Originally discovered as a relatively new anticancer therapeutic technology, photodynamic therapy (PDT) has since evolved and is now used in many therapeutic technologies. For example, it is used against viruses, such as the recently reported antiviral activity against COVID-19, bacteria, fungi, and parasites, in treating neovascular disease, in environmental sanitation and pest control, and in many other applications. We have reviewed some of the applications of antimicrobial photodynamic therapy (aPDT) in combination with antibiotic chemotherapy, photothermal therapy, magnetic hyperthermia, sonodynamic therapy, and nanozyme enhanced photodynamic therapy. Among these, the combination of photodynamic therapy with antibiotic chemotherapy has been most successful, while the combination with magnetic hyperthermia is glaringly neglected. We have proposed some reasons why the combination with magnetic hyperthermia appears to be neglected. As relatively new modalities, sonodynamic therapy and nanozyme enhanced photodynamic therapy are still mainly studied in-vitro, while preclinical experiments of the combinations with photothermal therapy and antibiotic chemotherapy have been reported.
Keywords: biofilm; planktonic bacteria; extracellular polymeric substance; antimicrobial photodynamic therapy; antibiotic chemotherapy; photothermal hyperthermia therapy; magnetic hyperthermia therapy; cold atmospheric pressure plasma; sonodynamic thera-py; nanozyme enhanced photodynamic therapy
- biofilm
- planktonic bacteria
- extracellular polymeric substance
- antimicrobial photodynamic therapy
- antibiotic chemotherapy
- photothermal hyperthermia therapy
- magnetic hyperthermia therapy
- cold atmospheric pressure plasma
- sonodynamic therapy
- nanozyme enhanced
1. Introduction
2. The Microbial Biofilm Structural Challenge
3. Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy
2. The Microbial Biofilm Structural Challenge
Deeper understanding of the biofilm structure and how it contributes to antibiotic resistance has improved since the late 1970s [38], when they were first recognized in clinical samples. Biofilms are constituted from microbial communities that intimately associate with surfaces to sustain viability and improve their resistance up to a thousand times more than their planktonic forms; the surface contact and association is a key requirement for the biofilm formation mechanism [39]. Biofilms are characterized by an extensive multi-channel-permeated extracellular 3D matrix among the cells, consisting of polymeric materials, including polysaccharides and peptides, nucleic acids and lipids [40]. The biomolecule constitution of the biofilm matrix and extracellular polymeric substances (EPS) has been described in more detail [41]. It plays a vital role as a living environment for the bacterial cells in the biofilm [42] and as an infective mechanism through detachment and re-attachment [43]. Researchers have recognized several stages in biofilm formation, including contact and adhesion, formation of the colony, biofilm architecture maturation, final detachment and distal infection. Therefore, bacterial biofilms enhance antibiotic resistance and further infection [44]. Furthermore, the formation of biofilm is a collective behavior that is triggered by cell-to-cell proximity and facilitated by a bacterial quorum-sensing mechanism [45]. Due to their importance for therapeutic strategy formulation, several studies on the physical, chemical and mechanical properties of biofilms such as substrate adhesion, adsorption of chemical substances, and admission of other cells, have been conducted [46][47][48][49]. These studies have revealed that antibiotics acting on their own do not alter the biofilm structure to gain sufficient access to the constituent bacterial community. Many of these properties can be exploited to overcome the formidable bacterial biofilm formation defense mechanism. For example, their sessile nature may permit therapeutic targeting and imaging for precision drug delivery. The bacterial biofilm is a hydrophilic and wettable environment, amenable to aqueous soluble drugs and delivery strategies. Variable oxygenation levels have been reported, and the multi-channel 3D structure and reported hypoxia suggest limited susceptibility to the type II mechanism of PDT [50]. The chemical composition of the EPS of the biofilm may be among the key considerations for drug design and targeting strategies, because drugs and photosensitizers that bind to any of the known constituents of the EPS biofilm matrix could contribute toward biofilm structure disruption [51]. For these reasons, the affinity for biofilm penetration may be a key factor in therapeutic strategies.3. Antimicrobial Photodynamic Therapy
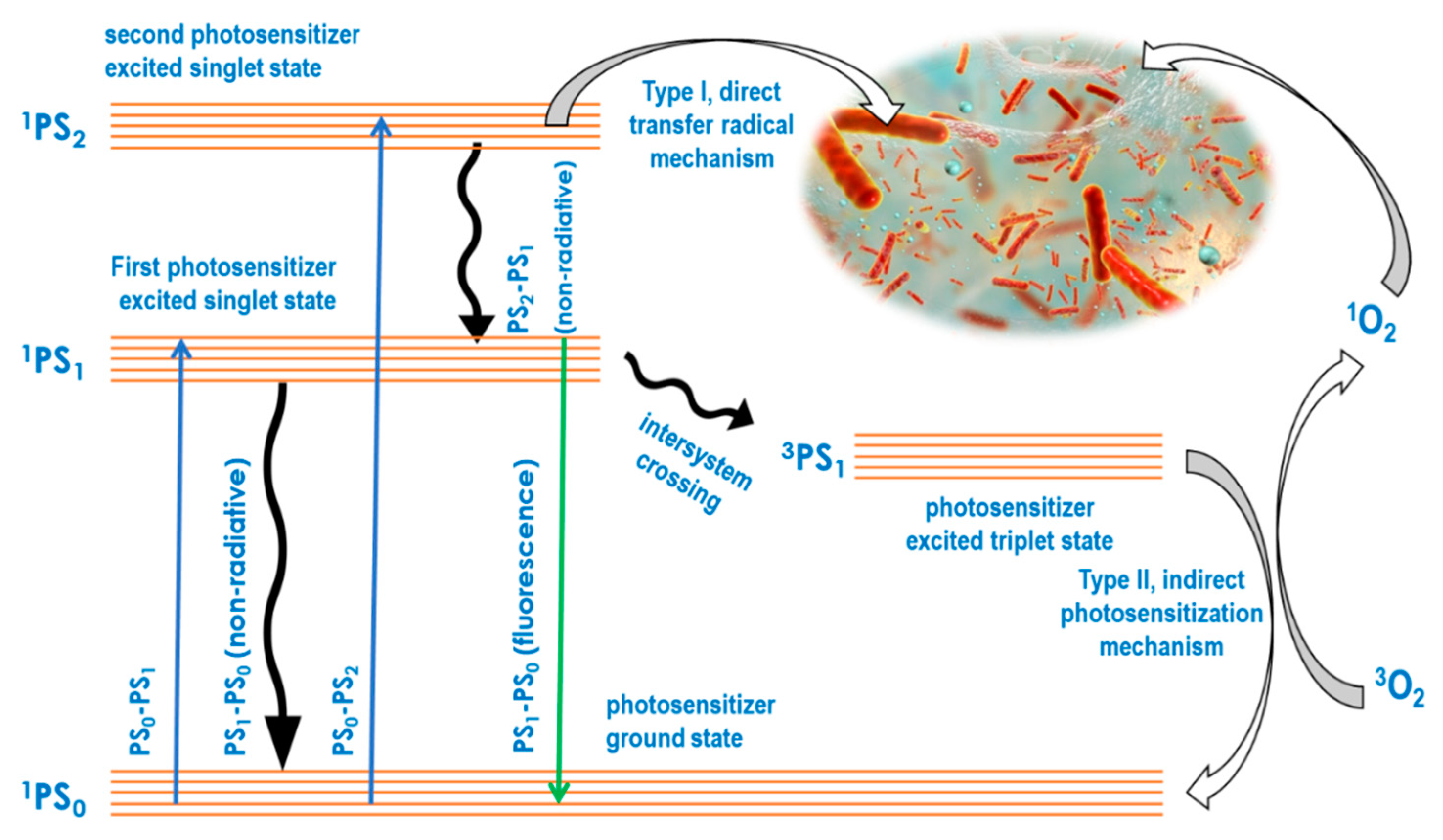
In the aPDT approach, absorbed light energy is always used for bactericidal or bacteriostatic impact through two key molecular photosensitizer-mediated mechanisms. While the type I mechanism is based on radical-forming hydrogen transfer from a light energized photosensitizer directly to biomolecules, the type II mechanism involves an initial photosensitization of oxygen to produce reactive oxygen species, which in turn attack biomolecules [52]. The mechanistic basics of type I and type II may be illustrated using a Jablonski diagram as shown in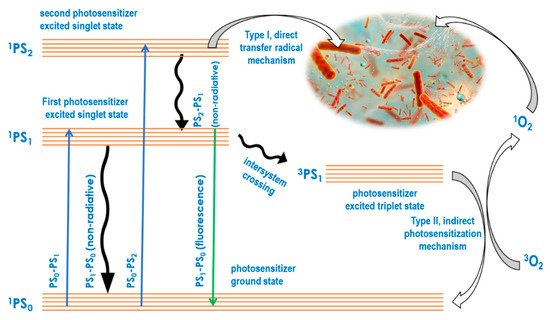
Photosensitizer | Nanoconjugate System Used | Gram | Negative | Gram | Positive | Study Phase | Impact Target | Ref | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
polyethylenimine-chlorin(e6) and tris-cationic-buckminsterfullerene | dendrimer nanoconjugate |
E. coli P. mirabilis P. aeruginosa |
S. aureus E. fecalis |
in vitro | in vivo | biofilm + planktonic |
[57] |
[53] |
||||||||||||||||
1-oxo-1H-phenalen-2-yl methyl pyridinium | chloride (SAPYR) and 1-oxo-1H-phenalen- | 2-yl-methyl-dodecan-1-aminium chloride (SA-PN-05) | None |
E. coli |
A. naeslundii S. mutans |
in vitro | biofilm + planktonic |
[58] |
[54] |
|||||||||||||||
porfimer sodium (hematoporphyrin derivative) | None |
F. nucleatuma |
in vitro | biofilm |
[61] |
[57] |
||||||||||||||||||
Methylene blue | None |
E. coli, K. pneumoniae, P. aeruginosa, S. marcescens, H. influenzae |
C. albicans, E. faecalis, S. aureus, S. pneumoniae |
in vitro | in vivo | biofilm |
[61] |
[57] |
||||||||||||||||
Chlorin-e6 | None |
H. influenzae |
M. catarrhalis, S. pneumoniae |
in vitro | biofilm + planktonic |
[63] |
[59] |
|||||||||||||||||
Protoporphyrin IX and Methylene blue | None |
A. baumannii |
in vitro | biofilm + planktonic |
[64] |
[60] |
