Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Conner Chen and Version 1 by Angela Rizzo.
The history of telomere was initially closely related to the concept of senescence. They were conceived as the internal biological clock limiting the proliferation potential of eukaryotic cells (Hayflick limit). Telomeres are crucial structures that preserve genome stability. Their progressive erosion over numerous DNA duplications determines the senescence of cells and organisms. As telomere length homeostasis is critical for cancer development, nowadays, telomere maintenance mechanisms are established targets in cancer treatment.
- telomeres
- cancer
- DNA damage
1. Introduction
The history of telomere was initially closely related to the concept of senescence. They were conceived as the internal biological clock limiting the proliferation potential of eukaryotic cells (Hayflick limit). It took several more years before Müller and McClintock discovered that the chromosome ends determined the Hayflick limit.
In 1978, Elizabeth Blackburn and Carol W. Greider delved into telomeric structure, studying the protozoan Tetrahymena thermophila. They discovered a tandem repeated hexameric sequence that formed the telomeres of the ciliate (CCCCTT), in which the telomeric ability to protect the extremities of chromosomes resides [1]. Moreover, they proved the existence of an enzyme which is able to lengthen telomeres by adding telomeric sequences to the extremities of chromosomes. This enzyme is now known as telomerase [2].
In the first part of the 20th century, telomeres were discovered as the nucleoprotein structures involved in triggering senescence processes. Nowadays, the ends of chromosomes are known to play a more important role because of their implication in cancer progression. In fact, if telomere shortening is fundamental for limiting the replicative potential in normal cells, tumoral cells are characterized by telomere maintenance that determines the limitless replicative potential of cancer cells. Telomeric preservation stems from the fact that most tumor cells can activate and upregulate telomerase, blocking the telomeric shortening that would trigger the senescence or apoptosis process counteracting tumor growth. While telomere shortening can be considered a mechanism of tumor suppression because it activates senescence, it has been also related to cancer progression. In fact, in human cells, if there is an accumulation of pro-oncogenic mutations, e.g., mutations on important cell cycle checkpoint genes, cells can escape senescence, continuing to divide and increasing the likelihood of genetic errors [3,4][3][4]. Telomere fusions and chromosome breakage–fusion-bridge events unleash telomere “crises”. At this point, there are two possible outcomes: genomic instability leading to an increase of autophagy and cell death, or the crisis can be overcome by the activation of telomerase or alternative lengthening mechanisms and progression to malignant cancers (Figure 1) [5].
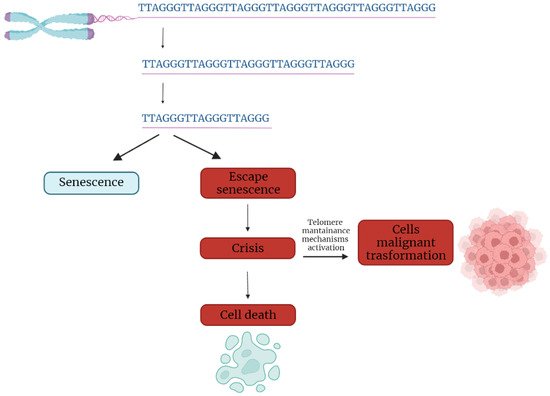
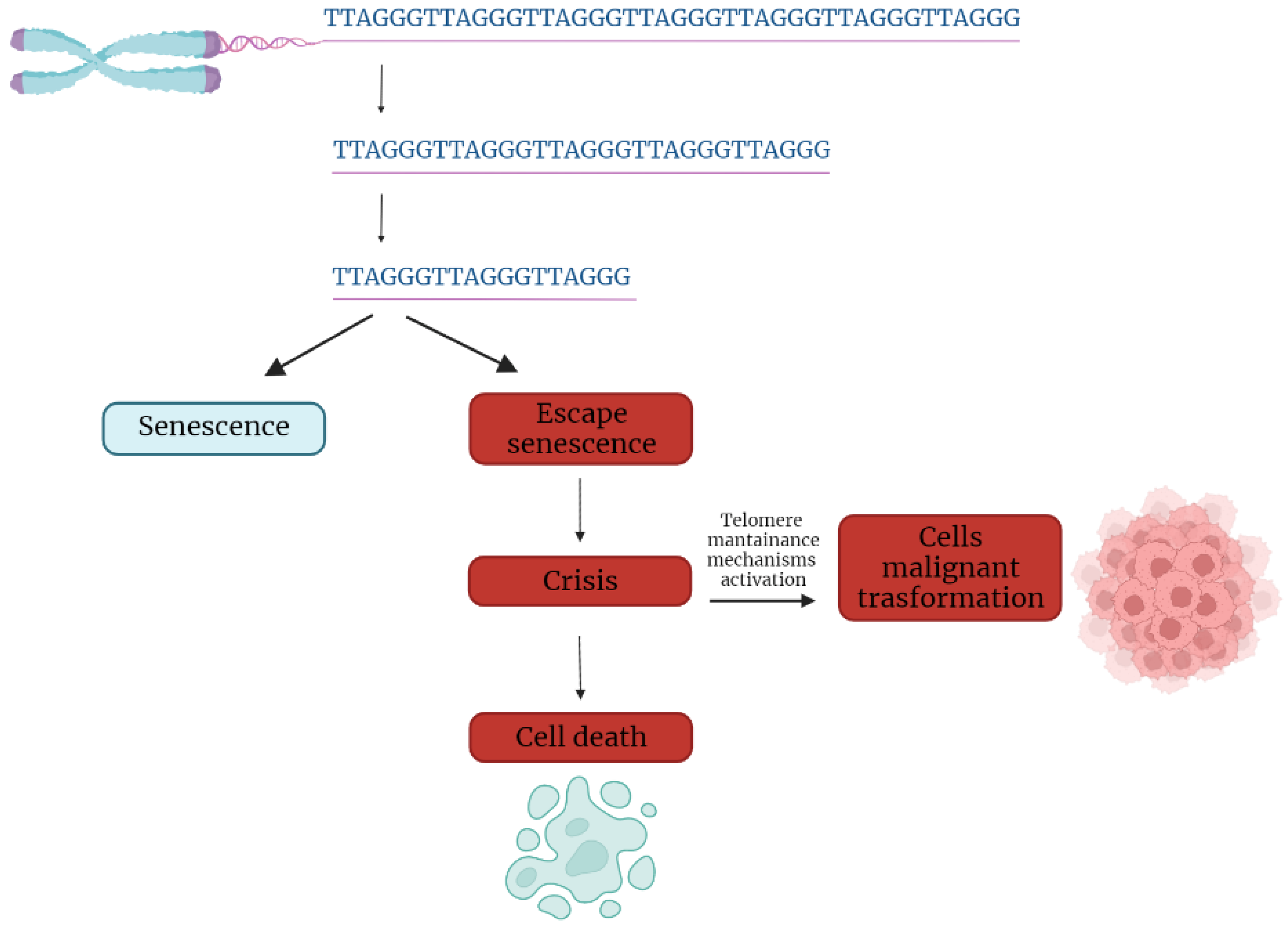
Figure 1. Telomere shortening triggers senescence. Escape from senescence, driven by checkpoint alteration, induces a state of “crisis” where telomeric and genetic instability lead to massive cell death. Surviving cells acquire malignant phenotypes.
2. Telomere Evolution and Length Maintenance in Aging and Cancer
Telomeres are specialized structures at the ends of chromosome that cap and protect genetic information during cell duplication [6]. Telomeres consist of noncoding, heterochromatic, repeated DNA containing both histones and telomere-specific protein complexes [7]. Evolutionarily, telomeres are deemed to originate from intron recombinations in circular DNA molecules, generating noncoding extremities [8]. Telomeric DNA repeats are species-specific, G-C rich conserved sequences (in human 5′-TTAGGG- 3′) terminating with a G-rich (or in some species both G and C-rich) overhang [9]. The extremities of linear DNA molecules are not completely replicated by the DNA replication machinery; therefore, the presence of noncoding DNA at the ends of chromosome evolved to overcome the progressive loss of terminal sequences in each round of cell divisions [10]. Since telomeres are lost with cell duplication, several studies have been conducted to find correlations between telomere length and age, showing that telomere length is overall reduced with increasing age [11]. Moreover, genetic defects reducing the inherited telomere length affect offspring lifespan and the self-renewal capacity of tissues due to stem cell exhaustion [11]. Telomere shortening is accompanied by the presence of DNA damage response markers that individuate dysfunctional telomeres and trigger replicative senescence [12]. Mounting evidence supports a role of telomere dysfunction in human ageing-related pathologies [13]. Recently, an extensive analysis of telomere length (TL) in different human tissue types and individuals clearly showed a significant correlation of TL with genetic background, gene expression and ageing. Furthermore, telomere shortening was shown to mediate aging-related gene expression. In fact, telomeres can be shortened by exogenous mechanisms such as oxidative stress or inflammation, and a “short-telomeres” genetic signature can drive the occurrence of aging cell phenotypes [14]. Some cells, like gametes, cancer cells and stem cells, have developed a successful strategy to overcome the replication end problem via the expression of telomerase, a ribonucleoprotein involved in counteracting the shortening of telomeric ends. Telomerase expression is strictly controlled throughout human development; if embryo stem cells have high telomerase activity, in most adult somatic cells, telomerase is not detectable, with the exception of lymphocytes in bone marrow and peripheral blood and a cluster of epithelial cells in the skin, hair follicles, endometrium and gastrointestinal tract [15,16][15][16]. Loss of telomerase function during the embryogenesis process, generating telomere shortening right from the beginning, makes the occurrence of telomeropathies highly probable [17,18][17][18]. Telomerase is a holoenzyme which is able to maintain telomere length, resynthesizing telomeric repetitions that are lost at each replication cycle [19]. It was discovered in 1985 in the ciliate Tetrahymena thermophila, and was called “telomere terminal transferase” to highlight its capacity to add telomeric sequence repeats [2]. Nowadays, human telomerase structure has been defined; it is a ribonucleoenzyme formed by hTERT, the reverse transcriptase that represents the catalytic enzyme core, hTERC, the lncRNA used as a template for telomere elongation, and a series of species-specific accessory proteins, i.e., dyskerin, NHP2, NOP10, reptin/pontin, Gar1 and TCAB1 (Figure 2) [20,21][20][21]. Accessory telomerase proteins regulate telomerase activity, biogenesis and localization, and are involved in many biological processes [22]; dyskerin, for example, is a pseudouridine synthase localized mainly in the nucleus, where it can participate in the formation of telomerase, Cajal body ribonucleoparticles (scaRNPs) and H/ACA small nucleolar ribonucleoparticles (snoRNPs), playing an important role not only for telomeres, but also for rRNA processing [23].
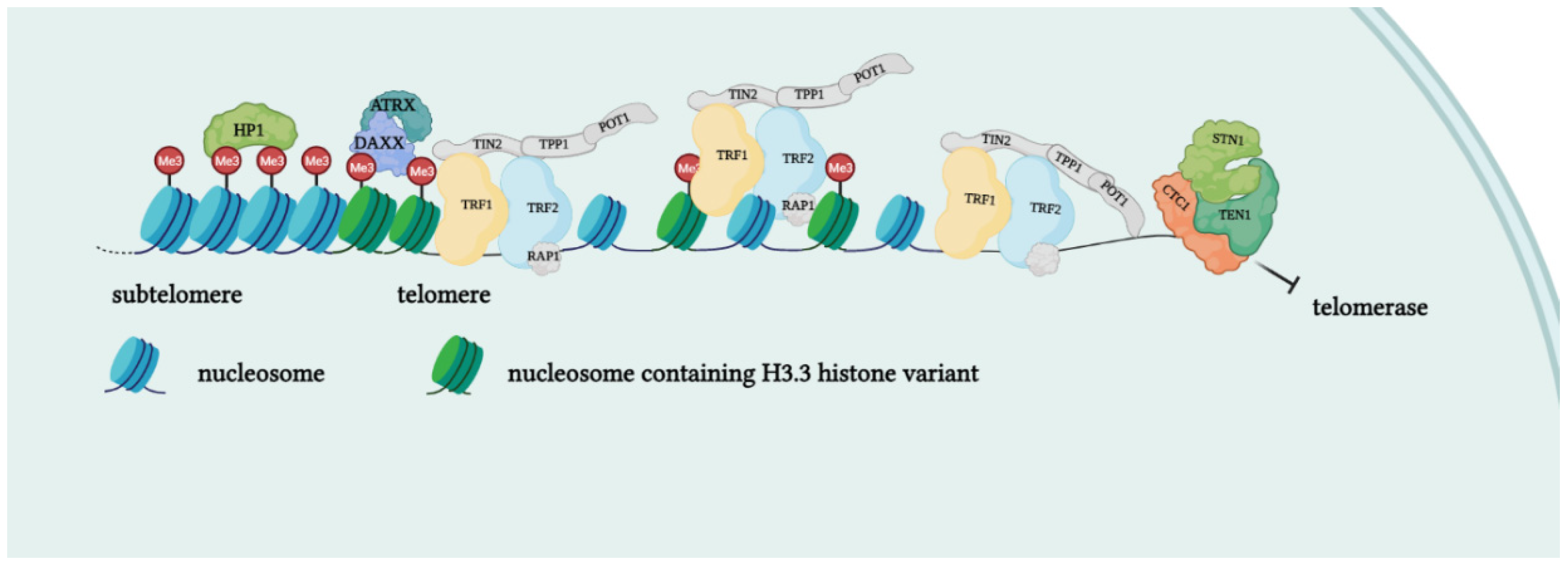
Figure 2. Protein complexes at telomeres. The shelterin complex binds telomeric sequences in an atypical nucleosome environment. Heterochromatic marks (histone trimethylation, HP1) and telomere-enriched histone variants (H3.3) are present. Telomeric ends are bound by the CST complex which antagonizes telomerase access.
Telomerase is reactivated in approximately the 80% of human tumors, as a mechanism of cell immortalization which is a hallmark of cancer. A small percentage of tumors (10–20%) which do not express telomerase restore telomeres length via an alternative mechanism (ALT). Preference for ALT or telomerase activation may depend on the histological origin of the tumor, the mutational background or epigenetic mechanisms. This confers different characteristics to the cancer type in terms of prognosis and response to treatments [24]. There are also a residual number of human tumors in which any detectable mechanism of telomere elongation may be found (telomere length maintenance deficient, TLM-); however, in tumor cells with ever-shorter telomeres, initial telomere length is sufficient to guarantee cell replication capacity. This demonstrates that prevention of telomere shortening is not required for oncogenesis [25].
References
- Blackburn, E.H.; Gall, J.G. A tandemly repeated sequence at the termini of the extrachromosomal ribosomal RNA genes in Tetrahymena. J. Mol. Biol. 1978, 120, 33–53.
- Greider, C.W.; Blackburn, E.H. Identification of a specific telomere terminal transferase activity in tetrahymena extracts. Cell 1985, 43, 405–413.
- Counter, C.M.; Avilion, A.A.; LeFeuvre, C.E.; Stewart, N.G.; Greider, C.W.; Harley, C.B.; Bacchetti, S. Telomere shortening associated with chromosome instability is arrested in immortal cells which express telomerase activity. EMBO J. 1992, 11, 1921–1929.
- Boutelle, A.M.; Attardi, L.D. p53 and Tumor Suppression: It Takes a Network. Trends Cell Biol. 2021, 31, 298–310.
- Cleal, K.; Baird, D.M. Catastrophic Endgames: Emerging Mechanisms of Telomere-Driven Genomic Instability. Trends Genet. 2020, 36, 347–359.
- De Lange, T. Protection of mammalian telomeres. Oncogene 2002, 21, 532–540.
- Smith, E.M.; Pendlebury, D.F.; Nandakumar, J. Structural biology of telomeres and telomerase. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 61–79.
- De Lange, T. T-loops and the origin of telomeres. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2004, 5, 323–329.
- Xin, H.; Liu, D.; Wan, M.; Safari, A.; Kim, H.; Sun, W.; O’Connor, M.S.; Songyang, Z. TPP1 is a homologue of ciliate TEBP-β and interacts with POT1 to recruit telomerase. Nature 2007, 445, 559–562.
- Wellinger, R.J. In the End, What’s the Problem? Mol. Cell 2014, 53, 855–856.
- Aubert, G.; Lansdorp, P.M. Telomeres and Aging. Physiol. Rev. 2008, 88, 557–579.
- d’Adda di Fagagna, F.; Reaper, P.M.; Clay-Farrace, L.; Fiegler, H.; Carr, P.; von Zglinicki, T.; Saretzki, G.; Carter, N.P.; Jackson, S.P. A DNA Damage Checkpoint Response in Telomere-Initiated Senescence. Nature 2003, 426, 194–198.
- Chakravarti, D.; Labella, K.A.; Depinho, R.A. Telomeres: History, health, and hallmarks of aging. Cell 2021, 184, 306–322.
- Demanelis, K.; Jasmine, F.; Chen, L.S.; Chernoff, M.; Tong, L.; Delgado, D.; Zhang, C.; Shinkle, J.; Sabarinathan, M.; Lin, H.; et al. Determinants of telomere length across human tissues. Science 2020, 369, eaaz6876.
- Hanaoka, S.; Nagadoi, A.; Nishimura, Y. Comparison between TRF2 and TRF1 of their telomeric DNA-bound structures and DNA-binding activities. Protein Sci. 2009, 14, 119–130.
- Collins, K.; Mitchell, J.R. Telomerase in the human organism. Oncogene 2002, 21, 564–579.
- Roake, C.M.; Artandi, S.E. Regulation of human telomerase in homeostasis and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 384–397.
- Victorelli, S.; Passos, J. Telomeres and Cell Senescence—Size Matters Not. EBioMedicine 2017, 21, 14–20.
- Zvereva, M.I.; Shcherbakova, D.M.; Dontsova, O.A. Telomerase: Structure, functions, and activity regulation. Biochemistry 2010, 75, 1563–1583.
- Gomez, D.E.; Armando, R.G.; Farina, H.G.; Menna, P.L.; Cerrudo, C.S.; Ghiringhelli, P.D.; Alonso, D.F. Telomere structure and telomerase in health and disease. Int. J. Oncol. 2012, 41, 1561–1569.
- Smogorzewska, A.; de Lange, T. Regulation of Telomerase by Telomeric Proteins. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2004, 73, 177–208.
- Podlevsky, J.D.; Chen, J.J.-L. It all comes together at the ends: Telomerase structure, function, and biogenesis. Mutat. Res. Mol. Mech. Mutagen. 2012, 730, 3–11.
- Angrisani, A.; Vicidomini, R.; Turano, M.; Furia, M. Human dyskerin: Beyond telomeres. Biol. Chem. 2014, 395, 593–610.
- Pompili, L.; Leonetti, C.; Biroccio, A.; Salvati, E. Diagnosis and treatment of ALT tumors: Is Trabectedin a new therapeutic option? J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2017, 36, 189.
- Dagg, R.A.; Pickett, H.A.; Neumann, A.A.; Napier, C.E.; Henson, J.; Teber, E.T.; Arthur, J.W.; Reynolds, C.P.; Murray, J.; Haber, M.; et al. Extensive Proliferation of Human Cancer Cells with Ever-Shorter Telomeres. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2544–2556.
More
