Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Amina Yu and Version 1 by Xiaoyan Yang.
茶多糖(TPS)是茶叶中仅次于茶多酚的第二丰富成分。作为一种复合多糖,TPS具有复杂的化学结构和多种生物活性,如抗氧化、降血糖、降血脂、免疫调节、抗肿瘤等。此外,在食品、化妆品、医药保健品等方面也显示出良好的开发和应用前景。茶叶、花和种子是茶多糖提取材料的三大主要来源。TPS的生产工艺主要有热水提取、超声波辅助提取、微波辅助提取、酶解提取等。ea polysaccharide (TPS) is the second most abundant ingredient in tea following tea polyphenols. As a complex polysaccharide, TPS has a complex chemical structure and a variety of bioactivities, such as anti-oxidation, hypoglycemia, hypolipidemic, immune regulation, and anti-tumor. Additionally, it shows excellent development and application prospects in food, cosmetics, and medical and health care products.
- tea
- polysaccharides
- extraction method
一、简介1. Introduction
As a traditional drink, tea has been cultivated and consumed for thousands of years, and it is deeply loved by consumers from many countries, such as China, Japan, and South Korea. Tea not only creates a lot of wealth but also generates tea culture and tea ceremony [1]. As a result, tea has become one of the most popular beverages in the world after water [2,3,4].
The unprecedented popularity of tea is due not only to its unique aroma and taste but also to the health benefits of drinking it. The primary bioactivities of tea, including anti-oxidation, hypoglycemic, antibacterial, hypolipidemic, and anti-cancer activities, have been studied and explored. Tea has also been broadly utilized in the food, medical, and health care industries [5,6]. Tea’s biological and pharmacological activities are mainly attributed to the diversity of its chemical components. The chemical features of tea mainly include tea polyphenols (TPPs), tea polysaccharides (TPSs), tea proteins, catechins, theanine, and inorganic elements [4]. Tea polyphenols have long received attention for their excellent antioxidant properties for which accumulating evidence has been presented [7]. Modern pharmacological studies have shown that TPS, an important bioactive component along with TPP, is also the main tea compound that helps lower blood glucose and lipids, resist oxidation, and enhance the body’s immune function [8,9,10]. It also has excellent potential for development and application in the cosmetic industry [11]. In general, the content of TPS decreases with increases in tea quality or grade [12]. Wang et al., reported that the TPS content in low-grade tea was twice that of high-grade tea [13]. Therefore, using low-grade tea as a raw material to extract TPS is conducive to the full utilization of tea resources and has important implication for preventing diseases and promoting human health.
Therefore, the authors of this paper conducted a detailed comparison and summary of the current research on tea polysaccharide’s extraction, preliminary physicochemical properties, and in vitro and in vivo bioactivities in order to provide new insights for the better utilization and development of TPS or TPS-related functional foods.
2. TPS Extraction
目前Tea leaves, flowers, and seeds are the three primary sources of TPS extraction materials. The current production process of TPS的生产工艺主要有热水提取、超声波辅助提取、微波辅助提取、酶解提取(表 mainly includes hot water extraction, ultrasonic-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, and enzymolysis extraction (Table 1)。其常规制备工艺如图). Its conventional preparation process is shown in Figure 1所示。.
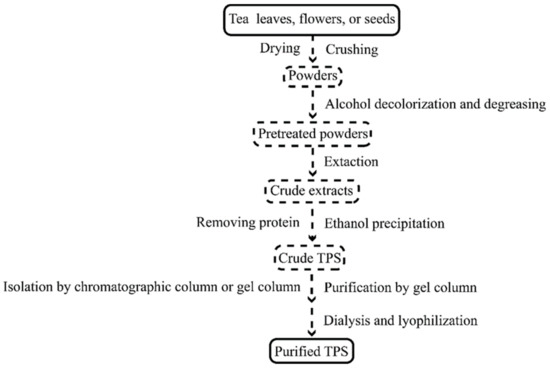
图Figure 1. The conventional process of TPS 制备的常规过程。preparation.
表Table 1茶多糖(. Comparison of extraction methods of tea polysaccharide (TPS)提取方法比较).
| 提取方法 | Extraction Method | TPS 起源 | TPS Origin | 提取步骤 | Extraction Step | 参考 | Ref | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 热水提取 | Hot water extraction | 绿茶叶和花 | Green tea leaves and flowers | 95%乙醇40℃预提取2 h,重复3次;60℃水浴萃取2小时,重复3次 | Pre-extraction with 95% ethanol at 40 °C for 2 h, repeated three times; a water bath extraction at 60 °C for 2 h, repeated 3 times | [ | [ | 14 ] | ] | ||||||
| 福安白茶、平阳特早茶 | Fuan Baicha and Pingyang Tezaocha | 80 °C 萃取 1.5 h,重复 2 次 | Extraction at 80 °C for 1.5 h, repeated two times | [ | [ | 15 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 茯砖茶 | Fuzhuan tea | 提取时间2 h,料液比1:20,提取温度95 ℃;重复三遍 | 2 h extraction time, 1:20 solid–liquid ratio, and 95 °C extraction temperature; repeated three times | [ | [ | 10 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 白茶 | White tea | 提取时间8 min,提取温度54.1 ℃,料水比12.48 L/g;重复四次 | 8 min extraction time, 54.1 °C extraction temperature, 12.48 L/g material–water ratio; repeated four times | [ | [ | 16 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 绿茶 | Green tea | 在 90°C 的水浴中加热 2 小时并持续搅拌 | Heating in a water bath at 90 °C for 2 h with continuous stirring | [ | [ | 17 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 绿茶 | Green tea | 无水乙醇预萃取 24 h,去离子水 60 °C 萃取 90 min | Pre-extraction with absolute ethanol for 24 h and extraction with deionized water at 60 °C for 90 min | [ | [ | 18 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 钦砖茶 | Chin brick tea | 80% 乙醇预处理并用蒸馏水 (1:20, | 80% ethanol pretreatment and continuous stirring with distilled water (1:20, | w / | / | v ) 在 90 °C 下连续搅拌 2 h | ) at 90 °C for 2 h | [ | [ | 19 ] | ] | ||||
| 六泡茶 | Liupao tea | 80%乙醇预处理24 h,去离子水70℃萃取2 h;重复三遍 | 80% ethanol pretreatment for 24 h and extraction with deionized water at 70 °C for 2 h; repeated three times | [ | [ | 20 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 茶花 | Tea flowers | 90 °C 萃取 1 小时(2 次) | Extraction at 90 °C for 1 h (2 times) | [ | [ | 21 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 绿茶 | Green tea | 80%乙醇70℃预处理1.5小时,40℃乙醇提取3小时 | 80% ethanol pretreatment at 70 °C for 1.5 h, extraction with ethanol at 40 °C for 3 h | [ | [ | 22 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 绿茶 | Green tea | 2倍体积95%乙醇50℃预处理4h,料液比1:8,50℃搅拌萃取120min | Pretreatment with two times volume of 95% ethanol at 50 °C for 4 h, 1:8 solid–liquid ratio, and extraction with stirring at 50 °C for 120 min | [ | [ | 23 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 绿茶 | Green tea | 用 95% 酒精(1:5, | Pretreatment with 95% alcohol (1:5, | w / | / | v )预处理 2 小时,在 80°C的热水(1:10, | ) for 2 h, extraction in hot water (1:10, | w / | / | v )中萃取;重复3次,每次1小时 | ) at 80 °C; repeated 3 times for 1 h each time | [ | [ | 24 ] | ] |
| 绿茶 | Green tea | 95% 乙醇(1:6, | 95% ethanol (1:6, | w / | / | v)在 60°C 预处理 4 小时,用蒸馏水(1:10, | ) pretreatment at 60 °C for 4 h and extraction with distilled water (1:10, | w / | / | v)在 80°C 提取 4 小时;重复3次 | ) at 80 °C for 4 h; repeated 3 times | [ | [ | 25 ] | ] |
| 祁门红茶 | Keemun black tea | 用 95% 乙醇(1:6, | Pretreatment with 95% ethanol (1:6, | w / | / | v)在 80°C 预处理 2h,然后浸入 80°C 蒸馏水(1:10, | ) at 80 °C for 2 h and immersed in distilled water (1:10, | w / | / | v)中 4h;重复四次 | ) at 80 °C for 4 h; repeated four times | [ | [ | 26 ] | ] |
| 超声辅助提取 | Ultrasonic-assisted extraction | 低档绿茶 | Low-grade green tea | 提取温度 80 °C,提取时间 60 min,超声波功率 400 W,液固比 22 mL:g | 80 °C extraction temperature, 60 min extraction time, 400 W ultrasonic power, and 22 mL:g liquid–solid ratio | [ | [ | 27 ] | ] | ||||||
| 粗茶 | Coarse tea | 在超声波浴(50 °C,200 W)中预处理 30 分钟,然后在水浴中提取 90 分钟;重复三遍 | Pretreatment in an ultrasonic bath (50 °C, 200 W) for 30 min followed by extraction in a water bath for 90 min; repeated three times | [ | [ | 23 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 绿茶花 | Green tea flowers | 超声波功率(25 °C、100、150、200、250 和 300 W)萃取 5 分钟;重复2次 | Ultrasonic power (25 °C, 100, 150, 200, 250, and 300 W) extraction for 5 min; repeated 2 times | [ | [ | 21 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 黄茶 | Yellow tea | 95% 乙醇预处理 6 h,90 °C 水浴萃取 55 min(重复两次),超声处理(20 kHz,500 W)55 min | 95% ethanol pretreatment for 6 h, 90 °C water bath extraction for 55 min (repeated twice), and sonication (20 kHz, 500 W) for 55 min | [ | [ | 21 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 微波辅助萃取 | Microwave-assisted extraction | 绿茶、红茶和乌龙茶 | Green, black, and oolong teas | 1:20 固液比,200–230 °C 提取温度,2 分钟提取时间 | 1:20 solid/liquid ratio, 200–230 °C extraction temperature, and 2 min extraction time | [ | [ | 28 ] | ] | ||||||
| 绿茶花 | Green tea flowers | 在受控微波功率下萃取 5 分钟,然后在相同微波功率下用蒸馏水萃取 5 分钟 | Extraction at controlled microwave power for 5 min followed by extraction with distilled water for 5 min at the same microwave power | [ | [ | 21 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 绿茶 | Green tea | 600W微波仪器萃取30min,水浴搅拌90min;重复三遍 | Extraction in a 600 W microwave apparatus for 30 min, followed by stirring in a water bath for 90 min; repeated three times | [ | [ | 29 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 酶解提取 | Enzymolysis extraction | 绿茶 | Green tea | 100℃萃取3小时,果胶酶和鞣酸酶水萃取35℃2小时 | Extraction at 100 °C for 3 h and aqueous extraction with pectinase and tannase at 35 °C for 2 h | [ | [ | 30 ] | ] | ||||||
| 绿茶 | Green tea | 用复合酶(纤维素酶:果胶酶:葡聚糖酶 = 1:1:2)在 50°C 提取 30 分钟,在 90°C 沸腾 10 分钟,然后在 50°C 水浴中提取 80 分钟 | Extraction with complex enzymes (cellulase:pectinase:glucanase = 1:1:2) at 50 °C for 30 min, boiling at 90 °C for 10 min, and then extraction in a water bath at 50 °C for 80 min | [ | [ | 29 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 绿茶叶和花 | Green tea leaves and flowers | 95%乙醇40℃预处理2h(重复3次),0.5%(m/v)戊聚糖复合酶溶液(45℃,pH 5.5)处理2h,45℃水浴萃取2小时 | 95% ethanol pretreatment at 40 °C for 2 h (repeated 3 times), treatment with 0.5% (m/v) pentosan complex enzyme solution (45 °C, pH 5.5) for 2 h, and extraction in 45 °C water bath for 2 h | [ | [ | 14 ] | ] | ||||||||
| 绿茶 | Green tea | 在90℃水浴中加热2-4小时,重复两次;与 0.5% 果胶酶 (260,001 PGU/mL, | Heating in a water bath at 90 °C for 2–4 h, repeated twice; incubating with 0.5% pectinase (260,001 PGU/mL, | v / | / | w ) 在 40 °C 下孵育 30 分钟;并在 90°C 下加热 1 小时以使酶失活 | ) at 40 °C for 30 min; and heating at 90 °C for 1 h to inactivate the enzyme | [ | [ | 31 ] | ] | ||||
| 水/溶剂热萃取 | Hydro/solvothermal extraction | 中国茶中茶108 | Chinese tea Zhongcha 108 | 120 °C 萃取 1 小时 | Extraction at 120 °C for 1 h | [ | [ | 1 ] | ] | ||||||
| 碱辅助萃取 | Alkali-assisted extraction | 福砖砖茶 | Fuzhuan brick tea | 在 60 °C 下用 0.1 M NaOH 溶液 (pH = 10.0) 萃取,重复 3 次 | Extraction with 0.1 M NaOH solution (pH = 10.0) at 60 °C, repeated 3 times | [ | [ | 32 ] | ] | ||||||
| 超临界流体萃取 | Supercritical fluid extraction | 绿茶 | Green tea | 380 μm 粒径,20% 无水乙醇,35 MPa 提取压力,45 °C 提取温度,2 h 提取时间 | 380 μm particle size, 20% absolute ethanol, 35 MPa extraction pressure, 45 °C extraction temperature, and 2 h extraction time | [ | [ | 33 ] | ] | ||||||
| 阴离子反胶束萃取 | Anionic reverse micelle extraction | 绿茶 | Green tea | pH = 4.6、0.06 M 盐酸胍、7% 甲醇和 0.05 M NaCl;前向提取 | pH = 4.6, 0.06 M guanidine hydrochloride, 7% methanol, and 0.05 M NaCl; forward extraction | [ | [ | 34 ] | ] |
2.热水提取
大多数生物活性多糖是极性的,因此通常使用热水或碱性溶液等极性溶剂提取多糖
2.1. Hot Water Extraction
Most bioactive polysaccharides are polar, so polar solvents such as hot water or alkaline solutions are usually used for polysaccharide extraction [ 33]. ]。热水提取是食品、医药等行业广泛用于制备多糖的经典方法Hot water extraction is a classic method widely used to prepare polysaccharides in food, medicine, and other industries [ 34]. ]。Chen 等人使用水浴加热(70 ℃,60 分钟)从黑茶、乌龙茶和绿茶叶中提取三种粗制 TPS Chen et al., used water bath heating (70 °C, 60 min) to extract three kinds of crude TPSs from black, oolong, and green tea leaves [ 35]. ]。Xu 等人在 70°C 的热水中用Xu et al., prepared TPS from Pu-erh tea three times for 180 min in hot water at 70 °C [36]. Fan et 3al., 次普洱茶制备 TPS,每次 180 分钟 [extracted TPS twice in Fuan Baicha and Pingyang Tezaocha by adding double-distilled water and heating in a water 36bath ]。范等人在福安白茶和平阳特早茶中加入双蒸水,在at 80 ℃水浴中加热 1.5 小时,两次提取 TPS °C for 1.5 h [ 37]。朱等人利用响应面法对茯砖茶粗多糖(. Zhu et al., used the response surface methodology to explore the extraction process of Fuzhuan tea crude polysaccharide (CDTPS)的提取工艺进行了探索,发现最佳提取条件(重复4次)为:提取时间为2 h,固液比例为 1:20,萃取温度为) and found that the optimal extraction conditions (repeated four times) were as follows: an extraction time of 2 h, a solid–liquid ratio of 1:20, and an extraction temperature of 95 °C。在此条件下,. Under these conditions, the yield of CDTPS 的收率为was 6.07% [ 10]. The ]。Jin等人采用响应面法,通过重复4次在白茶中预测TPS的最佳提取条件:最佳提取时间为response surface methodology used by Jin et al., predicted the optimal extraction conditions of TPS via repetition four times in white tea: the optimal extraction time was 97.8 min,提取温度为54.1 ℃,料水比为12.48升/克, the extraction temperature was 54.1 °C, and the material–water ratio was 12.48 L/g [ 14]。. Wang 等人将干燥的绿茶叶和花在 95% 乙醇和 40°C 中预处理 2 小时,然后重复该过程 3 次以去除色素和其他物质。然后,将 2 L 蒸馏水加入过滤后的茶样品中,在 60 ℃水浴中提取 2 h。过滤后,加入et al., pretreated dried green tea leaves and flowers in 95% ethanol and 40 °C for 2 h, then repeated the process three times to remove pigments and other substances. Then, 2 L of distilled water was added to the filtered tea samples for extraction in a water bath at 60 °C for 2 h. After filtration, 2.5 L 蒸馏水,再次重复热水萃取(60 ℃,2 h)of distilled water was added, and the hot water extraction was repeated again (60 °C, 2 h) [ 38]. ]。类似地,Cai 等人用无水乙醇预处理绿茶叶 24 小时以去除一些小分子色素和多酚,然后用去离子水在 60°C 下将茶叶样品干燥 90 分钟Similarly, Cai et al., pretreated green tea leaves with absolute ethanol for 24 h to remove some small-molecular pigments and polyphenols, and then they dried the tea samples with deionized water for 90 min at 60 °C [ 16]. ]。Li 等人也用 80% 乙醇预处理了金砖茶粉,离心后用蒸馏水(1:20,Li et al., also pretreated Chin brick tea powder with 80% ethanol, centrifuged it, and then continuously stirred it with distilled water (1:20, w/v) vfor 2 )h 在at 90 °C 下 2 小时以提取 to extract TPS [ 17]. ]。秦等人用 80% 乙醇预处理六泡茶样品 24 小时。过滤和干燥后,样品用去离子水在 70°C 下萃取 2 小时,该过程重复 3 次Qin et al., pretreated Liupao tea samples with 80% ethanol for 24 h. After filtration and drying, the samples were extracted with deionized water at 70 °C for 2 h, and the process was repeated three times [ 18]. ]。Wei 等人对干茶花多糖Wei et al., performed the hot water extraction of dried tea flower polysaccharides (TFPS) 进行热水提取,然后用蒸馏水提取 TFPS 两次(每次 1 小时)。他们发现TFPS的得率随着提取温度的增加而增加,90℃是TFPS的最佳提取温度。此条件下的收率接近s) and then extracted TFPSs twice with distilled water (1 h each). They found that the yield of TFPS increased with the extraction temperature, and 90 °C was the optimal extraction temperature for TFPS. The yield at this condition was close to 35% [ 19]。虽然热水提取是. Though hot water extraction is a commonly used method for TPS提取的常用方法,但传统的热水提取存在提取效率低、提取时间长、提取温度高等缺点,限制了其可用性[ extraction, conventional hot water extraction has disadvantages such as a low extraction efficiency, long extraction time, and high extraction temperature, all of which limit its availability [33,39]. For 33、39example, ]。例如,Wang et al., further compared the yields of hot water extraction, boiling 等人进一步比较了 TFPS 的热水提取、沸水提取和酶解提取的得率,他们发现酶解提取的water extraction, and enzymolysis extraction for TFPS, and they found that the yield of TFPS 的得率最高(2.01%),其次是煮沸。水萃取obtained with enzymolysis extraction was the highest (2.01%), followed by boiling water extraction (1.91%),最后是热水萃取 and finally hot water extraction (1.83%) [ 20]。朱等人比较了热水提取(. Zhu et al., compared the yields of crude green tea polysaccharides (CTPSs) under hot water extraction (WE)、酶促提取(EE)、微波辅助提取(MAE)和超声辅助提取(UAE)三种粗绿茶多糖(CTPSs)的得率,他们发现:这些提取方法下 CTPS 的四种收率分别为), enzymatic extraction (EE), microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) and ultrasonic-assisted extraction (UAE), and they found that the four yields of CTPS under these extraction methods were 3.98%、4.17%、4.31% 和, 4.17%, 4.31%, and 4.52% , respectively [ 21]。大量研究证实,虽然热水提取具有很强的实用性,但其获得的. Numerous studies have verified that although hot water extraction has strong practicability, its obtained TPS收率较低,容易造成不必要的原料浪费。因此,许多研究人员还在热水提取的基础上改进了该技术,并开发了其他辅助提取方法,如超声波辅助提取、微波辅助提取、酶辅助提取等,以提高 TPS 的提取效率 yield is relatively low and easily leads to the unnecessary waste of raw materials. Therefore, many researchers have also improved the technology on the basis of hot water extraction and developed other auxiliary extraction methods, such as ultrasonic-assisted extraction, microwave-assisted extraction, and enzyme-assisted extraction, to improve the extraction efficiency of TPS [ 40].
2.2. Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction (UAE)
UAE can accelerate ]。
3. 超声波辅助萃取 (UAE)
阿拉伯联合酋长国可以通过高频超声振动引起的样品中分子的高速运动,加速植物细胞壁的破裂,从而溶解和释放细胞内物质。the rupture of plant cell walls by the high-speed movement of molecules in samples caused by high-frequency ultrasonic vibration, thereby dissolving and releasing intracellular substances. Karadag et 等人利用阿联酋提取低品位绿茶多糖al., used UAE to extract low-grade green tea polysaccharides (GTPSs),然后通过响应面优化报告了最佳提取参数如下:提取温度 80 ℃,提取时间 60 分钟,超声波功率 and then reported the optimal extraction parameters through response surface optimization as follows: 80 °C for extraction temperature, 60 min for extraction time, 400 W , 和for ultrasonic power, and 22 mL/g 的液固比。在此条件下,GTPS 的收率为for liquid–solid ratio. Under these conditions, the yield of GTPS was 4.65%,高于无超声波的热水提取法(1.83%), which was higher than that of the hot water extraction method (1.83%) without ultrasound [ 25]。此外,他们还发现,超声辅助提取得到的. In addition, they also found that the Mw of GTPS 的 Mw 较低,这可能是由于超声过程导致 TPS 部分降解所致。朱等人用粗绿茶叶制备TPS,将茶叶置于超声波浴(50℃,200W)中预处理30分钟,然后在水浴中提取90分钟。用这种方法获得的 TPS 产量高于其他测试方法obtained with ultrasonic-assisted extraction was lower, which may have been due to the partial degradation of TPS caused by the ultrasonic process. Zhu et al., prepared TPS from coarse green tea leaves, placing the tea leaves in an ultrasonic bath (50 °C, 200 W) for pretreatment for 30 min and then performing extraction in a water bath for 90 min. The TPS yield obtained with this method was higher than other tested methods [ 21]。为了探索超声对黄茶多糖. To explore the effects of ultrasound on the structure and activity of yellow tea polysaccharide (YTPS) 结构和活性的影响,Wang 等人用超声, Wang et al., treated a YTPS fraction obtained after hot water extraction and deproteinization with ultrasound (20 kHz, 500 W) 处理热水提取和脱蛋白后获得的 YTPS 馏分 55 分钟。结果表明,超声波处理基本没有改变 YTPS 的主要化学成分,但确实导致其降解 for 55 min. The results showed that ultrasonic treatment basically did not change the main chemical composition of YTPS but did cause it to degrade [ 26]. ]。Wei 等人将干燥的绿茶花块与蒸馏水混合,在 100、150、200、250 和Wei et al., mixed dried green tea flower blocks with distilled water and extracted them for 5 min at 25 °C under ultrasonic powers of 100, 150, 200, 250, and 300 W 的超声波功率下,在 25°C 下提取 5 分钟。此过程重复两次以获得粗. This process was repeated twice to obtain crude TFPS [ 19]。总体而言,. Overall, the UAE方法具有省时、操作简单、实验安全、成本低、提取率高等优点。尽管如此,它可能会降解可溶性 TPS 并影响其生物活性。
4. 微波辅助萃取 (MAE)
近年来,微波辅助提取( method has the advantages of saved time, simple operation, experimental safety, low cost, and high extraction rate. Still, it may degrade soluble TPS and affect its bioactivity.
2.3. Microwave-Assisted Extraction (MAE)
Recently, microwave-assisted extraction (MAE)技术已广泛用于分析和提取植物中的活性成分。) technology has become widely used to analyze and extract active components in plants. MAE是一种利用高频电磁波(0.3- is a new extraction technology that uses high-frequency electromagnetic waves (0.3–300 GHZ)具有强穿透性和加热效应的提取植物活性成分的新型提取技术。高能微波可以穿透溶剂和植物细胞壁,将能量传递到细胞质,并与极性成分相互作用产生热量,从而提高细胞内的温度和压力。当压力达到一定水平时,细胞壁膨胀破裂,释放出胞内多糖等物质) with strong penetrability and heating effect to extract active plant components. High-energy microwaves can penetrate solvents and plant cell walls, transfer energy to the cytoplasm, and interact with polar components to generate heat, which increases the temperature and pressure inside cells. When the pressure reaches a certain level, the cell wall expands and ruptures, releasing intracellular polysaccharides and other substances [ 41]。. Shuntaro 等人使用 MAE 技术从茶渣(绿茶、红茶和乌龙茶)中提取 TPS。当提取条件为料液比为 1:20、提取温度为 200~230 ℃、提取时间为et al., used MAE technology to extract TPS from tea residues (green tea, black tea, and oolong tea). When the extraction conditions were a solid/liquid ratio of 1:20, an extraction temperature of 200–230 °C, and an extraction time of 2 min 时,茶渣 TPS 的得率为 40~, the yield of tea residue TPS was 40–50% [ 27]. ]。Wei 等人使用 MAE 设备提取Wei et al., used MAE equipment to extract TFPS 两次,每次 5 分钟。他们发现,随着微波功率的增加,TFPS 的产量发生了不规则的变化。此外,随着微波功率的增加,TFPS 中中性糖的含量增加,而酸性糖的含量先增加后减少twice, for 5 min each time. They found that the yield of TFPS changed irregularly with the increase in microwave power. In addition, with increases in microwave power, the content of neutral sugars in TFPS increased while the content of acidic sugars increased and then decreased [ 19]。. Li等人使用600 W微波仪器提取粗绿茶粗TPS(CTPS),提取过程重复3次。经MAE提取后,CTPS中可溶性蛋白的含量是所有测试方法中最高的,达到5.93%。此外,他们发现 MAE 处理对高 Mw 的 et al., used a 600 W microwave instrument to extract coarse green tea crude TPS (CTPS), and the extraction process was repeated three times. After extraction with MAE, the content of soluble protein in CTPS was the highest of all tested methods, reaching 5.93%. Furthermore, they found that MAE treatment had little effect on CTPS 链几乎没有影响,但会导致小 chains with high Mw but resulted in the drastic degradation of small-Mw CTPS 的急剧降解。根据相关报道,小分子量多糖往往比其高分子量多糖具有更好的生物活性. According to related reports, small-Mw polysaccharides tend to have better bioactivities than their high-Mw counterparts [ 42]. ]。随后朱等人用 MAE 法制备的The subsequent in vitro activity test of CTPS 的体外活性试验,也证实了这一结论prepared by the MAE method by Zhu et al., also confirmed this conclusion [ 21]。与其他提取方法相比,. Compared to other extraction methods, the MAE法具有提取效率高、纯度高、活性成分不可降解、操作方便、省时、环保等优点。这是一种“绿色提取工艺”,使其广受欢迎。MAE虽然在TPS提取方面具有良好的前景,但也存在提取成分复杂、后期分离纯化困难、需要极性溶剂等缺点 method has the advantages of high extraction efficiency, high purity, non-degradable active ingredients, convenient operation, saved time, and environmental friendliness. It is a “green extraction process”, which has made it popular. Although MAE has favorable prospects in TPS extraction, it also has disadvantages such as complex extract components, difficult separation and purification in the later stages, and the necessity of polar solvents [ 43]. Therefore, in addition to the basic closed and open systems, several improved microwave extraction technologies, such as vacuum microwave-assisted extraction, nitrogen-protected microwave-assisted extraction, ultrasonic microwave-assisted extraction, and dynamic ]。因此,除了基本的封闭和开放系统外,还开发了真空微波辅助萃取、氮气保护微波辅助萃取、超声微波辅助萃取和动态微波辅助萃取等几种改进的微波萃取技术。microwave-assisted extraction, have been developed [41].
2.4. Enzymolysis Extraction
The ]。
5. 酶解提取
酶解法是指用酶水解破坏植物细胞壁。细胞壁分解成易溶于萃取溶剂的小分子物质,从而加速活性成分的溶解。酶解提取的enzymolysis method refers to the destruction of plant cell walls with enzymatic hydrolysis. The cell wall is decomposed into small molecular substances readily soluble in the extraction solvent, thereby accelerating the dissolution of active ingredients. The yield of TPS的得率通常较高,混合酶的效果优于单一酶。但酶的活性易受反应温度、 extracted with enzymatic hydrolysis is usually higher and the effect of mixed enzymes is better than that of a single enzyme. However, the enzyme’s activity is easily affected by the reaction temperature, pH、浓度等因素的影响,因此对实验条件和成本的要求通常较高。Baik 等人研究了果胶酶和鞣酸酶同时处理对绿茶中 TPS 提取的影响。, and concentration, so the requirements for experimental conditions and costs are usually higher. Baik et al., investigated the effect of the simultaneous treatment of pectinase and tannase on TPS extraction from green tea. They found that the concurrent treatment of the two enzymes was an effective method for TPS extraction and could significantly improve TPS’s free radical scavenging activity [28]. ]。Chang等人利用果胶酶辅助提取获得绿茶TPS,初步提取工艺如下:将磨碎的茶粉在90°C的水浴中加热2-4小时,0.5%果胶酶(Chang et al., used pectinase-assisted extraction to obtain green tea TPS, and the primary extraction process was as follows: the ground tea powder was heated in a water bath at 90 °C for 2–4 h, 0.5% pectinase (260,001加入 PGU/mL, v/w) /was added wand )incubated 并在 40°C 下孵育 30 分钟,然后通过在 90°C 下加热 1 小时使酶失活。制备的 TPS 具有出色的免疫刺激和对免疫细胞的保护作用at 40 °C for 30 min, and then the enzyme was inactivated by heating at 90 °C for 1 h. The prepared TPS presented excellent immune stimulation and protection against immune cells [ 30]。除了生物活性外,产率也是酶解提取的一个问题。. In addition to bioactivity, yield is also a concern for enzymolysis extraction. Zhu 等人使用混合酶(纤维素酶:果胶酶:葡聚糖酶et al., used mixed enzymes (cellulase:pectinase:glucanase = 1:1:2)在) for crude green tea polysaccharide (CTPS) extraction at 50 °C(30 分钟)下提取粗绿茶多糖(CTPS),然后煮沸使酶失活(10 分钟)并在 50°C 水浴中萃取 80 分钟。整个过程重复了三遍。用该方法获得的 (30 min), followed by boiling to inactivate the enzyme (10 min) and extracting in a water bath at 50 °C for 80 min. The whole process was repeated three times. The CTPS 总糖含量较高(obtained with this method had a high total sugar content (71.83%),这主要归因于混合酶对细胞壁的温和有效破坏), which could mainly be attributed to the gentle and efficient destruction of the cell walls by mixed enzymes [ 21 , 44]。. Wang 等人使用et al., used a 0.5% (m/v) 戊聚糖复合酶溶液(45 °C, pentosan complex enzyme solution (45 °C, pH 5.5)从用 95% 乙醇预处理 2 小时的绿茶叶和花中提取 TPS。过滤后,在相同温度下重复相同的提取过程。用这种方法获得的两种 TPS 的收率分别为) to extract TPS from green tea leaves and flowers pretreated with 95% ethanol for 2 h. After filtration, the same extraction process at the same temperature was repeated. The yields of two TPSs obtained with this method were 4.08% 和and 6.88%,远高于相同条件下热水提取的收率(分别为 , respectively, which were much higher than those obtained with hot water extraction under the same conditions (1.28% 和and 2.93%), respectively) [ 38]。与传统的溶剂提取法相比,酶解提取法具有提取效率高、特异性强、提取率高等优点。此外,还可以减少因使用大量溶剂而造成的环境污染,具有广阔的应用前景。但由于酶的价格相对较高,其活性受多种因素影响,因此必须严格控制酶解提取的提取条件,才能有效获得较高的提取率。
6. 其他提取方法
除了上述常见的提取方法外,还报道了一些新的. Compared to the conventional solvent extraction method, the enzymolysis extraction method has the advantages of a high extraction efficiency, strong specificity, and high extraction rate. In addition, it can reduce the environmental pollution caused by using a large amount of solvent and thus has broad application prospects. However, since the price of the enzyme is relatively high and its activity is affected by various factors, the extraction conditions for enzymolysis extraction must be strictly controlled to effectively obtain a higher extraction rate.
2.5. Other Extraction Methods
Some new methods for TPS提取方法。例如, extraction in addition to the above-mentioned common extraction methods have also been reported. For example, Xu 等人使用水/溶剂热法优化了萃取条件。他们利用高温高压(120℃,0.1MPa)使水分渗入中茶108茶叶中,破坏泡孔结构,从而分离出TPSet al., optimized extraction conditions using a hydro/solvothermal method. They used high temperature and pressure (120 °C, 0.1 MPa) to infiltrate water into the tea leaves of Zhongcha 108 to destroy the cell structure, thereby separating TPS [1]. The extraction rate of 1crude polysaccharides obtained with this method was ]。该方法得到的粗多糖的提取率为4.7%,远高于紫阳绿茶(3.46%), which was much higher than that of TPS obtained with ordinary hot water extraction, such as Ziyang green tea (3.46%) [ 22], ]、黄山毛峰茶(2.3%)等普通热水提取得到的TPS。Huangshan Maofeng tea (2.3%) [23], and Keemun black ]、祁门红茶tea (3.2%) [ 24]。孙等人用碱辅助提取法提取茯砖茶多糖(. Sun et al., used alkali-assisted extraction to extract Fuzhuan brick tea polysaccharide (FBTPS);萃取条件为); the extraction conditions were a 60 °C 萃取温度和extraction temperature and a 0.1 mol/L NaOH 溶液(solution (pH = 10.0)。与热水提取相比,碱提取). Compared to hot water extraction, the yield of FBTPS 的产量对单糖组成和产量的影响更大by alkaline extraction was found to have a greater impact on the monosaccharide composition and yield [ 30]. ]。此外,近年来新兴的提取技术超临界流体萃取(SFE)也被用于提取多糖。许多研究人员已经使用 SFE 提取各种植物来源的多糖,尽管这种工艺在 TPS 提取中的应用仍然很少。Chen 等人用In addition, emerging extraction technology supercritical fluid extraction (SFE) has also been used to extract polysaccharides in recent years. Many researchers have used SFE to extract various plant-derived polysaccharides, though there are still few applications of this process for TPS extraction. Chen et al., extracted TPS with a CO 2提取 TPS基于-based SFE 方法,他们确定了该方法在method, and they determined the optimum parameters of this method in TPS 提取中的最佳参数为粒径extraction as a particle size of 380 μm、20% 无水乙醇、提取压力, 20% absolute ethanol, an extraction pressure of 35 MPa、提取温度 45 ℃、提取时间 2 h,TPS 提取率高达, an extraction temperature of 45 °C, an extraction time of 2 h, which enabled a TPS extraction rate of up to 92.5%。此外,用这种方法获得的 TPS 具有显着的生物活性. Moreover, the TPS obtained with this method was significantly bioactive [ 31]. ]。尽管 SFE 方法令人印象深刻、易于管理、高效且环保,但由于其昂贵且耗时的设备,在实际应用中仍不如其他提取方法普遍。此外,Li 等人发现通过阴离子反胶束系统萃取具有传质快、选择性高、成本低等优点Although the SFE method is impressive, manageable, efficient, and environmentally-friendly, it is still not as common as other extraction methods in practical applications due to its expensive and time-consuming equipment. In addition, Li et al., found that extraction via a anionic reverse micelle system exhibited the advantages of a fast mass transfer, high selectivity, and low cost [ 32]。总之,. In short, various auxiliary methods for TPS提取的各种辅助方法能够提高多糖的生物活性,缩短提取时间,提高提取得率。
extraction are able to improve the bioactivity of polysaccharides, shorten extraction times, and improve extraction yields.
