Neuromodulation is a promising new area with treatment applications for psychiatry. Electrical stimulation of the vagus nerve is associated with a reduction in peripheral sympathetic and inflammatory function and modulation of brain areas mediating fear and the stress response, and thus has potential applications to patients with stress-related psychiatric disorders, including posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and depression. Non-invasive Vagal Nerve Stimulation (nVNS) can be applied to vagus nerve locations at the neck (transcutaneous cervical, or tcVNS) or ear (transcutaneous auricular, or taVNS), intervening at the level of the underlying psychobiology with potential beneficial treatment effects.
- vagus nerve
- stress
- depression
- PTSD
- Vagal Nerve Stimulation
- neuromodulation
- stress disorders, posttraumatic
- depressive disorders
- major depression disorder
- inflammation
Note:All the information in this draft can be edited by authors. And the entry will be online only after authors edit and submit it.
Definition:Vagal Nerve Stimulation (VNS) has been shown to be efficacious for the treatment of depression, but to date, VNS devices have required surgical implantation, which has limited widespread implementation. Methods: New noninvasive VNS (nVNS) devices have been developed which allow external stimulation of the vagus nerve, and their effects on physiology in patients with stress-related psychiatric disorders can be measured with brain imaging, blood biomarkers, and wearable sensing devices. Advantages in terms of cost and convenience may lead to more widespread implementation in psychiatry, as well as facilitate research of the physiology of the vagus nerve in humans. nVNS has effects on autonomic tone, cardiovascular function, inflammatory responses, and central brain areas involved in modulation of emotion, all of which make it particularly applicable to patients with stress-related psychiatric disorders, including posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD) and depression, since dysregulation of these circuits and systems underlies the symptomatology of these disorders.
1. Introduction
Stress-related psychiatric disorders, including depression and posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), are important public health problems. Early life stress increases the risk of development of depression in adulthood [1][2][1,2], and stressful life events are associated with an increased risk for depressive episodes [3], while PTSD requires exposure to a traumatic stressor as part of the diagnosis [4]. At any given time, 10% of the United States population meets the criteria for major depression or other mood disorders based on Diagnostic and Statistical Manual (DSM) criteria [5], with an annual cost of lost productivity of USD 44 billion [6]. Similarly, PTSD affects 6% of the population at some time in their lives [7]. The cost of treating PTSD and comorbid depression in soldiers returning from the wars in Iraq and Afghanistan has been estimated to be USD 6.2 billion [8], and since PTSD affects a larger total number of civilians in the United States than military personnel, the costs for society as a whole are likely much higher [9]. The most common cause of PTSD in women is sexual abuse and assault in childhood, while, for men, it is physical assault [10]. On average, women have higher occurrence of PTSD compared to men in the civilian population [11][12][11,12]. PTSD is characterized by intrusive thoughts, nightmares, avoidance, emotional blunting, negative cognitions, hypervigilance, and hyperarousal [13]. Depression is associated with depressed mood, loss of appetite, decreased psychomotor activity, and, in extreme cases, suicidal ideation. Other symptoms, such as poor sleep and concentration, negative cognitions, loss of interest in things, and anhedonia, are common to both conditions. In fact, there is a degree of comorbidity between the two conditions [14][15][16][17][18][19][14,15,16,17,18,19]. Furthermore, patients with comorbid disorders have a worse clinical course, with, for instance, a higher risk of suicidal ideation [20][21][20,21].
The standard of care for both PTSD and depression includes psychotherapy and/or medication [22][23][22,23]. Psychotherapy treatments for PTSD, however, have dropout rates as high as 50%, which limit their applicability [24][25][24,25]. First-line medication treatments for stress-related psychiatric disorders involves the Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitor (SSRI) antidepressants [26][27][26,27]. However, as highlighted by a report from the Institute of Medicine, there is not sufficient evidence to conclude that they are effective for PTSD [28]. In fact, only one-third of those suffering from PTSD are able to achieve full remission with the current standard of care [26]. Similar limitations exist for treatment of major depression. As illustrated by the STAR*D study, only one-third of patients with major depression remitted to first-line therapy with antidepressants and only about two-thirds of patients met remission criteria after multiple algorithms that included psychotherapy, switching classes, and multiple heroic augmentation trials [29]. Given limitations of current treatment options, new paradigms are clearly needed for the management of stress-related psychiatric disorders.
2. Noninvasive Vagal Nerve Stimulation: Application to Stress-Related Psychiatric Disorders
The requirement for direct VNS to be surgically implanted has limited widespread implementation in stress-related psychiatric disorders to date due to cost and inconvenience [30][31][125,131]. These forms of VNS are also limited by the fact that true sham-controlled trials cannot be performed due to ethical reasons, which has led to questions about the true efficacy of these devices [32][261]. Since devices are only implanted in patients who have not responded to multiple antidepressants, the patient populations are also not necessarily representative of those typically seen in clinical psychiatry practices, which may explain why VNS, although yielding statistically significant improvements, did not lead to complete remission in all patients [33][283]. Additionally, treatments have not been reimbursed by Medicare or other insurance companies, which has further limited implementation [34][284]. Studies have shown the utility of both tcVNS and taVNS for various psychiatric disorders, including schizophrenia [35][285] and obsessive-compulsive disorder [36][286], as well as major depression [37][287]. Human studies also suggest that noninvasive VNS improves hyperarousal in PTSD patients with mild traumatic brain injury [38][288] and reduces symptoms in treatment-resistant anxiety disorders [39][289].
As proven by their cost and convenience, noninvasive VNS technologies have widespread applicability to patients with stress-related psychiatric disorders.
Neck-based tcVNS was recently approved by the FDA for the treatment of intractable cluster headache [40][41][42][43][264,290,291,292]. We have implemeneted this device in healthy human subjects with a history of exposure to traumatic stressful events since 2017, and have found it to be safe and feasible [44][45][46][277,278,279]. In our studies, we compared active tcVNS to a sham control in a randomized trial (Figure 12). Both were handheld devices that were applied to the left neck for stimulation with identical placement and operation (GammaCore, ElectroCore, Basking Ridge, New Jersey). nVNS or sham were applied using collar electrodes on the left side of the neck in order to permit placement while subjects were in the research-dedicated brain scanner, which had a small aperture. The treatment area on the neck was located by finding the carotid artery pulsation. An electrically conductive gel was applied on the stimulation surfaces and device is placed on the located treatment area. Active tcVNS devices produced a 5-kHz sine wave burst lasting for 1 millisecond (five sine waves, each lasting 200 microseconds), repeated one in every 40 milliseconds (25 Hz), generating 30-V peak voltage and 60-mA peak output current. The final stimulation intensity depended on the subject’s verbal feedback: The researcher was instructed to increase the intensity gradually until the subject voiced discomfort, at which point the intensity was reduced slightly below that threshold. Sham devices produced a nearly direct voltage signal, whose polarity was slowly varied (0.2-Hz biphasic voltage), in contrast to the higher-frequency, alternating current used for the active nVNS (25 Hz with 5-kHz bursts). The sham device delivered a biphasic signal generating a 14-V peak voltage and 60-mA peak output current, consisting of pulses repeating every 5 s (0.2 Hz). High-frequency voltage signals (such as the active stimulus) pass through the skin with minimal power dissipation due to the low skin-electrode impedance at kHz frequencies. In contrast, lower-frequency signals (such as the sham stimulus) are mainly attenuated at the skin-electrode interface due to the high impedance [47][293]. Accordingly, the active tcVNS can deliver substantial energy to the vagus nerve to facilitate stimulation, while the voltage levels appearing at the vagus would be expected to be orders of magnitude lower for the sham device and thus vagal stimulation is unlikely. Nevertheless, since the sham device does deliver relatively high voltage and current levels directly to the skin, it activates skin nociceptors, causing a similar feeling to a pinch. This sensation is necessary for blinding of the participants and is thought as a critical detail by the investigators for the valuation of the potential treatment in psychiatric populations. Both active and sham interventions lasted for two minutes. The subject, research staff, and investigators were all blind to the device category, and the key was kept in a locked office by an individual not involved in the research in two locations. The specific details are summarized as follows: The manufacturer sent the active and sham devices to an individual who was not involved in research, and the individual randomized patients to the devices prior to patient recruitment. In addition, every subject was given a different, dedicated device, hence the number of patients was equal to the number of devices. Every week when a new patient arrived, the individual not involved in research delivered a different device to the research staff for use for that subject.
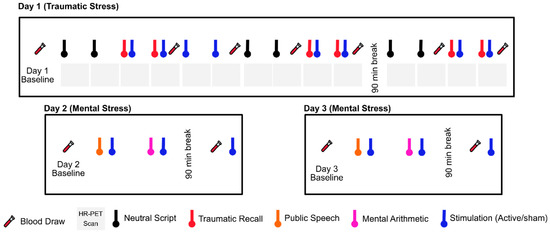
Figure 12. Study protocol undergoing since 2017. Physiological sensing data is collected continuously throughout three study days. The protocol timeline depicts neutral and trauma scripts, HR-PET scans (first day), mental stress tasks of public speech and mental arithmetic (second and third day), stimulation with active tcVNS or sham, and blood draws (all days).
In our study with physically healthy traumatized subjects and patients with PTSD, we constructed a multisignal dataset that include physiological signals related to cardiovascular and peripheral activity. The signals included electrocardiography (ECG), respiration (RSP), seismocardiography (SCG), photoplethysmography (PPG), electrodermal activity (EDA), and blood pressure (BP). Upon beat-by-beat signal processing, we extracted parameters related to autonomic tone with a beat-by-beat resolution. These parameters included both standard and nonstandard indices of psychophysiological reactivity, such as heart rate (HR), pre-ejection period of the heart (PEP), amplitude of the peripheral photoplethysmogram (PPG), pulse arrival time (PAT), properties of respiration signal (respiration rate, RR, width, RW, prominence, RP), frequency- and time- domain heart rate variability indices including low- and high-frequency heart rate variability (LF HRV, HF HRV), Poincare-based nonlinear heart rate variability (SD1, SD2), acceleration and deceleration capacity (AC, DC), and skin conductance level and response (SCL, SCR). In our healthy cohort, PEP, PPG amplitude, skin conductance, and respiratory indices resulted in marked differences between active and sham groups, indicating a blunted sympathetic response with tcVNS [48][49][277,294]. We later used this blunted physiological reactivity pattern to devise a machine learning based method that could indicate stimulation presence [45][46][278,279]. Brain imaging using High-Resolution Positron Emission Tomography (HR-PET) in traumatized participants without PTSD exposed to personalized traumatic scripts showed that tcVNS compared to sham stimulation blocked activations in the medial prefrontal cortex, parahippocampal gyrus, and insula, brain areas that play key roles in emotion and response to stress [50][295].
We also studied the effects of tcVNS on inflammatory markers in traumatized individuals with and without PTSD. We found that tcVNS paired with personalized traumatic scripts blocked stress-induced increases in proinflammatory biomarkers IL-6 and IFN-γ, and showed a pattern of decreased anger responses to scripts [51][87]. Increases in IL-6 and IFN-γ likely occur multiple times a day with minor stressors and triggers in PTSD patients, so tcVNS could result in a decrease in symptoms driven by inflammation and lead to improvements in clinical course. The reduction in subjective anger, in addition to improved mental health, also likely have beneficial health effects, for instance, in patients with comorbid PTSD and coronary artery disease (CAD), where we found not only an increase in mental stress-induced IL-6 in those with comorbid PTSD [52][63], but also that anger, PTSD, and other symptoms of psychological distress were associated with long-term adverse cardiovascular outcomes [53][296] and an increase in mental stress-induced myocardial ischemia [54][55][297,298].
Studies are ongoing with patients with PTSD, paired with assessment of the brain with High Resolution Positron Emission Tomography (HR-PET), and assessment of inflammatory and other blood biomarkers [56][278]. Due to low cost, increased convenience, limited side effects, feasibility for use at home or in the field for military medicine applications, and the ability to assess efficacy with true sham control comparison, tcVNS and taVNS show great promise in our opinion for the treatment of patients with stress-related psychiatric disorders and enhancement of human performance [32][261].
3. Conclusions
Current treatments for PTSD, major depression, and other stress-related psychiatric disorders, including medications and psychotherapy, have limitations and are not efficacious for all patients. Neuromodulation is an important alternative treatment, and noninvasive forms of VNS have the advantages of cost and noninvasiveness and can potentially be widely implemented for these patients. Both tcVNS and taVNS show promise for intervening at the level of the underlying neurobiology of these disorders.
PTSD is triggered by experiencing or witnessing exposure to traumatic events and leads to uncontrollable thoughts about the events. Our results from traumatized subjects without PTSD demonstrate decreased sympathetic and increased parasympathetic tone during tcVNS following acute traumatic stress, suggesting possible translation of this treatment to patients with PTSD, in the clinic or at home, as an acute treatment for these recurrent memories [44][45][46][57][277,278,279,299]. tcVNS has potential promise for enhancing recovery from acute traumatic stress by means of modulation of autonomic response in PTSD populations. As patients with PTSD show exaggerated responsivity to reminders of traumatic memories, the physiological changes induced by tcVNS observed in traumatized individuals without PTSD may be similarly observed in PTSD populations. Moreover, recent studies have shown that invasive VNS enhances the extinction of conditioned fear in rats [58][137]. Additionally, taVNS was shown to lead to improvement in vagal tone in patients with PTSD [38][288] and to inhibit long-term fear responses during extinction training in healthy human subjects [59][300]. Implanted VNS has already been approved by the FDA as a treatment for treatment resistant depression and epilepsy, but its cost and the intrusive nature of the surgery have limited its use. Noninvasive VNS technologies would be a significant addition to both facilitate further research into the circuitry of PTSD and treatment resistant depression, and would provide a new and highly acceptable treatment option for patients suffering from both severe and recurrent depression and PTSD [60][32][134,261].
