Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Maxence Lejars and Version 2 by Camila Xu.
RNase III endoribonucleases cleave dsRNA and are conserved from bacteria (e.g., RNase III) to eukaryotes (e.g., Rnt1, Drosha and Dicer) both in terms of structure and function.
- RNase III
- ribosome biogenesis
- bacteria
- eukaryotes
1. Introduction
Universally conserved, the ribosome is a complex ribonucleoparticle that acts as the catalyst for protein synthesis. Ribosomal RNAs (rRNAs) and ribosomal proteins are assembled in a stepwise manner involving a plethora of protein and RNA effectors. As one of the most elaborate biological machines, the ribosome remains a major object of study in regard to its complex nature and its heterogeneity in cells [1]. In prokaryotes and eukaryotes, ribosomal biogenesis relies on the transcription of precursors rRNAs, which are processed into mature rRNAs [2][3][2,3]. The complexity of the step-by-step process of maturation reveals a need for precision in the timing as well as robustness in the synthesis of rRNAs. In particular, rRNAs adopt complex structures, which are achieved through double-stranded RNA (dsRNA) motifs [4] and which are essential for both catalytic and structural integrity of the mature ribosome [5].
In cells, RNAs are protected by RNA-binding proteins (RBP) and RNA chaperones and are processed by ribonucleases (RNases). Although naked single-stranded RNAs can be cleaved by various RNases, the processing of stable dsRNA structures requires specialized RNase III domain (RIIID)-containing enzymes. RNase IIIs are endoribonucleases cleaving dsRNA conserved from bacteria (e.g., RNase III) to eukaryotes (e.g., Rnt1, Drosha and Dicer) both in terms of structure and function [6][7][8][9][10][11][6,7,8,9,10,11]. RNase III was first identified for its role in the initial step of rRNA maturation in the model organism Escherichia coli [12]. Subsequent studies demonstrated that RNase III is also involved in the regulation of gene expression in bacteria and the maturation of non-coding RNAs in eukaryotes.
2. The Founding Member
2.1. The rnc Gene
RNase III was discovered in E. coli (referred hereafter as Ec-RNase III) in 1967 [13] and shown to cleave natural and synthetic dsRNAs in vitro in 1968 [14]. Isolation of an RNase III-deficient derivative of E. coli in 1973 [15] revealed its importance in the initial steps of the maturation of rRNA precursors [12]. Assuming that Ec-RNase III could have an important role in cell physiology, Kindler et al. isolated thermosensitive mutants from an E. coli strain inactivated for RNase I [16]. The clone AB301-105 carrying the rnc105 mutation (Table 1) demonstrated a strongly reduced ability to cleave dsRNA substrates in vitro [15]. The rnc105 mutation was then mapped around 49 min on the chromosome of E. coli, identifying the rnc gene, which was subsequently confirmed to encode Ec-RNase III [17]. Although Ec-RNase III is not essential for growth [18], its inactivation was found to provoke slow growth and sensitivity to heat [19] and osmotic shock [20].
Table 1.
Functionally characterized RNase III mutants in
E. coli
.
| Allele | Mutation | Catalytic Activity | In Vitro dsRNA Binding | References | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| In Vivo | In Vitro | ||||
| E38A | n.d. | weak 1 | high | [21][21[22],22] | |
| E38V | no | n.d. | n.d. | [23] | |
| E41A | n.d. | weak 1 | low | [21] | |
| F42G, D or R | no | n.d. | n.d. | [23] | |
| F42M, W | yes | n.d. | yes | [23] | |
| rnc105 | G44D | no | no | no | [24][25][24,25] |
| D45A | no | low | yes | [21][23][21,23] | |
| D45E or N | n.d. | weak 1 | low | [21] | |
| E65A | no | weak 1 | low | [21][23][21,23] | |
| rnc97 | G97E | low | weak 1 | n.d. | [26] |
| E100A | n.d. | weak 1 | low | [21] | |
| D114A | n.d. | weak 1 | low | [21] | |
| E117D | n.d. | weak 1 | yes | [23][27][23,27] | |
| rnc70 | E117K, A or Q | no | no | yes | [28][29][30][28,29,30] |
| rnc10 | Q153P | n.d. 2 | weak | n.d. | [31] |
| rnc7 | D155E | n.d. 2 | no | n.d. | [31] |
| rev3 | A211V | n.d. 2 | n.d. | n.d. | [25][25[32],32] |
| rnc38 | insertion | no | no | no | [33] |
| rnc40 | insertion | no | no | no | [18] |
| rnc14 | insertion | no | no | no | [18] |
Mutations are either missense, indicated by the amino acid, its number relative to the sequence of Ec-RNase III followed by the replacing amino acid(s) or insertions of fragments derived from transposons and plasmids. 1 In excess of magnesium. 2 Suppressors of cold-sensitive mutant alleles. n.d. not determined.
Ec-RNase III is co-expressed with the essential GTPase Era within the rnc-era-recO-pdxJ-acpS operon. The recO gene encodes a DNA repair protein while the pdxJ and acpS genes, also transcribed from their own promoters, encode the pyridoxine synthase PdxJ, essential for growth in the absence of pyridoxine and the essential holo-acyl-carrier-protein synthase AcpS, respectively. Hence, as demonstrated by the absence of an rnc deletion mutant in the Keio collection [34], inactivating Ec-RNase III likely lead to polar effects on the expression of the gene era, which was shown to be essential but is also toxic when overexpressed [35]. Interestingly, insertion mutants of RNase III (rnc14 and rnc38, carrying large inserts containing transposons and fragments of plasmid) seem to provide the correct compensation of era expression. In addition, RNase III cleaves its own mRNA in its 5′ untranslated region (UTR), leading to the destabilization of both rnc and era mRNAs [36][37][36,37].
Bacterial RNase III carry two distinct domains: an N-terminal region containing the characteristic catalytic core of RNase III (RIIID) (amino acids 6–128) and the double-stranded RNA (dsRNA)-binding domain (dsRBD) in the C-terminal region (amino acids 155–225) (Figure 1). Various mutations were characterized, which disrupt the catalytic activity of Ec-RNase III (with or without affecting its binding affinity) or abolish its expression (Table 1). The mutations which affect catalytic ability are all located in the RIIID with the exception of rnc7 (D155E) and Q153 located in the dsRBD and the linker, respectively [31]. Importantly, as shown for a few mutants (e.g., rnc70), the catalytic activity of RNase III can be lost without affecting its binding to dsRNA. Moreover, the rnc70 mutant was shown to be dominant over the wt allele in the regulation of the N mRNA from the lambda phage, suggesting that dsRNA binding and cleavage are independent functions of Ec-RNase III [30].
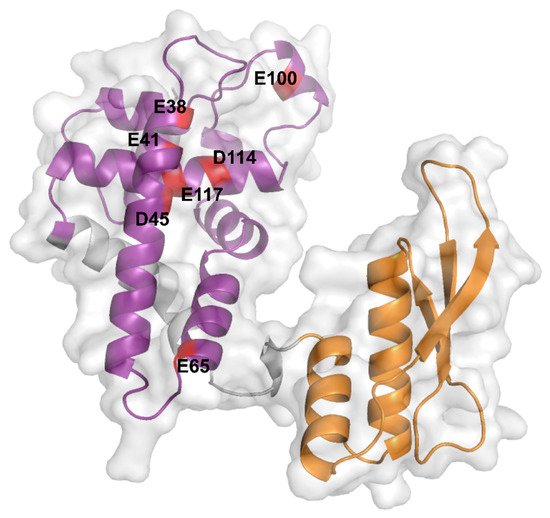

Figure 1. AlphaFold prediction of the Ec-RNase III structure. Ec-RNase III structure predicted by the AlphaFold program (AF-P0A7Y0-F1, https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk, accessed on the 11 October 2021). The N-terminal RIIID (6-128) and C-terminal dsRBD (155-225) are depicted in purple and orange, respectively. Critical negatively charged residues E38, E41, D45, E65, E100, D114 and E117, which are highly conserved among bacterial RNase III enzymes, are highlighted in red on the structure of the Ec-RNase III. The representation was generated using the PyMol software version 2.5.1.
2.2. How Does RNase III Work?
2.2.1. Structure
The dimerization of the active Ec-RNase III complex relies on the interaction of two RIIIDs to form a single processing center accommodating two divalent metallic ions, with a preference for magnesium [29]. The interaction of the two RIIIDs, achieved through a ball and socket junction, is essential for the correct positioning of the cleavage sites [23]. In the UniProt database (https://www.uniprot.org [38], accessed on the 11 October 2021), RNase III structures from various bacterial species (i.e., Aquifex aeolicus O67082, Campylobacter jejuni Q9PM40, Thermotoga maritima Q9X0I6 and Mycobacterium tuberculosis P9WH03) are available but not from E. coli. These structures revealed that the RIIID is composed of seven α-helices and adopts a unique fold while the dsRBD adopts an α-β-β-β-α topology, as found in other dsRBD containing enzymes [39]. While no complete structure of Ec-RNase III is currently available, Ec-RNase III dsRBD was solved by NMR spectroscopy showing a typical α-β-β-β-α topology [40]. Furthermore, structure prediction performed recently through the AlphaFold program (https://alphafold.ebi.ac.uk, accessed on the 11 October 2021) [41][42][41,42] supports a common structure between Ec-RNase III (P0A7Y0) and previously obtained RNase III structures in bacteria. In addition, important amino acid residues have been identified from a wide range of Ec-RNase III mutants (Table 1) and include residues E38, E41, F42, G44, D45, E65, G97, E100, D114, E117 in the RIIID, Q153 in the linker and D155 and A211 in the dsRBD. In particular, negatively charged residues E38, E41, D45, E65, E100, D114 and E117 are highly conserved among bacterial RNase III enzymes [21] (Figure 1).
2.2.2. Mechanism
Recruitment of an RNase III dimer is initiated by the interaction of a single dsRBD with a target dsRNA. The binding induces a conformational change of the dsRBD, bringing it closer to the dsRNA which facilitates the symmetric recruitment of the second dsRBD [43]. Upon binding, the second dsRBD is reoriented which renders the catalytic core functional. Of note, if the dsRNA structure does not correctly accommodate the dimer, a non-catalytic RNase III complex can form and the regulatory outcome of this interaction remains unclear. At the molecular level, RNA cleavage relies on a nucleophilic attack, allowing the hydrolysis (supposedly simultaneous) of the phosphodiester bond generating 3′-hydroxyl and 5′-phosphate ends on both strands but which are staggered by two bases on one strand of the dsRNA compared to the other (Figure 2). The release of the generated cleavage products remains poorly characterized but was shown to be the limiting step of the reaction likely due to the requirement for a second change in the conformation of the dimer to release the processed RNA fragments [44].
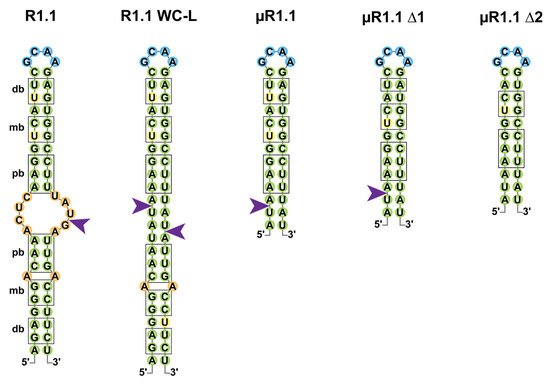

Figure 2. Cleavage of the T7 R1.1 RNA and its derivatives by Ec-RNase III. Secondary structures of RNase III target R1.1 RNA from the T7 phage and its artificial derivatives (R1.1 WC-L, µR1.1, µR1.1 Δ1 and µR1.1 Δ2) are represented in two dimensions as in [29][45][29,48]. Base pairs are represented in green; bulges and mismatches are represented in orange, loops in blue and uridine residues involved in wobble G-U base pairing in yellow. Proximal (pb), middle (mb) and distal (db) boxes are shown outlined in black and RNase III single-strand cleavage sites are represented by a purple arrow.
If the early studies of Ec-RNase III suggested that binding and (single or double-stranded) cleavage was not random, criteria for RNase III target selection remain poorly understood. In the pre-mRNA of the T7 phage, multiple single-stranded cleavages sites were identified, of which the “R1.1” cleavage, located at the 5887th nucleotide (nt) of the T7 phage pre-mRNA, drives the maturation and protection of T7 mRNAs (Figure 2) [46][47][45,46]. R1.1 is formed by a 49 nts long stem carrying symmetrical sets of proximal (relative to the cleavage site) boxes (pb, 4 nts), middle boxes (mb, 2 nts) and distal boxes (db, 2 nts) for each of the monomers to bind the dsRNA [11][48][11,47]. R1.1 became a model to understand the properties of RNase III binding and cleavage and a mutant named R1.1 WC-L, in which full complementarity is forced in the stem enabled the double-stranded cleavage of the RNA [29]. Shortening of the R1.1 stem revealed that a single set of boxes in a 12 base pair (bp) stem with a tetraloop is sufficient for single-strand cleavage by Ec-RNase III (µR1.1 Δ1) while the cleavage is lost upon removal of the last bp of the distal box (µR1.1 Δ2) [45][48]. It is noteworthy that the recent identification of thousands of staggered double-stranded Ec-RNase III cleavage sites in E. coli suggests that RNase III binding sites do not share a strong consensus sequence but likely depend on the structure of the targeted stem loop [49].
2.2.3. Physiological Roles of RNase III
In addition to its role in rRNA maturation, the importance of bacterial RNase III was highlighted through transcriptomic studies performed in diverse organisms, including but not limited to E. coli [49][50][51][52][49,50,51,52], Streptomyces coelicolor [53], Staphylococcus aureus [54], Synechococcus sp. PCC7002 [55] or Rhodobacter sphaeroides [56]. These studies demonstrate the pleiotropic role of RNase III in the control of gene expression and a comparison of the genes affected by RNase III inactivation in these organisms would be informative about the distribution and conservation (or not) of targets. In E. coli, RNase III is involved in the destabilization of numerous RNAs. For example, Ec-RNase III cleaves its own mRNA in the 5′UTR of the rnc-era mRNA, which destabilizes the whole transcript (Figure 3) [37]. Ec-RNase III can cleave in between coding sequences within polycistronic mRNAs such as rpsO-pnp, encoding the ribosomal protein S15 and the exoribonuclease PNPase. This cleavage leads to the destabilization of pnp mRNA without affecting the expression of rpsO (Figure 3). Cleavages within coding sequences were also found as in the arfA mRNA (Figure 3), encoding the alternative ribosome rescue factor ArfA, thus revealing a positive role of Ec-RNase III in an alternative pathway to rescue stalled ribosomes upon mRNA truncation [57]. While targets of RNase III in bacteria are usually expected to be negatively regulated, maturation can also lead to positive regulation as in the case of the pre-rRNA (see Section 4.1). RNase III is also involved in intermolecular dsRNA cleavages (i.e., where the dsRNA is composed of two distinct molecules) as in the case of regulatory RNAs bound to their targets. For the small RNA RhyB, binding to the sodB mRNA, encoding the superoxide dismutase FeSOD, RNase III cleavage leads to the degradation of both RNAs [58] while, on the other hand, the cleavage of the antisense RNA (asRNA) ArrS bound to the gadE mRNA leads to increased translation of GadE, an acid response transcriptional factor [59]. These and other examples demonstrate the pleiotropic functions of RNase III in bacterial physiology. For example, in the adaptation phase following an osmotic shock RNase III activity is repressed, which allows stabilization of proP (Figure 3), proU and betT mRNAs encoding proteins involved in the import of osmoprotectants [60][61][62][60,61,62]. Furthermore, RNase III was shown to be involved in thermotolerance [19], motility [63] and aminoglycoside resistance [64]. In other bacteria, RNase III was shown to be important for a whole range of functions, including but not limited to methionine biosynthesis in S. aureus [65] and cell wall homeostasis in Pseudomonas putida [66] and to be involved in virulence in Enterococcus faecalis [67], Listeria monocytogenes [68], S. aureus [54] or Campylobacter jejuni [69].
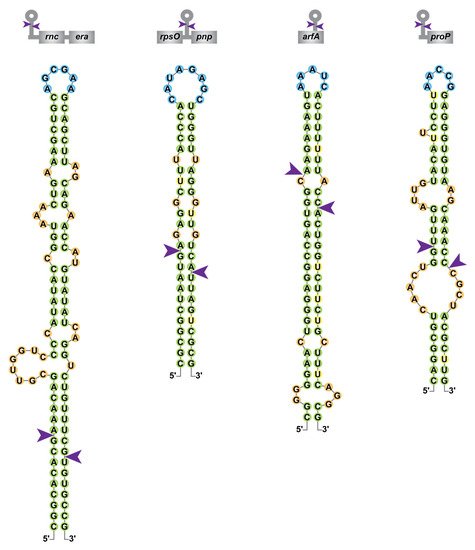

Figure 3. Diversity of RNase III cleavage sites within E. coli mRNAs. Secondary structure predictions of Ec-RNase III targets within the rnc-era, rpsO-pnp, arfA and proP mRNAs were obtained from [49][55][62][70][49,55,62,70] and color-coded as in Figure 2. A schematic representation of the targeted mRNAs is presented on top of each RNA structure with coding sequences in grey boxes.
Although the majority of characterized RNase III target sites in E. coli likely result from intramolecular dsRNA, it was recently shown that among the thousands of in vivo Ec-RNase III cleavage sites identified, around 40% are singletons, in the sense that there is no obvious staggered second cleavage site. Hence, this suggests that they either represent single-stranded cleavages or arise from intermolecular interactions (i.e., the second single-strand cleavage is located in a second molecule thus a complex analysis is required to predict candidate dsRNA partners) [49]. The plasticity of RNase III binding and cleavage sites in E. coli, as illustrated in Figure 3 for the rnc-era, rpsO-pnp, arfA and proP mRNAs, may provide an explanation for the abundance of putative RNase III cleavage sites (identified by transcriptomic approaches but not yet validated as direct targets) and is consistent with a larger role of RNase III in the regulation of gene expression.
3. RNase III Are Everywhere
RNase III enzymes are widely conserved and have been categorized into four classes according to their domain composition (Figure 4). The first one includes all bacterial RNase III (e.g., RNase III and Mini-III) and the yeast RNase III (e.g., Rnt1p and Pac1p) carrying an additional N-terminal domain. The second class includes eukaryotic RNase III carrying additional domains (see Section 3.2). The sole members of class III and IV are the eukaryotic Drosha and Dicer, respectively, where the RIIID is part of complex multidomain proteins. Class I and II RNase III enzymes are directly involved in ribosomal biogenesis and carry a single RIIID per monomer. On the contrary, classes III and IV enzymes carry two RIIIDs and their direct involvement in rRNA maturation has yet to be elucidated. In addition, RNase III enzymes were also found in viruses such as the essential class I RNase III in Ambystoma tigrinum virus [70]. Remarkably, RNase III has not been found in archaea where dsRNA cleavage is assured by enzymes belonging to the family of splicing endonucleases [71] which recognize bulge–helix–bulge secondary structure motifs and cut within single-stranded bulges [72].
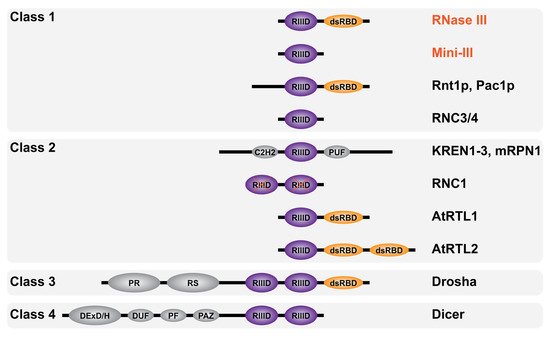

Figure 4. Domain diversity of RNase III enzymes. Schematic representation of RNase III enzymes domain composition categorized by classes as described in the text (not to scale). Bacterial RNase III are in red font and eukaryotic RNase III in black font. The RNase III catalytic domain (RIIID) is in purple and marked with a red X when inactive (in RNC1), the double-stranded RNA binding domain (dsRBD) is in orange while the Zinc finger domain C2H2, RNA-binding domain PUF, proline-rich domain PR, arginine/serine (RS)-rich domain, helicase DExD/H domain, RNA annealing domain DUF, structural domain PF and the anchoring domain PAZ are in gray.
3.1. Bacterial RNase III
The conservation of the RIIID within bacterial genomes allowed the identification of RNase III enzymes in the majority of bacterial species with, so far, the exception of Deinococcus radiodurans [6]. Similar to Ec-RNase III [18], RNase III is not essential in most bacteria (e.g., S. aureus [73], C. jejuni [69], Borrelia burgdorferi [74] or Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7002 [55]). However, RNase III was shown to be essential in B. subtilis due to its requirement for toxin silencing [75].
To obtain a better understanding of RNase III binding sites and cleavage determinants among species, complementation and substrate specificity assays have often been used. B. subtilis RNase III (referred hereafter as Bs-RNase III) exhibits 36% sequence identity with Ec-RNase III and is able to complement the maturation of rRNAs when expressed in an E. coli rnc mutant [76]. However, although Bs-RNase III can cleave at the same location of some Ec-RNase III substrates in vitro, the contrary is not valid for the Bs-RNase III targets tested [77]. Of note, B. subtilis also contains a shorter form of RNase III that lacks the dsRBD, named Mini-III (hereafter referred to as Bs-Mini-III) which catalyzes the 23S rRNA maturation [78]. Furthermore, while RNase III from Rhodobacter capsulatus can cleave some of Ec-RNase III substrates at the exact position in vitro, the contrary is not true, as Ec-RNase III is unable to process the R. capsulatus pre-23S rRNA [79][80][79,80]. In the cyanobacteria Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7002, three RNase III enzymes were identified, of which one is a homologue to the Bs-Mini-III [55]. Two of them are involved in independent maturation events of the pre-23S rRNA while another participates in plasmid copy number regulation.
3.2. Eukaryotic RNase III
The first eukaryotic RNase III enzymes were identified by sequence comparison with Ec-RNase III. Pairwise comparison of the entire Ec-RNase III revealed 24% identity with Pac1p from the yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe [81][82][81,82] and 25% identity with Rnt1p from the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae [83] (as compared to 36% identity between Ec and Bs-RNase III). Analogous to the known function of bacterial RNase III, Pac1p and Rnt1p were also shown to be involved in rRNA maturation [84][85][84,85]. Other RNase III members were identified, thanks to their RIIID signature domain, in higher eukaryotes. Drosha [86] and Dicer [87] are involved in different steps of the maturation of micro RNAs (miRNAs) and silencing RNAs (siRNAs) within the RNA interference pathway [88]. Additional eukaryotic RNase III enzymes demonstrating different domain compositions are represented in Figure 4. They include KREN1 to 3 and mRPN1 from Trypanosoma brucei mitochondrial kinetoplast, which contain a C2H2 Zinc finger and whose precise roles remain unclear [89][90][89,90], RNC1 in Zea mays chloroplasts, whose two RIIIDs are catalytically inactive [91], AtRTL1/2 class II RNase III-like enzymes in Arabidopsis thaliana nucleus [92][93][92,93] and RNC3/4 mini-RNase III-like enzymes in Arabidopsis thaliana chloroplast [94].
