Induced Humoral Immune Responses in Patients with Cancer. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 6273–6280.
- Redjoul, R.; Le Bouter, A.; Parinet, V.; Fourati, S.; Maury, S. Antibody response after third BNT162b2 dose in recipients of allogeneic HSCT. Lancet Haematol. 2021, 8, e681–e683.
- Debie, Y.; Vandamme, T.; Goossens, M.E.; van Dam, P.A.; Peeters, M. Antibody titres before and after a third dose of the SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine in patients with cancer. Eur. J. Cancer 2022, 163, 177–179.
- Rottenberg, Y.; Grinshpun, A.; Ben-Dov, I.Z.; Oiknine Djian, E.; Wolf, D.G.; Kadouri, L. Assessment of Response to a Third Dose of the SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 mRNA Vaccine in Patients With Solid Tumors Undergoing Active Treatment. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 300–301.
- Re, D.; Seitz-Polski, B.; Brglez, V.; Carles, M.; Graça, D.; Benzaken, S.; Liguori, S.; Zahreddine, K.; Delforge, M.; Bailly-Maitre, B.; et al. Humoral and cellular responses after a third dose of SARS-CoV-2 BNT162b2 vaccine in patients with lymphoid malignancies. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 864.
- Fenioux, C.; Teixeira, L.; Fourati, S.; Melica, G.; Lelievre, J.D.; Gallien, S.; Zalcman, G.; Pawlotsky, J.M.; Tournigand, C. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response to 2 or 3 Doses of the BNT162b2 Vaccine in Patients Treated With Anticancer Agents. JAMA Oncol. 2022, 8, 612–617.
- Ligumsky, H.; Dor, H.; Etan, T.; Golomb, I.; Nikolaevski-Berlin, A.; Greenberg, I.; Halperin, T.; Angel, Y.; Henig, O.; Spitzer, A.; et al. Immunogenicity and safety of BNT162b2 mRNA vaccine booster in actively treated patients with cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2022, 23, 193–195.
- Naranbhai, V.; St Denis, K.J.; Lam, E.C.; Ofoman, O.; Garcia-Beltran, W.F.; Mairena, C.B.; Bhan, A.K.; Gainor, J.F.; Balazs, A.B.; Iafrate, A.J. Neutralization breadth of SARS-CoV-2 viral variants following primary series and booster SARS-CoV-2 vaccines in patients with cancer. Cancer Cell 2022, 40, 103–108.
- Luangdilok, S.; Wanchaijiraboon, P.; Pakvisal, N.; Susiriwatananont, T.; Zungsontiporn, N.; Sriuranpong, V.; Sainamthip, P.; Suntronwong, N.; Vichaiwattana, P.; Wanlapakorn, N.; et al. Immunogenicity after a Third COVID-19 mRNA Booster in Solid Cancer Patients Who Previously Received the Primary Heterologous CoronaVac/ChAdOx1 Vaccine. Vaccines 2022, 10, 1613.
- Reimann, P.; Ulmer, H.; Mutschlechner, B.; Benda, M.; Severgnini, L.; Volgger, A.; Lang, T.; Atzl, M.; Huynh, M.; Gasser, K.; et al. Efficacy and safety of heterologous booster vaccination with Ad26.COV2.S after BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine in haemato-oncological patients with no antibody response. Br. J. Haematol. 2022, 196, 577–584.
- Sablerolles, R.S.G.; Rietdijk, W.J.R.; Goorhuis, A.; Postma, D.F.; Visser, L.G.; Geers, D.; Schmitz, K.S.; Garcia Garrido, H.M.; Koopmans, M.P.G.; Dalm, V.; et al. Immunogenicity and Reactogenicity of Vaccine Boosters after Ad26.COV2.S Priming. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 951–963.
More
