A DDE is a single-variable differential equation, usually called time, in which the derivative of the solution at a certain time is given in terms of the values of the solution at earlier times. Moreover, if the highest-order derivative of the solution appears both with and without delay, then the DDE is called of the neutral type. The neutral DDEs have many interesting applications in various branches of applied science, as these equations appear in the modeling of many technological phenomena. The problem of studying the oscillatory and nonoscillatory properties of DDEs has been a very active area of research in the past few decades.
- delay differential equation
- neutral
- oscillation
- noncanonical case
1. Introduction
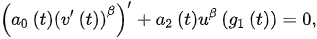
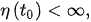
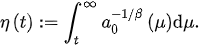
2. Oscillatory Properties of Noncanonical Neutral DDEs of Second-Order
We begin with the following notations: is the set of all eventually positive solutions of (1), ,
Lemma 1. Assume that and there exists a such that:
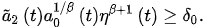
(3)
Then, v eventually satisfies:
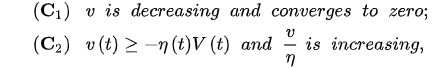
and:
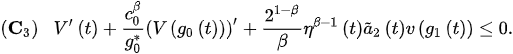
Proof. Let . Then, we have that , and are positive for , for some . Therefore, it follows from (1) that:
Using (1) and Lemma 1 in [1], we see that:
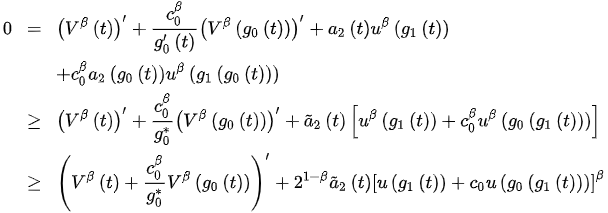
and so:
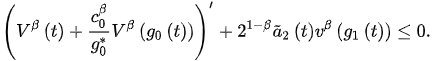
(4)
Integrating this inequality from to t and using the fact , we find:
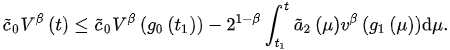
(5)
Assume the contrary, that for . Thus, from (5), we have:
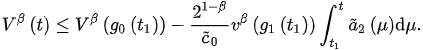
This, from (3), implies:
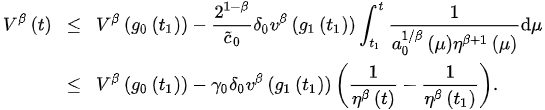
Letting and taking the fact that as , we obtain , which contradicts the positivity of .
Next, since v is positive decreasing, we have that . Assume the contrary, that . Then, for all , for some . Thus, from (3) and (5), we have:
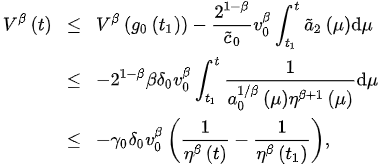
or
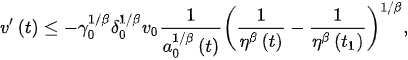
and so,
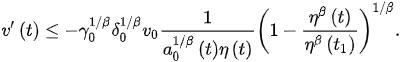
(6)
Using the fact that , we obtain that for all . Hence, by integrating (6) from to t, we obtain:
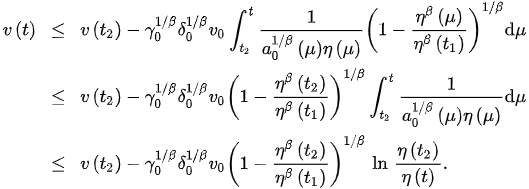
Letting and taking the fact that as , we obtain , which contradicts the positivity of . Therefore, .
Since is decreasing, we obtain:
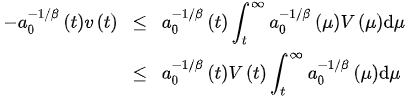
and:
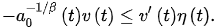
(7)
Then, .
From (7), we obtain:
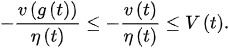
Thus, from (4) and the fact , we obtain:
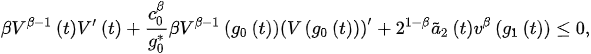
and then:
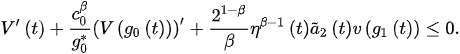
The proof is complete.
Lemma 2. Assume that and there exists a such that (3) holds. Then:
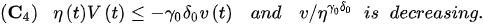
Proof. Let . From Lemma 1, we have that – hold for .
Integrating from to t, we arrive at:
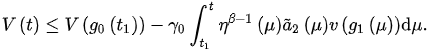
From (3), we obtain:
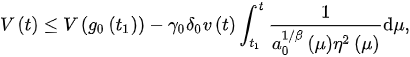
and:
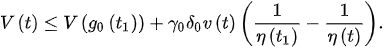
(8)
Using , we eventually have:
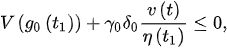
Hence, (8) becomes:
This implies that is a decreasing function.
The proof is complete.
References
- Baculikova, B.; Dzurina, J. Oscillation theorems for second-order nonlinear neutral differential equations. Comput. Math. Appl. 2011, 62, 4472–4478.
