Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 3 by Amina Yu and Version 2 by Amina Yu.
In Mexico, Diabetes mellitus (DM) is a serious health problem, and although the current pharmacological treatments for DM such as insulin and oral hypoglycemics are available, the Mexican population continues to use medicinal plants in the treatment of DM. The antidiabetic properties of the plant species that belong to the Cucurbitaceae family has already been recognized worldwide.
- Cucurbitaceae
- Diabetes mellitus
- hypoglycemic
- Mexico
1. Generalities of the Cucurbitaceae Family
Cucurbitaceae is a flowering plant family of annual or perennial herbs or shrubs, also known as cucurbits. The leaves are alternate and exstipulate, while the flowers are unisexual, paniculate, racemose, or subumbellate. Calyx are mostly 5-lobed and imbricated and the corolla is valvate and involute. Seeds are numerous [1]. The fruit is perhaps the most notorious organ of the members of the Cucurbitaceae family and presents high variation in size, shape, and color. Mostly the fruits and, in some cases also the flowers, are eaten, and they are also used in traditional medicine and industry. Some fruits possess a bottle shape that has been utilized as a container or a musical instrument. Among the most recognized cucurbits worldwide are pumpkin, watermelon, melon, zucchini, and cucumber [2].
The Cucurbitaceae family together with the Asteraceae and Brassicaceae families has been considered extraordinarily important to humans due to their medicinal, alimentary, botanical, cultural, and economic relevance. Cucurbitaceae has been related with human nutrition for more than 12,000 years in that several species are among the plants first domesticated by humans [2][3]. Therefore, an interesting prevalent characteristic of Cucurbitaceae plants is their adaptability to a wide range of agricultural environments, because they grow as crops but can also be found in private gardens, with medicinal or food purposes [4]. Consequently, Cucurbitaceae species are cultivated around the world under a variety of conditions, highlighting their great economic importance, and they also have been considered the most diverse plant family on the planet [5].
The oils extracted from the seeds of Cucurbitaceae plants are using for cooking in Africa and the Middle East, and interest in its industrial applications has been increasing in recent years, due to the fact that their fatty acid and tocopherol compositions reveal a potential utilization in the industrial area as foods, detergents, vitamin supplements and biodiesel fuel [6].
The Cucurbitaceae family with a predominantly tropical distribution comprises approximately 118 genera and 825 species. Mexico is one of the most important centres of diversity of Cucurbitaceae, due to the 141 taxa that thrive in this country. From these latter, some estimations have calculated that 128 taxa thrive as wild and that 13 species are cultivated in Mexico. More than one half of these 128 Mexican wild taxa are endemic to this country and 34 are actively employed by people in rural areas at present [3][7].
Numerous species of Cucurbitaceae have been employed to cure a variety of diseases in different countries, in which the fruits and frequently the seeds are the most utilized parts of the plant. Information about Cucurbitaceae and its uses in traditional medicine are vast and has previously been the subject of many reports. This was mentioned some of the most frequent traditional uses of Cucurbitaceae reported worldwide. The treatment of digestive diseases is reported very often, such as intestinal parasites, constipation, flatulence, indigestion, colic, and stomachache [8][9][10]. To treat dermatological affections, Cucurbitaceae species were mentioned for dermatitis, acne, and dandruff [11][12][13]. Moreover, an immense variety of diseases such as hemorrhoids, fever, sore chest, paralysis, herpes, lung inflammation, asthma, malaria, leprosy, for blood cures, and headache are also treated with the Cucurbitaceae species [14][15][16]. A variety of investigations have demonstrated the biological properties of the members of the Cucurbitaceae family, such as antibacterial, antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, anticancer, antidiabetic, anti-HIV, anti-pyretic, and antihelminthic [5][17]. However, the traditional use of Cucurbitaceae in the treatment of chronic diseases such as DM, cancer, and arthritis is also documented [18][19][20]. Thus, the Cucurbitaceae family is a well-recognized source of secondary metabolites with diverse biological activities tested in in vitro and in vivo assays, and more recently, in clinical trials. Because of the extensive and complex information on the Cucurbitaceae species, the botanical significance of this plant family to Mexico, and the importance of DM in Mexico, the present manuscript focuses on the necessary information for the future one of bioactive molecules that are useful in the treatment of DM, those molecules deriving from the selected species of the Cucurbitaceae family most frequently reported as employed in Mexican traditional medicine for the treatment of DM as follows: Cucurbita ficifolia, Cucurbita maxima, Cucurbita moschata, Cucurbita pepo, Ibervillea sonorae, Sechium edule, Citrullus lanatus, Cucumis sativus, and Cucumis melo.
2. Selected Species of the Cucurbitaceae Family Used in Mexico in the Treatment of DM
2.1. Cucurbita ficifolia Bouché
Cucurbita ficifolia is one of the domesticated Cucurbitaceae species whose origin has not been defined. Some authors suggest Central America or Southern Mexico as places of origin, while others propose South America, and more specifically the Andes [21][22]. In Mexico, C. ficifolia is known as chilacayote, and is widely consumed in different traditional dishes and also as sweets prepared with their seeds or fruits [22]. The entire plant and the fruit are utilized in traditional medicine: for example, in the state of Hidalgo, Mexico, the fruit has been employed topically to treat worms found under the skin (such as larva migrans) [23], and the fruit macerated in water is used for the treatment of diabetes [22][24].
2.2. Cucurbita maxima Duchesne
Cucurbita maxima is native to the Americas and was cultivated by the ancient civilizations of Central and South America more than 7000 years ago. Other varieties can be found in Australia, Africa (Zambia, Nigeria, and Zimbabwe), Asia (China, India, Iran, Afghanistan), and Europe (Spain and Turkey) [25][26]. It is known as winter squash, butternut squash, kalabazeam maboga, zapallo, parangi, giromon, cocozza [27], giant pumpkin, hubbard squash, kabocha squash or pumpkin [22]. Traditionally, the leaves, fruits and seeds are used to treat various ailments. The seeds are consumed orally for the treatment of intestinal worms, parasites [28][29], constipation [28], kidney problems [30], and prostatitis [31]. The leaves have been utilized for the treatment of anemia [32] and head and lung cancer [33]. Oral consumption of the fruit in traditional medicine for the treatment of urinary disorders [30], blood pressure control, and constipation has been recorded [34]. In Mexico, China, and Iran the juice of the fruit of C. maxima is employed for control of the blood glucose level [22][35].
2.3. Cucurbita moschata Duchesne
Archaeological evidence indicates that the possible territories where C. moschata was domesticated are localized in Mexico (about 5000 B.C.), Peru (3000 B.C.) or Guatemala (2000 B.C.) [26]. Currently, C. moschata is widely distributed in Asia, America, and Africa [36]. Common names for C. moschata include butternut squash, pumpkin, cheese pumpkin, golden cushaw, Japanese pumpkin, melon squash, musky gourd, musky pumpkin, musky squash, musky winter squash, seminole pumpkin, tropical pumpkin, winter crookneck squash, winter marrow, winter pumpkin, winter squash, and winter straightneck squash [37]. C. moschata is used to prepare a variety of traditional dishes, but is also utilized in traditional medicine. The seeds are employed to relieve kidney affections, as an antiparasitic, and in the treatment of intestinal infections. The flowers are used topically to soothe minor wounds [37][38]. In China, the seeds of C. moschata are officially prescribed by traditional medicine for the treatment of DM [39]. Research on the bioactivity of C. moschata reveals that polysaccharides exhibit antioxidant [40], antibacterial [41], anti-obesity [42], antitumoral [43], antiparasitic [44], and hypoglycemic effects [45][46]. A number of studies have been carried out to delve into the antidiabetic properties of the fruits, flowers and stems of C. moschata. Several reports showed that hypoglycemic activity has been related to the carbohydrate content.
Song and collaborators [47] identified, by gas chromatography, two galactose monosaccharides and glucose as components of the active aqueous extract of the fruit of C. moschata, with a presence of 86.4 and 13.6%, respectively. The aqueous extract was able to inhibit (97.4%) in a non-competitive mechanism, the enzyme α-glucosidase in a concentration of 0.7–0.9 mg/mL.
In addition to the identification of simple carbohydrates, the isolation and identification of two glyceroglycolipid tetrasaccharides from the fruit of C. moschata has been reported. The glyceroglycolipid tetrasaccharides QGMG2 and QGMG3 (50 mg/kg) were able to decrease serum glucose levels in a similar way to Metformin, when administered in diabetic mice induced by Streptozotocin and with a high-fat diet. The compound QGMG-3, with a side chain of three unsaturations, exhibited higher activity than QGMG-2, with a side chain of two unsaturations [45]. Similarly, Jin et al. evaluated the ethanolic extract of C. moschata in mice with Alloxan-induced diabetes. The fraction composed of glucose, galactose, arabinose, and rhamnose produced a significant reduction in blood glucose levels, from 15.90 ± 3.21 mM to 7.19 ± 2.54 mM [48].
Other evidence of the hypoglycemic effect of the C. moschata extract was shown by Zhang et al. [49]. These authors investigated the effect of the administration of a fraction of water-soluble carbohydrates obtained from the hydroethanolic extract (80%) of the C. moschata fruit in Alloxan-induced diabetic rabbits in a dose of 75 mg/kg for 21 days. The results indicated that this polysaccharide fraction improves the body-weight loss of rabbits and also a reduction in the levels of blood glucose (BG), total cholesterol (TC), triglycerides, and glycated hemoglobin (HbA1c) were observed. Additionally, in the analysis of the pancreatic tissue, the water-soluble carbohydrate fraction exerted the regeneration of damaged pancreatic islets by stimulating β-cell proliferation. The chemical analysis of this polysaccharide fraction revealed the presence of glucose, galactose, arabinose, rhamnose, and a small amount of hexuronic acid.
Chang et al. [50] reported some components of the stem of C. moschata and the hypoglycemic effect and the mechanism of action. Ten compounds from two fractions of the methanolic extract of the stem of C. moschata that presented hypoglycemic activity in Streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice were identified. These compounds include apocarotenoids (loliolide); phenolics [2-hydroxybenzoic acid; 4-hydroxycinnamic acid; ferulic acid]; lignans [(+)-(1R,2S,5R,6S)-2,6-di(4′-Hydroxyphenyl)-3,7 dioxabicyclo [3.3.0]octane; pinoresinol; 4-ketopinoresinol; syringaresinol]; and steroids [(22E,24R)-24-Methyl-6β-methoxy-5α-cholesta-7,22-diene-3β,5-diol; 3β-Hydroxy-(22E,24R)-ergosta-5,8,22-trien-7-one] and are shown in Figure 1. Steroid compounds 24-methyl-6β-methoxy-5α-cholesta-7,22-diene-3β,5-diol, and 3β-hydroxy-(22E,24R)-ergosta-5,8,22-trien-7-one promoted glucose uptake in normal hepatocytes in a similar way to that of insulin. The mechanism of action of these compounds may be mediated by AMPK activation. On the other hand, despite the structural difference of compounds ferulic acid, syringaresinol, and 24-methyl-6β-methoxy-5α-cholesta-7,22-diene-3β,5-diol, they showed an insulin-sensitization and/or insulin-substitution function in insulin-resistant cells. Thus, the stem of C. moschata contains compounds with the potential to control T1 or T2DM [50]. The hypoglycemic effect of the fruit of C. moschata has also been demonstrated for the seeds. Marbun et al. [51] reported the antidiabetic activity of the ethanolic extract of the seeds and pulp of C. moschata, which was comparable to the effect of Metformin in Streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice. Preliminary tests revealed the presence of flavonoids, terpenes, saponins, and tannins in both extracts.
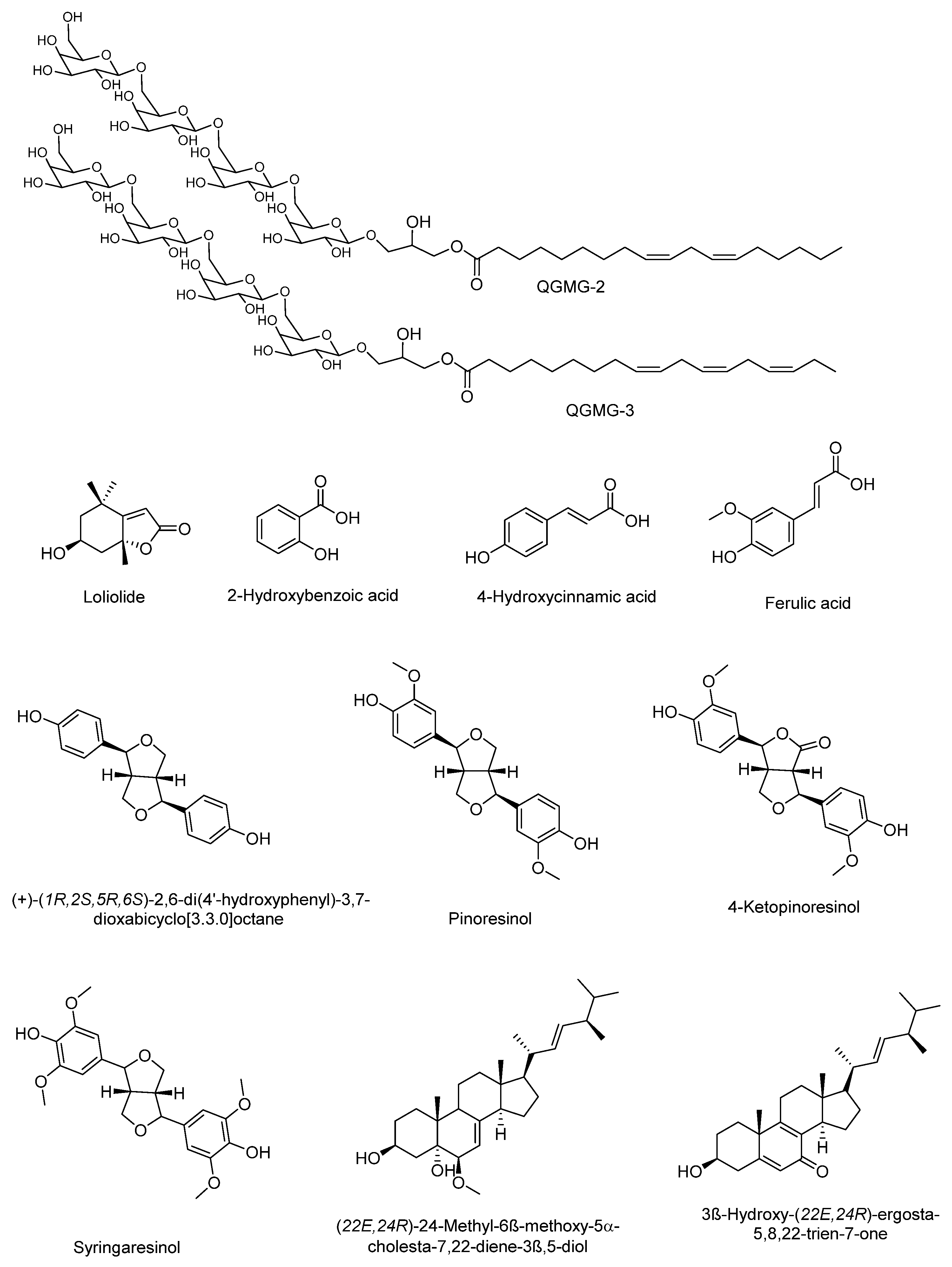
Figure 1. Molecules isolated of the extract of stem of C. moschata with hypoglycemic activity.
2.4. Cucurbita pepo L.
C. pepo is a Cucurbitaceae known as pumpkin that has been part of the human diet for more than 10,000 years and that possesses the oldest record of domesticated Mesoamerican species, over other members of the Cucurbitaceae family such as C. moschata, C. argyrosperma, and Lagenaria siceraria. Recent data suggested that pre-Columbian Mexican civilizations probably cultivated cucurbits prior to corn [52]. C. pepo is native to Mexico and today is cultivated in association with other plants as part of the cultivated corn field (milpa) or as a single crop [53]. The flowers and fruits are consumed in Mexico through the preparation of candies, cakes, or traditional dishes [54]. In traditional medicine, C. pepo had been used largely in a number of countries around the world as a diuretic and antihelminthic. However, one of the most common uses is in the treatment of irritable bladder for enlarged prostate-gland and micturition problems. Nonetheless, even these treatments with C. pepo seeds diminish micturition, it has not very effective in reducing the expanded size of the prostate gland [55].
Regarding the phytochemicals reported in C. pepo, the fruit is characterized by a high total carotenoid content of 171.9 to 461.9 μg·g−1, but also by a low content of fat (2.3%), and a poor polyphenol content, which was calculated as 0.02 mg GAE/100 mg sample by fresh fruit [56]. Nevertheless, 57 phenolics and other polar compounds were identified by HPLC coupled with two different detection systems: diode array (DAD) and quadrupole time-of-flight (Q-TOF) mass spectrometry. These phenolics were grouped as hydroxycinnamic acids and derivatives, hydroxybenzoic acids and derivatives, flavones and glycosides, flavonols and glycosides, organic acids and derivatives, amino-acids and derivatives, and nucleosides [57]. Studies on the chemicals present in the seeds of C. pepo are numerous and varied. Some variations in the composition of the main chemicals in the seeds have been detected. However, the seeds of pumpkin content are approximately 50% oil and are a good source of phytosterols, carotenoids, fatty acids, and vitamins. The seeds of C. pepo have been characterized by their tocopherol content, where γ-tocopherol is more abundant than α-tocopherol. The oils of seeds contain phenolics such as tyrosol, vanillic acid, vanillin, luteolin, and sinapic acid, where tyrosol was the most abundant compound detected in an amount of 1.6 mg/kg to 17.7 mg/kg [58]. Other reports found that p-hydroxybenzoic acid was the most conspicuous phenolic acid in all parts of the seeds of C. pepo, such as kernels and the hulls [27]. The main fatty acids reported in the pumpkin seeds are oleic, linoleic, linolenic, palmitic, and stearic acids, while among the most conspicuous carotenoids, it was found that lutein, α-carotene, β-carotene, auroxanthin, flavoxanthin, luteoxanthin, β-carotene violxanthin [56]. The terpenes found in the C. pepo seeds were studied by Kikuchi et al. [59], who reported the presence of 3-p-aminobenzoyl multiflorane-type triterpenes, 7-epi zucchini factor A and debenzoyl zucchini factor B. Additionally, five malutiflorane-type triterpenoids, two new ent-kaurane diterpene glycosides; and a new steroid, (24S)-stigmasta-7,22E,25-trien-3-one, were identified (Figure 2). From the sprouts of C. pepo, two novel multiflorane p-aminobenzoates were isolated: 7-epi zucchini factor A (1b) and debenzoyl zucchini factor B. None of these compounds were found in adult plants [60]. However, the triterpene squalene is one of the most conspicuous in pumpkin seeds and has been employed as a marker. Squalene has also been recognized to possess anticancer, antibacterial, and antifungal properties and plays an important role in the metabolism of cholesterol and steroid hormones [61]. The sterols are another group of compounds that are considered as prominent in C. pepo, particularly Δ7 and Δ5 sterols. Δ stigmastatrienol and Δ spinasterol have been considered as the main sterols isolated in seeds of C. pepo, followed by Δ stigmasterol, stigmastadienol, and β-sitosterol [62].
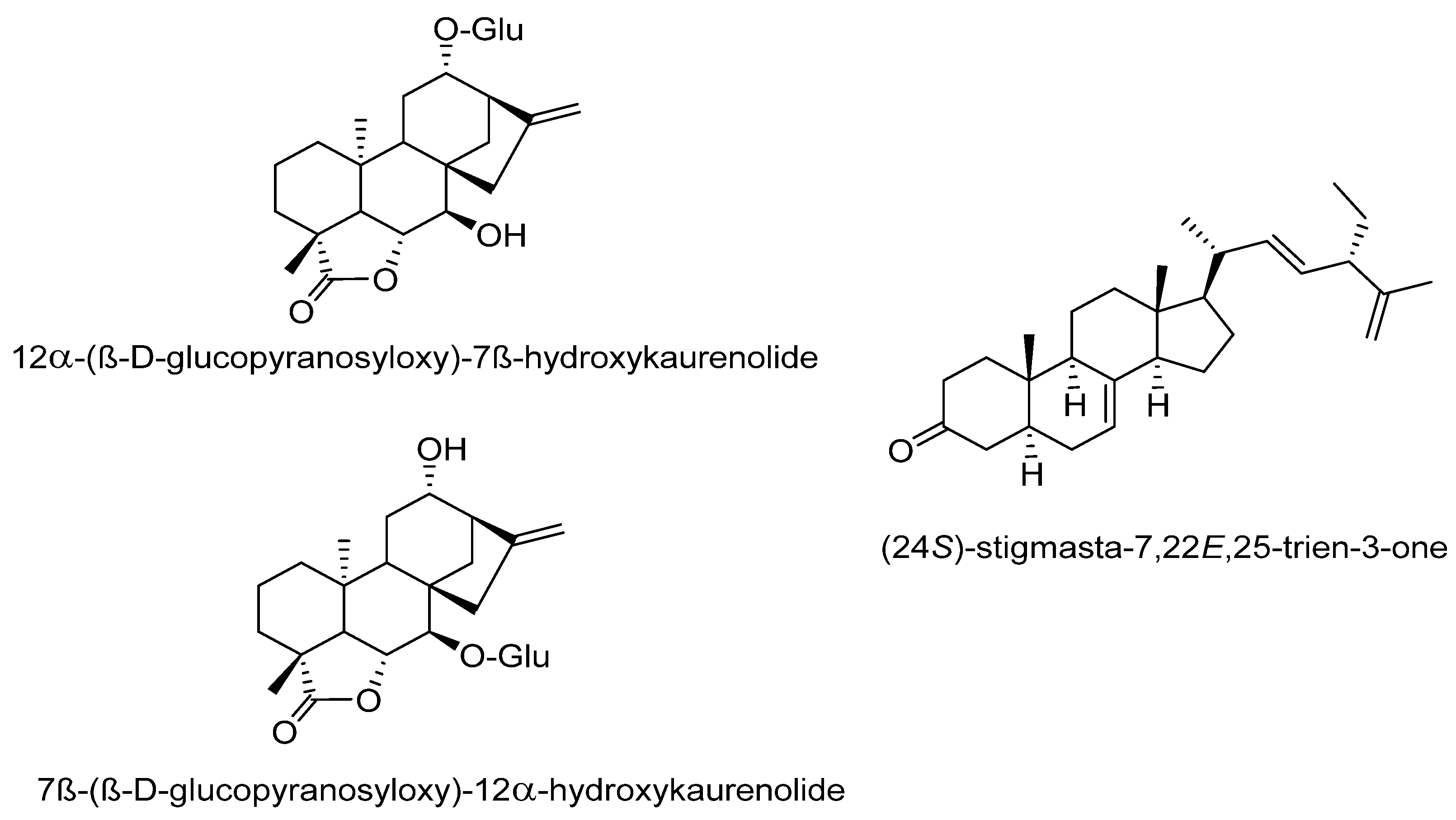
Figure 2. Novel isolated compounds of C. pepo seeds.
On the other hand, some pharmacological properties of pumpkin have been reported, such as antimicrobial, hepatoprotective, lipid lowering, antioxidant, antihypertension, anti-inflammatory, and antidiabetic properties [63]. However, these latter antidiabetic properties have been acquiring relevance in recent years, because of the traditional use of C. pepo in the treatment of DM in Mexico, in which local healers recommend the ingestion of crude aqueous extracts of pumpkin, which represents a source which is available for the entire population; therefore, it comprises an alternative treatment for the growing population that suffers from DM, especially in Mexico.
The hypoglycemic activity (blood sugar lowering) of C. pepo extracts was demonstrated in Alloxan-induced diabetic rats and rabbits, and interestingly, these active hypoglycemic properties of pumpkin were identified in the pulp and seed extracts, in contrast with those of the leaves and stems [63]. Pumpkin powder was administrated during 4 weeks to Alloxan-induced diabetic rats, where the results showed a significant reduction in the levels of glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides, low density lipoprotein (LDL) and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels. However, even the pumpkin powder increased the levels of blood insulin and high density lipoprotein (HDL), though not significantly. The histological analysis evidenced the restoration of the pancreatic tissue caused by the administration of the pumpkin powder, due to the increase in the diameter and number of the Langerhans islets observed in rats fed with pumpkin [64].
2.5. Ibervillea sonorae (S. Watson) Greene
Ibervillea sonorae, known as wareke o wereke, is a perennial plant distributed in the northern states of Mexico, including Sinaloa, Sonora, and Baja California, and the southern regions of the U.S. Some indigenous tribes of that Mexican region, such as the Mayo, Opata, Seri, and Yaqui, have traditionally used wareke for the treatment of skin diseases. Nevertheless, since pre-Hispanic times, knowledge about its empirical use for minor skin infections, arthritis, rheumatism, and heart conditions have been recorded [65].
In the 20th century, different activities have been found in the extracts of the roots, probably because these organs are the most notorious parts of I. sonorae, exhibiting a tuberculous appearance (root tuber) that is usually marketed. In 1993, Domínguez et al. [66][67] described the first formulas of the main chemical components of these tuberous roots of I. sonorae, describing the isolation and characterization of six compounds of the type of the cucurbitan series of tetracyclic system of 3-glycosides-tetramethyl-19-norpregnenedione-17-2,3,6,-trihydroxy-6-methyl cucurbitacin Kinoin A and Cucurbitacin B; Kinoin A and B glycosides; hexanorcucurbitacin Kinoin C [3a,16adihydroxy-4,4,9,14-tetramethyl-(9~,10~)-19-norp~gn-5-ene-l 1,20-dione] and Kinoin C triterpenes (Figure 3). These cucurbitacins were named in honor of Father Quino, an Austrian-Italian Jesuit missionary, explorer, cartographer, geographer, and astronomer, distinguished among the indigenous people in the present area of northwestern Mexico and in the southwestern U.S. for his methods of evangelization, the founder of 20 missions, and known for his ability to establish relationships between indigenous people and the religious institutions that he represented [66].
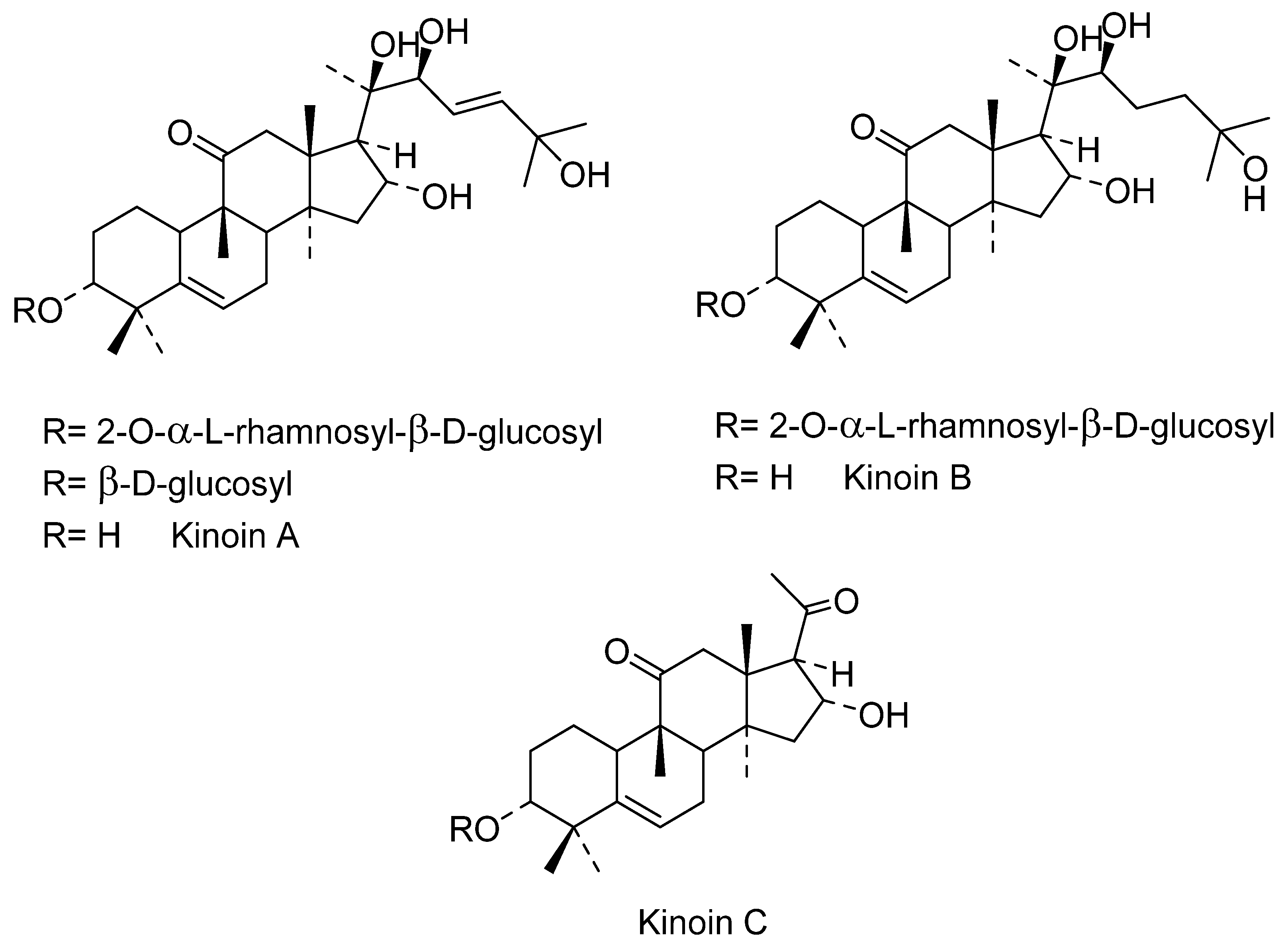
Figure 63. Novel isolated compounds of C. pepo seeds.
2.6. Sechium edule (Jacq.) Sw.
Sechium edule, popularly known as, chayote, is a native, perennial climbing plant domesticated by the Aztec and Maya civilizations. Chayote is an important element of the Mexican diet and is employed to prepare salads, jams, sweets, or desserts [68]. At present, chayote is cultivated in tropical and subtropical areas worldwide and is known by different names depending on the region where it is found, such as cidrayote, chiote, cho-cho, choko, chow-chow, christophene, custard, hayatouri, huisquil, mango squash, mirliton, sayote, vegetable pear, and xuxu [69]. Chayote is recognized in a wide range of shapes and sizes, but today it can be identified due to the existence of data on its genome and its proteome [70].
In recent years, S. edule has been investigated due to the therapeutic and nutritional potential of its natural product content [71]. Among some current uses of chayote are: its employment in the food industry due the production of starch; in the cosmetic industry, as an ingredient in moisturizers, cleansers, sun lotions, toothpastes, mouthwash, shaving creams, deodorants, and shampoos; and in the animal nutrition area due to its promotion of growth in pigs, because the chayote meals prepared with fruits and leaves were found to replace the standard grower ration in the diet of the pigs without any secondary effects; and this may be one of its most salient uses: in traditional medicine [72]. Chayote has been widely utilized in the treatment of diabetes, followed by uses such as a diuretic, in renal calculi, arteriosclerosis, hypertension, vermifuge, leprosy, and asthma [73][74].
A variety of in vitro and in vivo tests have been conducted in order to detect the pharmacological properties of S. edule in various organs or systems, such as the cardiovascular and the central nervous system, the gastrointestinal system, and in the liver and kidney, but very few of these are bioguided in order to identify the bioactive compounds. The phytochemical content of the chayote is diverse and the chemicals that have been identified are alkaloids, saponins, phenolic acids, flavonoids, carotenoids, coumarins, cucurbitane triterpenoids, and phytosterols [72]. According to some authors, the flavonoid and triterpene content that are the most relevant for biological activities in S. edule; thus, some of the main flavonoids identified in S. edule are apigenin 6-C-β-D-glucopyranosyl-8-C-β-D-apiofuranoside, diosmetin 7-O-rutinoside, luteolin 7-O-rutinoside, luteolin 7-O-β-D-glucoside, and apigenin 7-O-rutinoside [68]. In the same manner, the triterpenoids in S. edule are characterized by the presence of cucurbitacins such as the cucurbitancins B, E, P, and L [75].
On the other hand, as reported by Siahaan et al., flavonoids comprise the most relevant chemical content for the hypoglycemic effects observed in S. edule. A significant decrease in the blood sugar levels of mice was observed after the administration of the ethanolic extract of S. edule in a 200 mg/kg dose. However, no changes were observed in the activity of the glutathione peroxidase enzyme. Additionally, a difference in the diameter of the pancreatic β-cell was recorded in chayote-treated mice [76]. In a subsequent one, this same research group focused on the anti-hypoglycemia and antioxidant activities of S. edule in a rat model of T2DM. The ethanol extract and the ethyl acetate fraction of chayote possess antioxidant and anti-insulin resistant activities as they were able to reduce the levels of blood sugar and increase the antioxidant level of superoxide dismutase (SOD) [77].
Because the fruit of S. edule is widely recommended in Mexico for reducing not only the glucose blood levels, but also the risks related to diabetes, a series were carried out during the last decades. Dire et al. reported that the Sechium edule extract was able to modify the biodistribution of certain metabolites in the pancreas, such as AGE (Advanced Glycation End Products), which are characterized by inducing general inflammation in addition to other anomalies related to DM. Chayote modified and inactivated these molecules in an in vivo model with Windstar rats [78]. In another, the relation between DM and other diseases and risk factors usually present, such as obesity, fatty liver, and hypertension, originated the search for natural alternatives that could reduce one or some of these risk factors. Hence, S. edule sprouts, as well as its fresh leaves, were prepared to be macerated and tested in fatty liver, finding mixtures of polyphenols, which reduce the accumulation of lipids in the liver, and in an in vitro model of fatty acid accumulation induced in HepG2cells [79]. Additionally, because it has been revealed in recent years that diet is crucial to controlling diabetes and related illnesses, a number of food supplements have been proposed. Chaguro is a food supplement, made from chayote and tuna fish that is useful in specific plan diets for patients with diabetes. In the elaboration of chaguro, different proportions of tuna fish and S. edule were tested. Results revealed that the combination of 75% of dry tuna fish mixed with 25% of S. edule is useful to induce lower blood glucose and improve the lipid profile in DM and dyslipidemia [80].
The nutritional content of S. edule revealed great amounts of vitamin C, starch, proteins, peroxidases, and an interesting mineral content that includes metals such as iron, manganese, zinc, and calcium. In contrast, the sugar and carbohydrate content were detected in a notoriously low amount. Then, based on the mineral and carbohydrate content present in chayote, as well as flavonoids, chayote could be considered for use in the prevention of chronic diseases such as DM, cardiovascular diseases, and the metabolic syndrome [81].
2.7. Citrullus lanatus (Thunb.) Matsum. & Nakai
The most widespread common name worldwide for Citrullus lanatus is watermelon, but it is also called sandía, tarbooz, acendría, and cooking melon among others. The fruit of this cucurbit possesses approximately 93% water, and a large and globous shape with a sweet and pulpy flesh, the reasons for it being denominated watermelon. Africa has been considered as the center of origin of watermelon, where has been cultivated for more than 4000 years. At present, watermelon is a very popular cultivar through the world, where the main producers are China, Turkey, Greece, Italy, Spain, Mexico, and Japan [82][83]. The fruit of C. lanatus is consumed fresh and raw, but also cooked, especially in some parts of Asia. With regard to the traditional use of the watermelon, there are numerous and diverse reports for using as cooling, strengthening, aphrodisiac, expectorant, diuretic, blood purifier, to cure itches, urinary tract infections, and kidney stones. The rind of the fruit is recommended for the treatment of diabetes [69][82][84]. The pharmacological properties of watermelon have been identified as antibacterial, antifungal, antiulcer, anti-inflammatory, anti-prostatic hyperplasia, anti-atherosclerotic, gastroprotective, analgesic, hepatoprotective, antioxidant and antidiabetic [82][84][85]. Among the main phytochemicals detected in watermelon are carotenoids, which represent from 31% (yellow pulp cultivar) to 99% (red pulp cultivar) of the percentage of total carotenoids. It has been considered that watermelon is one of the best sources of lycopene, after tomato, but also the carotenoids vary depending on the variety of color of the watermelon, for example, red (lycopene and beta carotene), yellow (neoxanthin, violaxanthin, and luteoxanthin), orange (beta carotene, prolycopene, phytonene, and carotene), and white (carotene). Other phytochemicals reported in watermelon comprise phenolic compounds, vitamins, aminoacids, flavonoids, and alkaloids [82][86]. On the other hand, watermelon has also been recognized as a source of L-citrulline, a neutral, non-essential amino-acid, precursor of L-arginine in mammals, and an important component of the cycle of the urea in the liver and kidneys. L-citrulline is involved in the production of endogenous nitroxide (NO), which is considered essential for regulating vasodilatation, immune responses, neurotransmission, and the adhesion of platelets and leukocytes. Thus, in recent years, the potential benefits of supplementing L-citrulline have been explored in cardiometabolic areas that include skeletal muscle and adipose tissue metabolism [85][87].
The lycopene present in the pulp of the fruit of Citrullus lanatus was investigated for its possible antidiabetic properties in an in vitro assay, where it exerted the inhibition of the α-amylase and lipase enzymes, in addition to its high content of L-citrulline [87]. In one that included extracts prepared from different organs from the same plant (seed, flesh, rind, and leaves), the aqueous extract of the leaves of C. lanatus was able to inhibit α-glucosidase, and it also exhibited higher antioxidant capacities. Some of the molecules identified in the leaf extract were curcumenol, curcubitacin E, citrulline, 6-gingerol, citric acid, ascorbic acid, leucine, arginine, palmitic acid, arjunolic acid, naringenin 5,7-dimethyl ether 4′-O-xylosyl-(1->4)-arabinoside, 4′-apo-beta, psi-caroten-4′-al, caffeic acid 3-glucoside, luteolin 7-rhamnosyl (1->6) galactoside, and apigenin 7-(4″,6″-diacetylalloside)-4′-alloside. These results permit proposing that watermelon could potentially be useful in the treatment of diabetes, but not only employing the fruit, but also the raw leaves [88]. Others, exhibited that the administration of the juice of the watermelon to 40 Wistar rats and, was able to inhibit the enzymes α-amylase and α-glucosidase in a dose-dependent manner. The administration of different doses of watermelon juice reduced the fasting blood glucose level, serum lipid profile, glucose-6-phosphatase, lipid peroxidation, and anti-inflammatory activities in Alloxan-induced diabetic rats. These results revealed that the juice of the watermelon may be useful in the treatment of DM via multiple pathways, and could also be helpful in metabolic complications associated with DM [89]. Additionally, other investigations revealed that the ethanolic extract from the seeds of watermelon was not toxic when administered orally in rats in doses of 250, 500, 1000, and 2000 mg/kg for 28 days, in that no signs of toxicity, behavioral changes, or mortality were observed in the treated animals. Thus, the consumption of the entire pulp of the watermelon could be considered as safe [90]. The possible use of watermelon in the treatment of DM and in some related comorbidity diseases were explored in an in vivo one, where the extracts of the leaves of C. lanatus were administered in doses of 200 and 400 mg/kg to obese and diabetic-induced rats. The histological analysis demonstrated that the extracts of watermelon were able to attenuate the biochemical parameters and structural changes in the kidneys and liver of diabetic animals, indicating that the extract may be useful in complications associated with diabetes [91]. A different one was showed that dietary supplementation with watermelon and L-citrulline reduced blood pressure in trials in humans probably plays an important role in the metabolism of lipids and in the control of satiety, consequently, watermelon could be useful in cardiac disease associated with diabetes [92].
2.8. Cucumis sativus L.
C. sativus known as cucumber is a Cucurbitaceae from India but it is currently widespread around the world. The fruit has been an essential part of the Mediterranean diet for centuries, it is mainly eaten fresh in salads or fermented. The pulp has been utilized for cleansing of the skin traditionally and today, cucumber extracts are employed in the cosmetic industry for many products [93]. Concerning its medicinal uses, cucumber has been reported as a laxative, as astringent, an anthelminthic, and an antipyretic. Other reported uses are in the treatment of hepatitis, bronchitis, asthma, diarrhea, and leprosy [94]. Notoriously, these traditional uses are mostly reports from Asia and Europe, but it is widely used in the entire Mexican territory for the treatment of DM [95].
The fruit possess antibacterial, antitumoral, antifungal, hepatoprotective, gastroprotective, ultraviolet protectant, wound-healing, and hypoglycemic activities [96]. This latter activity has been the object of recent studies, for example, the oral administration of 500 mg/kg of methanolic extract of the fruit caused a significant decrease in the fasting blood glucose concentration of Alloxan-induced diabetic rats, exhibiting a similar effect to that of Glibenclamide [97]. The ethanolic extract of the fruit of C. sativus demonstrated antihyperglycemic activity and also gave rise to the reduction in elevated lipid profiles in Alloxan-induced diabetic rats. It was notorious that these effects were more pronounced than those exhibited by other species of Cucurbitaceae, such as Lagenaria siceraria and Cucurbita maxima [98]. In an in vivo model, the anti-hyperglycemic effect of the decoction of C. sativus by the subcutaneous glucose tolerance in rabbits was determined. C. sativus was able to reduce the hyperglycemic peak significantly and was considered by the authors as recommendable for the prevention and treatment of DM [99]. Thus, the existing one was revealed that the hypoglycemic effect of C. sativus extracts and their potential use in the treatment of DM. However, and to the best of the knowledge, none of the active molecule content in the extracts that have demonstrated this hypoglycemic activity has been isolated and identified by bio-guided studies of C. sativus.
On the other hand, general phytochemical screenings carried out on the leaf and fruit extracts of C. sativus revealed the presence of alkaloids, glycosides, steroids, saponins, flavonoids, and tannins [55]. Other investigations reported the presence of the triterpenoids cucurbitacins, which are characteristic of the Cucurbitaceae family in the fruits of C. sativus, such as the cucurbitancins A, B, C, D, E, and I, which are well known to confer the bitterness and toxicity found [100]. A comparative study of three different cultivars of Greek C. sativus showed the presence of 21 essential oils in which the majority compounds exhibited some variation among samples; however these main compounds comprised Z-6-nonenol (61.54%), E-2-nonenal (6.98%), E,Z-2,6-nonadienal (47.08%), E-2-nonenal (17.39%), Z-3-nonenol (14.79%), 3-nonenal (7.32%), pentadecanal (43.47%), 9,12,15-octadecatrienal (14.52%), and 9,17-octadecadienal (12.33%) [101]. It was focused on the interrelationships of the volatile constituents of cucurbits showed the presence of the 1-nonanol, trans-2-nonen-1-ol, cis-3-nonen-1-ol, cis-6-nonen-1-ol, trans, cis-2,6-nonadien-l-o1, cis, cis-3,6-nonadien-l-o1, cis-6-nonena1, cis-3-nonenal, and cis, cis-3,6-nonadienal in the fruit of C. sativus [102]. Other of the lipid composition of the fruit of cucumber with importance in the industry were focused on total lipids, neutral lipids, glycolipids, and phospholipids, among which palmitic and linolenic acids were the predominant fatty acids, followed by the lauric, myristic, stearic, oleic, imolenic, tricosanoic, tricosenoic, lignoceric, and nervonic acids [103].
2.9. Cucumis melo L.
Cucumis melo is one of the fruits most consumed worldwide due to its delicious and juicy taste. It is also known as cantaloupe, Musk melon, sweet melon, round melon, and melón. In recent years, C. melo has become widely known because of its increasingly nutritive and medicinal functions [104][105]. Its chemical content, mainly fatty acids, polyphenols, and carotenoids have been recorded as possessing a broad range of beneficial characteristics that can also enhance health. Notoriously, the main source of these molecules is the mesocarp, which became the most studied part of the melón, compared with the skin and the seeds [106]. Some of the most abundant phenolic compounds detected in C. melo were reported in its seeds by Quian et al. [107], in which naringenin-7-O-glycoside, gallic acid, and vanillic acid were identified, while in the seed oils, γ-tocopherol, showed the highest concentration above that of α-tocopherol, β-tocopherol, and γ-tocotrienol. Flavonoids such as ß-carotene, lentin, xanthin, and cryptoxanthin were also reported.
The pharmacological properties of C. melo have been studied in recent decades and anti-inflammatory, analgesic, anticancer, antioxidant, anthelminthic, antimicrobial, antidiabetic, diuretic, and hepatoprotective effects were found [108]. Even traditional medicine has described the use of the fruit and the roots, the fruit is the most utilized part in the treatment of flatulence, obesity, fever, leprosy, bronchitis, anemia, constipation, hypertension, and diabetes [109][110].
Regarding the antidiabetic properties of melón, it is known that the gut microbiota plays an important role in the production of the metabolic endotoxins that can potentiate or inhibit insulin resistance. The administration of C. melo in obese mice reduces the inflammation induced by endotoxins of the bacterial flora, in addition to activating the function of insulin [111]. On the other hand, the potential use of the juice of C. melo has been investigated in the management of T2DM with cardioprotective effects in arteriosclerosis [112]. Interestingly, because melón is a commercial crop, there are varieties that have exerted antidiabetic activity, and these have been employed in traditional medicine around the world, however, and to the best to the knowledge, the identification of the compounds responsible for the antidiabetic activities remain unknown.
References
- Xu, Z.; Chang, L. Cucurbitaceae. In Identification and Control of Common Weeds; Springer: Singapore, 2017; Volume 3, pp. 417–432.
- Lebeda, A.; Widrlechner, M.P.; Staub, J.; Ezura, H.; Zalapa, J.; Kristkova, E. Cucurbits (Cucurbitaceae; Cucumis spp., Cucurbita spp., Citrullus spp.). In Genetic Resources, Chromosome Engineering, and Crop Improvement: Vegetable Crops; Singh, R.J., Ed.; CRC Press; Taylor & Francis Group: BocaRaton, FL, USA, 2007; Volume 3, pp. 271–376.
- Lira, R.; Villaseñor, J.L.; Ortíz, E. A Proposal for the Conservation of the Family Cucurbitaceae in Mexico. Biodivers. Conserv. 2002, 11, 1699–1720.
- Jeffrey, C. Systematics of The Cucurbitaceae: An Overview. In Biology and Utilization of the Cucurbitaceae; Bates, D.M., Robinson, R.W., Eds.; Comstock Publishing Associates: New York, NY, USA, 1990; pp. 3–9. ISBN 978-1-5017-4544-7.
- Rolnik, A.; Olas, B. Vegetables from the Cucurbitaceae Family and their Products: Positive Effect on Human Health. Nutrition 2020, 78, 110788.
- Jorge, N.; da Silva, A.C.; Malacrida, C.R. Physicochemical Characterisation and Radical-Scavenging Activity of Cucurbitaceae Seed Oils. Nat. Prod. Res. 2015, 29, 2313–2317.
- Lira, R.; Rodriguez-Jimenez, C.; Alvarado, J.L.; Rodriguez, I.; Castrejon, J.; Dominguez-Marian, A. Diversidad e Importancia de la Familia Cucurbitaceae En México. Acta Bot. Mex. 1998, 43–77.
- Ishnava, K.B.; Patel, K.S. In Vitro Study of Praecitrulus fistulosus (Stocks) Pangalo (Cucurbitaceae) Fruit—A Potential Candidate of Anthelmintic Activity. Bull. Natl. Res. Cent. 2020, 44, 1–10.
- Ajuru, M.; Nmom, F. A Review on the Economic Uses of Species of Cucurbitaceae and their Sustainability in Nigeria. AJPB 2017, 2, 17–24.
- Ng, T.J. New Opportunities in the Cucurbitaceae. In New Crops; Janick, J., Simon, J.E., Eds.; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 538–546.
- Dey, P.; Karuna, D.S.; Bhakta, T. Medicinal Plants Used as Anti-Acne Agents by Tribal and Non-Tribal People of Tripura, India. AJPCT 2014, 2, 556–570.
- Dinakar, Y.H. Ethnobotanical Study of Medicinal Plants Used by the Tribes of Nalamalai Forests. IJMPNP 2018, 4, 19–21.
- Jeffrey, C. A Review of the Cucurbitaceae. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 1980, 81, 233–247.
- Huang, W.-C.; Kuo, M.-L.; Li, M.-L.; Yang, R.-C.; Liou, C.-J.; Shen, J.-J. Gynostemma pentaphyllum Decreases Allergic Reactions in a Murine Asthmatic Model. Am. J. Chin. Med. 2008, 36, 579–592.
- Shendge, P.N.; Belemkar, S. Acute and 28-Day Oral Toxicity Studies of Methanolic Extract of Lagenaria siceraria (Cucurbitaceae) Fruit in Rats. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 44, 493–501.
- Dhiman, K.; Gupta, A.; Sharma, D.K.; Gill, N.S.; Goyal, A. A Review on the Medicinally Important Plants of the Family Cucurbitaceae. Asian J. Clin. Nutr. 2012, 4, 16–26.
- Villarreal-La Torre, V.E.; Guarniz, W.S.; Silva-Correa, C.; Cruzado-Razco, L.; Siche, R. Antimicrobial Activity and Chemical Composition of Momordica charantia: A Review. Pharmacogn. J. 2020, 12, 213–222.
- Soto-Hernández, M.; Cadena_ Iñiguez, J.; Arévalo-Galarza, L.C.; Santiago-Osorio, E.; Aguiñiga-Sánchez, I.; Ruíz-Posadas, L.d.M. Lead Compounds from Cucurbitaceae for the Treatment of Cancer. In Phytochemicals—Isolation, Characterisation and Role in Human Health; Rao, A.V., Rao, L.G., Eds.; InTech: San Diego, CA, USA, 2015; pp. 289–303. ISBN 978-953-51-2170-1.
- Abdoul-Latif, F.M.; Ainane, A.; Aboubaker, I.H.; Ahmed, N.M.; Ainane, T. Effectiveness of a Diet for Type 2 Diabetics Based on Vegetables and Fruits of the Cucurbitaceae Family. JASAB 2021, 3, 107–113.
- Bortolotti, M.; Mercatelli, D.; Polito, L. Momordica charantia, a Nutraceutical Approach for Inflammatory Related Diseases. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 486.
- Andres, T.C. 9. Biosystematics, Theories on the Origin, and Breeding Potential of Cucurbita ficifolia. In Biology and Utilization of the Cucurbitaceae; Jeffrey, C., Ed.; Cornell University Press: Ithaca, NY, USA, 2019; pp. 102–119. ISBN 978-1-5017-4544-7.
- Andrade-Cetto, A.; Heinrich, M. Mexican Plants with Hypoglycaemic Effect Used in the Treatment of Diabetes. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2005, 99, 325–348.
- Atlas de Las Plantas de La Medicina Tradicional Mexicana. Available online: http://www.medicinatradicionalmexicana.unam.mx/apmtm/index.html (accessed on 2 December 2021).
- Jiménez-Estrada, M.; Huerta-Reyes, M.; Tavera-Hernández, R.; Alvarado-Sansininea, J.J.; Alvarez, A.B. Contributions from Mexican Flora for the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus: Molecules of Psacalium decompositum (A. Gray) H. Rob & Brettell. Molecules 2021, 26, 2892.
- Balkaya, A.; Kandemir, D. An Overview of Winter Squash (Cucurbita maxima Duch.) and Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Duch.) Growing in Turkey. AJA 2015, 3, 57–64.
- Ferriol, M.; Picó, B. Pumpkin and Winter Squash. In Vegetables I. Handbook of Plant Breeding; Prohens, J., Nuez, F., Eds.; Handbook of Plant Breeding; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 317–349. ISBN 978-0-387-72291-7.
- Salehi, B.; Capanoglu, E.; Adrar, N.; Catalkaya, G.; Shaheen, S.; Jaffer, M.; Giri, L.; Suyal, R.; Jugran, A.K.; Calina, D.; et al. Cucurbits Plants: A Key Emphasis to its Pharmacological Potential. Molecules 2019, 24, 1854.
- Menendez-Baceta, G.; Aceituno-Mata, L.; Molina, M.; Reyes-García, V.; Tardío, J.; Pardo-de-Santayana, M. Medicinal Plants Traditionally Used in the Northwest of the Basque Country (Biscay and Alava), Iberian Peninsula. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 113–134.
- Kujawska, M.; Pieroni, A. Plants Used as Food and Medicine by Polish Migrants in Misiones, Argentina. Ecol. Food Nutr. 2015, 54, 255–279.
- Mahomoodally, M.F.; Mootoosamy, A.; Wambugu, S. Traditional Therapies Used to Manage Diabetes and Related Complications in Mauritius: A Comparative Ethnoreligious Study. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2016, 2016, 1–25.
- Motti, R.; Motti, P. An Ethnobotanical Survey of Useful Plants in the Agro Nocerino Sarnese (Campania, Southern Italy). Hum. Ecol. 2017, 45, 865–878.
- Peter, E.L.; Rumisha, S.F.; Mashoto, K.O.; Malebo, H.M. Ethno-Medicinal Knowledge and Plants Traditionally Used to Treat Anemia in Tanzania: A Cross Sectional Survey. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 154, 767–773.
- Agyare, C.; Spiegler, V.; Asase, A.; Scholz, M.; Hempel, G.; Hensel, A. An Ethnopharmacological Survey of Medicinal Plants Traditionally Used for Cancer Treatment in the Ashanti Region, Ghana. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2018, 212, 137–152.
- Ramzan, S.; Soelberg, J.; Jäger, A.K.; Cantarero-Arévalo, L. Traditional Medicine among People of Pakistani Descent in the Capital Region of Copenhagen. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 196, 267–280.
- Mahmoodpoor, A.; Medghalchi, M.; Nazemiyeh, H.; Asgharian, P.; Shadvar, K.; Hamishehkar, H. Effect of Cucurbita maxima on Control of Blood Glucose in Diabetic Critically Ill Patients. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 2018, 8, 347–351.
- Habtemariam, S. The Chemical and Pharmacological Basis of Pumpkins (Cucurbita Species) as Potential Therapy for Type-2 Diabetes. In Medicinal Foods as Potential Therapies for Type-2 Diabetes and Associated Diseases; Habtemariam, S., Ed.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2019; pp. 473–502. ISBN 978-0-08-102922-0.
- Lim, T.K. Cucurbita moschata. In Edible Medicinal and Non-Medicinal Plants; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2012; pp. 266–280. ISBN 978-94-007-1763-3.
- Jacobo-Valenzuela, N.; Maróstica-Junior, M.R.; Zazueta-Morales, J.d.J.; Gallegos-Infante, J.A. Physicochemical, Technological Properties, and Health-Benefits of Cucurbita moschata Duchense vs. Cehualca: A Review. Food Res. Int. 2011, 44, 2587–2593.
- Jia, W.; Gao, W.; Tang, L. Antidiabetic Herbal Drugs Officially Approved in China. Phytother. Res. 2003, 17, 1127–1134.
- Nara, K.; Yamaguchi, A.; Maeda, N.; Koga, H. Antioxidative Activity of Water Soluble Polysaccharide in Pumpkin Fruits (Cucurbita maxima Duchesne). Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2009, 73, 1416–1418.
- Qian, Z.-G. Cellulase-Assisted Extraction of Polysaccharides from Cucurbita moschata and their Antibacterial Activity. Carbohydr. Polym. 2014, 101, 432–434.
- Choi, H.; Eo, H.; Park, K.; Jin, M.; Park, E.-J.; Kim, S.-H.; Park, J.E.; Kim, S. A Water-Soluble Extract from Cucurbita moschata Shows Anti-Obesity Effects by Controlling Lipid Metabolism in a High Fat Diet-Induced Obesity Mouse Model. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2007, 359, 419–425.
- Xia, H.C.; Li, F.; Li, Z.; Zhang, Z.C. Purification and Characterization of Moschatin, a Novel Type I Ribosome-Inactivating Protein from the Mature Seeds of Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata), and Preparation of its Immunotoxin against Human Melanoma Cells. Cell Res. 2003, 13, 369–374.
- Hesari, Z.; Sharifdini, M.; Sharifi-Yazdi, M.K.; Ghafari, S.; Ghasemi, S.; Mahmoudi, S.; Mohebali, M.; Nikmanesh, B. In Vitro Effects of Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) Seed Extracts on Echinococcus granulosus Protoscoleces. Iran. J. Parasitol. 2020, 15, 76–83.
- Jiang, Z.; Du, Q. Glucose-Lowering Activity of Novel Tetrasaccharide Glyceroglycolipids from the Fruits of Cucurbita moschata. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2011, 21, 1001–1003.
- Wang, S.; Lu, A.; Zhang, L.; Shen, M.; Xu, T.; Zhan, W.; Jin, H.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, W. Extraction and Purification of Pumpkin Polysaccharides and their Hypoglycemic Effect. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2017, 98, 182–187.
- Song, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, H.; Hu, X.; Li, Q. A Preliminary Study of Monosaccharide Composition and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Effect of Polysaccharides from Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata) Fruit: Study of Pumpkin Monosaccharide Composition and α-Glucosidase Inhibitory Effect. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2012, 47, 357–361.
- Jin, H.; Zhang, Y.J.; Jiang, J.X.; Zhu, L.-Y.; Chen, P.; Li, J.; Yao, H.Y. Studies on the Extraction of Pumpkin Components and their Biological Effects on Blood Glucose of Diabetic Mice. J. Food Drug. Anal. 2013, 21, 184–189.
- Zhang, Y.; Chen, P.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhu, L.; Li, J.; Yao, H. Effects of Polysaccharide from Pumpkin on Biochemical Indicator and Pancreatic Tissue of the Diabetic Rabbits. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 62, 574–581.
- Chang, C.-I.; Hsu, C.-M.; Li, T.-S.; Huang, S.-D.; Lin, C.-C.; Yen, C.-H.; Chou, C.-H.; Cheng, H.-L. Constituents of the Stem of Cucurbita moschata Exhibit Antidiabetic Activities through Multiple Mechanisms. J. Funct. Foods 2014, 10, 260–273.
- Marbun, N.; Sitorus, P.; Sinaga, S.M. Antidiabetic Effects of Pumpkin (Cucurbita moschata Durch) Flesh and Seeds Extracts in Streptozotocin Induced Mice. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2018, 11, 91–93.
- Perales, H.R.; Aguirre, J.R. Biodiversidad Humanizada. In Capital Natural de México; Sarukhán, J., Ed.; Comisión Nacional para el Conocimiento y Uso de la Biodiversidad: México City, Mexico, 2008; Volume 1, pp. 565–603.
- Basurto-Peña, F.; Castro-Lara, D.; Mera-Ovando, L.M.; Juárez-Castro, T. Ethnobotany of Cultivated Pumpkins (Cucurbita Spp.) in Oaxaca’s Central Valleys, México. Agroproductividad 2015, 8, 47–53.
- Lira Saade, R. Estudios Taxonómicos y Ecogeográficos de Las Cucurbitaceae Latinoamericanas de Improtanicia Económica; Systematic and ecogeographic studies on crop genepools; IPGRI: Minneapolis, MN, USA, 1995; ISBN 978-92-9043-263-0.
- Rajasree, R.S.; Sibi, P.I.; Francis, F.; William, H. Phytochemicals of Cucurbitaceae Family—A Review. IJPPR 2016, 8, 113–123.
- Perez-Gutierrez, R.M. Review of Cucurbita pepo (Pumpkin) Its Phytochemistry and Pharmacology. Med. Chem. 2016, 6, 12–21.
- Iswaldi, I.; Gómez-Caravaca, A.M.; Lozano-Sánchez, J.; Arráez-Román, D.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Profiling of Phenolic and other Polar Compounds in Zucchini (Cucurbita pepo L.) by Reverse-Phase High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled to Quadrupole Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry. Food Res. Int. 2013, 50, 77–84.
- Andjelkovic, M.; Van Camp, J.; Trawka, A.; Verhé, R. Phenolic Compounds and Some Quality Parameters of Pumpkin Seed Oil. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 2010, 112, 208–217.
- Kikuchi, T.; Ando, H.; Maekawa, K.; Arie, H.; Yamada, T.; Tanaka, R. Two New Ent-Kaurane-Type Diterpene Glycosides from Zucchini (Cucurbita pepo L.) Seeds. Fitoterapia 2015, 107, 69–76.
- Appendino, G.; Jakupovic, J.; Belloro, E.; Marchesini, A. Triterpenoid p-Aminobenzoates from the Seeds of Zucchini. Fitoterapia 2000, 71, 258–263.
- Ayyildiz, H.F.; Topkafa, M.; Kara, H. Pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) Seed Oil. In Fruit Oils: Chemistry and Functionality; Ramadan, M.F., Ed.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 765–788. ISBN 978-3-030-12472-4.
- Ratnam, N.; Najibullah, M.; Ibrahim, M. A Review on Cucurbita pepo. Int. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. Res. 2017, 9, 1190–1194.
- Caili, F.U.; Huan, S.; Quanhong, L.I. A Review on Pharmacological Activities and Utilization Technologies of Pumpkin. Plant Foods Hum. Nutr. 2006, 61, 70–77.
- Asgary, S.; Moshtaghian, S.J.; Setorki, M.; Kazemi, S.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Adelnia, A.; Shamsi, F. Hypoglycaemic and Hypolipidemic Effects of Pumpkin (Cucurbita pepo L.) on Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. Afr. J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 2011, 5, 2620–2626.
- Xolalpa-Molina, S. Flora Medicinal Mayo de la región de El Fuerte y Choix, Sinaloa In Flora Medicinal Indígena de México, Biblioteca de la Medicina Tradicional Mexicana; Aguilar, A., Argueta, A., Cano, L., Eds.; Instituto Nacional Indigenista: México City, Mexico, 1994; Volume 1, pp. 363–411.
- Achenbach, H.; Horn, K.; Dominguez, X.A.; Rombold, C.; Gómez López, E.G. Cucurbitanes and Cucurbitane-Type Glycosides from Ibervillea sonorae. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 437–445.
- Weckert, E.; Hümmer, K.; Dominguez, X.A.; Horn, K.; Achenbacht, H. The Absolute Configuration of Kinoin C. Phytochemistry 1993, 33, 447–448.
- Siciliano, T.; De Tommasi, N.; Morelli, I.; Braca, A. Study of Flavonoids of Sechium edule (Jacq) Swartz (Cucurbitaceae) Different Edible Organs by Liquid Chromatography Photodiode Array Mass Spectrometry. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2004, 52, 6510–6515.
- Coronel, O.A.D.Á.; León-García, E.; Vela-Gutiérrez, G.; Medina, J.D.l.C.; García-Varela, R.; García, H.S. Chayote (Sechium edule (Jacq.) Swartz). In Fruit and Vegetable Phytochemicals; Yahia, E.M., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2017; pp. 979–992. ISBN 978-1-119-15804-2.
- Pu, Y.-T.; Luo, Q.; Wen, L.-H.; Li, Y.-R.; Meng, P.-H.; Wang, X.-J.; Tan, G.-F. Origin, Evolution, Breeding, and Omics of Chayote, an Important Cucurbitaceae Vegetable Crop. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 739091.
- Veigas, G.J.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Hegde, K.; Shabaraya, A.R. A Brief Review on Sechium edule. IJPSRR 2020, 65, 165–168.
- Vieira, E.F.; Pinho, O.; Ferreira, I.M.P.L.V.O.; Delerue-Matos, C. Chayote (Sechium edule): A Review of Nutritional Composition, Bioactivities and Potential Applications. Food Chem. 2019, 275, 557–568.
- Iñiguez-Luna, M.I.; Cadena-Iñiguez, J.; Soto-Hernández, R.M.; Morales-Flores, F.J.; Cortes-Cruz, M.; Watanabe, K.N. Natural Bioactive Compounds of Sechium Spp. for Therapeutic and Nutraceutical Supplements. Front. Plant Sci. 2021, 12, 772389.
- Montes, R.C.; Gómez, G.A.A. Valoración de la cidra papa (Sechium edule) como alternativa de alimentación y recuperación de vínculos con el campo. Biotecnología Sector Agropecuario Agroindustrial 2011, 9, 198–209.
- Cadena Iñiguez, J.; Soto Hernández, M.; Arévalo Galarza, M.d.L.; Avendaño Arrazate, C.H.; Aguirre Medina, J.F.; Ruiz Posadas, L.d.M. Caracterización bioquímica de variedades domesticadas de chayote Sechium edule (Jacq.) Sw. comparadas con parientes silvestres. Rev. Chapingo Ser. Hortic. 2011, 17, 45–55.
- Siahaan, J.M.; Harahap, U.; Loesnihari, R. Effect of Ethanol Extract of Chayote (Sechium edule. Jacq. Swartz) on the Activity of Glutathione Peroxide (GPx) in House Mice (Musmusculus L.) Strain DD Webster Hyperglycemia Induced by Streptozotocin (STZ). Indones J. Med. 2016, 1, 44–49.
- Siahaan, J.M.; Illyas, S.; Lindarto, D.; Nainggolan, M. The Effect of Ethanol and Ethyl Acetate Fraction of Chayote Fruit (Sechium edule Jacq. Swartz) on the Oxidative Stress and Insulin Resistance of Male White Rat Model Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Open Access Maced. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 962–969.
- Dire, G.F.; Rodrigues, J.S.; Oliveira, J.C.S.; Vasconcelos, S.D.D.; Siqueira, P.R.A.; Duarte, R.M.; Almeida, M.C.L.; Fernandes, M.L.; Bernardo-Filho, M. Biological Effects of a Chayotte Extract in Wistar Rats with Induced Diabetes: A Radiopharmaceutically Analysis. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 2007, 10, 568–574.
- Wu, C.-H.; Ou, T.-T.; Chang, C.-H.; Chang, X.-Z.; Yang, M.-Y.; Wang, C.-J. The Polyphenol Extract from Sechium edule Shoots Inhibits Lipogenesis and Stimulates Lipolysis via Activation of AMPK Signals in HepG2 Cells. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2014, 62, 750–759.
- Sudargo, T.; Aulia, B.; Prameswari, A.A.; Isnansetyo, A.; Puspita, I.D.; Budiyanti, S.A.; Muslichah, R.; Aristasari, T.; Putri, S.R.; Alfionita, K. Effect of Administration of CHAGURO Made of Chayote (Sechium edule) and Tuna (Thunnus sp.) on Rats Induced with Streptozotocin-Nicotinamide and a High-Fat Diet. Curr. Res. Nutr. Food Sci. J. 2021, 9, 258–266.
- Premkumar, G. Preliminary Phytochemical and Nutritional Profiles of an Underutilized Vegetable Sechium edule (Jacq.) Swartz. SIJBS 2016, 2, 207–212.
- Deshmukh, C.D.; Jain, A.; Tambe, M.S. Phytochemical and Pharmacological Profile of Citrullus lanatus (THUNB). Biolife 2015, 3, 483–488.
- González-Palomares, S.; Hernández-Estrada, A.; González-Sánchez, M.; Bustos-Santana, H.R.; Rosales-Reyes, T. Comparación de dos Métodos de Extracción de Compuestos Volátiles en Sandía (Citrullus lanatus T.). Revista Quehacer Científico Chiapas 2009, 7, 23–27.
- Erhirhie, E.O.; Ekene, N.E. Medicinal Values on Citrullus lanatus (Watermelon): Pharmacological Review. Int. J. Res. Pharm. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 4, 1305–1312.
- Uuh Narvaez, J.J.; Segura Campos, M.R. Foods from Mayan Communities of Yucatán as Nutritional Alternative for Diabetes Prevention. J. Med. Food 2020, 23, 349–357.
- Zamuz, S.; Munekata, P.E.S.; Gullón, B.; Rocchetti, G.; Montesano, D.; Lorenzo, J.M. Citrullus lanatus as Source of Bioactive Components: An up-to-Date Review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2021, 111, 208–222.
- Casacchia, T. Nutraceutical Properties and Health-Promoting Biological Activities of Fruits of Watermelon Cultivars with Different Origins. Farmacia 2020, 68, 679–686.
- Jibril, M.M.; Abdul-Hamid, A.; Ghazali, H.M.; Dek, M.S.P.; Ramli, N.S.; Jaafar, A.H.; Karrupan, J.; Mohammed, A.S. Antidiabetic Antioxidant and Phytochemical Profile of Yellow-Fleshed Seeded Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) Extracts. J. Food Nutr. Res. 2019, 7, 82–95.
- Ajiboye, B.O.; Shonibare, M.T.; Oyinloye, B.E. Antidiabetic Activity of Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) Juice in Alloxan-Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Diabetes Metab. Disord. 2020, 19, 343–352.
- Belemkar, S.; Shendge, P.N. Toxicity Profiling of the Ethanolic Extract of Citrullus lanatus Seed in Rats: Behavioral, Biochemical and Histopathological Aspects. Biosci. Rep. 2021, 41, BSR20202345.
- Jibril, M.M.; Haji-Hamid, A.; Abas, F.; Karrupan, J.; Mohammed, A.S.; Jaafar, A.H.; Pak Dek, M.S.; Ramli, N.S. Watermelon (Citrullus lanatus) Leaf Extract Attenuates Biochemical and Histological Parameters in High-fat Diet/Streptozotocin-induced Diabetic Rats. J. Food Biochem. 2022, 46, e14058.
- Burton-Freeman, B.; Freeman, M.; Zhang, X.; Sandhu, A.; Edirisinghe, I. Watermelon and L-Citrulline in Cardio-Metabolic Health: Review of the Evidence 2000–2020. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2021, 23, 81.
- Trichopoulou, A.; Lagiou, P.; Kuper, H.; Trichopoulos, D. Cancer and Mediterranean Dietary Traditions. Cancer Epidemiol. Biomarkers Prev. 2000, 9, 869–873.
- Sahu, T.; Sahu, J. Cucumis sativus (Cucumber): A Review on Its Pharmacological Activity. J. Appl. Pharm 2015, 3, 4–9.
- Aguilar, A.; Xolalpa, S. La Herbolaria Mexicana en el Tratamiento de la Diabetes. Ciencia 2002, 53, 24–35.
- Khan, A.; Mishra, A.; Hasan, S.M.; Usmani, A.; Ubaid, M.; Khan, N.; Saidurrahman, M. Biological and Medicinal Application of Cucumis sativus Linn.—Review of Current Status with Future Possibilities. JCIM 2021.
- Abubakar, N.S.; Florence, I.O.; Iyanu, O.O. Phytochemical Screening and Hypoglycemic Effect of Methanolic Fruit Pulp Extract of Cucumis sativus in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats. JMPR 2014, 8, 1173–1178.
- Sharmin, R.; Khan, M.R.I.; Akhtar, M.A.; Alim, A.; Islam, M.A.; Anisuzzaman, A.S.M.; Ahmed, M. Hypoglycemic and Hypolipidemic Effects of Cucumber, White Pumpkin and Ridge Gourd in Alloxan Induced Diabetic Rats. J. Sci. Res. 2013, 5, 161–170.
- Roman-Ramos, R.; Flores-Saenz, J.L.; Alarcon-Aguilar, F.J. Anti-Hyperglycemic Effect of some Edible Plants. J. Ethnopharmacol. 1995, 48, 25–32.
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Nema, N.K.; Maity, N.; Sarkar, B.K. Phytochemical and Therapeutic Potential of Cucumber. Fitoterapia 2013, 84, 227–236.
- Sotiroudis, G.; Melliou, E.; Sotiroudis, T.G.; Chinou, I. Chemical Analysis, Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Activity of Three Greek Cucumber (Cucumis sativus) Cultivars. J. Food Biochem. 2010, 34, 61–78.
- Kemp, T.R.; Knavel, D.E.; Stoltz, L.P. Identification of some Volatile Compounds from Cucumber. J. Agric. Food Chem. 1974, 22, 717–718.
- Peng, A.C.; Gnsman, J.R. Lipid and Fatty Acid Composition of Cucumbers and their Changes during Storage of Fresh-pack Pickles. J. Food Sci. 1976, 41, 859–862.
- Endl, J.; Achigan-Dako, E.G.; Pandey, A.K.; Monforte, A.J.; Pico, B.; Schaefer, H. Repeated Domestication of Melon (Cucumis melo) in Africa and Asia and a New Close Relative from India. Am. J. Bot. 2018, 105, 1662–1671.
- International Plant Genetic Resources Institute (IPGRI). Descriptors for Melon (Cucumis melo L.); International Plant Genetic Resourses Institute: Rome, Italy, 2003; ISBN 978-92-9043-597-6.
- Gómez-García, R.; Campos, D.A.; Aguilar, C.N.; Madureira, A.R.; Pintado, M. Valorization of Melon Fruit (Cucumis melo L.) by-Products: Phytochemical and Biofunctional Properties with Emphasis on Recent Trends and Advances. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2020, 99, 507–519.
- Qian, O.Y.; Harith, S.; Shahril, M.R.; Shahidan, N. Bioactive Compounds in Cucumis melo L. and its Beneficial Health Effects: A Scoping Review. Malays. Appl. Biol. 2019, 48, 11–23.
- Vishwakarma, V.K.; Gupta, J.K.; Upadhyay, P.K. Pharmacological Importance of Cucumis melo L.: An Overview. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 2017, 10, 8.
- Asif, H.M.; Rehman, S.U.; Akram, M.; Akhtar, N.; Sultana, S.; Rehman, J.U. Medicinal Properties o Cucumis melo Linn. Int. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 2014, 2, 58–62.
- Geck, M.S.; Reyes García, A.J.; Casu, L.; Leonti, M. Acculturation and Ethnomedicine: A Regional Comparison of Medicinal Plant Knowledge among the Zoque of Southern Mexico. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2016, 187, 146–159.
- Lee, D.; Yoo, J.H.; Lee, B.-C. Therapeutic Effect of Cucumis melo L. Extract on Insulin Resistance and the Gut Microbiome in Lep ob /Lep ob Mice. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2018, 2018, 8159261.
- Mollik, A.H. Utilization of Cucumis melo L. as a Source of Reduces Serum Sialic Acid in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus for Delay the Process of Atherosclerosis. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2013, 68, e15.
More
