Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Conner Chen and Version 1 by Sana Saleem.
Serendipita indica has been found to be a prime beneficial microorganism that improved the growth and development of various plant species under normal and stress conditions.
- beneficial microorganism
- endophytic fungus
- symbiosis
- stress tolerance
- biofertiliser
1. Introduction
A diverse range of microorganisms in soil play critical functions, such as nutrient acquisition, organic matter cycling, soil and plant health maintenance, soil restoration and ecosystem primary production, and are thus considered as beneficial organisms [1]. By increasing crop yield, quality, and shielding the plants from various biotic and abiotic challenges, these microbes have shown several positive effects on the farming system. In addition, environmental protection, an increasing concern across the globe, is the main advantage these creatures provide [2]. Moreover, the rising demand and growing awareness of high-quality food has stimulated the development of sustainable and environmentally friendly agricultural production practices. These methods could be achieved by reducing the usage of chemicals and encouraging the application of beneficial microorganisms [3]. Apart from contributing to sustainability, beneficial microorganisms are also economically efficient [4]. These microorganisms can be symbiotic or non-symbiotic bacteria, actinomycetes, and mycorrhizal and endophytic fungi [5]. Throughout the study of various microorganisms, an emphasis is placed on studying endophytic fungi, as they can yield tangible beneficial effects within the host plant, such as improve plant growth, quality, and enhance host resistance to abiotic and biotic stresses, thereby confirming their significance in the agricultural sector [6,7][6][7].
Serendipita indica, formerly known as Piriformospora indica, belonging to the order Sebacinales (Basidiomycota), is one of the beneficial endophytic fungi known to possess numerous advantages and has been studied extensively for decades. S. indica, obtained by Ajeet Verma from the roots of Prosopis juliflora and Zizyphus nummularia in the Thar desert in Northwest India, is characterised by the formation of pear-shaped spores known as chlamydospores [8]. These spores are produced by thin walled, hyaline, and septate hyphae [9]. S. indica is distinguished by the unique trait that it can be cultivated without any plant material on a variety of artificial media, such as aspergillus medium, modified aspergillus medium, potato dextrose agar (PDA) or broth (PDB), malt extract, modified Melin-Norkrans (MMN) medium [10], and jaggery containing medium [11]. This property differentiates it from arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF), with which it shares biological similarities (Figure 1).
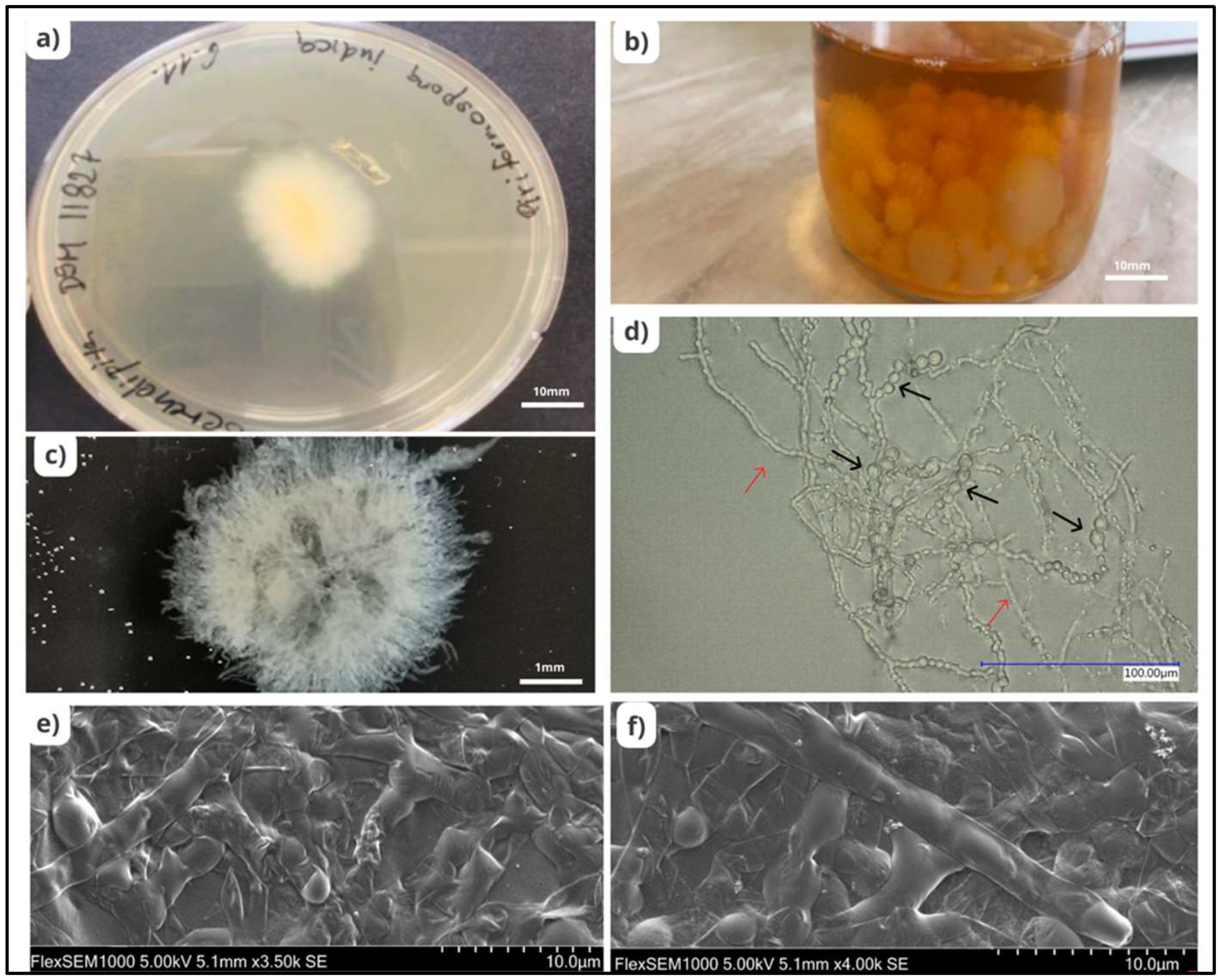
Figure 1. Morphology of Serendipita indica. (a) Growth of S. indica colony on PDA media; scale bars of 10 mm. (b) Growth of S. indica colony in PDB media; scale bars of 10 mm. (c) Growth of S. indica from PDB medium; scale bars of 1 mm. (d) Chlamydospores (black arrows) and mycelium (red arrows) of S. indica observed under a bright field microscope; scale bars of 100 µm. (e,f) Mycelial structure of S. indica observed under an electron microscope.
This endophytic fungus can colonise a wide range of plant species and develop symbiotic associations with them [12,13][12][13]. Mainly, colonisation takes place in the root zone and begins with the germination of chlamydospores, followed by the formation of a hyphal network on and inside the root. Hyphae form branches and continue to grow by penetrating the subepidermal layers of roots, and eventually, cover the rhizodermal and cortical cells (Figure 2). Mature root segments show intra- and intercellular colonisation patterns, while conductive tissues are free from colonisation. This fungus colonises different root zones, with maximum colonisation in the zone of cell differentiation. In addition, the fungus penetrates root hair cells, forming hyphae from germinating spores [14,15][14][15] (Figure 3). This process begins with the biotrophic phase, followed by the cell death phase, to build the symbiotic relationship with the host rhizosphere [16,17][16][17].
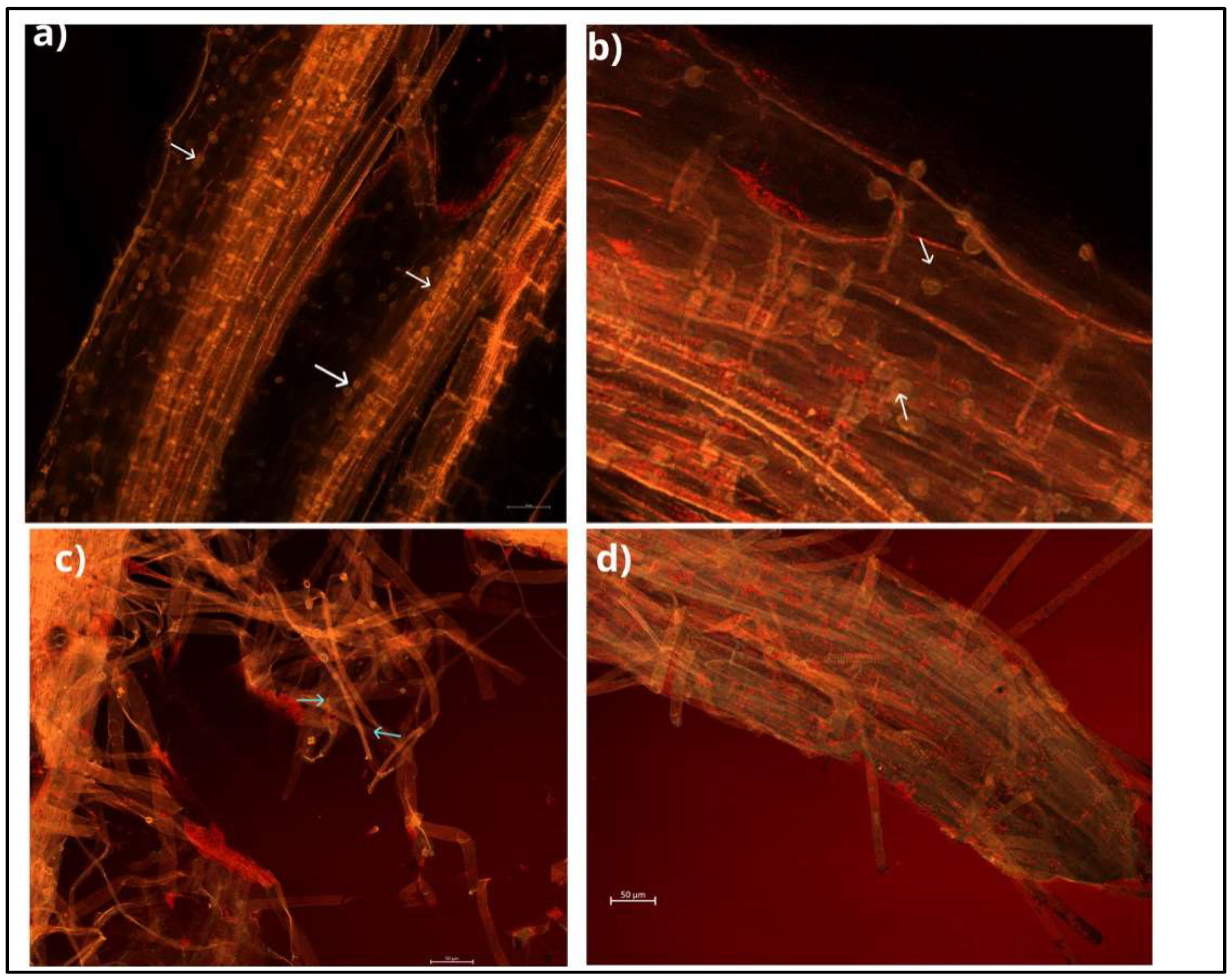
Figure 2. The roots of cabbage inoculated with S. indica observed under a fluorescent microscope; scale bars of 50 μm. (a) The cortex of cabbage roots covered with spores. (b) Close view of spores covering cabbage roots. (c) The fungal mycelium developing externally. (d) The fungus covering the root tip. White and blue arrows point to spores and mycelium, respectively.
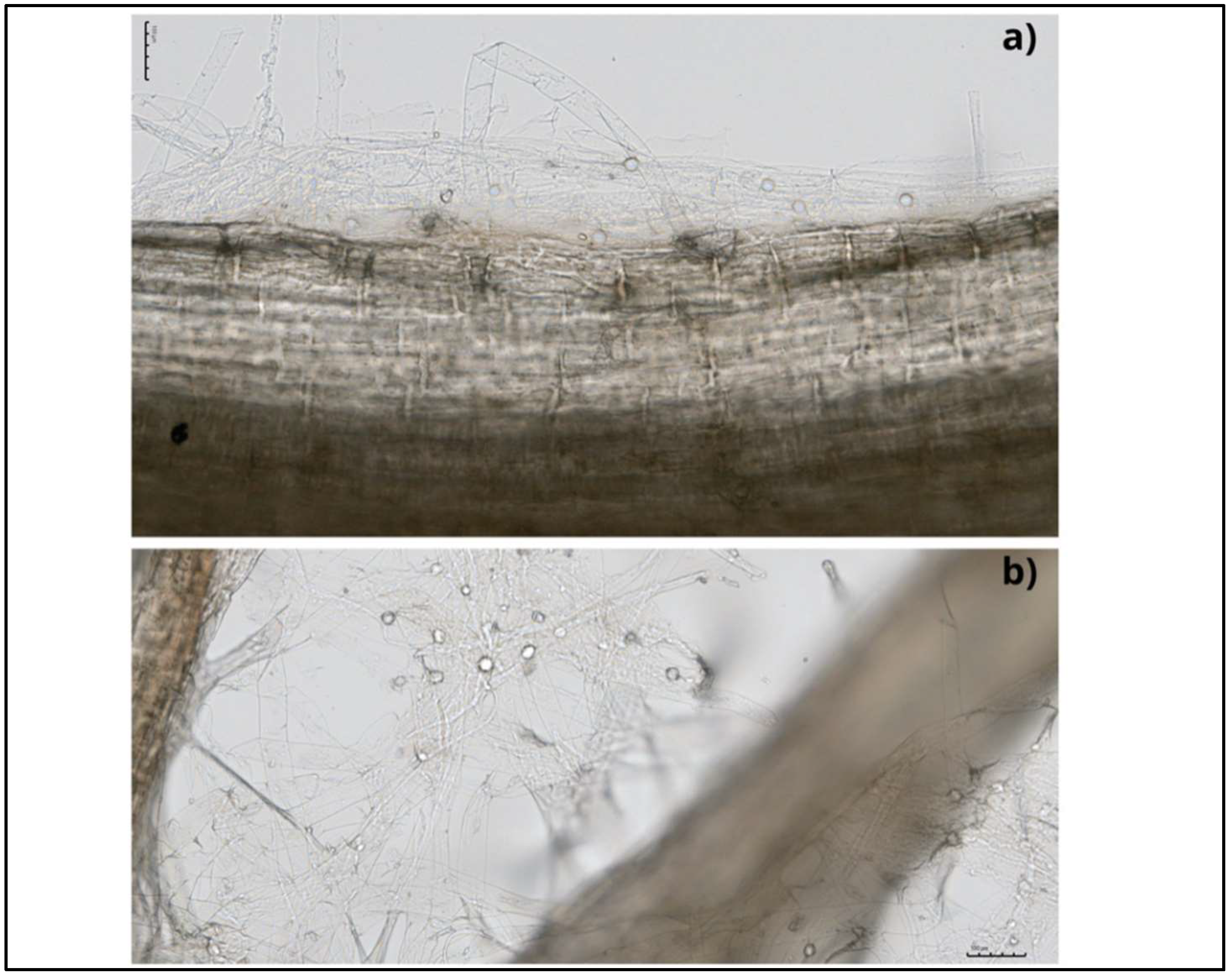
Figure 3. Bright-field microscope photos of the cabbage roots with internal (a) and external (b) colonisation by S. indica; scale bars of 100 µm.
Moreover, a successful symbiosis between S. indica and the host plant depends on administering the right quantity of inoculum, which can be assessed using a qPCR test [18]. According to Rokni et al. [19], optimising the S. indica inoculum concentration had an impact on the host plant’s development. Plant growth was enhanced by a 1–3% w/w concentration; however, higher doses did not show any positive benefits.
The production of calcium and lectin protein kinase induced during symbiotic association are suggested to be the early signalling factors in S. indica–host plant colonisation [20,21][20][21]. Additionally, the synthesis of the plant hormone ethylene is considered crucial for the interaction between plant hosts and fungi [22].
S. indica has been reported to provide numerous advantages to host plants upon colonisation of roots. These advantages include enhanced plant growth, nutrient uptake, and antioxidant activities; increased photosynthetic pigments, crop quality and yields; as well as the ability to mitigate various biotic and abiotic stresses [3,23,24,25,26,27,28][3][23][24][25][26][27][28]. Although mycelia and spores from fungi are typically considered the beneficial form of inoculum, some studies have demonstrated that cell wall extracts and culture filtrates from S. indica have a positive effect on plant growth [29,30][29][30].
Furthermore, to commercialise S. indica, biofertiliser formulation, known as ‘rootonic’, has been developed by culturing this fungus in a bioreactor [12,31,32][12][31][32] and mixing with carrier magnesium sulphite [33]. This endophytic fungus is proving to be an efficient source of bio-inoculant for the agricultural sector, with the least environmental hazards and improved agricultural sustainability.
2. S. indica as a Growth Promoter
S. indica has been found to be a prime beneficial microorganism that improved the growth and development of various plant species under normal and stress conditions [3,28][3][28] (Figure 4). This endophytic fungus improved the germination rate in various plant species, such as chilli, cabbage, cucumber, eggplant, maize, okra, spinach, rice, and tobacco [11,34,35,36][11][34][35][36]. Improved seed germination under intense cold conditions in beetroot, carrot, cauliflower, onion, and radish has also been reported [17]. The application of S. indica has been reported to promote seedling growth and development by enhancing root and shoot growth, biomass, photosynthetic pigment production, and seedling vigour. [36,37,38][36][37][38]. Sheramati et al. [39] reported that S. indica improved the growth of Arabidopsis and tobacco seedlings by enhancing the nitrogen accumulation and expression of genes governing nitrogen reductase and the starch degrading enzyme glucan-water dikinase in their roots. These enzymes are responsible for nitrogen and starch metabolism in seedlings, which is essential for their growth and development.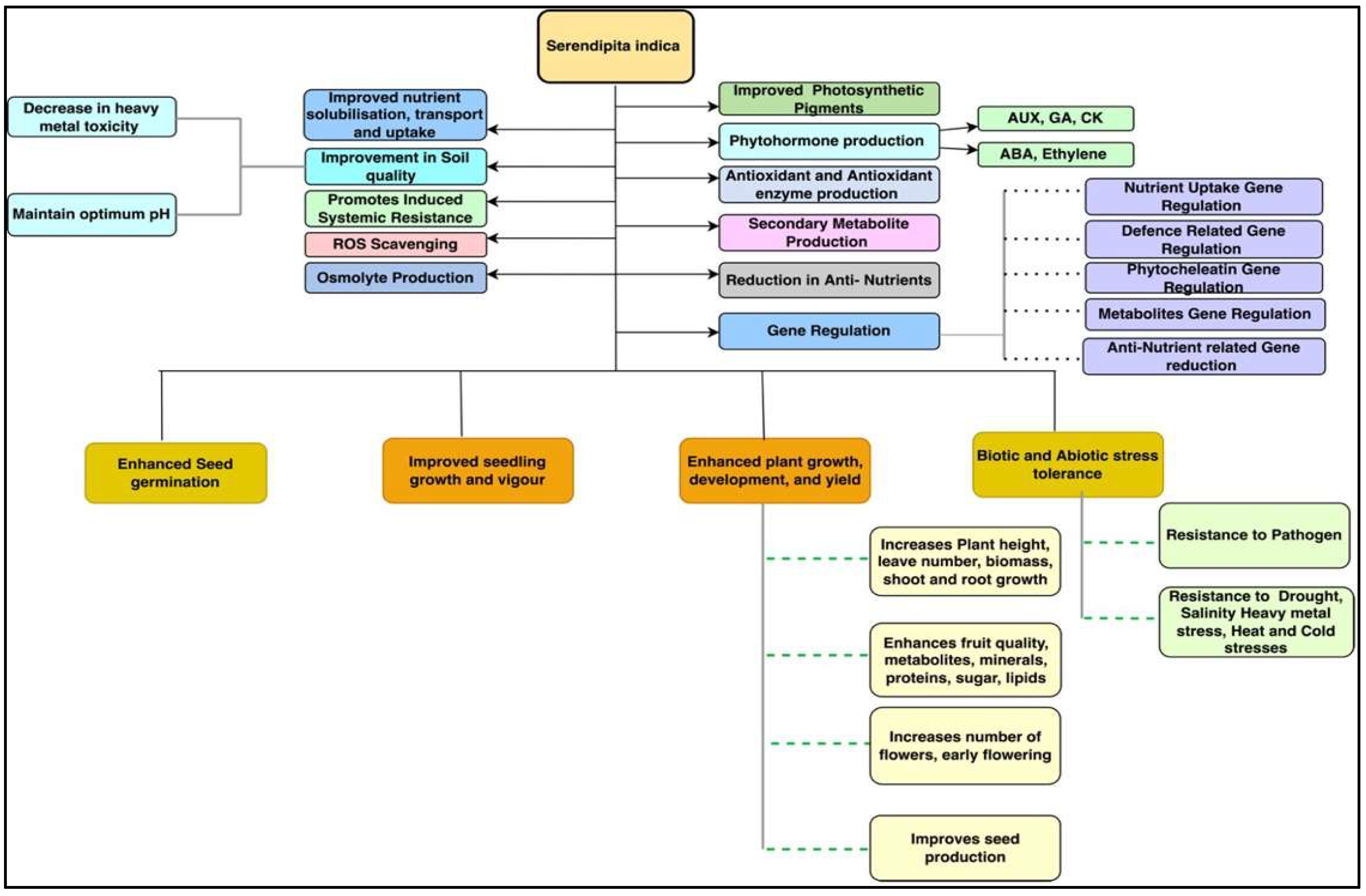
Figure 4.
Schematic representation of the effects of
S. indica
on plant growth, development, and response to various stresses.
Table 1.
Effects of
S. indica
on growth and quality of host plants.
| Host Plant | Method of Application | Effect of | S. indica | on Growth | Effect of | S. indica | on Quality | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tomato ( | Lycopersicon esculentum | ) | Seedling root application | Increase in plant growth, yield, early flowering | Improved firmness in fruits, total soluble solids, and acidity | [49] | ||
| Lettuce ( | Lactuca sativa | ) | Seedling application | Increase in plant height, fresh and dry weight, yield | Increase in chlorophyll, nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium content | [67] | ||
| Seedling root application | Increase in zinc and manganese content | [64] | ||||||
| Chinese cabbage ( | Brassica oleracea | ) | Seedling root application | Increase in root and shoot growth, biomass, and lateral root formation | _ | [68] | ||
| Cabbage ( | Brassica oleracea) | Substrate application and Seed application | Increase in plant height, number of leaves, NDVI, fluorescence level (Ft) | Increase in chlorophyll and carotenoids content, antioxidant capacity | [3] | |||
| Bell pepper ( | Capsicum annuum | ) | Seed treatment | Increase in plant growth and yield | _ | [19] | ||
| Spinach ( | Spinacia oleracea | ) | Seed application | Increase in plant height, dry and fresh weight | _ | [11] | ||
| Taro ( | Colocasia esculenta | ) | Sterile soil application | Increase in plant height, number and area of leaves | Increase in total phenol content and defence-related enzymes | [69] | ||
| Sweet potato ( | Ipomea batatas | ) | Seedling irrigation | Increase in plant biomass, number of leaves, and lateral roots | Increase in photosynthetic pigments, catalase, JA-mediated activity | [47] | ||
| Wheat ( | Triticum aestivum | ) | Seedling roots | Increase in shoot dry biomass | Increase in nitrogen, phosphorus, and iron uptake | [52] | ||
| Rice ( | Oryza sativa | ) | Seed and Seedling roots | Increase in plant growth, biomass, yield | NPK, chlorophyll, and sugar content | [59] | ||
| Seed treatment and Soil treatment | Increase in dry weight of plant | Increase in phosphorus and potassium uptake | [46] | |||||
| Barley ( | Hordeum vulgare | ) | Seed application | Increase in crop yield | _ | [70] | ||
| Finger Millets ( | Eleusine coracana | ) | Seed application | Increase in plant height, number of tillers, plant biomass, ear heads, test weight, grain, and dry straw yield | Increase in NPK content | [71] | ||
| Groundnut ( | Arachis hypogaea | ) | Seedling application | Increase in growth and number of pods, seeds per plant, shelling percentage, 100-seed weight, and pod yield | _ | [72] | ||
| Green gram ( | Vigna radiata | ) | Seed application | Increase in number of nodules per plant, leaf area, and yield | Increase in minerals uptake, chlorophyll content | [73] | ||
| Chickpeas ( | Cicer arietinum) | Seed application | Increase in growth and yield | Increase in phosphorus (P) uptake | [74] | |||
| Sugarcane ( | Saccharum | sp.) | Plantlets | Increase in growth and yield, cane height, tillering | Increase in iron and copper content, sugar content | [66] | ||
| Rapeseed ( | Brassica napus | ) | Seedling application | Increase in plant yield, biomass, early flowering | Increase in oil content, nutrient uptake, decrease in anti-nutrient content | [25] | ||
| Black pepper ( | Piper nigrum | ) | Root cuttings | Increase in fresh and dry weight, number and area of leaves, early flowering | Increase in chlorophyll content | [43] | ||
| Sunflower ( | Helianthus | ) | Seedling application | Increase in growth of plant and seed yield.Increase in root and stem growth, number and area of leaves. Increase in flower diameter, dry weight, and total biomass | Increase in seed oil content | [40] | ||
| Turmeric ( | Curcuma | sp.) | Bud application | Increase in productivity | Increase in secondary metabolite curcumin and oil content | [75] | ||
| Fennel ( | Foeniculum vulgare | ) | Seedling | Increase in plant height, dry weight of plant, fruit dry weight | Increase in essential oil content (anethole) | [45] | ||
| Thyme ( | Thymus vulgaris | ) | Shoot application | Increase in plant height, fresh and dry weight of shoot. Increase in root length, fresh and dry weight of roots | Increase in essential oil content (thymol) | [76] | ||
| Bacopa ( | Bacopa monnieri | ) | Micro propagated plants | Increase in plant growth | Increase in bacoside and antioxidant content | [77] | ||
| Aloe vera ( | Aloe barbadensis | ) | Root application | Increase in biomass, shoot and root length, shoot and root number | Increase in chlorophyll, gel, aloin, and phenol content in leaves | [78] | ||
| Artemisia ( | Artemisia annua | ) | Seedling root application | Increase in plant height, dry weight, leaf yield | Increase in chlorophyll, phosphorus, nitrogen, flavonoids, and artemisinin content | [79] | ||
| Root application | [80] | |||||||
| Centella asiatica | Root application | Increase in shoot and root biomass | Increase in asiaticoside content | [81] | ||||
| Coleus forskohlii | Root application | Increase in aerial biomass, flower development | Increase in chlorophyll content, phosphorus acquisition | [82] | ||||
| Lantana camara | Suspension culture of plant | _ | Increase in triterpenoids (ursolic acid, oleanolic acid, and betulinic acid) production | [83] | ||||
| Pine vines ( | Aristolochia elegans | Mart.) | Substrate application | Increase in plant height, number and length of leaves, total biomass | Increase in aristolochic acid in leaves | [30] | ||
| Alfalafa ( | Medicago sativa | ) | Seedling application | Increase in biomass, shoot dry weight | Increase in nutrient uptake, antioxidant enzyme activity | [84] | ||
| Sweet basil ( | Ocimum basilicum | ) | _ | Increase in plant growth, leaf area, leaf dry weight, yield | Increase in oil content (Geranial, Neral, and Estragole) | [85] | ||
| Gerbera ( | Gerbera jamesonii | ) | Root seedling application | Increase in above and underground plant biomass | Increase in photochemical efficiency | [86] | ||
| Anthurium | sp. | Seedling roots | Increase in plant and root growth | Increase in phosphorus uptake and chlorophyll content | [87] | |||
| Lolium multiflorum | Seed application | Increase in plant height, basal diameter, biomass relative growth rate | Increase in leaf relative water content and chlorophyll content | [38] | ||||
| Banana ( | Musa acuminata | ) | Plantlet roots | Increase in plant height, number and area of leaves, stem diameter, number of suckers, number of fingers per bunch, and yield per plant | Increase in chlorophyll, nitrogen, and phosphorus content | [88] | ||
| Passion fruit ( | Passiflora edulis | ) | Soil application | Plant growth in later stages, fruit size | Increase in fruit quality and secondary metabolites | [89] | ||
| Trifolium orange( | Poncirus trifoliata | ) | Substrate application | Increase in plant height, number of leaves, leaf, stem, and root biomass | Increase in nitrogen, phosphorus, and magnesium content | [7] | ||
| Melon | (Cucumis melo | ) | Substrate application | Increase in fresh and dry weight of plants | Increase in chlorophyll content | [90] | ||
| Pineapple ( | Ananas comosus | ) | Substrate inoculation in root zone | Increase in plant height, number of leaves, and shoot dry weight | Increase in photosynthetic efficiency, nitrogen, phosphorus, potassium, calcium, and magnesium content | [61] |
References
- Jacoby, R.; Peukert, M.; Succurro, A.; Koprivova, A.; Kopriva, S. The Role of Soil Microorganisms in Plant Mineral Nutrition—Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 1617.
- Koskey, G.; Mburu, S.W.; Awino, R.; Njeru, E.M.; Maingi, J.M. Potential use of beneficial microorganisms for soil amelioration, phytopathogen biocontrol, and sustainable crop production in smallholder agroecosystems. Fron. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 606308.
- Saleem, S.; Bytešníková, Z.; Richtera, L.; Pokluda, R. The Effects of Serendipita indica and Guanidine-Modified Nanomaterial on Growth and Development of Cabbage Seedlings and Black Spot Infestation. Agriculture 2021, 11, 1295.
- Garg, M.; Sharma, N.; Sharma, S.; Kapoor, P.; Kumar, A.; Chunduri, V.; Arora, P. Biofortified crops generated by breeding, agronomy, and transgenic approaches are improving lives of millions of people around the world. Front. Nutr. 2018, 5, 12.
- Meena, V.S.; Meena, S.K.; Verma, J.P.; Kumar, A.; Aeron, A.; Mishra, P.K.; Bisht, J.K.; Pattanayak, A.; Naveed, M.; Dotaniya, M.L. Plant beneficial rhizospheric microorganism (PBRM) strategies to improve nutrients use efficiency: A review. Ecol. Eng 2017, 107, 8–32.
- Bingzhu, Y.; Yanbin, W.; Xin, Z.; Ruoqing, Z.; Jinzhong, W.; Zhang, C.; Rahman, K.; Qin, L.; Han, T.; Zheng, C. Beneficial effects of endophytic fungi from the Anoectochilus and Ludisia species on the growth and secondary metabolism of Anoectochilus Roxburghii. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 3487–3497.
- Yang, L.; Zou, Y.N.; Tian, Z.H.; Wu, Q.S.; Kuča, K. Effects of beneficial endophytic fungal inoculants on plant growth and nutrient absorption of trifoliate orange seedlings. Sci. Hortic. 2021, 277, 109815.
- Verma, S.; Varma, A.; Rexer, K.H.; Hassel, A.; Kost, G.; Sarbhoy, A.; Bisen, P.; Bütehorn, B.; Franken, P. Piriformospora indica, gen. et sp. nov., a new root-colonising fungus. Mycologia 1998, 90, 896–903.
- Jha, Y.; Yadav, A.N. Piriformospora indica: Biodiversity, Ecological Significances, and Biotechnological Applications for Agriculture and Allied Sectors. In Industrially Important Fungi for Sustainable Development; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 363–392.
- Pham, G.H.; Kumari, R.; Singh, A.; Malla, R.; Prasad, R.; Sachdev, M.; Kaldorf, M.; Buscot, F.; OelmŘller, R.; Hampp, R.; et al. Axenic culture of symbiotic fungus Piriformospora indica. In Plant Surface Microbiology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2008; pp. 593–613.
- Attri, M.K.; Varma, A. Comparative Study of Growth of Piriformospora indica by using different Sources of Jaggery. J. Pure Appl. Microbiol. 2018, 12, 933–942.
- Qiang, X.; Weiss, M.; Kogel, K.H.; Schafer, P. Piriformospora indica—A mutualistic basidiomycete with an exceptionally large plant host range. Mol. Plant. Pathol. 2011, 13, 508–518.
- Ntana, F.; Bhat, W.W.; Johnson, S.R.; Jørgensen, H.J.; Collinge, D.B.; Jensen, B.; Hamberger, B. A sesquiterpene synthase from the endophytic fungus Serendipita indica catalyzes formation of viridiflorol. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 898.
- Gill, S.S.; Gill, R.; Trivedi, D.K.; Anjum, N.A.; Sharma, K.K.; Ansari, M.W.; Tuteja, N. Piriformospora indica: Potential and significance in plant stress tolerance. Front. Microbiol. 2016, 7, 332.
- Bleša, D. Orchideoid Mycorrhizal Fungi as Endophytes. Diploma Thesis, Masaryk University, Brno, Czech Republic, 2018.
- Deshmukh, S.; Hückelhoven, R.; Schäfer, P.; Imani, J.; Sharma, M.; Weiss, M.; Kogel, K.H. The root endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica requires host cell death for proliferation during mutualistic symbiosis with barley. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 18450–18457.
- Mensah, R.A.; Li, D.; Liu, F.; Tian, N.; Sun, X.; Hao, X.; Cheng, C. Versatile Piriformospora indica and its potential applications in horticultural crops. Hortic. Plant J. 2020, 6, 111–121.
- Abin, N.; Rokni, N.; Shafeinia, A.R.; Borhan, M.H.; Huyghe, C. Quantification of endophyte Serendipita indica in Brassica napus roots by qPCR. Crop. Pasture Sci. 2021, 72, 985–993.
- Rokni, N.; Alizadeh, H.S.; Bazgir, E.; Darvishnia, M.; Mirzaei-Najafgholi, H. The tripartite consortium of Serendipita indica, Trichoderma simmonsii, and bell pepper (Capsicum annum). Biol. Control 2021, 158, 104608.
- Vadassery, J.; Ranf, S.; Drzewiecki, C.; Mithöfer, A.; Mazars, C.; Scheel, D.; Lee, J.; Oelmüller, R. A cell wall extract from the endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica promotes growth of Arabidopsis seedlings and induces intracellular calcium elevation in roots. Plant J. 2009, 59, 193–206.
- Nivedita, Verma, P.K.; Upadhyaya, K.C. Lectin Protein Kinase Is Induced in Plant Roots in Response to the Endophytic Fungus, Piriformospora indica. Plant Mol. Biol. Rep. 2017, 35, 323–332.
- Camehl, I.; Sherameti, I.; Seebald, E.; Johnson, J.M.; Oelmüller, R. Role of defence compounds in the beneficial interaction between Arabidopsis thaliana and Piriformospora indica. In Piriformospora Indica; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2013; pp. 239–250.
- Unnikumar, K.R.; Sree, K.S.; Varma, A. Piriformospora indica: A versatile root endophytic symbiont. Symbiosis 2013, 60, 107–113.
- Singhal, U.; Prasad, R.; Varma, A. Piriformospora indica (Serendipita indica): The Novel Symbiont. In Mycorrhiza—Function, Diversity, State of the Art; Varma, A., Prasad, R., Tuteja, N., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 349–364.
- Su, Z.Z.; Wang, T.; Shrivastava, N.; Chen, Y.Y.; Liu, X.; Sun, C.; Yin., Y.; Gao, Q.K.; Lou, B.G. Piriformospora indica promotes growth, seed yield and quality of Brassica napus L. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 199, 29–39.
- Hosseini, F.; Mosaddeghi, M.R.; Dexter, A.R.; Sepehri, M. Maize water status and physiological traits as affected by root endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica under combined drought and mechanical stresses. Planta 2018, 247, 1229–1245.
- Liu, B.; Jing, D.; Liu, F.; Ma, H.; Liu, X.; Peng, L. Serendipita indica alleviates drought stress responses in walnut (Juglans regia L.) seedlings by stimulating osmotic adjustment and antioxidant defence system. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2021, 105, 8951–8968.
- Roylawar, P.; Khandagale, K.; Randive, P.; Shinde, B.; Murumkar, C.; Ade, A.; Singh, M.; Gawande, S.; Morelli, M. Piriformospora indica Primes Onion Response against Stemphylium Leaf Blight Disease. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1085.
- Upadhyaya, C.P.; Gururani, M.A.; Prasad, R.; Verma, A. A Cell Wall Extract from Piriformospora indica Promotes Tuberization in Potato (Solanum tuberosum L.) Via Enhanced Expression of Ca+2 Signaling Pathway and Lipoxygenase Gene. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 2013, 170, 743–755.
- Bagde, U.S.; Prasad, R.; Varma, A. Impact of culture filtrate of Piriformospora indica on biomass and biosynthesis of active ingredient aristolochic acid in Aristolochia Elegans Mart. Int. J. Biol. 2014, 6, 29.
- Oelmüller, R.; Sherameti, I.; Tripathi, S.; Varma, A. Piriformospora indica, a cultivable root endophyte with multiple biotechnological applications. Symbiosis 2009, 49, 1–17.
- Bagde, U.S.; Prasad, R.; Varma, A. Mass cultivation of Piriformospora indica in new brunswick fermenter and its formulation as biofertilizer. Asian J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Environ. Sci. 2010, 12, 911–916.
- Shrivastava, S.; Varma, A. From Piriformospora indica to rootonic: A review. Afr. J. Microbiol. Res. 2014, 8, 2984–2992.
- Barazani, O.; Benderoth, M.; Groten, K.; Kuhlemeier, C.; Baldwin, I.T. Piriformospora indica and Sebacina vermifera increase growth performance at the expense of herbivore resistance in Nicotiana attenuata. Oecologia 2005, 146, 234–243.
- Varma, A.; Bakshi, M.; Lou, B.; Hartmann, A.; Oelmüller, R. Piriformospora indica: A Novel Plant Growth-Promoting Mycorrhizal Fungus. Agric. Res. 2012, 1, 117–131.
- Jisha, S.; Sabu, K.K.; Manjula, S. Multifunctional aspects of Piriformospora indica in plant endosymbiosis. Mycology 2019, 10, 182.
- Jogawat, A.; Saha, S.; Bakshi, M.; Dayaman, V.; Kumar, M.; Dua, M.; Varma, A.; Oelmüller, R.; Tuteja, N.; Johri, A.K. Piriformospora indica rescues growth diminution of rice seedlings during high salt stress. Plant Signal. Behav. 2013, 8, e26891.
- Liu, B.; Liu, X.; Liu, F.; Ma, H.; Ma, B.; Zhang, W.; Peng, L. Growth improvement of Lolium multiflorum Lam. induced by seed inoculation with fungus suspension of Xerocomus badius and Serendipita indica. AMB Expr. 2019, 9, 145.
- Sherameti, I.; Shahollari, B.; Venus, Y.; Altschmied, L.; Varma, A.; Oelmüller, R. The endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica stimulates the expression of nitrate reductase and the starch-degrading enzyme glucan-water dikinase in tobacco and Arabidopsis roots through a homeodomain transcription factor that binds to a conserved motif in their promoters. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 26241–26247.
- Bagde, U.S.; Prasad, R.; Varma, A. Influence of culture filtrate of Piriformospora indica on growth and yield of seed oil in Helianthus annus. Symbiosis 2011, 53, 83–88.
- Li, L.; Zhu, P.; Wang, X.; Zhang, Z. Phytoremediation effect of Medicago sativa colonised by Piriformospora indica in the phenanthrene and cadmium co-contaminated soil. BMC Biotechnol. 2020, 20, 20.
- Murphy, B.R.; Doohan, F.M.; Hodkinson, T.R. Yield increase induced by the fungal root endophyte Piriformospora indica in barley grown at low temperature is nutrient limited. Symbiosis 2014, 62, 29–39.
- Anith, K.N.; Aswini, S.; Varkey, S.; Radhakrishnan, N.V.; Nair, D.S. Root colonization by the endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica improves growth, yield and piperine content in black pepper (Piper nigurm L.). Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 14, 15–220.
- Tsai, H.J.; Shao, K.H.; Chan, M.T.; Cheng, C.P.; Yeh, K.W.; Oelmüller, R.; Wang, S.J. Piriformospora indica symbiosis improves water stress tolerance of rice through regulating stomata behavior and ROS scavenging systems. Plant Signal. Behav. 2020, 15, 1722447.
- Dolatabadi, H.K.; Goltapeh, E.M.; Jaimand, K.; Rohani, N.; Varma, A. Effects of Piriformospora indica and Sebacina vermifera on growth and yield of essential oil in fennel (Foeniculum vulgare) under greenhouse conditions. J. Basic Microbiol. 2011, 51, 33–39.
- Bakhshandeh, E.; Pirdashti, H.; Lendeh, K.S.; Zahra, G.; Khanghahi, M.Y.; Crecchio, C. Effects of plant growth promoting microorganisms inoculums on mineral nutrition, growth and productivity of rice (Oryza sativa L.). J. Plant Nutr. 2020, 43, 1643–1660.
- Li, Q.; Kuo, Y.W.; Lin, K.H.; Huang, W.; Deng, C.; Yeh, K.W.; Chen, S.P. Piriformospora indica colonization increases the growth, development, and herbivory resistance of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas L.). Plant Cell Rep. 2021, 40, 339–350.
- Eliaspour, S.; Seyed, Sharifi, R.; Shirkhani, A. Evaluation of interaction between Piriformospora indica, animal manure and NPK fertilizer on quantitative and qualitative yield and absorption of elements in sunflower. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020, 8, 2789–2797.
- Wang, H.; Zheng, J.; Ren, X.; Yu, T.; Varma, A.; Lou, B.; Zheng, X. Effects of Piriformospora indica on the growth, fruit quality and interaction with Tomato yellow leaf curl virus in tomato cultivars susceptible and resistant to TYCLV. Plant Growth Regul. 2015, 76, 303–313.
- Azizi, M.; Fard, E.M.; Ghabooli, M. Piriformospora indica affect drought tolerance by regulation of genes expression and some morphophysiological parameters in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum L.). Sci. Hortic. 2021, 287, 110260.
- Hussin, S.; Khalifa, W.; Geissler, N.; Koyro, H.W. Influence of the root endophyte Piriformospora indica on the plant water relations, gas exchange and growth of Chenopodium quinoa at limited water availability. J. Agron. Crop. Sci. 2016, 203, 373–384.
- Baghaie, A.H.; Aghilizefreei, A. Iron enriched green manure can increase wheat Fe concentration in Pb-polluted soil in the presence of Piriformospora indica (P. indica). Soil Sediment Contam. 2020, 29, 721–743.
- Ahmadvand, G.; Hajinia, S. Effect of endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica on yield and some physiological traits of millet (Panicum miliaceum) under water stress. Crop Pasture Sci. 2018, 69, 594–605.
- Johnson, J.M.; Alex, T.; Oelmüller, R. Piriformospora indica: The versatile and multifunctional root endophytic fungus for enhanced yield and tolerance to biotic and abiotic stress in crop plants. J. Trop. Agric 2014, 52, 103–122.
- Serfling, A.; Wirsel, S.G.; Lind, V.; Deising, H.B. Performance of the biocontrol fungus Piriformospora indica on wheat under greenhouse and field conditions. Phytopathology 2007, 97, 523–531.
- Khalid, M.; Rahman, S.U.; Huang, D. Molecular mechanism underlying Piriformospora indica-mediated plant improvement/protection for sustainable agriculture. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2019, 51, 229–242.
- Swetha, S.; Padmavathi, T. Study of acid phosphatase in solubilization of inorganic phosphates by Piriformospora indica. Pol. J. Microbiol. 2016, 65, 7.
- Wu, M.; Wei, Q.; Xu, L.; Li, H.; Oelmüller, R.; Zhang, W. Piriformospora indica enhances phosphorus absorption by stimulating acid phosphatase activities and organic acid accumulation in Brassica napus. Plant Soil 2018, 432, 333–344.
- Das, J.; Ramesh, K.V.; Maithri, U.; Mutangana, D.; Suresh, C.K. Response of aerobic rice to Piriformospora indica. Indian J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 52, 237–251. Available online: http://nopr.niscpr.res.in/handle/123456789/27348 (accessed on 10 February 2022).
- Baghaie, A.H.; Aghili, F. Contribution of Piriformospora indica on improving the nutritional quality of greenhouse tomato and its resistance against cu toxicity after humic acid addition to soil. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2021, 28, 64572–64585.
- Moreira, B.C.; Mendes, F.C.; Mendes, I.R.; Paula, T.A.; Junior, P.P.; Salomão, L.C.; Stürmer, S.L.; Otoni, W.C.; Kasuya, M.C. The interaction between arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Piriformospora indica improves the growth and nutrient uptake in micropropagation-derived pineapple plantlets. Sci. Hortic. 2015, 14, 183–192.
- Prasad, D.; Verma, N.; Bakshi, M.; Narayan, O.P.; Singh, A.K.; Dua, M.; Johri, A.K. Functional characterization of a magnesium transporter of root endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 9, 3231.
- Narayan, O.P.; Verma, N.; Singh, A.K.; Oelmüller, R.; Kumar, M.; Prasad, D.; Kapoor, R.; Dua, M.; Johri, A.K. Antioxidant enzymes in chickpea colonised by Piriformospora indica participate in defence against the pathogen Botrytis Cinerea. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 13553.
- Padash, A.; Shahabivand, S.; Behtash, F.; Aghaee, A. A practicable method for zinc enrichment in lettuce leaves by the endophyte fungus Piriformospora indica under increasing zinc supply. Sci. Hortic. 2016, 213, 367–372.
- Chen, Y.Y.; Lou, B.G.; Gao, Q.K.; Lin, F.C. Preliminary study on mechanisms of drought resistance in Brassica napus L. conferred by Piriformospora indica. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2013, 21, 72–281.
- Gosal, S.K.; Sharma, M.; Gosal, S.S.; Chhibba, I.M.; Bhatnagar, K.; Varma, A. Bio hardening with Piriformospora indica improves survival rate, growth, iron uptake and cane yield of micro propagated sugarcane. Int. Sugar J. 2011, 113, 382–388.
- Abdelaziz, E.M.; Sabra, M.; Ali, M. Colonising Lettuce (Lactuca sativa L.) with Rhizophagus irregularis and Piriformospora indica fungi enhance plant yield and quality in sand soil. Middle East J. Appl. Sci. 2018, 8, 1173–1180.
- Sun, C.; Johnson, J.M.; Cai, D.; Sherameti, I.; Oelmüller, R.; Lou, B. Piriformospora indica confers drought tolerance in Chinese cabbage leaves by stimulating antioxidant enzymes the expression of drought-related genes and the plastid-localized CAS protein. J. Plant Physiol. 2010, 167, 009–1017.
- Lakshmipriya, P.; Nath, V.S.; Veena, S.S.; Anith, K.N.; Sreekumar, J.; Jeeva, M.L. Piriformospora indica, a cultivable endophyte for growth promotion and disease management in Taro (Colocasia esculenta (L.). J. Root Crops 2016, 42, 107–114.
- Waller, F.; Achatz, B.; Baltruschat, H.; Fodor, J.; Becker, K.; Fischer, M.; Heier, T.; Hückelhoven, R.; Neumann, C.; von Wettstein, D.; et al. The endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica reprograms barley to salt-stress tolerance, disease resistance, and higher yield. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2005, 102, 13386–13391.
- Arunkumar, G.P.; Shivaprakash, M.K. Influence of novel endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica on growth and yield of finger millet (Eleusine coracana G.) in combination with N fixer and P solubilizer. Int. J. Curr. Microbiol. App. Sci. 2017, 6, 1037–1042.
- Tarte, S.H.; Kareppa, B.M.; Kharde, A.V. Impact of Piriformospora indica on growth and yield parameters of groundnut (Arachis hypogea L.). Pharma innov. 2019, 8, 766–769.
- Ray, J.G.; Valsalakumar, N. Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and Piriformospora indica individually and in combination with rhizobium on green gram. J. Plant Nutr. 2010, 33, 285–298.
- Meena, K.K.; Mesapogu, S.; Kumar, M.; Yandigeri, M.S.; Singh, G.; Saxena, A.K. Co-inoculation of the endophytic fungus Piriformospora indica with the phosphate-solubilising bacterium Pseudomonas striata affects population dynamics and plant growth in chickpea. Biol. Fertil. Soils. 2010, 46, 169–174.
- Bajaj, R.; Agarwal, A.; Rajpal, K.; Asthana, S.; Kumar, R.; Prasad, R.; Kharkwal, A.C.; Sherameti, I.; Oelmüller, R.; Varma, A. Co-cultivation of Curcuma longa with Piriformospora indica enhances the yield and active ingredients. Am. J. Curr. Microbiol. 2014, 2, 6–17.
- Dolatabadi, H.K.; Goltapeh, E.M.; Moieni, A.; Jaimand, K.; Sardrood, B.P.; Varma, A. Effect of Piriformospora indica and Sebacina vermifera on plant growth and essential oil yield in Thymus vulgaris in vitro and in vivo experiments. Symbiosis 2011, 53, 29–35.
- Prasad, R.; Kamal, S.; Sharma, P.K.; Oelmüller, R.; Varma, A. Root endophyte Piriformospora indica DSM 11827 alters plant morphology, enhances biomass and antioxidant activity of medicinal plant Bacopa monniera. J. Basic Microbiol. 2013, 53, 1016–1024.
- Sharma, P.; Kharkwal, A.C.; Abdin, M.Z.; Varma, A. Piriformospora indica improves micropropagation, growth and phytochemical content of Aloe vera L. plants. Symbiosis 2014, 64, 11–23.
- Arora, M.; Saxena, P.; Choudhary, D.K.; Abdin, M.Z.; Varma, A. Dual symbiosis between Piriformospora indica and Azotobacter chroococcum enhances the artemisinin content in Artemisia annua L. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 19.
- Rahman, S.U.; Khalid, M.; Kayani, S.I.; Tang, K. The ameliorative effects of exogenous inoculation of Piriformospora indica on molecular, biochemical and physiological parameters of Artemisia annua L. under arsenic stress condition. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 206, 111202.
- Satheesan, J.; Narayanan, A.K.; Sakunthala, M. Induction of root colonization by Piriformospora indica leads to enhanced asiaticoside production in Centella asiatica. Mycorrhiza 2012, 22, 195–202.
- Das, A.; Kamal, S.; Shakil, N.A.; Sherameti, I.; Oelmüller, R.; Dua, M.; Tuteja, N.; Johri, A.K.; Varma, A. The root endophyte fungus Piriformospora indica leads to early flowering, higher biomass and altered secondary metabolites of the medicinal plant, Coleus forskohlii. Plant Signal. Behav. 2012, 7, 103–112.
- Kumar, P.; Chaturvedi, R.; Sundar, D.; Bisaria, V.S. Piriformospora indica enhances the production of pentacyclic triterpenoids in Lantana camara L. suspension cultures Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult. 2016, 125, 23–29.
- Sepehri, M.; Khatabi, B. Combination of siderophore-producing bacteria and Piriformospora indica provides an efficient approach to improve cadmium tolerance in alfalfa. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 202, 717–730.
- Keramati, S.; Pirdashti, H.; Babaeizad, V.; Dehestani, A. Essential oil composition of sweet basil (Ocimum basilicum L.) in symbiotic relationship with Piriformospora indica and paclobutrazol application under salt stress. Acta. Biol. Hung. 2016, 67, 412–423.
- Chen, W.; Lin, F.; Lin, K.H.; Chen, C.; Xia, C.; Liao, Q.; Chen, S.P.; Kuo, Y.W. Growth promotion and salt-tolerance improvement of Gerbera jamesonii by root colonization of Piriformospora indica. Plant Growth Regul. 2021, 41, 1219–1228.
- Lin, H.F.; Xiong, J.; Zhou, H.M.; Chen, C.M.; Lin, F.Z.; Xu, X.M.; Oelmüller, R.; Xu, W.F.; Yeh, K.W. Growth promotion and disease resistance induced in Anthurium colonised by the beneficial root endophyte Piriformospora indica. BMC Plant Biol. 2019, 19, 40.
- Madaan, G.; Gosal, S.K.; Gosal, S.S.; Saroa, G.S.; Gill, M.I. Effect of microbial inoculants on the growth and yield of micropropagated banana (Musa indica) cv. Grand. Naine. J. Hortic. Sci. Biotechnol. 2013, 88, 643–649.
- Yan, C.; Rizwan, H.M.; Liang, D.; Reichelt, M.; Mithöfer, A.; Scholz, S.S.; Oelmüller, R.; Chen, F. The effect of the root colonising Piriformospora indica on passion fruit (Passiflora edulis) development: Initial defence shifts to fitness benefits and higher fruit quality. Food Chem. 2021, 359, 129671.
- Hassani, D.; Khalid, M.; Huang, D.; Zhang, Y.D. Morphophysiological and molecular evidence supporting the augmentative role of Piriformospora indica in mitigation of salinity in Cucumis melo L. Acta Biochim. Biophys. Sin. 2019, 51, 301–312.
More
