Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Tariq Pervaiz and Version 2 by Jessie Wu.
The miRNAs and cDNA-microarrays are powerful tools to enhance abiotic stress tolerance in plants through multiple advanced sequencing and bioinformatics techniques, including miRNA-regulated network, miRNA target prediction, miRNA identification, expression profile, features (disease or stress, biomarkers) association, tools based on machine learning algorithms, NGS, and tools specific for plants. Such technologies were established to identify miRNA and their target gene network prediction, emphasizing current achievements, impediments, and future perspectives.
- salinity stress
- cold stress
- miRNAs
1. miRNAs and cDNA-Microarray Associated with Cold Stress
Cold stress (frost and chilling) decreases crop yields worldwide through tissue degradation and delayed growth. Most temperate plants have evolved cold resistance through cold-acclimatization [1][112]. Signaling pathways were being used in response to winter stress. The functional genes transform reactions, and reposts suggest that the signaling pathways for leaf senescence and plant defense responses may overlap [2][113]. The most characteristic region of cold-stress responsive genes includes transcription factors, such as CBF/DREB and stress-inducible candidate genes, identified as KIN (cold-induced), COR (cold-regulated), and LTI genes (induced by low temperature) or RD (dehydration) [3][114]. Several HSPs (heat shock proteins) are also reported for their functions against cold stress. HSPs, which perform as molecular chaperons, play an important regulatory function in protecting from stress by restoring normal protein conformation and thus maintaining cellular homeostasis in plants [4][115]. The number of the miRNA target genes in expression is intricate during stress and plant growth. These miRNAs are co-regulated by both developmental signals and ecological factors (Table 3). The cold-responsive miRNAs were detected by microarray analysis in Arabidopsis thaliana (miR165, miR31, miR156, miR168, miR171, miR396) and recommended by identifying their expression patterns in their promoter sequences and evaluating the cis-components (Table 3, Figure 1) [5][6][116,117]. Furthermore, high-intensity light (HL) responsive genes were assessed with the drought-inducible genes reported with a similar microarray system, which exposed an impenetrable intersection between drought and HL-induced genes. Moreover, 10 genes were identified as being involved in the regulation by HL, drought, salinity, and cold stress (Table 1 and Table 2). These genes are comprised of ERD10, RD29A, KIN1, LEA14, COR15a, and ERD7, and most of them are considered to be concerned in the defense of cellular components [7][8][9][78,118,119]. Along with the HL-inducible genes, some are also identified and encouraged by other stresses (heat, drought, and cold), including AtGolS, LEA, RAB, RD, COR, ERD, HSP, KIN, lipid-transfer proteins, and fibrillins [10][11][12][76,120,121].
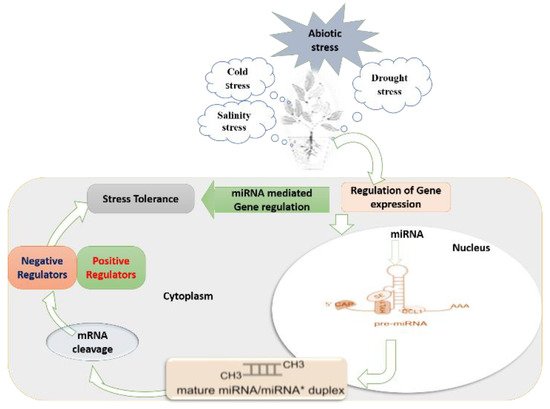
Figure 1. Schematic summary of miRNA-mediated regulatory mechanisms under abiotic stress in plant cells, with the particular formation process of miRNAs and miRNA mediated gene regulation: (1) miRNA gene is transcribed to a long sequence of primary miRNA (pri-miRNA). Primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs) are transcribed from nuclear-encoded MIR genes by RNA polymerase II (Pol II), leading to precursor transcripts with a characteristic hairpin structure. (2) The pri-miRNA is cleaved to a stem-loop intermediate called miRNA precursor or pre-miRNA.
Table 1. Examples of miRNAs identified in model plants under drought, cold and salinity stresses.
| Stress Condition |
|---|
| Stress Condition | Plant Species | Inducible Genes | Known Responsive miRNAs | Functions | Plant Species | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| miRNA | ||||||||
| Drought stress | Arabidopsis thaliana | Rd29A (At5g52310) | CCAAT-binding | transcription factors | miR164, miR169, miR389, miR393, miR396, miR397, miR402 |
Pathogen immune response Drought tolerance Oxidative stress tolerance Pathogen immunity response Syncytium formation response to parasitic nematodes |
[13][14][ | |
| miR156, miR158, miR159, miR397, miR398, miR482.2, miR530a, miR1445 | ||||||||
| Drought tolerance | ||||||||
| Pathogen immune response | ||||||||
| [ | ||||||||
| 15 | ] | [ | 18 | ] |
Table 2. Microarray analysis of genes involved in the drought, salinity and cold stress responses in Arabidopsis.
| Phenotype of Mutants | Genes | Function | AGI Code | Coded Proteins | Microarrays | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Key Functions | Response | References | ||||||||||||||||||||||
| Salt/drought/cold/oxidative | osmotic-stress responses | 15 | ] | [16 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Increased tolerance to drought |
AtPARP2 | ] | DNA repair | At2g31320 | [ | Poly (ADPribose) polymerase16,17,18,19] | ||||||||||||||||||
| Phosphate-deficiency response | 24K | Affymetrix | [ | 30 | ] | Up-regulated | [20][44][45][46][47][31][32] | [32,33,34] | Medicago truncatula | CCAAT Binding Factor (CBF) | Growth Regulating Factor (GRF) | |||||||||||||
| miR398b,c miR2111u,v miR5274b miR1510a-3p, 5p miR1510aCu/Zn superoxide dismutases (CSD1, CSD2) | TIR-NBS-LRR domain protein | miR169, miR396 miR398, miR2118 |
Drought tolerance Syncytium formation response to parasitic nematodes Oxidative stress tolerance Photoperiod-sensitive male sterility |
[13 | Drought tolerance Heat stress tolerance |
|||||||||||||||||||
| Hypersensitive to drought stress |
AHK1/ | ATHK1 | ][17] | [16,20] | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Heat stress tolerance | positive regulator of drought and salt stress responses | At2g17820 | Histidine kinase | Drought responsive Oxidative-stress tolerance triggering phasiRNA production from numerous NB-LRRs |
Down-regulated | [44][46 | 22K Agilent | ][30][33][34] | [32,35,36] | [47 | Oryza sativa | SalT (LOC_Os01g24710) | TIR1 | OsLEA3 (LOC_Os05g46480) |
miR393 miR402 |
Salt/cold tolerance | [18][[19] | [6 | 14][15] | ,17,18,21] | ||||
| ] | 22K Agilent | [ | 31 | ] | [ | 35][36] | [33,37,38] | Cold stress | [13 | |||||||||||||||
| Increased tolerance to salt stress |
AtbZIP60 | ] | encodes a predicted protein of 295 aa | At1g42990 | [ | bZIP TF | 14] | [16,17] | ||||||||||||||||
| 44K Agilent | [ | 35 | ] | [ | 37 | ] | [37,39] | Oryza Sativa | OsWRKY71 | (LOC_Os02g08440) | ||||||||||||||
| Increased tolerance to drought stress | OsMAPK2 | (LOC_Os03g17700) |
AtMYB60 | regulates stomatal movements and plant drought tolerance | At1g08810 | MYB TF | 7K cDNA | |||||||||||||||||
| Drought stress | Medicago truncatula | miR398a,b miR408 miR399k miR2089 miR2111a-f,h-s miR2111g miR4414a |
Oxidative stress tolerance |
|||||||||||||||||||||
| Glycine max | miR5554a-c | Drought responsive | [46] | |||||||||||||||||||||
| Salinity stress | Glycine max | miR169d miR395a miR395b,c miR1510a-5p miR1520d,e,l,n,q |
Drought tolerance Sulfate-deficiency response triggering phasiRNA production from numerous NB-LRRs |
Up-regulated | [20][48][49] | Os05g47550, Os03g42280 Os01g73250, Os12g16350 Os03g19380 |
miR319 | , | miR389 | , | miR393 | , miR1320, miR1435 miR1884b, CHY1 CP12-2 |
Drought/salt tolerance Cold tolerance | |||||||||||
| Heat stress tolerance | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
| [ | 20 | ] | ] | [22 | ||||||||||||||||||||
| Increased tolerance to drought stress |
AREB1/ | ABF2 | regulate the ABRE-dependent expression | At1g45249 | bZIP TF | Arabidopsis thaliana | Rd29A | (At5g52310) | CBF3 | (At4g25480) | miR165 | , | miR172 | , | miR169 | , | miR396 | , | miR397 | , | miR402 | Drought/cold tolerance Pathogen immunity response |
[ |
Using cDNA microarray in Synechocystis, 19 genes were reported to be instantaneously regulated under salinity stress. The salt- and osmo-regulated genes, and some putative sensor molecules, have been implicated during salinity stress signaling [33][35]. Several differentially regulated miRNAs have been reported against salinity stress. In A. thaliana, several microRNAs are regulated against salinity stress, such as miR156, miR158, miR159, miR165, miR167, miR168, miR169, miR171, miR319, miR393, miR394, miR396, and miR397 (Table 3, Figure 2) [70][84]. In Populus trichocarpa, miR1445, miR1447, miR1446a-e, miR530a, and miR171l-n were down-regulated (Table 3) [71][141]. Arenas-Huertero et al. [29][31] reported, in Proteus vulgaris, the production of miRS1 and miR159.2 expression in response to salinity. Furthermore, miR169g and family members of miR169n were induced in saline-rich conditions [72][142]. However, there is a need to discover and annotate novel functional genes which have a probable function against salinity stress. Subsequently, a large number of genes in plants still have unknown functions [73][143]. Recent studies revealed that specific down-regulation of the bacterial-type phosphoenolpyruvate carboxylase (PEPC) gene Atppc4 by artificial microRNA enhanced the salinity tolerance in A. thaliana. The increased salinity tolerance might be linked to enhanced PEPC activity [74][75][10,144]. Transcript control for salinity-tolerant rice with microarrays, like 1728 cDNAs from salinity-stressed roots libraries, was studied in response to high salinity (Table 3) [75][76][77][144,145,146].
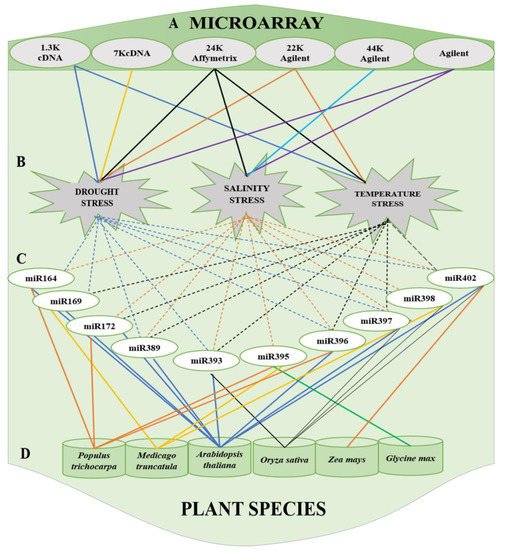
Figure 2. Summary of commonly used (A) microarrays (cDNA, Affymetrix, and Agilent) to stress and (B) miRNAs, categorized based on the stress, that respond to drought stress, salinity and temperature stress and (C) miRNAs reported in (D) plant species: Populus trichocarpa, Medicago truncatula, Arabidopsis thaliana, Oryza sativa, Zea mays and Glycine max.
Table 3. miRNAs regulated by drought stress, salinity stress, and cold stress in plants.
| Stress Condition | Plant Species | miRNA | Key Functions | Response | References | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Drought stress | Medicago truncatula | miR398a,b miR408 miR399k miR2089 miR2111a-f,h-s miR2111g miR4414a |
Oxidative stress tolerance Salt/drought/cold/oxidative osmotic-stress responses Phosphate-deficiency response |
Up-regulated | [ | ||
| 14 | |||||||
| ] | |||||||
| [ | [ | 21 | ] | [ | 38 | ] | [40] |
| Pathogen immune response Drought/Salt tolerance |
Down-regulated | [82] | |||||
| Phaseolus vulgaris | pvu-miR159.2 | Plant–nematode interaction | [31] | ||||
| Cold stress | Phaseolus vulgaris | pvu-miR2118 | regulate the expression of genes encoding the TIR-NBS-LRR resistance protein | Up-regulated |
A tiling path microarray was used to examine the high-throughput expression profiling patterns under various environmental stresses for all of the known miRNAs [13][60][16,70] (Table 1 and Table 4). The analysis revealed that the effects of miRNAs under low-temperature, drought, and high salinity with miRNA chips represent, approximately, all of the reported miRNAs cloned or recognized in A. thaliana (L.). High salinity stress agitates homeostasis in water potential. Extreme changes in water homeostasis and ions lead to molecular breakdown, stunted growth, and even the death of cells or whole plants [13][44][16,147].
Table 4. Software and tools used for the detection of plant miRNA and cDNA microarray data analysis.
| Software and Tools | Function | Website | Reference | Accessed | ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | , | 77 | , | |||||||||||||||||
| Software and tools used for detection of plant miRNA and data analysis | 78 | , | 79 | ,80] | ||||||||||||||||
| miR398b,c miR2111u,v miR5274b miR1510a-3p, 5p miR1510a |
Heat stress tolerance Drought responsive Oxidative-stress tolerance triggering phasiRNA production from numerous NB-LRRs |
Down-regulated | [77,79,80] | |||||||||||||||||
| MiPred | Random forest (RF)-based miRNA predictor, which can distinguish between real and pseudo-miRNA precursors | http://server.malab.cn/MiPred/ | [45] | [72] | 5 November 2021 | Glycine max | miR5554a-c | Drought responsive | [79] | |||||||||||
| Salinity stress | ||||||||||||||||||||
| miBridge | Algorithm and database | http://sitemaker.umich.edu/mibridge/home | [46] | [148] | 5 November 2021 | Glycine max | miR169d miR395a miR395b,c miR1510a-5p miR1520d,e,l,n,q |
Drought tolerance Sulfate-deficiency response triggering phasiRNA production from numerous NB-LRRs |
Up-regulated | [20 | ||||||||||
| miRTar | A novel rule-based model learning method for cell line specific microRNA target prediction | http://miRTar.mbc.nctu.edu.tw | [45] | [72 | ,81,82] | gma-miR159b,c | ||||||||||||||
| ] | 5 November 2021 | gma-miR169b,c gma-miR1520c |
gma-miR159b,c gma-miR169b,c gma-miR1520c | Pathogen immune response | ||||||||||||||||
| PolymiRTS | Drought/Salt tolerance | Linking polymorphisms in microRNAs and their target sites | http://compbio.uthsc.edu/miRSNP | [47] | [149][17 | 19][20] | Down-regulated | ,21,22,23] | ||||||||||||
| [ | 49 | ] | 25 November 2021 | Salinity stress | Increased sensitivity to drought stress | Arabidopsis thaliana | Rd29A | (At5g52310) | COR15A | (At2g42540) | AtMYB41miR389 | , | miR393 | , | Oxidative stress tolerance Heat stress tolerance |
[22] | control of primary metabolism and negative regulation[24] | |||
| At4g28110 | MYB TF | 24K | Affymetrix | [ | 39][40] | |||||||||||||||
| Phaseolus vulgaris | [ | 41 | pvu-miR159.2 | ,42] | ||||||||||||||||
| Plant–nematode interaction | [ | |||||||||||||||||||
| miRGator | 31 | ] | microRNA portal for deep sequencing, expression profiling and mRNA targeting | http://mirgator.kobic.re.kr | [48] | [150] | 10 November 2021 | Populus trichocarpa | Dihydropyrimidinase | miR162, miR164, miR166, miR167, miR168, miR172, miR395, miR396 | Pathogen immune response Drought tolerance Drought/cold tolerance Sulfate-deficiency response |
[23 | Increased tolerance to drought and salt stress | ][24][25 | AHK2] | positive regulators for cytokinin signaling[ | At5g3575025,26,27] | |||
| Histidine kinase | Agilent | [ | 33 | ] | [ | |||||||||||||||
| Cold stress | 34 | ] | [ | 35 | ,36] | Glycine max | ||||||||||||||
| Phaseolus vulgaris | pvu-miR2118 | regulate the expression of genes encoding the TIR-NBS-LRR resistance protein | Up-regulated | |||||||||||||||||
| Bowtie | Aligns efficiently, and short-read aligners | http://bowtie-bio.sourceforge.net | [45] | [72] | 5 November 2021 | Increased tolerance tomiR1507a, miR395 | Sulfate-deficiency response |
drought and salt | ||||||||||||
| miRBase | Provides handy and useful ID conversion tools | http://www.mirbase.org/ | [45 | [26] | [28] | |||||||||||||||
| stress | AHK3 | perception of cytokinin, downstream signal transduction | At1g27320 | ] | Histidine kinase | 22K Agilent | [72] | [33 | 25 November 2021 | ][34] | [35,36] | Oryza sativa | Increased tolerance to drought and freezing stress | SalT | (LOC_Os01g24710) | OsLEA3 | (LOC_Os05g46480) | [27] | DREB1A/ | |
| miRDB | CBF3 | miRNA target databases | http://www.mirdb.org | [49] | [151],29 | [28][29 | ,30,31] | |||||||||||||
| stress-inducible transcription factor | ERF/AP2 TF | ERF/AP2 TF | 1.3K cDNA | [ | 41 | ] | [ | 25 November 202143] | Zea mays | |||||||||||
| Increased tolerance to | ||||||||||||||||||||
| mirDIP | miR402 | drought stress | DREB2A | heat shock-stress responses.Seed germination and seedling growth of Arabidopsis under stress | At5g05410 | ERF/AP2 TF | 22K Agilent 7K cDNA |
[42] | [44] | |||||||||||
| Hypersensitive to salt |
HOS10 | coordinating factor for responses to abiotic stress and for growth and development. | At1g35515 | MYB TF | 24K Affymetrix |
[30][43] | [32,45] | |||||||||||||
| Increased tolerance to drought stress |
ZFHD1 | mediates all the protein-protein interactions | At1g69600 | Zinc finger HD TF |
22K Agilent | [34][37] | [36,39] | |||||||||||||
Table 3. miRNAs regulated by drought stress, salinity stress, and cold stress in plants.
DNA microarrays almost in all genes of the unicellular Synechocystis sp PCC6803 were used to investigate the gene expression sequential software [50][122]. A cDNA-microarray was used to test the profile expression in cold stress, and 328 temperature-regulated transcripts were reported. OsMYB3R-2 was studied further and was shown to be a dominant regulator against stress [51][123]. In this study, there was an attempt to use a 3.1K cDNA-microarray to express the cold-regulated transcripts in the Capsicum annuum. Several TFs, including the EREBP (CaEREBP-C1 to C4) family of four genes, a protein of the ring domain, a bZIP protein (CaBZ1), RVA1, a WRKY (CaWRKY1), and HSF1 protein have been observed among the cold stress-regulated genes. These genes included CaBZ1, CaEREBP-C3, NtPRp27, the SAR8.2 protein precursor, putative trans-activator factor, malate hydrogenase, putative protein of auxin-repressed, xyloglu-canendo-1, 4-D-gucanase precursor, LEA protein 5 (LEA5), homologous DNAJ protein, PR10 and Stns LTP [52][53][124,125]. cDNA microarray z1300 full-length cDNAs were used in Arabidopsis to identify cold stress-inducing genes and target genes of DREB1A/CBF3. Six genes were documented based on microarray and, in RNA gel blot analyses, it was observed that a novel DREB1A controls cold- and drought-inducible genes [41][54][43,126]. Furthermore, microarray with full-length cDNA was performed by 1300 full-length cDNAs and cDNA microarray to discover cold-induced genes. Previous reposts exhibited the target genes of DREB1A/CBF3 and stress-inducible gene expressions were controlled by transcription factors [10][76]; in contrast, stress-sensitive genes’ expressions were reported as specific to the growth stage [40][42]. Full-length cDNA microarray is convenient for analyzing the Arabidopsis gene expression patterns under cold stress, and can also be used to identify the functional genes of stress-related TFs that are likely to act as DNA elements by merging the genomic sequence data with the expression data [10][55][76,127]. Additionally, cold stress is also induced by the increase in the proline content in plants (osmoprotectant). Microarray and RNA gel blot research found that the proline can induce the expression of several genes with the proline-responsive elements in their promoters (PRE, ACTCAT) [11][55][56][120,127,128]. Microarray analysis was carried out to detect the cold-inducible AP2 gene family transcription factor RAV1 [57][129], which could control plant growth under stress. RAV1 is down-regulated by epibrassinolide, and transgenic Arabidopsis overexpressing RAV1 exhibits a rosette leaf and adjacent root growth retardation, although the early-flowering phenotype showed antisense to RAV1 plants [58][59][130,131].
2. miRNAs and cDNA-Microarray Response to Salinity Stress
Salt intrusion from saline soils and irrigation water is one of the most severe and harmful risks to reduce agricultural production and adverse effects on cultivated land and the geographical distribution of plant species [60][61][62][70,132,133], coupled with oxidative stress [63]
| Integrative database of microRNA target predictions | ||||||||
| http://ophid.utoronto.ca/mirDIP | ||||||||
| [ | ||||||||
| 78 | ||||||||
| ] | ||||||||
| [ | ||||||||
| 152 | ||||||||
| ] | ||||||||
| 25 November 2021 | ||||||||
| miRanda | Predict or collect miRNA targets | http://34.236.212.39/microrna/home.do | [45] | [72] | 25 November 2021 | |||
| RNAhybrid | microRNA target prediction | https://bibiserv.cebitec.uni-bielefeld.de/rnahybrid | [45] | [72] | 8 November 2021 | |||
| miTALOS | Analyzes tissue specific microRNA function. | http://mips.helmholtz-muenchen.de/mitalos | [79] | [153] | 5 November 2021 | |||
| RNA22 | microRNA target predictions | https://cm.jefferson.edu/rna22 | [80] | [154] | 5 November 2021 | |||
| psRNATarget | Small RNA target analysis server | http://plantgrn.noble.org/psRNATarget/ | [81] | [155] | 5 November 2021 | |||
| miRandola | Curated knowledge base of non-invasive biomarkers | http://mirandola.iit.cnr.it/ | [81] | [155] | 5 November 2021 | |||
| ChIPBase | Decoding transcriptional regulatory networks of non-coding RNAs and protein-coding genes from ChIP-seq data | http://rna.sysu.edu.cn/chipbase/ | [81][82] | [155,156] | 1 October 2021 | |||
| MirGeneDB | Curated miRNA gene database | http://mirgenedb.org/ | [83] | [157] | 28 November 2021 | |||
| TarHunter | Predicting conserved microRNA targets and target mimics in plants | http://tarhunter.genetics.ac.cn | [84] | [158] | 28 November 2021 | |||
| TissueAtlas | Tissue specificity miRNA database | https://ccb-web.cs.uni-saarland.de/tissueatlas/ | [45] | [72] | 28 November 2021 | |||
| miRNAme Converter | miRNA ID converter | http://163.172.134.150/miRNAmeConverter-shiny | [85] | [159] | 28 November 2021 | |||
| Software and tools used for detection of plant microarray and data analysis | ||||||||
| Array Designer | Design primers and probes for oligo and cDNA expression microarrays. | http://www.premierbiosoft.com/dnamicroarray/index.html | [86] | [160] | 1 November 2021 | |||
| Stanford Microarray Database SMD | Stores raw and normalized data from microarray experiments | http://smd-www.stanford.edu//download/ | [87] | [161] | 1 November 2021 | |||
| eArray | Designing Agilent arrays | http://earray.chem.agilent.com/earray/login.do | [86] | [160] | 1 November 2021 | |||
| Significance Analysis of Microarrays | Adjustments for multiple testing, statistical analysis for discrete, quantitative, and time series data, gene set enrichment analysis | http://www-stat.stanford.edu/~tibs/SAM/ | [88] | [162] | 5 November 2021 | |||
| Visual OMP | Design software for RNA, DNA, single or multiple probe design, microarrays, Taq Manassays, genotyping, single and multiplex PCR, secondary structure simulation, sequencing, genotyping. | http://www.dnasoftware.com/Products/VisualOMP | [86] | [160] | 5 November 2021 | |||
| caArray | Open-source, web and programmatically accessible microarray data management system that supports the annotation of microarray | http://caarray.nci.nih.gov/ | 5 November 2021 | |||||
| Gene Expression Model Selector | Diagnostic models and biomarker discovery | http://www.gems-system.org/ | [89] | [163] | 18 November 2021 | |||
| Gene index | Gene Index Project is to use the available EST and gene sequences, along with the reference genomes, to provide an inventory of likely genes and variants. | http://compbio.dfci.harvard.edu/tgi/plant.html | [86] | [160] | 5 November 2021 | |||
| Genesis | Java package of tools to simultaneously visualize and analyze a whole set of gene expression experiments | http://genome.tugraz.at/genesisclient/genesisclient_description.shtml | 18 November 2021 | |||||
| RMA Express | Standalone GUI program for Windows, OS X and Linux to compute gene expression summary values for Affymetrix | http://rmaexpress.bmbolstad.com | http://www.r-project.org | http://www.bioconductor.org | 18 November 2021 | |||
| dCHIP | Model-based expression analysis for Affymetrix gene expression arrays | http://www.dchip.org | [90] | [164] | 18 November 2021 | |||
| TM4 | Microarray Data Manager (MADAM), TIGR Spotfinder, Microarray Data Analysis System (MIDAS), and Multi experiment Viewer (MeV) | http://www.tm4.org/ | [90] | [164] | 18 November 2021 | |||
| Able Image Analyser | Software for image analysis. It enables dimensional measurements: distance, area, angle in digital images | http://able.mulabs.com | [86] | [160] | 18 November 2021 | |||
| ImaGene | Unique, robust, room-temperature preservation solutions for nucleic acids, biospecimens and bioreagents for in the living ectors | http://www.biodiscovery.com/index/imagene | [86] | [160] | 13 November 2021 | |||
| Spotfinder | Custom-designed cDNA array, the chips are scanned using a microarray scanner | http://www.tm4.org/spotfinder.html | [90] | [164] | 18 November 2021 | |||
| SNOMAD | Web-based tool and has various normalization options for two-channel and single-channel experiments | http://pevsnerlab.kennedykrieger.org/snomadinput.html | [90] | [164] | 18 November 2021 | |||
| Multiexperimet Viewer | Cloud-based application supporting analysis, visualization, and stratification of large genomic data | http://www.tm4.org/mev.html | 18 November 2021 | |||||
| Onto-Express and Pathway-Express | Automatically translates DE gene transcripts from microarray experiments into functional profiles characterizing the impact of the condition studied | http://vortex.cs.wayne.edu/projects.htm | [90] | [164] | 13 November 2021 | |||
| DAVID/EASE | Database for annotation, visualization and integrated discovery (DAVID) is an online tool for annotation and functional analysis. Expression analysis systematic sxplorer (EASE) | http://david.abcc.ncifcrf.gov | [90] | [164] | 13 November 2021 | |||
Oligo-DNA microarrays were developed in common wheat, and these microarrays were designed to include approximately 32,000 distinctive genes characterized by several expressed sequence tags (ESTs). To classify the salinity-stress responsive genes, the expression profiles of transcripts that responded to stress were examined using microarrays. It was concluded that 5996 genes were verified by more than a 2-fold change in expression. These genes were categorized into twelve groups based on gene expression patterns [91][165]. Transcription-regulator activity, DNA binding, and the genes’ assigned transcription factor functions were preferentially classified as immediate response genes. In wheat, candidate genes were identified as involved in salinity-stress tolerance [91][92][165,166]. These genes are active in the regulation of transcription [1][73][112,143] and the signal transduction that is engaged in metabolic pathways [93][167] or acting as ion transporters [94][168]. cDNA library in yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) was examined using a synthetic medium augmented with excessive salt concentrations (900 mM). A few clones showed comparatively improved growth. The notorious clones bore the Guanyl transferase (OsMPG1) mannose-1-phosphate gene [62][133]. Extreme salinity stress was significantly linked with the transcription factors of four tomato genes from the family of zinc finger. There has been prior evidence of the relationship between zinc finger transcription factors and plant salinity tolerance [95][96][169,170]. Overexpression of OSISAP1 in transgenic tobacco resulted in tolerance to salinity, dehydration, and cold stress in the new sprouts [97][171].
A microarray containing 384 genes associated with stress responses was used in Medicago truncatula genotypes (Jemalong A17 and 108-R) to compare rooting gene expression during salt stress. The homolog of flora TFIIIA-related TF, MtZpt2-1, and COLD-REGULATEDA1 genes were known to regulate the previous genes and were acknowledged in Jemalong A17 stress-tolerant genotypes. Two MtZpt2 Transcription factors (MtZpt2-1 and MtZpt2-2) have shown increased expression in the roots compared to 108-R [98][172]. Salinity stress is attributed to diverse stresses that persuade overlapping patterns in gene expression. For example, in an investigation of 8100 A. thaliana genes, approximately 2400 genes were reported to have a widespread expression in exposure to salt, oxidative and cold stress [99][92]. In addition, 23 genes were reported against NaCl stress. This also accounted for a small percentage of DEGs, including encoding transcription factors WOX2 and BZIP3, calcium-binding protein CML42, ubiquitin-protein ligase UBC17, and IDA-like 5 protein [99][92]. Most prominently, synthesized isiA encoded a novel chlorophyll (Chl)-binding protein [100][173] (Table 3).
