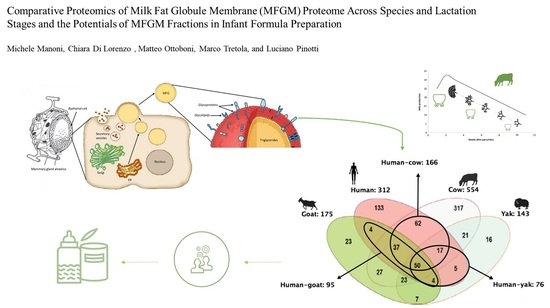
Milk fat globule membrane (MFGM) is an important component of milk lipids that showed several biological properties (such as anticarcinogenic, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anticholesterolemic activities). In this review we analyse the latest results obtained from comparative proteomic studies regarding the variations and the similarities of MFGM proteome across species and lactation stages. Infant formula supplementation with MFGM represents an interesting opportunity to implement the bioactive properties exerted by MFGM, in order to narrow the gap between human breast milk and infant formula.
- milk fat globules
- bovine milk proteins
- milk fat globule membrane
- comparative proteomics
- infant formula preparation
1. Introduction
Bovine milk is an oil-in-water emulsion and is rich in nutrients and bioactive factors
1. Introduction
Bovine milk is an oil-in-water emulsion and is rich in nutrients and bioactive factors
[1]
. Milk fat occurs as milk fat globules (MFGs), composed of a nonpolar triglyceride (TG) core and covered in a layer of surface-active material, called milk fat globule membrane (MFGM)
. It is made up of many different compounds: polar lipids such as phospholipids, sphingolipids and glycolipids, and also cholesterol, proteins, and surface glycoproteins
[6]
. This membrane acts as a natural emulsifier and encases the nonpolar triglyceride core of MFGs
. There are several health-promoting e ects of the MFGM (mainly from bovine but also from other species), such as anticarcinogenic, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anticholesterolemic activities
. The aim of this review is to provide a general overview about the formation of bovine MFGs and MFGM and to highlight the main similarities and di erences across the MFGM proteomes of the most-studied species (human, cow, goat, buffalo, etc.) through the analysis of comparative proteomic studies. Moreover, the potential supplementation of MFGM fractions in infant formula (IF) is investigated in order to underline the beneficial e ects exerted by MFGM bioactive components in infant feeding.
2. Lipids in MFG and MFGM
MFG core is predominantly composed of non-polar lipids, named TGs, accounting for 98% of total milk fat. Saturated fatty acids (FAs) in bovine milk fat account for 70% of the total milk FAs; MCFA (6:0–12:0) represent about 10% of total milk FAs, whereas SCFA (4:0) account for less than 3%. Mono-unsaturated FAs account for 25% of the total milk FAs, whereas Poly-unsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) constitute 2.5% of the total milk FAs
[10]
. Bovine MFGMis composed mainly of polar lipids that account for 0.2–1% of the total milk fat.
3. MFGM proteins
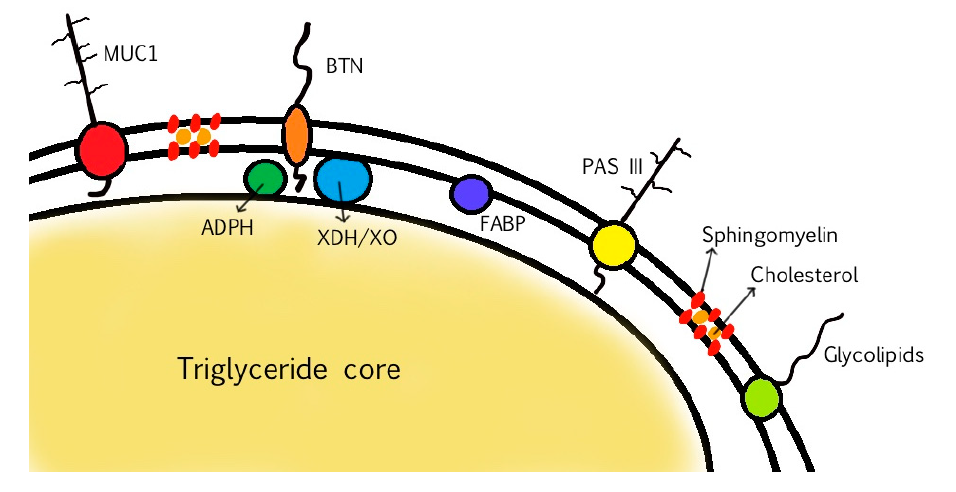
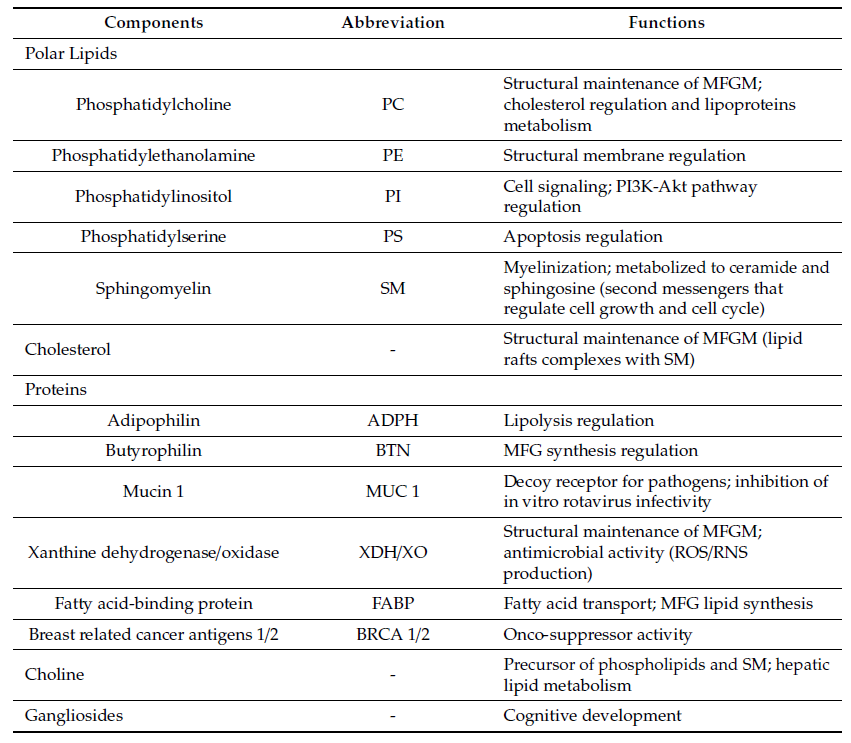
MFGM proteins account for 25–60% of the mass of the MFGM. The main MFGM proteins are adipophilin (ADPH), butyrophilin (BTN), mucin 1 (MUC1), xanthine dehydrogenase/oxidase (XDH/XO), CD36, periodic acid Schiff III (PAS III), PAS 6/7, lactadherin, and fatty acid-binding protein (FABP)
In the following table, the major components of bovine MFGM and their main functions are listed.
4. Comparative proteomics of MFGM proteome
Although most of the beneficial effects of MFGM are associated with its polar lipid fraction
.
In the following table, the major components of bovine MFGM and their main functions are listed.
3. Comparative proteomics of MFGM proteome
Although most of the beneficial effects of MFGM are associated with its polar lipid fraction
[5]
, studies on MFGM proteome are increasing since MFGM proteins show bioactive properties and new technologies have enabled more detailed analyses of the MFGM proteome. Comparative proteomic analyses have been performed to understand how proteomes vary between different species and between different stages of lactation
[13]
. To summarize, the principal MFGM proteins have been identified in all species. However, the main molecular functions exerted by MFGM proteomes vary according to species and lactation stage due to the variations in protein expression. For example, the human MFGM proteome (in particular that contained in colostrum) has more immune response-related proteins than the MFGM proteome from other species. There are similarities between human and cow MFGM proteome and molecular functions, suggesting that bovine milk, and more specifically bovine MFGM proteins, could be used as a supplement in infant formulas (IFs)
5. MFGM: Potentials in Infant Formula Preparation
Breast milk is considered the gold standard for infant nutrition and is required for optimal infant growth, brain and GI tract development, as well as establishing the immune system. Some of the bioactive factors of breast milk are present in the MFGM. In order to develop products that reflect the complexity of human milk, efforts have been made to imitate the nutritional profile and composition of human breast milk. IF has been designed in order to be a suitable alternative to human breast milk
.
4. MFGM: Potentials in Infant Formula Preparation
Breast milk is considered the gold standard for infant nutrition and is required for optimal infant growth, brain and GI tract development, as well as establishing the immune system. Some of the bioactive factors of breast milk are present in the MFGM. In order to develop products that reflect the complexity of human milk, efforts have been made to imitate the nutritional profile and composition of human breast milk. IF has been designed in order to be a suitable alternative to human breast milk
. Bovine milk is currently the basis for most IFs. In addition to nutrients, human breast milk also contains several bioactive compounds (Igs, enzymes, hormones) and live cells (e.g., leucocytes) that cannot be easily added to IFs
. All these elements prevent IFs from having the same composition as human breast milk, although the research in this field has advanced considerably. In fact, several studies
have suggested that supplementing IFs with MFGM could provide beneficial e ects because of the presence of bioactive compounds such as proteins and polar lipids in the MFGM, thus narrowing the gap between human breast milk and IFs. Many of these results were obtained through the supplementation of IF with the polar lipid fraction of the MFGM (phospholipids and sphingolipids), given that these compounds are the main contributors to the nutraceutical effects of the MFGM
[5]
. Few studies have investigated supplementing IF with MFGM proteins
[15]
. Timby and collaborators
[14]
evaluated the effect of a low-energy and low-protein formula supplemented with a protein-rich bovine MFGM fraction on healthy infants. Their results showed that the cognitive score (assessed with Bayley-III tests) was 4.0 points higher in the experimental formula group than in the standard formula group (105.8 vs. 101.8; p < 0.05), but was similar to the breastfed group (105.8 vs. 106.4; p > 0.05). This suggested that the experimental formula could decrease the gap in cognitive performance between breastfed and formula-fed infants
[14].
6. Conclusions
Milk has important nutritional features for newborns. Indeed, breast milk is a mixture of several bioactive compounds that modulate the GI tract and contribute to building the immune system of breast-fed infants. The growing interest in MFGM led researchers to study the MFGM proteins from a wider approach through proteomics. There are variations in terms of protein expression level and molecular function across species, even though the major MFGM proteins are observed among all the species considered. The properties of the MFGM proteome of each species could be exploited to design products supplemented with MFGM fractions that meet specific needs, for example, the enhancement of the immune system, the regulation of cholesterol metabolism, or the supply of beneficial polar lipids to support cognitive function. The promising results obtained with the supplementation of IF with MFGM proteins
.
5. Conclusions
Milk has important nutritional features for newborns. Indeed, breast milk is a mixture of several bioactive compounds that modulate the GI tract and contribute to building the immune system of breast-fed infants. The growing interest in MFGM led researchers to study the MFGM proteins from a wider approach through proteomics. There are variations in terms of protein expression level and molecular function across species, even though the major MFGM proteins are observed among all the species considered. The properties of the MFGM proteome of each species could be exploited to design products supplemented with MFGM fractions that meet specific needs, for example, the enhancement of the immune system, the regulation of cholesterol metabolism, or the supply of beneficial polar lipids to support cognitive function. The promising results obtained with the supplementation of IF with MFGM proteins
and polar lipids
[21] underline once again the importance of MFGM in IF preparation—since cow milk-based IF is formulated to better resemble human breast milk, the MFGM supplementation could increase the presence of bioactive compounds in IF (usually at low levels in standard formula). Future work is likely to be addressed towards a deeper comprehension of MFGM proteome and its variations across species and lactation stages. The overall aim is to further increase the knowledge of MFGM properties and to assess the potential of the supplementation of IFs with MFGM proteins.
underline once again the importance of MFGM in IF preparation—since cow milk-based IF is formulated to better resemble human breast milk, the MFGM supplementation could increase the presence of bioactive compounds in IF (usually at low levels in standard formula). Future work is likely to be addressed towards a deeper comprehension of MFGM proteome and its variations across species and lactation stages. The overall aim is to further increase the knowledge of MFGM properties and to assess the potential of the supplementation of IFs with MFGM proteins.
References
- Bernard, L.; Bonnet, M.; Delavaud, C.; Delosiere, M.; Ferlay, A.; Fougere, H.; Graulet, B. Milk Fat Globule in Ruminant: Major and Minor Compounds, Nutritional Regulation and Di erences Among Species. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Tech. 2018, 120, 1700039.
- Arranz, E.; Corredig, M. Invited review: Milk phospholipid vesicles, their colloidal properties, and potential as delivery vehicles for bioactive molecules. J. Dairy Sci. 2017, 100, 4213–4222.
- Evers, J.M. The milkfat globule membrane—Compositional and structural changes post secretion by the mammary secretory cell. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 661–674.
- Evers, J.M. The milkfat globule membrane—Methodologies for measuring milkfat globule (membrane) damage. Int. Dairy J. 2004, 14, 747–760.
- Spitsberg, V.L. Invited review: Bovine milk fat globule membrane as a potential nutraceutical. J. Dairy Sci. 2005, 88, 2289–2294.
- Danthine, S.; Blecker, C.; Paquot, M.; Innocente, N.; Deroanne, C. Évolution des connaissances sur la membrane du globule gras du lait: Synthèse bibliographique. Lait 2000, 80, 209–222.
- Pinotti, L.; Baldi, A.; Dell’Orto, V. Comparative mammalian choline metabolism with emphasis on the high-yielding dairy cow. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2002, 15, 315–331.
- Pinotti, L.; Baldi, A.; Politis, I.; Rebucci, R.; Sangalli, L.; Dell’Orto, V. Rumen-protected choline administration to transition cows: E ects on milk production and vitamin E status. J. Vet. Med. A 2003, 50, 18–21.
- Dewettinck, K.; Rombaut, R.; Thienpont, N.; Le, T.T.; Messens, K.; Van Camp, J. Nutritional and technological aspects of milk fat globule membrane material. Int. Dairy J. 2008, 18, 436–457.
- Månsson, H.L. Fatty Acids in Bovine Milk Fat. Food Nutr. Res. 2008, 52, 1–3.
- Mather, I.H. A review and proposed nomenclature for major proteins of the milk-fat globule membrane.J. Dairy Sci. 2000, 83, 203–247.
- Brink, L.R.; Herren, A.W.; McMillen, S.; Fraser, K.; Agnew, M.; Roy, N.; Lönnerdal, B. Omics analysis reveals variations among commercial sources of bovinemilk fat globule membrane. J. Dairy Sci. 2020, 103, 3002–3016.
- Cavaletto, M.; Giu rida, M.G.; Conti, A. The proteomic approach to analysis of human milk fat globule membrane. Clin. Chim. Acta. 2004, 347, 41–48.
- Timby, N.; Domellöf, E.; Hernell, O.; Lönnerdal, B.; Domellöf, M. Neurodevelopment, nutrition, and growth until 12 mo of age in infants fed a low-energy, low-protein formula supplemented with bovine milk fat globule membranes: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 860–868.
- Demmelmair, H.; Prell, C.; Timby, N.; Lönnerdal, B. Benefits of Lactoferrin, Osteopontin and Milk Fat Globule Membranes for Infants. Nutrients 2017, 9, 817.
- Hernell, O.; Timby, N.; Domellöf, M.; Lönnerdal, B. Clinical benefits of milk fat globule membranes for infants and children. J. Pediatr. 2016, 173, S60–S65.
- Institute of Medicine (IOM) of the National Academics. Infant Formula Evaluating the Safety of New Ingredients; The National Academics Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2004.
- Corkins, K.G.; Shurley, T. What’s in the Bottle? A Review of Infant Formulas. Nutr. Clin. Pr. 2016, 31, 723–729.
- Li, W.; Li, B.; Lv, J.; Dong, L.; Zhang, L.; Wang, T. Choline supplementation improves the lipid metabolism of intrauterine-growth-restricted pigs. Asian Australas. J. Anim. Sci. 2018, 31, 686–695.
- Gallier, S.; Vocking, K.; Post, J.A.; Van De Heijning, B.; Acton, D.; van der Beek, E.M.; Van Baalen, T. A novel infant milk formula concept: Mimicking the human milk fat globule structure. Colloid Surf. B 2015, 136, 329–339.
- Gurnida, D.A.; Rowan, A.M.; Idjradinata, P.; Muchtadi, D.; Sekarwana, N. Association of complex lipids containing gangliosides with cognitive development of 6-month-old infants. Early Hum. Dev. 2012, 88, 595–601.
- Pinotti, L.; Campagnoli, A.; Dell’Orto, V.; Baldi, A. Choline: Is there a need in lactating dairy cow? Livest. Prod. Sci. 2005, 98, 149–152.
References
- Laurence Bernard; Muriel Bonnet; Carole Delavaud; Mylène Delosière; Anne Ferlay; Hélène Fougère; Benoît Graulet; Milk Fat Globule in Ruminant: Major and Minor Compounds, Nutritional Regulation and Differences Among Species. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology 2018, 120, 1700039, 10.1002/ejlt.201700039.
- E. Arranz; M. Corredig; Invited review: Milk phospholipid vesicles, their colloidal properties, and potential as delivery vehicles for bioactive molecules. Journal of Dairy Science 2017, 100, 4213-4222, 10.3168/jds.2016-12236.
- Jaap M Evers; The milkfat globule membrane—compositional and structural changes post secretion by the mammary secretory cell. International Dairy Journal 2004, 14, 661-674, 10.1016/j.idairyj.2004.01.005.
- Jaap M. Evers; The milkfat globule membrane—methodologies for measuring milkfat globule (membrane) damage. International Dairy Journal 2004, 14, 747-760, 10.1016/j.idairyj.2004.01.006.
- V.L. Spitsberg; Invited Review: Bovine Milk Fat Globule Membrane as a Potential Nutraceutical. Journal of Dairy Science 2005, 88, 2289-2294, 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(05)72906-4.
- Sabine Braipson-Danthine; C. Blecker; Michel Paquot; Nadia Innocente; Claude Deroanne; �volution des connaissances sur la membrane du globule gras du lait : synth�se bibliographique. Le Lait 2000, 80, 209-222, 10.1051/lait:2000120.
- Luciano Pinotti; Antonella Baldi; V Dell'orto; Comparative mammalian choline metabolism with emphasis on the high-yielding dairy cow. Nutrition Research Reviews 2002, 15, 315-332, 10.1079/nrr200247.
- Luciano Pinotti; Antonella Baldi; I. Politis; R. Rebucci; L. Sangalli; V. Dell'orto; Rumen-Protected Choline Administration to Transition Cows: Effects on Milk Production and Vitamin E Status. Journal of Veterinary Medicine Series A 2003, 50, 18-21, 10.1046/j.1439-0442.2003.00502.x.
- Koen Dewettinck; Roeland Rombaut; Natacha Thienpont; Thien Trung Le; Kathy Messens; John Van Camp; Nutritional and technological aspects of milk fat globule membrane material. International Dairy Journal 2008, 18, 436-457, 10.1016/j.idairyj.2007.10.014.
- Helena Lindmark-Månsson; Fatty acids in bovine milk fat. Food & Nutrition Research 2008, 52, 1821, 10.3402/fnr.v52i0.1821.
- Ian H. Mather; A Review and Proposed Nomenclature for Major Proteins of the Milk-Fat Globule Membrane,. Journal of Dairy Science 2000, 83, 203-247, 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(00)74870-3.
- Lauren Brink; Anthony W. Herren; Shasta McMillen; Karl Fraser; Michael Agnew; Nicole C. Roy; Bo Lönnerdal; Omics analysis reveals variations among commercial sources of bovine milk fat globule membrane. Journal of Dairy Science 2020, 103, 3002-3016, 10.3168/jds.2019-17179.
- Maria Cavaletto; Maria Gabriella Giuffrida; Amedeo Conti; The proteomic approach to analysis of human milk fat globule membrane. Clinica Chimica Acta 2004, 347, 41-48, 10.1016/j.cccn.2004.04.026.
- Niklas Timby; Erik Domellöf; Olle Hernell; B. Lönnerdal; Magnus Domellöf; Neurodevelopment, nutrition, and growth until 12 mo of age in infants fed a low-energy, low-protein formula supplemented with bovine milk fat globule membranes: a randomized controlled trial. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 2014, 99, 860-868, 10.3945/ajcn.113.064295.
- Hans Demmelmair; Christine Prell; Niklas Timby; Bo Lönnerdal; Benefits of Lactoferrin, Osteopontin and Milk Fat Globule Membranes for Infants. Nutrients 2017, 9, 817, 10.3390/nu9080817.
- Olle Hernell; Niklas Timby; Magnus Domellöf; Bo Lönnerdal; Clinical Benefits of Milk Fat Globule Membranes for Infants and Children. The Journal of Pediatrics 2016, 173, S60-S65, 10.1016/j.jpeds.2016.02.077.
- Institute of Medicine; Infant Formula. Infant Formula 2004, 1, 220, 10.17226/10935.
- Kelly Green Corkins; Teresa Shurley; What’s in the Bottle? A Review of Infant Formulas. Nutrition in Clinical Practice 2016, 31, 723-729, 10.1177/0884533616669362.
- Wei Li; Bo Li; Jiaqi Lv; Li Dong; Lili Zhang; T. Wang; Choline supplementation improves the lipid metabolism of intrauterine-growth-restricted pigs. Asian-Australasian Journal of Animal Sciences 2016, 31, 686-695, 10.5713/ajas.15.0810.
- Sophie Gallier; Karin Vocking; Jan Andries Post; Bert Van De Heijning; Dennis Acton; Eline M. Van Der Beek; Ton Van Baalen; A novel infant milk formula concept: Mimicking the human milk fat globule structure. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 2015, 136, 329-339, 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.09.024.
- Dida A. Gurnida; Angela M. Rowan; Ponpon Idjradinata; Deddy Muchtadi; Nanan Sekarwana; Association of complex lipids containing gangliosides with cognitive development of 6-month-old infants. Early Human Development 2012, 88, 595-601, 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2012.01.003.
- Luciano Pinotti; A. Campagnoli; V. Dell'orto; Antonella Baldi; Choline: Is there a need in the lactating dairy cow?. Livestock Production Science 2005, 98, 149-152, 10.1016/j.livprodsci.2005.10.013.