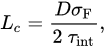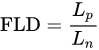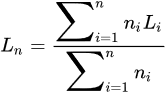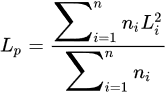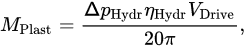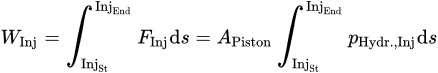1. Phenolic Molding Compounds and Their Applications
Phenolic resins are versatile polymers that are used in a variety of industrial and consumer applications. For example, they are used as binding systems for wood composites, paper, abrasives, and friction materials
[1]. They also serve as matrix systems in fiber-reinforced composite materials, such as continuous fiber-reinforced laminates
[2], long fiber-reinforced compression molding materials
[3], and short fiber-reinforced injection molding compounds
[4].
Typical applications for phenolic molding compounds that are established in the state of the art are oil pump housings, intake manifolds, valve blocks
[4][5][4,5], and other small automotive parts, for example in the air condition systems
[6] or turbochargers
[7]. In these applications, the beneficial properties of the phenolic resin, such as high heat resistance, chemical resistance, and an overall excellent dimensional accuracy and stability come into play. Usually, the mechanical strength of the material plays a subordinate role for these parts. In the latest developments, phenolic molding compounds are used in electric motors
[8][9][10][8,9,10], larger parts in combustion engines (such as camshaft modules)
[11], and entire parts of crank cases
[12]. In addition to the beneficial properties mentioned above, the mechanical requirements become more important due to the size and the structural nature of such large parts.
The most significant mechanical disadvantage of parts made from phenolic molding compounds are their low elongation at break and their high brittleness compared to thermoplastic polymers
[4]. Long fiber reinforcement is especially beneficial for increasing the impact strength of a fiber-reinforced polymer material. This was proven by Gupta et al.
[13], Thomason and Vlug
[14], Rohde et al.
[15], and Kim et al.
[16] for glass fiber-reinforced polypropylene. Boroson et al.
[17] conducted a study with glass fiber-reinforced phenolic resins with initial fiber length values in the molding compound ranging between
L=3.5 mm and
L=12.7 mm and found out that longer fibers significantly reduce the notch sensitivity during impact testing. However, they did not measure the residual fiber length in the molded part. Based on the literature data, it can be concluded that an attractive development aim is increasing the fiber length in parts manufactured from phenolic molding compounds to improve the impact toughness.
Typically, there are two possibilities for increasing the fiber length in molded parts: First, using a semi-finished material, such as a long fiber granulate; or second, using a direct process in which longer fibers are incorporated into the final part. This decision-making process is a trade-off between the higher material costs of a semi-finished long fiber material and the more complex manufacturing processes of a direct process, most of which also involve a higher capital investment
[18][19][18,19]. For fiber-reinforced thermoplastics, both process routes are well established and are available from multiple material and machinery equipment suppliers. However, in the case of phenolic molding compounds, neither long fiber-reinforced injection molding compounds nor established long fiber injection molding processes exist. Within th
eis research
paper, the development and the validation of a long fiber injection molding process for thermosetting phenolic resins is described.
2. Long Fiber Injection Molding Materials and Processes
Thermoplastic long fiber granulates are available in a variety of different lengths, typically ranging between
s=6 mm and s=25 mm pellet length. Due to the pellet manufacturing process, the maximum initial fiber length, i.e., the fiber length before taking into account any process-induced fiber shortening, is limited to the size of the granulate
[18]. The granulate size, in turn, is limited by the available dosing and feeding technology. For phenolic resin matrix systems, no long fiber granulates designed for injection molding are available on the market today. However, there are long fiber phenolic molding compounds for compression molding applications. They have a plate-like shape and are available in length classes of
5 mm,
12 mm, and
24 mm [20]. For compression molding applications, it is claimed that impact strength values that are 10 … 20 times superior to conventional short fiber phenolic molding
[4], but these values were never reached in injection molding trials by Saalbach et al.
[21] and Raschke
[22].
Several process variants with direct fiber feeding were developed for thermoplastic materials
[19][23][24][25][26][27][28][29][30][31][32][33][19,23,24,25,26,27,28,29,30,31,32,33]. In the injection molding compounder (IMC), a co-rotating twin screw extruder is combined with an injection unit. The process was patented by Putsch
[34] and first industrialized by KraussMaffei Technologies GmbH. Continuous roving strands are pulled into the extruder, which is coupled with the discontinuous injection process using a melt buffer. Besides the increase in fiber length, the main advantage of the inline compounding process is lowering the material costs. Due to the high capital investment costs and the responsibility for the material formulation, it is mostly only used for high-volume applications
[26]. Another inline compounding process was developed by Composite Products, Inc. (CPI). It combines a continuous compounding process with a discontinuous injection process using a melt buffer
[29]. The melting and compounding tasks are divided between two single-screw extruders. In contrast to the IMC process, the melt buffer and the injection unit are combined in one component. By using a check valve in the piston head, the compounding extruder can fill the backside of the piston head during the injection and holding phase. After the holding phase, the material can flow through the check valve to the other side of the piston head.
By conducting the melting and compounding discontinuously, matching the injection molding cycle, no melt buffer is required. This reduces the capital investment costs and makes the direct compounding feasible for lower-volume applications. The direct compounding injection molding (DCIM) process, invented by Exipnos and KraussMaffei Technologies, couples a single screw compounding extruder with a traditional injection molding machine
[30]. In the compounding extruder, the molder can tailor the material according to his needs by adding fibers, fillers, and other additives to the thermoplastic polymer. In the DIF process (direct incorporation of continuous fibers), invented by Truckenmüller at the University of Stuttgart, continuous fibers are directly pulled into the screw of the injection molding machine
[23][25][23,25]. Mixing elements on the injection molding screw are required for obtaining good fiber dispersion. The mechanical properties of the produced samples are comparable to conventional long fiber granulate. Another direct process for the injection molding of long fiber-reinforced thermoplastics was developed by Arburg GmbH & Co. KG in cooperation with SKZ Kunststofftechnik GmbH. In this process, called fiber direct compounding (FDC), the unreinforced thermoplastic granulate is passively pulled into the screw and melted, such as in a conventional injection molding machine
[31][32][33][31,32,33]. In contrast to the DIF process, the continuous fibers are cut to a selectable length of
L=2 mm … 100 mm using a fiber chopper and are fed to the injection molding machine via a twin screw sidefeed. Since the injection molding is a discontinuous process, the fiber feed is coordinated with the screw movement via the machine control system. At the position of the fiber feed, the screw core diameter is reduced to facilitate the incorporation of the fibers.
3. Fiber Shortening and Fiber Length
Using the adhesion between fiber and matrix
τint, the fiber diameter
D, and the tensile strength of the fiber
σF, the critical fiber length
Lc can be calculated according to Equation
[35].
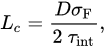
which is considered the minimum fiber length that is required for fully utilizing the reinforcement potential of the fibers. A fiber length L < Lc still leads to a reinforcing effect, but does not fully utilize the available potential. Literature values for the critical fiber length Lc in glass fiber-reinforced phenolic molding compounds vary between Lc=2 mm [36] and Lc=8 mm[37].
During the injection molding process, the fibers are subjected to high mechanical loads, causing fiber damage and breaking. Three distinct mechanisms for fiber shortening are identified
[15][38][39][40][15,38,39,40]. First, fluid–fiber interactions are caused by viscous forces transferred from the polymer matrix into the fibers. For example, Gupta et al.
[41] found in their study on the fiber length reduction of glass fiber-reinforced polypropylene, that a thin polymer film is initially formed on the surface of the screw and barrel wall when the matrix is melted. In this region, fibers that are anchored on one side in solid granulate are exposed to the shear flows of the molten polymer, which can lead to flexural failure of the fibers. According to their calculations, forces can occur that lead to fiber damage by buckling. Second, fiber–fiber interactions can be caused by fiber overlap. The amount of fiber–fiber interactions increases with increasing fiber content and increasing fiber length
[42]. At the junction points of two overlapping fibers, the contact forces cause bending deformation of the fibers, which might lead to fiber breakage. Third, fiber–wall interactions happen at contact locations to machine parts. This is visible by the abrasive wear that can be found on the screw, the barrel, and other machine parts.
Agglomerations and fiber bundles reduce the overall extent of the fiber shortening, resulting in a higher average fiber length compared to well-homogenized parts. Opening the fiber bundles works in the same way as breaking the fibers. Truckenmüller
[43] investigated the opening of fiber bundles in the DIF process and concluded that fiber bundles can be treated as a single fiber with a larger fiber diameter and therefore a smaller
L/D aspect ratio. This underlines the conclusion that fiber bundle opening is not possible without fiber shortening: Once the fiber bundle is opened, the aspect ratio of the individual fiber is significantly larger than the aspect ratio of the bundle from which the fiber originated. If the fluid forces are high enough for opening the fiber bundles, they likely will be high enough for shortening the individual fiber. An indicator for judging the existence of agglomerations and the degree of dispersion quality is the FLD ratio (fiber length distribution) defined by Meyer et al. according to Equation
[44].
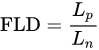
The average fiber length Ln and the weighted average fiber length Lp can be calculated according to Equations. Li is the length of the individual fiber i. The weighted average fiber length is the second moment of the fiber length distribution and is generally considered to be more descriptive because it has a higher emphasis on long fibers [45].
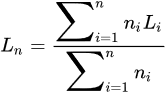
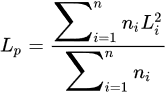
Meyer et al. calculated a theoretical value of FLD=1.44 for a fiber break in the middle due to viscous forces on the fibers. Once this value is reached, no further breakdown of the fibers due to fiber–fluid interactions shall occur.
4. Data Acquisition during the Injection Molding Process
With modern data acquisition technologies, the quantification of energy input into the polymer during plasticization and injection is possible. This is particularly important for reactive thermoset materials, such as phenolic resins. The screw torque during the plasticizing process
MPlast was monitored and analyzed by several
resea
rcheuthors. According to Rauwendaal
[46], it is a good measure to quantify the mechanical power consumed by the extrusion process. For hydraulic injection molding machines, this plasticizing torque is typically calculated by measuring the pressure drop
ΔpHydr over the screw drive according to Equation.
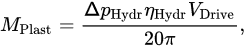
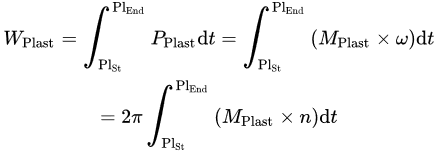
Using the hydraulic efficiency ηHydr and the hydraulic volume of the drive VDrive, Scheffler et al. identified an initial decrease in plasticizing torque with rising moisture content for phenolic molding compounds, followed by an increase towards very high moisture content values [47]. The fundamental softening effect of water in the polymer is the same for thermoplastics and thermosets, which explains the initial decrease in plasticizing torque. However, due to the lack of a non-return valve, further increasing the moisture content leads to a higher backflow during the injection phase for the thermoset molding compounds, and consequently a higher number of fully filled screw flights. In those fully filled screw flights, the molding compound is agitated and mixed during the screw rotation, leading to the rise in plasticizing torque [47]. In general, Scheffler [48] concludes that the plasticizing torque for thermosetting molding compounds is influenced by multiple factors, but has a strong correlation to the backflow during the injection phase. Several researcheuthors [49][50][49,50] used the injection work WPlast, which is the integral of the plasticizing power PPlast, as a measure for the total energy input into the polymer during the plasticization phase, see Equation.
In Equation, MPlast is the plasticizing torque and n is the screw rotational speed. For a standard injection molding process using thermoplastic materials, Kruppa [49] observed an increase in the plasticizing work with increasing screw speed. This increased energy input leads to a stronger shortening of glass fibers, as described by Truckenmüller [43]. With increasing plasticizing work, fiber length asymptotically approaches a threshold value, which appears to be independent of initial fiber length and glass fiber content. A similar approach to quantify the energy input into the material during the injection phase of the process is the calculation of the injection work WInj, which is the integral of the injection force FInj over the injection distance s according to Equation.
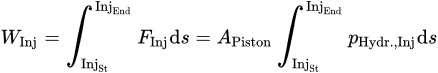
Lucyshyn et al.
[51], as well as Schiffers
[52], use the injection work as a measure for viscosity changes of thermoplastic polymers during the process, e.g., due to a change in moisture content. A higher moisture content leads to a lower viscosity and consequently to a lower injection work. The injection work is also used as a control parameter for the injection process by several
resea
rcheuthors. Woebcken
[53] described a method to compensate for changes in the material and/or the machine and mold setup by adjusting the screw movement during injection to reach a specific, previously defined injection work value. Cavic
[54] used the injection work for judging the reproducibility of the injection molding process. All cited works deal with thermoplastic materials. The usage of the injection work to evaluate the curing state of the material in the thermoset injection molding processes is not yet reported.
As outlined above, no process for the direct feeding of long glass fibers into the injection molding process for thermoset resins in general and for phenolic resins in particular exists in the state of the art. In this Tpaper, the development of such a process is described. An essential part of the process development and a significant addition to the state of the art is the application of a novel screw mixing element for the injection molding of fiber-reinforced phenolic resins. The machine process data are analyzed and used for the process development by calculating the injection and plasticizing work. By means of the structural and mechanical properties of the molded parts, the long fiber injection molding process is evaluated and compared to the state-of-the-art processing of short glass fiber-reinforced phenolic molding compounds.