Peripheral nerve injuries result in the loss of the motor, sensory and autonomic functions of the denervated segments of the body. Neurons can regenerate their injured axons and eventually reinnervate their target organs, but inaccuracy of this reinnervation causes a permanent loss of function that impairs complete recovery. Thus, understanding how regenerating axons respond to their environment and direct their growth is essential to improve the functional outcome of patients with nerve lesions. Schwann cells (SCs), the glial cells of the peripheral nerves, play a crucial role in the regeneration process, but little is known about their contribution to specific reinnervation.
- axon
- Schwann cell
- regeneration
- axon-glia interactions
- peripheral nerve injury
- reinnervation accuracy
- preferential motor reinnervation
- motor
- sensory.
1. Introduction
Peripheral nerve injuries may have devastating consequences, as they result in the loss of the motor, sensory and autonomic functions of the part of the body innervated by the injured nerve or trunk. Following peripheral nerve injury, neurons are disconnected from their target organs and initiate a regenerative response. Axotomy triggers molecular and cellular changes in the neuronal body which lead to the activation of regeneration associated genes. In this state, there is a downregulation of neurotransmitter-related proteins, whereas the expression of genes involved in cell survival and neurite outgrowth is increased [1][2]. Simultaneously, the distal segment of the nerve undergoes Wallerian degeneration. The axonal membrane breaks down, cytoskeletal components are degraded and myelin sheaths are dissolved, resulting in the denervation of Schwann cells (SCs). SCs are highly plastic cells that originate from the neural crest and differentiate into two mature phenotypes: myelinating and nonmyelinating [3][4][5]. Myelinating SCs produce myelin sheaths around large nerve fibers and express characteristic myelin markers, such as protein 0 (P0), myelin-associated protein (MAG) and galactocerobroside (Gal-C). In contrast, nonmyelinating or Remak SCs ensheath smaller unmyelinated axons and maintain some markers present in more immature states, like the cell adhesion molecule L1 and the p75 neurotrophic receptor (p75NTR). After nerve injury, these molecular markers (mostly those related to myelin formation) are downregulated and the denervated SCs acquire a repair phenotype that partially resembles that of immature SCs [6] (
Peripheral nerve injuries may have devastating consequences, as they result in the loss of the motor, sensory and autonomic functions of the part of the body innervated by the injured nerve or trunk. Following peripheral nerve injury, neurons are disconnected from their target organs and initiate a regenerative response. Axotomy triggers molecular and cellular changes in the neuronal body which lead to the activation of regeneration associated genes. In this state, there is a downregulation of neurotransmitter-related proteins, whereas the expression of genes involved in cell survival and neurite outgrowth is increased [1,2]. Simultaneously, the distal segment of the nerve undergoes Wallerian degeneration. The axonal membrane breaks down, cytoskeletal components are degraded and myelin sheaths are dissolved, resulting in the denervation of Schwann cells (SCs). SCs are highly plastic cells that originate from the neural crest and differentiate into two mature phenotypes: myelinating and nonmyelinating [3,4,5]. Myelinating SCs produce myelin sheaths around large nerve fibers and express characteristic myelin markers, such as protein 0 (P0), myelin-associated protein (MAG) and galactocerobroside (Gal-C). In contrast, nonmyelinating or Remak SCs ensheath smaller unmyelinated axons and maintain some markers present in more immature states, like the cell adhesion molecule L1 and the p75 neurotrophic receptor (p75NTR). After nerve injury, these molecular markers (mostly those related to myelin formation) are downregulated and the denervated SCs acquire a repair phenotype that partially resembles that of immature SCs [8] (
).
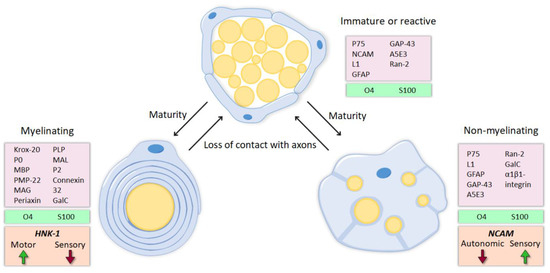
The activation of the transcription factor c-jun triggers this conversion to the repair state [7], which is characterized by numerous changes in gene expression. Many genes related to cell growth, response to external stimuli and neuritogenesis are regulated similarly to immature SCs, reactivating developmental mechanisms. However, an injury-specific program is activated as well, involving also up- or down- regulation of genes related to signal transduction, cell death, immune response, transcriptional regulation, protein transport and metabolism, among others [8][9][10]. Thus, SCs reenter the cell cycle and increase the expression of neurotrophic and chemotactic factors. Consequently, hematogenous macrophages are recruited and, together with SCs, they phagocytose myelin and axonal debris and create a permissive microenvironment to axonal regrowth [11]. Repair SCs proliferate, elongate and form processes, in contrast to the shorter and unbranched immature SCs [12]. Following Wallerian degeneration, these enlarged SCs align inside the endoneurial tubules, forming so-called bands of Büngner, where they direct axonal regeneration.
The activation of the transcription factor c-jun triggers this conversion to the repair state [9], which is characterized by numerous changes in gene expression. Many genes related to cell growth, response to external stimuli and neuritogenesis are regulated similarly to immature SCs, reactivating developmental mechanisms. However, an injury-specific program is activated as well, involving also up- or down- regulation of genes related to signal transduction, cell death, immune response, transcriptional regulation, protein transport and metabolism, among others [10,11,12]. Thus, SCs reenter the cell cycle and increase the expression of neurotrophic and chemotactic factors. Consequently, hematogenous macrophages are recruited and, together with SCs, they phagocytose myelin and axonal debris and create a permissive microenvironment to axonal regrowth [14]. Repair SCs proliferate, elongate and form processes, in contrast to the shorter and unbranched immature SCs [15]. Following Wallerian degeneration, these enlarged SCs align inside the endoneurial tubules, forming so-called bands of Büngner, where they direct axonal regeneration.
The ability of peripheral neurons to regenerate after axotomy is crucial for restoring lost functions, but it is usually not sufficient to ensure adequate functional restitution. Successful recovery also requires the specific reinnervation of target organs by appropriate axons, and this is mainly determined by the type and site of lesion [13]. In crush or compressive injuries, where axons are disrupted but connective layers surrounding fascicles maintain their continuity, spontaneous regeneration is observed without the need of repair. During the regenerative process, growing axons follow the paths within the endoneurial tubules to reinnervate their original target organs. In contrast, complete transection of the nerve results in a disruption of axons and the connective sheaths. Surgical intervention is then required to reconnect the severed nerve stumps and to guarantee that axons can regenerate into the distal nerve. However, even the best microsurgical repair techniques are not enough precise to align endoneurial tubules. Without endoneurial continuity, axons grow at random and are easily misdirected to incorrect targets [14]: motor axons may regenerate towards sensory targets, whereas sensory axons can be misrouted to the muscle. This inaccuracy in reinnervation causes a permanent loss of function that impairs complete recovery.
The ability of peripheral neurons to regenerate after axotomy is crucial for restoring lost functions, but it is usually not sufficient to ensure adequate functional restitution. Successful recovery also requires the specific reinnervation of target organs by appropriate axons, and this is mainly determined by the type and site of lesion [16]. In crush or compressive injuries, where axons are disrupted but connective layers surrounding fascicles maintain their continuity, spontaneous regeneration is observed without the need of repair. During the regenerative process, growing axons follow the paths within the endoneurial tubules to reinnervate their original target organs. In contrast, complete transection of the nerve results in a disruption of axons and the connective sheaths. Surgical intervention is then required to reconnect the severed nerve stumps and to guarantee that axons can regenerate into the distal nerve. However, even the best microsurgical repair techniques are not enough precise to align endoneurial tubules. Without endoneurial continuity, axons grow at random and are easily misdirected to incorrect targets [17]: motor axons may regenerate towards sensory targets, whereas sensory axons can be misrouted to the muscle. This inaccuracy in reinnervation causes a permanent loss of function that impairs complete recovery.
2. Current Strategies to Improve Functional Recovery After Peripheral Nerve Injury
2. Current Strategies to Improve Functional Recovery After Peripheral Nerve Injury
Plenty of studies have been performed on treatments to improve axonal regeneration after peripheral nerve injury, either by administering different drugs, adding trophic factors, gene therapy approaches, applying activity-dependent therapies or increasing the intrinsic growth capability of neurons (reviewed in [2][15][16][17][18]). However, the impact of these strategies on accurate reinnervation and functional recovery is usually limited.
Plenty of studies have been performed on treatments to improve axonal regeneration after peripheral nerve injury, either by administering different drugs, adding trophic factors, gene therapy approaches, applying activity-dependent therapies or increasing the intrinsic growth capability of neurons (reviewed in [2,18,19,20,21]). However, the impact of these strategies on accurate reinnervation and functional recovery is usually limited.
Another major line of interest has been focused on reparative methods after nerve transection when surgical intervention is essential to guarantee axonal regeneration. Nerve damage often results in tissue loss and nerve retraction, producing a resection. In these cases, the inclusion of an extrinsic bridge between the stumps is required to ensure regeneration [26]. The current gold standard in clinics is the use of an autologous nerve graft, a nerve segment from the same patient, which provides a suitable environment for regeneration, despite they present some drawbacks. Alternatives to autografts include allografts and synthetic nerve conduits, which can be improved adding growth factors or cells [19][20][21][22][23].
Another major line of interest has been focused on reparative methods after nerve transection when surgical intervention is essential to guarantee axonal regeneration. Nerve damage often results in tissue loss and nerve retraction, producing a resection. In these cases, the inclusion of an extrinsic bridge between the stumps is required to ensure regeneration [26]. The current gold standard in clinics is the use of an autologous nerve graft, a nerve segment from the same patient, which provides a suitable environment for regeneration, despite they present some drawbacks. Alternatives to autografts include allografts and synthetic nerve conduits, which can be improved adding growth factors or cells [30,31,32,33,34].
3. Preferential Motor Reinnervation
3. Preferential Motor Reinnervation
Several studies in mammals have described a preference for motor axons to regenerate towards the muscle pathway rather than to the cutaneous pathway, a phenomenon named “preferential motor reinnervation” (PMR) [24][25][26][27]. There are, however, considerable discrepancies in the literature about the mechanisms driving motor axons to their correct path. The most used model to investigate this issue has been the rat or mouse femoral nerve, a mixed nerve that divides into a muscle and a cutaneous branch of similar size.
Several studies in mammals have described a preference for motor axons to regenerate towards the muscle pathway rather than to the cutaneous pathway, a phenomenon named “preferential motor reinnervation” (PMR) [35,36,37,38]. There are, however, considerable discrepancies in the literature about the mechanisms driving motor axons to their correct path. The most used model to investigate this issue has been the rat or mouse femoral nerve, a mixed nerve that divides into a muscle and a cutaneous branch of similar size.
The PMR phenomenon opened the question of whether the pathway preference originates from signals arriving from the target organs or from the pathway itself. The most accepted hypothesis establishes that there is a hierarchy that determines pathway preference, being muscle contact the most important factor, followed by the number or density of SCs and the trophic support coming from the skin [28][29][30][31][32][33][42,44,45,46,47,48].
4. Motor and Sensory Schwann Cells
4. Motor and Sensory Schwann Cells
SCs can influence specific regeneration, but how they modulate this process is, however, controversial. Some authors propose that SCs maintain a specific molecular identity that axons can recognize during regeneration, favoring PMR. In contrast, others argue that the main effect of SCs is caused by the release of neurotrophic factors. In both cases, the identity or modality of the SCs seems to be important to guide regenerating axons towards their correct target.
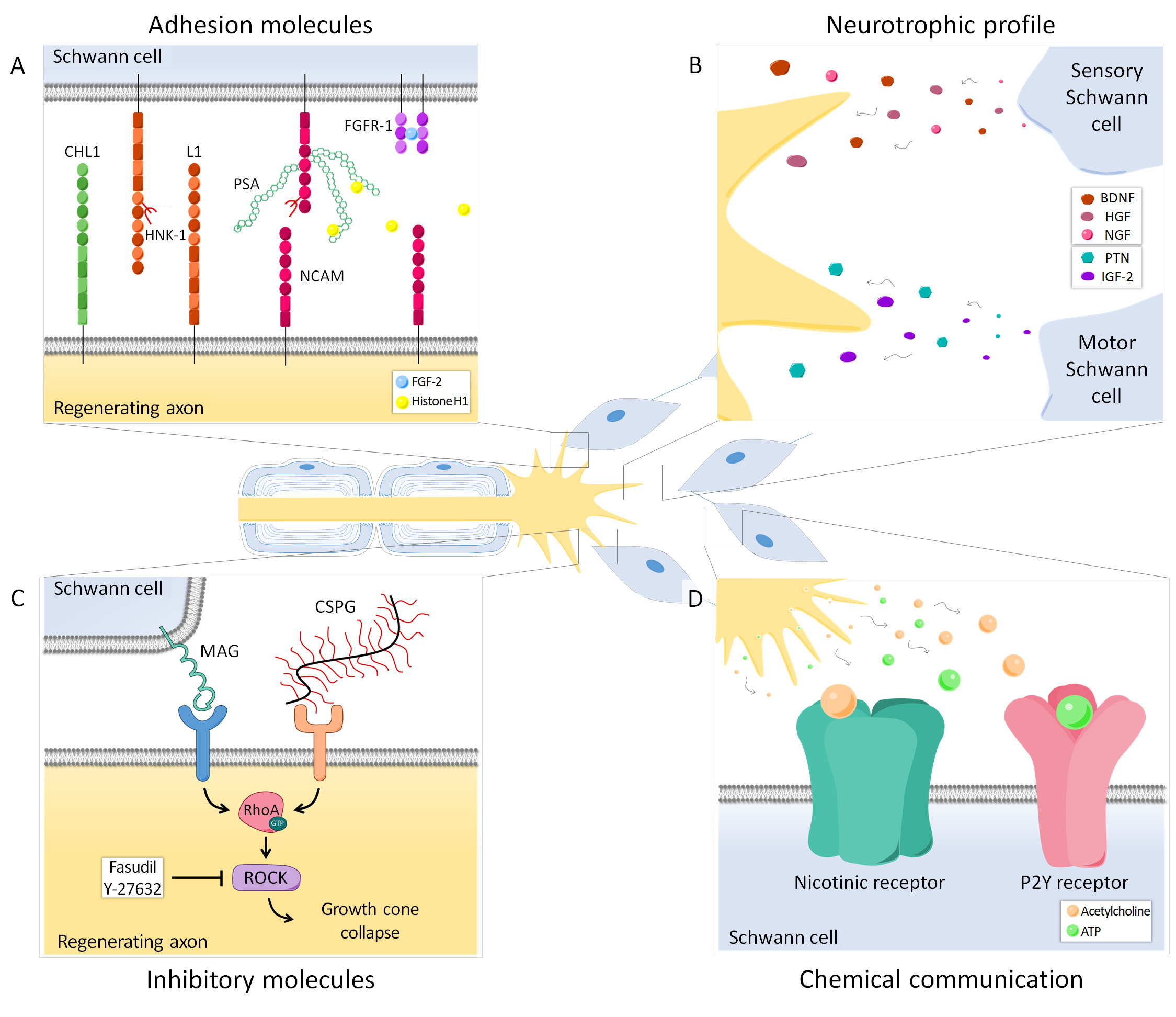
Figure 2. Axon-SC intercommunication during regeneration occurs in different ways and can modulate preferential reinnervation. (A) Several adhesion molecules play an important role in guiding axons to their target organs. Polysialic acid (PSA), mainly carried by NCAM, is differentially expressed in the cutaneous and muscle branch of the femoral nerve and its presence can be crucial for specific regeneration. Histone H1 is a PSA ligand that can enhance PMR, whereas FGF-2 promotes regeneration and could also favor specificity, presumably increasing FGFR1 and PSA-NCAM interaction. Other adhesion molecules such as CHL1, L1 and the HNK-1 carbohydrate are also relevant in this process. (B) Neurotrophic factors secreted by SCs after nerve injury are important for neuronal survival. Denervated motor and sensory SCs have a specific growth factor expression profile, therefore regenerating axons receive different signals from the cutaneous and muscle branch of the nerve that can influence axonal pathway choice. (C) Some molecules from SCs (MAG) or the extracellular matrix (CSPG) have an inhibitory effect on axonal regeneration. Both MAG and CSPG can activate the small GTPase RhoA and its downstream effector ROCK in axons, resulting in growth cone collapse. Blocking this cascade has a differential effect in motor and sensory axons, thus revealing these inhibitory molecules as candidates regulating PMR. (D) SCs can respond to neurotransmitters released by regenerating axons. Particularly, SCs have nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and purinergic P2Y receptors, which allow them to respond to acetylcholine and ATP respectively. This chemical interaction also modulates axon regeneration and specificity.
4.1. Molecular identity
Extensive evidence suggests that SCs associated with motor axons have different markers and expression patterns than those SCs associated with sensory axons (Figure 1, 2A-B), and such differences might allow to influence preferential regeneration. L2/HNK-1 carbohydrate and NCAM can be considered specific markers of muscle and cutaneous nerve branches, respectively. While NCAM is mostly found in the cutaneous branch because it is expressed in sensory non-myelinating SCs [34][35], L2/HNK-1 is found in the muscle branch because it contains motor SCs [36][37]. How this phenotypic heterogeneity influences regeneration is a complex issue and further research is essential to understand it.
4.2. Neurotrophic Profile
The expression profile of neurotrophic factors also differs between motor and sensory SCs (Figure 2B). It was described that intact ventral roots predominantly express PTN, VEGF-1 and IGF-1, whereas cutaneous nerves mostly express BDNF, NT-3, HGF and GDNF. After denervation, the expression of these trophic factors also differed between sensory and motor SCs, being PTN and GDNF strongly upregulated in ventral roots and NGF, BDNF, VEGF-1, HGF and IGF-1 mainly in cutaneous nerves [38]. Recently, the SC neurotrophic profile was found to vary not only by the modality of the associated axons, but also by their central-peripheral location [39].
5. Adhesion Molecules
SCs can influence specific regeneration, but how they modulate this process is, however, controversial. Some authors propose that SCs maintain a specific molecular identity that axons can recognize during regeneration, favoring PMR. In contrast, others argue that the main effect of SCs is caused by the release of neurotrophic factors. In both cases, the identity or modality of the SCs seems to be important to guide regenerating axons towards their correct target.
Figure 2. Axon-SC intercommunication during regeneration occurs in different ways and can modulate preferential reinnervation. (A) Several adhesion molecules play an important role in guiding axons to their target organs. Polysialic acid (PSA), mainly carried by NCAM, is differentially expressed in the cutaneous and muscle branch of the femoral nerve and its presence can be crucial for specific regeneration. Histone H1 is a PSA ligand that can enhance PMR, whereas FGF-2 promotes regeneration and could also favor specificity, presumably increasing FGFR1 and PSA-NCAM interaction. Other adhesion molecules such as CHL1, L1 and the HNK-1 carbohydrate are also relevant in this process. (B) Neurotrophic factors secreted by SCs after nerve injury are important for neuronal survival. Denervated motor and sensory SCs have a specific growth factor expression profile, therefore regenerating axons receive different signals from the cutaneous and muscle branch of the nerve that can influence axonal pathway choice. (C) Some molecules from SCs (MAG) or the extracellular matrix (CSPG) have an inhibitory effect on axonal regeneration. Both MAG and CSPG can activate the small GTPase RhoA and its downstream effector ROCK in axons, resulting in growth cone collapse. Blocking this cascade has a differential effect in motor and sensory axons, thus revealing these inhibitory molecules as candidates regulating PMR. (D) SCs can respond to neurotransmitters released by regenerating axons. Particularly, SCs have nicotinic acetylcholine receptors and purinergic P2Y receptors, which allow them to respond to acetylcholine and ATP respectively. This chemical interaction also modulates axon regeneration and specificity.
4.1. Molecular identity
Extensive evidence suggests that SCs associated with motor axons have different markers and expression patterns than those SCs associated with sensory axons (Figure 1, 2A-B), and such differences might allow to influence preferential regeneration. L2/HNK-1 carbohydrate and NCAM can be considered specific markers of muscle and cutaneous nerve branches, respectively. While NCAM is mostly found in the cutaneous branch because it is expressed in sensory non-myelinating SCs [55,56], L2/HNK-1 is found in the muscle branch because it contains motor SCs [53,54]. How this phenotypic heterogeneity influences regeneration is a complex issue and further research is essential to understand it.
4.2. Neurotrophic Profile
The expression profile of neurotrophic factors also differs between motor and sensory SCs (Figure 2B). It was described that intact ventral roots predominantly express PTN, VEGF-1 and IGF-1, whereas cutaneous nerves mostly express BDNF, NT-3, HGF and GDNF. After denervation, the expression of these trophic factors also differed between sensory and motor SCs, being PTN and GDNF strongly upregulated in ventral roots and NGF, BDNF, VEGF-1, HGF and IGF-1 mainly in cutaneous nerves [57]. Recently, the SC neurotrophic profile was found to vary not only by the modality of the associated axons, but also by their central-peripheral location [58].
5. Adhesion Molecules
Interactions between regenerating axons and SCs through adhesion molecules play an important role in guiding axons to their target organs (Figure 2A). One of these relevant molecules is polysialic acid (PSA), an anionic glycan that is mainly carried by NCAM in the cell surface of neurons and SCs [40][41][42][77,78,79]. PMR has also been linked to other adhesion-related molecules, such as the HNK-1 carbohydrate, the neural cell adhesion molecule L1 or the close homolog of L1 (CHL1) [43][44][45][84,85,89].
Evidence suggests that axon-SC intercommunication has a relevant role in the regulation of specific regeneration. So far, direct contact through adhesion molecules has received substantial attention, although the mechanisms and the exact interactions determining their influence in PMR are still poorly understood.
6. Inhibitory Molecules
6. Inhibitory Molecules
During Wallerian degeneration, myelin breakdown results in the exposure of growth inhibitory molecules such as myelin-associated glycoprotein (MAG) [46][47][91,92]. The blockade of this glycoprotein has been shown to increase PMR dramatically in mouse [48][94]. The growth cone collapse induced by MAG and other inhibitory cues is mediated through the activation of the small GTPase RhoA and its downstream effector Rho-kinase (ROCK) in regenerating neurons [49][50][97,98] (Figure 2C). Importantly, it was recently demonstrated that motor and sensory neurons respond differently to the pharmacological inhibition of this pathway. Thus, inhibitory molecules influence regeneration after nerve injury and, due to their differential effect on motor and sensory neurons, might also participate in the regulation of preferential reinnervation.
7. Electrical Stimulation
7. Electrical Stimulation
Electrical stimulation (ES) has been repeatedly demonstrated to improve axonal regeneration after nerve injury (for review see [51][100]). Al-Majed et al. showed that 1 h of low-frequency stimulation (20 Hz) proximal to the repair site was enough to accelerate PMR in the femoral nerve of rat [52][101]. Later, a similar effect was demonstrated for sensory neurons as well [102].
8. Conclusions
After peripheral nerve injury, guiding axons [53]back to their original target organ remains a major problem hindering complete functional recovery. Axonal regeneration is a complex process in which several components are involved. Hence, understanding the interactions between axons and their environment is essential to improve specific regeneration. Among the several factors influencing this process, target organs are perhaps the most relevant, either by their supply of trophic factors, or by direct contact with axons after reinnervation, which might determine the pruning of misdirected collaterals. However, many other factors have emerged as candidates that regulate preferential regeneration. SCs show modality-specific characteristics that can influence their interaction with regenerating axons. They are a major source of neurotrophic factors in the nerve, but they can also undergo direct communication through adhesion molecules, such as PSA or HNK-1, or even respond to neurotransmitters released by regenerating growth cones. Many of these specific cues and interactions can be modulated to achieve better and more accurate regeneration after axotomy and, thus, improve the functional recovery of patients suffering nerve injuries.
8. Conclusions
After peripheral nerve injury, guiding axons back to their original target organ remains a major problem hindering complete functional recovery. Axonal regeneration is a complex process in which several components are involved. Hence, understanding the interactions between axons and their environment is essential to improve specific regeneration. Among the several factors influencing this process, target organs are perhaps the most relevant, either by their supply of trophic factors, or by direct contact with axons after reinnervation, which might determine the pruning of misdirected collaterals. However, many other factors have emerged as candidates that regulate preferential regeneration. SCs show modality-specific characteristics that can influence their interaction with regenerating axons. They are a major source of neurotrophic factors in the nerve, but they can also undergo direct communication through adhesion molecules, such as PSA or HNK-1, or even respond to neurotransmitters released by regenerating growth cones. Many of these specific cues and interactions can be modulated to achieve better and more accurate regeneration after axotomy and, thus, improve the functional recovery of patients suffering nerve injuries.