Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Marcin Włodarczyk and Version 2 by Rita Xu.
Crohn’s disease (CD) is a relapsing systemic inflammatory disease that can cause persistent transmural inflammation anywhere along the gastrointestinal tract.
- mesenchymal stem cells
- perianal fistula
- Crohn’s disease
1. Introduction
Crohn’s disease (CD) is a relapsing systemic inflammatory disease that can cause persistent transmural inflammation anywhere along the gastrointestinal tract. A substantial number of CD patients present with various anorectal pathologies including perianal abscesses, fistulas, hemorrhoids, skin tags and fissures [1]. Perianal fistulas are described as an abnormal connection between the anal canal and the perianal skin.
According to population-based studies, around one in every four CD patients will develop perianal fistula at some point in their life. Patients with colonic or rectal localization of intestinal inflammatory lesions are at an even higher risk, at about 92% [2]. Diagnosis and management of perianal Crohn’s Disease (PCD) requires an expert, multidisciplinary approach, considering that most of the perianal fistulas are defined as complex (meaning they involve the upper part of the sphincters, are complicated with a perianal abscess, or have multiple external openings or penetrate to vagina). These patients’ quality of life is considerably impaired due to persistent drainage, pain, recurrent perianal sepsis and continuous need to seek medical attention [3]. Patients with perianal fistula are also more likely to have extraintestinal manifestations of CD including arthritis, oral ulcerations and skin manifestations.
The management of PCD remains a challenge, as 37% of patients experience refractory disease. The relapse rate is estimated at around 40% in 5-year follow-ups [4]. For this reason, many patients are exposed to the necessity to repeatedly take immunosuppressive medications, which increases the risk of opportunistic infections. Furthermore, about 90% of them undergo numerous surgical interventions, becoming liable to complications, including fecal incontinence [2][4][2,4]. Even with combined pharmacological and surgical therapy, 40% of patients do not achieve remission and are left with active disease, facing the risk of undergoing proctectomy.
This perspective encouraged us to seek more desirable treatment options to provide higher therapy effectiveness with a lack of adverse effects and lower risk of incontinence. Recently, promising results using local injections with mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) have been reported. This treatment has been proven to effectively induce as well as maintain fistula closure [5][6][5,6].
MSCs are stromal cells that have the ability to self-renew and differentiate into adipocytes, myocytes, osteocytes and chondrocytes. Moreover, they have powerful immunomodulatory effects and are able to reduce escalated inflammation, as they inhibit the proliferation and function of T, B and NK cells [6]. MSCs are present in almost all tissues; however, they are most commonly isolated from bone marrow, adipose tissue or an umbilical cord. In the last decade, physicians have been able to activate and supplement these cells to treat a variety of conditions, for instance, many autoimmune diseases. At present, multiple new studies on the use of MSCs for Multiple Sclerosis, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, cancer, lupus and Parkinson’s are being carried out [6].
2. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Mechanism in Crohn’s Disease Perianal Fistula
To this day, the exact mechanism in which MSCs heal perianal fistulas remains unknown, as no human studies have clarified it. It likely results from their immunomodulatory properties [7][8]. Firstly, they migrate to the sites of injury or inflammation and directly spur tissue healing by tissue specific differentiation and the secretion of factors with the ability to promote epithelial cell proliferation and angiogenesis. MSCs help maintain an anti-inflammatory habitat by modulating the function of macrophages, lymphocytes and dendritic cells.
Regarding CD, MSCs’ ability to upregulate the CD4+ T cell subset is particularly important, as patients with CD are known to have a deficiency of those cells [8][9][9,10]. Furthermore, MSCs secrete various anti-inflammatory particles (including TGFB1, growth factors, interleukins and indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase) and suppress M1 macrophages, cytotoxic T cells and dendritic cells [10][11]. They play a significant role in healing of the fistula, owing to their role in angio- and mitogenesis, as well as immunomodulatory effect [11][12]. They reduce inflammation in tissues around the fistula and accelerate healing. Due to its’ promising preclinical studies results, clinicians are more and more interested in CD treatment using MSCs.
3. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Application in Perianal Crohn’s Disease
Regrettably, there is no clear surgical protocol for the administration of stem cells in PCD therapy. To start with, there are no studies comparing side by side the use of adipose- vs. bone-marrow-derived MSCs. Adipose-derived stem cells are usually preferred because they are much easier to harvest with the use of liposuction. Furthermore, they are known to have a higher replication rate and longer proliferation in culture [5][12][5,13]. They might also induce a stronger immunomodulatory effect, due to the fact they have higher secretion levels of cytokines, including TGFB1 and IL-6 [8][9].
MSCs are typically used locally, to avoid side effects and help keep cells in direct contact with inflamed tissue [13][14]. In that case, either autologous or allogenic cells can be used. During treatment with the use of autologous cells, extraction and application happens in the course of the same procedure [12][14][13,15]. Thus, MSCs are injected without previous expansion, which results in their low dose [15][16].
According to a meta-analysis based on four clinical trials involving different doses of stem cell therapy ranging from 1 × 107 to 9 × 107 MSCs per mL, the dose of 2 × 107 and 3 × 107 cells/mL were characterized by a highest rate of fistula healing in Crohn’s patients [16][17]. However, the mentioned study is strongly limited by a low number of included patients (n = 31). Due to the lack of other studies based on a larger group, it is difficult to propose specific guidelines regarding the dosage of MSCs. Therefore, it is crucial to continue such studies.
However, allogenic cells are endowed with excellent homogeneity [17][18]. They might not create antibodies, which would be clinically relevant. Cells are previously expanded and frozen. It only takes 4 days to defrost them and prepare for administration. Allogenic MSCs are also considered particularly beneficial in CD.
To date, no definite conclusion about an optimal dosage has been made. According to Molendijk et al.’s study, the best results are achieved with the use of 30 million cells [18][19]. The most commonly used concentration contains 5 × 106 MSCs per mL; however, no studies have directly compared the outcome determined by the use of different MSCs concentrations.
Preoperatively, each patient should be thoroughly examined, to prepare a precise description of the fistula tract. It is necessary to estimate the needed MSCs volume. A magnetic resonance imaging or endorectal ultrasonography (ERUS) can be found helpful to provide information concerning the type, location and presence of branches of the fistula.
Prior to surgery, any active infection should be controlled by antibiotics, and any abscesses greater than 2 cm should be incised and drained. Fistula biopsy should also be considered to rule out any type of local neoplasia, since MSCs might promote tumor growth. There is no reason to discontinue systemic treatment for the CD.
As far as anesthesia is concerned, most frequently used local anesthetics such as lidocaine can cause a cytotoxic effect to the MSCs when in direct contact. For that reason, local anesthesia ought to be avoided. If necessary, the recommended approach is to perform a pudendal block. This concern should also be kept in mind if the MSCs are obtained by liposuction. During this procedure, the use of local anesthetics is discouraged, as they weaken the MSCs’ immunomodulatory properties and viability.
The antiseptic used to prepare the surgical site must not be harmful to the cells. Thus, the use of alcoholic, povidone solutions or hydrogen peroxide is discouraged. Rather, it is advised to use octenidine, chlorhexidine or normal saline.
The next step is to identify the internal fistula opening using a probe, or by injecting normal saline through the external orifice. To create an optimal environment for healing, the fistula tract needs to be mechanically debrided using curette and irrigated with saline. Afterwards, the internal opening needs to be securely closed with the use of an absorbable suture.
MSCs can be delivered in direct injections, united with fibrin glue or impregnated on a fistula plug. It is believed that healing rates are higher when scaffolding material is used, due to the fact that glue or plug help maintain MSCs at the desirable location. On the other hand, a randomized clinical trial involving 200 patients comparing the efficiency of treatments using MSCs, MScs mixed with fibrin glue or fibrin glue alone proved there are no significant differences in the healing rate with the use of these three methods. In Figure 1 we have provided a general overview regarding MCSc application process.
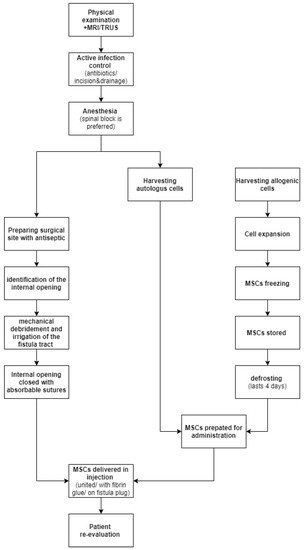

Figure 1. MSCs application process.
