Heavy metal contamination affects lives with concomitant environmental pollution, and seaweed has emerged as a remedy with the ability to save the ecosystem, due to its eco-friendliness, affordability, availability, and effective metal ion removal rate. Heavy metals are intrinsic toxicants that are known to induce damage to multiple organs, especially when subjected to excess exposure. With respect to these growing concerns, this review presents the preferred sorption material among the many natural sorption materials. The use of seaweeds to treat contaminated solutions has demonstrated outstanding results when compared to other materials. The sorption of metal ions using dead seaweed biomass offers a comparative advantage over other natural sorption materials. This article summarizes the impact of heavy metals on the environment, and why dead seaweed biomass is regarded as the leading remediation material among the available materials.
- heavy metals
- seaweed
- biosorption
- aqueous solution
- remediation
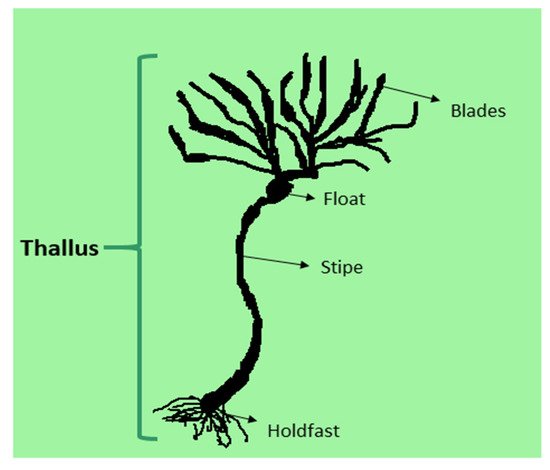
1. Structure and Classification of Seaweed
| Common Name (Phylum) | Body Form | Size | Pigments | Colour Composition | Cell Walls |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brown algae (Phaeophyta) | Multicellular | 60 cm–60 m | Chlorophyll, Fucoxanthin, and several other xanthophylls | Golden-brown, Greenish-brown | Cellulose, Alginate, Fucoidan |
| Red algae (Rhodophyta) | Multicellular | 50 cm–2 m | Chlorophyll, Phycocyanin, Phycoerythrin, and several xanthophylls | Brownish red, Purple | Cellulose, Xylans, Galactans |
| Green algae (Chlorophyta) | Unicellular, Colonial, Filamentous, Multicellular | 1–1000 μm | a and b Chlorophyll and several xanthophylls | Green | Cellulose Hydroxyl –proline glucosides β- xylans, β-mannans |
2. Seaweed: Metal Ion Biosorption Material
3. Various Natural Materials Used for Sorption
| Materials Used | Heavy Metals | References |
|---|---|---|
| Polymers | Fe and Cr | [21][74] |
| Sawdust and tree barks | Hg, Pb, and Zn | [22][75] |
| Electronic waste along with galvanic wastes | Cu, Ni, Mn, Pb, Sn | [23][76] |
| charcoal: | Cr(III) | [24][77] |
| Clay | Cr(III) | [25][78] |
| Fungi | Cr, Fe | [26][79] |
| Dead biomass | Cr | [27][80] |
| Peat moss | Cr, Fe | [28][81] |
| Peanut shells, Rice husk, Straw, and walnut cover | Cr, Cu, Ni | [29][82] |
| Cocoa shell | Al, Cd, Co, Cr, Cu, Fe, Mn, Ni, Pb, and Zn | [30][83] |
| Coconut husk | Cr, As | [29][82] |
| Caol and fly ashes | Cr, Cu, Ni | [31][84] |
| Banana pith and peels | Ni, Pb | [32][85] |
| Cassava fiber | Pb, Co | [33][86] |
| Chicken feathers | Al, As | [34][87] |
| Sheep manure wastes | Ca, Cd | [35][88] |
| Sunflower | Co, Cr | [36][89] |
| Rice byproducts | Cu, Fe | [37][90] |
| Orange peels | Cu, Fe, Hg | [38][91] |
| Palm kernel fiber | Fe, Hg | [29][82] |
| Grape stalks | Cr, Fe, Hg | [39][92] |
