Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Luis Puig and Version 3 by Conner Chen.
The interleukin-1 (IL-1) family is involved in the correct functioning and regulation of the innate immune system, linking innate and adaptative immune responses. This complex family is composed by several cytokines, receptors, and co-receptors, all working in a balanced way to maintain homeostasis.
- IL-36
- IL-36R
- IL-1
- IL-33
- pathogenesis
1. Introduction
The interleukin-1 (IL-1) family members are central players of the immune system. They are especially involved in the regulation of innate immune responses, maintaining endogenous hemostasis, and linking innate and adaptive responses. Several cytokines, receptors, and accessory proteins constitute this complex family; their activation and expression are balanced by different regulatory mechanisms, and their disturbance results in pathologic inflammatory responses. Disruption of IL-1-related pathways is involved in several inflammatory dermatoses such as psoriasis, hidradenitis suppurativa (HS), atopic dermatitis (AD), as well as several neutrophilic dermatoses.
2. IL-1 Family Cytokines, Receptors and Co-Receptors
The IL-1 family of cytokines is composed of 11 cytokine members, with seven agonists (IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-18, IL-33, IL-36α, IL-36β, and IL-36γ) and four antagonists (IL-1 receptor antagonist (Ra), IL-36Ra, IL-37, and IL-38) [1]. According to their structural and functional characteristics, these cytokines are further classified into four subfamilies (IL-1, IL-18, IL-33, and IL-36), each one having a cognate receptor (IL-1R1, IL-18Rα, IL-33R (suppression of tumorigenicity 2 or ST2), and IL-36R, respectively). Furthermore, IL-1RAcP is an accessory protein shared by all these cytokines, with the exception of IL-18 (IL-18RAcP or IL-18Rβ chain) (Table 1) [2].Table 1.
IL-1 family cytokine members
.
| Cytokines | Receptors (Other Names) | Co-Receptors (Other Names) | Function | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-1 | IL-1α | IL-1R1 | IL-1RAcP (IL1-R3) | Pro-inflammatory |
| IL-1β | IL-1R2 | |||
| IL-1Ra | IL-1R1 | N/A | Antagonist | |
| IL-18 | IL-18Rα (IL1-R5) | IL-18Rβ (IL-18RAcP or IL1R7) | Pro-inflammatory | |
| IL-33 | ST2 (IL-33R or IL1-R4) | IL-1RAcP | Pro-inflammatory Th2 responses | |
| IL-36 | IL-36α | IL-36R (IL-1Rrp2 or IL-R6) | IL-1RAcP (IL1-R3) | Pro-inflammatory |
| IL-36β | ||||
| IL-36γ | ||||
| IL-36Ra | IL-36R (IL-1Rrp2 or IL-R6) | N/A | Antagonist | |
| IL-37 | IL-18Rα (IL1-R5) | IL-1R8 (SIGIRR or TIR8) | Antagonist | |
| IL-38 | IL-36R (IL-1Rrp2 or IL1-R6) IL-R9 | IL1RAPL1 (TIGIRR-2) IL1RAPL2 (TIGIRR-1) | Antagonist/anti-inflammatory | |
SIGIRR: single immunoglobulin IL-1R-related molecule; TIR: toll-IL1R; IL1RAPL1 and IL1RAPL2: IL-1 receptor accessory protein like 1 and 2; TIGIRR 1 and 2: three immunoglobulin domain-containing IL-1 receptor-related 1 and 2.
To produce their pro-inflammatory functions, IL-1 cytokines form complexes with their respective receptor and a co-receptor (Figure 1). All of them except IL-1Ra are synthesized as precursors and require N-terminal processing in order to acquire their full function [3][4][3,4]. They can be activated both extracellularly by proteolytic cleavage and intracellularly via inflammasome-mediated cleavage [5]. Binding of cleaved IL-1α/β to the extracellular domain of IL-1R1 leads to recruitment of IL-1RAcP, resulting in the initiation of a signaling cascade with the recruitment of the myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) accessory protein and Interleukin 1 receptor-associated kinases (IRAKs). This in turn results in activation of the nuclear factor κB (NF-κB) and mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs), ultimately resulting in pro-inflammatory gene expression [6]. Furthermore, IL-1 signaling also induces activation of defense mechanisms (antigen recognition, phagocytosis, degranulation, and nitric oxide production) and activates lymphocyte functions implicated in adaptive immunity, thus acting as a link between innate and adaptive immune responses [7]. The other IL-1 family cytokines IL-33, IL-18, and IL-36α/β/γ form similar ternary complexes with their respective receptors and co-receptors and also act through Myd88 to induce pro-inflammatory gene expression.
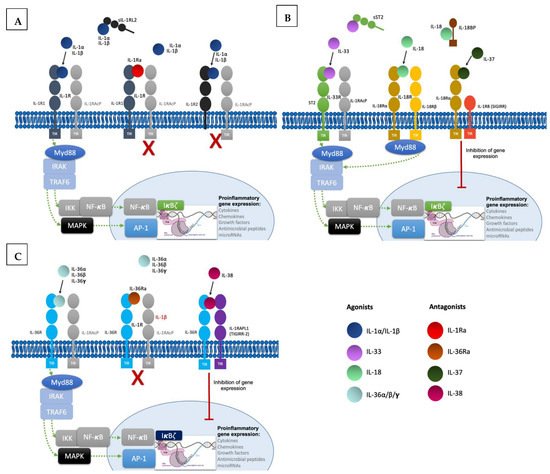 Regulatory mechanisms are necessary to maintain homeostasis; they include decoy receptors, receptor antagonists, and anti-inflammatory cytokines (Figure 1). IL-1R2 is a cytoplasmic soluble receptor without a functional TIR domain that binds to IL-1α/β precursors, preventing their processing and secretion. Under proinflammatory conditions, IL-1R2 is cleaved by an inflammasome-dependent mechanism [8][9][8,9]. Likewise, the soluble ST2 receptor (sST2) and the soluble protein IL-18 binding protein (IL-18BP) bind to IL-33 and IL-18, respectively, neutralizing their activities [10][11][10,11]. Furthermore, receptor antagonists IL-1Ra, IL-36Ra, and IL-38 compete with IL-1α/β and IL-36α/β/γ [4]. Lastly, IL-37 binding to IL-18Rα leads to recruitment of the IL-1R8 co-receptor (also called single immunoglobulin IL-1R-related molecule (SIGIRR), with activation of the inhibitory STAT3 signaling pathway [12].
Regulatory mechanisms are necessary to maintain homeostasis; they include decoy receptors, receptor antagonists, and anti-inflammatory cytokines (Figure 1). IL-1R2 is a cytoplasmic soluble receptor without a functional TIR domain that binds to IL-1α/β precursors, preventing their processing and secretion. Under proinflammatory conditions, IL-1R2 is cleaved by an inflammasome-dependent mechanism [8][9][8,9]. Likewise, the soluble ST2 receptor (sST2) and the soluble protein IL-18 binding protein (IL-18BP) bind to IL-33 and IL-18, respectively, neutralizing their activities [10][11][10,11]. Furthermore, receptor antagonists IL-1Ra, IL-36Ra, and IL-38 compete with IL-1α/β and IL-36α/β/γ [4]. Lastly, IL-37 binding to IL-18Rα leads to recruitment of the IL-1R8 co-receptor (also called single immunoglobulin IL-1R-related molecule (SIGIRR), with activation of the inhibitory STAT3 signaling pathway [12].

Figure 1. Signaling pathways and regulatory mechanisms involved in the IL-1 family. (A). Upon binding of IL-1α and IL-β to their receptor IL-1R1 altogether with co-receptor IL-1RAcP, induction of signal transduction with recruitment of myeloid differentiation primary response 88 (MyD88) accessory protein and IL-1R associated kinase (IRAK) proteins, ultimately ending in the activation of the transcription factor nuclear factor κB (NF- κB) and the transcription of proinflammatory genes. Regulatory mechanisms include IL-1R2 and IL-1Ra: IL-1R2 can exist as a soluble receptor or membrane bound, acting as a decoy receptor as it is unable to recruit the co-receptor to induce signal transduction. Finally, IL-1Ra acts as a competitive inhibitor by binding to IL-1R1. (B). Likewise, IL-33 binds to the receptor ST2, inducing the recruitment of co-receptor IL-1RAcP and resulting in signal transduction into the nucleus with transcription of proinflammatory genes. In this family, the soluble form of ST2 also acts as a decoy receptor. IL-18 binds to IL-18Rα and recruits the co-receptor IL-18Rβ resulting in pro-inflammatory signaling. IL-18 binds to the soluble protein IL-18BP preventing binding to the receptor. IL-37 is an anti-inflammatory cytokine and upon binding to IL-18Rα induces recruitment of the Single Ig and TIR Domain Containing (SIGIRR or IL-1R8), ultimately producing inhibitory signaling. (C). IL-36 cytokines also induce pro-inflammatory gene transcription by binding to the receptor IL-36R and recruiting co-receptor IL-1RAcP. IL-36Ra is the competitive antagonist of IL-36 cytokines. The anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-38 forms a complex with IL-36R and three immunoglobulin domain-containing IL-1 receptor-related 2 (TIGIRR-2 or IL1RAPL1), also inducing inhibitory signaling to regulate the pro-inflammatory gene activation.
