Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Gordon Tin Chun Wong and Version 3 by Lindsay Dong.
The functions of the complement system to both innate and adaptive immunity through opsonization, cell lysis, and inflammatory activities are well known. In contrast, the role of complement in the central nervous system (CNS) which extends beyond immunity, is only beginning to be recognized as important to neurodevelopment and neurodegeneration. In addition to protecting the brain against invasive pathogens, appropriate activation of the complement system is pivotal to the maintenance of normal brain function.
- complement
- astrocytes
- microglia
- neurons
- neurodevelopment
- neurodegeneration
- neuroinflammation
1. Introduction
The complement system is foundational to the innate immune response in defending the body against invading pathogens by phagocytosis or by the activation of the adaptive immune system. In the CNS, however, the complement system protects the brain from not only pathogens but other potentially harmful stimuli such as aberrant proteins and cellular debris [1]. Findings from studies presented in this review will show that complement components are produced by both neurons and glial cells. This local production of complement factors may be a developmental advantage as it enables a more rapid response than reliance on peripheral production and diffusion through the blood–brain barrier (BBB). Under normal circumstances, the activation of the complement system in the CNS consists of over 30 complement factors under tight regulation [2]. However, when this well-tuned regulatory machinery malfunctions, aberrant complement factors can exacerbate neurological symptoms of brain conditions and accelerate the development of aging-related or neurodegenerative diseases [3][4][5][3,4,5]. Emerging evidence suggests that higher levels of complement factors are present in developing and degenerating brains and perform novel functions in neurodevelopment and contribute to the pathophysiology of neurodegenerative diseases [3][6][7][8][3,6,7,8]. Therefore, an understanding of endogenous complement production and regulation in the brain can provide insights into aberrant neurodevelopment and the genesis of neurodegeneration (Table 1).
Table 1.
Complement expression in the CNS and their role in neurodevelopment and neurodegeneration.
| Complement Component |
Location | Role(s) in Normal Neurodevelopment | Pathophysiological Involvement in Neurodevelopmental and Neurodegenerative Diseases |
|||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1q | neuron [9][10][11] microglia [2] | neuron [9,10,11] microglia [2] |
Synpatic pruning [9][12] | Synpatic pruning [9,12] | AD: mediates glial activation and promote synapse loss [13][14] | AD: mediates glial activation and promote synapse loss [13,14] | ||||||
| ASD [15], MS [16][17][18], ALS [] | ASD [15], MS [16 | 19 | ,17 | ][ | ,18 | 20], HD | ], ALS [19 | [ | ,20 | 21 | ], HD [21] | |
| C3 | astrocyte [22][23][24][25] microglia [2] neuron [10][11][26] | astrocyte [22,23,24,25] microglia [2] neuron [10,11,26] |
Progenitor proliferation [27], neuronal migration [28], Synaptic pruning [9] |
ASD: mediates microglia synaptic pruning [29][30] | ASD: mediates microglia synaptic pruning [29,30] | |||||||
| AD: mediates microglial synaptic engulfment, direct neuronal toxicity, and Aβ clearance [31][32][33][34]] | AD: mediates microglial synaptic engulfment, direct neuronal toxicity, and Aβ clearance [31,32 | [ | ,33 | 35] | ,34 | [36] | ,35 | [ | ,36 | 37 | ,37] | |
| MS: activates the alternative pathway, mediate microglia and synaptic engulfment [16][17][18][38][39][40] | MS: activates the alternative pathway, mediate microglia and synaptic engulfment [16,17,18,38,39,40] | |||||||||||
| ALS [19][20][41], PD [42][43], HD [21][44] | ALS [19,20,41], PD [42,43], HD [21,44] | |||||||||||
| PNDs: related to increase microglial activation, neuronal loss, and BBB disruption [45] | ||||||||||||
| C4 | neuron [10][11][23][24] | neuron [10,11,23,24] | - | Schizophrenia: each C4 allele increases the risk [46][47] | Schizophrenia: each C4 allele increases the risk [46,47] | |||||||
| ALS [48][49], HD [21] | ALS [48,49], HD [21] | |||||||||||
| C5 | astrocyte [8][50] neuron [10][11][26] | astrocyte [8,50] neuron [10,11,26] |
Progenitor proliferation [51], neuronal migration [52] |
AD: mediates pro-inflammatory responses [53][54][55] | AD: mediates pro-inflammatory responses [53,54,55] | |||||||
| ALS: mediates pro-inflammatory responses [56][57][58] | ALS: mediates pro-inflammatory responses [56 | [ | ,57 | 59 | ,58 | ] | ,59] | |||||
| ASD [29] | ||||||||||||
| MAC, C5-C9 | astrocyte [50] neuron [10][11][26] | astrocyte [50] neuron [10,11,26] |
- | MS [60], ALS [49] | ||||||||
| CR3 | microglia [8][24] | microglia [8,24] | Synaptic pruning [61][62] | Synaptic pruning [61,62] | AD: mediates microglial synaptic engulfment [32][37][63] PD: mediate microglial activation | AD: mediates microglial synaptic engulfment [32 | [ | ,37 | 64 | ,63 | ] | ] PD: mediate microglial activation [64] |
| CR4 | microglia [8][24] | microglia [8,24] | - | - | ||||||||
| C3aR | microglia [8][24] neuron | 24 | [65][66] asotrycte [ | ] neuron [65 | 67] | microglia [8,,66] asotrycte [67] |
Progenitor proliferation [27], neuronal migration [52] |
AD:mediate microglial synaptic engulfment [35][68] | AD:mediate microglial synaptic engulfment [35,68] | |||
| C5aR | microglia [8][24][69] neuron [65] | microglia [8,24 | ] | ,69 | [70] astrocyte [ | ] neuron [65,70 | 71 | ] astrocyte [71] |
Progenitor proliferation [51], neuronal migration [52] |
AD: mediates pro-inflammatory response [53][54] | AD: mediates pro-inflammatory response [53,54] | |
| ALS: recruits immune cells including peripheral cell infiltration [56][57][58][59] | ALS: recruits immune cells including peripheral cell infiltration [56,57,58,59] | |||||||||||
| MS: mediates pro-inflammatory response [60][72] | MS: mediates pro-inflammatory response [60,72] | |||||||||||
| Crry | - | - | AD: anti-C3 inhibition and promotes Aβ plague formation [73] | |||||||||
| MS: anti-C3 inhibition and prevents synapse loss [38] |
||||||||||||
| C1INH | astrocyte [24] neuron [2][24] | astrocyte [24] neuron [2,24] |
Neuronal migration [52] | MS [16] | ||||||||
| MASP1, 2 | - | Neuronal migration [28] | - | |||||||||
| Factor H | astrocyte [24] microglia [74][75] | astrocyte [24] microglia [74,75] |
- | AD [76] | ||||||||
| Factor B | astrocyte [22][24] | astrocyte [22,24] | - | ALS [77] | ||||||||
| Factor I | asotrycte [8] | - | - | |||||||||
| C4BP | astrocyte [8] | - | - | |||||||||
| CD55 | astrocyte [8][66] neuron [2][24] | astrocyte [8,66] neuron [2,24] |
- | ALS [77] | ||||||||
| CD59 | asotrycte [8][66] | asotrycte [8 | ] neuron | ,66 | [2][24 | ] neuron [2,24] |
- | ALS [77] |
MAC: membrane attack complex; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; ALS: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; MS: multiple sclerosis; PD: Parkinson’s disease; HD: Huntington’s disease; PNDs: perioperative neurocognitive disorders.
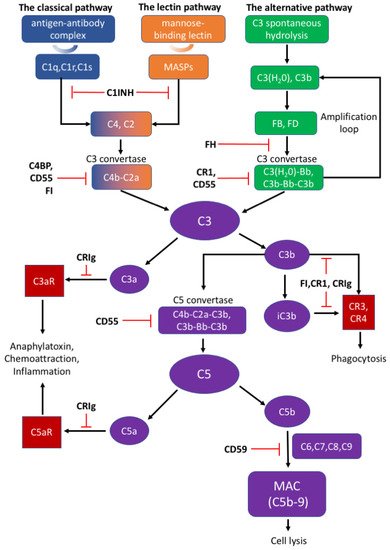 The appropriate activation of the complement cascades rely on a series of tightly regulated soluble and membrane-bound complement inhibitors. Such complement inhibitors have been shown to successfully control complement activation in animal models with CNS disorders [4]. Soluble complement inhibitors include C1 inhibitor (C1INH), complement inhibitor C4b binding protein (C4BP), factor H (FH) and factor I (FI) while complement receptor type 1 (CR1), CRIg, CD55, and CD59 belong to the membrane-bound complement inhibitors [83]. C1INH, also known as SERPING1, inactivates the proteolytic effects of the C1 complex, MASP1, and MASP2, to inhibit the classical and lectin pathways [79][84][79,84]. Deficiency of C1INH can affect normal neurodevelopment, indicating that appropriate complement system function is important to the CNS [1]. C4BP can bind to C4b and act as a decay-accelerating factor [83]. Moreover, FH is the dominant regulatory factor of the alternative pathway and by competitively binding to C3b, it destabilizes C3 and C5 convertase both on cell surfaces and in plasma [79]. FI can permanently inactivate C3b and iC3b and degrade C3 convertase by cleaving the C4b component aside by cofactors such as FH, C1INH, and C4BP [79]. CR1 is a single-pass membrane glycoprotein expressed on different cells and acts as a cofactor to FI in accelerating the dissociation of C3 convertase [79][81][79,81]. Rodents bear only the complement receptor type-1 related protein (Crry) in place of CR1 [85]. Another potent inhibitory factor CRIg converts C3a or C5a into inactive forms, which impairs signal transmission through the C3a or C5a receptors [79]. An inactive C3b product (iC3b) also interacts with CR1 or CRIg for further degradation [78][79][78,79]. CD55 is widely expressed on various cells and inhibits the formation of and accelerates the dissociation of C3 convertases among all three complement pathways [78][83][78,83]. Different from other complement inhibitors, CD59 binds to C5b-8 on the host cell surface and blocks the binding and polymerization of C9 to prevent MAC formation [79].
It is well-known that 90% of soluble serum complement components are derived from the liver constitutively and activated immune cells are an important source of inducible complement protein [81]. However, the CNS may not be exposed to the same composition of complement components as in the periphery due to selective restriction of the BBB [1][2][17][1,2,17]. Recent studies reveal that complement components could be synthesized locally by resident cells in the CNS that provide “immunosurveillance” to maintain normal functionality in the brain [86].
The appropriate activation of the complement cascades rely on a series of tightly regulated soluble and membrane-bound complement inhibitors. Such complement inhibitors have been shown to successfully control complement activation in animal models with CNS disorders [4]. Soluble complement inhibitors include C1 inhibitor (C1INH), complement inhibitor C4b binding protein (C4BP), factor H (FH) and factor I (FI) while complement receptor type 1 (CR1), CRIg, CD55, and CD59 belong to the membrane-bound complement inhibitors [83]. C1INH, also known as SERPING1, inactivates the proteolytic effects of the C1 complex, MASP1, and MASP2, to inhibit the classical and lectin pathways [79][84][79,84]. Deficiency of C1INH can affect normal neurodevelopment, indicating that appropriate complement system function is important to the CNS [1]. C4BP can bind to C4b and act as a decay-accelerating factor [83]. Moreover, FH is the dominant regulatory factor of the alternative pathway and by competitively binding to C3b, it destabilizes C3 and C5 convertase both on cell surfaces and in plasma [79]. FI can permanently inactivate C3b and iC3b and degrade C3 convertase by cleaving the C4b component aside by cofactors such as FH, C1INH, and C4BP [79]. CR1 is a single-pass membrane glycoprotein expressed on different cells and acts as a cofactor to FI in accelerating the dissociation of C3 convertase [79][81][79,81]. Rodents bear only the complement receptor type-1 related protein (Crry) in place of CR1 [85]. Another potent inhibitory factor CRIg converts C3a or C5a into inactive forms, which impairs signal transmission through the C3a or C5a receptors [79]. An inactive C3b product (iC3b) also interacts with CR1 or CRIg for further degradation [78][79][78,79]. CD55 is widely expressed on various cells and inhibits the formation of and accelerates the dissociation of C3 convertases among all three complement pathways [78][83][78,83]. Different from other complement inhibitors, CD59 binds to C5b-8 on the host cell surface and blocks the binding and polymerization of C9 to prevent MAC formation [79].
It is well-known that 90% of soluble serum complement components are derived from the liver constitutively and activated immune cells are an important source of inducible complement protein [81]. However, the CNS may not be exposed to the same composition of complement components as in the periphery due to selective restriction of the BBB [1][2][17][1,2,17]. Recent studies reveal that complement components could be synthesized locally by resident cells in the CNS that provide “immunosurveillance” to maintain normal functionality in the brain [86].
2. Complement Component and Pathways
There are three distinct pathways that activate the complement system: the classical, lectin, and alternative pathways (Figure 1). The classical pathway is initiated by C1q complex formation when C1q recognizes antigen–antibody complex [78]. The lectin pathway is analogous to the classical pathway, which begins from the binding of mannose residues by mannose-binding lectin (MBL). C1q complex and mannose-binding lectin associated proteases (MASPs) cleave C2 and C4 into C2a and C4b, followed by C3 convertase (C4b–C2a) formation [79][80][79,80]. The alternative pathway can be initiated from C3 hydrolysis or from C3b directly. Once factor B binds with C3(H2O) or C3b, it is cleaved by factor D to become C3(H2O)Bb or C3b-Bb as another C3 convertase, which further produces more C3b to amplify the complement cascade [81]. Thus, the alternative pathway accounts for around 80–90% of complement activation [9][10][12][13][9,10,12,13]. C3 convertases cleave C3 into C3a and C3b; C3a can induce downstream activation by binding to C3aR, and C3b binds to CR3 or CR4 to mediate phagocytosis [82]. C3b can further combine with C4b–C2a and C3b-Bb to generate C5 convertases (C4b–C2a–C3b and C3b–Bb–C3b) and activate the terminal pathway which is regarded as the effector pathway of the complement system [6][10][11][13][6,10,11,13]. Similar to C3, C5 convertases cleave C5 into C5a and C5b; C5a is another important chemotactic protein similar to C3a, and C5b assembles with C6–9 to generate the membrane attack complex (MAC) [79][80][79,80].
Figure 1.
The activation and regulation of the complement system.
3. Complement System in the Developing Brain
Neurodevelopment is a complicated process involving various signaling pathways and molecular mechanisms. It has been shown that complement components are upregulated during pre- and post-natal developmental stages of the CNS, while dramatically decreasing in the matured brain. This development-dependent dynamic change is essential for appropriate development, while imbalances in the complement cascades may result in vulnerability to developmental diseases, such as schizophrenia and autism [1][2][6][7][85][1,2,6,7,85].4. The Complement System in Neurodegenerative Diseases
The pattern of complement expression changes throughout life, with high levels appearing in young or aged brains, but dramatically decreases and remains relatively low and stable in healthy adult brains [63]. In addition to the complement system’s function and contribution during neurodevelopment, increased levels of complement components are also observed in neurodegenerative diseases, including AD, multiple sclerosis (MS), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), Parkinson’s disease (PD), Huntington’s disease (HD), and perioperative neurodegenerative disorders (PNDs). Emerging evidence suggests that the activation of complement system plays a critical role in the pathological mechanisms of these neurodegenerative diseases.5. Therapies Targeting the Complement System
Targeting complement activation bears the therapeutic potential to minimize complement-mediated tissue damage that may occur in trauma, autoimmune diseases, neurological diseases, and neurodegenerative diseases. Currently, anti-complement agents are available which mainly inhibit convertase assembly and cleavage, MAC formation, and the C5–C5aR interaction. The clinical trials on neurological diseases mainly focus on the PNS, neuromuscular junction, and muscle. To date, agents targeting C5 provide the most successful therapeutic strategy, with complement treatment in myasthenia gravis (MG) and neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders (NMOSD) being the most developed [85][87][88][85,144,145].Table 2.
Complement Therapies, Current Clinical Development and Preclinical Studies on CNS Disease.
| Therapy | Drug Class | Mechanism | Approved Clinical Trials | Preclinical Study on CNS Disease | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C1q | Anti-C1q antibody (ANX005) | Monoclonal antibody | Bind to C1q, inhibit Classical pathway | none | GBS, AD [89] | GBS, AD [146] | ||||
| C1s | Sutimlimab (BIVV009) | Monoclonal antibody | Bind to C1s | CAD [90][91][92] PNH [93] | CAD [147,148,149] PNH [150] |
None | ||||
| C3 | high-dose IVIg | IgG | Unspecific, form complex with C3b, inhibit C3 convertase | Clinical trials on MG, GBS and others [87][94] | Clinical trials on MG, GBS and others [144 | [88] MCI: | ,145] MCI: [151] |
Stroke: [95][96] AD: [97][98] | Stroke: [152,153] AD: [154,155] |
|
| Compstatin (APL-2 or Pegcetacoplan, AMY-101) |
cyclic peptides | Bind to C3, interfere C3 convertase function and C3 cleavage | PNH: APL-2, Phase III, compared with eculizumab [99] AMD: phase 2 [100] Periodontitis: AMY-101, phase 2 [101] | PNH: APL-2, Phase III, compared with eculizumab [156] AMD: phase 2 [157] Periodontitis: AMY-101, phase 2 [158] |
none | |||||
| C5 | Eculizumab | Monoclonal antibody | Bind to C5, prevent C5 cleavage, inhibit MAC assembly | PNH: FDA-approved treatment; compared with Ravulizumab [102] MG: | PNH: FDA-approved treatment; compared with Ravulizumab [159] MG: | REGAIN, phase3 [103][104] NMOSD: | phase3 [160,161] NMOSD: | PREVENT, phase3 [105][106] GBS: phase 2, compared with IVIg [107] | phase3 [162,163] GBS: phase 2, compared with IVIg [164] |
none |
| Ravulizumab (ALXN1210) |
Monoclonal antibody | Bind to C5, prevent C5 cleavage, inhibit MAC assembly | PNH: FDA-approved Treatment; compared with Eculizumab [102] MG: phase 3 [108] NMOSD: phase 3 [109] | PNH: FDA-approved Treatment; compared with Eculizumab [159] MG: phase 3 [165] NMOSD: phase 3 [166] |
none | |||||
| Tesidolumab | Monoclonal antibody | Neutralization of C5, Inhibit terminal complement activation |
PNH: phase 2 [87] | PNH: phase 2 [144] | none | |||||
| SKY59 | Monoclonal antibody | Long-lasting Neutralization of C5 | PNH: phase1/2 [88] | PNH: phase1/2 [145] | none | |||||
| Zilucoplan | peptide | prevents the cleavage of C5 into C5a and C5b | MG: phase 2 [110] | MG: phase 2 [167] | none | |||||
| Cemdisiran | RNAi | Suppress C5 production | PNH: pharmacological study [111] | PNH: pharmacological study [168] | none | |||||
| C5aR | PMX53 | cyclic hexapeptides | C5aR1 antagonists | none | I/R injury: [112] | I/R injury: [169] | ||||
| PMX205 | cyclic hexapeptides | C5aR1 antagonists | none | AD: [54][69] ALS: [57][113] | AD: [54,69] ALS: [57,170] |
CAD: cold agglutinin disease; PNH: Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria; MG: myasthenia gravis; GBS: Guillain-Barré syndrome; MCI: mild cognitive impairment; AMD: Age-Related Macular Degeneration; NMOSD: neuromyelitis optica spectrum disorders; I/R injury: ischemia/reperfusion injury.
