Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Yingjie Li and Version 3 by Jessie Wu.
Autophagy is a stress-induced process that eliminates damaged organelles and dysfunctional cargos in cytoplasm, including unfolded proteins. Autophagy is involved in constructing the immunosuppressive microenvironment during tumor initiation and progression. It appears to be one of the most common processes involved in cancer immunotherapy, playing bidirectional roles in immunotherapy. Accumulating evidence suggests that inducing or inhibiting autophagy contributes to immunotherapy efficacy. Exploring autophagy targets and their modifiers to control autophagy in the tumor microenvironment is an emerging strategy to facilitate cancer immunotherapy.
- autophagy
- cancer
- immunotherapy
1. Introduction
Autophagy in cancer cells often occurs in response to cytokines and damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) derived from the tumor microenvironment (TME). Several pattern recognition receptors have been verified as autophagy inducers when they receive extracellular DAMPs, including ATP, DNA complexes, and high-mobility group box 1 protein (HMGB1). [1][39]. For example, polyinosinic:polycytidylic acid and lipopolysaccharide (LPS) activate Toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3) and TLR4, thus triggering autophagy in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) cells [2][40]. Another study demonstrated that advanced glycosylation end product-specific receptor (AGER) is crucial for HMGB1-induced autophagy in pancreatic and colon cancer cells [3][41]. As for cytokines, they participate in autophagy initiation in a context-dependent way. Accumulated evidence suggests that transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) and interferons (type I and II) induce autophagy in various kinds of cancer cells [4][42]. For instance, TGF-β activates autophagy in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by upregulating the levels of Beclin 1, Atg5 and Atg7 [5][43]. In addition, tumor necrosis factor (TNF) and interleukin-6 (IL-6) were found to be autophagy inducers that are associated with carcinogenesis and tumor progression [6][44]. As a major mechanism of autophagy-associated tumor progression, the immunosuppressive microenvironment shaped by autophagy is ouresearcher's focus. The immune system is essential for preventing the development and metastasis of tumors and for shaping the tumor response to treatment. The immune system recognizes and eliminates tumor cells by immune surveillance. However, some tumor cells survive because of immune evasion, a process where the immunogenicity of tumor cells is reduced, and the immunosuppressive networks are formed [7][45]. In TME, changes in the autophagy pathway are observed in cancer cells and immune cells, which shape tumor immunity and affect immunotherapy [8][17].
The role of autophagy in immune system activation and immunosuppressive TME formation is complex. On the one hand, autophagy may participate in the process of antigen presentation by APCs through proteasome degradation and the vacuolar pathway [9][46]. Autophagic degradation can promote APC efficiency by accelerating antigen processing [10][47]. Autophagy deficiency in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma stimulates PD-L1 expression, which may aid in the formation of immunosuppressive TME [11][48]. Similarly, autophagy inhibition can upregulate PD-L1 expression by accumulating p62/SQSTM1 and activating NF-κB in gastric cancer [12][49] (Figure 1a). Autophagy contributes to immune evasion by suppressing the innate and adaptive immune response. The inducers of the innate immune response, such as damaged proteins, organelles, and bacteria, are cleared by autophagy. DAMPs and pathogen-associated molecular patterns (PAMPs) are both inducers of innate immunity, which can be captured and degraded in autolysosomes [13][50]. These facts indicate that autophagy seems to be a key negative regulator of innate immune responses when activated [14][51]. As a consequence, inhibition of autophagy facilitates the production and secretion of proinflammatory cytokines such as IFNs (type I, II) and TNF-α in vitro and in vivo [15][52]. Inhibition of autophagy can also trigger programmed cell death of cancer cells, producing DAMPs to activate the adaptive immune system [16][53]. Moreover, autophagy can suppress the adaptive immune response by weakening T cells’ ability to kill tumor cells [17][54]. It has been shown that antigenic tumors are recognized and eliminated by T cells when autophagy is inhibited in mice [18][55]. There are several mechanisms by which autophagy restrains the antitumor T cell response. Autophagy suppresses the functions of NK cells, CD4+ T cells, and CD8+ T cells to help tumor cells combat immunosurveillance, acting as a protective mechanism in tumors [19][56]. For example, hypoxia-induced autophagy can impair NK cell-mediated killing of breast cancer cells by degrading NK-derived granzyme B in autophagosomes [20][57] (Figure 1b). Hypoxia-induced autophagy is also reported to attenuate cancer cell sensitivity to CTL by regulating the STAT3 pathway in IGR-Heu lung carcinoma cells [21][58]. Hence, autophagy in tumors may be a potential target to block immune evasion in the TME. Meanwhile, the initiation of immune response often needs a major histocompatibility complex (MHC) to present antigens to T cells. MHC includes class I and II, that are recognized by CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, respectively [22][59]. MHC-I presents peptides that prime and activate CD8+ CTLs. Then, CTLs clear the targeted tumor cells by detecting a matching antigen by the MHC-I [23][60]. The expression of MHC-I is downregulated in pancreatic cancer, resulting in defective antigen presentation, which limits the ability of tumor killing by T cells and immunotherapy. Mechanistically, MHC-I is recognized by NBR1 and degraded in lysosomes through autophagy [18][55] (Figure 1c). Additionally, in dendritic cells (DCs), autophagy has been shown to accelerate the internalization and degradation of MHC-I. DCs with autophagy inhibition enhance the presentation of viral antigens to CD8+ T cells [24][25][61,62]. Recently, hepatic autophagy immune tolerance (HAIT) has been studies and is regarded as another immune evasion mechanism. A study by Laura et al. revealed that autophagy in the liver induces tumor immune tolerance by promoting Treg function and inhibiting T-cell response and interferon-γ production, resulting in the growth of tumors with high tumor mutational burden (TMB). Therefore, autophagy may be a potential target to overcome HAIT [15][52].
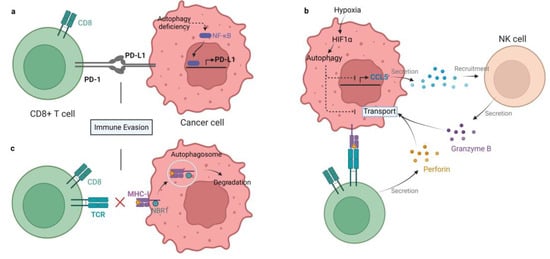
Figure 1. Mechanisms of autophagy-mediated immune evasion. (a) Autophagy deficiency in gastric cancer enhances PD-L1 expression by activating NF-κB, therefore promoting PD1/PD-L1-induced immune evasion. (b) Hypoxia-induced autophagy impairs killing of breast cancer by degrading NK and CD8+ T cell-derived granzyme B in autophagosomes. In addition, autophagy inhibits chemokine CCL5 production. As a result, the recruitment of NK cells to the TME is blocked. (c) MHC-I is recognized by NBR1 and degraded in lysosomes by autophagy in pancreatic cancer cells, which impairs antigen presentation and tumor killing by T cells.
2. Autophagy in Immune Cells
Tumor development and therapeutic response are influenced by tumor-infiltrating immune cells in TME [26][63]. A growing number of studies have revealed that autophagy is involved in the differentiation, homeostasis, and development of immune cells [27][64]. Hence, the alterations of autophagy pathway in immune cells may shape their phenotypes and functions in the TME [28][65].
2.1. Autophagy in T cells
Autophagy plays a vital role in the survival and proliferation of T cells. In TME of tumor-bearing mice and cancer patients, T cells undergo apoptosis. Xia et al. found that tumor-infiltrating T cells exhibit defective autophagy and a decreased level of FIP200, which is necessary for autophagosome formation. This process is mediated by tumor-derived lactate, which lowers FIP200 expression and causes T cell death by disrupting the balance between pro- and anti-apoptotic factors in the Bcl-2 family to boost immune evasion of cancer [29][66] (Figure 2). The interactions of T cell receptor (TCR) with stromal cells and IL-7 signaling are essential for naive T cells to survive in the periphery, and it appears that Atg3-dependent autophagy is intrinsically required for these processes [30][67]. Atg7-deficient T cells have poor proliferative capacity and cannot enter the S phase when TCR is activated. Mechanistically, this is attributed to the accumulation of CDKN1B, which cannot be degraded in autophagy-deficient naive T cells, and negatively regulates cell cycle [31][68]. Defective autophagy can also disturb T cell activation, differentiation, and stemness. It has been reported that the differentiation from T cells to invariant natural killer T (iNKT) and Treg is facilitated by autophagy [32][69]. Yang et al. found that deletion of autophagy-related protein PIK3C3/VPS34 reduced the activity of mitochondria upon T cell activation, so that CD4+ T cells failed to differentiate into T helper 1 cells [33][70]. Similarly, the quality of mitochondria declines when the mitochondrial components cannot be degraded adequately, resulting in ROS accumulation and T cell damage [34][71]. Depolarized mitochondria were also detected in IL-15-induced resident memory CD8+ T cells with autophagy inhibited by MRT68921 dihydrochloride and 3-methyladenine (3MA), causing T cells exhaustion [35][72]. CD4+ Treg cells in TME confer another primary mechanism of immune evasion and immunotherapy resistance. Autophagy was shown to participate in maintaining Treg cell function [36][73]. Inhibition of autophagy by Atg5, Atg7 and AMBRA1 deletion induces Treg cell apoptosis and dysfunction in vivo [37][38][39][74,75,76] (Figure 2).
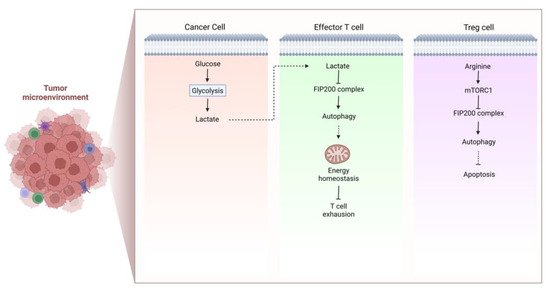
Figure 2. The formation of immunosuppressive TME. Cancer cell-derived lactate lowers FIP200 expression and attenuates autophagy, which is pivotal for energy homeostasis of effector T cells, thus facilitating T cell exhaustion and formation of immunosuppressive TME. In Treg cells, decreased intracellular arginine suppresses mTOR, leading to autophagy activation that is responsible for Treg cell survival. As a consequence, the function of Treg cell is improved to form the immunosuppressive TME.
Autophagy also serves a crucial function in other types of immune cells that interact with T cells. Lysosomal proteolysis of autophagy is necessary for the antigen presentation in dendritic cells [40][77]. Deleting PIK3C3 (a key player in autophagy) in dendritic cells contributes to reduced CD8α+ dendritic cells and B16 melanoma-specific CTL activity [25][62]. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) dampen antitumor immune responses and treatment effectiveness by directly suppressing T cell activation in TME [41][78]. An elevated level of autophagy has been detected in MDSCs [42][79]. Blocking autophagy in MDSCs leads to increased MHC-II expression and impaired tumor growth in vivo [43][80].
2.2. Autophagy in B cells
The survival and development of B cells depends on autophagy. For instance, the development of B cells depends on Atg5 [44][81]. After ligand LPS activation, basal levels of autophagy are required to preserve the survival of a normal number of peripheral B cells [45][82]. Intrinsic autophagy in B cells is necessary to sustain the normal function of alloreactive B memory cells. Atg7 deletion in B cell blocks B cell autophagy, inhibiting secondary alloantibody responses and decreasing the frequencies of alloreactive B memory cells [46][83].
2.3. Autophagy in Natural Killer (NK) Cells
The survival of iNKT cells requires intrinsic autophagy. Facing viral infection, autophagy is activated with the aid of phosphorylated FoxO1 and Atg7, which promotes the development and function of NKT cells against viral infection [47][84]. Autophagy-deficient iNKT cells undergo apoptosis in the mitochondrial pathway. Absence of autophagy not only hinders the maturation of iNKT cells by reducing NKT cell proliferation, but also limits the transition of iNKT cells to a quiescent state [48][85]. Moreover, the secretion of iNKT can be affected by autophagy. Autophagy-deficient iNKT cells release low levels of IL-4 and IFN-γ compared with normal iNKT cells [49][86].
2.4. Autophagy in Dendritic Cells (DCs)
Autophagy is indispensable for cytokine secretion and antigen presentation in dendritic cells (DCs). It has been reported that Atg5 is essential for DCs to activate CD4+ T cells through antigen presentation [47][48][84,85]. Atg5 deficiency in DCs reduces the secretion of IL-2 and IFN-γ by CD4+ T cells, but the levels of IL-12, IL-6, and TNF-α are not affected [50][87]. Moreover, antigen presentation was hampered by Atg5 deficiency through the MHC-II pathway, which may be resulted from the delay of lysosome-phagosome fusion [47][48][49][50][51][52][84,85,86,87,88,89].
2.5. Autophagy in Macrophages
The generation of macrophages requires autophagy at different stages. It is well accepted that tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) originate from monocytes. The recruitment of monocytes to tumors requires chemokines and cytokines derived from tumor cells and stromal cells. One of the chemokines, [C-C motif] ligand 2 (CCL2), protects monocytes from apoptosis and induces a high level of autophagy in TAMs [53][90]. The transition from monocytes into macrophages requires colony-stimulating factor 1 (CSF1), which upregulates and activates ULK1 to trigger autophagy [54][91]. CSF2 also facilitates the differentiation of monocytes. Autophagy in monocytes maintains a high-level during differentiation, since JNK signaling is activated to release Beclin 1 and inhibits Atg5 cleavage. Autophagy inhibition restrains the differentiation process [55][92]. In addition, autophagy is involved in macrophage polarization. Downregulated autophagy promotes M1 polarization and upregulated autophagy promotes M2 polarization in macrophages [56][93]. M1 macrophages stimulate immune responses, whereas M2 macrophages play an immunosuppressive role, indicating that autophagy is a potential target to modulate macrophage polarization toward the M1 phenotype [57][94].
3. Autophagy in Regulating Immune Checkpoint Molecules
Immune checkpoint molecules, including PD-1 and CTLA-4, play crucial roles in tumor immune tolerance, which is the main reason for the poor clinical outcomes of immunotherapy. These immune checkpoint molecules regulate tumor immune tolerance through autophagy. For example, activation of PD-1 by PD-L1 promotes immunologic tolerance, suppresses effector T cells and maintains tumor Tregs, boosting tumor survival [58][95]. Hence, elucidating the regulation of immune checkpoints by autophagy is of great significance in immunotherapy.
As a T cell checkpoint molecule, PD-1 inhibits T cell proliferation and impedes the recognition of tumor cells once activated by PD-L1. Clark et al. found that tumor cells initiate autophagy in response to anti-PD1 or anti-PD-L1 antibody treatment. Engagement of PD-1 to PD-L1 induces autophagy in nearby T cells [59][96]. A study indicated that inhibition of autophagy by the Sigma1 inhibitor leads to degradation of PD-L1 and impaired PD-1/PD-L1 interaction, suggesting the Sigma1 inhibitor as a promising tool to block PD-1/PD-L1 [60][97]. Therefore, combining antibodies with autophagy inhibitors may be an attractive therapeutic strategy [61][98].
CTLA-4 was confirmed to be another immune checkpoint molecule that mediates tumor immune tolerance. Shukla et al. identified a subcluster of MAGE-A cancer-germline antigens that confer resistance to the CTLA-4 blockade. Autophagy activation combats this resistance by decreasing MAGE-A protein levels in human melanomas [62][99]. However, another study reported that mTORC1 inhibitor-induced autophagy restores CTLA-4 expression and corrects Treg cell function in systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) [63][100]. CTLA4 engagement inhibits autophagy by activating PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway [64][101].
IDO promotes immunologic tolerance by suppressing responses of CTLs and maturation of DCs, magnifying tolerogenic APCs, and inducing Tregs generation. Autophagy can prevent inflammation-induced IDO synthesis by reducing inflammation [65][102]. IDO triggers the activation of general control nonderepressible 2 (GCN2) and inhibition of eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α (eIF2α), which participate in inflammatory carcinogenesis [66][103]. Autophagy induced by IDO1-GCN2 plays a protective role against fatal inflammation disease [67][104]. Another mechanism of IDO-induced autophagy has been reported. The inhibition of tryptophan sufficiency signaling by IDO causes mTOR inactivation, thus triggering autophagy in an LC3-dependent way [66][103].
4. Autophagy in Immune Cytokines
Autophagy can increase or inhibit cytokine production and affect tumor progression. Autophagy and cytokines can regulate each other. Numerous cytokines have been demonstrated to govern or be governed by autophagy.
4.1. Interleukins
IL-1 is a class of pro-inflammatory cytokines that promotes cancer progression by inhibiting COX-1, IkB, and JNK signaling pathways. Inhibition of IL-1 in tumor cells restrains tumor development [68][105]. IL-1β is negatively regulated by autophagy in most situations, whereas IL-1α is only negatively regulated by autophagy [69][106]. However, both IL-1α and IL-1β triggers autophagy, indicating that autophagy is a negative feedback mechanism in regulating IL-1 [70][107]. Autophagy activation in Atg5-deficient macrophages causes decreased IL-1β secretion, suppressing T cell activation and cytokine production [50][87]. Conversely, IL-1 level is elevated in autophagy-deficient macrophages to promote tumorigenesis through ROS-NF-κB signaling pathway [71][108]. IL-2 induces autophagy in an ATG5, HMGB1, and Beclin1-dependent way [72][109]. High-dose interleukin-2 (HDIL-2) inhibits the growth of metastatic liver tumors in vivo, accompanied by elevated levels of HMGB1, IFN-γ, IL-6, and IL-18 in serum. HMGB1 is translocated from the nucleus to the cytosol to trigger autophagy, and suppression of autophagy by CQ may enhance the proliferation and infiltration of immune cells in the liver and spleen [73][110]. IL-6 negatively regulates autophagy by activating STAT3 and inhibiting LC3-II and Beclin 1 expression in vitro [74][111]. However, IL-6 trans-signaling stimulates autophagy when IL-6 interacts with soluble IL-6R in vivo, which is mediated by AMPK and AKT activation [75][112]. In addition, IL-10 is also an autophagy suppressor by activating the JAK/STAT3 and PI3K/Akt/mTORC1 pathway [76][113]. As Th2 cytokines, IL-4, IL-13, and IL-10 can activate the PI3K/mTORC1 pathway to inhibit autophagy in most environments [77][114]. In turn, autophagy may exert dual effects on the production of IL-10, which needs further investigation [78][115].
4.2. Interferons
Autophagy is needed in the synthesis of IFN-γ. IFN can be categorized into type I, II, and III. Type I IFN directly induces autophagy by activating JAK/STAT pathway [79][116]. IFN-α is a class of type I IFN, and the effect of IFN-α varies on different cell types [80][117]. As a type II IFN, IFN-γ induces autophagy in various types of immune cells and tumor cells, which is mediated by the acceleration of autophagosome formation and maturation [81][118]. In addition, IFN-γ can facilitate the MHCI expression and induce autophagy [82][119]. It has been reported that effector CD4+ T cells lacking Atg7 express low amounts of IFN-γ in the absence of autophagy [83][120].
4.3. Transforming Growth Factor Beta (TGF-β)
TGF-β contributes to immune evasion by directly suppressing effector cells and indirectly facilitating the differentiation of Treg cells. TGF-β can also inhibit NK cells and IFN-γ to form immunosuppressive TME [84][121]. Inhibition of autophagy upregulates TGF-β expression by impairing its degradation [85][122]. In turn, TGF-β is responsible for autophagy induction in cancer cells [80][117]. For example, TGF-β induces autophagy in HCC and breast cancer cells by increasing the levels of ATGs, including Beclin1, Atg5, and Atg7. Autophagy promotes the expression of proapoptotic genes such as Bim and Bmf in the Bcl-2 family to mediate apoptosis, suggesting the correlations between autophagy and apoptosis [86][87][123,124].
4.4. Tumor Necrosis Factor Alpha (TNF-α)
TNF-α is an apoptosis and necrosis inducer in multiple cells and can impair autophagy by decreasing lysosomal acidification [88][125]. Inhibition of autophagy by Bafilomycin A1 contributes to TNF-α-induced cell death by increasing oxidative stress and toxicity, indicating that autophagy is a negative regulator of TNF-α [89][126]. A mechanism study revealed that autophagy inhibits TNF-α expression through p38MAPK dephosphorylation and TRAF6 downregulation [90][127].
