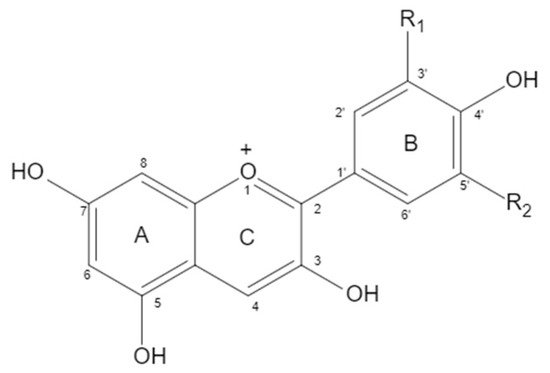
Anthocyanidin is a kind of water-soluble natural pigment that widely exists in natural plants. Like other natural flavonoids, anthocyanin has a 花青素是一种广泛存在于天然植物中的水溶性天然色素。像其他天然类黄酮一样,花青素具有C6-C3-C6 carbon skeleton. Due to the different carbon substituents (-OH, -OCH3) on the B ring, different types of anthocyanins were derived. The six common anthocyanins were Pelargonidin (Pg), Cyanidin (Cy), 碳骨架。由于B环上的碳取代基(-OH,-OCH3)不同,因此衍生出不同类型的花青素。六种常见的花青素是天竺葵素(Pg),花青素(Cy),Delphinidin (Dp), (Dp),Peonidin (Pn), (Pn),Petunidin (Pt), and (Pt)和Malvidin (Mv). In addition to giving food a variety of bright colors, anthocyanin also has important biological activities, such as antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and anti-aging effects, among others. A large number of studies have shown that dietary anthocyanins have a good preventive effect on cardiovascular diseases.(Mv)。花青素除了赋予食物多种鲜艳的色彩外,还具有重要的生物活性,如抗氧化、抗炎、抗衰老等。大量研究表明,膳食花青素对心血管疾病具有良好的预防作用。
1. Structure of Anthocyanin
Anthocyanin is a water-soluble flavanol compound that widely exists in fruits, vegetables, and flowers, such as blueberry, sunflower, grape, pitaya, purple sweet potato, and purple cabbage. It is an extremely important secondary metabolite in plants. The structure of anthocyanin is mainly composed of C6-C3-C6 as the basic C skeleton. The differences between anthocyanin molecules are mainly due to the number of hydroxyl groups, the type and bonding position of sugars, and the type and bonding position of acyl groups of modified sugar molecules. There are six kinds of anthocyanins in plants. When positions 3, 5, and 7 of a and C rings are Oh, anthocyanins are aglycones, mainly including delphinidin (12%), cyanidin (50%), pelargonidin (12%), petunidin (7%), malvidin (7%), and peonidin (12%) (Figure 1 and Table 1). Delphinidin and its derivatives, petunidin and malvidin, are the sources of blue and purple, while cyanidin and pelargonidin are the main pigments of bright red fruits. Under natural conditions, the free anthocyanin is unstable, so it is rare that anthocyanin mainly exists in the form of glycoside. The hydroxyl at positions 3, 5, and 7 of anthocyanin can form anthocyanin through glycosidic bond with one or more monosaccharides (glucose, galactose, etc.), disaccharides (rutinose, etc.), or trisaccharides. Due to the different types, positions, and quantities of sugars that are glycosides of anthocyanin, the types of anthocyanin formed are also different. At present, there are more than 250 known natural anthocyanins.
Figure 1.
Chemical structure of anthocyanins.
2. Physiological Activities of Anthocyanins
2.1. Anti-Cancer
Cancer is a disease caused by uncontrolled growth and progressive development of abnormal cells, killing millions of people every year. By 癌症是由不受控制的生长和异常细胞的逐渐发育引起的疾病,每年杀死数百万人。到2030
, there will be more than 20 million new cancer cases年,将有超过2000万例新的癌症病例。花青素已被证明具有抑制各种癌症的发生,促进和进展的能力,例如结肠癌[6],肝癌和膀胱癌[7],乳腺癌[8],脑癌[9],肾癌和皮肤癌[10],胃癌[11]和甲状腺癌[12]].
Anthocyanins have been shown to have the ability to inhibit the initiation, promotion, and progression of various cancers, such as colon cancer [1], liver and bladder cancer [2], breast cancer [3], brain cancer [4], kidney cancer and skin cancer [5], gastric cancer [6], and thyroid cancer [7]. The ability of anthocyanins to inhibit tumorigenesis and development is closely related to their ability to enhance antioxidant defense花青素抑制肿瘤发生和发展的能力与其增强抗氧化防御的能力密切相关;
exert anti-inflammatory effects发挥抗炎作用;
and interfere with ERK, JNK, 并干扰 ERK、JNK、PI3K/Akt
, MAPK, and、MAPK 和 NF-κB
signaling pathways. Yun et al. reported that purple grape anthocyanins prevented tumor-necrosis-factor-α-induced NF-κB activation by inhibiting IκBα phosphorylation and resisted the invasion of human colon cancer cells in a dose-dependent manner [8]. 信号通路。Yun等人报道,紫葡萄花青素通过抑制IκBα磷酸化来预防肿瘤坏死因子α诱导的NF-κB活化,并以剂量依赖性方式抵抗人结肠癌细胞的侵袭[13]。Fragoso
et al. proved through experiments that cyanidin-3-O-rutinoside at 等人通过实验证明,25
µmol/L can effectively reduce the motility of human colon adenocarcinoma cells, reduce the metastasis of cancer cells, and play an anticancer effect [9]. μmol/L的花青素-3-O-芸香苷可有效降低人结肠腺癌细胞的运动性,减少癌细胞的转移,起到抗癌作用[14]。Mazewski
et al. reported that anthocyanins extracted from purple and red maize enhanced the expression of apoptotic factors 等人报道,从紫色和红玉米中提取的花青素增强凋亡因子BAX
, Bcl-2, cytochrome C, and TRAILR2/D5 and inhibited vascular endothelial growth factor in ,Bcl-2,细胞色素C和TERR2 / D5的表达,并抑制HCT-116
and HT-29 human colorectal cancer cell (Tie-2, 和HT-29人结直肠癌细胞(Tie-2,ANGPT2
, and PLG) expression to achieve anti-cancer efficacy [10]. The results of 和PLG)的血管内皮生长因子表达,以实现抗癌功效[15]。Lage
et al. showed that black sweet cherry anthocyanins can inhibit the growth of breast cancer cells and have no toxicity to normal 等人的结果表明,黑甜樱桃花青素可以抑制乳腺癌细胞的生长,对正常的MCF-10A
breast cells. Anthocyanins work against cancer by reducing oxidative stress, regulation of Akt/mTOR, p38, and survivin, preventing cancer cell proliferation and promoting apoptosis. Anthocyanins can significantly downregulate the mRNA expression of invasive/metastatic biomarkers (Sp1, Sp4, 乳腺细胞没有毒性。花青素通过减少氧化应激,调节Akt / mTOR,p38和生存素,防止癌细胞增殖和促进细胞凋亡来对抗癌症。花青素可以显着下调侵入性/转移性生物标志物(Sp1,Sp4,VCAM-1
), and anthocyanins from black sweet cherry can effectively prevent and treat cancer [3]. )的mRNA表达,来自黑甜樱桃的花青素可以有效预防和治疗癌症[8]。Su
et al. reported that hibiscus calyx anthocyanin could inhibit the growth, metastasis, and angiogenesis of B16-F1 cells by triggering 等人报道,芙蓉花青素通过触发PI3K/Akt
and 和Ras/MAPK
signaling pathways and downregulating the expression of VEGF and 信号通路,下调VEGF和MMP-2/-9
, which could effectively prevent and treat melanoma cancer [11]. 的表达,抑制B16-F1细胞的生长、转移和血管生成,有效预防和治疗黑色素瘤[16]。Sugata
et al. found that 等人发现,紫甘薯花青素通过作用于细胞周期调节剂(如p
urple sweet potato anthocyanin blocked all stages of cell cycle by acting on cell cycle regulators (such as p53, p21, p27, 53,p21,p27,Cyclin D1
, and 和Cyclin A
), thereby inhibiting the proliferation of breast cancer, colon cancer, and gastric cancer cells in a concentration- and time-dependent manner [12].)来阻断细胞周期的所有阶段,从而以浓度和时间依赖性的方式抑制乳腺癌,结肠癌和胃癌细胞的增殖[17]。
2.2. Anti-Inflammatory
抗炎药
Inflammation is usually regulated by the body to secrete inflammatory cytokines and mediators. Therefore, it is generally believed that the downregulation of factor secretion may contribute to the treatment of diseases such as inflammation [13]. Epidemiology and research have shown that anthocyanin has an anti-inflammatory effect and can improve a variety of inflammation-related diseases, such as colitis [14], periodontitis, pharyngitis, and postprandial inflammatory response. Anthocyanin can change the redox state of cells and affect redox-sensitive inflammatory mediators through 炎症通常由身体调节,分泌炎症细胞因子和介质。因此,人们普遍认为,因子分泌的下调可能有助于炎症等疾病的治疗[18]。流行病学和研究表明,花青素具有抗炎作用,可以改善多种炎症相关疾病,如结肠炎[19],牙周炎,咽炎和餐后炎症反应。花青素可改变细胞的氧化还原状态,并通过Nrf2-ARE
signal modulation [15]. 信号调节影响氧化还原敏感的炎症介质[20]。Hou
et al. showed that anthocyanin inhibited 等人表明,花青素通过抑制C
OX-2 by inhibiting C/EBP, AP-1, and NF-κB, thereby reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α [16]. /EBP、AP-1和NF-κB来抑制COX-2,从而减少促炎细胞因子IL-1β、IL-6、IL-8和TNF-α的产生[21]。Min
et al. found that cyanidin等人发现,花青素-3-
glucoside showed an effective anti-inflammatory effect by regulating NF-κB and MAPK activity [17]. Studies have shown that fenugreein can inhibit 葡萄糖苷通过调节NF-κB和MAPK活性显示出有效的抗炎作用[22]。研究表明,胡芦苇素可抑制HcPT
degradation, 降解、p65
nuclear translocation, and JNK phosphorylation, showing an indigenous anti-inflammatory activity [18]. In general, 核易位和JNK磷酸化,显示出本土的抗炎活性[23]。一般来说,B-
ring o-dihydroxyphenyl anthocyanin, such as fayashinin and cyanidin, has strong anti-inflammatory activity, while geranium pigment, peony pigment, and kumquat pigment do not show the above activity without o-dihydroxy structure [19]. 环邻二羟基苯基花青素,如法亚希宁和花青素,具有很强的抗炎活性,而天竺葵色素、牡丹色素和金桔色素在没有邻二羟基结构的情况下不表现出上述活性[24]。Aboonabi
et al. showed that 等人表明,代谢综合征患者每日摄入320
mg anthocyanidin daily intake in people with metabolic syndrome can significantly inhibit the expression of NF-κB-pathway-related proinflammatory factor genes and enhance the expression of mg花青素可显著抑制NF-κB通路相关促炎因子基因的表达,增强PPAR-γ gene to reduce the risk of inflammation [20]. 基因的表达,降低炎症风险[25]。Duarte
et al. showed that geranium pigment等人表明,草莓中的天竺葵色素-3-O-
glucoside in strawberry could inhibit the activation of IkB-α and reduce the phosphorylation of 葡糖苷可以抑制IkB-α的活化并减少JNK-MAPK
, leading to the decrease in NF-κB and AP-1 activation factors in the inflammatory pathway stimulated by TLR4, indicating that geranium pigment-3-O-glucoside had an anti-inflammatory effect [21]. The study of 的磷酸化,导致TLR4刺激的炎症途径中NF-κB和AP-1活化因子的降低,表明天竺葵色素-3-O-葡萄糖苷具有抗炎作用[26]。Karnarathne
and other studies have shown that anthocyanin from Hibiscus can inhibit the secretion of nitric oxide and prostaglandin 的研究表明,来自芙蓉的花青素可以抑制LPS诱导的内毒性休克斑马鱼中一氧化氮和前列腺素E
2的分泌,同时下调可诱导的一氧化氮合酶和环氧合酶2
in LPS-induced endotoxic shock zebrafish, while down-regulating the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase and cyclooxygenase 2. Furthermore, LPS inhibited the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6 and IL-12 in RAW 264.7 macrophages. Anthocyanin also inhibits LPS-induced TLR4 dimerization or cell surface formation, thereby reducing MyD88 growth and IRAK4 phosphorylation, thereby inhibiting NF-κB activity [22].的表达。此外,LPS抑制了RAW 264.7巨噬细胞中促炎细胞因子的产生,如TNF-α,IL-6和IL-12。花青素还抑制LPS诱导的TLR4二聚化或细胞表面形成,从而减少MyD88生长和IRAK4磷酸化,从而抑制NF-κB活性[27]。
2.3. Anti-Oxidation
抗氧化
Humans produce free radicals during metabolism. Excessive free radicals can lead to lipid, protein, 人类在新陈代谢过程中产生自由基。过量的自由基可导致脂质、蛋白质、DNA
, RNA, and sugar oxidation, which is closely related to cancer, Alzheimer′s disease, Parkinson′s disease, autoimmune deficiency, diabetes, obesity, and other diseases. As a natural plant pigment, anthocyanin not only can be used as a colorant, but also has prominent antioxidant activity. Anthocyanins can scavenge reactive oxygen species (ROS) and reactive nitrogen (RNS), such as superoxide anion (、RNA和糖氧化,这与癌症、阿尔茨海默病、帕金森病、自身免疫性缺乏、糖尿病、肥胖等疾病密切相关。作为一种天然植物色素,花青素不仅可以用作着色剂,而且具有突出的抗氧化活性。花青素可以清除活性氧(ROS)和活性氮(RNS),如超氧阴离子(O
2−), singlet oxygen (),单线态氧(1O
2), peroxide free radical (),过氧化自由基(RCOO
·), hydrogen peroxide, hydroxyl free radical (),过氧化氢,羟基自由基(OH
·), and peroxynitrite anion ()和过氧亚硝酸盐阴离子(ONOO
)··−)
[23]. The phenolic ring, hydroxyl side chain, and double bond in the glycosylation reaction of anthocyanin are helpful to scavenge free radicals. Compared with cyanidins and philoxerin, anthocyanin lacking [花青素糖基化反应中的酚环、羟基侧链和双键有助于清除自由基。与花青素和菲洛色林相比,B环中缺乏O-
phenyl structure in the B ring (sunflower pigment, geranium pigment, petunia pigment, and peony pigment) had low 苯基结构的花青素(向日葵色素、天竺葵色素、矮牵牛色素和牡丹色素)的DPPH
radical scavenging efficiency. 自由基清除效率较低。Peonidin
has methyl at 3′ position and OH at 4′ position, which is more active than pelargonidin. As reported by 在3'位置具有甲基,在4'位置具有OH,其比天竺葵素更具活性。正如Fukumoto
and Mazza, the hydroxyl at the third position of the B ring enhances the activity. Similarly, delphinidin with hydroxyl at 3′, 4′, and 5′ is more effective than cyanidin with hydroxyl at only 3′ and 4′ [24]. 和Mazza所报道的那样,B环第三位置的羟基增强了活性。同样,在3'、4'和5'处含羟基的花青素比在3'和4'处具有羟基的花青素更有效[29]。Harakotr
et al. reported that the anthocyanin extract of purple corn had strong 等人报道,紫玉米花青素提取物具有较强的DPPH
radical scavenging activity, and the anthocyanin content in the extract was positively correlated with antioxidant capacity [25]. 自由基清除活性,提取物中的花青素含量与抗氧化能力呈正相关[30]。Matera
et al. reported that cyanidins in radish buds could significantly inhibit the automatic oxidation of linoleic acid and scavenge hydrogen-peroxide-free radicals [26]. 等人报道,萝卜芽中的花青素可以显着抑制亚油酸的自动氧化并清除过氧化氢自由基[31]。Coklar
et al. reported that anthocyanin extracts from Mahonia aquifolium (cyanidins, delphinidin, malvidin, peonidin, pelargonidin) had strong 等人报道,来自马蹄莲(花青素、花青素、麦芽维丁、牡丹素、天竺葵素)的花青素提取物具有较强的DPPH
and 和ABTS
radical scavenging ability and FRAP reduction ability [27]. 自由基清除能力和FRAP还原能力[32]。Lu
et al. fed 等人喂食D-
galactose-induced aging mice black rice anthocyanin extract (cyanidin-3-O-glucoside). The activities of superoxide dismutase and catalase in mice were significantly improved, and the content of malondialdehyde and the activity of monoamine oxidase were reduced. Black rice anthocyanin extract showed a strong anti-aging effect in mice [28]. 半乳糖诱导的老年小鼠黑米花青素提取物(花青素-3-O-葡萄糖苷)。小鼠超氧化物歧化酶和过氧化氢酶活性显著提高,丙二醛含量和单胺氧化酶活性降低。黑米花青素提取物在小鼠中显示出很强的抗衰老作用[33]。Huang
et al. studied the antioxidant effect of main anthocyanins in blueberry on endothelial cells. The results showed that brocade pigment and its two glycosides decreased the levels of reactive oxygen species (等人研究了蓝莓中主要花青素对内皮细胞的抗氧化作用。结果表明,锦缎色素及其两种糖苷降低了活性氧(ROS
) and xanthine oxidase-1 (XO-1), but increased superoxide dismutase (SOD) and heme oxygenase-1 (HO-1). Moreover, the presence of glycoside greatly improved the antioxidant capacity of malvidin [29].)和黄嘌呤氧化酶-1(XO-1)的水平,但增加了超氧化物歧化酶(SOD)和血红素加氧酶-1(HO-1)。此外,糖苷的存在大大提高了麦芽维丁的抗氧化能力[34]。
2.4. Protective Effect on the Liver
2.4. 对肝脏的保护作用
Daveri
et al. fed high-fat diet mice with 等人喂食高脂肪饮食小鼠40
mg anthocyanin/kg BW (cyanidins and delphinidins). The changes of chemokine MCP-1, cytokine TNF-α, macrophage marker F4/80, and enzyme NOS2 were measured. The results showed that anthocyanin played a role in preventing liver injury [30]. 毫克花青素/ kg BW(花青素和花青素)。测定趋化因子MCP-1、细胞因子TNF-α、巨噬细胞标志物F4/80和酶NOS2的变化。结果显示,花青素在预防肝损伤方面发挥作用[35]。Jiang
et al. showed that when carbon tetrachloride等人表明,当四氯化碳诱导的肝损伤小鼠喂食花青素-
induced liver injury mice were fed with cyanidin-3-O-glucoside 3-O-葡萄糖苷800 mg/kg BW
, cyanidin-3-O-glucoside could significantly alleviate liver injury and prevent fibrosis in mice. Cyanidin-3-O-glucose can protect the liver by reducing liver oxidative stress, reducing liver cell apoptosis, inhibiting liver inflammatory response, and ultimately inhibiting the activation of liver star [31]. 时,花青素-3-O-葡萄糖苷可显著缓解小鼠肝损伤,预防纤维化。矢车菊素-3-O-葡萄糖可以通过减少肝脏氧化应激、减少肝细胞凋亡、抑制肝脏炎症反应并最终抑制肝星的激活来保护肝脏[36]。Arjinajarn
et al. showed that the anthocyanin extract of riceberry bran could prevent gentamicin-induced liver injury in rats by inhibiting intracellular oxidative stress and the activation of 等人表明,米莓麸皮的花青素提取物可以通过抑制细胞内氧化应激和NF-κB
factor, reducing liver cell inflammation and apoptosis [32]. 因子的活化,减少肝细胞炎症和凋亡来预防庆大霉素诱导的大鼠肝损伤[37]。Zhang
et al. found that purple sweet potato anthocyanin could effectively inhibit the production of reactive oxygen species in mice and inhibit the accumulation of liver fat induced by high等人发现,紫甘薯花青素通过激活腺苷-
fat diet by activating adenosine-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway [33]. Cai et al. studied the effects of different doses of purple sweet potato anthocyanin on the main liver function indexes, liver histological changes, and oxidation state of mice with alcoholic fatty liver, finding that medium dose of purple sweet potato anthocyanin had an obvious protective effect on the release of alanine aminotransferase (单磷酸活化蛋白激酶(AMPK)信号通路,可有效抑制小鼠活性氧的产生,抑制高脂饮食诱导的肝脏脂肪积累[38]。蔡等人研究了不同剂量紫甘薯花青素对酒精性脂肪肝小鼠主要肝功能指标、肝脏组织学变化和氧化状态的影响,发现中等剂量的紫甘薯花青素对肝损伤小鼠丙氨酸氨基转移酶(ALT
) in the mice with liver injury [34].)的释放有明显的保护作用[39]。2.5. Lowering Blood Glucose
2.5. 降低血糖
Diabetes is a non-infectious endocrine metabolic disease that can lead to serious complications of various organs, and the number of patients with diabetes is increasing. Maintaining normal blood glucose level is a necessary condition for maintaining body function. In the human body, glucose homeostasis is controlled by various organs, including the pancreas, liver, and other tissues, as well as complex networks of hormones and neuropeptides. The pancreas plays a key role in glucose homeostasis by secreting hypoglycemic hormone insulin [35]. Purple corn anthocyanins have significant effects on 糖尿病是一种非传染性内分泌代谢性疾病,可导致各种器官的严重并发症,糖尿病患者的数量正在增加。维持正常的血糖水平是维持机体机能的必要条件。在人体内,葡萄糖稳态由各种器官控制,包括胰腺,肝脏和其他组织,以及激素和神经肽的复杂网络。胰腺通过分泌降血糖激素胰岛素在葡萄糖稳态中起关键作用[40]。紫玉米花青素对β
-cell function and insulin secretion, which can protect pancreatic 细胞功能和胰岛素分泌有显著影响,可保护胰β
cells from high-glucose-induced oxidative stress and improve insulin secretion ability of β cells [36]. The liver is the main part of human body and plays a fundamental role in glycogen storage, plasma protein synthesis, and detoxification [37]. Studies have shown that anthocyanin-rich mulberry extract inhibits gluconeogenesis and stimulates glycogen synthesis by increasing 细胞免受高糖诱导的氧化应激,提高β细胞的胰岛素分泌能力[41]。肝脏是人体的主要组成部分,在糖原储存、血浆蛋白合成和解毒中起着重要作用[42]。研究表明,富含花青素的桑树提取物通过增加肝脏中的AMPK
phosphorylation in the liver [38].磷酸化来抑制糖异生并刺激糖原合成[43]。
2.6. Anti-Aging
抗衰老
Oxidative stress is one of the main inducing factors of aging, and excessive expression of inflammatory factors, 氧化应激是衰老的主要诱发因素之一,炎症因子的过度表达、DNA
damage, and a series of inflammatory reactions activated by NLPR3 and NF-κB can also promote the aging of the body [39]. Many studies have shown that anthocyanin has an anti-aging effect. 损伤以及NLPR3和NF-κB激活的一系列炎症反应也可以促进机体衰老[44]。许多研究表明,花青素具有抗衰老作用。Jin
et al. fed aged mice with anthocyanin from purple sweet potato and found that compared with the control group, anthocyanin from purple sweet potato could significantly reduce the serum 等用紫甘薯花青素喂养老年小鼠,发现与对照组相比,紫甘薯花青素可显著降低血清MDA
level and improve the activities of SOD and 水平,提高SOD和GSH-PX
, and low-dose anthocyanin could achieve the same effect as the equivalent amount of vitamin, indicating that anthocyanin from purple sweet potato could play a role in delaying aging by improving antioxidant activity [40]活性,低剂量花青素可达到与等量维生素相同的效果,表明紫甘薯花青素可通过提高抗氧化活性,在延缓衰老方面发挥作用[45]].
Wang
et al. showed that 等人表明,Cy-3-glu
and 和Pg-3-glu
treatments could significantly inhibit the galactosidase in the aging process of human retinal pigment epithelium (RPE) cells induced by visible light irradiation and play a protective role in anti-aging [41]. 处理可显著抑制可见光照射诱导的人视网膜色素上皮(RPE)细胞衰老过程中的半乳糖苷酶,并在抗衰老中起保护作用[46]。Gao
et al. found that 等人发现,Ribes meyeri
anthocyanins can promote the proliferation of neural stem cells, improve cell senescence phenotype, reduce ROS and senescence-associated 花青素可以促进神经干细胞的增殖,改善细胞衰老表型,降低ROS和衰老相关的P16Ink4a gene expression levels, increase 基因表达水平,增加DNA
synthesis, and prolong telomeres [42]. 合成,延长端粒[47]。Wei
et al. showed that anthocyanin could maintain the stability of the redox system in plasma and liver structure, as well as reduce the levels of inflammatory factors such as 等人表明,花青素可以维持血浆和肝脏结构中氧化还原系统的稳定性,并降低肝脏中IL-1
, IL-6, and TNF-α in the liver. At the same time, the decrease in the expression levels of sensors (ATM and ATR), media (H2AX and ,IL-6和TNF-α等炎症因子的水平。同时,DNA损伤信号通路中传感器(ATM和ATR)、培养基(H2AX和γ-H2AX
), and effectors (Chk1, Chk2, p53 and p-p53) in the DNA damage signaling pathway indicate that anthocyanin can slow down aging by inhibiting DNA damage [43].)和效应子(Chk1、Chk2、p53和p-p53)的表达水平下降表明,花青素可以通过抑制DNA损伤来延缓衰老[48]。
2.7. Other Effects
2.7. 其他影响
Qin et al. used purple sweet potato anthocyanin (秦等人用紫甘薯花青素(PSPC 500 mg/kg/d
ay) to orally take high-fat model mice. The results showed that PSPC corrected the abnormal metabolic indexes induced by HFD, including improving obesity, reducing fasting blood glucose concentration, and improving glucose tolerance [44]. )口服高脂模型小鼠。结果显示,PSPC纠正了HFD诱导的代谢指标异常,包括改善肥胖、降低空腹血糖浓度和改善葡萄糖耐量[49]。Lee
et al. found the effect of black soybean anthocyanin on obesity. 等人发现了黑大豆花青素对肥胖的影响。结果显示,服用黑大豆花青素的肥胖患者的T
he results showed that TC/HDLc/LDLc/HDLc
of obese patients taking black soybean anthocyanin were significantly decreased [45]. 显著降低[50]。Farrell
et al. established a mouse model of hyperlipidemia and high-density lipoprotein dysfunction to explore and determine that an anthocyanin-rich blackcurrant extract (等人建立了高脂血症和高密度脂蛋白功能障碍的小鼠模型,以探索和确定富含花青素的黑醋栗提取物(BEE
) (13% anthocyanin) can prevent inflammation-related HDL functional damage and apolipoprotein E atherosclerosis. The results showed that the total cholesterol content in the aorta of mice was significantly decreased, and the aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and fasting blood glucose were decreased, indicating that blackberry may affect chronic inflammation-related HDL dysfunction by affecting liver gene expression [46]. In addition, studies have shown that purple sweet potato anthocyanin has a protective effect on the kidneys. )(13%花青素)可以预防炎症相关的HDL功能损伤和载脂蛋白E动脉粥样硬化。结果显示,小鼠主动脉总胆固醇含量显著降低,天冬氨酸氨基转移酶(AST)和空腹血糖降低,表明黑莓可能通过影响肝脏基因表达来影响慢性炎症相关的HDL功能障碍[51]。此外,研究表明,紫甘薯花青素对肾脏有保护作用。Qun
and other studies have found that purple sweet potato anthocyanin can significantly improve kidney injury in mice fed with high fat diet by reducing the production of 等研究发现,紫甘薯花青素可以通过减少AGEs
and ROS and improving insulin sensitivity. Its protective effect is played by inhibiting the expression of TXNIP and RAGE and further inhibiting the activation of NLRP3 inflammasome and 和ROS的产生和提高胰岛素敏感性,显著改善高脂饮食喂养小鼠的肾损伤。其保护作用是通过抑制TXNIP和RAGE的表达并进一步抑制NLRP3炎症小体和IKKb/NFκB
pathway [39]. 通路的活化来发挥作用的[44]。
The physiological activities of anthocyanins are summarized in Table 2.
Table表 2. Physiological activities of anthocyanins.
花青素的生理活性。
| Effects | 影响 |
Source | 源 |
Mechanisms | 机制 |
Ref. | 裁判。 |
| Anti-cancer | 抗癌 |
colon cancer | 肠癌 |
Purple grape anthocyanins | 紫色葡萄花青素 |
| |
|
[8] | [13] |
| colon cancer | 肠癌 |
Cyanidin-3-O-rutinoside | 矢车菊素-3-O-芜香苷 |
| |
|
[9] | [14] |
| colon cancer | 肠癌 |
Purple and red maize anthocyanins | 紫色和红色玉米花青素 |
|
-
Enhanced增强型 BAX, Bcl-2, cytochrome C, and、Bcl-2、细胞色素 C 和 TRAILR2/D5
-
Inhibited抑制 Tie-2, 、ANGPT2, and 和 PLG
|
|
[10] | [15] |
| breast cancer | 乳腺癌 |
Black sweet cherry anthocyanins | 黑甜樱桃花青素 |
| |
|
[3] | [8] |
| melanoma cancer |
Hibiscus calyx anthocyanin |
| |
|
[11] | [16] |
| |
Purple sweet potato anthocyanin |
|
-
Acted on cell cycle regulators (such as p53, p21, p27, Cyclin D1, and Cyclin A)
|
|
[12] | [17] |
| Anti-inflammatory |
|
| |
|
[15] | [20] |
| |
|
-
Inhibited C/EBP, AP-1, and NF-κB
-
Inhibited COX-2
-
Reduced IL-1β, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α
-
Enhanced PPAR-γ gene
|
|
[16]
[19] | [21]
[24] |
| Cyanidin-3-glucoside |
| |
|
[17] | [22] |
| Geranium pigment-3-O-glucoside in strawberry |
| |
|
[21] | [26] |
| Hibiscus | anthocyanin |
| |
|
[22] | [27] |
| Anti-oxidation |
Purple corn anthocyanin |
| |
|
[25] | [30] |
| Cyanidins in radish buds |
| |
|
[26] | [31] |
| Mahonia aquifolium | anthocyanin |
| |
|
[27] | [32] |
| Black rice anthocyanin extract (cyanidin-3-O-glucoside) |
| |
|
[28] | [33] |
| Blueberry anthocyanins |
| |
|
[29] | [34] |
| Protective effect on liver |
Cyanidin-3-O-glucoside |
|
-
Prevented fibrosis
-
Reduced liver oxidative stress
-
Reduced liver cell apoptosis
-
Inhibited liver inflammatory response
|
|
[31] | [36] |
| Riceberry bran anthocyanin |
| |
|
[32] | [37] |
| Purple sweet potato anthocyanin |
|
-
Activated adenosine-monophosphate-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway
-
Inhibited the production of reactive oxygen species
-
Inhibited the accumulation of liver fat
|
|
[33] | [38] |
| Purple sweet potato anthocyanin |
| |
|
[34] | [39] |
| Lowering blood glucose |
Purple corn anthocyanins |
| |
|
[47] | [52] |
| Mulberry anthocyanin |
| |
|
[36] | [41] |
| Anti-aging |
Purple sweet potato anthocyanin |
|
-
Reduced the serum MDA level
-
Improved the activities of SOD and GSH-PX
-
Delayed aging by improving antioxidant activity
|
|
[40] | [45] |
Cy-3-glu
Pg-3-glu |
| |
|
[41] | [46] |
| Ribes meyeri anthocyanins |
|
-
Promoted the proliferation of neural stem cells
-
Improved cell senescence phenotype
-
Reduce ROS
-
Reduced senescence-associated P16Ink4a gene expression levels
-
Increased DNA synthesis
-
Prolonged telomeres
|
|
[42] | [47] |
| |
|
-
Maintained the stability of redox system
-
Reduced the levels of IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α
-
Decreased in the expression levels of sensors, media, and effectors in the DNA damage signaling pathway
-
Slowed down aging by inhibiting DNA damage
|
|
[43] | [48] |