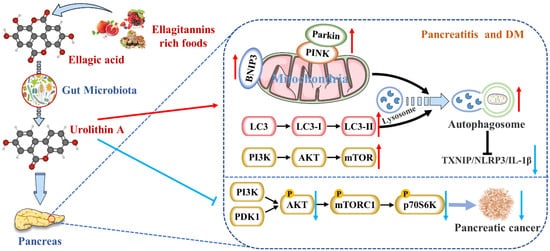
尿石素Urolithin A (Uro A) 是哺乳动物摄入植物性食物成分鞣花单宁和鞣花酸后肠道微生物群的饮食代谢物。越来越多的研究报告了它对多种疾病的多种潜在健康益处,包括心血管疾病、癌症、认知障碍和糖尿病。特别是,Uro A 通过直接口服给药是安全的,并且没有遗传毒性。胰腺通过分泌消化酶和激素在调节能量消耗和新陈代谢方面发挥核心作用。许多病理生理因素,如炎症、线粒体自噬缺陷和内质网应激,会对胰腺产生负面影响,导致胰腺疾病,包括胰腺炎、胰腺癌和糖尿病。 is a dietary metabolite of the intestinal microbiota following the ingestion of plant-based food ingredients ellagitannins and ellagic acid in mammals. Accumulating studies have reported its multiple potential health benefits in a broad range of diseases, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, cognitive impairment, and diabetes.
1. 减少胰腺炎症因子的表达Reduces the Expression of Pancreatic Inflammatory Factors
胰腺炎性微环境导致胰腺炎,是内分泌功能下降的主要原因The inflammatory microenvironment of the pancreas led to pancreatitis and was the main reason for the decline in endocrine function [
83 ]
。一些研究人员认为,如果. Some researchers suggested that if cells would express high β 细胞表达高水平的levels of NF-κB
信号标记,细胞的增殖和再生潜力就会降低。表达signaling marking, cells’ proliferative and regenerative potential were reduced. The NF-κB
的 β-expressed β cells also emerged with a premature upregulation of 细胞也出现了socs2的过早上调,这是一种抑制增殖的基因, a gene that inhibits proliferation [
84 ]。
已广泛报道It has been widely reported that EA
可抑制胰腺炎症(表can inhibit pancreatic inflammation (Table 1)。在自发性慢性胰腺炎的实验模型中,雄性). In an experimental model of spontaneous chronic pancreatitis, male Wistar Bonn/Kobori
大鼠被喂食添加 EA(rats were fed a diet supplemented with EA (100 mg/kg
体重/天)的饮食十周。他们发现 EA 通过增加胰腺重量和降低 MPO 活性(中性粒细胞浸润指数)、胶原蛋白含量、转化生长因子body weight/day) for ten weeks. They found that EA attenuated pancreatic inflammation and fibrosis by increasing pancreatic weight and decreasing MPO activity (a neutrophil infiltration index), collagen content, transforming growth factor-β1 (TGF-β1)
表达、活化胰腺星状细胞 (PSC) 和 ED- 来减轻胰腺炎症和纤维化。 1 阳性细胞expression, activated pancreatic stellate cells (PSCs), and ED-1-positive cells [
85 ]。
正宗等人。还报道Masamune et al. also reported that EA
抑制 PSC 中单核细胞趋化蛋白 inhibited the production of monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1)
的产生和激活蛋白 and activation of activator protein-1 (AP-1)
和 MAPK 的激活,所有这些均由白细胞介素and MAPK in PSCs, all induced by interleukin (IL)-1β
和and TNF-α
诱导 [
86 ]。
同时,Meanwhile, EA
抑制inhibited PDGF-BB
诱导的-induced tyrosine phosphorylation of PDGF P
受体酪氨酸磷酸化以及 PSC 中下游 ERK 和 Akt 的活化。特别是,EA 抑制 PSC 中响应-receptors and the downstream ERK and Akt activation in PSCs. In particular, EA inhibited ROS production in PSCs in response to TGF-β1
或血小板衍生生长因子or platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF)
的 ROS 产生 [
87 ]。
尽管Although EA
有许多有希望的发展,但它在人体肠道中的吸收很差,限制了它的抗炎作用。如上所述,EA 被微生物代谢成一系列下游化合物,如had many promising developments, it was poorly absorbed in the human gut, limiting its anti-inflammatory effects. As mentioned above, EA was metabolized by microorganisms into a series of downstream compounds, such as Uro A [
5 ]
。暴露于. A well-known effect of preclinical models exposed to Uro A
的临床前模型的一个众所周知的效果是有害炎症反应的减弱 was the attenuation of harmful inflammatory responses [
94 ]
。. Uro A
显示出比 EA 或 ET 更有效的抗炎特性,表明它可能是治疗 AP 或 CP 的主要化合物(表showed more potent anti-inflammatory properties than EA or ETs, suggesting that it might be the main compound for treating AP or CP (Table 1)。首次报道抗炎作用可降低急性结肠炎大鼠炎症标志物). The anti-inflammatory effects were first reported to reduce the mRNA and protein levels of inflammatory marker COX-2
的 mRNA 和蛋白质水平 in rats with acute colitis [
95 ]
。张等人。首次报道. Zhang et al. had firstly reported that Uro A
通过调节 AMPK 抑制 MIN6 β 细胞中含有inhibited the thioredoxin-interacting protein (TXNIP)/Nod-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3 (NLRP3)/IL-1β
炎症信号的硫氧还蛋白相互作用蛋白 (TXNIP)/Nod 样受体家族 pyrin 结构域(图 inflammation signal in MIN6 β cells by modulating AMPK (Figure 2)) [
88 ]
。最后,他们证明. Finally, they testified that Uro A
还下调蛋白激酶also down-regulated the protein kinase RNA (PKR)
样 ER 激酶-like ER kinase (PERK)
并促进and promoted AMPK
磷酸化phosphorylation [
96 ]
。最新研究表明,. The latest research showed that Uro A
可以通过调节can attenuate the severity of alcohol-associated chronic pancreatitis (ACP) in C56BL6/J mice by regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR
信号轴来减轻 C56BL6/J 小鼠酒精相关慢性胰腺炎 (ACP) 的严重程度 signaling axis [
89 ]
。.
图Figure 2. Uro A 在哺乳动物摄入is metabolized by gut microbiota after ingestion of ET 和 EA 后被肠道微生物群代谢,具有多种潜在的健康益处。Uro A 可通过抑制炎症信号通路、激活自噬、维持线粒体功能和改善免疫微环境来减轻胰腺疾病。s and EA in mammals and has multiple potential health benefits. Uro A can attenuate pancreatic diseases by inhibiting inflammatory signaling pathways, activating autophagy, maintaining the mitochondrial function, and improving the immune microenvironment.
然而,U
Nevertheless, studies on reducing pancreatic inflammation by Uro A had only been verified in animals and cells without clinical studies. The upstream mediators of Uro A’s anti-inflammatory effects, including the NF-κB and AhR-Nrf2 pathways, were mainly studied in vitro [36]. Nevertheless, the mechanisms of Uro A action in the context of inflammation seemed to vary with tissues and conditions. Hence, the differences in Uro A’s mitigation degree and mechanism on AP and CP need to be further explored.
2. Activates Autophagy and Maintains Mitochondrial Function in the Pancreas
Mitochondr
ial damage, such as the lo
A 减少胰腺炎症的研究仅在动物和细胞中得到验证,而没有进行临床研究。Uro A 抗炎作用的上游介质,包括 NF-κB 和 AhR-Nrf2 通路,主要在体外进行了研究ss of mitochondrial DNA (mt DNA) integrity, the alteration of mitochondrial morphology, and dysfunction, can lead to cellular senescence and apoptosis [
3697 ]
。然而,Ur. On the o
A 在炎症背景下的作用机制似乎因组织和条件而异。因此,Uro A 对 AP 和 CP 的缓解程度和机制的差异需要进一步探讨。
2. 激活自噬并维持胰腺中的线粒体功能
线粒体损伤,例如线粒体ne hand, mitochondria acted as both nutrient sensors and signal generators for DNAinsulin (mt DNA) 完整性的丧失、线粒体形态的改变和功能障碍,可导致细胞衰老和凋亡 [secretion in β cells. Moreover, 97nutrients ]。一方面,线粒体在can β 细胞中既充当营养传感器,又充当胰岛素分泌的信号发生器。此外,营养物质可以抑制 ATP 敏感的 inhibit the ATP-sensitive K
+ (K
ATP) ) 通道,然后通过作为线粒体 ATP 合成的底物(触发途径)或通过调节channel and then enhance insulin secretion either by acting as substrates for mitochondrial ATP synthesis (the triggering pathway) or by regulating Ca
2+来增强胰岛素分泌。通道(放大途径)。另一方面,线粒体是电子传递链水平上活性氧 channels (the amplifying pathway). On the other hand, mitochondria were the primary source of reactive oxygen species (ROS)
的主要来源,因此线粒体可能是at the level of the electron transport chain so that mitochondria might be the main targets of ROS
损伤的主要目标 damage [
98 ]
。此外,许多研究揭示了胰腺疾病与线粒体动力学失调(包括融合和裂变)之间的因果关系. Additionally, many studies have revealed a causal relationship between pancreatic diseases and dysregulation of mitochondrial dynamics (including fusion and fission) [
97 ,
99 ,
100 ]
。因此,线粒体损伤导致胰腺功能下降。. Thus, mitochondrial damage gave rise to decreased pancreatic function. The most consistent effect of Uro A
在不同物种(包括细胞、蠕虫、小鼠和人类)中最一致的效果是改善线粒体健康across species, including cells, worms, mice, and humans, was improved mitochondrial health [
94 ]
。这种益处是由功能失调的线粒体(称为选择性自噬)的清除和回收驱动的. This benefit was driven by the clearance and recycling of dysfunctional mitochondria, known as selective autophagy [
101 ]
。例如,. For example, Uro A
增加了编码increased the expression of mitochondrial autophagy genes lgg-1, pink-1, and pdr-1, encoding for LC-3B
, and 的线粒体自噬基因lgg-1、pink-1和pdr-1的表达,并增加了秀丽隐杆线虫中自噬体囊泡的形成formation of autophagosome vesicles in C. elegans [
29 ]
。.
有趣的是,小胶质细胞中的Interestingly, Pink1
敲低消除了knockdown in microglia eliminated Uro A
介导的-mediated reductions in TNF-α
减少并增加了and increased IL-10
,这表明, suggesting that Uro A
通过诱导线粒体自噬来减少神经炎症reduces neuroinflammation by inducing mitochondrial autophagy [
34 ]
。张等人。还证明. Zhang et al. also proved that Uro A
通过调节自噬抑制 MIN6 β 细胞中糖脂毒性诱导的 ER 应激和inhibited glucolipotoxicity-induced ER stress and the TXNIP/NLRP3/IL-1β
炎症信号inflammation signal in MIN6 β cells by modulating autophagy [
88 ]
。值得注意的是,. Remarkably, the inhibitory effects of Uro A
对 p62 的抑制作用强于on p62 were stronger than TXNIP
抑制剂维拉帕米-inhibitor verapamil (
p p <
0.05) [
102 ]
。在糖尿病小鼠的胰腺细胞中也报道了. Uro A
促进promoting PINK1/Parkin
介导的线粒体自噬-mediated mitophagy was also reported in pancreatic cells of diabetic mice [
90 ]
。因此,. Therefore, Uro A
恢复正确的线粒体自噬水平以维持正常的线粒体功能极有可能是Uro A减少胰腺疾病的机制(图 restoring the correct level of mitochondrial autophagy to maintain normal mitochondrial function is highly likely to be the mechanism of Uro A reducing pancreatic diseases (Figure 2)。).
3. 抑制胰腺内质网应激Inhibits Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in the Pancreas
内质网The misfolding and inhibition of protein folding in the endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
中蛋白质折叠的错误折叠和抑制导致未折叠蛋白质的聚集,从而导致 ER 应激 lead to the aggregation of unfolded proteins, resulting in ER stress [
103 ]
。李等人。表明伴随蛋白质聚集体积累的. Li et al. showed that the ER
应激和未折叠蛋白反应(UPR)成为受衰老影响的重要途径,特别是在β细胞中。同时,UPR 成分的转录组失调与激活转录因子 stress and unfolded protein response (UPR) accompanied by the accumulation of protein aggregates emerged as a significant pathway affected by aging, specifically in β cells. Simultaneously, the transcriptomic dysregulation of UPR components was linked to activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6)
和肌醇需要酶and inositol-requiring enzyme 1 (IRE1)
信号通路有关signaling pathways [
8 ]
。. ER
应激相关的细胞凋亡导致 β 细胞增殖和再生减少,最终导致胰岛素分泌减少和stress-related apoptosis lead to a reduction in β-cell proliferation and regeneration, ultimately resulting in reduced insulin secretion and increased T2DM
发病率增加morbidity [
104 ]
。因此,在衰老过程中保持转录稳定性和减少蛋白质稳态损失对于恢复胰腺功能至关重要。据报道,U. Therefore, maintaining transcriptional stability and reducing pro
A 可抑制胰腺 β 细胞中糖脂毒性诱导的 ER 应激 [tein homeostasis loss during aging was crucial to recovering pancreatic function. It has been 88reported ]。然而,需要对that Uro A
在胰腺中的上游和下游通路进行更多的研究,以改善 ER 应激 suppresses glucolipotoxicity-induced ER stress in pancreatic beta cells [ 88 ]。
However, more studies are needed on Uro A’s upstream and downstream pathways in the pancreas to improve ER stress.
4. 抑制胰腺肿瘤的发生和发展Inhibits the Occurrence and Development of Pancreatic Tumors
大量摄入富含High intakes of berries rich in ET
的浆果,包括草莓、石榴和蓝莓,与s, including strawberries, pomegranates, and blueberries, were inversely associated with PDAC
发病率呈负相关incidence [
105 ]
。. EA
是鞣花单宁的一种肠道代谢产物,可抑制 PDAC 中激活的多种致癌途径,例如, an intestinal metabolite of ellagic tannins, inhibited multiple carcinogenic pathways activated in PDAC, such as COX-2
、NF-κB 和 Wnt 信号传导,因此 EA 成功地阻止了细胞周期并逆转了 PDAC 中的上皮向间质转化, NF-κB, and Wnt signaling, so that EA successfully arrested cell cycles and reversed epithelial to mesenchymal transition in PDAC [
106 ]
。作为. As a downstream compound of EA
的下游化合物,, Uro A
显示出更有效的抗氧化和抗炎特性,提高生物利用度和抗肿瘤作用showed more potent antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, improving bioavailability and anti-tumor effect [
107 ]
。已经证明. It has been demonstrated AKT 的that the S473
磷酸化位点被phosphorylation site of AKT is activated by PI3K
激活 [
108 ]
。. Uro A
治疗导致 PDAC 细胞系中磷酸化 treatment resulted in a dose-dependent reduction in phospho-AKT (p-AKT)
表达呈剂量依赖性降低,从而导致 mTORC1 复合物调节的磷酸化 expression in PDAC cell lines, leading to a significant down-regulation of phospho-p70 S6
激酶kinase (p-PS6K)
表达显着下调。因此,expression regulated by the mTORC1 complex. Therefore, Uro A
通过下调inhibited the proliferation and migration of PDAC cells and enhanced apoptosis by down-regulating the PI3K/AKT/mTOR
通路抑制 PDAC 细胞的增殖和迁移,增强细胞凋亡 pathway [
109 ]
(图 (Figure 2)。此外,). Furthermore, Uro A
治疗还下调 PDK1(AKT 的上游靶点)和treatment also down-regulated PDK1 (the upstream target of AKT) and p-GSK3β
和and p-4E-BP1
(AKT 的下游靶点),表明 (the downstream targets of AKT), suggesting that Uro A
有效抑制effectively inhibited the PDK1/AKT/mTOR [
110 ]
。. Uro A
治疗还减少了 PDAC 工程化 PKT 小鼠模型中的免疫抑制性肿瘤相关巨噬细胞 (TAM) 和调节性 T 细胞。这意味着treatment also reduced immunosuppressive tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) and regulatory T cells in the engineered PKT mouse model of PDAC. It meant that Uro A
治疗通过诱导 treatment attenuated tumor growth and prolonged survival in mice by inducing changes in the immunosuppressive microenvironment of PDAC
免疫抑制微环境的变化来减弱肿瘤生长并延长小鼠的存活时间 [
91 ]
。斯里尼瓦桑等人。还指出. Srinivasan et al. also pointed out that Uro A
抑制 AKT、PS6K 和inhibited AKT, PS6K, and STAT3
信号传导,从而减少 Ki67 阳性肿瘤细胞并增加 PDAC 小鼠胰腺组织中signaling, thereby reducing the Ki67-positive tumor cells and increasing cleaved caspase-3
的表达expression in the pancreatic tissues of PDAC mice [
92 ]
。这些结果表明,. These results suggest that Uro A
是一种新型的 PDAC 多信号通路抑制剂/调节剂,具有预防和治疗胰腺癌的潜力(表is a novel inhibitor/regulator for multi-signal pathways in PDAC and has potential in the prevention and treatment of pancreatic cancer (Table 1)。).
5. 保护胰腺Protects Pancreatic β细胞 Cells
关于There have been many studies on the ameliorative effect of Uro A
对 DM 及其并发症的改善作用已有许多研究。具体来说,Savi 等人。首次表明on DM and its complications. Specifically, Savi et al. first showed that Uro A
在糖尿病心肌病recovered cardiomyocyte contractility and calcium dynamics in diabetic cardiomyopathy (DCM)
大鼠中恢复了心肌细胞的收缩力和钙动力学rats [
111 ]
。阿尔巴舍等人。进一步证明. Albasher et al. further demonstrated that Uro A
通过激活 SIRT1 表达和脱乙酰酶活性来预防大鼠中链脲佐菌素 (STZ) 诱导的 DCM prevents streptozotocin (STZ)-induced DCM in rats by activating SIRT1 expression and deacetylase activity [
112 ]
。肖等人。表明. Xiao et al. suggested that Uro A
可以通过 N-聚糖生物合成途径改善全身炎症和肠道屏障功能障碍,从而减轻 DM 相关的认知障碍 can attenuate DM-related cognitive impairment by ameliorating systemic inflammation and intestinal barrier dysfunction through the N-glycan biosynthesis pathway [
113]
。这一结论也得到了. This conclusion was also supported by Lee
等人的支持。他们指出,et al. They pointed out that Uro A
通过减少 2 型转谷氨酰胺酶 prevented DM-associated AD by reducing transglutaminase type 2 (TGM2)
依赖性线粒体相关 ER 膜-dependent mitochondria-associated ER membrane (MAM)
的形成和维持线粒体钙和 ROS 稳态来预防 DM 相关的 AD formation and maintaining mitochondrial calcium and ROS homeostasis [
35 ]
。徐等人。表明 Xu et al. indicated that Uro A
通过激活ameliorated diabetic retinopathy by activating the Nrf2/HO-1
通路抑制炎症和氧化应激来改善糖尿病视网膜病变pathway to inhibit inflammation and oxidative stress [
114 ]
。周等人。发现余甘子通过调节由. Zhou et al. found that Phyllanthus emblica L. facilitated vascular function in EST
代谢物介导的Z-induced hyperglycemia rats by regulating Akt/β-
连环蛋白信号传导促进 STZ 诱导的高血糖大鼠的血管功能 catenin signaling, mediated by the ETs metabolites[
115 ]
。.
胰岛素抵抗是Insulin resistance is one of the core mechanisms of DM. However, as a complex systemic metabolic disease, insulin resistance alone is not enough to cause DM
的核心机制之一。然而,作为一种复杂的全身性代谢疾病,仅靠胰岛素抵抗是不足以引起糖尿病的。胰岛β细胞总量减少引起的胰岛功能障碍也是DM发病的关键。研究表明,T2DM 中的 β 细胞可分为三种主要状态:易感性、适应和失效. Islet dysfunction caused by the decrease in the total amount of islet β cells is also the key to the pathogenesis of DM. Studies have shown that β cells in T2DM can be divided into three main states: susceptibility, adaptation, and failure [
116、117、118 ]。在胰岛素抵抗期间,. During insulin resistance, β
细胞通过分泌胰岛素增加胰岛素需求来补偿功能障碍 cells compensate for the dysfunction by increasing insulin demand through insulin secretion [
90 ]
。当. When β
细胞不能补偿葡萄糖稳态时,就会发生高血糖症。更重要的是,来自余甘子的cells fail to compensate for glucose homeostasis, hyperglycemia occurs. More importantly, EA
from Phyllanthus emblica L.
增加糖尿病大鼠increased the size or number of β
细胞的大小或数量。EA 还直接增加分离胰岛的葡萄糖刺激的胰岛素分泌,这表明 EA 直接作用于胰腺 β 细胞以发挥抗糖尿病活性,从而刺激胰岛素分泌并减少葡萄糖耐受不良cells in diabetic rats. EA also directly increased glucose-stimulated insulin secretion from isolated islets, suggesting that EA acted directly on pancreatic β cells to exert anti-diabetic activity, thereby stimulating insulin secretion and reducing glucose intolerance [
93 ]
。组织病理学结果表明,. Histopathological results showed that Uro A
对 β 细胞具有保护作用,例如改善胰腺结构和增加胰岛大小和数量。Uro A 治疗后 DM 小鼠胰腺的超微结构损伤,包括 ER 扩张、线粒体肿胀、嵴骨折和髓鞘形成,也得到了显着改善 [ had protective effects on β cells, such as improving the pancreatic structure and increasing islet size and number. Ultrastructural damages in DM mice pancreas after 90]。我们之前还讨论过,Uro A
通过激活自噬和调节treatment, including AKT/mTOR 信号来预防 T2DM 模型小鼠的 β 细胞凋亡 [ER expansion, mitochondria swelling, cristae fracture, and myelin 88sheath formation,
were also significantly improved [ 90]. ,We also discussed earlier 102that ]。然而,Uro A
改善 β 细胞结构和功能以降低 DM 风险的具体机制需要进一步探索。
总之,本节广泛讨论了prevented β-cell apoptosis in T2DM model mice by activating autophagy and Uro A 在改善胰腺疾病中的代谢和作用(总结在图 2中)。通过阐明egulating the AKT/mTOR signal [90,98,99]. However, the specific mechanisms of Uro A 的体内代谢和improving β-cell Uro A 保护胰腺的机制,它可能为通过富含 ET 和 EA 的植物性食物管理胰腺损伤提供新的思路。structure and function to mitigate DM risk need to be explored further.
In summary, the metabolism and the roles of Uro A in ameliorating pancreatic diseases have been extensively discussed in this section (summarized in Figure 2). By clarifying Uro A’s metabolism in vivo and Uro A’s mechanisms for protecting the pancreas, it might shed new light on managing pancreatic injuries via plant-based foods rich in ETs and EA.