Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Peipei Wang and Version 1 by Peipei Wang.
海洋微生物独特的生存环境赋予它们产生具有多种生物活性的新型化合物的潜力。胞外多糖(The unique living environment of marine microorganisms endows them with the potential to produce novel compounds with diverse biological activities. Exopolysaccharide (EPS)是一种高分子量碳水化合物聚合物,由微生物在生长和代谢过程中分泌。EPS复杂多样的结构赋予了它们独特的生物活性和功能。) is a high molecular weight carbohydrate polymer secreted by microorganisms during growth and metabolism. The complex and diverse structures of EPS endow them with unique biological activities and functions.
- exopolysaccharides
- marine
- antioxidant activity
一、简介1. Introduction
海洋微生物The structure of marine microbial EPS的结构复杂多样 is complex and diverse [ 101 ],与多种生物活性有关,如抗菌、抗氧化、抗癌、抗冻、抗炎、增强免疫活性和血压、降脂等。, which is related to various biological activities, such as antibacterial, antioxidant, anticancer, antifreeze, anti-inflammatory, enhancing immune activity and blood pressure, lipid lowering, etc. [ 102、 , 103、104、, 104, 105 ]。 . _ _ _ _ _ 此外,由于海洋微生物环境的特殊性,海洋微生物生产的In addition, due to the particularity of the marine microbial environment, EPS在海洋生态环境中也具有潜在的应用价值。在这里,我们主要介绍了海洋微生物EPS的抗氧化活性、抗癌活性、抗感染活性和免疫增强生物活性( produced by marine microorganisms also has potential application value in the marine ecological environment. Here, we mainly introduce the antioxidant activity, anticancer activity, anti-infection activity, and immune-enhancing biological activity of marine microbial EPS ( 如图 as shown in Figure 1所示) ) 及其在生物修复和碳封存中的潜在应用。and its potential applications in bioremediation and carbon sequestration.
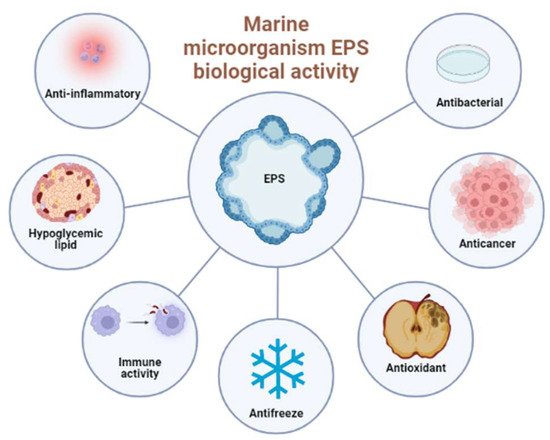
图Figure 1. 海洋微生物 EPS 的主要生物活性。Main biological activities of marine microbial EPS.
2. 抗氧化活性Antioxidant activity
氧气是好氧生物正常生命代谢的关键物质Oxygen is a key substance for the normal life metabolism of aerobic organisms [ 106 ]。在生物体的新陈代谢中,生物体不可避免地会产生活性氧(. In the metabolism of organisms, the organisms inevitably generate reactive oxygen species (ROS)) [ 107 ]。高水平的. High levels of ROS 可能会破坏生物体内的促氧化剂/抗氧化剂平衡,导致氧化应激may disrupt the pro-oxidant/antioxidant balance in organisms, leading to oxidative stress [ 108 ];过量的; excess ROS 会破坏人体细胞中脂质、蛋白质和 DNA 的正常功能,从而诱发各种疾病 can disrupt the normal function of lipids, proteins, and DNA in human cells, thereby inducing various diseases [ 109 ]。多项证据证明,抗氧化剂在保护人类免受与不同类型氧化损伤相关的癌症、糖尿病、心血管疾病和神经退行性疾病方面发挥着重要作用 ]. Multiple lines of evidence demonstrate that antioxidants play an important role in protecting humans from cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and neurodegenerative diseases associated with different types of oxidative damage [ 110 , 111 , 112 ].
海洋细菌的EPS通常具有很强的抗氧化活性,这与EPS的结构特征有关,包括硫酸盐含量及其结合位点、单糖残基和糖苷键 from marine bacteria generally has strong antioxidant activity, which is related to the structural features of EPS, including sulfate content and its binding sites, monosaccharide residues, and glycosidic bonds [ 13 ]。海洋细菌. Marine bacterial EPS 通常有助于生物膜的形成,从而适应极端环境,例如高盐度、低温和高渗透压often contributes to the formation of biofilms, which adapt to extreme environments, such as high salinity , low temperature, and high osmotic pressure [ 113、,114、,115 ]。例如, . For example, AEPS of Rhodella reticulata的 has a stronger scavenging ability for superoxide anion than the standard AEPS 对超氧阴离子的清除能力强于标准抗氧化剂 α-生育酚antioxidant α-tocopherol [ 116 ]。从北极海洋极杆菌中分离出的. EPS sp。 isolated from Polaris marine arcticum. SM1127具有良好的抗氧化能力。抗氧化能力明显高于化妆品中常见的自由基清除粘合剂透明质酸( has good antioxidant capacity. The antioxidant capacity is significantly higher than that of hyaluronic acid (HA),这表明该EPS在未来化妆品抗氧化领域具有良好的应用前景), a common free radical scavenging binder in cosmetics, which indicates that this EPS has a good application prospect in the field of cosmetic antioxidants in the future [ 59 ]。此外,. In addition, SM1127可以去除伤口感染和炎症产生的多余活性氧,从而加速伤口愈合。因此,这种 EPS 很可能用于加速冻伤、烧伤和其他伤口的愈合 can remove excess reactive oxygen species produced by wound infection and inflammation, thereby accelerating wound healing. Therefore, this EPS is likely to be used to accelerate the healing of frostbite, burns and other wounds [ 60 ]。吴等人。报道了由. Wu et al. reported that the marine bacterium EPS EPS27 produced by P. stutzeri 273产生的海洋细菌 EPS had EPS2a good hydroxyl radical scavenging rate, up to 7 具有良好的羟基自由基清除率,当 EPS 浓度为0% when the EPS concentration was 60 μg/mL 时可达 70%。因此,EPS27具有良好的抗氧化活性,在食品和保健领域具有潜在的应用前景. Therefore, EPS27 has good antioxidant activity and has potential applications in food and health care fields [ 49 ]。皮肤是人体最大的器官,皮肤伤口愈合是一个重要的临床问题. The skin is the largest organ of the human body, and skin wound healing is an important clinical problem [ 117、, 118、, 119 ]。由于合成药物具有很高的副作用风险,例如过敏和耐药性, . Since synthetic drugs carry a high risk of side effects, such as allergy and drug resistance, natural products such as EPS 等天然产物变得越来越重要,并被强烈推荐作为伤口愈合的替代药物。are becoming increasingly important and are strongly recommended as alternative medicines for wound healing.
抗氧化剂的另一个来源是海洋真菌产生的Another source of antioxidants is EPS。王等人。从海洋真菌 白曲霉中发现了一种新的细胞外多糖( produced by marine fungi. Wang et al. A novel extracellular polysaccharide (YSS)), consisting of Man and Gal units with a molecular weight of ,它由分子量为18.6 kDa的Man和Gal单元组成[, was discovered from the marine fungus Aspergillus kawachi [ 85 ]。. YSS对DPPH自由基有很强的清除能力,EC50为 has a strong scavenging ability to DPPH free radical with EC50 of 2.8 mg/mL。陈等人。据报道,海洋真菌. Chen et al. It has been reported that the marine fungus 尖孢镰刀菌产生了一种新型的含呋喃半乳糖的 Fusarium oxysporum produces a novel galactofuranos-containing EPS Fw-1,主要由, mainly composed of Gal、Glc和Man组成,分子量为, Glc and Man, with a molecular weight of 61.2 kDa [ 83 ]。Fw-1对羟基和超氧自由基清除的EC50分别为1.1和2.0 The EC50 of Fw-1 for hydroxyl and superoxide radical scavenging was 1.1 and 2.0 mg/mL, respectively, which was greater than that of the EPS A. mg/mL,大于从海洋中分离出来的名为AVP的EPS 杂色曲霉 versicolor LCJ-5-4(EC named AVP isolated from the ocean ( EC50 为of 4.0 mg/mL)。从海洋真菌中提取的抗氧化剂EPS单糖组成相对简单,分子量较小,更适合研究海洋多糖结构与抗氧化剂的关系 ). The antioxidant EPS monosaccharide extracted from marine fungi is relatively simple in composition and small in molecular weight, which is more suitable for studying the relationship between marine polysaccharide structure and antioxidants [ 80 , 120 ]。.
流行病学调查证明,抗氧化剂的利用与降低患心血管疾病和癌症等常见慢性疾病的风险之间存在很强的相关性。与很多关于海洋微生物Epidemiological investigations have demonstrated a strong correlation between antioxidant utilization and reduced risk of common chronic diseases such as cardiovascular disease and cancer. Compared with many reports on the antioxidant activity of marine microbial EPS抗氧化活性的报道相比,关于海洋微生物EPS的分离纯化和结构分析的报道较少。有必要深入研究它们的构效关系。, there are few reports on the isolation, purification and structural analysis of marine microbial EPS. It is necessary to study their structure-activity relationship in depth.
3. 抗癌活动Anticancer activity
现在,正在积极研究具有潜在抗癌作用的无毒天然物质的新来源Now, new sources of nontoxic natural substances with potential anticancer effects are being actively researched [ 121 ]。在过去的十年中,人们对开发抗癌多糖药物产生了极大的兴趣。海洋微生物具有独特的代谢和生理能力,使它们能够产生各种生物化合物. In the past decade, there has been great interest in developing anticancer polysaccharide drugs. Marine microorganisms have unique metabolic and physiological capabilities that enable them to produce various biological compounds [ 122、123、122, 123, 124 ],例如 , such as EPS 。据报道,几种海洋微生物. Several marine microbial EPS have been 通过线粒体功能障碍、抑制细胞增殖或调节免疫系统而具有抗癌活性reported to have anticancer activity through mitochondrial dysfunction, inhibition of cell proliferation, or modulation of the immune system [ 42 , 58 , 94 , 125 , 126 , 127 , 128 ]。松田等人。研究了海洋. Matsuda et al. investigated marine 假单胞菌 Pseudomonas 多糖polysaccharide B1,发现它可以诱导U937细胞凋亡 and found that it could induce apoptosis in U937 cells [ 128 ]。陈等人。据报道,南极细菌 . Chen et al. The Antarctic bacterium Pseudoaltermonas sp。 has been reported . S-5 产生一种杂胞外多糖(称为 PEP),可显着抑制人白血病细胞produces a hetero-exopolysaccharide (called PEP) that significantly inhibits the growth of human leukemia cell K562 的生长 [ 58 ]。此外,. Additionally, Ramamoorthy Sathishkumar 等人。发现来自海鞘共生细菌 et al. Discovery of EPS from ascidian symbiotic 苏云金芽孢杆菌的 Bacillus EPSthuringiensis 在体外具有良好的抗癌活性。与正常It has good anticancer activity in vitro. Compared to normal Vero 细胞相比,这种多糖对癌细胞系cells, this polysaccharide showed potential cytotoxicity against cancer cell lines A549 和and HEP-2 显示出潜在的细胞毒性。EPS对两种癌细胞系的抑制率均呈剂量依赖性增加. The inhibitory rate of EPS on both cancer cell lines increased in a dose-dependent manner [ 42 ]。由链格孢菌生产的. AS2-1 produced by Alternaria . The growth 。还可以以浓度依赖性方式抑制of Hela、, HL-60 和and K562 细胞的生长cells can also be inhibited in a concentration-dependent manner [ 84 ]。海洋细菌胞外多糖. The marine bacterial exopolysaccharide EPS11能有效抑制肝癌细胞的粘附、迁移和侵袭;这种潜在的靶蛋白和分子机制首先通过靶向 I 型胶原蛋白的 β 1-整合素信号通路进行了探索 can effectively inhibit the adhesion, migration and invasion of hepatoma cells; this potential target protein and molecular mechanism were first explored by targeting the β1-integrin signaling pathway of type I collagen [ 126 ]。最近,一项研究表明,新分离的海洋细菌 EPS 可以通过影响关键的凋亡因子和激活 toll 样受体 (TLR . Recently, a study showed that newly isolated marine bacterial EPS could enhance the antitumor activity of HepG2 cells by affecting key apoptotic factors and activating toll-like receptors (TLRs) [ 129 ]. Other ]studies have shown 来增强 HepG2 细胞的抗肿瘤活性。其他研究表明,EPS 的化学修饰,如乙酰化、羧甲基化和磺化,也可以增强其生物活性that chemical modifications of EPS, such as acetylation, carboxymethylation, and sulfonation, can also enhance its biological activity [ 130 , 131 ],进而增强其抗癌活性。马扎等人。证实了两种多糖, which in turn enhances its anticancer activity. Maza et al. Two polysaccharides, EPS-DR和 and EPS-DRS可以与钪形成复合物,并且这些复合物显示出多种生物活性,尤其是在癌细胞中的抗增殖特性。, were demonstrated to form complexes with scandium, and these complexes displayed various biological activities, especially antiproliferative properties in cancer cells.
4. 抗传染病Anti-infectious disease
EPS 在对抗传染病方面也发挥着重要作用。大量研究表明,海洋微生物also plays an important role in fighting infectious diseases. Numerous studies have shown that the immunological and antiviral activities of marine microbial EPS的免疫活性和抗病毒活性在抑制某些流感病毒和细菌方面具有潜在价值 have potential value in inhibiting certain influenza viruses and bacteria [ 132 ]。. EPS作为一种强效抗菌剂,主要通过抑制生物膜形成来抑制细菌生长。米赫利德 H 等人。报道了, as a potent antibacterial agent, mainly inhibits bacterial growth by inhibiting biofilm formation. Mihlid H et al. Enterobacteriaceae are reported 肠杆菌 属。来自沙特阿拉伯Tabuk地区的. ACD2 EPS对 from Tabuk region of Saudi Arabia 大肠杆菌 showed some inhibitory effect on Escherichia coli 和and 金黄色葡萄球菌有一定的抑制作用 [ Staphylococcus aureus [ 48 ]。. Durairajan Rubini 等人。报道了一种海洋多糖,具有良好的抗菌活性和对泌尿致病et al. reported a marine polysaccharide with good antibacterial activity and 性大肠杆菌的强抑制作用 strong inhibitory effect against uropathogenic Escherichia coli (UPEC),为治疗尿路感染提供了一种无抗生素的方法, providing an antibiotic-free approach for the treatment of urinary tract infections [ 133 ]。同样,吴等人。据报道,来自海洋细菌. Similarly, Wu et al. The exopolysaccharide EPS273 from the culture supernatant of the marine bacterium P. stutzeri 273 was reported to inhibi 273 培养上清液的胞外多糖 EPS273 通过抗生物膜活性抑制铜绿假单胞菌t P. aeruginosa via anti-biofilm activity [ 49 ]。它不仅对动物细菌有效,对植物细菌也有效。. It is not only effective against animal bacteria but also plant bacteria. Marwa Drira 等人。发现 et al. EPS produced by Porphyridium sordidum产生的 was EPS 导致植物对真菌生长的控制,EPS 可以作为诱导剂增强拟南芥对found to lead to plant control of fungal growth, and EPS could act as an inducer to enhance the resistance of Arabidopsis to 尖孢镰刀菌的抗性 Fusarium oxysporum [ 24 ]。此外,来自 Porphyr. In addidtium的硫酸化on, sulfated EPS from sp。已显示对疱疹病毒( Porphyridium sp. Antiviral effects have been shown against herpesviruses (HSV-1 和and HSV-2)的抗病毒作用) [ 134 , 134,135 ] ]。.
5. 免疫调节活性Immunomodulatory activity
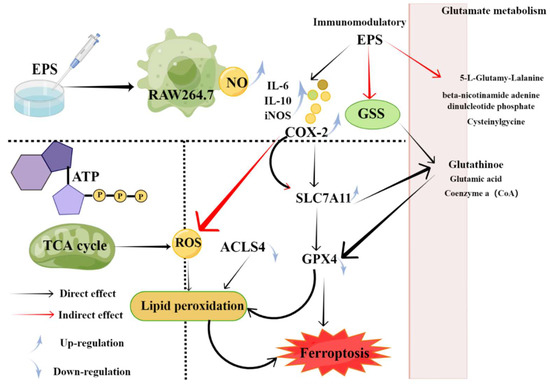
免疫系统的主要功能是识别和消除病原体,以维持生理平衡和稳定The main function of the immune system is to recognize and eliminate pathogens to maintain physiological balance and stability [ 136 ]。当免疫力受损时,会导致各种不良免疫反应. When immunity is compromised, various adverse immune responses result [ 137 ]。海洋微生物合成的几种. Several EPS具有免疫调节活性[s synthesized by marine microorganisms have immunomodulatory activities [ 45, 60, 61, 74, 138, 139, 45、60、61、74、138、139、1440 ]. 。_ 例如,一种名为For example, an EPS called EPS2E1 was extracted 的 EPS 是从海洋from the marine Halomonas sp. 中提取的。并显示出良好的免疫增强活性,主要是通过激活And showed good immune-enhancing activity, mainly by activating MAPK 和and NF-κB 途径pathways [ 56 ]。. Soumya Chatterjee 等人。报道了鞘氨醇杆菌,一种来自北极鞘氨醇杆菌的新et al. reported Sphingobacter sp., a new α-甘露聚糖mannan EPS 。 from Sphingobacter arcticum. IITKGP-BTPF3 显着降低了 LPS 诱导的巨噬细胞的 NO 产生。这些结果表明,鞘氨醇对体外巨噬细胞的抗炎作用具有潜在的激活作用significantly reduced LPS-induced NO production in macrophages. These results suggest that sphingosine has a potential activating effect on the anti-inflammatory effects of macrophages in vitro [ 57 ]。一方面,有证据表明,海洋微生物. On the one hand, there is evidence that marine microbial EPS可诱导细胞因子的表达,如白细胞介素(IL)、肿瘤坏死因子(IF-α)和干扰素 can induce the expression of cytokines, such as interleukin (IL), tumor necrosis factor (IF-α), and interferon [ 141 ]。此外,. Additionally, Adriana 等人。报道称, et al. It has been reported that EPS-1 可通过引发有利于 Th1 亚群的极化,从而有助于改善 PBMCmay help improve immune surveillance of PBMCs against viral infection by inducing polarization in favor of Th1 subsets. 对病毒感染的免疫监视。地衣芽孢杆菌生产的Bacillus licheniformisProduced EPS-1 可诱导细胞因子的产生以增强免疫调节 induces cytokine production to enhance immune regulation [ 138 ]。它主要促进巨噬细胞分泌在. It mainly promotes macrophage secretion of mediators and enzymes, RAW264.7 巨噬细胞中发挥重要介导炎症和组织修复作用的介质和酶,如 NO、COX-2、IL-1、IL-6 和such as NO, COX-2, IL-1, IL-6 and TNF-α。, which play an important role in mediating inflammation and tissue repair in RAW264.7 macrophages. 142、, 143、144、, 144, 145 ]。 . _ _ _ _ _ YCP, 是一种来自海洋丝状真菌a native EPS derived from the mycelium of the marine filamentous fungus Phoma herbarum YS4108 YS4108, 菌丝体的天然 EPS,可与binds to TLR-2 和and TLR-4 结合,并通过表现出由 T 细胞和树突状细胞 (DC) 介导的特定免疫调节能力而具有巨大的抗肿瘤潜力。, and is expressed by T cells and dendritic cells (DC) It has great antitumor potential due to specific immunomodulatory ability mediated. 146 ]. 。最近,从海洋Recently, a novel EPS (AUM-1) SCAU-266 was obtained from marine Aureobasidium melanogenum中获得了一种新型 with potential effects EPS (AUM-1) SCAU-266,对on ferroptosis-related immunomodulatory properties in RAW264.7 细胞中与铁死亡相关的免疫调节特性具有潜在影响。机理研究表明,由于谷氨酸代谢和TCA循环的活性氧水平较高,它可以调节GPX4的表达,调节谷胱甘肽(氧化),直接引起脂质过氧化(图cells. Mechanistic studies have shown that due to higher levels of reactive oxygen species in glutamate metabolism and TCA cycle, it can regulate the expression of GPX4, regulate glutathione (oxidation), and directly cause lipid peroxidation ( Figure 2) ) [ 74 ]。.