You're using an outdated browser. Please upgrade to a modern browser for the best experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Qiangbo Liu and Version 4 by Dean Liu.
Cold stress is a major environmental factor affecting the growth, development, and productivity of various crop species. With the current trajectory of global climate change, low temperatures are becoming more frequent and can significantly decrease crop yield. Wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) is the first domesticated crop and is the most popular cereal crop in the world. Because of a lack of systematic research on cold signaling pathways and gene regulatory networks, the underlying molecular mechanisms of cold signal transduction in wheat are poorly understood.
- cold stress
- wheat
- hormonal
- reactive oxygen species
1. ICE-CBF-COR Signaling Pathway in Cold Stress
ICE genes encode a class of MYC-like bHLH transcriptional factors upstream of the cold signaling pathway [1][25]. The C-terminal regions of ICE have highly conserved regions for specific interactions with downstream cold regulatory genes [1][2][3][4][5][5,24,25,26,27]. The homologs of ICE have been identified as TaICE41 and TaICE87 in wheat (Figure 1). Overexpression of TaICE41 or TaICE87 in Arabidopsis enhanced cold tolerance, suggesting the significance of ICE homologs in cold stress response [3][24]. HOS1 (HIGH EXPRESSION OF OSMOTICALLY RESPONSIVE GENE 1), an E3 ubiquitin ligase, reduces the stability of ICE1 protein by ubiquitination under cold stress [6][28]. In addition, the stability of ICE1 protein is enhanced by SUMO E3 ligase SIZ1 (SAP and Miz) through sumoylation in response to cold stress [7][29]. ICE1 is phosphorylated by the cold-activated protein kinase OPEN STOMATA 1 (OST1), resulting in weakened interaction between ICE1 and HOS1 to increase the stability of ICE1 under cold stress [8][30]. Furthermore, the stability of OsICE1 is up-regulated by OsMPK3 (MAP KINASE 3) through phosphorylation in rice in response to cold stress [9][31]. These results indicate that the posttranslational modification of ICE1 is crucial for its role in response to cold stress. However, whether TaICEs have similar regulatory mechanisms in wheat responses to cold stress needs further study.
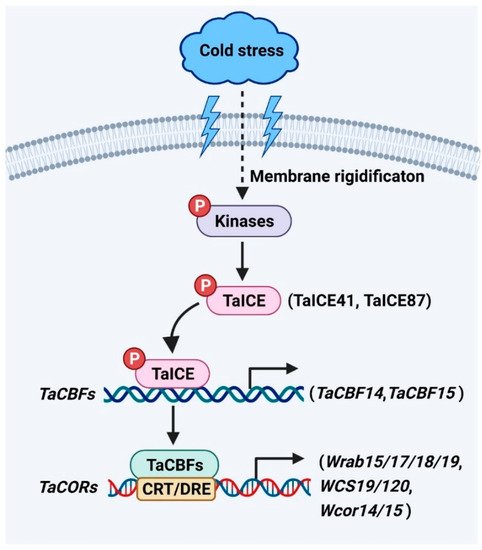
Figure 1.
ICE
-
CBF
-
COR
signaling pathway plays a vital role in wheat. Cold stress alters the fluidity of plasma membrane and activates protein kinases.
CBFs (CBF1, CBF2, and CBF3), which belong to the AP2/ERF multi-gene family, can be activated by ICE in the cold signaling pathway of plants [1][10][3,25]. CBFs are key components for increasing the cold tolerance of plants [11][12][13][32,33,34]. The overexpression of CBFs in rice, maize, barley, wheat, and other plant species significantly enhances the cold tolerance of transgenic plants [14][15][16][17][18][35,36,37,38,39]. However, the cbfs triple mutant in Arabidopsis show reduced cold tolerance and larger biomass than wild type [19][40]. These results indicate CBFs may act to balance cold tolerance and plant growth. However, whether CBFs are important regulators of growth and cold tolerance to enhance the biomass of wheat requires further study. Several CBF genes have been characterized in Triticeae species, including 37 genes from hexaploid wheat [20][41], 20 genes from barley [15][36], 13 genes from Triticum monococcum [21][42], 11 genes from rye [22][43], ten genes from durum wheat [23][44], ten genes from Aegilops biuncialis [2][5], four genes from Brachypodium distachyon [24][25][45,46], and one gene from Aegilops tauschii [20][41]. TaCBF14 and TaCBF15, two wheat CBF transcription factors, play significant roles in cold stress response (Figure 1) [17][38]. Overexpression of TaCBF14 or TaCBF15 in barley enhances the expression of HvCOR14b, a cold-regulated gene in barley, increasing cold tolerance [17][38]. Additionally, T. aestivum ABIOTIC STRESS-INDUCED DNA BINDING FACTOR a (TaAIDFa) is markedly activated by cold stress [26][47]. Overexpression of TaAIDFa in Arabidopsis increases the transcription of the cold-regulated genes like RD29A and COR15A to enhance the cold tolerance of transgenic lines [26][47].
CORs generally refer to the protective substances encoded by cold-regulated genes. The protective substances such as osmolytes and cryoprotective proteins accumulate to facilitate cold acclimation and freezing tolerance [27][28][1,6]. CBFs are known to bind to the C-REPEAT/DEHYDRATION RESPONSIVE ELEMENT (CRT/DRE) sequence (TACCGCAT) in the promoters of COR genes for their transcription activation in response to cold stress [29][30][48,49]. The expression of ABA-dependent COR genes (Wrab15/17/18/19) and ABA-independent COR genes (WCS19, WCS120, Wcor14, and Wcor15) are significantly increased by cold stress in wheat (Figure 1) [31][50]. The expression of DRE-BINDING PROTEIN 1 (TaDREB1), a wheat homolog of Arabidopsis DREB2, is elevated under cold stress [32][51]. The transcription of the WHEAT COLD SPECIFIC 120 (WCS120) gene is activated by TaDREB1 and increases cold tolerance in winter wheat [33][52]. The expression of wheat DREB2 (WDREB2), also a wheat homolog of Arabidopsis DREB2, is activated by cold [34][53]. The WDREB2 transcription factor directly affects the expression of wheat COR genes such as Wrab19 in response to cold stress [34][53].
2. Cold Stress Influences Hormonal Responses
Plant hormones (Phytohormones), which function as small molecules to regulate various cellular processes and work as chemical messengers to communicate cellular activities, are produced in very low concentrations in higher plants [35][54]. Phytohormones are needed for plants to deal with abiotic stresses, including salinity, drought, and low temperature, by mediating a wide range of adaptive responses [36][55]. These phytohormones include auxin, abscisic acid (ABA), ethylene, cytokinins (CKs), gibberellins (GAs), jasmonic acid (JA), brassinosteroids (BRs), salicylic acid (SA), and strigolactones (SLs). In recent years, the phytohormone signaling pathway has been investigated by genetic and biochemical approaches, and a growing body of evidence indicates that the elements in hormonal signaling pathways contribute to regulating plant cold tolerance [12][33].
Auxin, a tryptophan derivative most commonly present in the form of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), plays an essential role in plant development and cold stress response. The YUCCA genes encode the key rate-limiting enzymes in the auxin biosynthetic pathway and are involved in the regulation of plant growth and development. The transcript levels of OsYUCCAs are strongly induced by low temperatures; however, the expression of IAA catabolism-related genes, Oryza sativa GRETCHEN HAGENs (OsGHs), is down-regulated, resulting in significantly increased IAA content in rice under cold stress (Table 1) [37][56]. In colder/ambient temperatures, CLAVATA (CLV) peptide signaling promotes flower development by stimulating auxin-dependent growth. In contrast, at higher temperatures, YUCCA genes are activated to maintain flower development bypass CLV signaling [38][39][40][57,58,59]. There are 15 genes among 63 TaYUCCAs that are induced by drought and heat stress in wheat, though it is unclear whether the expression of these genes is regulated by cold stress. Arabidopsis AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR (ARF) genes, which regulate the expression of auxin-responsive genes by binding to the auxin response element in their promoters, are up-regulated during cold acclimation (Table 1) [41][60]. In wheat, 46 genes from 69 TaARFs are also up-regulated in response to cold stress (Table 1) [42][61].
Abscisic acid (ABA) is the most important phytohormone due to its role in plant adaptation to biotic and abiotic stresses [43][62]. ABA-deficient mutants in Arabidopsis show defects in freezing tolerance, with the induced expression of COR genes, suggesting that ABA is involved in cold signaling [44][45][63,64]. Additionally, ABA contents are moderately decreased after cold treatment [8][30]. SUCROSR NON-FERMENTING 1-RELATED PROTEIN KINASE 2s (SnRK2s) are important protein kinases in ABA signaling, and their role in abiotic and biotic stress signaling has been extensively characterized in Arabidopsis. The SnRK2 homologs in wheat appear to play a critical role in cold signaling. PKABA1, the first SnRK2 protein identified in wheat, is rapidly induced in seedlings when ABA levels increase in response to cold stress [46][65]. Furthermore, the expression of TaSnRK2.3, TaSnRK2.4, and TaSnRK2.8 can be induced by cold stress, suggesting that they are essential in cold signal transduction (Table 1) [47][48][49][66,67,68]. Overexpression of TaSnRK2.3 or TaSnRK2.8 in Arabidopsis increases cold tolerance, which is due to the increased expression of cold-responsive genes, and the enhanced accumulation of stress-associated metabolites such as proline [48][67]. Recent studies have identified 10 SnRK2 homologs in wheat, and the expression of these genes is induced by cold stress [50][69]. Although ABA and cold signaling are closely related, it is unclear what the exact role of ABA in regulating plant cold stress responses is. Further work is needed to elucidate the molecular mechanisms of ABA when regulating cold signaling pathways.
Ethylene, a gaseous plant hormone, is important in various cellular and developmental processes, as well as during abiotic and biotic stress responses [51][52][53][54][55][56][70,71,72,73,74,75]. It is reported that cold stress can alter endogenous ethylene levels in many plant species. Cold stress inhibits ethylene production in Arabidopsis [57][76]; however, the ethylene levels are increased in winter rye under cold stress [58][77]. T. aestivum ethylene-responsive factor 1 (TaERF1), the first member of the ERF gene family identified in wheat, is induced by cold stress (Table 1). Additionally, TaERF1 overexpression can activate COR genes and improve freezing tolerance in transgenic Arabidopsis [59][78]. Pathogen-induced ethylene response factor 1 (TaPIE1) in wheat positively regulates freezing stresses by activating cold-regulated genes downstream of the ethylene signaling pathway and by modulating related physiological traits (Table 1) [60][79].
Gibberellins (GAs) play vital roles in abiotic stress response and adaptation. DELLA proteins are master regulators of GA-responsive growth and development [61][80]. Cold stress activates the expression of GA 2-oxidase genes to reduce the content of GA, resulting in the enhanced accumulation of DELLA proteins [62][81]. It is reported that overexpression of CBFs reduces the bioactive GA levels to suppress plant growth and flowering. CBF1-overexpression plants exhibit dwarfism and late-flowering phenotypes due to limited accumulation of bioactive GA [62][81]. Additionally, the cbfs mutants display impaired cold tolerance and larger architecture than the wild type after cold acclimation [19][63][40,82]. These results indicate that both the content and signal components of GA are related to cold signaling and CBFs may be associated with GA signaling to balance low-temperature adaption and growth. DELLAs act early in the cold signaling pathway as regulators of GROWTH REGULATORY FACTORs (GRFs). Cold-induced CBF genes are decreased in GRF5-overexpression lines, indicating that GRFs can repress CBF expression under cold stress (Table 1) [64][83]. Overexpression of SLENDER RICE 1 (SLR1), a gene that encodes the rice DELLA protein, enhances chilling tolerance. When rice seedlings are subjected to chilling stress, the cold-induced SLR1 (Table 1) releases the repressive effect of OsGRF6 on OsGA2ox1. The increased OsGA2ox1 expression then decreases the active GA levels to enhance rice chilling tolerance [65][84]. Rht-B1b and Rht-D1b, the most important and common semi-dwarfing genes, encode GA-insensitive forms of DELLA proteins that likely have a reduced affinity for the GA receptor in wheat [66][85]. It has been reported that the Rht-B1b and Rht-D1b mutant alleles are not responsive to GA at warmer temperatures but are responsive at colder temperatures (Table 1) [67][86].
The phytohormone jasmonic acid (JA) and its methyl ester, methyl jasmonate (MJ), act as signaling molecules in response to environmental stimuli. Cold stress rapidly increases endogenous JA levels by up-regulating the expression of JA biosynthesis genes, such as LIPOXYGENASE 1 (LOX1), ALLENE OXIDE SYNTHASE 1 (AOS1), ALLENE OXIDE CYCLASE 1 (AOC1), JASMONATE RESISTANT 1 (JAR1) in Arabidopsis and OsLOX2, OsAOS, OsAOC, Oryza sativa 12-OXOPHYTODIENOATE REDUCTASE 1 (OsOPR1) in rice (Table 1) [37][68][56,87]. The accumulation of JA induced by cold stress is due to the repression of ICE1 by JASMONATE ZIM-DOMAIN 1/4 (JAZ1/4), repressors of jasmonate signaling, resulting in the induction of CBFs expression in Arabidopsis [68][87]. Wheat TaJAZ genes are up-regulated in response to low temperatures (Table 1) [69][88]. Additionally, endogenous JA levels increase under cold stress in wheat [70][89]. Exogenous MJ treatment tends to up-regulate of the transcription of COR genes, such as WCS19 and WCS120, and increase the activity of superoxide dismutase (SOD) and peroxidase (PO) to promote wheat cold tolerance [71][72][90,91]. Rice HAN1 (“han” means “chilling” in Chinese), which functions as an oxidase to reduce the accumulation of the active to inactive, decreases the expression of CBF/DREB1s in rice under cold stress [73][92]. Arabidopsis OPR3 is one of the major players in the JA biosynthesis pathway. Transgenic wheat plants with AtOPR3-overexpression have increased the accumulation of JA and improved cold tolerance [74][93].
Brassinosteroids (BRs) play a vital role in plant development and stress tolerance. COR gene expression and cold tolerance in Arabidopsis are increased by exogenous BR treatment [75][94]. Exogenous BR treatment promotes growth recovery of maize seedlings following chilling treatment [76][95] and increases cold tolerance in winter rye and winter wheat [77][78][96,97]. BRASSINOSTEROID INSENSITIVE 2 (BIN2) negatively regulates the freezing tolerance in Arabidopsis [79][98]. Knockout mutants of Oryza sativa GLYCOGEN SYNTHASE KINASE 3-LIKE GENE 1 (OsGSK1), an ortholog of Arabidopsis BIN2, show enhanced cold tolerance (Table 1) [80][99]. The expression of T. aestivum SHAGGY KINASE 5 (TaSK5), an abiotic stress-inducible GSK3/SHAGGY-like kinase in wheat, is induced at the early stages of cold acclimation (Table 1) [81][100]. The BRASSINOSTEROID-INSENSITIVE 1 (BRI1) encodes a transmembrane receptor kinase as a BR receptor. Its mutation results in defective BR signaling and increases cold stress tolerance in Arabidopsis (Table 1) [82][101]. The enhanced expression of its wheat homologous TaBRI1 in Arabidopsis leads to better cold tolerance than the wild-type plants by maintaining membrane integrity [83][102]. Furthermore, overexpression of TaBRI1 in Arabidopsis and the ortholog of BRI1 in rice or barley increases the silique size and seed yield [84][85][103,104].
Table 1. List of phytohormones in response to cold stress.
| Item | Gene | Function of Gene | Regulated by Cold Stress | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Auxin | OsYUCCA2/3/6/7 | Important gene in Auxin/IPA (indole-3-pyruvic acid) biosynthesis | Up-regulated | [37][56] |
| OsGH3-1/2/5/6/11 | Auxin/IAA (indole-3-acetic acid) catabolism-related genes | Down-regulated | [37][56] | |
| ARFs | Regulate the expression of auxin-responsive genes | Up-regulated | [41][60] | |
| TaARFs | Regulate the expression of auxin-responsive genes | Up-regulated | [42][61] | |
| ABA | TaSnRK2.3/2.4/2.8 | Important serine/threonine protein kinase in ABA signaling network | Up-regulated | [47][48][49][66,67,68] |
| Ethylene | TaERF1 | A member of the ethylene response factor subfamily of ERF/AP2 transcription factor family | Up-regulated | [59][78] |
| TaPIE1 | Pathogen-induced ethylene response factor to active stress-related genes | Up-regulated | [60][79] | |
| Gibberellin | GRF5 | Growth regulating factor encoding transcription activator. | Up-regulated | [64][83] |
| SLR1 | A gene that encodes the rice DELLA protein to active OsGA2ox1 expression | Up-regulated | [65][84] | |
| Rht-B1b, Rht-D1b |
The most important and widely used semi-dwarfing genes | Up-regulated | [67][86] | |
| Jasmonic acid | LOX1, AOS1, AOC1, JAR1 | JA biosynthesis genes in Arabidopsis | Up-regulated | [37][56] |
| OsLOX2, OsAOS, OsAOC, OsOPR1 | JA biosynthesis genes in rice | Up-regulated | [68][87] | |
| TaJAZs | The repressors of jasmonate signaling | Up-regulated | [69][88] | |
| Brassinosteroids | OsGSK1 | BR negative regulator | Up-regulated | [80][99] |
| TaSK5 | An abiotic stress-inducible GSK3 in wheat | Up-regulated | [81][100] | |
| TaBRI1 | BR receptor | Up-regulated | [82][101] |
