You're using an outdated browser. Please upgrade to a modern browser for the best experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Yusof Kamisah and Version 2 by Camila Xu.
Parkia is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Fabaceae (subfamily, Mimosoideae) with pan-tropical distribution. The word Parkia was named after the Scottish explorer Mungo Park, who drowned in the Niger River, Nigeria in January 1805. The genus Parkia (Fabaceae, Subfamily, Mimosoideae) comprises about 34 species of mostly evergreen trees widely distributed across neotropics, Asia, and Africa.
- Parkia
- Mimosoideae
- traditional medicine
- secondary metabolite
1. Introduction
Parkia is a genus of flowering plants belonging to the family Fabaceae (subfamily, Mimosoideae) with pan-tropical distribution [1]. The word Parkia was named after the Scottish explorer Mungo Park, who drowned in the Niger River, Nigeria in January 1805 [2]. Thirty-one species from this genus were reported in 1995 [3]. Another four more species were discovered in 2009 [4]. Out of these species, 10 species found in Asia, four in Africa, and 20 in neotropics. Meanwhile, according to a plant list (2018), 80 scientific names are recorded from the genus Parkia containing 41 accepted names and 39 synonym species (The Plant List, 2018). These plants bear fruits called pods. Each pod contains up to 25–30 seeds. Many species from Parkia have been reported to be rich in carbohydrate [5][6][7][5,6,7], protein [8][9][10][8,9,10] and minerals [11][12][13][14][11,12,13,14].
125]. In addition, some minor components, such as 82–84 are also identified. Meanwhile, 132 content in P. speciosa seed was reported to be 4.15 mg/100 g [85][37], but that of P. biglobosa in a recent study was found to be much higher (53.47 mg/100 g). Phospholipid content of P. biglobosa seeds was about 451 mg/100 g [122]. The seeds also contain palmitic acid, stearic acid, oleic acid, arachidic acid, and linoleic acid, the most abundant fatty acid [22][121][130][22,121,130]. Similar fatty acids are also reported in the raw seeds of P. roxburghii chloroform/methanol extract, in addition to total free phenol (0.56 g/100 g seed flour) and tannins (0.26 g/100 g seed flour) contents [87][41].
 Steroidal compounds are also reported in the genus of Parkia (Table 2 and Figure 34). β-Sitosterol (60) is one of the major components in P. speciosa [120] and P. biglobosa seeds [121]. The steroid together with stigmasterol are purified from recrystallization of chloroform/methanol fraction of P. speciosa seeds. Its composition in P. biglobosa seeds was reported to be about 377 mg/100 g dry weight [122]. It is also purified from methanol extract of P. javanica leaves [88][42]. Apart from 60, 61, and 65, which are present in P. javanica and/or P. biglobosa, all other steroids 62–64 and 66 reported from different studies are found in P. speciosa seeds. Other than β-sitosterol (60), stigmasterol (61), and campesterol (65) are also among the numerous compounds identified from the seeds of P. speciosa [117][119][120][124][117,119,120,124]. The percentage composition of 60, 61, 62 and a triterpenoid 49 in the plant was reported as 3.42%, 2.18%, 2.29%, and 0.71% w/w, respectively [85][37]. In the case of P. biglobosa, the percentage composition of 60, 61 and 62 in the seeds is higher with values of 55.7%, 3.42%, 37.1% for the unfermented, and 56.8%, 3.38%, 35.9% for the fermented, respectively, indicating that fermentation process may lower 61 and 62, but increases 60 contents [129]. Meanwhile, Akintayo (2004) had recorded 60 as the most abundant compound in P. biglobosa seeds, constituting approximately 39.5% w/w. Compound 60 was isolated as a pure compound through column chromatographic separation of benzene fraction of P. bicolor leaves [88][42].
Steroidal compounds are also reported in the genus of Parkia (Table 2 and Figure 34). β-Sitosterol (60) is one of the major components in P. speciosa [120] and P. biglobosa seeds [121]. The steroid together with stigmasterol are purified from recrystallization of chloroform/methanol fraction of P. speciosa seeds. Its composition in P. biglobosa seeds was reported to be about 377 mg/100 g dry weight [122]. It is also purified from methanol extract of P. javanica leaves [88][42]. Apart from 60, 61, and 65, which are present in P. javanica and/or P. biglobosa, all other steroids 62–64 and 66 reported from different studies are found in P. speciosa seeds. Other than β-sitosterol (60), stigmasterol (61), and campesterol (65) are also among the numerous compounds identified from the seeds of P. speciosa [117][119][120][124][117,119,120,124]. The percentage composition of 60, 61, 62 and a triterpenoid 49 in the plant was reported as 3.42%, 2.18%, 2.29%, and 0.71% w/w, respectively [85][37]. In the case of P. biglobosa, the percentage composition of 60, 61 and 62 in the seeds is higher with values of 55.7%, 3.42%, 37.1% for the unfermented, and 56.8%, 3.38%, 35.9% for the fermented, respectively, indicating that fermentation process may lower 61 and 62, but increases 60 contents [129]. Meanwhile, Akintayo (2004) had recorded 60 as the most abundant compound in P. biglobosa seeds, constituting approximately 39.5% w/w. Compound 60 was isolated as a pure compound through column chromatographic separation of benzene fraction of P. bicolor leaves [88][42].
2. Traditional Medicinal Uses
Parkia species are being used across all tropical countries to cure different ailments. Virtually, all parts of Parkia plants are utilized traditionally for different medicinal purposes. The materials of different parts of Parkia plants are processed as paste, decoction, and juice for the treatment of various ailments (Table 1). Almost all reported Parkia species are used in different forms to cure diarrhea and dysentery [15]. Different parts of P. biglobosa, P. clappertoniana, P. roxburghii, and P. speciosa are reported to be traditionally used for the treatment of diabetes [16][17][18][16,17,18]. Furthermore, skin-related diseases, such as eczema, skin ulcers, measles, leprosy, wound, dermatitis, chickenpox, scabies, and ringworm are treated using leaves, pods, and roots of P. speciosa and P. timoriana [19][20][21][19,20,21]. The stem barks of P. bicolor, P. clappertoniana, P. biglobosa, P. roxburghii as well as roots of P. speciosa are applied in the form of paste and decoction to treat different skin problems [22][23][24][25][22,23,24,25]. Decoction and paste of stem bark, pod, or root of P. biglobosa and P. speciosa are used to treat hypertension [22][26][27][22,26,27]. Moreover, stem barks of P. bicolor, P. biglobosa and leaves of P. speciosa are used for severe cough and bronchitis [28][29][30][28,29,30]. These aforementioned uses suggested that Parkia plants are likely to contain constituents with broad and diverse biological activities, such as antidiabetic, antimicrobial, antihypertensive, and anti-inflammatory.Table 1.
The medicinal uses of plants from genus
Parkia
.
| Species | Part Used | Method of Preparation | Medicinal Uses | Region/Country | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P. bicolor | Stem bark | Pulverized powder | Wound healing | West coast of Africa and Nigeria |

Figure 45.
Structural formulas of cyclic polysulfides
81
–
93
, as previously listed in
Table 2
.
4. Pharmacological Activities of Parkia Species
Numerous bioactive constituents such as phenolics, flavonoids, terpenoids, and volatile compounds present in Parkia species may account for its various health benefits, and therefore responsible for the vast pharmacological properties (Table 3). However, only few species have been extensively studied.Table 3.
Pharmacological activities of
Parkia species
extracts and fractions.
| Activity | Species | Part | Type of Extract/Compound | Key Findings | References | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antimicrobial | P. biglobosa | Leaf, stem bark, and root | Methanolic and aqueous | Active against S. aureus, B. subtilis, E. coli, P. aeruginosa | [23] | ||||||
| . | [ | 44 | ] | [ | 38] | Tree | Diarrhea, dysentery | Southwest Nigeria | [31][55] | ||
| P. biglobosa | Root bark | Aqueous and methanol | Active against E. coli, S. aureus, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa. Activity: Aqueous > methanol |
[82][34] | Stem barks | Decoction | Bad cough, measles, and woman infertility |
||||
| P. biglobosa | Leaves and pod | Aqueous and ethanol | Active against S. aureus, E. aerogenes, S. typi, S. typhimurium, Shigella spp., E. coli, and P. aeruginosa | Cameroon | (bacteria), Mucor spp., and Rhizopus spp. (fungi)[ | [131][133]28] | |||||
| Stem barks | Decoction | Diarrhea and skin ulcers | |||||||||
| P. biglobosa | Ghana | [ | Bark and leaves | Hydro-alcohol and aqueous | Active against E. coli, S. enterica, and S. dysenteriae. Activity: hydroalcoholic > aqueous | [42][65]32][56] | |||||
| P. biglobosa | Roots & bark | Paste | Dental disorder | Ivory Coast | |||||||
| P. speciosa | Seeds | Water suspension | Active against S. aureus, A. hydrophila, S. agalactiae, S. anginosus, and V. parahaemolyticus isolated from moribund fishes and shrimps | [132][143 | [29] | ||||||
| ] | Seed and stem bark | Fresh seeds | |||||||||
| P. speciosa | Seed peel | Ethyl acetate (EA) Hexane | Fish poison | West Africa | Ethanol[33 |
EA: Four times higher than streptomycin against S. aureus and three times higher for E. coli][34][57,58] | |||||
| . Hexane: 50% inhibitory ability of streptomycin for both bacteria. Ethanol: no inhibition | [ | 133 | ] | [148] | Root | Decoction combined with other plants | Infertility | ||||
| P. speciosa | Pod extract and its silver | Nigeria | Aqueous | Pod: active against P. aeruginosa Silver particles: active against P. aeruginosa | [134][145][34][58] | ||||||
| Bark infusion with lemon | Diarrhea | Nigeria | [35][59] | ||||||||
| P. speciosa | Sapwood, heartwood, and bark | Methanol | Bark: Active against G. trabeum. Sapwood and heartwood: No effect | [135][147] | Stem bark | Anti-snake venom | Nigeria | ||||
| P. speciosa | Seeds | Chloroform, petroleum ether, Aqueous and methanol | Active against H. pylori except aqueous extract. Activity: chloroform > methanol > petroleum ether | [136][222] | [36][60] | ||||||
| Bark | Paste, decoction | Wound healing leprosy, hypertension, mouth wash, toothpaste | Nigeria | ||||||||
| P. speciosa | Seed | Methanol Ethyl acetate |
Methanol: active against H. pylori. Ethyl acetate: active against E. coli Both: no effect on S. typhimurium, S. typhi, and S sonnei | [ | 22 | [137][][23][22,23] | |||||
| 144 | ] | Leaves and roots | Eyesore | Lotion | Gambia | ||||||
| P. javanica | Stem bark | Methanol | Good inhibitory activity against E. coli, S. aureus S. pyogenes found in chronic wound | [138][223] | [23] | ||||||
| Bark | Hot decoction | Fever | Gambia | [23 | |||||||
| P. javanica | Stem bark | Methanol | Active against four Vibrio cholerae strains | ] | |||||||
| [ | 139 | ] | [ | 224] | Bark | Decoction | Malaria, diabetes, amenorrhea, and hypertension | Senegal, Mali, Ghana Togo, and South Africa | [11][37][38][39 | ||
| P. javanica | Leaves | Gold and silver nanoparticles | Good inhibitory activity against S. aureus | ] | [11[, | [140]4040,61,62],63] | |||||
| [ | 151 | ] | Roots and bark | Decoction of the roots with Ximenia americana | Weight loss | Burkina Faso | [ | ||||
| P. javanica | Bark | 41 | ] | [ | 64] | ||||||
| Methanol extract and semi-polar fractions (chloroform and ethyl acetate) | Active against | Neisseria gonorrhoeae | . Chloroform showed the best activity | [76][97] | Stem bark | Boiled bark | Diarrhea, conjunctivitis, severe cough, and leprosy | West Coast Africa | [ | ||
| P. javanica | 23 | ] | Seeds, leaves and skin pods | Aqueous | Active against S. aureus, A. hydrophila, and S. typhimurium Not active against E. coli | [141][152[42][43][23,65,66] | |||||
| ] | Leaves | Decoction | Violent colic chest and muscular pain | Northern Nigeria | |||||||
| P. clappertoniana | Leaves and barks | Ethanol | Active against Salmonellae and Shigella | [51][73 | [44][38] | ||||||
| ] | bark | Infusion | Dental caries and astringent | Guinea Bissau | |||||||
| P. clappertoniana | Stem bark and leaves | Aqueous and methanol | Active against S. aureus and P. aeruginosa. Methanol extract was more potent |
[49] | [45][67] | ||||||
| [ | 71 | ] | P. biglandulosa | Seed bark | |||||||
| P. biglandulosa | Saponins | Leaf | Astringent | Methanol | Active against E. coli, India | P. aeruginosa, and S. aureus | [142][154][46][68] | ||||
| Stem bark | Hemagglutination, ulcer | ||||||||||
| P. filicoidea | Stem barks | Aqueous, acetone and ethanol | Active against | India | S. aureus, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, S. viridans and B. subtilis. Not active against E. coli | [96][[47][69] | |||||
| 50 | ] | Tree | Inflammation and ulcer | India | |||||||
| P. bicolor | Leaves | Ethyl acetate, ethanol and aqueous | Active against E. coli, S. aureus, P. aeruginosa, A. niger, B. cereus and a fungus, C. utilis | [ | 48 | [23]][70] | |||||
| P. clappertoniana | Tree | Hypertension | Southwest Nigeria | ||||||||
| P. bicolor | Roots | Methanol, ethyl acetate and Aqueous | Active against C. diphtheria, K. pneumoniae, P. mirabilis, S. typhi, and S. pyogenes | [28] | [31][55] | ||||||
| P. pendula | Root | Seeds | LectinDental caries and conjunctivitis | African | [49 | Reduced cellular infectivity of human cytomegalovirus in human embryo lung (HEL) cells. | [143][225]][50][71,72] | ||||
| Seed | Crudely pounded | Labor induction | Ghana | [17] | |||||||
| Hypoglycemic | P. speciosa | Seeds and pods | Chloroform | Strong glucose-lowering activity in alloxan-induced diabetic rats Activity: seeds > pod |
[ | Tree | Diarrhea | Kaduna and Nigeria | [51][73] | ||
| Leaves and bark | Maceration | Epilepsy | Northern Nigeria | [52][74] | |||||||
| Stem bark | Chickenpox and measles | Southwest Nigeria | [24] | ||||||||
| 144 | ] | [ | 157 | ] | |||||||
| P. speciosa | Rind, leaves and seeds | Ethanol | Inhibited α-glucosidase activity in rat Activity: rind > leaf > seed |
[145][158] | |||||||
| P. speciosa | Seed | Chloroform | Reduced plasma glucose levels in alloxan-induced diabetic rats | [120] | |||||||
| P. biglobosa | Fermented seeds | Methanol and aqueous | Reduced fasting plasma glucose in alloxan-induced diabetic rats | [146][147][160,161] | Tree | Diabetes, leprosy, and ulcers | Ghana | [53][75] | |||
| P. biglobosa | Seeds | Protein | Significantly increased lipid peroxidation product levels in brain and testes of diabetic rats | [148][226] | Tree | Mouthwash and toothache | Nigeria | ||||
| P. biglobosa | Seeds | Methanol and fractions (chloroform and n-hexane) | Showed glucose-lowering effect Activity: chloroform > methanol > n-hexane |
[37][40] | [54][76] | ||||||
| Tree | Eczema and skin diseases | Nigeria | |||||||||
| P. javanica | Fruits | Ethyl acetate fraction | Reduced blood glucose inhibited α-glucosidase and α-amylase in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats | [ | [55][77] | ||||||
| 18 | ] | Bark | Infusion | Hernia | Ghana | [53 | |||||
| Antitumor/ Anticancer | ] | [ | 75 | ] | |||||||
| P javanica | Fruits | Aqueous methanol | Increased apoptosis in sarcoma-180 cancer cell lines | [ | 149][227] | P. pendula | Leaves bark | Genital bath | Netherland | [56 | |
| P javanica | Seeds | Methanol | Caused 50% death in HepG2 (liver cancer cell) but not cytotoxic to normal cells | [90][44] | ][78] | ||||||
| Bark | Decoction | Malaria | Brazil | [57 | |||||||
| P javanica | ] | [ | 79 | ] | |||||||
| Seeds | Lectin | Inhibited proliferation in cancerous cell lines; P388DI and J774, B-cell hybridoma and HB98 cell line | [ | 150][173] | P. speciosa | Seed | |||||
| P. speciosa | Eaten raw or cooked oral decoction | Seed coats | Diabetes | Methanol extractMalaysia | Demonstrated selective cytotoxicity to MCG-7 and T47D (breast cancer), HCT-116 (colon cancer) | [151][228][58][80] | |||||
| Leaves | Pounded with rice and applied on the neck | Cough | Malaysia | [30] | |||||||
| P. speciosa | Pods | Methanolic ethyl acetate fraction | Showed selective cytotoxicity on breast cancer cells MCF-7 | [152][170] | Root | Decoction | Skin problems | Southern Thailand | [ | ||
| P. biglobosa | 21 | ] | |||||||||
| Leaves and stem | Methanol | Antiproliferative effect in human cancer cells T-549, BT-20, and PC-3 | [ | 153][174] | Root | Decoction taken orally | Hypertension and diabetes | Malaysia | [26] | ||
| P. filicoidea | Leaves | Methanol | Antiproliferative effect in in human cancer cells T-549, BT-20, and PC-3 | [153][174] | Fruit | Eaten raw | Diabetes | Malaysia | [30] | ||
| Antiproliferative and anti-mutagenic | P. biglandulosa | Seeds | Lectin | T cell mitogen and antiproliferative against P388DI and J774 cancer cell lines | [150][173] | Seed | Eaten raw | Detoxification and hypertension | Singapore | [ | |
| Antihypertensive | P. speciosa | 59 | ] | [ | 81] | ||||||
| Seeds | Aqueous | Showed moderate ACE-inhibitory activity in in vitro | [ | 154 | ][191] | Ringworm | Malaysia | [ | |||
| P. speciosa | Seeds | Peptide | Inhibited angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) in rats. No effect observed in non-hydrolyzed samples | [155][156][189,190] | 60][82] | ||||||
| Leaf | Decoction | Dermatitis | Indonesia | ||||||||
| P. speciosa | Pods | Methanol | [ | 20 | Prevented the increases in blood pressure and angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) and restored nitric oxide in hypertensive rat model | [112]] | |||||
| Root | |||||||||||
| P. biglobosa | Oral decoction | Stem bark | Toothache | AqueousMalaysia | Induced hypotension in adrenaline-induced hypertensive rabbits | [157[27] | |||||
| ] | [ | 181 | ] | Tree | Heart problem, constipation and edema | India | |||||
| P. biglobosa | Roasted and fermented seeds | Aqueous | Induced relaxation in rat aorta precontracted with phenylephrine in the presence or absence of endothelium. | [158][180] | [61][62][83,84] | ||||||
| Leaves | Dermatitis | Indonesia | [63][85] | ||||||||
| Seed | Loss of appetite | Indonesia | [64][86] | ||||||||
| Seed | Cooked | Kidney disorder | West Malaysia | [65][87] | |||||||
| P. timoriana | Bark and twig | Decoction of bark and twig paste | Diarrhea, dysentery, and wound | India | [66][88] | ||||||
| Bark | Decoction used to bath | Fever | Gambia | [67][89] | |||||||
| Pulp bark | Mixed with lemon | Ulcer and wound | Gambia | [67][89] | |||||||
| Fruit | Diabetes | Thailand | [68][90] | ||||||||
| Pod | Pounded in water | Hair washing, skin diseases, and ulcers | India | [19] | |||||||
| Bark and leaves | Head washing, skin diseases, and ulcers | India | [19] | ||||||||
| Bark | Decoction with Centella. asiatica and Ficus glomerata | Diabetes | India | [16] | |||||||
| P. roxburghii | Tree | Tender pod and bark taken orally | Diarrhea, dysentery, intestinal disorder, and bleeding piles | India | [69][91] | ||||||
| The fruit or young shoot | Green portion of the fruit mixed with water to be taken orally | Dysentery, diarrhea, food poisoning, wound, and scabies | India | [70][92] | |||||||
| Seed | Grounded and mixed with hot water | Postnatal care, diarrhea, edema and tonsillitis | Malaysia | [71][93] | |||||||
| Pod | Diabetes, hypertension, and urinary tract infections | India | [18] | ||||||||
| Leaves, pod, peals, and bark | Diarrhea and dysentery | India | [72][94] | ||||||||
| Stem bark | Hot water extraction | Diarrhea and dysentery | India | [73][95] | |||||||
| Bark | Turn into paste | Used as plaster for eczema | India | [25] | |||||||
| P. javanica | Bark, pod, and seed | Taking orally as vegetable | Dysentery and diarrhea | India | [15] | ||||||
| Tree | Inflammation | India | [74][96] | ||||||||
| Bark fruit | Dysentery and piles | India | [75][51] | ||||||||
| Stomachache and cholera | India | [76][97] | |||||||||
| Bark and leaves | Lotion | Sores and skin diseases | [77][98] | ||||||||
| Tree | Diarrhea, cholera dysentery, and food poisoning | India | [78][99] |
3. Phytochemistry of Genus Parkia
Among the numerous species of Parkia plant, the chemistry of only few are known. However, different parts of the reported ones have been validated as good sources of phenolic compounds [11][79][80][11,31,32], saponins [81][82][83][33,34,35], terpenoids [83][84][85][35,36,37], steroids [23][44][86][23,38,39], tannins [37][44][86][38,39,40], fatty acids [23][87][23,41], and glycosides [88][89][90][42,43,44]. Various phytochemicals are found in the stem barks, leaves, seeds, and pods of these plants. The stem bark of P. biglobosa is reported to contain phenols, flavonoids, sugars, tannins, terpenoids, steroids, saponins [11][44][11,38], alkaloid, and glycosides [83][89][91][35,43,45], while the leaves contain glycosides, tannins, and alkaloids in trace amount [11][23][92][11,23,46], in addition to flavonoids, phenols, and anthraquinones [93][47]. Phytochemical screening of the seeds shows the presence of saponins, alkaloids, flavonoids, polyphenols, terpenoids, glycosides and tannins [94][95][48,49]. Fermentation or roasting of P. biglobosa seeds results in the alteration of the bioactive components. P. bicolor leaves contain chemical constituents similar to that of P. biglobosa such as glycosides, tannin, and alkaloids in trace amount [23]. The stem bark of P. bicolor contains alkaloids, tannins, saponins, glycosides, flavonoids, and terpenoids [83][35], while P. biglandulosa contains tannins, saponins, and glycosides, and P. filicoidea possesses flavonoids, sugars, saponins, and tannins [96][50]. The seed of P. javanica contains flavonoid, saponins, alkaloids, terpenoids, anthraquinones, steroids, and glycosides [90][44]. The pods are reported to have tannins, flavonoids, and saponins, all of which are significantly diminished when subjected to various processing methods, such as ordinary and pressure cooking methods [75][97][51,52]. Alkaloids, glycosides, saponins, and tannins are present in the whole plant of P. clappertoniana [79][31]. Phytochemical analysis of the leaves of P. platycephala revealed the presence of phenols, terpenoids, flavonoids [98][53], tannins and saponins [99][54]. Furthermore, flavonoids, alkaloids, phenols, and terpenoids were reported to be present in all parts of P. speciosa plant [85][37]. Phytochemicals (primary and secondary metabolites) are well known for their vast medicinal benefits to plants and human [100]. The primary metabolites—such as carbohydrate, proteins, chlorophyll, lipids, nucleic, and amino acids [101][102][103][101,102,103]—are responsible for plants’ biochemical reactions such as respiration and photosynthesis [102]. The secondary metabolites are majorly alkaloids, phenols, terpenoids, flavonoids, saponins, steroids, tannins, and glycosides, which play important roles in protecting the plants against damages and improving plant aroma, coloration and flavor [101][103][101,103], The phytochemicals are present in various parts of the plants especially in the three major parts viz. the leaves, stems and roots. Their percentage composition in each plant may vary depending on environmental conditions, variety and processing methods [101]. Previous studies have shown that phenolic compounds are the most abundant and widely distributed phytoconstituents (45%), followed by steroids and terpenoids (27%), and alkaloids (18%) [101][104][101,104]. Alkaloids, flavonoids, tannins, and phenolic compounds are the most common constituents that have been studied in phytochemistry [104][105][104,105]. Several compounds from these classes have been identified and investigated from Parkia plants for various pharmacological activities. Despite the enormous reports on the phytochemical screening of different species from the genus Parkia, structure identification and purification of compounds from these species are scarcely reported compared to other genera. The compounds were identified using high-performance liquid chromatography with diode-array detector (HPLC-DAD), liquid chromatography mass spectrometry (LCMS), flow analysis-ionization electrospray ion trap tandem mass spectrometry (FIA-ESI-IT-MS), gas chromatography time-of-flight mass spectrometry (GC/ToF-MS), high-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ion mass spectrometry (HPLC-ESI-MS), and chromatographic purification from the fraction and characterization through nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR).3.1. Polyphenolic Compounds
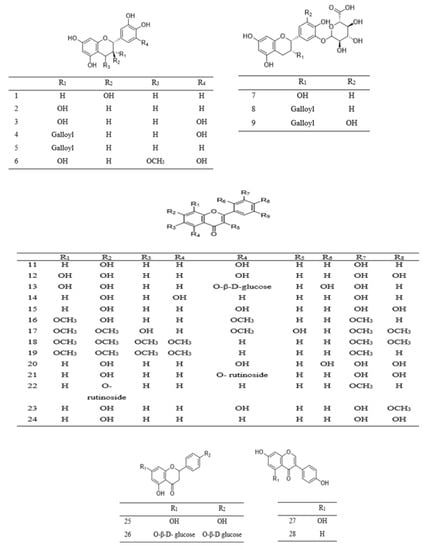
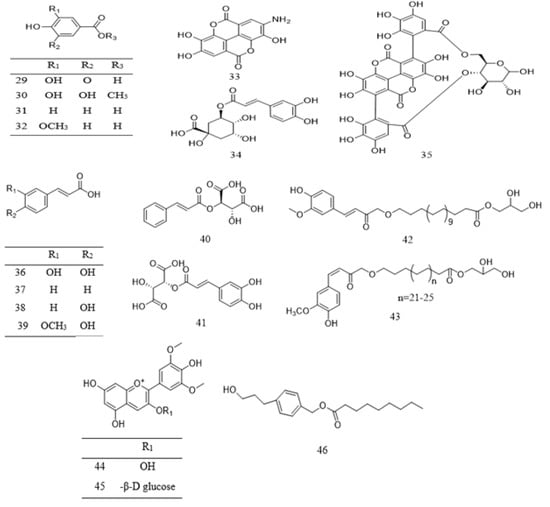
Phenolic compounds found in Parkia species are grouped into simple phenol (10 and 31), phenolic acids 29–41, flavone 15–19 and 24, flavanone 25–26, flavonol 11–14 and 20–22, methoxyflavonol 23, as well as flavanol 1–10 (Table 2). Phenolic acids are mostly found in the pods and edible parts of Parkia, while polyphenolic compounds are present in the leaves, stem barks, roots, or seeds. The most commonly reported flavonoid in Parkia species are flavanol 1 and its isomer 8, which are obtained from the pod and bark of P. speciosa and P. biglobosa, respectively [106][107][108][106,107,108] and the remaining flavanols 11–18 are mainly galloylated catechins. Compound 11 is isolated from ethyl acetate fraction of P. roxburghii pod [18], while compounds 12–18 are identified from the ethyl acetate fraction of root/stem of P. biglobosa [18]. One methoxyflavonol 23, two flavanone 26–27 and isoflavones 27–28 are identified in the edible parts of P. javanica [108]. A new flavanone, naringenin-1-4′-di-O-ß-D-glucopyranoside 26 is isolated from n–butanol fraction of P. biglobosa [109], while a new phenylpropanoid is elucidated as 4-(3-hydroxypropyl)benzyl nonanoate from the leaves of P. javanica [110]. Isolation of compounds 42–43 for the first time as a pure compound was reported from the ethanol extract of P. biglobosa bark [111]. The structures of these compounds are illustrated in Figure 12 and Figure 23.
Figure 12.
Structural formulas of polyphenolics
1
–
28
, as previously listed in
Table 2
.

Figure 23.
Structural formulas of polyphenolics
29
–
46
, as previously listed in
Table 2
.
Table 2.
Phytochemical compounds from
Parkia
.
| Structure Number | Type | Compound | Species | Part | Reference | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Polyphenolics | |||||||||||
| 1 | Flavanol | Catechin | P. speciosa | Pod | [107] | ||||||
| P. biglobosa | Root/bark | [106] | |||||||||
| P. javanica | Edible part | [108] | |||||||||
| 2 | Flavanol | Epicatechin | P. speciosa | Pod | [107] | ||||||
| P. javanica | Edible part | [108] | |||||||||
| 3 | Flavanol | Epigallocatechin | P. biglobosa | Root/bark | [111] | ||||||
| P. javanica | Edible part | [108] | |||||||||
| 4 | Flavanol | Epigallocatechin gallate | P. roxburghii | Pod | [18] | ||||||
| P. biglobosa | Root/bark | [106][111][106,111] | |||||||||
| 5 | Flavanol | Epicatechin-3-O-gallate | P. biglobosa | Bark | [111] | ||||||
| 6 | Flavanol | 4-O-methyl-epigallocate-chin | P. biglobosa | Bark | [111] | ||||||
| 7 | Flavanol | Epigallocatechin-O-glucuronide | P. biglobosa | Root/bark | [106] | ||||||
| 8 | Flavanol | Epicatechin-O-gallate-O-glucuronide | P. biglobosa | Root/bark | [106] | ||||||
| 9 | Flavanol | Epigallocatechin-O-gallate-O-glucuronide | P. biglobosa | Root/bark | [106] | ||||||
| 10 | Flavanol | Theaflavin gallate | P. speciosa | Pod | [112] | ||||||
| 11 | Flavonol | Kaempferol | P. speciosa | Pod | [107] | ||||||
| P. javanica | Edible part | [108] | |||||||||
| 12 | Flavonol | Quercetin | P. speciosa | Pod | [107] | ||||||
| 13 | Flavonol | Hyperin | P. roxburghii | Pod | [18] | ||||||
| 14 | Flavonol | Apigenin | P. speciosa | Pod | [112] | ||||||
| 15 | Flavone | 3,7,3′,4′-Tetrahydroxyflavone | P. clappertoniana | Seeds | [113][114][113,114] | ||||||
| 16 | Flavone | 7-Hydroxy-3, 8, 4′-trimethoxyflavone | P. clappertoniana | Leaves | [115] | ||||||
| 17 | Flavone | 2′-Hydroxy-3,7,8,4′,5′′pentamethoxyflavone | P. clappertoniana | Leaves | [115] | ||||||
| 18 | Flavone | Nobiletin | P. speciosa | Pod | [112] | ||||||
| 19 | Flavone | Tangeritin | P. speciosa | Pod | [112] | ||||||
| 20 | Flavonol | Myricetin | P. javanica | Edible part | [108] | ||||||
| P. speciosa | Pod | [112] | |||||||||
| 21 | Flavonol glycoside | Rutin | P. javanica | Edible part | [108] | ||||||
| P. speciosa | Pod | [112] | |||||||||
| 22 | Flavonol glycoside | Didymin | P. speciosa | Pod | [112] | ||||||
| 23 | Methoxy flavonol | Isorhamnetin | P. javanica | Edible part | [108] | ||||||
| 24 | Flavone | Luteolin | P. javanica | Edible part | [108] | ||||||
| 25 | Flavanone | Naringenin | P. javanica | Edible part | [108] | ||||||
| 26 | Flavanone | Naringenin-1-4′-di-O-ß-d-glucopyranoside | P. biglobosa | Fruit pulp | [109] | ||||||
| 27 | Isoflavone | Genistein | P. javanica | Edible part | [108] | ||||||
| 28 | Isoflavone | Daidzein | P. javanica | Edible part | [108] | ||||||
| 29 | Phenolic acid | Gallic acid | P. speciosa | Pod | [107] | ||||||
| P. bicolor | Root | [28] | |||||||||
| 30 | Phenolic acid | Methyl gallate | P. bicolor | Root | [28] | ||||||
| 31 | Phenolic acid | Hydroxybenzoic acid | P. speciosa | Pod | [107] | ||||||
| 32 | Phenolic acid | Vanillic acid | P. speciosa | Pod | [107] | ||||||
| 33 | Phenolic acid | Chlorogenic acid | P. speciosa | Pod | [107] | ||||||
| P. biglobosa | fermented seeds | Aqueous | Lower blood pressure, blood glucose, and heart rate, high level of magnesium as well as improved lipid profile in patients with hypertension | [159][178] | P. javanica | Edible part | [108] | ||||
| Antidiarrheal | P. biglobosa | Stem bark | Aqueous and fractions | The extract of stem bark exhibit dose-dependent antidiarrheal activity at different concentrations in albino rats with castor oil-induced diarrhea | [91][45] | 34 | Phenolic acid | ||||
| P. biglobosa | Ellagic acid | Leaves and stem bark | P. speciosa | Aqueous and ethanolPod | Reduced frequency of stooling in castor-oil induced diarrhea in rats | [160[107] | |||||
| ] | [ | 193 | ] | 35 | Phenolic acid | Punicalin | P. speciosa | Pod | [112] | ||
| P. biglobosa | Stem-bark | 70% Methanol | The extract exhibited 100% protections at 100 and 200 mg/kg bw in the diarrheal rats | [35][59] | 36 | ||||||
| P. filicoidea | Phenolic acid | Stem bark | Caffeic acid | AqueousP. speciosa | Reduced frequency of stooling and improved transit time at 100 and 200 mg/kg bwPod | [161][192[107] | |||||
| ] | P. javanica | Edible part | |||||||||
| Antiulcer | [ | 108 | P. speciosa] | ||||||||
| Leaves | Ethanol | Reduced mucosal injury and increased in periodic acid-Schiff (PAS) staining induced by ethanol | [ | 162 | ][198] | 37 | Phenolic acid | Cinnamic acid | P. speciosa | Pod | [107] |
| P. speciosa | Seed | Ethanol | Decreased gastric juice acidity, lesion length, collagen content and fibrosis in indomethacin-induced peptic ulcer in rats | [163][197] | 38 | Phenolic acid | P-Coumaric acid | P. speciosa | Pod | [ | |
| P. platycephala | Leaves | 107 | ] | ||||||||
| Ethanol | Reduced gastric mucosal lesion induced by ethanol, ischemia-reperfusion and ethanol-HCl | [ | 164 | ][199] | P. javanica | Edible part | |||||
| Antianemic | [ | 108 | P. biglobosa] | ||||||||
| Combination of fermented seed with other fermented products | Aqueous | Increased hemoglobin, red blood cell, white blood cell levels and packed cell volume in albino rats | [ | 165 | ][204] | 39 | Phenolic acid | Ferulic acid | P. speciosa | ||
| P. biglobosa | Seeds | Ethanol | Increased hemoglobin levels in NaNO2 | Pod | -induced anemic mice | [166][205][107] | |||||
| P. javanica | Edible part | [108] | |||||||||
| P. speciosa | Seeds | Ethanol | Increased hemoglobin levels in NaNO2-induced anemic mice | [166][205] | 40 | Phenolic acid | Coutaric acid | P. speciosa | Pod | [ | |
| Antiangiogenic | P.biglandulosa | 112 | ] | ||||||||
| Fruit and β-sitosterol | Ethanol | The extract and the isolated compound showed antiangiogenic activity on the caudal fin of adult zebrafish | [ | 167 | ][175] | 41 | Phenolic acid | Caftaric acid | P. speciosa | Pod | [112] |
| P. speciosa | Pods | Methanol and water sub-extract | Inhibited more than 50% micro vessel outgrowth in rat aortae and HUVECs | [152][170] | 42 | Phenolic | 1-(w-Feruloyllignoceryl) -glycerol | P. biglobosa | Bark | ||
| Antimalarial | P. biglobosa | Stem bark | [ | 111 | Methanol and fractions] | ||||||
| Showed antiplasmodial activity caused by | P. berghei | and | P. falciparum | [ | 11] | 43 | Phenolic | 1-(w-Isoferuloylalkanoyl) -glycerol | P. biglobosa | Bark | [111] |
| Nephroprotective | P. clappertoniana | Seed | Aqueous | Reduced serum creatinine, Na, urine proteins and leukocytes and kidney weight in gentamicin-induced renal damage in rats | [53][75] | 44 | Phenolic | Malvidin | P. speciosa | Pod | [112] |
| Hepatoprotective | P. biglobosa | Stem barks | Methanol | Reduced serum alanine and aspartate transaminases, and alkaline phosphatase in paracetamol-induced hepatotoxicity rat model | [168][216] | 45 | Phenolic | Primulin | P. speciosa | Pod | [112] |
| Wound healing | P. pendula | Seeds | Lectin | Increased skin wound repair in immunosuppressed mice | [169][217] | 46 | Pheny propanoid | Parkinol | P. javanica | Leaves | [110] |
| Anti-inflammatory | P. speciosa | Pods | Ethyl acetate fraction | Reduced iNOS activity, COX-2, VCAM-1 and NF-κB expressions in cardiomyocytes exposed to tumor necrosis factor-α | [170][229] | 47 | Phenol | 2-Methoxy phenol | P. biglobosa | Seed | [116] |
| P. speciosa | Pods | Ethyl acetate fraction | Reduced iNOS activity, COX-2, VCAM-1 and NF-κB expressions in HUVECs exposed to tumor necrosis factor-α | [171][230] | 48 | Phenol | 2,4-Disiopropyl-phenol | P. biglobosa | Seed | [116] | |
| P. biglobosa | Stalk | Methanol | Inhibited croton pellet granuloma formation and carrageenin-induced rat paw edema | [ | Terpenoid and steroid | ||||||
| 172 | ] | [ | 206 | ] | 49 | ||||||
| P. biglobosa | Seeds | Lectin | Lectin showed anti-inflammatory effect by inhibition of pro-inflammatory cytokine release and stimulation of anti-inflammatory cytokine release on peritonitis induced model mice | [173][208] | Triterpenoid | Lupeol | P. biglobosa | Bark | [111] | ||
| P. biglobosa | Stem bark | Hexane | Reduced carrageenan- and PMA-induced edema in mice | [29] | P. bicolor | Root | [28] | ||||
| P. biglobosa | Fruit | 70% Methanol | Increased percentage protection of the human red blood cell membrane | [174][209] | P. speciosa | Seeds | [117] | ||||
| P. platycephala | Seeds | Lectin | Lectin showed antinociceptive effect in the mouse model of acetic acid-induced | [175][207] | 50 | Monoterpenoid | Limonene | P. biglobosa | Seed | [116] | |
| Antioxidant | P. javanica | Leaves | Hexane, ethyl acetate, and methanol | Methanol extract showed the highest antioxidant potential activities (DPPH test) of about 85% and (FRAP test) of about 0.9 mM Fe (II)/g dry | [176][231] | 51 | Triterpenoid | Ursolic acid | P. javanica | Leaf/stem | [ |
| P. javanica | Leaves | 88 | ] | [ | 42] | ||||||
| Aqueous, ethanol and methanol | All the extracts exhibited good antioxidant activity. The aqueous extract showed the highest values of 47.42 and 26.6 mg of ascorbic acid equivalent/g in DPPH and FRAP tests, respectively | [ | 177 | ][232] | 52 | Triterpenoid | Parkibicoloroside A | P. bicolor | Root | [118] | |
| P. javanica | Pods | Methanol and acetone | High content of total phenolic and flavonoid. Showed high reducing power and strong radical scavenging activity. | [178][212] | 53 | Triterpenoid | Parkibicoloroside B | P. bicolor | Root | [118] | |
| P. javanica | Fruit | Methanol | Showed increased DPPH and ferric-reducing power activities concentration-dependently | [179][210] | 54 | Triterpenoid | Parkibicoloroside C | P. bicolor | Root | [118] | |
| P. speciosa | Pod | Methanol | Increased DPPH scavenging activity | [180][233] | 55 | Triterpenoid | Parkibicoloroside D | P. bicolor | Root | [118] | |
| P. speciosa | Pod | Ethyl acetate fraction | Reduced NOX4, SOD1, p38 MAPK protein expressions and ROS level | [171][230] | 56 | Triterpenoid | Parkibicoloroside E | P. bicolor | Root | [118] | |
| P. speciosa | Pod | Aqueous and ethanolic | Increased DPPH and ABTS scavenging activities, reduced lipid peroxidation Activity: ethanol > aqueous | [107] | 57 | Monoterpenoidal glucoside | 8-O-p-Hydroxl-6′-O-p-coumaryl-missaeno-sidic acid | P. javanica | Leaf | [88] | |
| P. speciosa | Seeds | Ethanol | Extract exhibited significant activity (DPPH and FRAP tests) | [181][213] | [42] | ||||||
| 58 | |||||||||||
| P. speciosa | Monoterpenoidal glucoside | Seed coats and pods7-O-E-3,4-Dimethoxycinnamoyl-6′-O-ß-d-glucopyranosylloganic acid | P. javanica | Leaf | [88][42 | Ethanol | Reduced Heinz body formation in erythrocytes incubated with acetyl phenylhydrazine. Activity: seed coat > pods >] |
||||
| [ | 182 | ] | [ | 215] | 59 | Diterpene | 16-O-Methyl-cass-13(15) ene-16,18-dionic acid | P. bicolor | Root | [118] | |
| P. speciosa | Pods | Ethanol | Increased DPPH scavenging activity | [183][234] | 60 | Steroid | β-Sitosterol | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][119][120][117,119,120] | |
| P. biglobosa | Fermented and unfermented seed | Aqueous | Fermented seed increased reduction of Fe3+ to Fe2+. | [184][211] | P. javanica | Leaf/stem | [88][42 | ||||
| P. biglobosa | Stem bark | ] | |||||||||
| Aqueous-methanolic | Mitigated ferric-induced lipid peroxidation in rat tissues and increased scavenging activities against DPPH and ABTS, ferric-reducing ability | [ | 185 | ][235] | P. biglobosa | Seed oil | [ | ||||
| P. biglobosa | 121 | ][122][ | Fruit121,122] | ||||||||
| Methanol and hydro-ethanol | Increased DPPH scavenging activity and reducing power. | [ | 179 | ][210] | 61 | Steroid | Stigmasterol | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][ | |
| P. biglobosa | Fruit | Hydroethanolic and methanol | 119 | ] | [120][117,119,120] | ||||||
| Increased scavenging activity against DPPH free radical | Activity: methanol > hydroethanolic | [ | 179][210] | P. biglobosa | Seed oil | [121][122][121,122] | |||||
| 62 | Steroid | Stigmasterol methyl ester | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][119][117,119] | ||||||
| 63 | Steroid | Stigmast-4-en-3-one | P. speciosa | Seed | [123] | ||||||
| 64 | Steroid | Stigmasta-5,24(28)-diene-3-ol | P. speciosa | Seed | [117] | ||||||
| 65 | Steroid | Campesterol | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][119][117,119] | ||||||
| P. biglobosa | Seed oil | [121][122][121,122] | |||||||||
| 66 | Steroid | Stigmastan-6,22-diien,3,6-dedihydo- | P. speciosa | Seed | [119] | ||||||
| Miscellaneous Compounds | |||||||||||
| 67 | Fatty acid | Arachidonic acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][119][117,119] | ||||||
| P. bicolor | Seed | [22] | |||||||||
| P. biglobosa | Seed | [22] | |||||||||
| 68 | Fatty acid | Linoleic acid chloride | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][119][117,119] | ||||||
| 69 | Fatty acid | Linoleic acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][117[119],119] | ||||||
| P. biglobosa | Seed | [22] | |||||||||
| P. bicolor | Seed | [22] | |||||||||
| 70 | Fatty acid | Squalene | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][119][117,119] | ||||||
| 71 | Fatty acid | Lauric acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][124][117,124] | ||||||
| 72 | Fatty acid | Stearic acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][119][124][117,119,124] | ||||||
| P. biglobosa | Seed | [22] | |||||||||
| P. bicolor | Seed | [22] | |||||||||
| 73 | Fatty acid | Stearoic acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [124] | ||||||
| 74 | Fatty acid | Eicosanic acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [124] | ||||||
| 75 | Fatty acid | Oleic acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][119][117[124],119,124] | ||||||
| 76 | Fatty acid | Palmitic acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][119][124][117,119,124] | ||||||
| P. biglobosa | Seed | [22] | |||||||||
| P. bicolor | Seed | [22] | |||||||||
| 77 | Fatty acid | Myristic acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][119][124][117,119,124] | ||||||
| 78 | Fatty acid | Undecanoic acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [119][124][119,124] | ||||||
| 79 | Fatty acid | Stearolic acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [119] | ||||||
| 80 | Fatty acid | Hydnocarpic acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [124] | ||||||
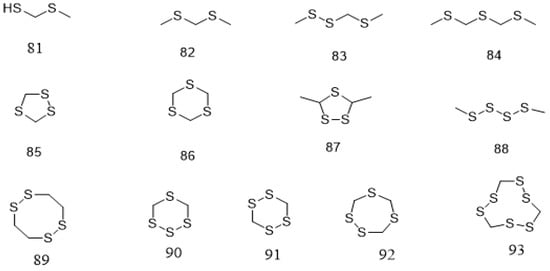
| 81 | Cyclic polysulfide | 1,3-dithiabutane | P. speciosa | Seed | [125] | ||||||
| 82 | Cyclic polysulfide | 2,4- Dithiapentane | P. speciosa | Seed | [125] | ||||||
| 83 | Cyclic polysulfide | 2,3,5-Trithiahexane | P. speciosa | Seed | [125] | ||||||
| 84 | Cyclic polysulfide | 2,4,6-Trithiaheptane | P. speciosa | Seed | [125] | ||||||
| 85 | Cyclic polysulfide | 1,2,4-Trithiolane | P. biglobosa | Seed | [116][126][116,126] | ||||||
| P. speciosa | Seed | [126][127][128][126,127,128] | |||||||||
| 86 | Cyclic polysulfide | 1,3,5-Trithiane | P. speciosa | Seed | [128] | ||||||
| 87 | Cyclic polysulfide | 3,5-Dimethyl-1,2,4-trithiolane | P. speciosa | Seed | [128] | ||||||
| 88 | Cyclic polysulfide | Dimethyl tetrasulfid | P. speciosa | Seed | [128] | ||||||
| 89 | Cyclic polysulfide | 1,2,5,6-Tetrathio-cane | P. speciosa | Seed | [128] | ||||||
| 90 | Cyclic polysulfide | 1,2,3,5-Tetrathiane | P. speciosa | Seed | [128] | ||||||
| 91 | Cyclic polysulfide | 1,2,4,5-Tetrathiane | P. speciosa | Seed | [128] | ||||||
| 92 | Cyclic polysulfide | 1,2,4,6-Tetrathie-pane | P. speciosa | Seed | [126][128][126,128] | ||||||
| 93 | Cyclic polysulfide | 1,2,4,5,7,8- Hexathiolnane |
P. speciosa | Seed | [126] | ||||||
| 94 | Cyclic poly-sulfide | Lenthionine | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][124][126][128][117,124,126,128] | ||||||
| 95 | Esters | n-Tetradecyl acetate | P. speciosa | Seed | [124] | ||||||
| 96 | Esters | Methyl linoleate | P. speciosa | Seed | [124] | ||||||
| 97 | Esters | Ethyl linoleate | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][124][117,124] | ||||||
| P. biglobosa | Seed | [116] | |||||||||
| 98 | Ester | Butyl palmitate | P. speciosa | Seed | [117] | ||||||
| 99 | Esters | Ethyl palmitate | P. speciosa | Seed | [124] | ||||||
| 100 | Esters | Methyl palmitate | P. speciosa | Seed | [124] | ||||||
| 101 | Esters | Methyl laurate | P. speciosa | Seed | [124] | ||||||
| 102 | Esters | Dodecyl acrylate | P. speciosa | Seed | [124] | ||||||
| 103 | Esters | Methyl hexadecanoate | P. biglobosa | Seed | [116] | ||||||
| 104 | Ester | Ethyl stearate | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][124][117,124] | ||||||
| 105 | Ester | Methyl octadecanoate | P. biglobosa | Seed | [116] | ||||||
| 106 | Ester | Butyl stearate | P. speciosa | Seed | [124] | ||||||
| 107 | Ester | Propanoic acid, 3,3′-thiobis-didodecyl ester | P. speciosa | Seed | [124] | ||||||
| 108 | Ester | Linoleaidic acid methyl ester | P. speciosa | Seed | [119] | ||||||
| 109 | Alcohol | 2,6,10,14-Hexadecatetraen-1-ol | P. speciosa | Seed | [117] | ||||||
| 110 | Alcohol | 1-Octen-3-ol | P. biglobosa | Seed | [116] | ||||||
| 111 | Alcohol | 3-Ethyl-4-nonanol | P. speciosa | Seed | [117] | ||||||
| 112 | Alcohol | 1-Tridecanol | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][124][117,124] | ||||||
| 113 | Acid | Eicosanoic acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [117] | ||||||
| 114 | Acid | 16-O-Methyl-cass-13(15)ene-16,18-dionic acid | P. bicolor | Root | [118] | ||||||
| 115 | Acid | Elaidic acid | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][124][117,124] | ||||||
| 116 | Pyrazine | 2,5-Dimethyl pyrazine | P. biglobosa | Seed | [116] | ||||||
| 117 | Pyrazine | Trimethyl pyrazine | P. biglobosa | Seed | [116] | ||||||
| 118 | Pyrazine | 2-Ethyl-3,5-dimethyl pyrazine | P. biglobosa | Seed | [116] | ||||||
| 119 | Ketone | 2-Nonade-canone | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][124][117,124] | ||||||
| 120 | Ketone | 2-Pyrrolidi-none | P. speciosa | Seed | [117] | ||||||
| 121 | Ketone | Cyclodecanone | P. speciosa | Seed | [124] | ||||||
| 122 | Alkane | Cyclododecane | P. biglobosa | Seed | [116] | ||||||
| 123 | Alkane | Tetradecane | P. speciosa | Seed | [119] | ||||||
| 124 | Benzene glucoside | 3,4,5-Trimethoxyphenyl-1-O-ß-d-glucopy-ranoside | P. bicolor | Root | [118] | ||||||
| 125 | Aldehyde | 2-Decenal | P. speciosa | Seed | [117] | ||||||
| 126 | Aldehyde | Cyclo-decanone-2,4-decadienal | P. speciosa | Seed | [117] | ||||||
| 127 | Aldehyde | Pentanal | P. biglobosa | Seed | [116] | ||||||
| P. speciosa | Seed | [125] | |||||||||
| 128 | Aldehyde | 3-Methylthio-propanal | P. biglobosa | Seed | [116] | ||||||
| 129 | Aldehyde | Tetradecanal | P. speciosa | Seed | [119][124][119,124] | ||||||
| 130 | Aldehyde | Pentadecanal | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][124][117,124] | ||||||
| 131 | Aldehyde | Hexadecanal | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][124][117,124] | ||||||
| 132 | Amine | Hexanamide | P. speciosa | Seed | [117] | ||||||
| 133 | Oil | Vitamin E | P. speciosa | Seed | [117][124][117,124] | ||||||
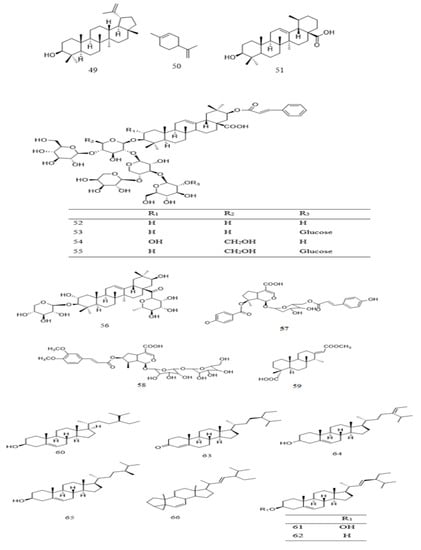
3.2. Terpenoid and Steroid
To date, few terpenoid compounds have been reported in Parkia plants. Most of these compounds were identified from barks, roots, leaves, and seeds of Parkia plants. One is monoterpenoid 50 with two of its glucosides 57 and 58, a diterpene 49, while the rest are triterpenoid 49 and 51–56 (Table 2 and Figure 34). Seven out of the triterpenoids 52–58 were reported as new compounds. Only 49 is reported in three species (P. biglobosa, P. bicolor, and P. speciosa). Two of the new compounds 57 and 58 are iridoid type of terpenoidal glycoside purified from methanol extract of P. javanica, together with ursolic acid and other steroidal compounds [88][42]. Compounds 52–56 are isolated through different chromatographic techniques from 80% methanol extract of P. bicolor root, with a known diterpene 59 and a benzene glucoside 105. These compounds are reported to exhibit moderate antiproliferative activity with median inhibitory concentration (IC50) ranging from 48.89 ± 0.16 to 81.66 ± 0.17 µM [118].
Figure 34.
Structural formulas of terpenoids
49
–
59
and steroids
60
–
66
, as previously listed in
Table 2
.
3.3. Miscellaneous Compounds
In addition to polyphenolic and terpenoids, several other compounds that are mainly volatile including aldehydes, esters, pyrazines, ketones, fatty acids, benzenes, alcohols, amines, sulfides, alkanes, and alkenes have been reported from Parkia species (Table 2). These compounds are identified mainly from the seeds. Compound 81 is identified from the natural product for the first time in pentane/dichloromethane fraction of P. speciosa seed using GC/ToF-MS [125]. A greater number of these compounds is identified through phytochemical quantification using different spectroscopic methods. Seven constituents are detected from the fresh seeds of P. speciosa through GC/ToF/MS and the compounds are dominated by linear polysulfide, alcohol, and 3′-thiobis-didodecyl ester. Other major compounds include palmitic acid, arachidonic acid, linoleic acid, linoleic acid chloride, and myristic acid [124]. However, cyclic polysulfides are the major constituents found in cooked P. speciosa seeds (Figure 45) [Abbreviations: HUVECs, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; DPPH, 2,2-Diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazy; ABTS, 2,20-Azinobis (3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) diammonium salt; FRAP, ferric reducing antioxidant power; iNOS, inducible nitric oxide synthase; PMA, phorbol myristate acetate; COX-2, cyclooxygenase-2; VCAM-1, vascular cell adhesion moelcule-1; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa-B; ACE, angiotensin converting enzyme; HEL, human embryo lung; PAS, periodic acid-Schiff; bw, body weight.
