Your browser does not fully support modern features. Please upgrade for a smoother experience.
Please note this is a comparison between Version 1 by Norman Toro and Version 2 by Rita Xu.
Heap leaching is a firm extractive metallurgical technology facilitating the economical processing of different kinds of low-grade ores that are otherwise not exploited.
- hydrometallurgy
- leaching
- gangues
- clays minerals
- heap leaching
- agglomeration
1. Introduction
According to Toro et al. [1], copper mining is an industry that is in constant growth, and approximately 25 million tons are produced annually worldwide [2]. Among the copper minerals on the planet, the vast majority correspond to sulfide ores [3]. Within these copper minerals, chalcopyrite stands out as the most abundant, representing 70% of all minerals that contain copper in the Earth’s crust [4][5][6][7][4,5,6,7]. Copper is recovered from these minerals mainly through flotation, followed by pyrometallurgical processing, representing 80–85% of world’s copper production [8][9][8,9]. However, pyrometallurgical treatment is difficult and expensive for low-grade copper ores producing high emissions of sulfur dioxide (SO2), NOx, and CO2, which cause problems, such as acid rain and increased local pollution [10][11][12][10,11,12].
In addition, flotation techniques generate a large amount of waste, which results in tailings dams with a high possibility of generating acid mine drainage (AMD) due to the oxidation of minerals with a high presence of pyrite [13]. The latter is essential to consider since the drainage of mining waste rocks is one of the most important environmental challenges facing the global mining industry due to its dynamics and persistence [14][15][16][17][14,15,16,17]. AMD creates a severe environmental problem allied with mining and mineral processing due to its very low pH (<3.0) and high concentrations of possibly toxic dissolved metals, metalloids, and sulfate. Without appropriate management, AMD can result in considerable environmental degradation, water, and soil contamination, severe health deterioration among neighboring communities, and damaged biodiversity in aquatic ecosystems [18][19][20][21][18,19,20,21].
All of the above has led to the need to investigate the development of a profitable hydrometallurgical process to treat these minerals since hydrometallurgy is a good alternative to process both oxidized minerals and sulfide minerals environmentally friendly [22][23][24][22,23,24]. Heap leaching is a hydrometallurgical approach and continuously developing mineral processing and extraction technology that is gaining attractiveness and recognition in the mineral industry. Heap leaching has solid benefits over traditional metallurgical methods where economically viable options have become limited [25].
2. Heap Leaching as an Alternative Route in Hydrometallurgy
For Watling et al. [26], certain issues motivate the use of hydrometallurgical methods, even for sulfide ores, for example, the high copper demand; the continuous decay of the ore grades; and the extensive exploitation of oxide and secondary sulfide minerals. The low-grade may eventually leave large amounts of low-grade chalcopyrite ores as an important, but so far, uneconomical source of copper. This has prompted the use of processes such as heap leaching. Heap leaching began to be used in the middle of the 20th century.
Nevada’s gold and silver heap leaching as the “birthplace” of modern gold heap leaching [25][27][28][25,27,28]. The first modern copper heap leach operation may have been the Bluebird copper oxide mine in 1968, followed in the early 1970s by other small operations in the United States. Uranium producers have already utilized the heap leaching of uranium through either acid or alkaline solutions since the late 1950s. Large-scale heap leaching can be said to have started in 1980 when three major copper projects were commissioned in Chile, and, at approximately the same time, a large number of gold projects were commissioned in the United States [25].
Heap leaching has been developed for many different types of minerals, climates, and operations of any size [25]. Further than copper oxide, uranium, and gold, today there are an extensive variety of applications, including copper sulfide ores, gold-bearing pyritic ores, and non-metallic minerals (such as saltpeter [29]) as well as soil remediation [25][30][31][25,30,31]. Heap leaching is typically applied for low-grade deposits; however, it might also be applied to small higher-grade deposits in remote or politically high-risk locations to reduce capital cost. Heap leaching from low-grade ores has contributed to the total global production of copper, gold, silver, and uranium [25][32][33][25,32,33]. Heap leaching has also been considered for zinc [25][34][35][25,34,35] and nickel [36] and more lately for platinum group metal (PGM)-bearing ores and electronic scrap [37][38][37,38].
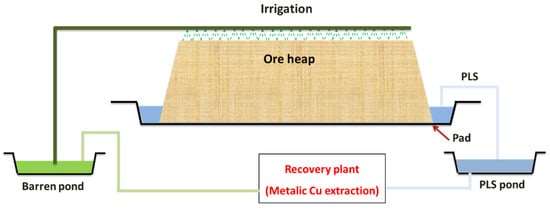
In heap leaching, the crushed ore is stacked on an impermeable pad, and leaching reagents (a strong acid, commonly sulfuric acid for copper or nickel ores or a dilute cyanide solution for gold and silver-bearing ores) are added by irrigation from the top. The wanted mineral is extracted, and the solution is gradually loaded as it penetrates through the pile. Leaching may be aided by microorganisms resident within the ore bed, particularly in the existence of sulfide minerals. A drainage system collects the pregnant leach solution (PLS) at the base of the heap. The PLS is then pumped to the processing units to extract the value metal.
The barren leach solution (BLS) is sent to the barren solution pond, from where, after solution makeup, it is reapplied to the heap’s surface [25]. A typical heap leaching circuit is shown in Figure 1. This process is conducted in leaching piles, where their typical height is between 4 and 10 m, although in some cases, they can reach 18 m [28]. In addition, the largest sizes generally range between 10 and 40 mm in heap leaching, and sizes less than 6 mm are unacceptable. This is because small-sized particles affect the heap’s permeability, mainly clay minerals result in increased clogging of heaps over time due to swelling and gradual decrepitation [39].
For the leaching process to be efficient, the fine particles tend to agglomerate around the larger particles with water and concentrated sulfuric acid, a process known as “curing.” This process improves the strength of the material while having good mineral permeability in heap leaching. In addition, it helps to achieve adequate heap heights, improve copper recovery rates, and control processing times [40][41][40,41]. It is worth mentioning that another emerging method is bio-hydrometallurgy, which plays an important role in the recovery of copper with economic, environmental, and social benefits. To date, it has been reported that many investigations on the acid bioleaching of secondary [42][43][44][45][46][42,43,44,45,46] and primary sulfides have presented good results.
3. Effect of Ore Mineralogy on Copper Heap Leaching Performance
Copper heap leach projects are sometimes evaluated without adequate mineralogy, despite the lack of a clear and comprehensive mineralogical sturdy, which could significantly affect the heap efficiency and expected recovery and operating costs [47][48][49][47,48,49]. Heap leaching processes operate over approximately three months for sulfide minerals in chlorinated media and lower ore grades in typical operations. This is why several studies have emphasized the essential need to characterize the mineral’s physical, chemical, and mineralogical properties to be leached [49][50][49,50].
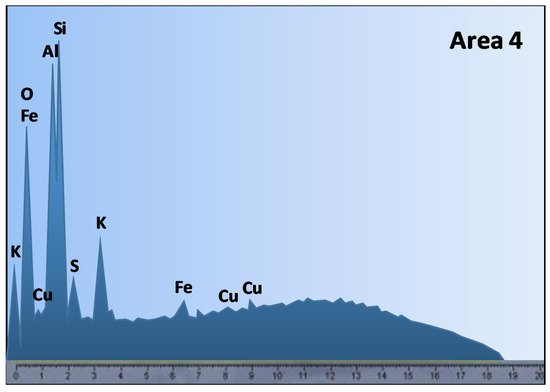
Problems with copper heap leaching may arise from the ore mineralogy, more specifically, the presence of reagent consuming gangues and clays minerals. Ghomi et al. [51] analyzed the effect of polar organic reagents on chalcopyrite leaching, Scanning Electron Microscopy-Energy Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) analysis was performed (Figure 2), where the presence of aluminosilicate or clay-type gangues was detected in area 4, with a high percentage of aluminum, silicon, and oxygen, which can be corroborated by Figure 3.
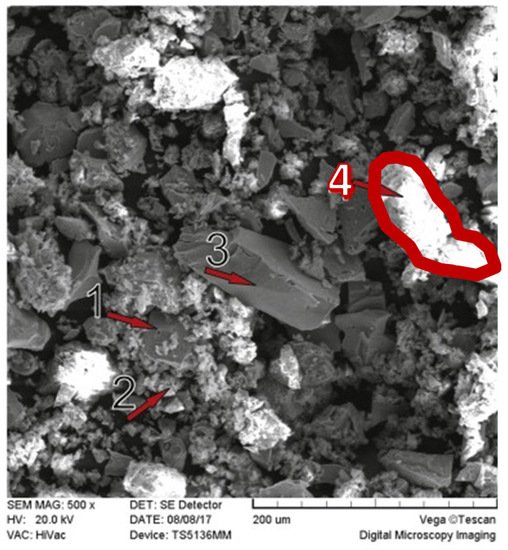


Figure 2. SEM image of the chalcopyrite leaching residue after 120 min of leaching in 1.5 mol/L of [H2SO4], 2 mol/L of [H2O2], and 2 mol/L of isopropanol solution at 65 °C (Modified from [51]).
For their part, Helle and Kelm [52] studied leaching with sulfuric acid, focusing on the retention of copper by the reactive gangue. Gangue minerals can considerably affect acid consumption and copper recovery and change the acid requirements in different unit operations [53][54][53,54]. Critical factors for acid consumption in oxidized copper ores include the presence of carbonate; the presence of other short-term and long-term acid consumers; and the degree of acid adsorption by different non-carbonate minerals (e.g., clays, oxides of hydrated iron, highly porous copper minerals, and/or mineral-forming silts) [48].