At electrical power distribution networks, energy is consumed at the same time as it is generated, since its storage is unfeasible on large scale. Therefore, load forecasting is required by Transmission System Operators (TSO) to manage energy grid operations and supplies. Load forecastings are required very often everyday, then a lot of prediction calculations are executed during every forecasting interval. In Europe, owing to directives and new technologies, prediction systems will change from hour to quarter-hour intervals. Therefore, a predictive system may not have sufficienought time to compute all future forecasts. If all future intervals cannot be predicted by aThis article shows a tested solution to the computation time problem, while increasing accuracy of the forecasting load system, it will need a daily. The solution is based on making a schedule to decide, which establishes which future intervals will be forecascalculations must be executed at everyach moment of the day.
- short-term load forecasting
- computational burden
- forecasting schedule
- forecasting accuracy
1. Introduction
Short-term load forecasting (STLF) is required to manage production, distribution and economic operations of electric energy from the current hour to the following days. Every Transmission System Operator (TSO) needs accurate energy forecasts, otherwise it will suffer extra production costs with corresponding economic losses. In addition, accurate demand forecasts allow for managing electrical energy from renewable energies. Other entities require load forecasts to manage future operations, such as power marketers, independent system operators, or load aggregators.
Forecasting electricity load is a complex problem, which has been approached through various methods and from different points of view over the last few decades., In consequence, there is which has led to a great variety of forecasting algorithms implemented in different electricity networks. Many techniques are based on neural networks [1] [2] [3] [4] [5]. Other algorithms use statistical methods [6] [7]. and hHybrid systems that combine neural networks with other techniques are also common [8] [9] [10] [11].
2. Main Problem
1.1. Main Problem
TSOs require fast and frequent forecasts to read the results and manage the actions that adjust to future load. When operators with hourly intervals change to quarter-hour, they will have to forecast four times more values due to increase of intervals per day, they will also do this four times more often because of the reduced available time. This article addresses the problem of computational burden while increasing accuracy of the STLF systems already implemented.
The Spanish TSO, Red Eléctrica de España (REE), is working on hourly intervals. It needs forecasts for 19 electrical regions, which is 19 times more calculations than a single STLF system. Due to time limits for submitting predictions, it is not always feasible to calculate all future hours. Therefore, there is a schedule that determines which future intervals are predicted during each hour of the day. However, this schedule was not made with a reasoned basis.
The REE forecasting system cannot keep the previous forecasting schedule with quarter-hour intervals, since it is too computationally heavy to work within the new time restriction. Therefore, it needs a new schedule to forecast only the most useful intervals. A numerical criterion is required to define the usefulness of forecasts, in order to design a method which decides the better calculations to execute. As a result of that need, the main motivation of this work is to make a systematic method to optimize schedules.
3. Solution
1.2. Solution Approach
Previously, it was generally assumed that as rwesearchers approach to the forecast moment in time, the forecast becomes more accurate, since the information available (weather and load) has more correlation with the forecasted load. However, this hypothesis does not always hold true. Sometimes, predictions calculated in the past are more accurate than recent ones. If the accuracy loss can be known in advance, then the unproductive forecasts made at these times can be canceled, saving computational effort and gaining accuracy.
All forecast calculations must be computed within a time limit; therefore, each computer has a number N of maximum predictions to compute. This limit depends on available time and computation speed, which depends on the computer itself and the forecasting algorithm used. In order to select the best N forecasts that can be calculated at each moment, a method to prioritize them needs to be developed. In addition, even if all predictions can be calculated, they may be counterproductive, since some of them have larger error than previous ones.
Alfredo Candela et al. [12] d The papescr ribed, for the first time,elated to this article describes an algorithm that makes the optimal schedule of forecasts, so that the system only computes new forecasts when an accuracy improvement is expected. Therefore, the work presents a systematic method to optimize schedules according to accuracy and computational burden. The mentioned work also presents a formula that numerically defines the value of predictions, in order to decide the best calculations to execute at every moment of the day.
4. Literature Review of Scheduling for Short-Term Load Forecasting
2. Literature Review
The STLF field is extensive, since innumerable works have been published for decades; consequently, reviews of the state of the art have been published, such as those made by Mamum et al. [1312], Hippert et al. [1413], or Hong et al. [1514].
Other researchers [15] [16] [17] [18] [19] [20] [21][22] built and compared different STLF mathematical models employing error measures as performance indicators. After that, they did not consider how to apply those models in an optimized schedule, to avoid producing larger errors than past predictions that had already been calculated. J. Mohammed et al. [2322] did something similar, which also included reliability indicators to assess the model’s performance.
Another example is the work carried out by G. Veljanovski et al. [2423], in which they proposed a forecasting system based on a neural network. They did not consider the best time at which to obtain data and execute the computation. Weyermüller et al. [2524] built a minimalistic adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference model. It forecasts the load of one hour 24 h before, so this research could be applied to organize the calculation schedule if more forecast hours are added to the model.
The idpresea of optimizing the execution schedule cnt work could complement automatic forecasting systems, since it offers an eautomated extra step at the end of the modeling process, in order to reduce computational burden and increase accuracyobtain an optimized execution schedule. An example of automatically modeled systems is the work conducted by L. Shufen et al. [2625], in which they proposed an algorithm to automate time series forecasting for nonexperts. The analysis proposed in this work could be applied to future works of theoretical research. For example, the research by T. Panapongpakorn et al. [2726] or the work by D. Shuai [2827].
Jiang et al. [2928] examined their model for different anticipation times; they also compared different STLF models, taking into account error and computation times. However, anticipation times varied just from 5 min to 16 h ahead and they were used to assess models, in the same way that calculation times were employed to compare entire models.
There is research which focuses on reducing computational burden, such as that by A. McIlvenna et al. [3029]. This research aims to optimize the use of a previously built forecasting system regardless of which one it is. With a different approach, M. Weimar et al. [3130] evaluated the improvement of a STLF system according to the economic savings with an econometric model. This is an example of how improving accuracy offers benefits that overcome developing costs.
3. Methodology
Ap
3.1. Forecasting system employed
The STLF system used in this research, as t from the researchesesting benchmark, is the developed by the University Miguel Hernández (UMH) [128], which was implementhere is not previous worked in REE. The system has been operating for more than 4 years, and during this time REE and UMH have continued to collaborate in continuous improvement efforts [31] [32].
3.2. Computation limit
The time a computer needs to calculate a set of predictions depends on three factors: the time that it takes to load new input data (I), the number of forecasts (n), and the time that it takes to make each prediction (P). So, the run time (t) can be modeled with the linear equation (1).

Variables I and P depend on the computer and code employed. At the beginning of each hour, the forecasting system loads new input data (temperatures and previous measured load). As mentioned before, due to the limitation of accuracy or computational burden, for each execution, there is a maximum number N of predictions that can be performed without exceeding the response time limit. Therefore, for each execution period, up to N predictions with greater value can be selected.
3.3. Algorithm employment
The result obtained by applying the proposed algorithm is a schedule, which defines the forecasts to execute at each hour of the day. The algorithm does not depend on the mathematical model used, but on the errors that it makes regarding historical records. In this way, it can be applied to any system that is organized by time intervals.
The Figure 1 shows abhout scheduling forw to use and place the algorithm in a forecasting systems. The mentioned resear. First, the maximum number of predictions that can be calculated per interval is obtained, which [16][17][18][19][20][21][22][23][29][30][31]depends on arvailable the most similar works which tackle thime and computing power, as discussed previously at equation (1). At the same time, the previous year can be prediction evaluation or the computational burden, wed to calculate historical error records. Finally, the algorithm is applied to obtain a schedule that will serve to forecast load during the next year.
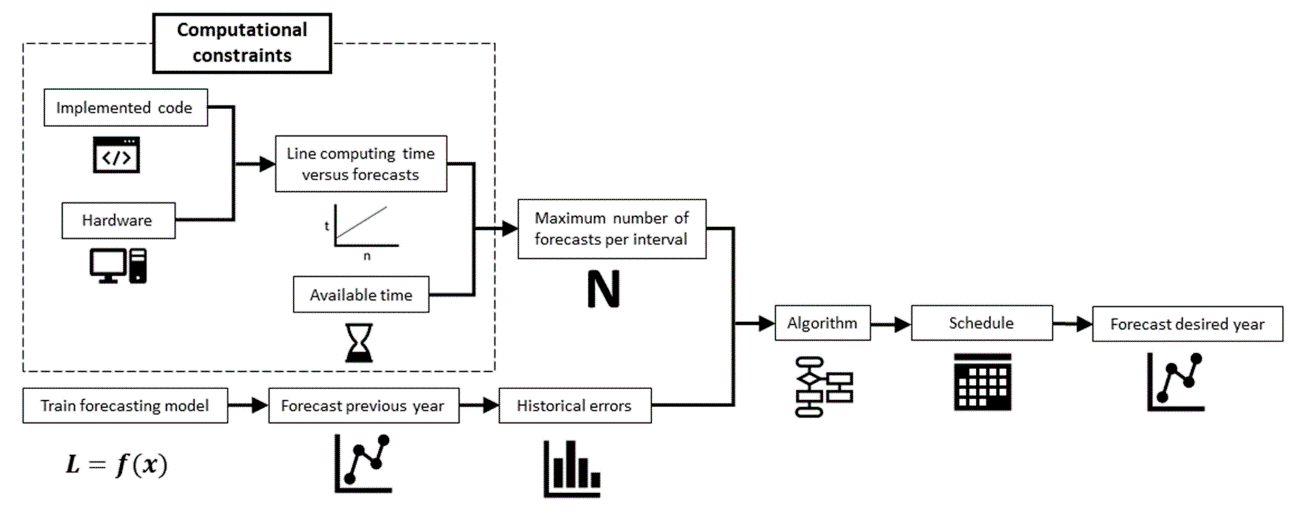
Figure 1. Process summary.
Othier sch is requireduling alternatives have been tested to decide the mcompare the performance of the proposed algorithm. They are summarized in Table 1.
| Name | Explanation |
|
Proposed algorithm |
Employ the proposed algorithm to obtain a sechedule and then use it to forecast during the entire year. |
| Complete schedule | Predict every future interval up to 9 days in advance, at every hour of the day (computationally unfeasible). |
| Current planning | The current schedule from REE. |
| Optimized algorithm | Employ the proposed algorithm, the with optimal number of calculations to minimize error. |
| Random selection | Forecast a number, n, of random future intervals at each hour of the day. |
| Last-day selection | This algorithm, at each moment, predicts the current day. It also forecasts the future day that has gone the longest time without updating, prioritizing those days which haver never been forecasted. |
Table 1. Scheduling options.
4. Proposed Algorithm
To meast usefulure the value of a predictions and then schedule the forecast execution.
5. Computational Burden
, a numerical indicator called accuracy improvement expectation (AIE) is used. As the name suggests, it represents the expectation of improvement in accuracy of a predicted demand if it is recalculated. Tho calculate time a computer needs tohis parameter, historical records of predictions calculated under the same conditions are used; that is, forecast a set of futurs calculated at the same time of day with the same advance period.
The implementervals depends on three variables: the time required to load new input data (I),d algorithm prioritizes the hourly forecasts according to larger AIE over the results of a full year, so only the best N forecasts will be executed in order to adhere to the time allowed. Before executing the algorithm, it is necessary to determine the number of future intervals to forecast (n),maximum forecasts, N, that the computer employed can execute. This is determined empirically by its computational speed and the time requicalculation time limit, as explained at equation (1).
5. Accuracy Results
The paper related to compute each prediction (P). So, the run time (t) can be obtained with the Equation (1)this article explains the tests to validate the proposed algorithm. The main test forecasts the year 2019 with every scheduling option, the accuracy average has been calculated for all the advances of all the hours of the year. In most advances, the optimized algorithm performs better than other methods. In addition, the Optimized Algorithm has a global improvement compared to the current schedule of the spanish TSO.
6. Computational burden
ALast-day selection example applied to this equation is tand optimized algorithm compute predictions under 7 min and the first one requires less time. However, the optimized algorithm offers better accuracy in most cases.
The Spanish electricity system operator REE. It requires future load of 19 electrical regions, n. Nowadays, the entire forecasting horizon spans up to 240 hours, thus the total of future loads that can be predicted extends to 4,560, which require 10.16 min. However, if the quarter-hour system is employed, the number of future intervals to forecast will multiply by four. This new system would entail 18,240 numbers to be calculated in 40.62 min, which is unfeasible since REE requires results before 7 min have passed.
According to Equation (1) and quarter-hour intervals, the maximum number of forecasts to compute in 7 min is 3,140. So, there is time to forecast 165 intervals in every electrical region. Therefore 165 is the maximum value that can be used on the algorithm as maximum number N of forecasts.
67. Conclusions
Thise developed research presented the need for a method tooffers an algorithm that organizes the calculation schedule of a STLF system along thfor the entire day. The schedule must beobtained is adapted to the computational capacity of the computer while increasing the system accuracy. The main idea couldethodology can be applied to any forecasting technique, even if computational burden is not an issue because it has been proven that limiting the number of forecasts can be beneficial for accuracy, as it has been demonstrated for the case of REE.
On the Spother hanish TSOd, according to results, the main [12].
Icon addtrition, solvingbution of the work is to reduce the computational burden problemload of a predictive system without sacrificing accuracy. This will allow a transition to the quarter-hour system with an optimal execution schedule. This research showe study offers a first approach to improve forecasting systems through calculation planning. Applying a similar study to other time series prediction systems could improve them in a similar way. As future work, it is proposed to use the algorithm to plan the new quarter-hour system of the Spanish TSO.
References
- Weicong Kong; Zhao Yang Dong; David J. Hill; Fengji Luo; Yan Xu; Short-Term Residential Load Forecasting Based on Resident Behaviour Learning. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2017, 33, 1087-1088, 10.1109/tpwrs.2017.2688178.
- Qifang Chen; Mingchao Xia; Teng Lu; Xichen Jiang; Wenxia Liu; Qinfei Sun; Short-Term Load Forecasting Based on Deep Learning for End-User Transformer Subject to Volatile Electric Heating Loads. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 162697-162707, 10.1109/access.2019.2949726.
- Dong-Xiao Niu; Qiang Wanq; Jin-Chao Li; Short term load forecasting model using support vector machine based on artificial neural network. 2005 International Conference on Machine Learning and Cybernetics 2005, 7, 4260, 10.1109/icmlc.2005.1527685.
- Singh, S.; Hussain, S.; Bazaz, M.A. Short Term Load Forecasting Using Artificial Neural Network. In Proceedings of the 2017 Fourth International Conference on Image Information Processing (ICIIP), Shimla, India, 21–23 December 2017; p. 5.
- Kunjin Chen; Kunlong Chen; Qin Wang; Ziyu He; Jun Hu; Jinliang He; Short-Term Load Forecasting With Deep Residual Networks. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2018, 10, 3943-3952, 10.1109/tsg.2018.2844307.
- Pu Wang; Bidong Liu; Tao Hong; Electric load forecasting with recency effect: A big data approach. International Journal of Forecasting 2016, 32, 585-597, 10.1016/j.ijforecast.2015.09.006.
- Yang, L.; Yang, H. A Combined ARIMA-PPR Model for Short-Term Load Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE Innovative Smart Grid Technologies—Asia (ISGT Asia), Chengdu, China, 21–24 May 2019; pp. 3363–3367.
- Miguel López; Sergio Valero; Ana Rodriguez; Iago Veiras; Carolina Senabre; New online load forecasting system for the Spanish Transport System Operator. Electric Power Systems Research 2017, 154, 401-412, 10.1016/j.epsr.2017.09.003.
- Filippo Maria Bianchi; Enrico De Santis; Antonello Rizzi; Alireza Sadeghian; Short-Term Electric Load Forecasting Using Echo State Networks and PCA Decomposition. IEEE Access 2015, 3, 1931-1943, 10.1109/access.2015.2485943.
- Ma, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Ding, J.; Wang, Q.; Ma, J. Short Term Load Forecasting Based on iForest-LSTM. In Proceedings of the 2019 14th IEEE Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications (ICIEA), Xi’an, China, 19–21 June 2019; pp. 2278–2282.
- Oveis Abedinia; Nima Amjady; Hamidreza Zareipour; A New Feature Selection Technique for Load and Price Forecast of Electrical Power Systems. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2016, 32, 62-74, 10.1109/tpwrs.2016.2556620.
- Alfredo Candela Esclapez; Miguel López García; Sergio Valero Verdú; Carolina Senabre Blanes; Reduction of Computational Burden and Accuracy Maximization in Short-Term Load Forecasting. Abdullah Al Mamun; Sohel; Naeem Mohammad; Samiul Haque Sunny; Debopriya Roy Dipta; Eklas Hossain; A Comprehensive Review of the Load Forecasting Techniques Using Single and Hybrid Predictive Models. IEEEn Accergiess 2022, 15, 3670, 10.3390/en15103670.0, 8, 134911-134939, 10.1109/access.2020.3010702.
- Abdullah Al Mamun; Sohel; Naeem Mohammad; Samiul Haque Sunny; Debopriya Roy Dipta; Eklas Hossain; A Comprehensive Review of the Load Forecasting Techniques Using Single and Hybrid Predictive Models. H.S. Hippert; Carlos Eduardo Pedreira; R.C. Souza; Neural networks for short-term load forecasting: a review and evaluation. IEEE ATransaccestions on Power Systems 2020, 8, 134911-134939, 10.1109/access.2020.3010702.1, 16, 44-55, 10.1109/59.910780.
- H.S. Hippert; Carlos Eduardo Pedreira; R.C. Souza; Neural networks for short-term load forecasting: a review and evaluation. Tao Hong; Shu Fan; Probabilistic electric load forecasting: A tutorial review. IEEE Tnteransactions on Power Systems national Journal of Forecasting 2001, 16, 44-55, 10.1109/59.910780.6, 32, 914-938, 10.1016/j.ijforecast.2015.11.011.
- Tao Hong; Shu Fan; Probabilistic electric load forecasting: A tutorial review. International Journal of Forecasting 2016, 32, 914-938, 10.1016/j.ijforecast.2015.11.011.Sethi, R.; Kleissl, J. Comparison of Short-Term Load Forecasting Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Sustainability (SusTech), Santa Ana, CA, USA, 23–25 April 2020; pp. 1–6.
- Sethi, R.; Kleissl, J. Comparison of Short-Term Load Forecasting Techniques. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Conference on Technologies for Sustainability (SusTech), Santa Ana, CA, USA, 23–25 April 2020; pp. 1–6.Jie-sheng, W.; Qing-wen, Z. Short-term electricity load forecast performance comparison based on four neural network models. In Proceedings of the The 27th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (2015 CCDC), Qingdao, China, 23–25 May 2015; pp. 2928–2932
- Jie-sheng, W.; Qing-wen, Z. Short-term electricity load forecast performance comparison based on four neural network models. In Proceedings of the The 27th Chinese Control and Decision Conference (2015 CCDC), Qingdao, China, 23–25 May 2015; pp. 2928–2932Mehmood, S.T.; El-Hawary, M. Performance Evaluation of New and Advanced Neural Networks for Short Term Load Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Electrical Power and Energy Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 12–14 November 2014; pp. 202–207
- Mehmood, S.T.; El-Hawary, M. Performance Evaluation of New and Advanced Neural Networks for Short Term Load Forecasting. In Proceedings of the 2014 IEEE Electrical Power and Energy Conference, Calgary, AB, Canada, 12–14 November 2014; pp. 202–207Xiaorong Sun; Peter B. Luh; Kwok Cheung; Wei Guan; Laurent D. Michel; S. S. Venkata; Melanie T. Miller; An Efficient Approach to Short-Term Load Forecasting at the Distribution Level. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2015, 31, 2526-2537, 10.1109/tpwrs.2015.2489679.
- Xiaorong Sun; Peter B. Luh; Kwok Cheung; Wei Guan; Laurent D. Michel; S. S. Venkata; Melanie T. Miller; An Efficient Approach to Short-Term Load Forecasting at the Distribution Level. IEEE Transactions on Power Systems 2015, 31, 2526-2537, 10.1109/tpwrs.2015.2489679.Rafi, S.H.; Nahid-Al-Masood, N.-A.-M. Highly Efficient Short Term Load Forecasting Scheme Using Long Short Term Memory Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 8th International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 4–6 March 2020; pp. 1–4
- Rafi, S.H.; Nahid-Al-Masood, N.-A.-M. Highly Efficient Short Term Load Forecasting Scheme Using Long Short Term Memory Network. In Proceedings of the 2020 8th International Electrical Engineering Congress (iEECON), Chiang Mai, Thailand, 4–6 March 2020; pp. 1–4Weicong Kong; Zhao Yang Dong; Youwei Jia; David J. Hill; Yan Xu; Yuan Zhang; Short-Term Residential Load Forecasting Based on LSTM Recurrent Neural Network. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2017, 10, 841-851, 10.1109/tsg.2017.2753802.
- Weicong Kong; Zhao Yang Dong; Youwei Jia; David J. Hill; Yan Xu; Yuan Zhang; Short-Term Residential Load Forecasting Based on LSTM Recurrent Neural Network. Shafiul Hasan Rafi; Nahid- Al Masood; Shohana Rahman Deeba; Eklas Hossain; A Short-Term Load Forecasting Method Using Integrated CNN and LSTM Network. IEEE TranAccesactions on Smart Grid 20217, 10, 841-851, 10.1109/tsg.2017.2753802., 9, 32436-32448, 10.1109/access.2021.3060654.
- Shafiul Hasan Rafi; Nahid- Al Masood; Shohana Rahman Deeba; Eklas Hossain; A Short-Term Load Forecasting Method Using Integrated CNN and LSTM Network. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 32436-32448, 10.1109/access.2021.3060654.Mohammed, J.; Bahadoorsingh, S.; Ramsamooj, N.; Sharma, C. Performance of exponential smoothing, a neural network and a hybrid algorithm to the short term load forecasting of batch and continuous loads. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Manchester Power Tech, Manchester, UK, 18–22 June 2017; pp. 1–6.
- Mohammed, J.; Bahadoorsingh, S.; Ramsamooj, N.; Sharma, C. Performance of exponential smoothing, a neural network and a hybrid algorithm to the short term load forecasting of batch and continuous loads. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Manchester Power Tech, Manchester, UK, 18–22 June 2017; pp. 1–6.Veljanovski, G.; Atanasovski, M.; Kostov, M.; Popovski, P. Application of Neural Networks for Short Term Load Forecasting in Power System of North Macedonia. In Proceedings of the 2020 55th International Scientific Conference on Information, Communication and Energy Systems and Technologies (ICEST), Niš, Serbia, 10–12 September 2020; pp. 99–101.
- Veljanovski, G.; Atanasovski, M.; Kostov, M.; Popovski, P. Application of Neural Networks for Short Term Load Forecasting in Power System of North Macedonia. In Proceedings of the 2020 55th International Scientific Conference on Information, Communication and Energy Systems and Technologies (ICEST), Niš, Serbia, 10–12 September 2020; pp. 99–101.Weyermüller, E.; Vermeulen, H.J.; Groch, M. Short-Term Load Forecasting using Minimalistic Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 International SAUPEC/RobMech/PRASA Conference, Cape Town, South Africa, 29–31 January 2020; pp. 1–6.
- Weyermüller, E.; Vermeulen, H.J.; Groch, M. Short-Term Load Forecasting using Minimalistic Adaptive Neuro Fuzzy Inference Systems. In Proceedings of the 2020 International SAUPEC/RobMech/PRASA Conference, Cape Town, South Africa, 29–31 January 2020; pp. 1–6.Shufen Liu; Songyuan Gu; Tie Bao; An Automatic Forecasting Method for Time Series. Chinese Journal of Electronics 2017, 26, 445-452, 10.1049/cje.2017.01.011.
- Shufen Liu; Songyuan Gu; Tie Bao; An Automatic Forecasting Method for Time Series. Chinese Journal of Electronics 2017, 26, 445-452, 10.1049/cje.2017.01.011.Panapongpakorn, T.; Banjerdpongchai, D. Short-Term Load Forecast for Energy Management Systems Using Time Series Analysis and Neural Network Method with Average True Range. In Proceedings of the 2019 First International Symposium on Instrumentation, Control, Artificial Intelligence, and Robotics (ICA-SYMP), Bangkok, Thailand, 16–18 January 2019; pp. 86–89.
- Panapongpakorn, T.; Banjerdpongchai, D. Short-Term Load Forecast for Energy Management Systems Using Time Series Analysis and Neural Network Method with Average True Range. In Proceedings of the 2019 First International Symposium on Instrumentation, Control, Artificial Intelligence, and Robotics (ICA-SYMP), Bangkok, Thailand, 16–18 January 2019; pp. 86–89.Di, S. Power System Short Term Load Forecasting Based on Weather Factors. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd World Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Intelligent Manufacturing (WCMEIM), Shanghai, China, 4–6 December 2020; pp. 694–698.
- Di, S. Power System Short Term Load Forecasting Based on Weather Factors. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd World Conference on Mechanical Engineering and Intelligent Manufacturing (WCMEIM), Shanghai, China, 4–6 December 2020; pp. 694–698. Huaiguang Jiang; Yingchen Zhang; Eduard Muljadi; Jun Jason Zhang; David Wenzhong Gao; A Short-Term and High-Resolution Distribution System Load Forecasting Approach Using Support Vector Regression With Hybrid Parameters Optimization. IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid 2016, 9, 3341-3350, 10.1109/tsg.2016.2628061.
- Huaiguang Jiang; Yingchen Zhang; Eduard Muljadi; Jun Jason Zhang; David Wenzhong Gao; A Short-Term and High-Resolution Distribution System Load Forecasting Approach Using Support Vector Regression With Hybrid Parameters Optimization. Amelia McIlvenna; Andrew Herron; Joshua Hambrick; Ben Ollis; James Ostrowski; Reducing the computational burden of a microgrid energy management system. Computers & IEEE Transactions on Smart Grid dustrial Engineering 202016, 9, 3341-3350, 10.1109/tsg.2016.2628061., 143, 106384, 10.1016/j.cie.2020.106384.
- Amelia McIlvenna; Andrew Herron; Joshua Hambrick; Ben Ollis; James Ostrowski; Reducing the computational burden of a microgrid energy management system. Computers & Industrial Engineering 2020, 143, 106384, 10.1016/j.cie.2020.106384.Weimar, M.; Somani, A.; Etingov, P.; Miller, L.; Makarov, Y.; Loutan, C.; Katzenstein, W. Benefit Cost Analysis of Improved Forecasting for Day-Ahead Hourly Regulation Requirements. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Power Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Portland, OR, USA, 5–10 August 2018; pp. 1–5.
- Weimar, M.; Somani, A.; Etingov, P.; Miller, L.; Makarov, Y.; Loutan, C.; Katzenstein, W. Benefit Cost Analysis of Improved Forecasting for Day-Ahead Hourly Regulation Requirements. In Proceedings of the 2018 IEEE Power Energy Society General Meeting (PESGM), Portland, OR, USA, 5–10 August 2018; pp. 1–5.Miguel López; Carlos Sans; Sergio Valero; Carolina Senabre; Empirical Comparison of Neural Network and Auto-Regressive Models in Short-Term Load Forecasting. Energies 2018, 11, 2080, 10.3390/en11082080.
- Miguel López; Carlos Sans; Sergio Valero; Carolina Senabre; Classification of Special Days in Short-Term Load Forecasting: The Spanish Case Study. Energies 2019, 12, 1253, 10.3390/en12071253.
