Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 2 by Amina Yu and Version 1 by Mustapha Umar Imam.
Ferroptosis, mainly mediated by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation, is closely linked to multiple physiological and pathological processes in humans and animals, including cancer, arteriosclerosis, ischemia-reperfusion injury, neurodegenerative diseases, and acute renal failure.
- ferrroptosis
- iron metabolism
- lipid peroxidation
- glutathione peroxidase 4
- mechanisms
1. An Overview of Ferroptosis
Cell fate determination largely depends on the oxidative stress in cells. Oxidative modification of lipids in membrane bilayers, especially lipid peroxidation, is a key regulator of cell fate. In fact, ferroptosis-like cell death has been observed for a long time. As early as 2001, Tan et al. discovered a unique oxidative stress-induced programmed cell death pathway which is entitled “oxytosis” [21][1]. Then, in 2003, Dolma et al. found a new small molecular, erastin, which initiated a nonapoptotic cell death process without classic morphological or biochemical features of apoptosis and the process could not be inhibited by caspase inhibitors [22][2]. Afterwards, researchers successively unveiled that this unique cell death mode could be suppressed by iron chelators and another compound RSL3 was identified being able to activate a similar pattern of non-apoptotic and iron-dependent cell death [23,24][3][4]. After these findings, ferroptosis was coined to depict this pattern of cell death in 2012 [4][5]. The cystine/GSH/GPX4 signaling axis is regarded as the predominant control system of ferroptosis. Distinctive lipid peroxidation and reactive oxygen species (ROS) overproduction are considered as the fatal factors. Some studies have discovered that ferroptosis is widely involved in the process of numerous diseases [13][6]. It is implied that ferroptosis is a pathophysiological process widely existing in organism rather than an organ-specific process. Meanwhile, multiple organelles such as mitochondria, endoplasmic reticulum, golgi apparatus and lysosomes are implicated in the process of iron metabolism and redox imbalance in ferroptosis [25][7]. It is reported that ferroptotic cell death can be excellently counteracted by lipophilic antioxidants (ferrostatin-1 and α-tocopherol), iron chelating agents, lipid peroxidation inhibitors and consumption of polyunsaturated fatty acids [3][8]. However, whether ferroptosis is strongly involved in more human diseases and more organelles, the precise mechanisms and biological functions of ferroptosis remain poorly understood.
2. Mechanisms of Ferroptosis
Ferroptosis is controlled and executed by an integrated cell signaling network. Researchers have revealed that amino acid and glutathione (GSH) metabolism, iron metabolism, lipid peroxidation, ferroptosis-suppressor-protein 1 (FSP1)-coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10) axis and other regulators are involved in the regulatory mechanisms of ferroptosis (Figure 1) [4,5,26,27][5][9][10][11].
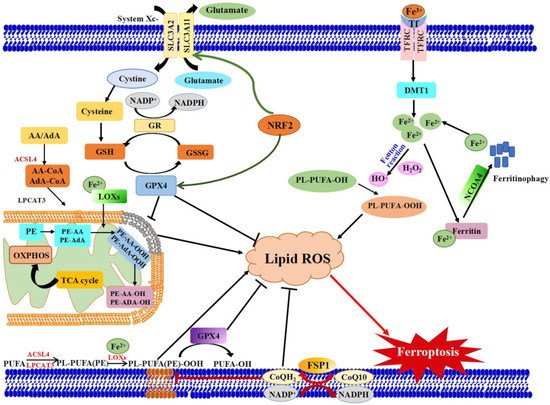
Figure 1. Schematic view of the molecular pathways of ferroptosis regulation. Three main metabolic pathways are GSH/GPX4 pathway, lipid peroxidation and iron metabolism pathways. Ferroptosis is initiated by the suppression of system Xc− and depletion of GSH, or inhibition of GPX4, which results in cell death. Lipid ROS is in charge of the process of ferroptosis. The peroxidation of PUFAs is identified as a vital contributor. Excess iron is the basis for ferroptosis execution. In addition, the latest researches have revealed that the FSP1-CoQ10-NAD(P)H pathway with its unique mechanistic properties engages in ferroptosis. AA: Arachidonic acid, ACSL4: Acyl-CoA Synthetase Long Chain Family Member 4), AdA: Adrenoyl, DMT1: Divalent metal transporter 1, FSP1: Ferroptosis suppressor protein 1, FPN1: Ferroportin 1, GPX4: Glutathioneperoxidase 4, GSH: glutathione, GSSG: Oxidized GSH; LPCAT3: Lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase 3, lipoxygenases: LOXs, NCOA4: Nuclear receptor coactivator 4, GR: Glutathione reductase. PL: Phospholipids, Tf: Transferrin.
2.1. Amino Acid and GSH Metabolism
Amino acid and GSH metabolism are tightly linked to the regulation of ferroptosis. The amino acid antiporter system Xc− is consisted of solute carrier family 3 member 2 (SLC3A2) and the catalytic subunit solute carrier family 7 member 11 (SLC7A11) [28][12]. The system Xc− takes charge of redox homeostasis by exchange of extracellular cystine and intracellular glutamate at the ratio of 1:1. The imported cystine can be promptly converted to cysteine and serves as substrate for GSH synthesis. Then, GPX4, a central regulator of ferroptosis, utilizes the antioxidant GSH to detoxify lipid peroxidation and modulate the initiation of ferroptosis [5][9]. Inhibiting system Xc− with small molecular (e.g., erastin) can decrease the cellular uptake of cysteine, inhibit GSH synthesis and inactivate GPX4, which in turn, triggers excessive lipid peroxidation and ferroptotic cell death [5,29][9][13]. According to study, tThe alteration of GPX4 level and/or activity will immediately affect cell survival [30][14]. In vivo study has confirmed the core role of GPX4 in ferroptosis. Inactivation of GPX4 could cause severe acute renal failure in mice [11][15]. Acting as an essential cofactor of GPX4, GSH could reduce lipid peroxides, playing the ferroptosis-resistance activity [3][8]. The ferroptotic agonist (1S, 3R)-RSL3 can bind and irreversibly inactivate GPX4, leading to cell death [17][16]. Therefore, gene knockout and inactivation of GPX4 is vital way to induce ferroptosis. It is suggested that system Xc−-GSH-GPX4 may be effective therapeutic approach in organ damage mediated by ferroptosis.
2.2. Iron Metabolism
Iron is a redox-active metal. Excessive iron contributes to the execution of ferroptosis through inducing the production of ROS by Fenton chain reaction. Thus, the sensitivity of ferroptosis is closely associated with iron homeostasis including iron uptake, export, storage and turnover. Iron homeostasis is a complex process, which relies on coordination of multiple genes such as IREB2 (iron responsive element binding protein 2), FTH1 (ferritin heavy chain 1), FTL (ferritin light chain), TF (transferrin), TFR1 (transferring receptor 1), FPN (ferropotein) and DMT1 (divalent metal-ion transporter-1). These genes encoded proteins could affect ferroptosis trigger via regulating intracellular iron. A recent study found that Tf and TfR1, mainly responsible for intestinal iron absorption, play the critical role in ferroptotic cell death [23,31][3][17]. Elevated plasma level of TfR1 increased the amount of intracellular iron, which might promote ferroptosis, e.g., leading to auditory cortex neurodegeneration [32][18]. The redundant intracellular iron is stored in ferritin which is composed of FTL and FTH1. RSL3-sensitive cells transformed with oncogenic RAS significantly could increase cellular iron level via increasing TfR1 and decreasing FTL and FTH1 mRNA expression [23][3]. The selective cargo receptor-nuclear receptor coactivator 4 (NCOA4)-regulated degradation of ferritin (referred to as ferritinophagy) influences the availability of labile iron and stimulates erastin-induced ferroptosis [33,34,35][19][20][21]. The bromodomain protein BRD4 inhibitor (+)-JQ1 could induce ferroptosis via ferritinophagy and regulate ferroptosis-related genes in cancer cells [36][22]. IREB2 is a master regulator of iron metabolism. Silencing of IREB2 by shRNA inhibits the sensitivity to erastin-induced ferroptosis in HT1080 cells [4][5]. Based on these findings, the cellular iron metabolism is indispensable for the induction of ferroptosis. Strategy targeting iron metabolism genes might be a promising method to treat the cancers which are drug-resistant or alleviate ferroptosis-induced diseases.
2.3. Lipid Metabolism
Lipid metabolism is closely associated with the process of ferroptosis. The accumulation of lipid peroxide could directly damage cellular and organelle membrane, initiating ferroptotic cell death. Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) serve as the main substrates of lipid peroxidation during ferroptosis [37][23]. Thus, the extent of lipid peroxidation and the process of ferroptosis in cells largely depend on the content and localization of PUFAs. According to some reports, PUFA- phosphatidylethanolamines (PEs) esterified with arachidonoyl (AA) and adrenoyl (AdA) acyl chains are the key phospholipids in triggering ferroptosis [26,38][10][24]. The free AA/AdA could bind to coenzyme A (CoA) to form AA/AdA-CoA under the action of Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 (ACSL4), facilitating their esterification into phospholipids. Subsequently, lysophosphatidylcholine acyltransferase-3 (LPCAT3) catalyzes AA/AdA-CoA esterified into PEs and then the formed AA/AdA-PEs would be oxidized into lipid hydroperoxides by lipoxygenase (LOX), inducing ferroptosis [39][25]. Therefore, ACSL4 and LPCAT3, two enzymes involved in the biosynthesis and remodeling of PUFA-PEs in cellular membranes, are critical determinants of ferroptosis sensitivity [3][8]. Genetic disruption of ACSL4 and LPCAT3 depletes the substrates for lipid peroxidation and decreases ferroptosis sensitivity [38,39,40][24][25][26]. It is reported that cells treated with arachidonic acid or other PUFA are sensitized to ferroptosis [26][10]. Peroxidation of n-3 and n-6 PUFA exerted selective cytotoxic effects in acidic cancer cells, leading to ferroptosis-mediated antitumor effects [41][27]. In addition, LOXs also contribute to ferroptosis. The suppression of LOX by ferroptosis inhibitors, including vitamin E, zileuton and baicalein, can relieve ferroptosis [42,43,44][28][29][30]. However, some LOXs are essential for normal embryonic development in vertebrates. Knockdown of 12S-LOX in zeberafish could severely impair embryonic phenotype, characterized by abnormal brain, eyes, tails as well as yolk sac and pericardial edema [45][31]. It is suggested that lipid metabolism is required for both ferroptosis and normal physiological function. Abnormal lipid metabolism could be a crucial trigger for ferroptosis.
2.4. The FSP1-CoQ10 Axis
FSP1 was previously called apoptosis inducing factor mitochondria associated 2 (AIFM2). Recently, two momentous back-to-back research by Doll et al. and Bersuker et al. disclosed that FSP1 is a novel inhibitor of ferroptosis and could counteract ferroptosis independently even in the absence of GPX4 [46,47][32][33]. AIFM2 is proposed before the concept of ferroptosis, whose activation could suppress tumor proliferation and enhance apoptosis [48][34]. In human lung cancer cell lines, the activation of AIFM2 markedly contributed to cancer cells apoptosis undergoing exogenous toxicological stimulus [49][35]. Recently, Bersuker and his colleagues identified that FSP1 was a potent ferroptosis-resistance factor through using a synthetic lethal CRISPR-Cas9 knockout screen [47][33]. Almost simultaneously, Doll et al. also executed relevant studies on FSP1 [46][32]. By using an overexpression screen, their group demonstrated that FSP1 complemented the loss of GPX4 or inhibition of GPX4 in human cancer cells. The inhibition of ferroptosis by FSP1 was mediated by antioxidant CoQ10, while FSP1 could catalyze the regeneration of CoQ10 by NAD(P)H [46,47][32][33]. Therefore, FSP1-CoQ10-NAD(P)H axis is an independent parallel system, cooperating with GPX4 and GSH/GSSG to inhibit lipid peroxidation and control the process of ferroptosis. Both studies disclosed that the expression of FSP1 was negatively correlated with the ferroptosis sensitivity in many cancer cell lines. In conclusion, the discovery of FSP1 supplemented and perfected the ferrroptosis pathway. FSP1 can be used as a valuable biomarker of ferroptosis resistance. Exploiting FSP1 inhibitors can be effective strategy to overcome ferroptosis resistance in cancer cells.
2.5. Other Regulators
There are some regulators and key components that act vital roles in the ferroptosis cascade (Figure 1).
2.5.1. Nrf2
The transcription factor Nrf2 is a key regulator that maintains cellular redox homeostasis and plays a critical role in mediating iron/heme metabolism [50][36]. It is reported that most of the transcription of ferroptosis-related genes are regulated by Nrf2. Both iron metabolism-related genes (TFR1, FPN, FTH1 and FTL) and heme metabolism–related genes (HO-1, SLC48A1) are Nrf2 target genes [51][37]. Nrf2 activation enables decrease in the intracellular iron pool to restore iron homeostasis, restricts the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and upregulates SLC7A11. The expression of SLC7A11 is positive correlation with activity of system Xc−. Upregulation of SLC7A11 expression at the transcription level could enhance cystine uptake and consequently inhibit ferroptosis [52][38] (31,908,494). Therefore, Nrf2 is considered to be a negative regulator of ferroptosis. As expected, activation of Nrf2 pathways confers resistance to GPX4 inhibitor induced ferroptosis in cancer cells [53][39]. These results indicate that targeting Nrf2 or its downstream targets could be a dependable approach to regulate ferroptosis. Paradoxically, ferroptosis activators erastin and sorafenib can enhance Nrf2 expression in HCC cells, whereas Nrf2 activation could negatively regulate ferroptosis [53,54][39][40]. Thus, the modification of Nrf2 signaling can be a good strategy for disease intervention via regulating ferroptosis process.
2.5.2. P53
The p53 tumor suppressor is distinguished as the most frequently mutated gene in human cancer, which is involved in cell-cycle arrest, cellular senescence and apoptosis [55][41]. Recent studies revealed the dual effects of p53 on ferroptosis (Figure 2). On one hand p53 can remarkably stimulate ferroptosis through downregulation of SLC7A11 expression or upregulation of spermidine/spermine N’-acetyltransferase 1 (SAT1) and glutaminase 2 (GLS2) expression [56][42]. The inhibition of SLC7A11 by p53 could facilitate cells to ferroptosis via suppressing cysteine uptake. SAT1 and GSL2 genes are both transcriptional target of p53. SAT1 activation can promote the expression of ALOX 15, induce lipid peroxidation and sensitize cells to undergo ferroptosis [57][43]. GLS2 takes part in the process of ferroptosis via promoting cellular ROS production and decreasing GSH [58][44]. ALOX12 (arachidonate 12-lipooxygenase), a member of a nonheme lipoxygenase family of dioxygenases, has been regarded as an essential factor of p53-mediated ferroptotic responses, but not required for GPX4 and ACSL4-mediated ferroptosis [59][45]. On the other hand, p53 can restrain ferroptosis through directly inhibiting dipeptidyl peptidase 4 (DPP4) activities or through inducing cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor 1A/p21 (CDKN1A/p21) in a transcription-independent manner. Absence of p53 could facilitate DPP4 to interact with NADPH oxidase 1 (NOX1) and form NOX1-DPP4 complex, triggering lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. In human colorectal cancer, p53 could inhibit ferroptosis by transforming DPP4 from plasma membrane to nucleus to form DPP4-p53 complex, resulting in the dissociation of NOX1 and suppressing lipid peroxidation [60][46]. The p53 transcriptional target CDKN1A (encoding p21) is an important regulator of p53-dependent cell-cycle arrest, which is required for wild-type p53 stabilization. The p53-p21 transcriptional axis can suppress system Xc− activity and simultaneously decline sensitivity to ferroptosis [61][47]. It is proposed that the converse effect of p53 on ferroptosis may due to different cell types.
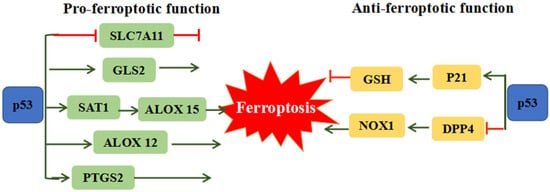
Figure 2. The dual function of p53 on ferroptosis. P53 can promote ferroptosis through regulating SLC7A11, GLS2, SAT1/ALOX15, ALOX12 and PTGS2. Meanwhile, p53 also could restrain ferroptosis via the mediation of p21 and DPP4. ALOX12: Arachidonate 12-Lipoxygenase, ALOX15: Arachidonate 15-Lipoxygenase, DPP4: Dipeptidyl peptidase 4, GLS2: Glutaminase 2, SLC7A11: Solute carrier family 7 member 11, SAT1: Spermidine/spermine N1-acetyltransferase 1.
2.5.3. Heme Oxygenase (HO)-1
HO-1 is the first rate-limiting enzyme in the breakdown of heme, in converting heme into biliverdin, ferrous iron and carbon monoxide. As HO-1 is one of Nrf2 target genes, induction of HO-1 exerts important cytoprotective and antioxidant properties [62][48]. SItudy has demonstrated the important antiferroptotic role of HO-1 in renal proximal tubule cells. The absence of HO-1 significantly increased erastin- and RSL3-induced cell death in renal proximal tubule cells isolated from HO-1−/− mice [63][49]. Similar results reported the negative function of HO-1 in erastin- and sosrafenib-induced hepatocellular carcinoma ferroptosis as knockdown of HO-1 [7][50]. Intriguingly, the regulatory effect of HO-1 on ferroptosis is complicated. Upregulated HO-1 activity could stimulate heme degradation and increase cellular iron level. Emerging evidence has revealed that HO-1 could induce ferroptosis via the induction of iron overload and excessive accumulation of ROS and lipid peroxidation [64,65][51][52]. The overexpression of HO-1 augments erastin-induced ferroptotic cell death in HT1080 cells [64][51]. Therefore, HO-1 has dual effects in ferroptosis process.
References
- Tan, S.; Schubert, D.; Maher, P. Oxytosis: A novel form of programmed cell death. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2001, 1, 497–506.
- Dolma, S.; Lessnick, S.L.; Hahn, W.C.; Stockwell, B.R. Identification of genotype-selective antitumor agents using synthetic lethal chemical screening in engineered human tumor cells. Cancer Cell 2003, 3, 285–296.
- Yang, W.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Synthetic lethal screening identifies compounds activating iron-dependent, nonapoptotic cell death in oncogenic-RAS-harboring cancer cells. Chem. Biol. 2008, 15, 234–245.
- Yagoda, N.; von Rechenberg, M.; Zaganjor, E.; Bauer, A.J.; Yang, W.S.; Fridman, D.J.; Wolpaw, A.J.; Smukste, I.; Peltier, J.M.; Boniface, J.J.; et al. RAS-RAF-MEK-dependent oxidative cell death involving voltage-dependent anion channels. Nature 2007, 447, 864–868.
- Dixon, S.J.; Lemberg, K.M.; Lamprecht, M.R.; Skouta, R.; Zaitsev, E.M.; Gleason, C.E.; Patel, D.N.; Bauer, A.J.; Cantley, A.M.; Yang, W.S.; et al. Ferroptosis: An iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell 2012, 149, 1060–1072.
- Jiang, X.; Stockwell, B.R.; Conrad, M. Ferroptosis: Mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2021, 22, 266–282.
- Zhou, B.; Liu, J.; Kang, R.; Klionsky, D.J.; Kroemer, G.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis is a type of autophagy-dependent cell death. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2020, 66, 89–100.
- Stockwell, B.R.; Friedmann Angeli, J.P.; Bayir, H.; Bush, A.I.; Conrad, M.; Dixon, S.J.; Fulda, S.; Gascon, S.; Hatzios, S.K.; Kagan, V.E.; et al. Ferroptosis: A Regulated Cell Death Nexus Linking Metabolism, Redox Biology, and Disease. Cell 2017, 171, 273–285.
- Yang, W.S.; SriRamaratnam, R.; Welsch, M.E.; Shimada, K.; Skouta, R.; Viswanathan, V.S.; Cheah, J.H.; Clemons, P.A.; Shamji, A.F.; Clish, C.B.; et al. Regulation of ferroptotic cancer cell death by GPX4. Cell 2014, 156, 317–331.
- Kagan, V.E.; Mao, G.; Qu, F.; Angeli, J.P.; Doll, S.; Croix, C.S.; Dar, H.H.; Liu, B.; Tyurin, V.A.; Ritov, V.B.; et al. Oxidized arachidonic and adrenic PEs navigate cells to ferroptosis. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 81–90.
- Yang, W.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Ferroptosis: Death by Lipid Peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol. 2016, 26, 165–176.
- Yan, H.F.; Tuo, Q.Z.; Yin, Q.Z.; Lei, P. The pathological role of ferroptosis in ischemia/reperfusion-related injury. Zool. Res. 2020, 41, 220–230.
- Dixon, S.J. Ferroptosis: Bug or feature? Immunol. Rev. 2017, 277, 150–157.
- Zheng, J.; Conrad, M. The Metabolic Underpinnings of Ferroptosis. Cell Metab. 2020, 32, 920–937.
- Friedmann Angeli, J.P.; Schneider, M.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Tyurin, V.A.; Hammond, V.J.; Herbach, N.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; Eggenhofer, E.; et al. Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat. Cell Biol. 2014, 16, 1180–1191.
- Xie, Y.; Hou, W.; Song, X.; Yu, Y.; Huang, J.; Sun, X.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Ferroptosis: Process and function. Cell Death Differ. 2016, 23, 369–379.
- Feng, H.; Schorpp, K.; Jin, J.; Yozwiak, C.E.; Hoffstrom, B.G.; Decker, A.M.; Rajbhandari, P.; Stokes, M.E.; Bender, H.G.; Csuka, J.M.; et al. Transferrin Receptor Is a Specific Ferroptosis Marker. Cell Rep. 2020, 30, 3411–3423.
- Chen, X.; Li, D.; Sun, H.Y.; Wang, W.W.; Wu, H.; Kong, W.; Kong, W.J. Relieving ferroptosis may partially reverse neurodegeneration of the auditory cortex. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 4747–4766.
- Gao, M.; Monian, P.; Pan, Q.; Zhang, W.; Xiang, J.; Jiang, X. Ferroptosis is an autophagic cell death process. Cell Res. 2016, 26, 1021–1032.
- Hou, W.; Xie, Y.; Song, X.; Sun, X.; Lotze, M.T.; Zeh, H.J., 3rd; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin. Autophagy 2016, 12, 1425–1428.
- Quiles Del Rey, M.; Mancias, J.D. NCOA4-Mediated Ferritinophagy: A Potential Link to Neurodegeneration. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 238.
- Sui, S.; Zhang, J.; Xu, S.; Wang, Q.; Wang, P.; Pang, D. Ferritinophagy is required for the induction of ferroptosis by the bromodomain protein BRD4 inhibitor (+)-JQ1 in cancer cells. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 331.
- Yang, W.S.; Kim, K.J.; Gaschler, M.M.; Patel, M.; Shchepinov, M.S.; Stockwell, B.R. Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E4966–E4975.
- Doll, S.; Proneth, B.; Tyurina, Y.Y.; Panzilius, E.; Kobayashi, S.; Ingold, I.; Irmler, M.; Beckers, J.; Aichler, M.; Walch, A.; et al. ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2017, 13, 91–98.
- Yan, N.; Zhang, J.J. The Emerging Roles of Ferroptosis in Vascular Cognitive Impairment. Front. Neurosci. 2019, 13, 811.
- Dixon, S.J.; Winter, G.E.; Musavi, L.S.; Lee, E.D.; Snijder, B.; Rebsamen, M.; Superti-Furga, G.; Stockwell, B.R. Human Haploid Cell Genetics Reveals Roles for Lipid Metabolism Genes in Nonapoptotic Cell Death. ACS Chem. Biol. 2015, 10, 1604–1609.
- Dierge, E.; Debock, E.; Guilbaud, C.; Corbet, C.; Mignolet, E.; Mignard, L.; Bastien, E.; Dessy, C.; Larondelle, Y.; Feron, O. Peroxidation of n-3 and n-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids in the acidic tumor environment leads to ferroptosis-mediated anticancer effects. Cell Metab. 2021, 33, 1701–1715.
- Liu, Y.; Wang, W.; Li, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Cheng, J.; Jia, J. The 5-Lipoxygenase Inhibitor Zileuton Confers Neuroprotection against Glutamate Oxidative Damage by Inhibiting Ferroptosis. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2015, 38, 1234–1239.
- Li, Q.; Li, Q.Q.; Jia, J.N.; Sun, Q.Y.; Zhou, H.H.; Jin, W.L.; Mao, X.Y. Baicalein Exerts Neuroprotective Effects in FeCl3-Induced Posttraumatic Epileptic Seizures via Suppressing Ferroptosis. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 638.
- Carlson, B.A.; Tobe, R.; Yefremova, E.; Tsuji, P.A.; Hoffmann, V.J.; Schweizer, U.; Gladyshev, V.N.; Hatfield, D.L.; Conrad, M. Glutathione peroxidase 4 and vitamin E cooperatively prevent hepatocellular degeneration. Redox. Biol. 2016, 9, 22–31.
- Haas, U.; Raschperger, E.; Hamberg, M.; Samuelsson, B.; Tryggvason, K.; Haeggstrom, J.Z. Targeted knock-down of a structurally atypical zebrafish 12S-lipoxygenase leads to severe impairment of embryonic development. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 20479–20484.
- Doll, S.; Freitas, F.P.; Shah, R.; Aldrovandi, M.; da Silva, M.C.; Ingold, I.; Goya Grocin, A.; Xavier da Silva, T.N.; Panzilius, E.; Scheel, C.H.; et al. FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature 2019, 575, 693–698.
- Bersuker, K.; Hendricks, J.M.; Li, Z.; Magtanong, L.; Ford, B.; Tang, P.H.; Roberts, M.A.; Tong, B.; Maimone, T.J.; Zoncu, R.; et al. The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature 2019, 575, 688–692.
- Wu, M.; Xu, L.G.; Li, X.; Zhai, Z.; Shu, H.B. AMID, an apoptosis-inducing factor-homologous mitochondrion-associated protein, induces caspase-independent apoptosis. J. Biol. Chem. 2002, 277, 25617–25623.
- Lu, J.; Chen, J.; Xu, N.; Wu, J.; Kang, Y.; Shen, T.; Kong, H.; Ma, C.; Cheng, M.; Shao, Z.; et al. Activation of AIFM2 enhances apoptosis of human lung cancer cells undergoing toxicological stress. Toxicol. Lett. 2016, 258, 227–236.
- Kerins, M.J.; Ooi, A. The Roles of NRF2 in Modulating Cellular Iron Homeostasis. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 29, 1756–1773.
- Dodson, M.; Castro-Portuguez, R.; Zhang, D.D. NRF2 plays a critical role in mitigating lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis. Redox Biol. 2019, 23, 101107.
- Shi, Z.Z.; Fan, Z.W.; Chen, Y.X.; Xie, X.F.; Jiang, W.; Wang, W.J.; Qiu, Y.T.; Bai, J. Ferroptosis in Carcinoma: Regulatory Mechanisms and New Method for Cancer Therapy. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, 12, 11291–11304.
- Fan, Z.; Wirth, A.K.; Chen, D.; Wruck, C.J.; Rauh, M.; Buchfelder, M.; Savaskan, N. Nrf2-Keap1 pathway promotes cell proliferation and diminishes ferroptosis. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e371.
- Houessinon, A.; Francois, C.; Sauzay, C.; Louandre, C.; Mongelard, G.; Godin, C.; Bodeau, S.; Takahashi, S.; Saidak, Z.; Gutierrez, L.; et al. Metallothionein-1 as a biomarker of altered redox metabolism in hepatocellular carcinoma cells exposed to sorafenib. Mol. Cancer. 2016, 15, 38.
- Jiang, L.; Kon, N.; Li, T.; Wang, S.J.; Su, T.; Hibshoosh, H.; Baer, R.; Gu, W. Ferroptosis as a p53-mediated activity during tumour suppression. Nature 2015, 520, 57–62.
- Zhang, W.; Gai, C.; Ding, D.; Wang, F.; Li, W. Targeted p53 on Small-Molecules-Induced Ferroptosis in Cancers. Front. Oncol. 2018, 8, 507.
- Ou, Y.; Wang, S.J.; Li, D.; Chu, B.; Gu, W. Activation of SAT1 engages polyamine metabolism with p53-mediated ferroptotic responses. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2016, 113, E6806–E6812.
- Kang, R.; Kroemer, G.; Tang, D. The tumor suppressor protein p53 and the ferroptosis network. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2019, 133, 162–168.
- Chu, B.; Kon, N.; Chen, D.; Li, T.; Liu, T.; Jiang, L.; Song, S.; Tavana, O.; Gu, W. ALOX12 is required for p53-mediated tumour suppression through a distinct ferroptosis pathway. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2019, 21, 579–591.
- Xie, Y.; Zhu, S.; Song, X.; Sun, X.; Fan, Y.; Liu, J.; Zhong, M.; Yuan, H.; Zhang, L.; Billiar, T.R.; et al. The Tumor Suppressor p53 Limits Ferroptosis by Blocking DPP4 Activity. Cell Rep. 2017, 20, 1692–1704.
- Tarangelo, A.; Magtanong, L.; Bieging-Rolett, K.T.; Li, Y.; Ye, J.; Attardi, L.D.; Dixon, S.J. p53 Suppresses Metabolic Stress-Induced Ferroptosis in Cancer Cells. Cell Rep. 2018, 22, 569–575.
- Parfenova, H.; Leffler, C.W.; Basuroy, S.; Liu, J.; Fedinec, A.L. Antioxidant roles of heme oxygenase, carbon monoxide, and bilirubin in cerebral circulation during seizures. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2012, 32, 1024–1034.
- Adedoyin, O.; Boddu, R.; Traylor, A.; Lever, J.M.; Bolisetty, S.; George, J.F.; Agarwal, A. Heme oxygenase-1 mitigates ferroptosis in renal proximal tubule cells. Am. J. Physiol. Ren. Physiol. 2018, 314, F702–F714.
- Sun, X.; Ou, Z.; Chen, R.; Niu, X.; Chen, D.; Kang, R.; Tang, D. Activation of the p62-Keap1-NRF2 pathway protects against ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Hepatology 2016, 63, 173–184.
- Kwon, M.Y.; Park, E.; Lee, S.J.; Chung, S.W. Heme oxygenase-1 accelerates erastin-induced ferroptotic cell death. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 24393–24403.
- Chang, L.C.; Chiang, S.K.; Chen, S.E.; Yu, Y.L.; Chou, R.H.; Chang, W.C. Heme oxygenase-1 mediates BAY 11-7085 induced ferroptosis. Cancer Lett. 2018, 416, 124–137.
More
