Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Jason Zhu and Version 3 by Jason Zhu.
The impact of plastics on the environment can be mitigated by employing biobased and/or biodegradable materials (i.e., bioplastics) instead of the traditional “commodities”. In this context, poly (butylene succinate) (PBS) emerges as one of the most promising alternatives due to its good mechanical, thermal, and barrier properties, making it suitable for use in a wide range of applications. Still, the PBS has some drawbacks, such as its high crystallinity, which must be overcome to position it as a real and viable alternative to “commodities”.
- Synthesis
- Poly (Butylene Succinate)
- Bio-Based Polymerization
- Petroleum-Based Synthesis
- Copolymerization
- Biocomposites
- Mechanical Properties
- Crystallization
- Barrier Properties
- Degradation
1. Introduction
Poly (butylene succinate) is obtained from two monomers: succinic acid (SA) and 1,4-butanediol (BD). SA can be obtained through the hydrogenation of fossil-derived maleic acid (anhydride) or 1,4-butanediol. The BD is produced through the hydrogenation of 1,4-butynediol, previously obtained from acetylene and formaldehyde. The BD can also be obtained through the hydrogenation of methyl maleate ester derived from maleic anhydride. In order to move to greener production methods, SA can be prepared through fermentation, whereas it is possible to obtain the BD monomer from a genetically modified organism [1][2]. The polymerization routes for the production of PBS can be divided into two categories: petroleum-based synthesis and bio-based polymerization. The petroleum-based synthesis relies on polycondensation reactions, generating higher molecular weights (MW) than the bio-based polymerization. However, the latter is based on enzymes as catalysts of the reaction, representing a greener alternative. The description of the experimental methodology for each of the polymerization routes is provided below.
2. Petroleum-Based Synthesis: Transesterification Polymerization: Melt, Chain Extender, and Solution
The petroleum-based synthesis is based on transesterification polymerization (shown in Scheme 1), carried out in the melt or in solution. Through these methods, PBS of intermediate and high MWs can be obtained.
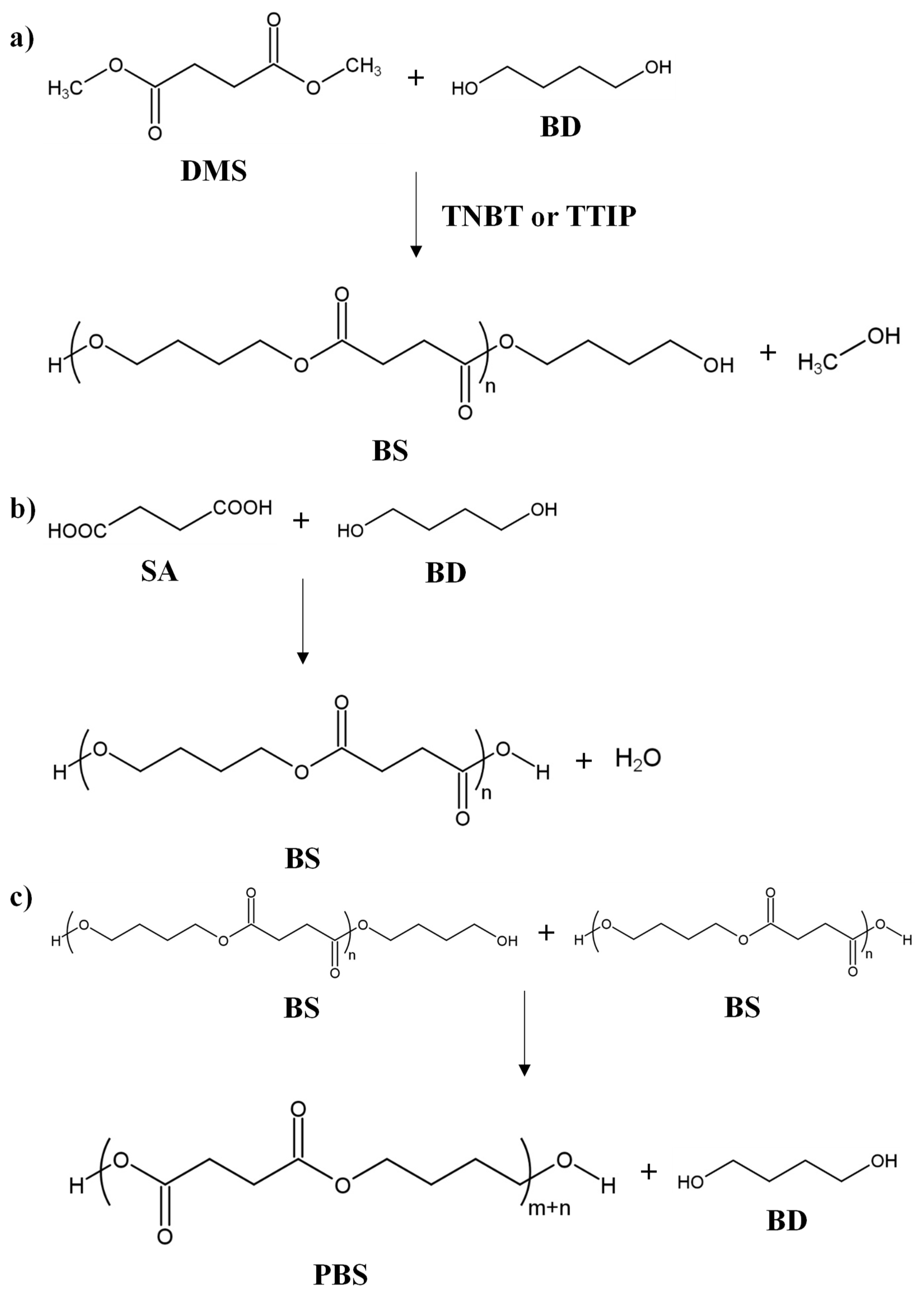
Scheme 1.
Transesterification polymerization of PBS: (
a
) transesterification step; (
b
) direct polymerization step; (
c
) polycondensation step.
Intermediate MWs, e.g., the number average molecular weight, Mn ~60,000 g/mol and the weight average molecular weight, Mw ~100,000 g/mol [3][4], are obtained through a transesterification polymerization carried out in the melt. This polymerization employs dimethyl succinate (DMS) and BD, as monomers, in stoichiometric relation or with an excess of BD below 10 mol%. Titanium (IV) butoxide (TNBT) or titanium (IV) isopropoxide (TTIP) are commonly used as catalysts of the reaction [5] (see Figure 1). Before the reaction process, the reactor is filled with nitrogen at room temperature to remove air and avoid oxidation during the transesterification step. After that, the reaction system is heated at a temperature ranging from 150 °C to 190 °C, with constant stirring and under a nitrogen atmosphere to start the transesterification reaction (see Scheme 1a). Then, a distillation step is needed to discard most of the methanol and water produced during the reaction. In a second stage, polycondensation (see Scheme 1c) is carried out under vacuum at a higher temperature to remove the BD formed in the reaction and polymerize the oligomers to the polymer [6].
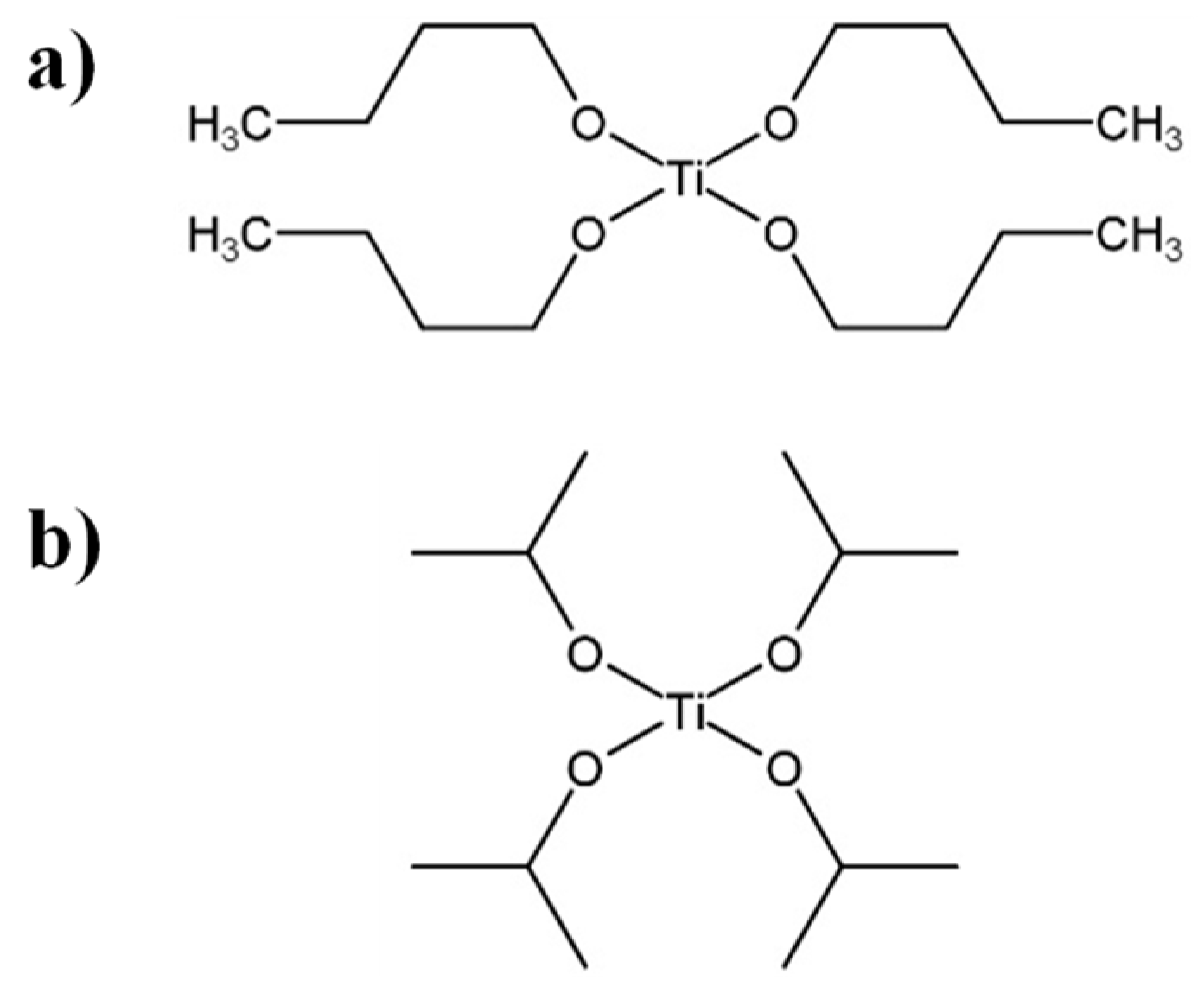
Figure 1. Chemical structures of different catalysts employed in the transesterification step: (a) titanium (IV) butoxide (TNBT) and (b) titanium (IV) isopropoxide (TTIP).
A second option for petroleum-based syntheses is the direct polymerization (see Scheme 1b) of both monomeric units (SA and BD), starting from dicarboxylic acids and alkyl diols. High MWs can be obtained by using a chain-extension step. Direct polymerization can be carried out in the melt or in solution. In the melt, the polymerization consists of two steps: first, the esterification reaction occurs at temperatures from 150 °C to 200 °C, under atmospheric pressure, or in a low vacuum. In the second step, the polycondensation is carried out under a high vacuum at a higher temperature (220–240 °C) for deglycolization. It is important to note that both steps should be done under a nitrogen atmosphere to avoid oxidation [7]. For high-MW PBS production, an extra chain-extension step (see Scheme 2) is added to the melt condensation polymerization, achieving Mn ~80,000 g/mol and Mw ~250,000 g/mol. Some researchers have reported even higher values: Mn ~180,000 g/mol and Mw ~450,000 g/mol [8], Mw ~500,000 g/mol [9], or up to Mw ~1,000,000 g/mol [10]. These values are supported by Showa Denko, which commercially produced high-MW PBS (Bionolle) with a chain extender (hexamethylene diisocyanate, HMDI), reaching Mn ~200,000 g/mol and Mw ~300,000 g/mol (see Scheme 2). A chain extender with two functional groups can react with the terminal –OH or –COOH of PBS. The reaction conditions for the chain extension are not as critical as the direct melt polycondensation. Therefore, the chain extender incorporation decreases the biosafety and could affect the biodegradability of PBS, which might prevent the employment of the so-obtained PBS in food packaging. Many chain extenders have been investigated, e.g., isocyanate [4], oxazoline [11], anhydride, biscaprolactamate [12], silazane [13], and epoxy compound [9]. Diisocyanate and anhydride are suitable for extending the –OH of the PBS, whereas oxazoline and epoxy compounds are used to extend the –COOH groups of PBS [5].
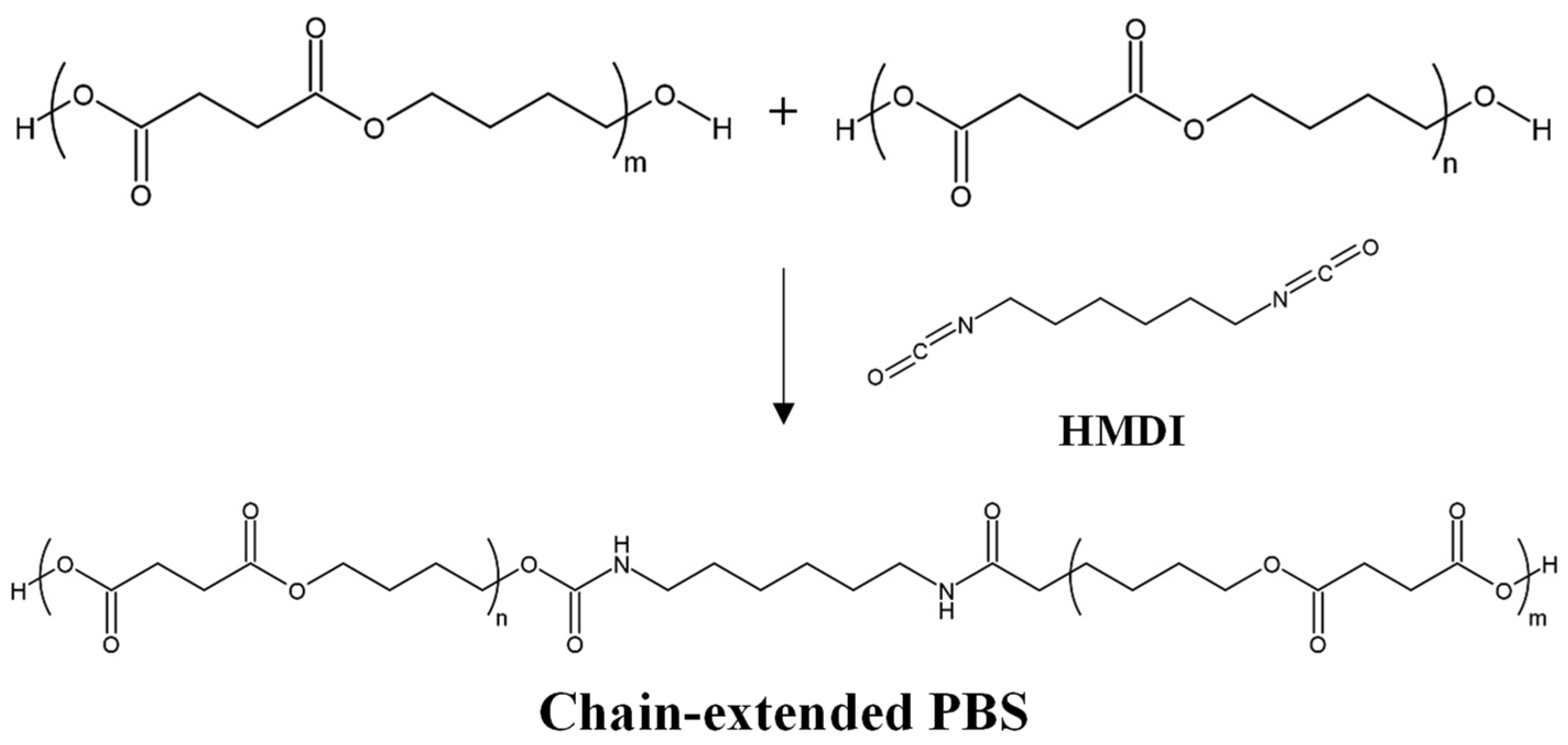
Scheme 2. Chain-extension step with hexamethylene diisocyanate (HMDI) to produce high-MW PBS.
In the polymerization from solution, the monomers are dissolved in a solvent, such as xylene or decahydronaphthalene. This procedure improves the removal of the small molecular materials formed in the reaction process. Both reactions, esterification, and polycondensation proceed at lower temperatures, which avoids the oxidation of PBS, although the reaction time increases [5]. Regarding the MWs obtained, Mn ~120,000 g/mol and Mw ~280,000 g/mol can be achieved [14], although lower values are also obtained [15][16].
3. Bio-Based Polymerization: Enzymatic Synthesis
This method is relatively recent with respect to petroleum-based synthesis and presents the advantages of milder reaction conditions and the absence of residual metals and metal salts. Candida antarctica lipase B (CALB) is usually employed as a catalyst in synthesizing PBS from the monophasic reaction mixtures of diethyl succinate (DES) and 1,4-butanediol (see Scheme 3). In this case, the reaction temperature dramatically affects the MW of the polymer. In general, reaction temperatures are below 100 °C, with reaction times of 24 h. Another remarkable result obtained from this procedure is the narrow dispersity index of the PBS obtained. However, the MW is low compared to other polymerization methods [17]. Debuissy et al., reported a “green” enzymatic procedure to obtain PBS starting from telechelic hydroxylated poly((r)-3-hydr-oxybutyrate) (PHB-diol) oligomers and employing CALB and BD in a single-step process. The same researchers also described another procedure for this enzymatic synthesis, where the main difference is that the PHB-diol oligomers were introduced after 24 h of the CALB-catalyzed reaction [18]. Cyclic butylene succinate oligomers have also been obtained through enzymatic ring-opening polymerization (eROP) employing CALB as the catalyst at temperatures below 100 °C. The obtained oligomers presented low MWs: 4700 g/mol and 6100 g/mol for Mn and Mw, respectively [19].
References
- Burk, M.J.; Van Dien, S.J.; Burgard, A.; Niu, W. Compositions and Methods for the Biosynthesis of 1,4-Butanediol and Its Precursors. U.S. Patent US8067214 B2, 29 November 2011.
- Díaz, A.; Katsarava, R.; Puiggalí, J. Synthesis, properties and applications of biodegradable polymers derived from diols and dicarboxylic Acids: From Polyesters to poly(ester amide)s. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 7064–7123.
- Tserki, V.; Matzinos, P.; Pavlidou, E.; Vachliotis, D.; Panayiotou, C. Biodegradable aliphatic polyesters. Part I. Properties and biodegradation of poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene adipate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 367–376.
- Tserki, V.; Matzinos, P.; Pavlidou, E.; Panayiotou, C. Biodegradable aliphatic polyesters. Part II. Synthesis and characterization of chain extended poly(butylene succinate-co-butylene adipate). Polym. Degrad. Stab. 2006, 91, 377–384.
- Xu, J.; Guo, B.-H. Microbial succinic acid, its polymer poly(butylene succinate), and applications. In Plastics from Bacteria: Natural Functions and Applications; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2010; Volume 14, pp. 347–388. ISBN 978-3-642-03286-8.
- Xu, J.; Guo, B.H. Poly(butylene succinate) and its copolymers: Research, development and industrialization. Biotechnol. J. 2010, 5, 1149–1163.
- Luyt, A.S.; Malik, S.S. Can biodegradable plastics solve plastic solid waste accumulation? In Plastics to Energy: Fuel, Chemicals, and Sustainability Implications; Elsevier Inc.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 403–423. ISBN 9780128131404.
- Zhu, Q.Y.; He, Y.S.; Zeng, J.B.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Y.Z. Synthesis and characterization of a novel multiblock copolyester containing poly(ethylene succinate) and poly(butylene succinate). Mater. Chem. Phys. 2011, 130, 943–949.
- Zhou, H.; Wang, X.; Du, Z.; Li, H.; Yu, K. Preparation and characterization of chain extended Poly(butylene succinate) foams. Polym. Eng. Sci. 2015, 55, 988–994.
- Fujimaki, T. Processability and properties of aliphatic polyesters, “BIONOLLE”, synthesized by polycondensation reaction. Polym. Degrad. Stab. 1998, 59, 209–214.
- Huang, C.Q.; Luo, S.Y.; Xu, S.Y.; Zhao, J.B.; Jiang, S.L.; Yang, W.T. Catalyzed chain extension of poly(butylene adipate) and poly(butylene succinate) with 2,2′-(1,4-phenylene)-bis(2-oxazoline). J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2010, 115, 1555–1565.
- Zhao, J.B.; Li, K.Y.; Yang, W.T. Chain extension of polybutylene adipate and polybutylene succinate with adipoyl- and terephthaloyl-biscaprolactamate. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2007, 106, 590–598.
- Zhao, J.B.; Wu, X.F.; Yang, W.T. Synthesis of aliphatic polyesters by a chain-extending reaction with octamethylcyclotetrasilazane and hexaphenylcyclotrisilazane as chain extenders. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2004, 92, 3333–3337.
- Ishii, M.; Okazaki, M.; Shibasaki, Y.; Ueda, M.; Teranishi, T. Convenient synthesis of aliphatic polyesters by distannoxane-catalyzed polycondensation. Biomacromolecules 2001, 2, 1267–1270.
- Zhu, C.; Zhang, Z.; Liu, Q.; Wang, Z.; Jin, J. Synthesis and Biodegradation of Aliphatic Polyesters from Dicarboxylic Acids and Diols. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2003, 90, 982–990.
- Jie, S. Synthesis and Characterization of High Relative Molecular Mass Poly(butylene succinate). Fine Chem. 2007, 24, 117.
- Azim, H.; Dekhterman, A.; Jiang, Z.; Gross, R.A. Candida antarctica lipase B-catalyzed synthesis of poly(butylene succinate): Shorter chain building blocks also work. Biomacromolecules 2006, 7, 3093–3097.
- Debuissy, T.; Pollet, E.; Avérous, L. Enzymatic Synthesis of a Bio-Based Copolyester from Poly(butylene succinate) and Poly((R)-3-hydroxybutyrate): Study of Reaction Parameters on the Transesterification Rate. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 4054–4063.
- Ciulik, C.; Safari, M.; Martínez de Ilarduya, A.; Morales-Huerta, J.C.; Iturrospe, A.; Arbe, A.; Müller, A.J.; Muñoz-Guerra, S. Poly(butylene succinate-ran-ε-caprolactone) copolyesters: Enzymatic synthesis and crystalline isodimorphic character. Eur. Polym. J. 2017, 95, 795–808.
More
