2. Drosophila Trachea as a Model to Reveal Underlying Mechanisms of Tube Morphogenesis
The
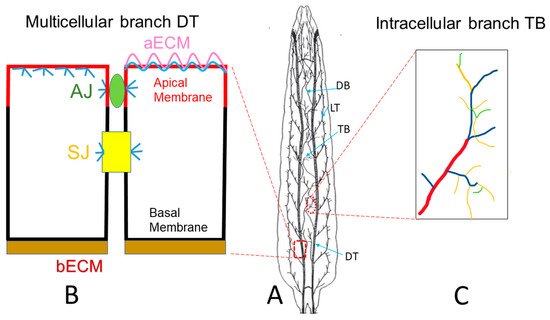
Drosophila trachea is a ramifying interconnected network of epithelial tubes with a monolayer of tightly-adhered polarized cells surrounding a central lumen
[21] (
Figure 1A larval trachea). Following the specification of branch identities, fibroblast growth factor receptor (FGFR) signaling guides the migration of tracheal cells in typical directions to form distinct tubes
[22]. There are a total of four different types of tubes
[23]. Type I multicellular branches are formed by multiple cells connecting together via intracellular junctions, such as the major branch of the trachea, the dorsal trunk (DT). Type II unicellular branches are formed by a linear arrangement of single cells through autocellular junctions, such as the lateral branch (LT) and dorsal branch (DB). Type III tubes are formed by two fusion cells of the adjacent tracheal metameres, with their apical surfaces spanning the inner wall of the ring or donut shape, resulting in seamless tubes without intracellular junctions. Type IV tubes are highly branched intracellular cytoplasmic extensions that form in terminal cells at the tips of the unicellular tubes, such as the branches formed in larval terminal cells. Tube morphogenesis has been extensively studied in Type I multicellular branches such as the DT (
Figure 1B) and Type IV larval terminal branches (
Figure 1C). In the DT, neighboring cells are connected together by adherens junctions (AJs) and septate junctions (SJs), which are equivalent to tight junctions (TJs) in mammals. SJs control the paracellular barrier function of the trachea while AJs stabilize cell–cell adhesion through the actin cytoskeleton. In
Drosophila, the SJ is basal to AJ. In addition, cortical actin is highly concentrated beneath the apical membrane as well as the AJ and SJ and to a lesser degree at the basolateral membrane.
Figure 1. Drosophila tracheal branches. (
A) Schematic larval trachea, an interconnected tubular network. The dorsal trunk (DT) is the multicellular major branch of the trachea. The lateral trunk (LT) and dorsal branch (DB) are unicellular branches. Terminal branches (TB) are intracellular branches, which are formed at the tip of unicellular branches. (
B) Neighboring cells in DT are connected together by adherens junctions (green AJ) and septate junctions (yellow SJ), the latter of which is equivalent to the tight junction in mammalian systems. Cortical actin (blue) is highly concentrated beneath the apical membrane (red) as well as at the AJ and SJ, and relatively weaker at the basolateral membrane (black). Tracheal cells secrete apical luminal matrix (pink aECM), together with actin (blue), which forms a barrier to protect the apical membrane (red). (
C). Schematic terminal branches (TB), which are formed in terminal cells, residing at the tip of the unicellular branch such as DB. There are 4 types of TB branches, including Type I (red), Type II (blue), Type III (yellow) and Type IV (green). (
A) has been adapted from
[24].
During tracheal development, the tracheal cells secrete material apically to form a transient apical luminal cable at the mid embryonic stage. This apical extracellular matrix (aECM) coordinates apical membrane growth and cell contractility to control tube growth
[25][26][25,26]. This aECM cable is then degraded and absorbed by tracheal cells
[27][28][27,28]. From the late embryonic stages through the larval stages, the tracheal cells secrete aECM material to form taenidial ridges that cover the apical membrane. This aECM is soft and flexible to provide ventilation but is also tight enough to function as a protective barrier that shields the tubes from dehydration, infections, and environmental stresses
[29][30][29,30]
The formation of functional tracheal tubes depends on the sufficient transport of apical proteins, controlled plasma membrane expansion, effective cell junction maintenance, proper connection between the aECM and apical membrane, and coordinated cortical cytoskeleton reorganization. For example, defects in components of the apical secretion pathway such as COPI and COPII complex components Gartenzwerg (garz) and Sec24CD, respectively, lead to the defective secretion of luminal proteins
[31][32][31,32]; mutations in
lachesin or
sinuous, which encode SJ components, lead to the defective secretion of aECM proteins
[33][34][33,34]; mutations in
dumpy or
uninflated (uif) disrupt the connection between apical membrane and aECM
[35][36][35,36]; the formin DAAM regulated actin nucleation and the subsequent polymerization through RhoA is required for actin ring formation, which is critical for the formation of taenidial folds
[37][38][37,38]; mutations in either
tramtrack or
grainy head cause defective apical membrane expansion
[39][40][39,40]. Taken together, disruption in any of these processes will lead to malformations in the trachea.
In addition to Type I multicellular tubes, such as the DT, tube morphogenesis has also been extensively studied in Type IV intracellular branches in larval terminal cells. Type IV terminal branches contact target tissues for gas exchange, which is similar to alveoli in human lung. The differentiation of terminal cell involves two processes, branching and subcellular lumen formation. Branching in the terminal cells heavily relies on cell migration. FGFR signaling, likely through the downstream GTPases Rac1 and Rac, allows cytoskeleton remodeling and filopodia formation for terminal cells to start branching
[41]. Following the branching morphogenesis, it is essential to form a lumen within these branched structures primarily for the transport of gases.
Terminal cell branching and subcellular lumen formation are intimately associated. Subcellular lumen formation involves the structured expansion of the apical plasma membrane through the dynamic modulation of vesicle transport, which depends on the reorganization of the cytoskeleton. The initial subcellular lumen develops by invagination of the apical membrane inside the cell. The ingrowing apical membrane accumulates apical markers such as the PAR-polarity complex components aPKC/Par6/-Baz and Crumbs (Crb)
[42][43][42,43]. Following apical membrane formation, aECM material is accumulated inside the lumen creating the aECM
[44]. The growth of the subcellular lumen depends on intracellular trafficking of membrane and lumen material
[41]. For example, Rab11 is involved in the trafficking of recycled and newly synthesized proteins to the apical plasma membrane
[45]. In addition, other endosomes coordinate plasma membrane redistribution. For example, organelles carrying late endosomes and multivesicular bodies (MVBs) markers act as a transit station to redistribute the membrane apically and basally in terminal cells
[46]. Therefore, coordination between cytoskeleton reorganization and vesicular trafficking is critical for terminal branch formation.
Unlike the embryonic tracheal system, which develops in a stereotypical and genetically controlled manner, the development of the larval trachea exhibits plasticity and also adapts to particular oxygen needs of the different tissues of the body. Insufficient oxygen levels activate the hypoxia signaling pathway, which is largely regulated by hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α)
[47]. HIF-1α is a transcription factor that is considered to be a master transcriptional regulator of O2 homeostasis
[48]. HIF-1α induces the transcription of genes related to angiogenesis, cell proliferation/survival, as well as inflammation
[49][50][49,50]. The HIF-1α signaling pathway is activated in smokers with COPD. Thus, the increased expression of HIF-1α, VEGF, and VEGF receptor 2 were associated with decreased lung function, reduced quality of life, and progression of COPD
[51]. The
Drosophila functional homolog of HIF-1α is Similar
[52]. Hypoxia-induced activation of Similar leads to over branching caused by elevated
Drosophila FGF, Branchless (Bnl)
[53] as well as increased ROS levels, similar to what was observed in COPD patients
[54].
The
Drosophila adult tracheal system, called air sacs, forms during the pupal period. The development of the air sacs starts from the third instar larval stage. The air sac precursor cells bud from the larval trachea, proliferate, and migrate towards the wing imaginal disc to form air sac primordia (ASPs). During pupal stages, the cells in ASPs migrate to form branches. Thereafter, they cease migrations and begin to elaborate into air sacs, which will further expand in adults. The air sacs are associated with numerous bundles of trachea, which extensively interdigitate with flight muscle to supply oxygen
[55]. The development of ASPs involves three processes: cell proliferation, downregulation of adhesion molecules at tip cells, and extracellular matrix remodeling.
The morphogenesis of ASP is directed by FGFR signaling-induced outward migration of distal tip cells towards the wing imaginal disc, which secretes the
Drosophila FGF, Bnl
[55][56][55,56]. In addition, FGFR signaling induces the expression of epithelial growth factor (EGF)/vein, which activates epithelial growth factor receptor (EGFR) signaling to stimulate cell proliferation and survival
[56][57][56,57]. The turnover of EGFR and FGFR is mediated by endosomes. For example, compromised endosomal sorting complex leads to impaired ASP development
[58]. For the proper cell migration during ASP development, down-regulation of cell adhesion molecules such as
Drosophila E-cadherin (shotgun), and
Drosophila β-catenin (armadillo) is required in the tip cells
[59]. Furthermore, remodeling of the ECM is necessary to facilitate the growth of ASPs. ASPs arise from a region of a tracheal branch that is directly juxtaposed to the wing disc
[55]. This tracheal region lacks a visible tracheal-specific ECM, called basal lamina (BL), which is proteolyzed by the endopeptidase Mmp2
[60][61][60,61]. It was reported that elevated BL in
mmp2 mutants leads to stunted ASP growth and failed formation of functional air sacs
[61]. Another class of proteases, cathepsins, have also been implicated in ECM remodeling around the ASP
[59]. The reduced BL thickness allows for greater FGF signaling response, similar to what is observed during mammalian lung development
[62][63][62,63].
3. Drosophila Trachea as a COPD Model to Systematically Study the Development of COPD
Long-term CS exposure is by far the most important risk factor for COPD. Thus, chronic CS exposure has been used to investigate the mechanisms of COPD in mouse models
[64][65][64,65]. Overall, for COPD, the failure of repair mechanisms to cope with the increased ROS and inflammation in the lungs leads to the loss of functional alveolar structure. As such, signaling pathways associated with tissue repair and ROS production have been extensively studied. For example, tissue repair relevant Wnt signaling
[11] and JAK/STAT signaling
[66], as well as cytokines (IL5 and IL6) that activate the JAK/STAT signaling, have been identified as potential drug targets
[66]. In addition, the Nrf2 (NF-E2-related factor 2) pathway is also strongly activated by CS exposure and linked to COPD development
[67]. The Nrf2 pathway is a potential drug target due to its function in controlling the expression of antioxidant genes that ultimately exert anti-inflammatory functions
[68]. Despite the progress made towards COPD research, the molecular mechanisms underlying the development of COPD are still not well understood. This is reflected by the lack of effective treatments for this disease
[15][69][15,69]. Thus, informative and druggable animal models are highly valued and desired. A simple model, such as the
Drosophila trachea, may provide promising new candidates that are complementary to the current knowledge of COPD.
CS exposure affects functions in various organs in
Drosophila. CS exposure has been shown to increase heart rate and cause alterations in the dynamics of the transient increase in intracellular calcium in myocardial cells
[70]. CS and nicotine exposure have also been linked to changes in
Drosophila sexual behavior, larval brain size, and the adult fly dopaminergic system
[71][72][71,72]. Recently, the CS-induced
Drosophila COPD model showed a complex set of pathological phenotypes that resemble those seen in human COPD patients
[73]. These phenotypes include premature death, reduced physical activity, enhanced metabolic rates, and reduced respiratory surfaces in
Drosophila trachea. Due to the short life span of fruit flies, the survival rate was measured within 2 weeks, compared to a survival rate of months in the mouse model. The physical activity of a large quantity of flies was automatically evaluated by the
Drosophila activity monitoring system
[74]. Metabolic rate was measured by body fat content using ELISA
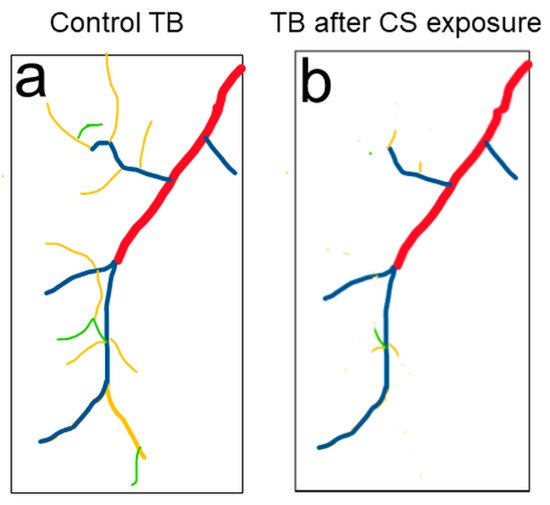
[75]. The reduced respiratory surface was analyzed in live 2nd instar larval terminal cells by using a btl:GFP transgenic line without an invasive procedure (
Figure 2). Similar to the reduced alveolar surface area observed in human COPD lungs, Type III and Type IV branches in CS-induced COPD
Drosophila larvae show the most obvious COPD phenotype: reduced numbers and overall length
[73]. Comparably, as chronic CS exposure in the mouse model leads to the development of COPD, chronic CS exposure also leads to the development of COPD-like phenotypes in
Drosophila larval trachea.
Figure 2. Tracheal morphology changes were observed in 2nd instar larvae upon CS exposure. (a) Schematic of a terminal cell of the dorsal branch in the third segment of Drosophila 2nd instar larvae. Terminal branches (TB) include Type I (red), Type II (blue), Type III (yellow) and Type IV (green) branches. (b) Type III (yellow) and Type IV (green) TBs are significantly reduced upon CS exposure.
The early junctional defects upon pollutant exposure in the mouse model suggest other early structural damages. These damages can be studied in the
Drosophila larval multicellular DT. Various structures, including the aECM, basal ECM (bECM), apical membrane, basal membrane, junctions, and cytoskeleton in DT, can be easily observed using available transgenic lines with fluorescently-tagged structural proteins in live organisms (
Figure 1B). These lines include the aECM (Vermiform:RFP and Serpentine:GFP
[76] and bECM (type IV collagen Col41A:GFP
[77]), apical membrane (Crumb:RFP and Crumb:GFP
[78]), basal membrane (αSpectrin:GFP
[79]) actin cytoskeleton (actin:GFP
[80], AJ junction (DEcad:GFP, RFP
[81]), SJ (Discs Large:GFP
[76]). The later structural damage, reduced numbers, and length in terminal branches can be observed in larval trachea using btl:GFP lines
[82]. Therefore, the
Drosophila larval trachea can be used as a COPD model to systematically study the timeline of early- and late-stage structural damage upon chronic pollutant exposure.
In addition to the timeline of structural changes in the
Drosophila COPD model, their relevance to known molecular mechanisms and components of tube morphology can be tested. For example, the activation of the MAPK/ERK pathway leads to the disruption of the tight junction
[83]. The RhoA/ROCK signaling pathway leads to disruption of the tight junction through the aggregation of cytoskeletal actin
[84]. Pollutant exposure could also cause structural damages through other mechanisms such as defective apical membrane expansion, aECM formation, or tube size maintenance. Similarly, the involvement of the underlying mechanisms, such as the protein trafficking pathway and cytoskeleton reorganization, in the development of COPD can be further studied in the larval trachea.
Along with structural damage, the intracellular production of ROS can be indirectly measured by ROS-inducible gstD (glutathione S transferase D)-GFP reporter, gstD-GFP
[85]. Overall levels of peroxides can be detected using 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescein (H2DCF) followed by imaging as described
[86]. Furthermore, increased concentrations of multiple cytokines, such as TNFα and interleukins, orchestrate chronic inflammation in COPD
[12][13][87][12,13,87]. The only
Drosophila TNF superfamily member is Eiger (Egr)
[88][89][88,89]. Three cytokine molecules, namely Unpaired (Upd), Upd2 and Upd3, function similarly as interleukins
[90][91][92][90,91,92]. Reporter lines
egr-lacZ and
upd-lacZ lines are available to measure the expression of these inflammatory cytokines
[73]. It is also possible to observe the production of these inflammatory cytokines in vivo by generating fluorescent protein-tagged reporter lines. Previous studies in
Drosophila trachea have revealed genes, pathways, and cellular processes involved in tube morphogenesis. The relevance of these mechanisms to the development of COPD can be further studied in the
Drosophila trachea. Thus, the larval trachea provides an excellent model to systematically study the timeline of early and late structural damage, production of ROS, and inflammation upon pollutant exposure in vivo. However, the larval trachea is roughly equivalent to adolescence, while the adult trachea is comparable to adult human lungs. A recent study showed that early COPD in young adults is associated with clinical COPD 10 years later
[93]. Therefore, the mechanisms of COPD revealed by studies of
Drosophila larval trachea would be more relevant to the initiation of COPD in young adults. Although the current knowledge of the
Drosophila adult trachea is still limited, studies of the development of air sacs provide opportunities to unveil mechanisms of COPD in relation to the disease progression in adult trachea. For example, the morphological changes in the air sac (
btlenhancer-mRFP1moesin [57]), tracheal BL (collagen IV:GFP and Perlecan:GFP
[61]), and junction proteins (Dα-cat-GFP, RFP
[81]) can be visualized through fluorescently-tagged structural proteins in the late pupal stage, when air sacs form.