Fragaria genus (Rosaceae), commonly known as strawberry, represents one of the most important food plants all over the world, with a double global production compared with all other fruit berries combined. Usually appreciated because of their specific flavor, the strawberries also possess biological properties, including antioxidant, antimicrobial, or anti-inflammatory effects.
- Fragaria genus
- chemical composition
- biological properties
1. Introduction
2. Composition of Fragaria L. Genus
Giampieri et al. [3] reviewed the composition of the strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa), while Morales-Quintana and Ramos [4] reviewed the composition and potential applications of the Chilean strawberry (Fragaria chiloensis (L.) Mill.), while the functional properties of the berries, in general, and of the strawberries, in particular, were reviewed by Jimenez-Garcia et al. [5]. As resulting from various literature studies [3][4][5][6][7], the general composition of the strawberries (in terms of major components) can be summarized in Table 1 (with a general image provided in Figure 1).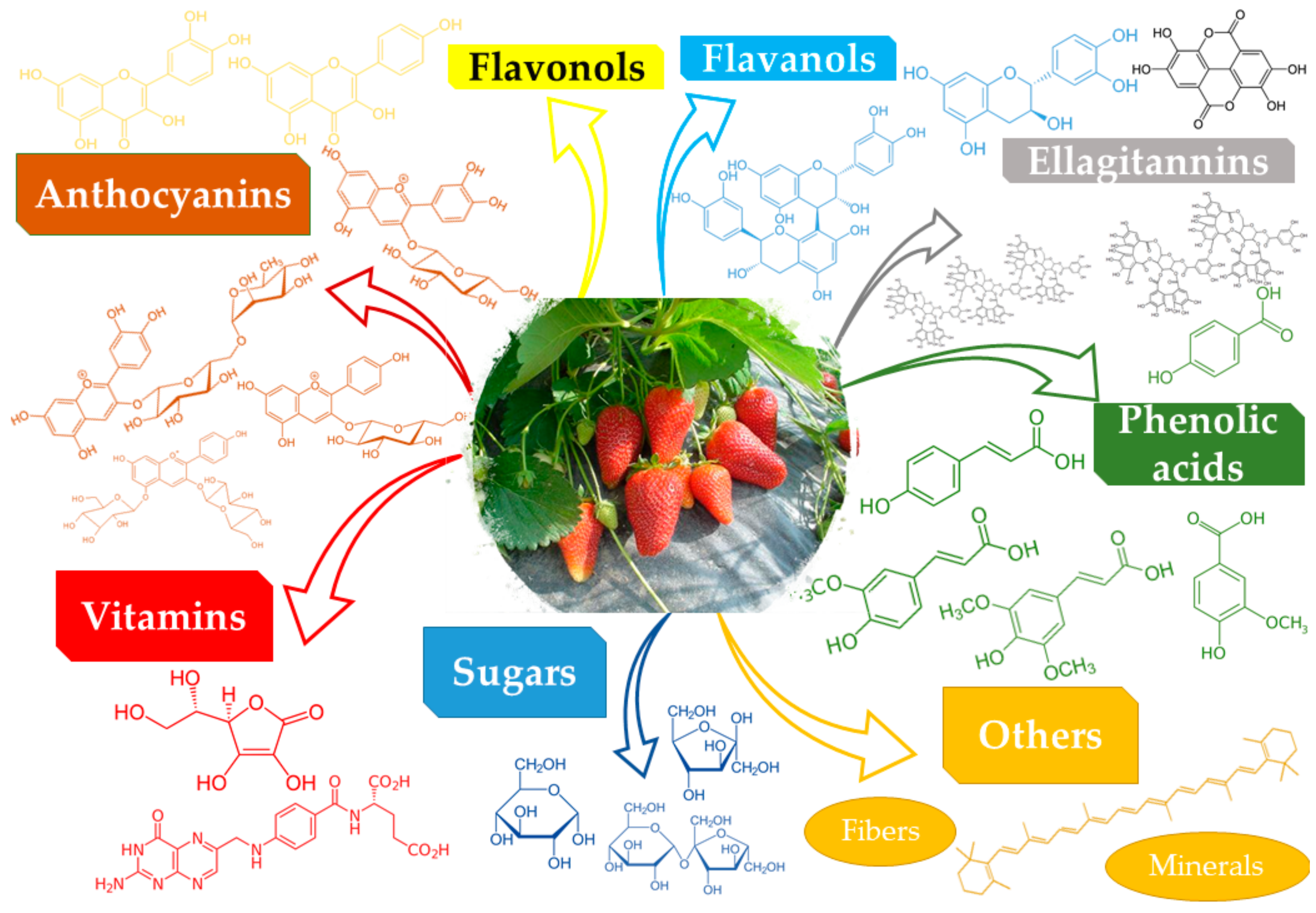
|
Class |
|---|
|
Species |
Compound |
Plant Part, Other Variables Ref. |
||
|---|---|---|---|---|
Identified Compounds and Main Findings |
Identification Method |
Ref. |
||
|
Anthocyanins |
Pelargonidin 3-glucoside, cyanidin 3-glucoside, cyanidin 3-rutinoside, pelargonidin 3-galactoside, pelargonidin 3-rutinoside, pelargonidin 3-arabinoside, pelargonidin 3-malylglucoside |
|
Species |
Extraction Method |
Antioxidant Assay |
Antioxidant Potential |
Responsible Compounds |
Ref. |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
[ | ][ | |||||||||
|
F. chiloensis | ][5] |
|||||||||
Ripe fruits |
Anthocyanins (cyanidin 3-O-glucoside, pelargonidin 3-O-glucoside cyanidin-malonyl-glucoside and pelargonidin-malonyl-glucoside); procyanidins, ellagitannins, ellagic acid and flavonol derivatives |
HPLC-DAD, LC-ESI-MS |
[9] |
[10] |
Flavonols |
|||||
|
F. chiloensis |
Quercetin, kaempferol, fisetin, their glucuronides, and glycosides |
Leaves | ||||||||
|
Fragaria chiloensis spp. chiloensis form chiloensis fruits |
Methanol: formic acid (99:1 v/v | |||||||||
Procyanidins, ellagitannins, ellagic acid and flavonol derivatives |
HPLC-DAD, LC-ESI-MS |
) extraction [9] |
Flavanols |
Catechin, proanthocyanidin B1, proanthocyanidin trimer, proanthocyanidin B3 |
||||||
|
F. chiloensis |
||||||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa, Camarosa var. fruits |
Anthocyanins isolated using CCC | |||||||||
DPPH, SAS | ||||||||||
Rhizomes | [3] |
|||||||||
ORAC, FRAP |
ORAC: 2.7–24.46 mmol Trolox/g; FRAP: 2.75–12.5 mmol Fe2+/g (depending on the fraction) |
Anthocyanins |
DPPH assay: IC50 = 38.7 mg/L; SAS: 79.3%) |
Aglycone and glycosylated ellagic acid and flavonoids |
[9] |
|||||
|
Fragaria chiloensis spp. chiloensis form chiloensis leaves |
Methanol: formic acid (99:1 v/v) extraction |
Procyanidins, ellagitannins, ellagic acid and flavonol derivatives |
DPPH, SAS HPLC-DAD, LC-ESI-MS |
DPPH assay: IC50 = 49.4 mg/L; SAS: 67.60% [9] |
Aglycone and glycosylated ellagic acid and flavonoids |
[9] |
Ellagitannins |
Sanguiin H-6, ellagitannin, ellagic acid, lambertianin C, galloylbis-hexahydroxydiphenoyl-glucose |
||
|
Fragaria × ananassa |
||||||||||
|
Fragaria chiloensis spp. chiloensis form chiloensis rhizomes |
Fruits |
Methanol: formic acid (99:1 v/v) extraction[3] |
||||||||
Anthocyanins (pelargonidin-3-glucoside, pelargonidin-3-rutinoside, cyanidin-3-rutinoside, pelargonidin-3,5-diglucoside, pelargonidin-3-(6-acetyl)-glucoside, 5-carboxypyranopelargonidin-3-glucoside, delphinidin-3-glucoside, peonidin-3-glucoside, cyanidin-3-galactoside), p-hydroxybenzoic acid, (+)-catechin, ellagic acid, p-coumaric acid, quercetin glucoside |
DPPH, SAS LC-MS/MS, HPLC-UV/Vis |
DPPH assay: IC50 = 64.8 mg/L; SAS: 55% [10] |
Aglycone and glycosylated ellagic acid and flavonoids |
[9] |
Phenolic acids |
4-coumaric acid, p-hydroxybenzoic acid, ferulic acid, vanillic acid, sinapic acid |
[ | |||
|
Fragaria × ananassa |
Fruits, cultivar and seasonal variations | 7] |
||||||||
|
Fragaria x ananassa Osogrande var. frozen fruits |
Acetone (80%) extraction | Vitamin C, β-carotene, total phenolics, total anthocyanins; genotype influence is stronger than the environmental influence |
DPPH, FRAP Colorimetric |
DPPH: 11.91–12.83 μmol BHT eq./g FW; best results for ripe fruits FRAP: 27.37–36.75 μmol FS eq./g FW; best results for green fruits [11] |
Total phenolic content, vitamin C |
[12] |
Vitamins |
Vitamin C, vitamin B9 |
[ | |
|
Fragaria × ananassa |
Fruits, different cultivars on different ripeness stage | 6] |
||||||||
Total vitamin C, total phenolics, total anthocyanins, total ellagic acid/pelargonidin-3-glucoside and cyanidin-3-glucoside; higher amounts in pink fruits compared with fully ripped fruits | ||||||||||
|
Fragaria x ananassa Camino Real var. frozen fruits |
Acetone (80%) extraction |
DPPH, FRAP |
Colorimetric/HPLC-DAD |
[12] |
DPPH: 9.75–12.01 μmol BHT eq./g FW, FRAP: 24.13–28.49 μmol FS eq./g FW (best results for pink fruits) |
Minerals |
Mn, K, Mg, P, Ca |
[ | ||
|
Fragaria × ananassa |
Fruits, different farming methods | 3] |
||||||||
|
Others |
Sugars (glucose, fructose, and sucrose), fibers |
[3] |
Total phenolic content, vitamin C | |||||||||||
Total phenolics/pelargonidin-3-glucoside and cyanidin-3-glucoside, vitamin C, higher in organic farming fruits | |||||||||||
Colorimetric/HPLC-DAD |
[13] |
||||||||||
[ |
Fragaria × ananassa |
Fruits, different cultivars (27) and ripening stages |
Phenolic compounds (multiple classes, including anthocyanins, flavanols and ellagitannins); composition dependent on cultivar, cinnamic acid conjugates and anthocyanins levels increased with the ripening stage |
HPLC-DAD-MS |
[14] |
||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa, F. vesca |
Fruits |
Quercetin and isorhamnetin glycosides (higher levels in wild strawberry) |
HPLC-DAD, LC-ESI-MS |
[15] |
|||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa, F. vesca |
Fruits, different cultivars |
Volatile esters (including ethyl acetate, hexyl acetate, methyl butanoate, ethyl butanoate, hexyl butanoate, methyl hexanoate, ethyl hexanoate, hexyl hexanoate); higher levels in cultivated strawberries. |
GC-MS |
[16] |
|||||||
|
F. vesca |
Fruits, two different cultivars |
Anthocyanins (cyanidin 3-O-glucoside, pelargonidin 3-O-glucoside, peonidin 3-O-glucoside, cyanidin 3-O-malonylglucoside, pelargonidin 3-O-malonylglucoside, peonidin 3-O-malonylglucoside), dihydroflavonol and flavonols (taxifolin 3-O-arabinoside, kaempferol 3-O-glucoside, quercetin 3-O-glucoside, quercetin-acetylhexoside, kaempferol 3-O-acetylhexosides), flavan-3-ols and proanthocyanidins (catechin, B type proanthocyanidin dimers, trimers, and tetramers), ellagic acid and derivatives (glycosylated, methyl pentoside, methylellagic acid methyl pentoside, ellagitannins), other compounds (benzoic acid, ferulic acid hexose derivative, citric acid, furaneol glucoside) |
HPLC-DAD |
[17] |
|||||||
Anti-lipase assay, adipocyte differentiation inhibition assay, melanogenesis inhibition assay, β-hexosaminidase inhibition assay, tyrosinase inhibition assay | Crown, stolon leaf and flowers extracts exhibited the highest effects |
Total phenolic content |
[21] |
Fragaria × ananassa, F. vesca |
Fruits |
Anthocyanins (cyanidin, pelargonidin), cyanidin glycosides (cyanidin 3-glucoside, cyanidin 3-arabinoside, cyanidin 3-sambubioside, delphinidin 3-galactoside, delphinidin 3-glucoside, delphinidin 3-malonylglucoside); higher levels of cyanidin glycosides in wild species |
|||||
|
Antihyperuricemic |
Fragaria x ananassa cv. Tochiotome leaves |
Supercritical CO2 extraction with different entrainers |
HPLC-DAD |
Uric acid production in AML12 hepatocytes [18] |
|||||||
Reduction of uric acid at 100 mg/mL (96 mmol/2 h/mg protein), compared with the control (16,096 mmol/2 h/mg protein) | Kaempferol, quercetin |
[40] |
F. vesca |
Leaves |
|||||||
|
Cytotoxic, anti-proliferative |
Fragaria x ananassa fruits |
Ellagitannins (sanguiin H-2 isomer, sanguiin H-10 isomer, sanguiin H-6/agrimoniin/lambertianin A isomer, castalagin/vescalagin isomer, sanguiin H-10 isomer, sanguiin H-2 isomer, casuarictin/potentillin isomer) |
LC-PDA-ESI-MS |
[ |
Meth. extraction 19] |
||||||
Ex vivo: cell viability assay; in vivo: developing tumor size determination | Cytotoxic on cancer cells, blocked the proliferation of tumor cells |
Phenolic compounds |
[56] |
Fragaria × ananassa |
|||||||
|
Antineoplastic |
Fruits, different cultivars and production years |
Vitamin C, anthocyanins (pelargonidin 3-glucoside, cyanidin 3-glucoside, pelargonidin 3-rutinoside), ellagic acid; strongly dependent on the cultivar and production year |
Fragaria x ananassa var. Pajaro HPLC-UV/Vis |
fruits |
Acidified hydro-eth. extraction |
Transglutaminase assay and polyamine detection, immunoblot analysis [20] |
|||||
reduction of cell proliferation, lowering of the intracellular levels of polyamine, enhancement of tissue transglutaminase activity | Anthocyanins |
[57] |
Fragaria × ananassa |
Fruits, at different ripening stage |
Vitamin C, pelargonidin-3-rutinoside, ellagic acid, cyanidin-3-glucoside, quercetin (red fruits), neochlorogenic, pelargonidin-3-glucoside, pelargonidin-3-rutinoside, epicatechin, quercetin-3-β-d-glucoside, ellagic acid (green fruits) |
LC-ESI-TOF |
[21] |
||||
|
Cytotoxic |
Fragaria vesca L. leaves |
Hydroalcoholic extract at room temperature, ellagitannins-enriched fraction |
Effects on HepG2 cells—cell viability assessment, cell proliferation, cell cycle and cell death analysis, Western blot analysis, proteasome chymotrypsin-like activity |
Inhibition of HepG2 cell viability IC50 = 690 mg/L (extract)/113 mg/L (fraction); fraction induced necrosis and apoptosis, influenced the cellular proteolytic mechanisms |
Ellagitannins |
[19] |
Fragaria × ananassa |
||||
|
Chemopreventive |
Calyx (red and green) |
Lyophilized Fragaria x ananassa fruits Quercetin-3-β-d-glucoside, ellagic acid, kaempferol-3-O-glucoside, vitamin C (red), catechin, quercetin-3-β-d-glucoside, ellagic acid (green) |
Ultrasound-assisted extraction with acidified acetone LC-ESI-TOF |
Histological studies, Western blot analysis, PGE2 [21] |
|||||||
measurement, and nitrate/nitrite colorimetric assay | Decreased tumor incidence, decreased levels of TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-6, COX-2 and iNOS, inhibition of the phosphorylation of PI3K, Akt, ERK, and NFκB |
anthocyanins, ellagitannin/ellagic acid/ellagic acid derivatives flavonols |
[58] |
Fragaria × ananassa |
Flower |
Catechin, quercetin-3-β-d-glucoside, ellagic acid, kaempferol-3-O-glucoside, vitamin C |
|||||
|
Cytotoxic |
Fragaria x ananassa leaves | LC-ESI-TOF |
[21] |
||||||||
Hydroalcoholic extracts (meth., eth., isopropanol) from in vitro cell suspension |
Cell proliferation, cell viability |
Under 50% viable cells for colorectal adenocarcinoma and colon adenocarcinoma upon treatment with extracts containing 0.29 mM ethoxy-dihydrofuro-furan |
Polyphenols |
[59] |
Fragaria × ananassa |
Leaf |
Procyanidin dimer and trimer, catechin, quercetin-3-β-d-glucoside, vitamin C, ellagic acid |
LC-ESI-TOF |
[21] |
||
|
Fragaria × ananassa |
Stolon |
Neochlorogenic, procyanidin dimer, catechin, quercetin-3-β-d-glucoside, ellagic acid, vitamin C, kaempferol-3-O-glucoside |
LC-ESI-TOF |
[21] |
|||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa |
Stem |
Procyanidin dimer, catechin, ferulic acid, quercetin-3-β-d-glucoside, ellagic acid |
LC-ESI-TOF |
[21] |
|||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa |
Crown |
Procyanidin dimer and trimer, catechin, propelargonidin dimer, ellagic acid |
LC-ESI-TOF |
IC50 (mg/mL) ranging from 76.73 (Camarosa)—100 (Camino Real) [21] |
|||||||
Total anthocyanin content | [ | 26] |
Fragaria × ananassa |
Root |
Procyanidin dimer and trimer, catechin, neochlorogenic, propelargonidin dimer |
LC-ESI-TOF |
|||||
|
F. vesca leaves native to Italy |
Ultrasonic extraction with ethanol: water solvent (70:30, v/v) |
TEAC | [ |
0.34–0.35 mg/mL Trolox eq., compared with quercetin (0.40)21] |
|||||||
Condensed tannins and flavonoid derivatives | [28] |
Fragaria × ananassa |
Fruits, different novel cultivars |
Phenolic acids (p-coumaric acid, ellagic acid, ferulic acid derivative, p-coumaric acid derivatives), monomeric flavanols ((+)-catechin), flavonols (quercetin 3-O-glucoside, fisetin, quercetin 3-O-glucoside derivative), anthocyanins (cyanidin 3-glucoside, cyanidin 3-rutinoside, cyanidin pentoside, pelargonidin 3-galactoside, pelargonidin 3,5-diglucoside, pelargonidin 3-glucoside, pelargonidin 3-rutinoside, cyanidin 3-Oacetylglucoside, cyanidin hexoside, pelargonidin 3-O-monoglucuronide, pelargonidin derivatives) |
|||||||
|
Fragaria x ananassa cv. Tochiotome | HPLC-DAD, LC-ESI-QTOF | [22] |
|||||||||
leaves |
Supercritical CO2 extraction with different entrainers |
DPPH |
0.07 (simple supercritical extraction)—5.82 μmol BHT/g sample (with ethanol, dried at 40 °C) |
Phenolic compounds |
[40] |
Fragaria × ananassa |
|||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa fruits (90 cultivars) |
Fruits, grown on different altitudes, on consecutive years |
Ultrasonic aqueous methanol (70%) acidified with 1.5% formic acid, at room temperature |
DPPH, ABTS |
Average values (μmol Trolox/100 g):765.06 (DPPH), 1637.96 (ABTS) |
Tannin-based compounds. |
[31] |
where: ABTS—2,2′-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulfonic acid) assay; BHT—butylated hydroxytoluene; DPPH—reduction of 2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl; DW—dry weight; eq.—equivalents; FRAP—ferric reducing ability of plasma; FS—ferrous sulphate; FW—fresh weight; IC50—half maximal inhibitory concentration; ORAC—oxygen radical absorbance capacity; SAS—superoxide anion assay; TBARS—thiobarbituric acid reactive substances assay; TEAC—Trolox equivalent antioxidant capacity.
3.2. Anti-Inflammatory Properties
3.3. Other Potential Applications
|
Action |
Plant |
Extraction Method |
Assay |
Results |
Responsible Compounds |
Ref. |
||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Anti-inflammatory on inflammatory bowel disease |
Fragaria vesca leaves |
Eth. extraction |
MPO activity; GSH, SOD and CAT levels |
Prevention of increase in colon weight and disease activity index, decrease in macroscopic and microscopic lesion score; significant improvement of MPO, CAT and SOD levels at 500 mg/kg 5 days oral treatment |
Phenolic acids, flavonoids |
[51] |
||||||
|
Anti-inflammatory |
Fragaria vesca leaves |
Eth. extraction at room temperature, infusion |
Nitric oxide production, western blot analysis (expression of pro-inflammatory proteins in lipopolysaccharide-triggered macrophages); nitric oxide scavenger activity |
Inhibition of nitrite production on pre-treated cells (at 80 and 160 mg/L—31%/40%); 23% inhibition in culture media, at 160 mg/L |
Phenolic content |
[46] |
||||||
|
Anti-inflammatory |
Fragaria x ananassa, var. Alba fruits |
Meth. extraction at room temperature, infusion |
Determination of ROS intracellular levels, apoptosis detection, antioxidant enzyme activities, immunoblotting analysis, determination of mitochondrial respiration and extracellular acidification rate in cells |
Reduction of intracellular ROS levels (significant at 100 mg/L), decreased apoptotic rate (significant at 50 and 100 mg/L); Increased ARE-antioxidant enzymes expression, reduced NO and inflammatory cytokines production (at 50 and 100 mg/L) to control levels |
Vitamin C, anthocyanins, flavonoids |
[52] |
||||||
|
Anti-inflammatory, hepatoprotective |
Fragaria chiloensisssp. Chiloensis fruits |
Aq. extracts |
Histological analyses, determination of transaminases, cytokines, F2-isoprostanes, and glutathione assays |
maintained hepatocellular membrane, structural integrity, attenuated hepatic oxidative stress, and inhibited inflammatory response in LPS-induced liver injury; downregulation of cytokines (TNFa, IL-1β, and IL-6) |
Phenolic content |
[53] |
||||||
|
Anti-inflammatory |
Fragaria x ananassa var. Camarosa fruits |
Ultrasonic-assisted, acidified meth. extraction, separation |
In vivo: quantification of the leukocyte content, exudate concentration, MPO and ADA activities, nitric oxide products, TNF-α and IL-6 levels; in vitro: MTT assay, measurement of nitric oxide products, TNF-α and IL-6 levels, western blot analysis |
Inhibition of the carrageenan-induced leukocyte influx to the pleural cavity; reduction of myeloperoxidase activity, exudate concentration, NO levels. |
Phenolic compounds, anthocyanins (particularly pelargonidin-3-O-glucoside) |
[54] |
||||||
|
Anti-inflammatory, wound healing |
Fragaria x ananassa var. San Andreas fruits | ] | ||||||||||
Ultrasound-assisted extraction, acidified meth.: aq. (80:20); separation of different fractions |
MTT assay, ROS, NO levels, effects on inflammatory markers and on skin fibroblast migration |
ROS reduction, suppression of IL-1β, IL-6 and iNOS gene expressions; enhanced skin fibroblast migration |
Polyphenolic compounds, especially anthocyanins |
[55] |
F. vesca leaves |
Methanol, ultrasounds extraction |
DPPH, FRAP |
|||||
|
Anti-microbial | DPPH: IC | 50 = 13.46 mg/L; FRAP: 0.878 mmol Fe2+/g DW |
Total phenols, total tannins |
[ |
Fragaria vesca leaves and roots |
Centrifugation extraction with meth.: aq. (80:20) |
Disc diffusion assay |
6–9 mm inhibition zones for leaves, 5–9 mm for roots (depending on S. aureus strain) ] |
||||
Phenolic compounds | [ | ] |
F. vesca roots, wild-growing |
Hydromethanolic extraction, infusion, decoction |
DPPH, FRAP, β-Carotene bleaching inhibition, TBARS |
IC50, mg/L: DPPH—50.03/50.56/50.62; FRAP—40.98/44.78/49.23; β-C bleaching—116.26/44.88/66.10; TBARS—35.76/4.76/6.14 |
Total phenolics, total flavan-3-ols, total dihydroflavonols, |
|||||
|
Anti-microbial |
Fragaria vesca leaves |
Hydroalcoholic extraction, separation | [ |
Disc diffusion assay | 38] |
|||||||
Good inhibition potential at 25 mg/mL, better effect for the ellagitannin-enriched fraction | Ellagitannins |
[48] |
F. vesca roots, commercial |
|||||||||
|
Anti-allergenic |
Hydromethanolic extraction, infusion, decoction |
DPPH, FRAP, β-Carotene bleaching inhibition, TBARS |
IC50, mg/L: DPPH—68.89/255.81/51.32; FRAP—327.75/78.99/67.92; β-C bleaching—68.34/23.44/114.67; TBARS—6.69/24.25/10.62 |
Total phenolics, total flavan-3-ols, total dihydroflavonols, |
[ |
Fragaria x ananassa var. Minomusume38] |
||||||
fruits |
Methanol fraction of fruits juice (obtained by squeezing) |
Antigen-stimulated degranulation in RBL-2H3 cells |
degranulation suppression (95–60% inhibition for linocinnamarin, cinnamic acid, chrysin, kaempferol, trans-tiliroside) |
Best results - phenylpropanoid glycoside |
[49] |
Fragaria × ananassa var. Amaou, fruits, at different ripening stage |
Ethanol or water room temperature extraction |
Modified ABTS assay |
||||
|
Anti-diabetic | Ethanol: 150.5/151.9; water: 227.2/189.4 (red/green fruits) μmol TE/100 g FW |
Fragaria x ananassa var. Falandi fruits Total phenolic content |
Compounds isolated from eth. extracts |
α-glucosidase inhibitory activity |
IC50[21] |
|||||||
values better than the positive control (acarbose) for nine compounds (537.43 to 25.39 μM) | Individual compounds | [24] |
Fragaria × ananassa var. Amaou calyx (red and green) |
|||||||||
|
Anti-obesity, anti-allergy, skin-lightening |
Ethanol or water room temperature extraction |
Fragaria ×ananassa var. Amaou, entire plant (red fruit, green fruit, red calyx, green calyx, flower, leaf, stolon, stolon leaf, stem, crown and root) Modified ABTS assay |
Ethanol: 241.1/1239.9; water: 1716.6/577.7 μmol TE/100 g FW (red/green calyx) |
Total phenolic content |
[21] |
|||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa var. Amaou flower |
Ethanol or water room temperature extraction |
Modified ABTS assay |
4234.4/387.5 μmol TE/100 g FW (ethanol/water) |
Total phenolic content |
[21] |
|||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa var. Amaou leaves |
Ethanol or water room temperature extraction |
Modified ABTS assay |
2401.7/241.1 μmol TE/100 g FW (ethanol/water) |
Total phenolic content |
[21] |
|||||||
Eth. or aq. room temperature extraction |
Fragaria × ananassa var. Amaou stolon |
Ethanol or water room temperature extraction |
Modified ABTS assay |
1089.4/1856.7 μmol TE/100 g FW (ethanol/water) |
Total phenolic content |
[21] |
||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa var. Amaou stem |
Ethanol or water room temperature extraction |
Modified ABTS assay |
1338.6/1123.1 μmol TE/100 g FW (ethanol/water) |
Total phenolic content |
[21] |
|||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa var. Amaou crown |
Ethanol or water room temperature extraction |
Modified ABTS assay |
6213.3/128.7 μmol TE/100 g FW (ethanol/water) |
Total phenolic content |
[21] |
|||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa var. Amaou root |
Ethanol or water room temperature extraction |
Modified ABTS assay |
253.1/69.2 μmol TE/100 g FW (ethanol/water) |
Total phenolic content |
[21] |
|||||||
|
F. vesca vegetative parts (leaves and stems), wild-growing |
Hydromethanolic and aqueous extracts; wild-growing infusion microencapsulated in alginate and incorporated in k-carrageenan gelatine |
DPPH, FRAP, β-Carotene bleaching inhibition, TBARS |
IC50, mg/L: DPPH—123.67/86.17/109.10; FRAP—81.40/62.36/77.28; β-C bleaching—56.71/12.34/13.40; TBARS—12.63/3.12/5.03 (hydromethanolic/infusion/decoction); Final formulation (mg/mL)—DPPH—2.74; FRAP = 1.23 |
Total phenolics, total flavan-3-ols, total dihydroflavonols, |
[39] |
|||||||
Hydroxybenzoic acid, p-coumaric acid, other hydroxycinnamic acids, (+)-catechin, (−)-epicatechin, procyanidins, flavonols, anthocyanins (cyanidin 3-glucoside, pelargonidin 3-glucoside, pelargonidin derivative); higher levels recorded at lower altitudes. |
HPLC-DAD |
[23] |
||||||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa |
Fruits |
Kaempferol 3-(6-methylglucuronide), quercetin 3-(6-methylglucuronide), isorhamnetin 3-(6-methylglucuronide), trichocarpin, 2-p-hydroxybenzoyl-2,4,6-tri hydroxyphenylacetate, 2-p-hydroxyphene thyl-6-caffeoylglucoside, zingerone 4-glucoside, b-hydroxypropiovanillone 3-glucoside, (+)-isolariciresinol 90-glucoside, (−)-isolariciresinol 90-glucoside, aviculin, (−)-secoisolariciresinol 4-glucoside, cupressoside A, cedrusin, icariside E4, dihydrodehydrodiconiferyl alcohol 90-glucoside, massonianoside A, urolignoside, (−)-pinoresinol 4-glucoside, 2,3”-epoxy-4-(butan-2-one-3-yl)-5,7,40-trihydroxy flavane 3-glucoside, kaempferol 3-(6-butylglucuronide), benzyl 2-glucosyl-6-rhamnosylbenzoate | ||||||||||
|
F. vesca vegetative parts (leaves and stems), commercial |
Hydromethanolic and aqueous extracts |
DPPH, FRAP, β-Carotene bleaching inhibition, TBARS |
IC50, mg/L: DPPH—139.33/121.94/118.89; FRAP—324.49/91.88/88.20; β-C bleaching—388.90/76.41/69.98; TBARS—24.36/23.07/17.52 (hydromethanolic/infusion/decoction). |
Total phenolics, total flavan-3-ols, total dihydroflavonols, |
[39] |
|||||||
|
Fragaria x ananassa cv. Falandi fruit |
22 compounds isolated from ethanolic extracts |
ABTS, DPPH, FRAP |
Best results (IC50): ABTS—4.42 μM kaempferol 3-(6-methylglucuronide); DPPH—32.12 μM quercetin 3-(6-methylglucuronide); FRAP—0.05 mmol/g—urolignoside. |
Individual compounds |
[24] |
|||||||
|
Fragaria x ananassa cv. Albion, Aromas, Camarosa, Camino Real, Monte Rey, Portola, and San Andreas fruits |
Ultrasonic extraction with acidified methanol |
DPPH |
1H NMR, 13C NMR, HMBC, HPLC-UV/Vis, LC-MS/MS, HR-ESI-MS, |
[24] |
||||||||
|
F. vesca |
Fruits, wild and cultivated, from different geographical areas |
39 phenolic compounds (including cyanidin 3-O-glucoside, delphinidin-3-O-glucoside, pelargonidin-3-O-glucoside, pelargonidin-3-O-rutinoside, (+) catechin, (−) epicatechin, procyanidin B1 and B2, isoquercetin, gallic acid, p-coumaric acid, phloridzin); composition dependent on the geographical area |
LC-ESI-Orbitrap-MS, LC-ESI-QTrap-MS, LC-ESI-QTrap-MS/MS |
[25] |
||||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa |
Fruits, different cultivars |
Cyanidin 3-O-glucoside, pelargonidin-3-O-glucoside, pelargonidin-O-rutinoside, total anthocyanins content, dependent on the cultivar |
UPLC-PDA-ESI-MS, HPLC-DAD |
[26] |
||||||||
|
F. vesca |
Fruits |
Volatile composition—one hundred compounds (including esters, aldehydes, ketones, alcohols, terpenoids, furans and lactones). |
GS-MS |
[27] |
||||||||
|
F. vesca |
Leaves |
27 metabolites (organic acids, flavonoids, catechin and its oligomers, ellagitannins), including quinic acid, chelidonic acid, quercetin derivatives, catechin and procyanidins, phloridzin, pedunculagin, methyl ellagic acid glucuronide. |
LC-ESI-Orbitrap-MS |
[28] |
||||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa, F. vesca |
White-fruited mutants, different genotypes |
Anthocyanins, flavonols, flavan-3-ols, hydroxycinnamic acids, and ellagic acid—derived compounds, dependent on genotype |
LC-ESI-MS/MS |
[29] |
||||||||
|
F. chiloensis |
Fruits |
Anthocyanins (cyanidin-3-O-glucoside, pelargonidin hexoside, cyanidin manlonyl hexoside, pelargonidin-malonyl hexoside), ellagitannins (ellagic acid hexoside, pentoside, rhamnoside), proanthocyanidin dimers, epicatechin, flavonols (quercetin pentoside, glucuronide) |
HPLC-DAD, LC-ESI-MS |
[30] |
||||||||
|
Fragaria × ananassa |
Fruits, different cultivars |
Anthocyanins, flavonoids, cinnamic acid derivatives, tannins and related compounds, triterpenoids; concentration dependent on the cultivar |
UPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS, HPLC-DAD |
[31] |
where:13C NMR—Carbon-13 nuclear magnetic resonance; GC-MS—gas chromatography–mass spectrometry; 1H NMR—proton nuclear magnetic resonance; HMBC —heteronuclear multiple bond correlation; HPLC-DAD—high-performance liquid chromatography with diode array detector; HPLC-UV/Vis—high-performance liquid chromatography equipped with UV/vis detector; HR-ESI-MS—high-resolution electrospray ionization mass spectrometry analysis; LC-ESI-MS(/MS)—liquid chromatography electrospray ionization (tandem) mass spectrometry analysis; LC-ESI-Orbitrap-MS—liquid chromatography electrospray ionization Orbitrap mass spectrometry; LC-ESI-QTrap-MS(/MS)—liquid chromatography electrospray ionization quadrupole ion trap mass spectrometry; LC–ESI–(Q)TOF—liquid chromatography electrospray ionization with (quadrupole) time-of-flight; LC-MS/MS—liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry; LC-PDA-ESI-MS—liquid chromatography equipped with photodiode array detector coupled to mass spectrometry using the electrospray ionization interface; UPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS/MS—ultra-performance liquid chromatography equipped quadrupole time of flight coupled to tandem mass spectrometry using the electrospray ionization interface; UPLC-PDA-ESI-MS—ultra-performance liquid chromatography equipped with photodiode array detector coupled to mass spectrometry using the electrospray ionization interface.
3. Biological Activities of Fragaria Genus
3.1. Antioxidant Properties
where: ADA—adenosine-deaminase; Akt—Protein Kinase B; aq.—water (aqueous); CAT—catalase; COX-2—cyclooxygenase-2 enzyme; ERK—extracellular signal-regulated kinase; eth—ethanol; GSH—glutathione; HepG2—human liver cancer cell line; IC50—half maximal inhibitory concentration; IL-1β—Interleukin 1 beta cytokine protein; IL-6—interleukin 6; iNOS—inducible nitric oxide synthase; meth.—methanol; MPO—myeloperoxidase; MTT—3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide; NFκB—nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells; NO—nitric oxide; PGE2—Prostaglandin E2; PI3K—phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase; RBL—rat basophilic leukemia cells; ROS—reactive oxygen species; SOD—superoxide dismutase; TNF-α—tumor necrosis factor alpha;.
References
- Liston, A.; Cronn, R.; Ashman, T.L. Fragaria: A genus with deep historical roots and ripe for evolutionary and ecological insights. Am. J. Bot. 2014, 101, 1686–1699.
- Awad, M.A.; De Jager, A. Influences of air and controlled atmosphere storage on the concentration of potentially healthful phenolics in apples and other fruits. Postharv. Biol. Technol. 2003, 27, 53–58.
- Giampieri, F.; Tulipani, S.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Quiles, J.L.; Mezzetti, B.; Battino, M. The strawberry: Composition, nutritional quality, and impact on human health. Nutrition 2012, 28, 9–19.
- Morales-Quintana, L.; Ramos, P. Chilean strawberry (Fragaria chiloensis): An integrative and comprehensive review. Food Res. Int. 2019, 119, 769–776.
- Jimenez-Garcia, S.N.; Guevara-Gonzalez, R.G.; Miranda-Lopez, R.; Feregrino-Perez, A.A.; Torres-Pacheco, I.; Vazquez-Cruz, M.A. Functional properties and quality characteristics of bioactive compounds in berries: Biochemistry, biotechnology, and genomics. Food Res. Int. 2013, 54, 1195–1207.
- Nile, S.H.; Park, S.W. Edible berries: Bioactive components and their effect on human health. Nutrition 2014, 30, 134–144.
- Vuong, Q.V.; Hirun, S.; Phillips, P.A.; Chuen, T.L.; Bowyer, M.C.; Goldsmith, C.D.; Scarlett, C.J. Fruit-derived phenolic compounds and pancreatic cancer: Perspectives from Australian native fruits. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 227–242.
- Khan, N.; Syed, D.N.; Ahmad, N.; Mukhtar, H. Fisetin: A dietary antioxidant for health promotion. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2013, 2, 151–162.
- Simirgiotis, M.J.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G. Determination of phenolic composition and antioxidant activity in fruits, rhizomes and leaves of the white strawberry (Fragaria chiloensis spp. Chiloensis form chiloensis) using HPLC-DAD–ESI-MS and free radical quenching techniques. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2010, 23, 545–553.
- Cerezo, A.B.; Cuevas, E.; Winterhalter, P.; Garcia-Parrilla, M.C.; Troncoso, A.M. Isolation, identification, and antioxidant activity of anthocyanin compounds in Camarosa strawberry. Food Chem. 2010, 123, 574–582.
- Singh, A.; Singh, B.K.; Deka, B.C.; Sanwal, S.K.; Patel, R.K.; Verma, M.R. The genetic variability, inheritance and inter-relationships of ascorbic acid, β-carotene, phenol and anthocyanin content in strawberry (Fragaria×ananassa Duch.). Sci. Horticult. 2011, 129, 86–90.
- Pineli, L.L.O.; Moretti, C.L.; dos Santos, M.S.; Campos, A.B.; Brasileiro, A.V.; Cordova, A.C.; Chiarello, M.D. Antioxidants and other chemical and physical characteristics of two strawberry cultivars at different ripeness stages. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2011, 24, 11–16.
- Crecente-Campo, J.; Nunes-Damaceno, M.; Romero-Rodrıguez, M.A.; Vazquez-Oderiz, M.L. Color, anthocyanin pigment, ascorbic acid and total phenolic compound determination in organic versus conventional strawberries (Fragaria x ananassa Duch, cv Selva). J. Food Compos. Anal. 2012, 28, 23–30.
- Aaby, K.; Mazur, S.; Nes, A.; Skrede, G. Phenolic compounds in strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa Duch.) fruits: Composition in 27 cultivars and changes during ripening. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 86–97.
- Mikulic-Petkovsek, M.; Slatnar, A.; Stampar, F.; Veberic, R. HPLC-MSn identification and quantification of flavonol glycosides in 28 wild and cultivated berry species. Food Chem. 2012, 135, 2138–2146.
- Dong, J.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, X.; Jin, W.; Han, Z. Differences in volatile ester composition between Fragaria×ananassa and F. vesca and implications for strawberry aroma patterns. Sci. Horticult. 2013, 150, 47–53.
- Sun, J.; Liu, X.; Yang, T.; Slovin, J.; Chen, P. Profiling polyphenols of two diploid strawberry (Fragaria vesca) inbred lines using UHPLC-HRMSn. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 289–298.
- Veberic, R.; Slatnar, A.; Bizjak, J.; Stampar, F.; Mikulic-Petkovsek, M. Anthocyanin composition of different wild and cultivated berry species. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 60, 509–517.
- Liberal, J.; Costa, G.; Carmo, A.; Vitorino, R.; Marques, C.; Domingues, M.R.; Domingues, P.; Goncalves, A.C.; Alves, R.; Sarmento-Ribeiro, A.B.; et al. Chemical characterization and cytotoxic potential of an ellagitannin-enriched fraction from Fragaria vesca leaves. Arab. J. Chem. 2015.
- Kim, S.K.; Kim, D.S.; Kim, D.Y.; Chun, C. Variation of bioactive compounds content of 14 oriental strawberry cultivars. Food Chem. 2015, 184, 196–202.
- Zhu, Q.; Nakagawa, T.; Kishikawa, A.; Ohnuki, K.; Shimizu, K. In vitro bioactivities and phytochemical profile of various parts of the strawberry (Fragaria × ananassa var. Amaou). J. Funct. Food 2015, 13, 38–49.
- Fernández-Lara, R.; Gordillo, B.; Rodríguez-Pulido, F.J.; González-Miret, M.L.; del Villar-Martínez, A.A.; Dávila-Ortiz, G.; Heredia, F.J. Assessment of the differences in the phenolic composition and color characteristics of new strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa Duch.) cultivars by HPLC-MS and Imaging Tristimulus Colorimetry. Food Res. Int. 2015, 76, 645–653.
- Guerrero-Chavez, G.; Scampicchio, M.; Andreotti, C. Influence of the site altitude on strawberry phenolic composition and quality. Sci. Horticult. 2015, 192, 21–28.
- Yang, D.; Xie, H.; Jiang, Y.; Wei, X. Phenolics from strawberry cv. Falandi and their antioxidant and α-glucosidase inhibitory activities. Food Chem. 2016, 194, 857–863.
- D’Urso, G.; Maldini, M.; Pintore, G.; d’Aquino, L.; Montoro, P.; Pizza, C. Characterisation of Fragaria vesca fruit from Italy following a metabolomics approach through integrated mass spectrometry techniques. LWT Food Sci. Technol. 2016, 74, 387–395.
- Chaves, V.C.; Calvete, E.; Reginatto, F.H. Quality properties and antioxidant activity of seven strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa Duch) cultivars. Sci. Horticult. 2017, 225, 293–298.
- Urrutia, M.; Rambla, J.L.; Alexiou, K.G.; Granell, A.; Monfort, A. Genetic analysis of the wild strawberry (Fragaria vesca) volatile composition. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2017, 121, 99–117.
- D’Urso, G.; Pizza, C.; Piacente, S.; Montoro, P. Combination of LC–MS based metabolomics and antioxidant activity for evaluation of bioactive compounds in Fragaria vesca leaves from Italy. J. Pharmaceut. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 150, 233–240.
- Roy, S.; Wu, B.; Liu, W.; Archbold, D.D. Comparative analyses of polyphenolic composition of Fragaria spp. Color mutants. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2018, 125, 255–261.
- Chamorro, M.F.; Reiner, G.; Theoduloz, C.; Ladio, A.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Gómez-Alonso, S.; Jiménez-Aspee, F. Polyphenol composition and (bio)activity of berberis species and wild strawberry from the Argentinean Patagonia. Molecules 2019, 24, 3331.
- Nowicka, A.; Kucharska, A.Z.; Sokół-Łętowska, A.; Fecka, I. Comparison of polyphenol content and antioxidant capacity of strawberry fruit from 90 cultivars of Fragaria × ananassa Duch. Food Chem. 2019, 270, 32–46.
- Wichtl, M. Herbal drugs and phytopharmaceuticals. In A Handbook of Practice on a Scientific Basis; Brinckmann, J.A., Lindenmaier, M.P., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2004; pp. 220–221.
- Saric-Kundalic, B.; Dobes, C.; Klatte-Asselmeyer, V.; Saukel, J. Ethnobotanical study on medicinal use of wild and cultivated plants in middle, south and west Bosnia and Herzegovina. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 33–55.
- Zhu, F. Anthocyanins in cereals: Composition and health effects. Food Res. Int. 2018, 109, 232–249.
- Sinopoli, A.; Calogero, G.; Bartolotta, A. Computational aspects of anthocyanidins and anthocyanins: A review. Food Chem. 2019, 297, 124898.
- Braga, A.R.C.; Murador, D.C.; de Souza Mesquita, L.M.; Rosso, V.V. Bioavailability of anthocyanins: Gaps in knowledge, challenges and future research. J. Food Compos. Anal. 2018, 68, 31–40.
- Zugic, A.; Ðordevic, S.; Arsic, I.; Markovic, G.; Zivkovic, J.; Jovanovic, S.; Tadi, V. Antioxidant activity and phenolic compounds in 10 selected herbs from Vrujci Spa, Serbia. Ind. Crop Prod. 2014, 52, 519–527.
- Dias, M.I.; Barros, L.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Phenolic profile and antioxidant properties of commercial and wild Fragaria vesca L. roots: A comparison between hydromethanolic and aqueous extracts. Ind. Crop Prod. 2015, 63, 125–132.
- Dias, M.I.; Barros, L.; Fernandes, I.P.; Ruphuy, G.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Santos-Buelga, C.; Barreiro, M.F.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. A bioactive formulation based on Fragaria vesca L. vegetative parts: Chemical characterization and application in κ-carrageenan gelatin. J. Funct. Food. 2015, 16, 243–255.
- Sato, T.; Ikeya, Y.; Adachi, S.I.; Yagasaki, K.; Nihei, K.I.; Itoh, N. Extraction of strawberry leaves with supercritical carbon dioxide and entrainers: Antioxidant capacity, total phenolic content, and inhibitory effect on uric acid production of the extract. Food Bioprod. Process 2019, 117, 160–169.
- Giampieri, F.; Alvarez-Suarez, J.M.; Battino, M. Strawberry and human health: Effects beyond antioxidant activity. J. Agricult. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 3867–3876.
- Vendrame, S.; Klimis-Zacas, D.J. Anti-inflammatory effect of anthocyanins via modulation of nuclear factor-κB and mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling cascades. Nutr. Rev. 2015, 73, 348–358.
- Li, S.; Wu, B.; Fu, W.; Reddivari, L. The anti-inflammatory effects of dietary anthocyanins against ulcerative colitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 2588.
- Szymanowska, U.; Złotek, U.; Karaś, M.; Baraniak, B. Anti-inflammatory and antioxidative activity of anthocyanins from purple basil leaves induced by selected abiotic elicitors. Food Chem. 2015, 172, 71–77.
- Peng, Y.; Yan, Y.; Wan, P.; Chen, D.; Ding, Y.; Ran, L.; Mi, J.; Lu, L.; Zhang, Z.; Li, X.; et al. Gut microbiota modulation and anti-inflammatory properties of anthocyanins from the fruits of Lycium ruthenicum Murray in dextran sodium sulfate-induced colitis in mice. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 136, 96–108.
- Liberal, J.; Francisco, V.; Costa, G.; Figueirinha, A.; Amaral, M.T.; Marques, C.; Girão, H.; Lopes, M.C.; Cruz, M.T.; Batista, M.T. Bioactivity of Fragaria vesca leaves through inflammation, proteasome and autophagy modulation. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 158, 113–122.
- Gomes, F.; Martins, N.; Barros, L.; Rodrigues, M.E.; Oliveira, M.B.P.P.; Henriques, M.; Ferreira, I.C.F.R. Plant phenolic extracts as an effective strategy to control Staphylococcus aureus, the dairy industry pathogen. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 112, 515–520.
- Cardoso, O.; Donato, M.M.; Luxo, C.; Almeida, N.; Liberal, J.; Figueirinha, A.; Batista, M.T. Anti-Helicobacter pylori potential of Agrimonia eupatoria L. and Fragaria vesca. J. Funct. Food. 2018, 44, 299–303.
- Ninomiya, M.; Itoh, T.; Ishikawa, S.; Saiki, M.; Narumiya, K.; Yasuda, M.; Koshikawa, K.; Nozawa, Y.; Koketsu, M. Phenolic constituents isolated from Fragaria ananassa Duch. Inhibit antigen-stimulated degranulation through direct inhibition of spleen tyrosine kinase activation. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2010, 18, 5932–5937.
- Abdulazeez, S.S. Effects of freeze-dried Fragaria x ananassa powder on alloxan-induced diabetic complications in Wistar rats. J. Taibah Univ. Med. Sci. 2014, 9, 268–273.
- Kanodia, L.; Borgohain, M.; Das, S. Effect of fruit extract of Fragaria vesca L. on experimentally induced inflammatory bowel disease in albino rats. Indian. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 43, 18–21.
- Gasparrini, M.; Giampieri, F.; Forbes-Hernandez, T.Y.; Afrin, S.; Cianciosi, D.; Reboredo-Rodriguez, P.; Varela-Lopez, A.; Zhang, J.; Quiles, J.L.; Mezzetti, B.; et al. Strawberry extracts efficiently counteract inflammatory stress induced by the endotoxin lipopolysaccharide in Human Dermal Fibroblast. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2018, 114, 128–140.
- Molinett, S.; Nuñez, F.; Moya-León, M.A.; Zúñiga-Hernández, J. Chilean strawberry consumption protects against LPS-induced liver injury by anti-inflammatory and antioxidant capability in Sprague-Dawley rats. Evid.-Based Compl. Alt. Med. 2015, 2015, 320136.
- Duarte, L.J.; Chaves, V.C.; dos Santos Nascimento, M.V.P.; Calvete, E.; Li, M.; Ciraolo, E.; Ghigo, A.; Hirsch, E.; Simões, C.M.O.; Reginatto, F.H.; et al. Molecular mechanism of action of Pelargonidin-3-O-glucoside, the main anthocyanin responsible for the anti-inflammatory effect of strawberry fruits. Food Chem. 2018, 247, 56–65.
- Van de Velde, F.; Esposito, D.; Grace, M.H.; Pirovani, M.E.; Lila, M.A. Anti-inflammatory and wound healing properties of polyphenolic extracts from strawberry and blackberry fruits. Food Res. Int. 2019, 121, 453–462.
- Somasagara, R.R.; Hegde, M.; Chiruvella, K.K.; Musini, A.; Choudhary, B.; Raghavan, S.C. Extracts of strawberry fruits induce intrinsic pathway of apoptosis in breast cancer cells and inhibits tumor progression in mice. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, 47021.
- Forni, C.; Braglia, R.; Mulinacci, N.; Urbani, A.; Ronci, M.; Gismondi, A.; Tabolacci, C.; Provenzano, B.; Lentini, A.; Beninati, S. Antineoplastic activity of strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa Duch.) crude extracts on B16-F10 melanoma cells. Mol. Biosyst. 2014, 10, 1255–1263.
- Shi, N.; Clinton, S.K.; Liu, Z.; Wang, Y.; Riedl, K.M.; Schwartz, S.J.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Z.; Chen, T. Strawberry phytochemicals inhibit azoxymethane/dextran sodium sulfate-induced colorectal carcinogenesis in Crj: CD-1 mice. Nutrients 2015, 7, 1696–1715.
- Lucioli, S.; Pastorino, F.; Nota, P.; Ballan, G.; Frattarelli, A.; Fabbri, A.; Forni, C.; Caboni, E. Extracts from cell suspension cultures of strawberry (Fragaria x ananassa Duch): Cytotoxic effects on human cancer cells. Molecules 2019, 24, 1738.
