Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Vy Ngo and Version 2 by Rita Xu.
Organisms are continually exposed to exogenous and endogenous sources of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and other oxidants that have both beneficial and deleterious effects on the cell. ROS have important roles in a wide range of physiological processes; however, high ROS levels are associated with oxidative stress and disease progression. Oxidative stress has been implicated in nearly all major human diseases, from neurogenerative diseases and neuropsychiatric disorders to cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and cancer. Antioxidant defence systems have evolved as a means of protection against oxidative stress, with the transcription factor Nrf2 as the key regulator.
- Nrf2
- Keap1
- oxidative stress
- antioxidant
- free radicals
1. Oxidative Stress
1.1. Reactive Oxygen Species
Free radicals are unstable atoms, ions, or molecules containing one or more unpaired electrons in the outermost electron shell. An unpaired valence electron is unstable and highly reactive. To attain stability, free radicals attack and acquire electrons from other compounds or molecules within their proximity. The attacked entity loses an electron to become oxidized and becomes a free radical itself, thereby initiating a chain reaction that can result in cellular damage [1]. ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are unstable molecules containing oxygen and/or nitrogen and include both free radical and non-radical species. The oxygen molecule (O2••) is a weak free radical itself due to the presence of two unpaired electrons in its valence shell; however, it is less reactive than other oxygen species due to the parallel spin of its electrons [2]. Major ROS and RNS are listed in Table 1.
Table 1. Major Reactive Oxygen and Reactive Nitrogen Species.
| Molecule Type | Radical Status | Name | Symbol | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ROS | Radical | Molecular oxygen | O | 2 | •• | |
| Superoxide | O | 2 | • | − | ||
| Hydroxyl | •OH | |||||
| Alkoxyl | RO• | |||||
| Peroxyl | ROO• | |||||
| Hydroperoxyl | HO | 2 | • | |||
| Non-radical | Hydrogen peroxide | H | 2 | O | 2 | |
| Peroxide | ROOR | |||||
| Singlet oxygen | O | 2 | ||||
| Ozone | O | 3 | ||||
| Hydroxyl ion | OH | − | ||||
| Peroxynitrite | ONOO | − | ||||
| RNS | Radical | Nitric oxide | •NO | |||
| Nitrogen dioxide | •NO | 2 | ||||
| Non-radical | Peroxynitrite | ONOO | − | |||
| Alkyl peroxynitrite | ROONO | |||||
| Nitronium cation | NO | 2+ | ||||
| Nitroxyl cation | NO | + | ||||
| Nitroxyl anion | NO | − | ||||
| Nitrogen oxides | N | x | O | x |
RNS is a family of nitrogen moieties associated with oxygen. They are produced when nitric oxide (•NO) reacts with oxygen species. For example, nitric oxide can react with superoxide (O2•−) to form peroxynitrite (ONOO−):
•NO + O2•−→ONOO−
Peroxynitrite is very reactive and readily attacks lipid molecules, resulting in lipid peroxidation and lipoprotein oxidation [3]. However, like ROS, low levels of RNS have important roles in physiological processes. For example, nitric oxide produced by nitric oxide synthase (NOS) regulates blood vessel dilation and is involved in synaptic transmission in the brain [4][5][4,5]. On the other hand, high levels of RNS result in nitrosative stress, macromolecule damage, and activation of transcription factors NF-ΚB and activator protein 1 (AP-1) involved in inflammation and other pathological pathways [6][7][6,7]. RNS and ROS often act together to cause cellular damage [8].
ROS are oxidants (i.e., a molecule that removes electrons from other molecules) predominantly produced as byproducts of cellular metabolism and biochemical processes within the cell. Mitochondria are a primary source of ROS produced by aerobic respiration [9][10][11][12][9,10,11,12], where the reduction of molecular oxygen in the electron transport chain results in the leaking of superoxide radicals which are readily detoxified to hydrogen peroxide (H2O2) by antioxidant enzymes such as catalase and glutathione peroxidase. Hydrogen peroxide may react with transition metals such as iron (Fe2+) to produce hydroxyl radicals via the Fenton reaction to further produce hydroxyl radicals (•OH) which are highly reactive toward all components of DNA molecules as well as lipids [13]. Peroxisomes also generate ROS from aerobic metabolism [14], and phagocytic neutrophils and macrophages produce ROS to eliminate invading pathogens [15]. At low to moderate levels, ROS plays an important role in normal cellular processes, serving as secondary messengers in intracellular signalling cascades that mediate cell growth, autophagy, inflammatory and immune function, and contribute to overall redox regulation [16][17][16,17]. However, both radical and non-radical ROS can be powerful oxidants that are detrimental to the cell upon high or chronic exposure. Toxic exogenous sources of ROS include pollution, tobacco smoke, alcohol, ozone, environmental and industrial toxins, and radiation [1]. Due to their reactive nature, ROS production and elimination must be strictly regulated by the cell. Figure 1 summarizes the major sources of exogenous and endogenous ROS and their outcomes in the cell.
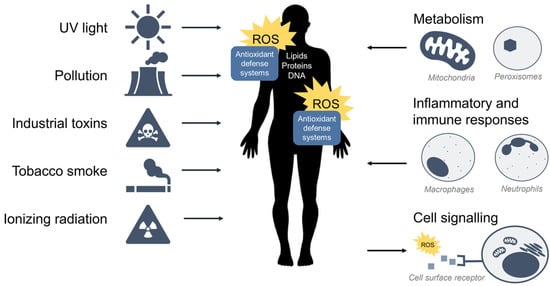
Figure 1. Sources of exogenous and endogenous ROS. ROS can come from toxic exogenous sources in the environment, or be produced as by-products of normal cell metabolism, inflammation, and immunity. ROS may also function as secondary messengers within cell signalling pathways.
1.2. Oxidative Stress
Extensive or prolonged exposure to ROS results in oxidative stress, a deleterious process that damages lipids, proteins, and nucleic acids in the cell, thereby inhibiting their normal function [2]. In this scenario, there is an imbalance between the production of ROS and cellular defence mechanisms against oxidative stress, i.e., the antioxidant response. Chronic oxidative stress and the resultant oxidative damage have been implicated in many human diseases including cardiovascular disease, neurodegenerative diseases, diabetes, cancer, and the aging process [18][19][20][21][22][18,19,20,21,22].
The consequence of ROS or oxidants and the extent of oxidative stress depends on the strength, duration, and context of exposure. In response to oxidative stress, cells typically undergo cell cycle arrest and enter the G0 phase (i.e., a quiescent, non-dividing stage) due to activation of the p53-regulated cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p21, which halts cell cycle progression and inhibits DNA synthesis [23][24][23,24]. ROS can also trigger the p53 and p21-mediated dephosphorylation and activation of the tumour-suppressor retinoblastoma protein (Rb) resulting in further inhibition of cell cycle progression [25]. It is interesting to note that p21 is also involved in the regulation of the antioxidant response through its binding to the antioxidant transcription factor, Nrf2 [26] (to be discussed in Section 2.6). Depending on the nature of the exposure, cells can activate adaptive cell survival pathways; however, chronic exposure or excessively high levels of ROS may result in the induction of maladaptive autophagic or apoptotic pathways [27][28][27,28].
To preserve the delicate balance between the beneficial and harmful effects of ROS, living organisms have evolved cellular defence mechanisms against oxidative stress to maintain redox homeostasis. Alterations in redox status can lead to the transcriptional activation of pathways and enzymes involved in the detoxification, transport, and elimination of ROS. For further reading on oxidative stress, the reader is encouraged to refer to the comprehensive review by Sies et al., (2017) [29].
1.3. Antioxidant Response Enzymes
Complex antioxidant defense systems have evolved to protect cells and tissue against oxidative stress. Halliwell and Gutteridge have defined antioxidants as “any substance that, when present in low concentrations compared to that of an oxidizable substrate, significantly delays or inhibits the oxidation of that substrate” [30]. Key antioxidant defenses include (1) antioxidants that directly scavenge ROS, such as glutathione, vitamin C, and vitamin E, and (2) antioxidant enzymes including superoxide dismutase, catalase, and glutathione peroxidase.
Superoxide dismutases (SOD) are a class of enzymes found within the cytosol and mitochondria of nearly all aerobic cells and contain metal ion cofactors such as copper, zinc, manganese, or iron. SOD isoenzymes include Cu/Zn-SOD (SOD1), Mn-SOD (SOD2), and extracellular (EC) SOD (SOD3) [31][32][31,32]. SODs are responsible for the dismutation (simultaneous oxidation and reduction) and breakdown of superoxide radicals into molecular oxygen and hydrogen peroxide
SOD
2O2•− + 2H+→O2 + H2O2
2O2•− + 2H+→O2 + H2O2
Molecular oxygen and hydrogen peroxide are weak oxidants that are relatively stable; however, hydrogen peroxide can be converted into extremely reactive hydroxyl radicals and must therefore be targeted for further breakdown. Two enzymes responsible for the decomposition of hydrogen peroxide are catalase and glutathione peroxidase.
Catalase is found in nearly all living eukaryotic organisms and exists primarily within peroxisomes as well as in the mitochondria and nucleus [33]. Catalases catalyze the breakdown of hydrogen peroxide into molecular oxygen and water:
catalase
2H2O2→O2 + 2H2O
2H2O2→O2 + 2H2O
Glutathione peroxidases (GPx) are a class of enzymes that also break down hydrogen peroxide but do so specifically through the oxidation of a glutathione (GSH) cofactor:
GPx
2GSH + H2O2→GSSG + 2H2O
2GSH + H2O2→GSSG + 2H2O
Paraoxonase 2 (PON2) is a ubiquitously expressed member of the paraoxonase family of enzymes with dual functions as a lactonase and as an antioxidant enzyme. PON2 has been shown to prevent oxidation and modification of low-density lipoproteins and also counteract lipid peroxidation in the plasma membrane [34]. Additionally, PON2 interacts with the electron transport chain in the inner mitochondrial membrane to significantly reduce the production of superoxide ions [35]. The importance of PON2 as an antioxidant is demonstrated by work showing that the downregulation of PON2 significantly sensitizes cells to oxidative stress [36].
Glutathione (GSH) is a tripeptide comprised of three amino acids (cysteine, glutamic acid, and glycine) and is the most abundant and important low molecular weight antioxidant synthesized in both eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. GSH plays a critical role in protecting cells from oxidative damage through direct antioxidant activity or coupled to GPx enzymatic activity [37][38][37,38]. Enzymes in the GPx family include GPx1 through 8, each with different expression patterns within the body [39]. GPx1 is the most abundant isoform and is ubiquitously expressed in the cytosol and mitochondria. GPx2 is an intestinal extracellular enzyme, while GPx3 is extracellular, and GPx4 prefers lipid peroxides. Four additional isoforms of GPx (GPx5–8) have been identified in humans but are not well studied. GPx enzymes are part of a family of critical proteins known as the phase II enzymes responsible for the conjugation of xenobiotics with peptides and sugars for detoxification.
Xenobiotic metabolism consists of phase I, phase II, and phase III enzymes involved in oxidation, conjugation/detoxification, and elimination, respectively [40][41][40,41]. Phase II enzymes are particularly important in cellular responses to oxidative stress and include GPx, glutathione S-transferase (GST), and UDP-glucuronosyltransferase (UGT). Other important antioxidant enzymes include sulfiredoxin (Srx), thioredoxin (Trx), thioredoxin reductase (TrxR), heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1), and NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase 1 (NQO1). Activation of these enzymes leads to robust xenobiotic detoxification and/or antioxidant effects. Early mechanistic studies on the induction of the rat glutathione S-transferase subunit genes, GSTA1 and GSTA2, led to the discovery of a specific enhancer sequence within their promoter region termed the antioxidant response element (ARE) [42]. Since then, AREs have been found in many other antioxidant genes including, among others, NQO1 and HMOX1 [42][43][42,43].
1.4. Antioxidant Response Element
The antioxidant response element (ARE) [42], also referred to as the electrophile response element (EpRE), is a cis-acting enhancer sequence found within the promoter region of many cytoprotective antioxidant and phase II enzyme genes. It has a core sequence of 5′-TGACnnnGC-3′ and participates in inducible gene expression in response to oxidative stress [42]. The ARE is also responsible for low-level basal gene expression to mitigate the ROS produced by cellular respiration. Thus, the ARE is important for redox regulation under both stressed and non-stressed conditions. Using in vivo studies in mice, Itoh et al. discovered that the induction of phase II enzymes through the ARE is mediated by a protein transcription factor called Nrf2 [44] (Figure 2). Nrf2-deficient mice showed marked reductions in the expression of the phase II enzyme GST α1 subunit and the antioxidant enzyme NQO1 [44], and ensuing studies demonstrated increased sensitivity to carcinogens and impaired detoxification of acetaminophen in Nrf2−/− mice [45][46][47][45,46,47]. This illustrates the key role of Nrf2 in the activation of ARE-regulated antioxidant and phase II enzyme genes.
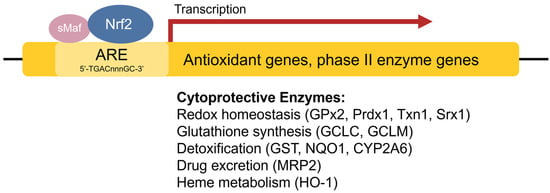
Figure 2. Transcriptional regulation of antioxidant genes by the ARE and Nrf2. Nrf2 heterodimerizes with sMaf proteins and binds to the ARE found within the promoter regions of antioxidant and phase II enzyme genes to activate their transcription.
2. Keap1-Nrf2 Antioxidant Pathway
2.1. Keap1-Nrf2 Signalling
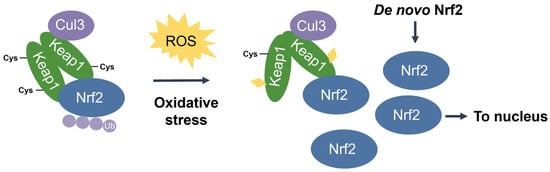
Nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) [48] is the transcriptional master regulator of cellular responses against oxidative stress. Nrf2 regulates the expression of a multitude of antioxidant and phase II enzyme genes and is negatively regulated by Kelch-like ECH-associated protein (Keap1) [49], a substrate adaptor protein that binds to Nrf2 in the cytosol to facilitate its polyubiquitination by the Cullin 3 (Cul3) E3 ubiquitin ligase for proteasomal degradation [50][51][52][50,51,52]. Constitutive Nrf2 degradation allows low basal expression under non-stressed conditions. Upon oxidative stress, specific stress-sensing cysteine residues in Keap1 are modified [53][54][55][53,54,55], leading to a conformational change that prevents Keap1 from mediating the ubiquitination of Nrf2 by Cul3 [56]. This results in Nrf2 stabilization, accumulation, and nuclear translocation where Nrf2 heterodimerizes with sMaf proteins and binds to the ARE for the robust induction of cytoprotective genes for enzymes involved in the detoxication of ROS and other oxidants [44] (Figure 3).
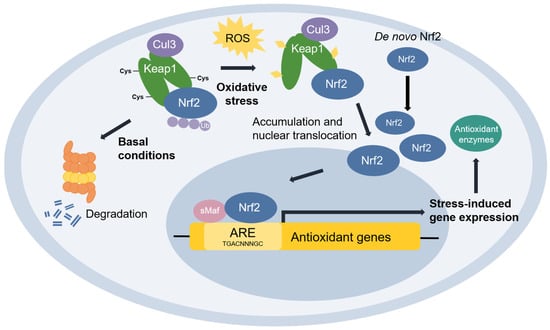
Figure 3. The Keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Under basal conditions, Keap1 is bound to Nrf2, and Nrf2 is ubiquitinated by the Cul3 E3 ubiquitin ligase for degradation by the proteasome. Upon oxidative stress, sensor cysteines in Keap1 are modified by ROS, leading to Nrf2 stabilization, accumulation, and translocation to the nucleus where Nrf2 heterodimerizes with sMaf and binds to the ARE to activate the transcription of antioxidant genes.
2.2. Nuclear Factor Erythroid 2-Related Factor 2 (Nrf2)
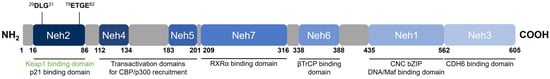
Nrf2 [48] belongs to the cap ‘n’ collar (CNC) subfamily of basic leucine zipper (bZIP) transcription factors together with NF-E2 p45-related factors 1 and 3 (Nrf1 and Nrf3), NF-E2 p45, and transcriptional repressors BTB Domain and CNC homolog 1 and 2 (Bach1 and Bach2) [57]. Nrf2 contains seven conserved domains that are referred to as the Nrf2-ECH homology (Neh) domains, designated Neh1 through 7 (Figure 4). The key function of each domain is summarized in Table 2.

Figure 4. Domain structure of human Nrf2. Nrf2 contains seven conserved Neh domains. The Neh2 domain contains two motifs (29DLG31 and 79ETGE82) wherein Keap1 binds as a substrate adaptor for the Cul3-mediated ubiquitination and degradation of Nrf2.
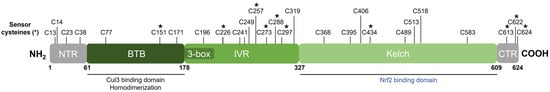
Table 2. Summary of functional domains of Nrf2 and their key binding proteins.
| Domain | Key Associated Function | Binds to | Ref. | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Neh1 | DNA-binding via the ARE; dimerization with sMaf proteins | sMaf, ARE | ||||||
| (Nrf2) | 373 | DSAPGS | 378 | (Nrf2) | [44][48] | [44,48] | ||
| Neh6 | − | ; Nrf2 degradation | [ | Neh2 | Keap1-binding for negative regulation | Keap1 | [49][58] | [49,58] |
| Neh3 | Transactivation | CHD6 | [59] | |||||
| Neh4, Neh5 | Transactivation | CBP | [60][61] | [60,61] | ||||
| Neh6 | βTrCP-binding for negative regulation | βTrCP | [62][63] | [62,63] | ||||
| Neh7 | RXRα-binding for suppressed transactivation | RXRα | [64] |
Neh1 is the DNA-binding domain that contains the CNC-bZIP region important for the association of Nrf2 with sMafs, binding to the ARE, and transcription factor activity [44][48][44,48]. The N-terminal Neh2 domain is a redox-sensitive degron that negatively regulates Nrf2 activity and contains two highly conserved 29DLG31 and 79ETGE82 motifs to which Keap1 binds, as well as seven lysine residues that are targets for ubiquitination by the Cul3 E3 ubiquitin ligase [49][65][49,65]. The C-terminal Neh3 domain is a transactivation domain responsible for the transcriptional activation (transactivation) of Nrf2 and has been shown to interact with chromodomain helicase DNA-binding protein 6 (CHD6) which plays a role in chromatin remodelling [59]. Neh4 and Neh5 are also transactivation domains where the binding of the CREB-binding protein (CBP) [60] or the nuclear cofactor RAC3/AIB1/SRC-3 [61] increases the rate of Nrf2 transcriptional activity. The Neh6 domain is a redox-insensitive degron that provides Keap1-independent negative Nrf2 regulation. Similar to Neh2, Neh6 contains two highly conserved 334DSGIS338 and 373DSAPGS378 motifs to which the β-transducin repeat-containing protein (βTrCP) binds, and within the DSGIS motif, a phosphorylation site for glycogen synthase kinase-3 (GSK3) that enhances βTrCP activity upon GSK3-mediated phosphorylation of Nrf2 [62][63][62,63]. Neh7 is the binding domain for retinoid X receptor α (RXRα), which upon binding impairs the recruitment of cofactors to Neh4 and Neh5 necessary for transactivation, thereby suppressing transcriptional activation [64].
2.3. Kelch-Like ECH-Associated Protein (Keap1)
Keap1 [49] belongs to the BTB-Kelch family of proteins which includes about 50 members, all of which assemble with the Cul3 E3 ubiquitin ligase and RING box protein-1 (Rbx1) to form the Cullin-RING E3 ubiquitin ligases (CRLs) involved in the ubiquitination of BTB-Kelch proteins, such as Keap1 [51][66][51,66]. Cul3 assembly requires a “3-box” motif that is characteristic of BTB-Kelch proteins [67]. Accordingly, Keap1 contains three functional domains (Figure 5). The N-terminal BTB (broad complex, tramtrack, and bric à brac) domain mediates Keap1 homodimerization and contributes to its interaction with Cul3 [68]. Additional Cul3 interaction is provided by a 3-box motif found within the proximal part of the intervening region (IVR) [67]. The IVR contains key reactive cysteine residues through which Nrf2 activity is regulated, including Cys226, Cys257, Cys273, and Cys288 [53][54][55][69][53,54,55,69]. The C-terminal Kelch domain, also known as the double glycine repeat (DGR) domain, is important for Nrf2 binding [58][70][58,70].

Figure 5. Domain structure of human Keap1. Keap1 contains three functional domains and a 3-box motif within the proximal part of the IVR domain. The location of all cysteine (C) residues in Keap1 is shown, and key stress-sensing cysteines are marked with an asterisk (*).
Dissociation of Nrf2 from Keap1 occurs through the oxidative modification of specific stress-sensing cysteine residues of Keap1 (Figure 6) [55]. Intriguingly, Keap1 contains a very high content of cysteines, with the 27 cysteine residues in human Keap1 accounting for approximately 4% of its total amino acid content, which is notably greater than the 2% average for the human proteome [71]. Cys273 and Cys288 are required for sensing oxidative stress under both basal and stress conditions, whereas Cys151 may be required only during oxidative stress conditions [53][54][53,54]. These three key cysteines may function independently or collaboratively depending on the class of Nrf2-inducing compounds, characterized by Yamamoto et al. [72], who also found some inducers to function independently of these three specific cysteines. Correspondingly, Cys226, Cys613, Cys622, and Cys624 are specifically involved in sensing hydrogen peroxide through a mechanism that is distinct from that used for sensing electrophilic Nrf2 inducers such that combinations of these four cysteine residues can form a disulfide bond to sense hydrogen peroxide [73]. Additional cysteine residues that respond to redox-active agents include the Cys288 alkenal sensor, the zinc sensor comprised of His225, Cys226, and Cys613, and the nitric oxide sensor comprised of a cluster of basic amino acids (His129, Lys131, Arg135, Lys150, and His154) that facilitate the S-nitrosylation of Cys151 within Keap1 [69].

Figure 6. Stress-induced cysteine modification of Keap1. Under oxidative stress conditions, specific stress-sensing cysteine residues in Keap1 are modified, leading to a conformational change in Keap1 that results in Nrf2 stabilization, accumulation, and nuclear translocation for the induction of ARE-containing cytoprotective genes.
2.4. Keap1-Dependent Nrf2 Regulation
As previously mentioned, Nrf2-regulated genes contain an ARE in their regulatory region and encode numerous antioxidant and phase II enzymes [44]. Transcriptional activation of the ARE is primarily dependent on Nrf2 stabilization, accumulation, and nuclear translocation through its dissociation from the cytoskeleton-associated Keap1 [49]. Thus, Nrf2 activity is tightly regulated by its interaction with Keap1.
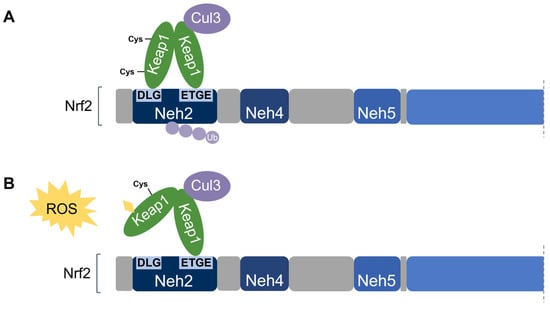
Nrf2 association requires the homodimerization of Keap1 [74]. Keap1 recruits Nrf2 first through the binding of one Keap1 molecule to the high-affinity ETGE motif within the Nrf2’s Neh2 domain. Subsequent binding of the other Keap1 molecule at the low-affinity DLG motif locks Nrf2 in place by orienting the lysine residues within Neh2 in the correct position for ubiquitination by Cul3 and degradation by the 26S proteasome [58][65][58,65]. This is known as the two-site substrate recognition model and has been accepted as the primary mechanism of Nrf2 regulation (Figure 7).

Figure 7. Two-site substrate recognition model for Keap1-dependent Nrf2 regulation. (A) A Keap1 homodimer binds to the Neh2 domain of Nrf2 at the DLG and ETGE motifs, allowing for the ubiquitination of Nrf2 by Cul3. (B) Stress-sensing cysteine residue(s) in Keap1 are modified by oxidative stress (ROS) causing a conformational change in Keap1 that impairs Nrf2-binding. Nrf2 is stabilized and no ubiquitination occurs.
Notably, the ETGE motif has a binding affinity that is two orders of magnitude higher than that of the DLG motif due to the presence of additional electrostatic interactions [75]. The DLG motif utilizes hydrogen bonding whereas the ETGE motif utilizes both hydrophobic interactions and hydrogen bonding [76]. Accordingly, stress-induced cysteine modifications that alter the structural conformation of Keap1 result in the prompt dissociation of Keap1 from the weak-binding DLG motif, thereby impairing Nrf2 ubiquitination. On the other hand, the Keap1-Nrf2 association may remain intact via the tight-binding ETGE motif even though ubiquitination is impaired without DLG binding [56][58][56,58]. Taken together, the DLG motif is particularly important in the Keap1-dependent degradation of Nrf2 by functioning as an “on/off switch” for Nrf2 ubiquitination. Under basal conditions, Nrf2 has a short half-life of only 10–30 min [50][77][50,77].
When Keap1-Nrf2 binding is impaired, Nrf2 may be stabilized, accumulates, and translocates to the nucleus. Within the nucleus, Nrf2 cannot bind to the ARE as a monomer and must heterodimerize with the small Maf protein (sMaf) family (MafF, MafG, MafK) for transcriptional activation of antioxidant genes [44]. Table 3 lists key examples of Nrf2-regulated genes and their associated protein function.
Table 3. Examples of cytoprotective genes regulated by Nrf2.
| Primary Role | Gene | Protein | Function | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Redox homeostasis | GPX2 | Glutathione peroxidase 2 (GPx2) | Reduces hydrogen peroxide and lipid hydroperoxides at the expense of glutathione | |||||||||||
| 62 | ] | [ | 63 | ] | [62,63] | PRDX1 | Peroxiredoxin 1 (Prdx1) | Reduces hydrogen peroxide and alkyl hydroperoxides | ||||||
| RXRα | 209 | ETT…NGP | 316 | (Nrf2) | Neh7 | − | ; ↓ transactivation | [64] | TXN1 | Thioredoxin 1 (Trx1) | Reduces oxidized protein thiols | |||
| p21 | 29DLG31 | (Nrf2) | 79 | ETGE | 82 | (Nrf2) | 154KRR156 | (p21) | Neh2 | +; Nrf2 stabilization | [26] | SRXN1 | Sulfiredoxin 1 (Srx1) | Contributes to the thioredoxin system by reducing sulfinic acid to thiols |
| DJ-1 | Currently unknown | --- | +; Nrf2 stabilization | [81] | ||||||||||
| BRCA1 | 79 | ETGE | 82 | (Nrf2) BRCT domain | (1591–1784) | (BRCA1) | Neh2 | +; Nrf2 stabilization | [82][83] | [ | Glutathione biosynthesis | GCLC | Glutamate-cysteine ligase catalytic subunit (GCLC) |
The first rate-limiting enzyme of glutathione synthesis (heavy subunit) |
| 82 | , | 83 | ] | |||||||||||
| GCLM | Glutamate-cysteine ligase modifier subunit (GCLM) | The first rate-limiting enzyme of glutathione synthesis (light subunit) | ||||||||||||
| Interacting Protein | Interaction Motif(s) | Keap1 Domain | + or −Nrf2 Regulation | Ref. | ||||||||||
| Keap1 | p62/SQSTM1 | 349 | DPSTGE | 354 | (p62) | Kelch | +; Keap1 inhibition | [84][86][87][88] | [84,85,86,87,88] | Detoxification | GST | Glutathione S-transferase (GST) | Catalyzes the conjugation of glutathione to electrophilic compounds | |
| ] | [ | |||||||||||||
| ProTα/PTMA | 38 | NANEENGE | 45 | (ProTα) | Kelch | NQO1 | NAD(P)H:quinone oxidoreductase-1 (NQO1) | Reduces quinone to hydroquinone | ||||||
| 85 | +; Keap1 inhibition | [ | 89 | ] | ||||||||||
| DPP3 | 480ETGE483 | (DPP3) | Kelch | + | ; Keap1 inhibition | [90] | CYP2A6 | Cytochrome P450 2A6 (CYP2A6) | Involved in the hydroxylation of some anti-cancer drugs | |||||
| WTX | 286SPETGE291 | (WTX) | Kelch | + | ; Keap1 inhibition | [91] | ||||||||
| PALB2/FANCN | 91ETGE94 | (PALB2) | BTB | +; Keap1 inhibition | [92] | Drug Excretion | ABCC2 | Multidrug resistance protein 2 (MRP2) | Mediates hepatobiliary excretion; implicated in multidrug resistance | |||||
| Heme metabolism | HMOX1 | Heme oxygenase 1 (HO-1) | Cleaves heme to form biliverdin during heme catabolism |
For further details on the mechanisms regulating the Keap1-Nrf2 pathway, the reader is encouraged to refer to the following comprehensive reviews: [78][79][80][78,79,80]
2.5. Non-Canonical Nrf2 Regulation
Apart from its regulation by Keap1, Nrf2 is subject to further non-canonical regulation by other proteins, summarized in Table 4. Direct interaction of these proteins with either Nrf2 or Keap1 results in competitive inhibition that disrupts the Keap1-Nrf2 complex, decreases Nrf2 ubiquitination and increases Nrf2 stabilization and stress-induced ARE activation. Some of these non-canonical forms of Nrf2 regulation are discussed in further detail.
Table 4. Non-canonical Nrf2 regulation by direct protein interaction.
| Interacting Protein | Interaction Motif(s) | Keap1 Domain | + or −Nrf2 Regulation | Ref. | |
| Nrf2 | βTrCP | 334 | DSGIS | 338 | |
| KPNA6/Importin α7 | |||||
| ARM domain | |||||
| (108–563) | |||||
| (KPNA6) | |||||
| Kelch | |||||
| −; Nrf2 degradation | |||||
| [ | 93 | ] |
