The multifunctional protein, voltage-dependent anion channel 1 (VDAC1), is located on the mitochondrial outer membrane. It is a pivotal protein that maintains mitochondrial function to power cellular bioactivities via energy generation. VDAC1 is involved in regulating energy production, mitochondrial oxidase stress, Ca2+ transportation, substance metabolism, apoptosis, mitochondrial autophagy (mitophagy), and many other functions. VDAC1 malfunction is associated with mitochondrial disorders that affect inflammatory responses, resulting in an up-regulation of the body’s defensive response to stress stimulation. Overresponses to inflammation may cause chronic diseases. Mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA) acts as a danger signal that can further trigger native immune system activities after its secretion. VDAC1 mediates the release of mtDNA into the cytoplasm to enhance cytokine levels by activating immune responses. VDAC1 regulates mitochondrial Ca2+ transportation, lipid metabolism and mitophagy, which are involved in inflammation-related disease pathogenesis.
- VDAC1
- inflammation
- mitochondria
- metabolism
- mitophagy
- Calcium
- targeting therapy
1. Introduction
2. Inflammation, VDAC1 Mediates Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress
2.1. VDAC1 Regulates Inflammation via Mediating Apoptosis
The mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) is about 1.4 nm in diameter, and supports solute and ion diffusion under 1500 kDa. It is also known as the mitochondrial macro-channel that plays an important role in cell survival and apoptosis [38][39][50,51]. The voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC) is located in the outer mitochondrial membrane (OMM); adenine nucleotide translocase (ANT) is located in the inner mitochondrial membrane (IMM). VDAC and ANT are considered to be the structural components of the MPTP [40][41][42][52,53,54]. The Bcl-2 family has a close relationship with mitochondria and apoptosis [43][55]. It is known that Bcl-2 family member, Bcl-2-associated X protein (BAX), interacts with VDAC1 to regulate the release of cytochrome c (Cyto c) during apoptosis [44][45][56,57] (Figure 12). Oligomerization of BAX is one of the mechanisms that is involved in the mitochondrial apoptosis pathway [46][58]. A rat brain model indicates BAX promotes apoptosis by interacting with VDAC1 to expand the associated pore size, resulting in the increased permeability of mitochondria [47][59]. During apoptosis, VDAC1 assembles into oligomeric structures, forming a channel that is sufficient to pass Cyto c and release it into the cytoplasm. Cyto c forms oligomeric apoptosomes by binding to Apaf-1, apostasy activator and deoxyadenosine triphosphate (dATP); this results in the activation of cysteine protease 9 (caspase-9) that further activates effector caspases, caspase-3, caspase-6 and caspase-7 [43][48][49][55,60,61]. Ultimately, the caspase-mediated apoptosis pathway proteolytic cascade begins to cleave organelles and cellular components, resulting in apoptosis [48][60].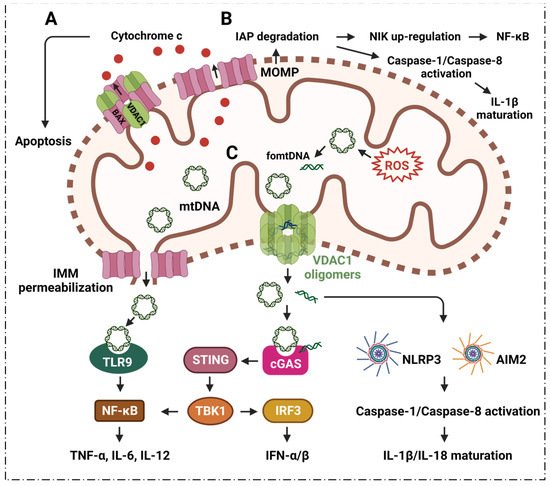
2.2. VDAC1 Mediates Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress in Immune Responses
ROS from mitochondria can be dramatically induced under the stimulation of radiation, cigarette smoke, air pollution, inflammatory factors, tumor necrosis factor, hyperlipidemia, hypoxia, and so on. Notably, the ROS are mainly generated from the respiratory complex that is located in the IMM [50][51][65,66]. Malfunctioning mitochondria hyperproduce ROS which negatively affect other components of mitochondria, for example, mtDNA, membrane lipids, oxidative phosphorylation, etc. [52][53][67,68]. The mtDNA is mainly localized in the IMM, and mtDNA can easily be oxidized by ROS to generate oxidized mtDNA fragments (fomtDNA) [54][69]. The released mtDNA acts as ligands for different danger signal sensors, activating the innate immune response (Figure 12). These risk sensors include the cytoplasmic cyclic GMP-AMP synthase (cGAS); Toll-like receptor 9 (TLR9); nucleotide-binding domain and leucine-rich repeat (LRR) containing P3 (NLRP3) inflammasome; and absent in melanoma 2 (AIM2) inflammasome [50][65]. Through these pathways, mtDNA can induce the secretion of inflammatory cytokines, and induce the recruitment of immune cells at different sites, providing the conditions for inflammation in many diseases [50][65]. It has been shown that VDAC1 oligomer pores promote MOMP and allow the release of mtDNA into the cytoplasmic matrix in living cells, where mtDNA fragments escape from the mitochondria through direct interactions at the N-terminus of VDAC1 [28][32]. At the same time, the inhibition of VDAC1 oligomerization eliminates cytoplasmic and circulating mtDNA. Therefore, single-stranded or double-stranded DNA escapes into the cytoplasm through the permeability transition pore that is composed of VDAC1. VDAC1 indirectly participates in mtDNA induction by mediating the translocation of the subsequent mtDNA inflammatory response [28][32]. VBIT-3 and VBIT-4, as well as VBIT-12, were reported to interact with VDAC1 by disrupting its oligomerization, resulting in altered intracellular Ca2+ concentration and decreased ROS levels, thereby protecting mitochondrial malfunction related to apoptosis and inflammation [55][56][70,71]. This response was found to alleviate type 2 diabetes [57][72], lupus [28][32], atrial myocardium fibrosis [58][73], ulcerative colitis [59][74] and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis [56][71].3. Inflammation and VDAC1 Mediates Mitochondrial Ca2+ Transportation
Mitochondrial Ca2+ uptake and release play a key role in cellular physiology by regulating intracellular Ca2+ signaling, energy metabolism and cell death [60][93]. The transportation of Ca2+ across the inner or outer mitochondrial membranes (IMM, OMM) is mainly mediated by several proteins, including VDAC1, mitochondrial Ca2+ monotransporter (MCU) and Na+-dependent mitochondrial Ca2+ efflux transporter (NCLX) [61][62][94,95]. VDAC1 was shown to be highly permeable to Ca2+, and contains a binding site for ruthenium red, thereby inhibiting channel opening [63][64][96,97]. VDAC1 may be a key component of the mitochondrial Ca2+ homeostatic mechanism, enhancing the Ca2+ response through different mechanisms. VDAC1 acts as a large conductance channel that allows for the rapid diffusion of Ca2+ across the OMM, thereby allowing the exposure of low-affinity single transporters in the inner membrane to the high Ca2+ microdomains that are generated by the opening of the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)-Ca2+ channel [63][64][96,97]. Moreover, VDAC1 has been proposed to be part of a larger complex of members, including the adenine nucleotide transporter, cyclophilin D, peripheral benzodiazepine receptors and Bcl-2 family members [65][98], which can interact with the ER. The structural components interact with each other, and thus become part of the molecular mechanism of mitochondrial docking with Ca2+. VDAC1 is the major permeation pathway for Ca2+ across the OMM, and VDAC1 mediates Ca2+ transport through the OMM to the IMM space. It can also facilitate Ca2+ transport from the inner mitochondrial membrane space (IMS) into the cytoplasm [61][94] (Figure 23A).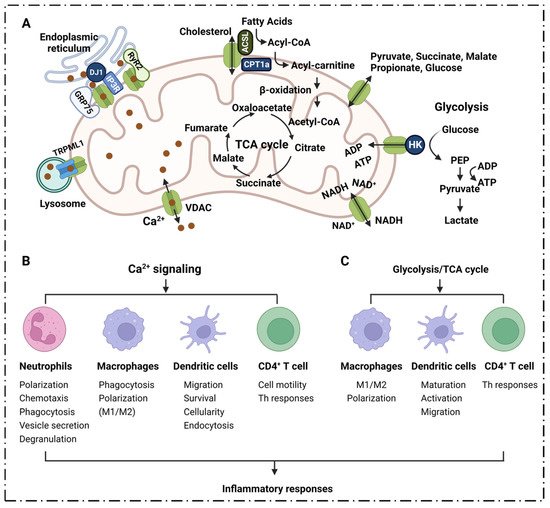
3.1. Neutrophils
3.2. Macrophages
3.3. Dendritic Cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are the most powerful antigen-presenting cells in the body. DCs uptake, process and present antigens efficiently that are crucial for initiating T cell responses. They play a central role in initiating, regulating and maintaining immune responses [82][117]. Ca2+ signaling plays a key role in the function of DCs. Migration of DCs to secondary lymphoid organs is indispensable for subsequent T helper cell-mediated adaptive immunity. It has been shown that chemokine-induced DC migration is Ca2+-dependent [83][118]. Ca2+ is involved in the regulation of chemokine receptor expression, cell swelling, cytoskeletal changes and amphipod formation activities; DC migration relies tightly on the cytosolic Ca2+ concentration [84][119]. Activated DCs rapidly up-regulate chemokine receptor 7 (CCR7) expression, and acquire the ability to migrate into afferent lymphatics and drain lymph nodes [85][120]. CCR7 is a G protein-coupled receptor [86][121] that regulates DC chemotaxis, survival, migration velocity, cellularity and endocytosis; furthermore, its activation is accomplished by inducing the mobilization of intracellular calcium stores through the inositol 1,4,5-triphosphate (IP3) pathway [87][88][122,123]. Ca2+ plays an important role in the inflammatory response because it regulates the function of DCs in various links (Figure 3B).4. Inflammatory Diseases and VDAC1 in Energy Metabolism
4.1. TCA Cycle
Metabolites in the process of energy metabolism can participate in inflammatory responses through different pathways, affecting the secretion of cytokines, the production of pro-inflammatory mediators, and the activation and differentiation of immune cells. VDAC1 plays an important role in energy metabolism, and participates in the inflammatory response by directly mediating the transport of metabolites during respiration and regulating Ca2+ as well as the activity of respiration-related enzymes (Figure 23A,C). Succinic acid is one of the metabolites that accumulates from the disturbance of the TCA cycle and the breakdown of hyperglutamine. Succinate accumulation leads to macrophage M1 polarization through the direct inhibition of proline hydrolase, prompting HIF-1α and IL-1β secretion [89][90][143,144]; it acts as an inflammatory stimulator in an autocrine-dependent manner [89][91][143,145]. Lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced succinate promotes IL-1β expression via HIF-1α signaling [90][92][144,146]. Extracellular succinate induces a pro-inflammatory response in diverse immune cells, increasing the migration and secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α and IL-1β in dendritic cells and macrophages [90][144].4.2. Glycolysis
The initial and rate-limiting steps of glycolysis are mainly catalyzed by HK1, most of which is bound to the OMM, mainly through mitochondria formed by VDAC1 and adenine nucleotide translocator (ANT) intermembrane contact sites for transport [93][176]. It has also been shown that Hexokinase-2 (HK2) binds to VDAC1 on the OMM to facilitate the preferential entry of ATP into HK2 for glycolysis [94][177]. The binding of HK2 with mitochondrial VDAC1 can be inhibited by chrysin, resulting in decreased glucose uptake and lactate production [95][178]. VDAC1 is directly involved in the regulation of the glycolytic pathway; it affects the activation, differentiation and migration of various immune cells such as macrophages, DCs, T cells, etc., and affects the production, migration, and release of various cytokines and pro-inflammatory mediators. VDAC1 can affect mitochondrial respiration, as a result of its important role in controlling the transportation of substances and metabolites. The intermediates in the Krebs cycle have a close relation with the inflammation process [96][127]. The metabolism of PEP, lactic acid, succinic acid, citric acid, etc., plays an important role in the occurrence and development of inflammation. In conclusion, VDAC1 could become a new therapeutic target for inflammation, and this necessitates further study.5. Inflammatory Diseases and VDAC1 in Lipid Metabolism
VDAC1 is involved in cholesterol transport, and is generally considered to be part of a complex that mediates fatty acid transport through the OMM [97][98][99][75,125,183]. Meanwhile, VDAC1 also serves as an anchoring site for long-chain acyl-CoA synthase (ACSL), which is associated with the outer surface of the OMM, and for carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a (CPT1a), which faces the intermembrane space [99][183] (Figure 23A). ACSL catalyzes the synthesis of fatty acyl-CoA in vivo, which is the first reaction in the human body to utilize fatty acids; meanwhile, CPT1a is involved in the process of transporting long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria so that fatty acids can be broken down to generate usable energy for cells. It has been reported that CPT1a, ACSL and VDAC1 can form a complex, and that the long-chain fatty acyl-CoA synthesized by ACSL is transferred from the OMM to the intermembrane space through VDAC1; furthermore, CPT1a converts acyl-CoA into long-chain fatty acylcarnitine [99][183], followed by a series of subsequent oxidation reactions. It has been found that the phosphorylation state of VDAC1 mediated by glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) can control the permeability of the OMM [100][184]. It has been observed that a loss of VDAC1 may cause mitochondria to stop oxidizing fatty acids, and VDAC1 inhibitors can inhibit palmitate oxidation [101][102][185,186]. In addition, the VDAC1-based peptide, R-Tf-D-LP4, can stimulate catabolic pathways that are involved in promoting fatty acid transfer to the mitochondria, fatty acid oxidation and increasing the expressions of enzymes and factors that are associated with fatty acid transport to the mitochondria, thereby enhancing β-oxidation and production of energy [101][185]. VDAC1 is involved in cholesterol transport, and is generally considered to be part of a complex that mediates fatty acid transport through the OMM [97][98][99][75,125,183]. Meanwhile, VDAC1 also serves as an anchoring site for long-chain acyl-CoA synthase (ACSL), which is associated with the outer surface of the OMM, and for carnitine palmitoyltransferase 1a (CPT1a), which faces the intermembrane space [99][183] (Figure 23A). ACSL catalyzes the synthesis of fatty acyl-CoA in vivo, which is the first reaction in the human body to utilize fatty acids; meanwhile, CPT1a is involved in the process of transporting long-chain fatty acids into the mitochondria so that fatty acids can be broken down to generate usable energy for cells. It has been reported that CPT1a, ACSL and VDAC1 can form a complex, and that the long-chain fatty acyl-CoA synthesized by ACSL is transferred from the OMM to the intermembrane space through VDAC1; furthermore, CPT1a converts acyl-CoA into long-chain fatty acylcarnitine [99][183], followed by a series of subsequent oxidation reactions. It has been found that the phosphorylation state of VDAC1 mediated by glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) can control the permeability of the OMM [100][184]. It has been observed that a loss of VDAC1 may cause mitochondria to stop oxidizing fatty acids, and VDAC1 inhibitors can inhibit palmitate oxidation [101][102][185,186]. In addition, the VDAC1-based peptide, R-Tf-D-LP4, can stimulate catabolic pathways that are involved in promoting fatty acid transfer to the mitochondria, fatty acid oxidation and increasing the expressions of enzymes and factors that are associated with fatty acid transport to the mitochondria, thereby enhancing β-oxidation and production of energy [101][185]. There are experimental results that show that R-Tf-D-LP4 significantly reduces pathophysiological features, such as hepatocyte ballooning, and inflammation and liver fibrosis in the HFD-32/STAM mouse model that is associated with steatohepatitis and/or NASH; meanwhile, this peptide also reduces the expression of inflammatory macrophages and cytokines (IL-1β and IL-6) in the liver of HFD-32-fed mice [101][185]. Dysfunction or deletion of VDAC1 will lead to fat deposition and abnormal lipid metabolism, increasing inflammatory macrophages and the expression of cytokines (IL-1β and IL-6). Heightened expression of IL-6 increases autocrine IL-4, which enhances Th2-type immune responses through automated feedback loops, playing an important role in inflammation [101][185].6. Inflammatory Diseases Pathogenesis and VDAC1 in Mitophagy
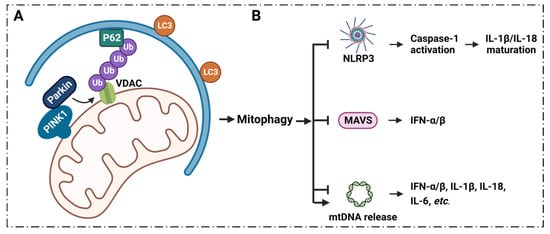
6.1. Mitophagy Regulates Inflammation via VDAC1
Mitophagy plays a key role in the regulation of inflammatory signaling, and the process of mitophagy limits inflammatory cytokines secretion [32][33][103][104][105][36,37,188,189,190] (Figure 34).