Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 4 by Jessie Wu and Version 3 by Jessie Wu.
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are important players in post-transcriptional gene expression regulation in multicellular species. miRNAs can modify/decrease the expression of fully or partially complementary mRNA molecules. Plant miRNAs are powerful regulators of gene expression at the post-transcriptional level, which was repeatedly proved in several model plant species. miRNAs are considered to be key regulators of many developmental, homeostatic, and immune processes in plants.
- miRNAs
- plants
- gene
- barley
1. Plant miRNAs
Mature plant miRNAs are 19–25-nucleotide-long ribonucleic acids that can have either intergenic (miRNA gene is localized between two protein-coding sequences of the DNA) or intragenic origin [1], where miRNAs are cleaved from the mRNA sequences during the splicing (also called intron-derived miRNAs [2]). Specifically, in barley, more than 75% of miRNAs are transcribed from intergenic loci [3]. The biogenesis of miRNAs is ensured by the DNA-dependent RNA polymerase II which is responsible for the biosynthesis itself [4]. In some cases, multiple plant miRNAs are synthesized all at once (multiple miRNAs localized in one long transcript) [5] and often form a miRNA family, which is a group of miRNAs derived from a common ancestor [6]. Emerging miRNAs can be modified co-transcriptionally, or post-transcriptionally. Similar to other transcripts, a 7-methylguanosine (m7G) cap is attached to the 5′ end of the miRNA, and the 3′ end is polyadenylated (or can be spliced) [7]. Later, the transcript encoding miRNA (or multiple miRNAs) is folded to the stem-loop structure which is called pri-miRNA [4] (meaning primary miRNA transcript). Such pri-miRNAs are further cleaved by the dicing bodies. Dicing bodies consists of several proteins including DICER-LIKE 1 (DCL1), DAWDLE (DDL), HYL1, TGH, and SE [8][9], resulting in miRNA duplex formation which can be later 2′-O-methylated by the HEN1 methylase [10] and incorporated into the RNA-induced silencing complex (RISC) [4][11]. The complex issue of further proteins involved in plant miRNA biogenesis is reviewed in Li et al., 2021 [12]. miRNAs of both origins (intragenic as well as intergenic) lead to the formation of a mature RISC with incorporated mature miRNA. In most cases, only the sense/guide miRNA strand is incorporated into the RISC, while the antisense/passenger miRNA (miRNA*) strand is disrupted, but recently also the regulation potential of the passenger miRNA became the center of interest [13][14][15]. For a clear summary of miRNA biogenesis see Figure 1 below.
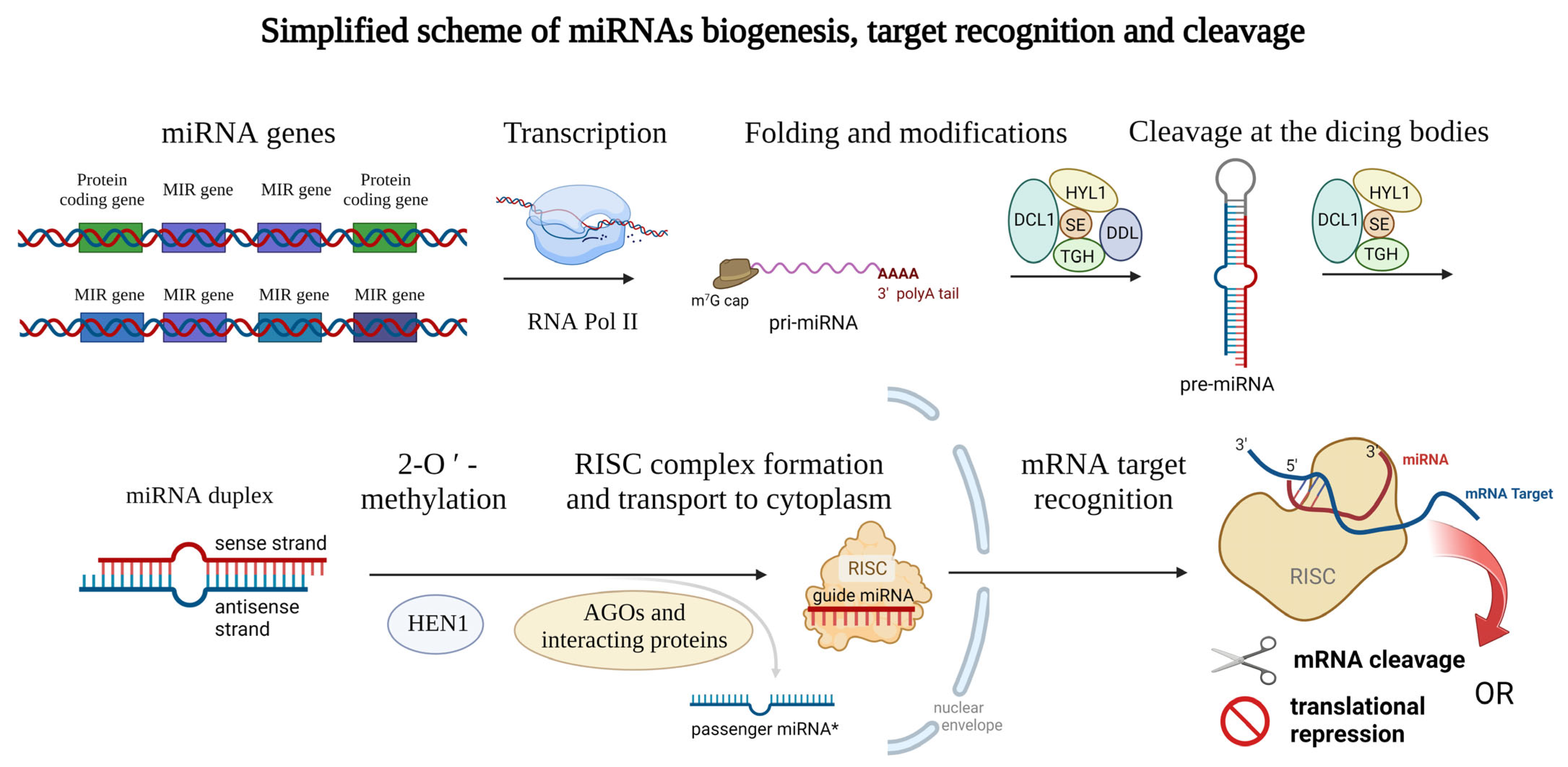
Figure 1. Schematic representation of the miRNAs biogenesis. Genes encoding miRNAs are transcribed by RNA polymerase II and modified on their ends (m7G cap and polyA tail) and thus the primary microRNA (pri-miRNA) arise. Then, the typical stem-loop structure is formed by complementary base pairing and cleaved at the dicing bodies (consisting of several proteins including DCL1, HYL1, SE, TIGH, and DDL) resulting in miRNA duplex formation which can be later 2′-O-methylated (ensured by the HEN1 protein). Guide miRNA is incorporated into the RISC consisting of several proteins, and transported into the cytoplasm, where mRNA target recognition and cleavage can take place while the passenger miRNA is released away. Proteins from the Argonaute family (AGOs) can modify the stability of the miRNAs and also affect the interaction with target mRNAs. This figure was created using BioRender (https://biorender.com/; accessed on 20 June 2022).
miRNAs interact with their target mRNAs mostly at their 3′ UTRs, but interactions occurring in the 5′ UTRs or coding regions were documented as well [16][17]. RISC is directed to the complementary mRNA transcript, whereby the Watson–Crick base-pairing aligns guide miRNA and target mRNA transcript, and depending on the central miRNA region complementarity, mRNA is cleaved (usually when there is perfect base-pair complementarity), or translation repression occurs (central miRNA region is not completely complementary to mRNA) [18]. Moreover, in the case the target mRNA is cleaved, so-called phased secondary small interfering RNAs (phasiRNAs) can arise [19]. phasiRNAs are 21 or 24-nucleotide-long siRNAs having important roles in plant stress responses [19], development [20], and reproduction [21].
Similar to the other genes, miRNA transcription is precisely fine-tuned. This is assured mainly by transcription factors binding [22] and methylation status of DNA [23], both heavily influenced by endogenous and exogenous stimuli. In 2018, protein WHIRLY1 was found to be involved in increased levels of nuclear miRNAs in high-light conditions in barley. It was therefore proposed that WHIRLY1 can bind to RNA and it might be a general factor influencing the biogenesis and/or stability of various miRNAs [24].
An additional level of miRNA complexity is their dynamic stability [9][25]. It was documented that the processes such as 3′-end modifications and interaction with Argonaute proteins (AGOs) can both reduce and increase the stability of miRNAs depending on the actual needs of the plant. For example, AGO1 from Arabidopsis thaliana was proposed to stabilize miRNAs, and miRNA–mRNA target interaction [4].
Besides post-transcriptional gene silencing (PTGS), miRNAs can regulate plant genes via RNA-induced methylation of DNA [26][27]. Such a process was in detail described in the Arabidopsis thaliana, where miRNAs (miR165, miR166) regulate the methylation status of PHB and PHV genes [28], and are responsible for the determination of the abaxial and adaxial leaf side. Similarly, the miRNA-induced gene methylation was described even in the Oryza sativa where the miR1873 ensures the methylation of its own gene [27]. To make our understanding of miRNAs-based regulation of gene expression more challenging, the stimulative effect of miRNAs on gene expression was observed and documented as well [29].
Last but not least, in 2015 it was proposed that plant pri-miRNAs are capable of encoding small functional peptides [30][31] described as miPEPs. The best-characterized miPEPs (miPEP171d, miPEP172c, and miPEP858a) were found in plant species including Arabidopsis thaliana (miPEP165a [30], miPEP858 [32]), Medicago truncatula (miPEP171b [18]), Glycine max (miPEP172c [33]), and Vitis vinifera (miPEP171d1 [34]). The mechanism of miPEPs molecular function is still largely unclear, but generally, miPEPs positively affect the accumulation of their associated miRNAs [31]. It is also likely that many of miPEPs will be species-specific [34].
2. miRNAs in Barley Physiology and Stress Responses
miRNAs in plants are important regulators of various physiological processes including shoot apical meristem development [35], leaf growth [36], flower formation [37], seed production [38], and root expansion [36]. It was found that miRNA171 in barley is responsible for the regulation of shoot meristem development through three independent pathways, i.e., firstly through the down-regulation of SCARECROW-LIKE (SCL) transcription factors, secondly via up-regulation of miRNA156 and repressing vegetative phase transitions (a possibly monocotyledon-specific mechanism), and thirdly by repressing expression of TRD and HvPLA1 genes [39]. Additionally, flower development in grasses including barley is tightly regulated by miRNAs. It was found that miRNA159, miRNA171, miRNA172, and miRNA396 regulate the expression of floral organ identity genes in barley, rice, and maize [40]. In barley, cleistogamous flowering (i.e., shedding its pollen before opening) arises from the suppression of the AP2 transcription factor via miR172, originally thought to be a result of target mRNA cleavage [41], but later it was proved that miR172-mediated AP2 regulation occurs at the translational level [42]. It is also known that the expression of barley miR393 is active in the developmental period, and its misexpression affects seedling growth and stomatal density [43]. In 2018, it was found that miR160 in barley simultaneously targets class II ARF members which are functionally involved in developmental stages by regulating the auxin-mediated genes [44]. Figure 2 illustratively depicts some of the most known barley miRNAs (and their targets) that play important roles in developmental processes.
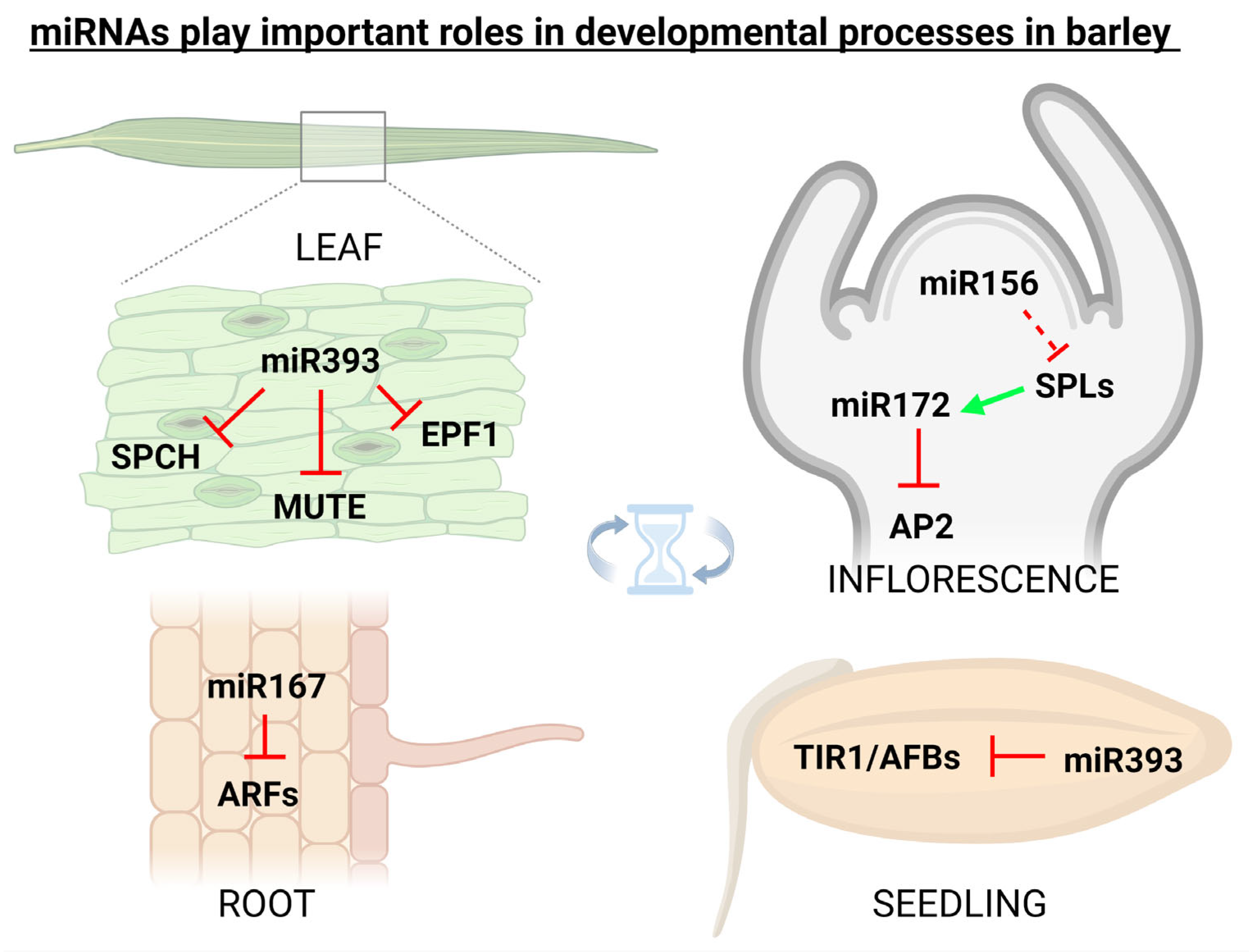
Figure 2. miRNAs play important roles also in the developmental processes. In spring barley (Hordeum vulgare), specific miRNAs were linked with the targets involved in the regulation of flowering, root development, seed germination, and also with stomata development. Inhibition is indicated by the red ┴ mark, while positive effect by the green arrow. This figure was created using BioRender (https://biorender.com/; accessed on 20 June 2022).
Besides the non-stress conditions, miRNAs play key roles in gene expression regulation in response to a variety of abiotic stimuli, including several stress responses. In plants, their involvement in many abiotic stress responses including heat stress responses, low-temperature responses, drought exposure responses, carbon dioxide responses, light stress responses, or gamma radiation responses was reported [45][46][47][48][49]. Specifically in barley, miRNAs responsive to salinity stress [50][51][52][53], drought [54][55][56][57][58], nitrogen [59], boron [60], phosphorus [61][62], aluminum [51][63][64], cadmium [65], cold deacclimation [66], heat stress [67], and possibly to light [68] were identified till date. A chronological summary of the most impactful miRNA studies in barley (starting from 2010) can be found below in Table 1.
Table 1. Chronological summary of studies dealing with miRNAs in barley species and most important results obtained.
| Title of the Study and Reference | Barley Cultivars Inspected |
Year of | Publication | Most Important Findings | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Regulation of barley miRNAs upon dehydration stress correlated with target gene expression | [56] | Hordeum vulgare | 2010 | A total of 28 potential miRNAs were identified using bioinformatic approaches (BLASTn of known plant miRNAs and barley expressed sequence tags (ESTs), and RNA folding algorithms). | |||||||||
| Discovery of barley miRNAs through deep sequencing of short reads | [69] | Hordeum vulgare | cultivars Golden Promise and Pallas | 2011 | The first large-scale study of miRNAs in | Hordeum Vulgare | , 100 miRNAs were identified (only 56 of them had orthologs in wheat, rice, or Brachypodium) and 3 candidates were validated in vitro using a Northern blot assay. | ||||||
| Identification and Characterization of MicroRNAs from Barley ( | Hordeum vulgare | L.) by High-Throughput Sequencing | [70] | Hordeum vulgare | L. | 2012 | 126 conserved miRNAs (belonging to 58 families), and 133 novel miRNAs (50 families) were identified in this study. | ||||||
| miRNA regulation in the early development of barley seed | [38] | Hordeum vulgare | 2012 | 84 known miRNAs and 7 new miRNAs together with 96 putative miRNA target genes were identified during the early development of barley seeds (first 15 days post anthesis). | |||||||||
| Developmentally regulated expression and complex processing of barley pri-microRNAs | [71] | Hordeum vulgare | cultivar Rolap | 2013 | miRNA genes in barley often contain introns which may play important role in miRNA processing. | ||||||||
| A Comprehensive Expression Profile of MicroRNAs and Other Classes of Non-Coding Small RNAs in Barley Under Phosphorous-Deficient and -Sufficient Conditions | [61] | Hordeum vulgare | L., cultivar Pallas | 2013 | 221 conserved miRNAs and 12 novel miRNAs were identified, many of them were phosphorus condition-specific. A total of 47 miRNAs were significantly differentially expressed between the two phosphorus treatments. | ||||||||
| Boron Stress Responsive MicroRNAs and Their Targets in Barley | [60] | Hordeum vulgare | L. cultivar Sahara | 2013 | 31 known and 3 new miRNAs were identified in barley, and 25 of them were found to respond to boron treatment. | ||||||||
| Transcriptionally and post-transcriptionally regulated microRNAs in heat stress response in barley | [67] | Hordeum vulgare | cultivar Rolap | 2014 | Four heat stress up-regulated barley miRNAs were found (miR160a, miR166a, miR167h, and miR5175a). | ||||||||
| Differential expression of microRNAs and other small RNAs in barley between water and drought conditions | [57] | Hordeum vulgare | cultivar Golden Promise | 2014 | Three novel miRNAs, designated as hvu-miRX33, hvu-miRX34, and hvu-miRX35 were identified. hvu-miRX34 had no homologous miRNA in wheat. | ||||||||
| The miR9863 Family Regulates Distinct Mla Alleles in Barley to Attenuate NLR Receptor-Triggered Disease Resistance and Cell-Death Signaling | [72] | Hordeum vulgare | L. | 2014 | The key role of the miR9863 family in the immune response to the pathogen (powdery mildew fungus, | Blumeria graminis | f. sp. | hordei | ) was proposed | ||||
| Polycistronic artificial miRNA-mediated resistance to Wheat dwarf virus in barley is highly efficient at low temperature | [73] | Artificially transformed | Hordeum vulgare | cultivar Golden Promise | 2015 | Polycistronic artificial miRNA in plasmid vector was successfully transformed into barley embryos and mediated resistance to Wheat dwarf virus. | |||||||
| Global Identification of MicroRNAs and Their Targets in Barley under Salinity Stress | [50] | Hordeum vulgare | cultivar Morex | 2015 | Authors identified 152 miRNAs (142 conserved and 10 novel ones), and 44 miRNAs (39 conserved and 5 novel ones) were found to be salinity-responsive. | ||||||||
| Characterization of microRNAs and their targets in wild barley ( | Hordeum vulgare | subsp. spontaneum) using deep sequencing | [74] | Hordeum vulgare | subsp. | spontaneum | 2016 | A total of 70 known miRNAs and 18 novel miRNA candidates were identified and many of them were predicted to target mRNAs encoding transcription factors. | |||||
| Developmental changes in barley microRNA expression profiles coupled with miRNA target analysis | [75] | Hordeum vulgare | cultivar Rolap | 2016 | miRNA transcriptomes of five barley developmental stages were inspected. Overall, miR168-3p and miR1432-5p levels increased while the 5′U-miR156-5p level decreased during barley development. | ||||||||
| miR393-Mediated Auxin Signaling Regulation is Involved in Root Elongation Inhibition in Response to Toxic Aluminum Stress in Barley | [63] | Hordeum vulgare | cultivar Golden Promise | 2017 | Barley miR393 was functionally characterized. It regulates root sensitivity to aluminum through the alteration of auxin signaling. | ||||||||
| Differential expression of microRNAs and potential targets under drought stress in barley | [55] | Hordeum vulgare | L. cultivars Commander, Fleet, Hindmarsh, and breeding line WI4304 | 2017 | miRNA regulation under drought stress in barley is genotype-specific. | ||||||||
| microRNAs participate in gene expression regulation and phytohormone cross-talk in barley embryo during seed development and germination | [76] | Hordeum vulgare | cultivar Golden Promise | 2017 | A total of 1324 known miRNAs and 448 novel miRNA candidates were identified. miR393-mediated auxin response regulation significantly affected grain development. | ||||||||
| Small RNA Activity in Archeological Barley Shows Novel Germination Inhibition in Response to Environment | [77] | Ancient | Hordeum vulgare | 2017 | Sequencing of miRNAs obtained from archeological barley samples (600–900 years BP) revealed their local adaptation to an agrarian environment around the river Nile. | ||||||||
| Genome-wide analysis of the SPL/miR156 module and its interaction with the AP2/miR172 unit in barley | [78] | Hordeum vulgare | L. | 2018 | The study identified 17 barley | SPL | genes, and 7 of them contain a putative miR156 target site. | ||||||
| Identification of microRNAs in response to aluminum stress in the roots of Tibetan wild barley and cultivated barley | [64] | Hordeum vulgare | Al-sensitive Golden Promise and Tibetan wild barley (Al-tolerant XZ29) | 2018 | 50 miRNAs responsive to aluminum stress were detected, and some of them were found to be exclusively expressed in Al-tolerant XZ29. | ||||||||
| Identification of microRNAs responding to salt stress in barley by high-throughput sequencing and degradome analysis | [53] | Tibetan wild barley accession XZ16; | Hordeum vulgare | cultivar Golden Promise | 2019 | miR393a, miR156d, and miR172b (regulating | HvAFB2/HvTIR1 | , | UGTs | , and | HvAP2 | ) are responsible for salt tolerance in barley roots. | |
| Genotypic difference of cadmium tolerance and the associated microRNAs in wild and cultivated barley | [65] | Hordeum vulgare | cultivar Golden Promise and wild barley WB-1 | 2019 | 216 conserved miRNAs (in 59 miRNA families) and 87 novel miRNAs were identified. Authors suggest that miRNAs may play critical roles underlying the genotypic difference of cadmium tolerance in barley. | ||||||||
| Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Drought Stress Responsive microRNAs in Tibetan Wild Barley | [58] | Tibetan wild barley | Hordeum vulgare | L. ssp. Spontaneum | 2020 | 69 conserved miRNAs and 1574 novel miRNAs were identified, some of them were differentially expressed in drought conditions. | |||||||
| Barley microRNAs as metabolic sensors for soil nitrogen availability | [59] | Hordeum vulgare | cultivar Golden Promise | 2020 | Authors identified 13 barley miRNAs that are nitrogen excess responsive with the possible function of metabolic sensors for soil nitrogen availability. | ||||||||
| The Impact of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity, and miRNA Expression in Barley ( | Hordeum vulgare | L.) Seedlings | [79] | Hordeum vulgare | L. var. Abava | 2020 | ZnO nanoparticles significantly changed the expression of barley miR156a, miR159a, and miR159c in a dosage-dependent manner. | ||||||
| Identification of microRNAs in response to low potassium stress in the shoots of Tibetan wild barley and cultivated | [80] | A Tibetan wild barley accession (XZ153) and a cultivar (ZD9) differing in low K tolerance | 2021 | A total of 1088 miRNAs were identified in the two barley genotypes under low potassium conditions. 65 of them were significantly differentially expressed. | |||||||||
| Barley Seeds miRNome Stability during Long-Term Storage and Aging | [81] | Hordeum vulgare | cultivar Damazy | 2021 | miRNome of barley seeds harvested in 1972 was inspected. 61 known and 81 novel miRNA were identified pointing to the fact that miRNAs in dry seeds are extremely stable. | ||||||||
| Identification microRNAs and target genes in Tibetan hulless barley to BLS infection | [82] | Hordeum vulgare | L. variety nudum Hook. f. | 2021 | A total of 36 conserved and 56 novel miRNAs were identified, some of them were differentially expressed between BLS (barley leaf stripe fungal disease)-sensitive and BLS-tolerant barley genotypes. | ||||||||
| Pi-starvation induced transcriptional changes in barley revealed by a comprehensive RNA-Seq and degradome analyses | [62] | Hordeum vulgare | L. | 2021 | Authors suggest that barley adapts to inorganic phosphate (Pi)-starvation also via differential expression of several miRNAs. | ||||||||
| Identification of microRNAs Responding to Aluminium, Cadmium and Salt Stresses in Barley Roots | [51] | Hordeum vulgare | cultivar Golden Promise | 2021 | 525 miRNAs (198 known and 327 novel miRNAs) were identified through high-throughput sequencing. 31 miRNAs were differentially expressed under inspected stresses. | ||||||||
| An miR156-regulated nucleobase-ascorbate transporter 2 confers cadmium tolerance via enhanced anti-oxidative capacity in barley | [83] | Hordeum vulgare | genotypes Zhenong8 (ZN8) (Cd-tolerant genotype) and W6nk2 (Cd-sensitive genotype) | 2022 | miR156g-3p_3 targets a novel nucleobase-ascorbate transporter gene ( | HvNAT2 | ). | HvNAT2 | evolved from the | Zygnematales | in | Streptophyte algae | and positively regulates cadmium tolerance → genetic engineering of NAT in plants may have potential in the remediation of soil/water cadmium pollution |
| Regulation of Phenolic Compound Production by Light Varying in Spectral Quality and Total Irradiance | [68] | Hordeum vulgare | L. cultivar Bojos | 2022 | Several barley miRNAs were differentially expressed in response to the spectral quality of incident light. |
From the above-mentioned studies, it is evident that barley miRNAs play a complex role in responses to various abiotic and biotic stresses or stimuli, which is schematically depicted in Figure 3.
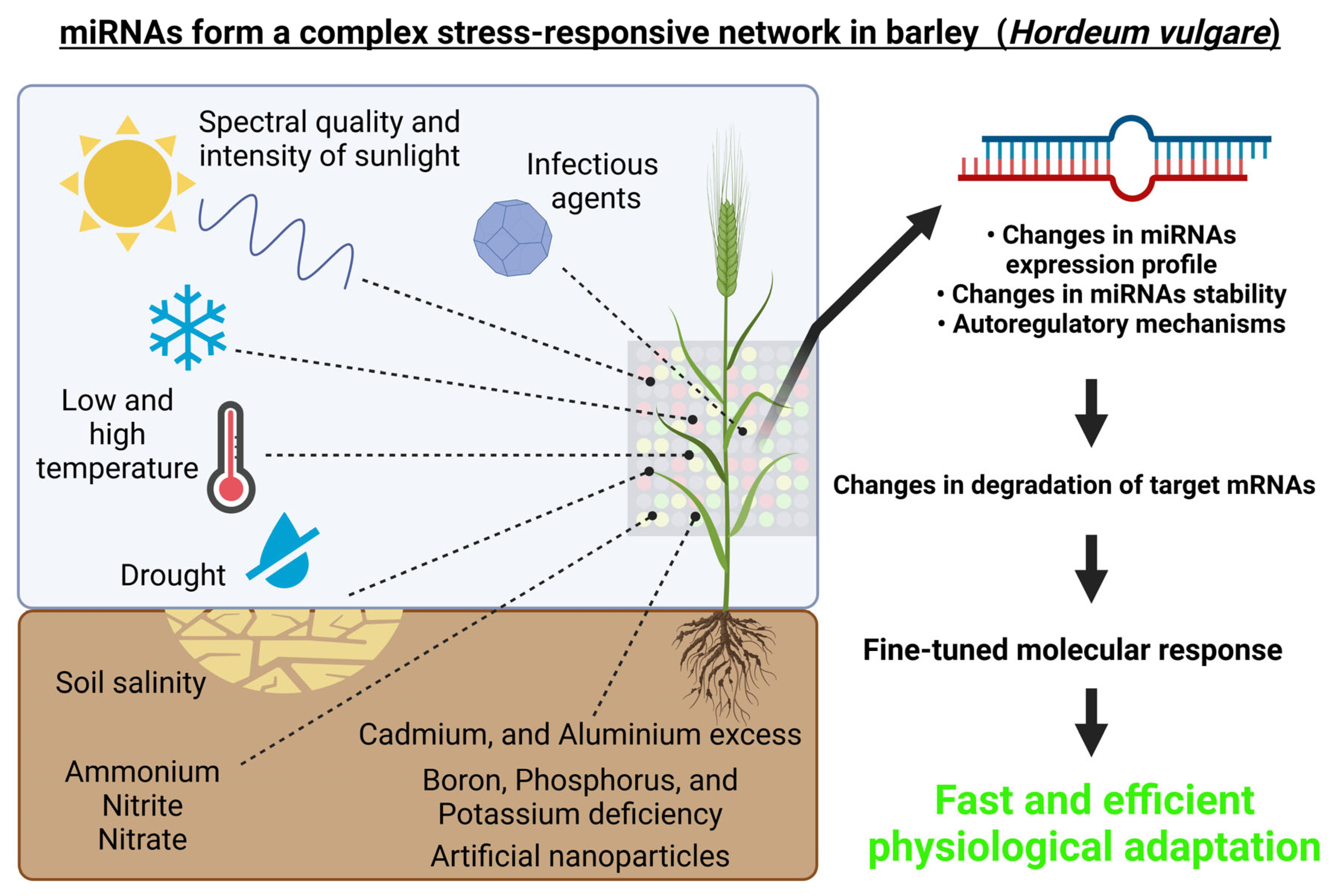
Figure 3. miRNAs form a complex regulatory network in barley (Hordeum vulgare). Environmental cues, both abiotic (i.e., spectral quality and intensity of the incident light, growth temperature, drought, high salinity, heavy metals exposure, etc.) and biotic (for example pathogens) can affect the expression of miRNAs and thus also their target genes. This figure was created using BioRender (https://biorender.com/; accessed on 20 June 2022).
References
- Sato, F.; Tsuchiya, S.; Meltzer, S.J.; Shimizu, K. MicroRNAs and Epigenetics. FEBS J. 2011, 278, 1598–1609.
- Shapulatov, U.; van Hoogdalem, M.; Schreuder, M.; Bouwmeester, H.; Abdurakhmonov, I.Y.; van der Krol, A.R. Functional Intron-Derived MiRNAs and Host-Gene Expression in Plants. Plant Methods 2018, 14, 83.
- Wu, X.; Hornyik, C.; Bayer, M.; Marshall, D.; Waugh, R.; Zhang, R. In Silico Identification and Characterization of Conserved Plant MicroRNAs in Barley. Open Life Sci. 2014, 9, 841–852.
- Wang, J.; Mei, J.; Ren, G. Plant MicroRNAs: Biogenesis, Homeostasis, and Degradation. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 360.
- Baldrich, P.; Hsing, Y.-I.C.; San Segundo, B. Genome-Wide Analysis of Polycistronic MicroRNAs in Cultivated and Wild Rice. Genome. Biol. Evol. 2016, 8, 1104–1114.
- Zou, Q.; Mao, Y.; Hu, L.; Wu, Y.; Ji, Z. MiRClassify: An Advanced Web Server for MiRNA Family Classification and Annotation. Comput. Biol. Med. 2014, 45, 157–160.
- O’Brien, J.; Hayder, H.; Zayed, Y.; Peng, C. Overview of MicroRNA Biogenesis, Mechanisms of Actions, and Circulation. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 402.
- Zhang, S.; Dou, Y.; Li, S.; Ren, G.; Chevalier, D.; Zhang, C.; Yu, B. DAWDLE Interacts with DICER-LIKE Proteins to Mediate Small RNA Biogenesis. Plant Physiol. 2018, 177, 1142–1151.
- Zhang, L.; Xiang, Y.; Chen, S.; Shi, M.; Jiang, X.; He, Z.; Gao, S. Mechanisms of MicroRNA Biogenesis and Stability Control in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2022, 13, 844149.
- Yu, B.; Yang, Z.; Li, J.; Minakhina, S.; Yang, M.; Padgett, R.W.; Steward, R.; Chen, X. Methylation as a Crucial Step in Plant MicroRNA Biogenesis. Science 2005, 307, 932–935.
- Djami-Tchatchou, A.T.; Sanan-Mishra, N.; Ntushelo, K.; Dubery, I.A. Functional Roles of MicroRNAs in Agronomically Important Plants—Potential as Targets for Crop Improvement and Protection. Front. Plant Sci. 2017, 8, 378.
- Li, M.; Yu, B. Recent Advances in the Regulation of Plant MiRNA Biogenesis. RNA Biol. 2021, 18, 2087–2096.
- Mengistu, A.A.; Tenkegna, T.A. The Role of MiRNA in Plant–Virus Interaction: A Review. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2021, 48, 2853–2861.
- Medley, J.C.; Panzade, G.; Zinovyeva, A.Y. MicroRNA Strand Selection: Unwinding the Rules. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA 2021, 12, e1627.
- Meijer, H.A.; Smith, E.M.; Bushell, M. Regulation of MiRNA Strand Selection: Follow the Leader? Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2014, 42, 1135–1140.
- Vimalraj, S.; Selvamurugan, N. MicroRNAs: Synthesis, Gene Regulation and Osteoblast Differentiation. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2013, 15, 7–18.
- Forman, J.J.; Coller, H.A. The Code within the Code: MicroRNAs Target Coding Regions. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 1533–1541.
- Yu, B.; Wang, H. Translational Inhibition by MicroRNAs in Plants. Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol. 2010, 50, 41–57.
- Liu, Y.; Teng, C.; Xia, R.; Meyers, B.C. PhasiRNAs in Plants: Their Biogenesis, Genic Sources, and Roles in Stress Responses, Development, and Reproduction. Plant Cell 2020, 32, 3059–3080.
- Araki, S.; Le, N.T.; Koizumi, K.; Villar-Briones, A.; Nonomura, K.-I.; Endo, M.; Inoue, H.; Saze, H.; Komiya, R. MiR2118-Dependent U-Rich PhasiRNA Production in Rice Anther Wall Development. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 3115.
- Xia, R.; Chen, C.; Pokhrel, S.; Ma, W.; Huang, K.; Patel, P.; Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Liu, Z.; Li, J.; et al. 24-Nt Reproductive PhasiRNAs Are Broadly Present in Angiosperms. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 627.
- Xie, Z.; Khanna, K.; Ruan, S. Expression of MicroRNAs and Its Regulation in Plants. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2010, 21, 790–797.
- Chhabra, R. MiRNA and Methylation: A Multifaceted Liaison. ChemBioChem 2015, 16, 195–203.
- Świda-Barteczka, A.; Krieger-Liszkay, A.; Bilger, W.; Voigt, U.; Hensel, G.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z.; Krupinska, K. The Plastid-Nucleus Located DNA/RNA Binding Protein WHIRLY1 Regulates MicroRNA-Levels during Stress in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). RNA Biol. 2018, 15, 886–891.
- Zhao, Y.; Mo, B.; Chen, X. Mechanisms That Impact MicroRNA Stability in Plants. RNA Biol. 2012, 9, 1218–1223.
- Gallego-Bartolomé, J. DNA Methylation in Plants: Mechanisms and Tools for Targeted Manipulation. New Phytol. 2020, 227, 38–44.
- Wu, L.; Zhou, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, J.; Ni, F.; Liu, C.; Qi, Y. DNA Methylation Mediated by a MicroRNA Pathway. Mol. Cell 2010, 38, 465–475.
- Bao, N.; Lye, K.-W.; Barton, M.K. MicroRNA Binding Sites in Arabidopsis Class III HD-ZIP MRNAs Are Required for Methylation of the Template Chromosome. Dev. Cell 2004, 7, 653–662.
- Vasudevan, S. Posttranscriptional Upregulation by MicroRNAs. WIREs RNA 2012, 3, 311–330.
- Lauressergues, D.; Couzigou, J.-M.; Clemente, H.S.; Martinez, Y.; Dunand, C.; Bécard, G.; Combier, J.-P. Primary Transcripts of MicroRNAs Encode Regulatory Peptides. Nature 2015, 520, 90–93.
- Prasad, A.; Sharma, N.; Prasad, M. Noncoding but Coding: Pri-MiRNA into the Action. Trends Plant Sci. 2021, 26, 204–206.
- Sharma, A.; Badola, P.K.; Bhatia, C.; Sharma, D.; Trivedi, P.K. Primary Transcript of MiR858 Encodes Regulatory Peptide and Controls Flavonoid Biosynthesis and Development in Arabidopsis. Nat. Plants 2020, 6, 1262–1274.
- Couzigou, J.-M.; André, O.; Guillotin, B.; Alexandre, M.; Combier, J.-P. Use of MicroRNA-Encoded Peptide MiPEP172c to Stimulate Nodulation in Soybean. New Phytol. 2016, 211, 379–381.
- Chen, Q.; Deng, B.; Gao, J.; Zhao, Z.; Chen, Z.; Song, S.; Wang, L.; Zhao, L.; Xu, W.; Zhang, C.; et al. A MiRNA-Encoded Small Peptide, Vvi-MiPEP171d1, Regulates Adventitious Root Formation. Plant Physiol. 2020, 183, 656–670.
- Wong, C.E.; Zhao, Y.-T.; Wang, X.-J.; Croft, L.; Wang, Z.-H.; Haerizadeh, F.; Mattick, J.S.; Singh, M.B.; Carroll, B.J.; Bhalla, P.L. MicroRNAs in the Shoot Apical Meristem of Soybean. J. Exp. Bot. 2011, 62, 2495–2506.
- Choudhary, A.; Kumar, A.; Kaur, H.; Kaur, N. MiRNA: The Taskmaster of Plant World. Biologia 2021, 76, 1551–1567.
- Waheed, S.; Zeng, L. The Critical Role of MiRNAs in Regulation of Flowering Time and Flower Development. Genes 2020, 11, 319.
- Curaba, J.; Spriggs, A.; Taylor, J.; Li, Z.; Helliwell, C. MiRNA Regulation in the Early Development of Barley Seed. BMC Plant Biol. 2012, 12, 120.
- Curaba, J.; Talbot, M.; Li, Z.; Helliwell, C. Over-Expression of MicroRNA171 Affects Phase Transitions and Floral Meristem Determinancy in Barley. BMC Plant Biol. 2013, 13, 6.
- Smoczynska, A.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z. MicroRNA-Mediated Regulation of Flower Development in Grasses. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2016, 63, 687–692.
- Nair, S.K.; Wang, N.; Turuspekov, Y.; Pourkheirandish, M.; Sinsuwongwat, S.; Chen, G.; Sameri, M.; Tagiri, A.; Honda, I.; Watanabe, Y.; et al. Cleistogamous Flowering in Barley Arises from the Suppression of MicroRNA-Guided HvAP2 MRNA Cleavage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2010, 107, 490–495.
- Anwar, N.; Ohta, M.; Yazawa, T.; Sato, Y.; Li, C.; Tagiri, A.; Sakuma, M.; Nussbaumer, T.; Bregitzer, P.; Pourkheirandish, M.; et al. MiR172 Downregulates the Translation of Cleistogamy 1 in Barley. Ann. Bot. 2018, 122, 251–265.
- Yuan, W.; Suo, J.; Shi, B.; Zhou, C.; Bai, B.; Bian, H.; Zhu, M.; Han, N. The Barley MiR393 Has Multiple Roles in Regulation of Seedling Growth, Stomatal Density, and Drought Stress Tolerance. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 142, 303–311.
- Tombuloglu, H. Genome-Wide Analysis of the Auxin Response Factors (ARF) Gene Family in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.). J. Plant Biochem. Biotechnol. 2019, 28, 14–24.
- Shriram, V.; Kumar, V.; Devarumath, R.M.; Khare, T.S.; Wani, S.H. MicroRNAs as Potential Targets for Abiotic Stress Tolerance in Plants. Front. Plant Sci. 2016, 7, 817.
- Barczak-Brzyżek, A.; Brzyżek, G.; Koter, M.; Siedlecka, E.; Gawroński, P.; Filipecki, M. Plastid Retrograde Regulation of MiRNA Expression in Response to Light Stress. BMC Plant Biol. 2022, 22, 150.
- Subburaj, S.; Ha, H.-J.; Jin, Y.-T.; Jeon, Y.; Tu, L.; Kim, J.-B.; Kang, S.-Y.; Lee, G.-J. Identification of γ-Radiation-Responsive MicroRNAs and Their Target Genes in Tradescantia (BNL Clone 4430). J. Plant Biol. 2017, 60, 116–128.
- Visentin, I.; Pagliarani, C.; Deva, E.; Caracci, A.; Turečková, V.; Novák, O.; Lovisolo, C.; Schubert, A.; Cardinale, F. A Novel Strigolactone-MiR156 Module Controls Stomatal Behaviour during Drought Recovery. Plant Cell Environ. 2020, 43, 1613–1624.
- Saminathan, T.; Alvarado, A.; Lopez, C.; Shinde, S.; Gajanayake, B.; Abburi, V.L.; Vajja, V.G.; Jagadeeswaran, G.; Raja Reddy, K.; Nimmakayala, P.; et al. Elevated Carbon Dioxide and Drought Modulate Physiology and Storage-Root Development in Sweet Potato by Regulating MicroRNAs. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2019, 19, 171–190.
- Deng, P.; Wang, L.; Cui, L.; Feng, K.; Liu, F.; Du, X.; Tong, W.; Nie, X.; Ji, W.; Weining, S. Global Identification of MicroRNAs and Their Targets in Barley under Salinity Stress. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0137990.
- Kuang, L.; Yu, J.; Shen, Q.; Fu, L.; Wu, L. Identification of MicroRNAs Responding to Aluminium, Cadmium and Salt Stresses in Barley Roots. Plants 2021, 10, 2754.
- Liu, B.; Sun, G. Micro RNA s Contribute to Enhanced Salt Adaptation of the Autopolyploid Hordeum bulbosum Compared with Its Diploid Ancestor. Plant J. 2017, 91, 57–69.
- Kuang, L.; Shen, Q.; Wu, L.; Yu, J.; Fu, L.; Wu, D.; Zhang, G. Identification of MicroRNAs Responding to Salt Stress in Barley by High-Throughput Sequencing and Degradome Analysis. Environ. Exp. Bot. 2019, 160, 59–70.
- Smoczynska, A.; Pacak, A.M.; Nuc, P.; Swida-Barteczka, A.; Kruszka, K.; Karlowski, W.M.; Jarmolowski, A.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z. A Functional Network of Novel Barley MicroRNAs and Their Targets in Response to Drought. Genes 2020, 11, 488.
- Ferdous, J.; Sanchez-Ferrero, J.C.; Langridge, P.; Milne, L.; Chowdhury, J.; Brien, C.; Tricker, P.J. Differential Expression of MicroRNAs and Potential Targets under Drought Stress in Barley. Plant Cell Environ. 2017, 40, 11–24.
- Kantar, M.; Unver, T.; Budak, H. Regulation of Barley MiRNAs upon Dehydration Stress Correlated with Target Gene Expression. Funct. Integr. Genom. 2010, 10, 493–507.
- Hackenberg, M.; Gustafson, P.; Langridge, P.; Shi, B.-J. Differential Expression of MicroRNAs and Other Small RNAs in Barley between Water and Drought Conditions. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2015, 13, 2–13.
- Qiu, C.-W.; Liu, L.; Feng, X.; Hao, P.-F.; He, X.; Cao, F.; Wu, F. Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of Drought Stress Responsive MicroRNAs in Tibetan Wild Barley. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2795.
- Grabowska, A.; Smoczynska, A.; Bielewicz, D.; Pacak, A.; Jarmolowski, A.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z. Barley MicroRNAs as Metabolic Sensors for Soil Nitrogen Availability. Plant Sci. 2020, 299, 110608.
- Ozhuner, E.; Eldem, V.; Ipek, A.; Okay, S.; Sakcali, S.; Zhang, B.; Boke, H.; Unver, T. Boron Stress Responsive MicroRNAs and Their Targets in Barley. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e59543.
- Hackenberg, M.; Huang, P.-J.; Huang, C.-Y.; Shi, B.-J.; Gustafson, P.; Langridge, P. A Comprehensive Expression Profile of MicroRNAs and Other Classes of Non-Coding Small RNAs in Barley Under Phosphorous-Deficient and -Sufficient Conditions. DNA Res. 2013, 20, 109–125.
- Sega, P.; Kruszka, K.; Bielewicz, D.; Karlowski, W.; Nuc, P.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z.; Pacak, A. Pi-Starvation Induced Transcriptional Changes in Barley Revealed by a Comprehensive RNA-Seq and Degradome Analyses. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 165.
- Bai, B.; Bian, H.; Zeng, Z.; Hou, N.; Shi, B.; Wang, J.; Zhu, M.; Han, N. MiR393-Mediated Auxin Signaling Regulation Is Involved in Root Elongation Inhibition in Response to Toxic Aluminum Stress in Barley. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017, 58, 426–439.
- Wu, L.; Yu, J.; Shen, Q.; Huang, L.; Wu, D.; Zhang, G. Identification of MicroRNAs in Response to Aluminum Stress in the Roots of Tibetan Wild Barley and Cultivated Barley. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 560.
- Yu, J.; Wu, L.; Fu, L.; Shen, Q.; Kuang, L.; Wu, D.; Zhang, G. Genotypic Difference of Cadmium Tolerance and the Associated MicroRNAs in Wild and Cultivated Barley. Plant Growth Regul. 2019, 87, 389–401.
- Chen, F.; He, J.; Jin, G.; Chen, Z.-H.; Dai, F. Identification of Novel MicroRNAs for Cold Deacclimation in Barley. Plant Growth Regul. 2020, 92, 389–400.
- Kruszka, K.; Pacak, A.; Swida-Barteczka, A.; Nuc, P.; Alaba, S.; Wroblewska, Z.; Karlowski, W.; Jarmolowski, A.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z. Transcriptionally and Post-Transcriptionally Regulated MicroRNAs in Heat Stress Response in Barley. J. Exp. Bot. 2014, 65, 6123–6135.
- Pech, R.; Volná, A.; Hunt, L.; Bartas, M.; Červeň, J.; Pečinka, P.; Špunda, V.; Nezval, J. Regulation of Phenolic Compound Production by Light Varying in Spectral Quality and Total Irradiance. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 6533.
- Schreiber, A.W.; Shi, B.-J.; Huang, C.-Y.; Langridge, P.; Baumann, U. Discovery of Barley MiRNAs through Deep Sequencing of Short Reads. BMC Genom. 2011, 12, 129.
- Lv, S.; Nie, X.; Wang, L.; Du, X.; Biradar, S.S.; Jia, X.; Weining, S. Identification and Characterization of MicroRNAs from Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) by High-Throughput Sequencing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 2973–2984.
- Kruszka, K.; Pacak, A.; Swida-Barteczka, A.; Stefaniak, A.K.; Kaja, E.; Sierocka, I.; Karlowski, W.; Jarmolowski, A.; Szweykowska-Kulinska, Z. Developmentally Regulated Expression and Complex Processing of Barley Pri-MicroRNAs. BMC Genom. 2013, 14, 34.
- Liu, J.; Cheng, X.; Liu, D.; Xu, W.; Wise, R.; Shen, Q.-H. The MiR9863 Family Regulates Distinct Mla Alleles in Barley to Attenuate NLR Receptor-Triggered Disease Resistance and Cell-Death Signaling. PLoS Genet. 2014, 10, e1004755.
- Kis, A.; Tholt, G.; Ivanics, M.; Várallyay, É.; Jenes, B.; Havelda, Z. Polycistronic Artificial MiRNA-Mediated Resistance to Wheat Dwarf Virus in Barley Is Highly Efficient at Low Temperature. Mol. Plant Pathol. 2016, 17, 427–437.
- Deng, P.; Bian, J.; Yue, H.; Feng, K.; Wang, M.; Du, X.; Weining, S.; Nie, X. Characterization of MicroRNAs and Their Targets in Wild Barley (Hordeum vulgare Subsp. Spontaneum) Using Deep Sequencing. Genome 2016, 59, 339–348.
- Pacak, A.M.; Kruszka, K.; Świda-Barteczka, A.; Nuc, P.; Karlowski, W.; Jarmołowski, A.; Szweykowska-Kulińska, Z. Developmental Changes in Barley MicroRNA Expression Profiles Coupled with MiRNA Targets Analysis. Acta Biochim. Pol. 2016, 63, 799–809.
- Bai, B.; Shi, B.; Hou, N.; Cao, Y.; Meng, Y.; Bian, H.; Zhu, M.; Han, N. MicroRNAs Participate in Gene Expression Regulation and Phytohormone Cross-Talk in Barley Embryo during Seed Development and Germination. BMC Plant Biol. 2017, 17, 150.
- Smith, O.; Palmer, S.A.; Clapham, A.J.; Rose, P.; Liu, Y.; Wang, J.; Allaby, R.G. Small RNA Activity in Archeological Barley Shows Novel Germination Inhibition in Response to Environment. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2555–2562.
- Tripathi, R.K.; Bregitzer, P.; Singh, J. Genome-Wide Analysis of the SPL/MiR156 Module and Its Interaction with the AP2/MiR172 Unit in Barley. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 7085.
- Plaksenkova, I.; Kokina, I.; Petrova, A.; Jermaļonoka, M.; Gerbreders, V.; Krasovska, M. The Impact of Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles on Cytotoxicity, Genotoxicity, and MiRNA Expression in Barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) Seedlings. Sci. World J. 2020, 2020, 6649746.
- Ye, Z.; Zeng, J.; Long, L.; Ye, L.; Zhang, G. Identification of MicroRNAs in Response to Low Potassium Stress in the Shoots of Tibetan Wild Barley and Cultivated. Curr. Plant Biol. 2021, 25, 100193.
- Puchta, M.; Groszyk, J.; Małecka, M.; Koter, M.D.; Niedzielski, M.; Rakoczy-Trojanowska, M.; Boczkowska, M. Barley Seeds MiRNome Stability during Long-Term Storage and Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 4315.
- Yao, X.; Wang, Y.; Yao, Y.; Bai, Y.; Wu, K.; Qiao, Y. Identification MicroRNAs and Target Genes in Tibetan Hulless Barley to BLS Infection. Agron. J. 2021, 113, 2273–2292.
- Wang, N.-H.; Zhou, X.-Y.; Shi, S.-H.; Zhang, S.; Chen, Z.-H.; Ali, M.A.; Ahmed, I.M.; Wang, Y.; Wu, F. An MiR156-Regulated Nucleobase-Ascorbate Transporter 2 Confers Cadmium Tolerance via Enhanced Anti-Oxidative Capacity in Barley. J. Adv. Res. 2022, in press.
More
