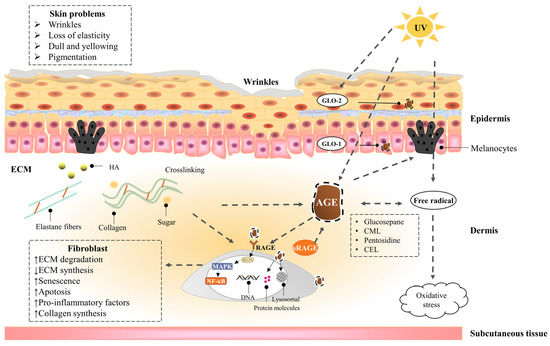
Skin saccharification, a non-enzymatic reaction between proteins, e.g., dermal collagen and naturally occurring reducing sugars, is one of the basic root causes of endogenous skin aging. During the reaction, a series of complicated glycation products produced at different reaction stages and pathways are usually collectively referred to as advanced glycation end products (皮肤糖化是蛋白质(例如真皮胶原蛋白和天然还原糖)之间的非酶促反应,是内源性皮肤老化的基本根本原因之一。在反应过程中,在不同反应阶段和途径产生的一系列复杂的糖基化产物通常统称为晚期糖基化终产物(AGEs). AGEs cause cellular dysfunction through the modification of intracellular molecules and accumulate in tissues with aging. AGEs are also associated with a variety of age-related diseases, such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, renal failure (uremia), and Alzheimer’s disease. AGEs accumulate in the skin with age and are amplified through exogenous factors, e.g., ultraviolet radiation, resulting in wrinkles, loss of elasticity, dull yellowing, and other skin problems. )。AGEs通过细胞内分子的修饰引起细胞功能障碍,并随着年龄的增长在组织中积累。AGEs还与多种与年龄有关的疾病有关,如糖尿病,心血管疾病,肾衰竭(尿毒症)和阿尔茨海默病。AGEs随着年龄的增长在皮肤中积累,并通过紫外线辐射等外源性因素放大,导致皱纹,弹性丧失,暗淡发黄和其他皮肤问题。
- skin glycation
- anti-glycation
- AGEs inhibitors
1. The Hazards of Skin Glycation
1.1. The Harm of High Glucose to the Skin
1.1. The Harm of High Glucose to the Skin
1.2. Advanced Glycaion End Products Induce Skin Aging
1.2. 高级糖最终产品诱导皮肤老化
1.2.1. Epidermis
表皮
1.2.2. Dermis真皮—Fibroblast
成纤维细胞
1.2.3. Dermis真皮—Extracellular matrix (ECM)
细胞外基质 (ECM)
1.3. UVA Induces Advanced Glycation End Products of the Skin
1.3. UVA 诱导皮肤的晚期糖基化终产物
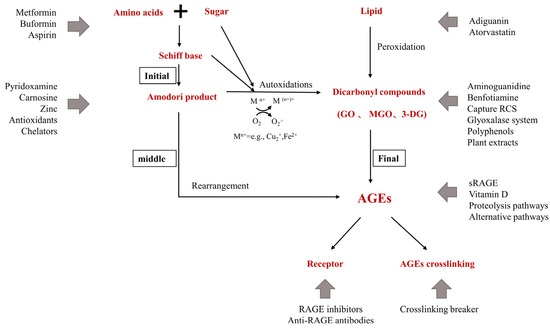
2. Inhibitors of Advanced Glycation End ProductGEs
的抑制剂