CAD (Carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 2, Aspartate transcarbamoylase, and Dihydroorotase) is a multifunctional protein that participates in the initial three speed-limiting steps of pyrimidine nucleotide synthesis. Over the past two decades, extensive investigations have been conducted to unmask CAD as a central player for the synthesis of nucleic acids, active intermediates, and cell membranes. Meanwhile, the important role of CAD in various physiopathological processes has also been emphasized.
- carbamoyl phosphate synthetase
- aspartate transcarbamoylase
- dihydroorotase
- regulation
- pyrimidine
- diseases
- cancer
1. Introduction
The route of formation of carbamoyl phosphate (CAP) was first discovered in microorganisms in 1955 [1]. Later, genetic studies revealed the role of enzymatic synthesis of CAP in the pyrimidine pathway in Neurospora [2,3][2][3]. It was also found that carbamyl phosphate synthetases (CPSases) CPS-1 and CPS-2 provide CAP pools for arginine and pyrimidine synthesis, respectively [4,5,6][4][5][6]. In animals, aspartate transcarbamoylase (ATC) and dihydroorotase (DHO) were subsequently co-purified with CPS-2. These three enzymes form a single multi-enzymatic protein named CAD to participate in the de novo pyrimidine pathway in mammals [7,8][7][8].
Over the past two decades, studies from dozens of labs have revealed that CAD takes part in the de novo pyrimidine nucleotide synthesis, and plays a leading role in cellular and organismal physiology in various forms of life [9,10,11,12,13][9][10][11][12][13]. Moreover, CAD is also involved in protein glycosylation and biosynthesis of phospholipids [14]. In recent years, extensive studies have been carried out on the molecular functions and pathways of CAD to address the unanswered questions in this area. In this review, we provide an overview of the current understanding of CAD and its critical roles in metabolism, physiological regulation, as well as disease progression.
2. CAD Structure and Function
CAD is a multifunctional protein that takes part in the initial three speed-limiting steps of pyrimidine nucleotide synthesis. Moreno-Morcillo et al. have shown that CAD is a hexamer of a 243 kDa polypeptide chain [15]. Human CAD involves the concerted action of four domains: glutamine amidotransferase (GATase), carbamylphosphatesynthetase II (CPSIIase), aspartate transcarbamylase (ATCase), and dihydroorotase (DHOase) ( Figure 1 A). CPSIIase consists of two highly homologous fragments, which are designated as CPSase A and CPSase B. Specifically, GATase and CPSase (CPSase A and CPSase B) jointly form the glutamine-dependent CPSase. GATase transfer HCO 3− , glutamine, and ATP to form carbamoylphosphate (CP) at the site of CPSIIase domain. CP formation is the first rate-limiting step for the nucleotide synthesis [16,17][16][17]. We will discuss the details of CPSIIase and its regulations in the latter text. ATCase, consisted of a catalytic homotrimer, catalyzes carbamoylphosphate (CP) and aspartate (Asp) into carbamoyl aspartate (CA-asp) [18]. The DHOase domain catalyzes the reversible cyclization of CA-asp to dihydroorotate (DHO), the first cyclic compound of de novo pyrimidine nucleotide synthesis pathway [15,19,20][15][19][20]. Dihydroorotate dehydrogenase (DHODH) subsequently reduces DHO to orotate in mitochondria [21]. Finally, uridine monophosphate synthase (UMPS) converts orotic acid to produce the end product uridine monophosphate (UMP) [22,23,24][22][23][24] ( Figure 1 B).
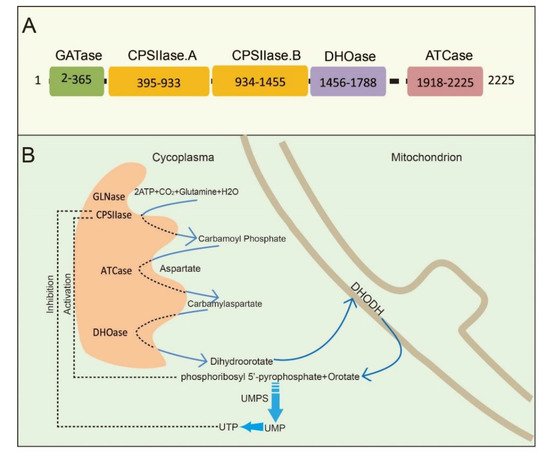
Structural studies of CAD have provided significant insights into its internal structural organization and function. The crystal structures of CAD and its fragments have been determined, and CAD is evolutionarily conserved in a variety of organisms [25,26,27][25][26][27]. Human CAD has a hexamer structure of 1.5 MDa, which is made of a couple of 243 kDa polypeptide chains. This particular structure endows human CAD a series of sophisticated catalytic and regulatory properties [28]. As briefly mentioned earlier, feedback inhibition and allosteric activation by UTP and PRPP play a predominant role in the overall regulation of CAD’s CPSIIase domin [17,29][17][29]. The DHOase and ATCase domains are connected by a linker to form a hexamer, which is proposed as the central structural element of CAD [15]. Interestingly, CAD, as a fusion of the first three enzymatic activities, only occurs in animals. De novo biosynthesis of pyrimidine nucleotide is mainly catalyzed by distinct or independent enzymes but not a single multi-enzymatic protein in prokaryotes [11].
The de novo biosynthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides provides essential precursors for multiple growth-related events in higher eukaryotes [30,31,32][30][31][32]. Intracellular pyrimidine nucleotides regulate the steps of many metabolic pathways ( Figure 2 A,B), mainly including nucleic acid precursors, activated intermediates, and membrane synthesis. Indeed, the de novo biosynthetic pathway in mammals is capable of supplying all pyrimidine ribonucleotides and deoxyribonucleotides for RNA and DNA biosynthesis [33,34][33][34]. UMP, as an intermediate product of the synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides, can be further dephosphorylated to uridine (UR) and phosphorylated to corresponding di- (UDP) and triphosphorylated (UTP) forms, respectively. As described in the latter, UTP is involved in protein glycosylation and glycogen synthesis with the form of UDP-linked sugars [35]. CTP synthetase (CTPS) converts UTP into CTP in an ATP-dependent reaction that uses glutamine as an amine donor. Same as UTP, CTP can also be dephosphorylated into CDP and CMP. Alternatively, UDP and CDP can be deoxygenated into deoxy-UDP (dUDP) and dCDP, respectively, by ribonucleotidereductase (RNR), and further phosphorylated by NDPK. To avoid misincorporation into DNA, dUTP is rapidly broken down by dUTPase into dUMP. Importantly, thymidylate synthase (TS) transfers UMP intodeoxy-TMP (dTMP) and is phosphorylated subsequently into dTTP. Thus, the de novo biosynthetic pathway in mammals is capable of supplying all pyrimidine ribonucleotides (CTP, UTP) and deoxyribonucleotides ( dCTP, dTTP) for RNA and DNA biosynthesis, respectively [33,34,36][33][34][36].
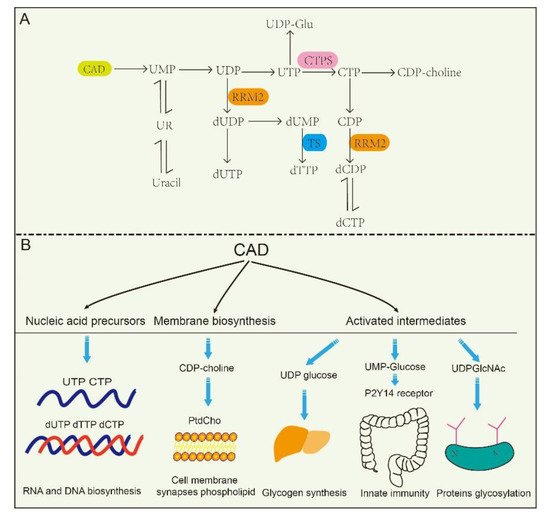
At the same time, CAD plays predominant roles in the production of activated intermediates, including pyrimidine sugars, polysaccharide, and phospholipid synthesis [37]. UDP, as one of the products of CAD, is also a precursor of UDP-sugar intermediates, which are required in UDP-dependent glycosylation events and post translational modification of proteins. Besides, these UDP-sugar intermediates are potential extracellular signaling molecules. For example, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine (UDPGlcNAc) is involved in post-translational modifications of proteins and is required for UDP-dependent glycosylation of proteins. [38]. Of interest, a recent report found that the UDP-nucleotide sugar, as well as UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase, correctly response to cancer process in pancreatic cancer and breast cancer by disrupting cancer cell glycosylation [39,40][39][40]. However, CAD mutants decrease glycosylation precursors. It has been identified that CAD mutants (CAD hu10125 ) regulates angiogenesis in the embryo in Zebrafish via CAD mediated glycosylation process [31]. Additionally, biallelic mutations in CAD (c.1843- 1G > A, c.6071G > A) also confirm the previous study, and manifest with a reduction in a subset of UDP nucleotide sugar levels (UDP-glucose, UDP-N-acetylglucosamine, UDP-galactose, etc.) that serve as donors for glycosylation in human [41]. Despite these insights, how is nucleotide sugar level regulated? Why are glycosylation levels alleviated in cancer? These questions have been elusive until very recently.
3. The Regulation of CAD
Recently, the identification and characterization of CAD-interacting proteins has yielded deep insights into the regulation of CAD catalytic activity. The first identified CAD-interacting protein is the Rad9 checkpoint protein, a subunit of heterotrimeric Rad9-Rad1-Hus1 (9-1-1) complex. The role of Rad9 in predicting disease is likely important. Its overproduction is essential for tumor cells’ tumorigenicity and metastasis [47,48,49][42][43][44]. Additionally, Rad9 binds to CAD at its CPSIIase domain, resulting in a 2-fold stimulation of the CPSase activity of CAD and thus promoting the ribonucleotide biosynthesis [50][45]. It is supposed that CAD is likely a target gene of Rad9 and is controlled by transcription regulation. Additionally, Nakashima et al. have shown that mLST8, a component of the mTOR complexes, interacts with CAD and its binding with CAD is stronger than that of mTORC1. The activity of CAD is upregulated through the association with mLST8 [51][46]. Consistent with this, CAD activity is enhanced when it binds to Rheb, a member of the Ras superfamily small GTPases, which regulates protein synthesis and cell proliferation in an mTOR-independent pathway [52][47]. These data suggest that CAD interaction proteins are involved in CAD regulation.
Furthermore, posttranslational modifications (PTMs), such as phosphorylation [53,54][48][49], acetylation [55[50][51],56], methylation [57][52], and ubiquitination [58][53], modulate the activity, localization and other properties of a protein, thereby regulating a variety of biological processes, including gene transcription, protein biosynthesis, cellular signaling, and metabolism [59][54]. Additionally, protein acetylation plays a pivotal role in mediating protein function, stability, and localization. Functionally, N-terminal acetylationis were found to regulate protein degradation and inhibit protein translocation into the endoplasmic reticulum. It is inferred from combination of experimental and computational evidence that CAD can be potentially acetylated at alanine residue (amino acid 2), N6-acetyllysine (amino acid 747) and N6-acetyllysine (amino acid 1411), while their functions in cellular process still needs to be further demonstrated [60,61,62][55][56][57]. Nowadays, researches on PTMs of CAD protein mostly focus on the phosphorylation; the phosphorylation of CAD protein and the involved pathway is depicted in Figure 3 . Unfortunately, less research is conducted on other PTMs of CAD.
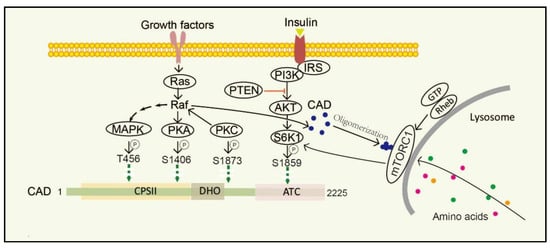
Stimulation of dormant cells by growth factors, such as epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-1) and platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) (Erk1/2) cascade and triggers the transition to the proliferating stage [63,64][58][59]. One of the important substrates of MAPK is CAD. In resting cells, CAD stays cytosolic and keeps an unphosphorylated condition. Once cells are activated by EGF, CAD translocates to the nucleus and phosphorylation reaction occurs at CAD Thr456 by the MAPK [65][60]. Moreover, after sequential phosphorylations of CAD CPSII via MAPK at CAD Thr456, which occurs just before entry into the S phase of the cell cycle, CAD loses its feedback inhibition by UTP, turning more sensitive to phosphoribosyl pyrophosphate (PRPP) [16]. Protein kinase C (PKC) not only promotes phosphorylation at CAD Ser1873, but also activates Raf and MAPK, thereby promoting phosphorylation of CAD Thr456 [13]. Phosphorylation of CAD Thr456 plays important roles in cell cycle-dependent regulation of de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis [66,67,68][61][62][63]. However, the phosphorylation of CAD at the site of Ser1406 by cAMP-dependent protein kinase A (PKA) can decrease its sensitivity to PRPP and abolish UTP inhibition, while phosphorylation of the site of Ser1859 has a minor effect on the catalytic activities or allosteric transitions of CAD [69][64]. In the process, PKA-mediated phosphorylation of a distinct site on Raf can downregulate MAPK, whereas PKC activates MAPK through direct phosphorylation and activation of Raf [70][65]. PKC and PKA display synergistic and antagonistic interactions in MAPK-mediated cell cycle-dependent regulation of pyrimidine biosynthesis to ensure that up-and down-regulated signals do not conflict [71][66].
The mechanistic target of rapamycin (mTOR) is a serine/threonine protein kinase, which is usually assembled into two complexes, including mTOR complex 1 (mTORC1) and 2 (mTORC2) [72][67]. mTOR senses and integrates growth signals to regulate cell growth, proliferation, and homeostasis [53[48][68][69][70],73,74,75], mostly by regulating several anabolic and catabolic processes [76,77][71][72]. Physically, mTORC1 stays in the cytoplasm, while it turns to be located on the lysosomal surface via amino acids stimulation and is activated by Rheb, a small GTPase, which is localized on the lysosomal membrane. mTORC1 phosphorylates its downstream target ribosomal protein S6 kinase 1 (S6K1) and subsequently directly phosphorylates CAD Ser1859 and Ser1900 [52,78,79,80][47][73][74][75]. Interestingly, CAD accumulates on lysosomes with Rheb in a GTP- and effector domain-dependent manner [52][47]. Additionally, insulin also stimulates the Ser1859 phosphorylation of CAD in a manner sensitive to rapamycin as well as phosphatase and tensin homolog (PTEN) deletion in the PI3K–AKT pathway [53,81,82][48][76][77]. That is, CAD can be regulated both by amino acids and growth factors. Recent studies have suggested that once amino acids are taken up into cells and accumulated on lysosomes, CAD might associate with mLST8 and Rheb [51,72][46][67]. Thus, CAD localization to lysosomes may provide a physical environment and give itself better access to glutamine, which is needed for de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis [83][78].
4. Implications for Therapy of CAD-Related Diseases
The production of pyrimidine nucleotide is constantly changing to meet the pyrimidine nucleotide needs of cells. Some conditions, such as the microenvironment of tissues, hormonal context, and nucleic acid integrity, may disturb the homeostasis of pyrimidine nucleotide metabolism [84,85][79][80]. Upregulation of de novo pyrimidine synthesis plays pivotal roles in human diseases, which highlights the importance of its diagnostic potential in associated clinical settings and contributes to the elucidation of the development of novel therapeutic strategies.
Metabolic reprogramming mostly indicates the proliferation and survival of cancer cells [82][77]. Numerous findings have strong implications for cancer therapeutic strategies. Wang et al. found pyrimidine metabolism signaling pathway was disrupted and CAD was enriched in a set of cancer types (liver cancer, breast cancer, colon cancer, etc.) with poor clinical outcomes by using online cancer datasets [86][81]. In 2021, it was reported that carbamoyl–phosphate synthetase 1 (CPS1), a rate-limiting enzyme in urea cycle, was down-regulated in hepatocellular carcinoma. Reduction in CPS1 increased shunting of glutamine to CAD, making it easier for the de novo pyrimidine pathway to participate in cancer cell proliferation [87][82]. Additionally, the reduction of another enzyme in cancers, argininosuccinate synthase (ASS1), as well as CPS1, elevates cytosolic aspartate levels, thus providing substrates to CAD by facilitating pyrimidine synthesis [88][83]. This is to say that cancer cells hijack and redistribute existing metabolic pathways for cancer progression.
References
- Jones, M.E.; Spector, L.; Lipmann, F. CARBAMYL PHOSPHATE, THE CARBAMYL DONOR IN ENZYMATIC CITRULLINE SYNTHESIS1. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1955, 77, 819–820.
- Lacroute, F.; Pierard, A.; Grenson, M.; Wiame, J.M. The Biosynthesis of Carbamoyl Phosphate in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Gen. Microbiol. 1965, 40, 127–142.
- Jones, M.E. Carbamyl Phosphate: Many forms of life use this molecule to synthesize arginine, uracil, and adenosine triphosphate. Science 1963, 140, 1373–1379.
- Pierard, A.; Wiame, J.M. Regulation and mutation affecting a glutamine dependent formation of carbamyl phosphate in Escherichia coli. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1964, 15, 76–81.
- Issaly, I.M.; Issaly, A.S.; Reissig, J.L. Carbamyl phosphate biosynthesis in Bacillus subtilis. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Enzym. 1970, 198, 482–494.
- Jones, M.E. Pyrimidine Nucleotide Biosynthesis in Animals: Genes, Enzymes, and Regulation of UMP Biosynthesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1980, 49, 253–279.
- Hoogenraad, N.J.; Levine, R.L.; Kretchmer, N. Copurification of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase and aspartate transcarbamoylase from mouse spleen. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1971, 44, 981–988.
- Shoaf, W.T.; Jones, M.E. Initial steps in pyrimidine synthesis in ehrlich ascites carcinoma. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1971, 45, 796–802.
- Novak, D.A.; Carver, J.D.; Barness, L.A. Dietary Nucleotides Affect Hepatic Growth and Composition in the Weanling Mouse. J. Parenter. Enter. Nutr. 1994, 18, 62–66.
- Pluske, J.R.; Fenton, T.W.; Lorschy, M.L.; Pettigrew, J.E.; Sower, A.F.; Aherne, F.X. A modification to the isotope-dilution technique for estimating milk intake of pigs using pig serum. J. Anim. Sci. 1997, 75, 1279–1283.
- del Caño-Ochoa, F.; Moreno-Morcillo, M.; Ramón-Maiques, S. CAD, A Multienzymatic Protein at the Head of de Novo Pyrimidine Biosynthesis. Macromol. Protein Complexes II Struct. Funct. 2019, 93, 505–538.
- Tu, H.-F.; Ko, C.-J.; Lee, C.-T.; Lee, C.-F.; Lan, S.-W.; Lin, H.-H.; Ku, C.-C.; Lee, D.-Y.; Chen, I.-C.; Chuang, Y.-H.; et al. Afatinib Exerts Immunomodulatory Effects by Targeting the Pyrimidine Biosynthesis Enzyme CAD. Cancer Res. 2021, 81, 3270–3282.
- Sigoillot, F.D.; Kotsis, D.H.; Masko, E.M.; Bame, M.; Evans, D.R.; Evans, H.I. Protein kinase C modulates the up-regulation of the pyrimidine biosynthetic complex, CAD, by MAP kinase. Front. Biosci. 2007, 12, 3892–3898.
- Koch, J.; Mayr, J.A.; Alhaddad, B.; Rauscher, C.; Bierau, J.; Kovacs-Nagy, R.; Coene, K.L.; Bader, I.; Holzhacker, M.; Prokisch, H.; et al. CAD mutations and uridine-responsive epileptic encephalopathy. Brain 2017, 140, 279–286.
- Moreno-Morcillo, M.; Grande-García, A.; Ruiz-Ramos, A.; del Caño-Ochoa, F.; Boskovic, J.; Ramón-Maiques, S. Structural Insight into the Core of CAD, the Multifunctional Protein Leading De Novo Pyrimidine Biosynthesis. Structure 2017, 25, 912–923.e5.
- Sigoillot, F.D.; Berkowski, J.A.; Sigoillot, S.M.; Kotsis, D.H.; Guy, H.I. Cell Cycle-dependent Regulation of Pyrimidine Biosynthesis. J. Biol. Chem. 2003, 278, 3403–3409.
- Hervé, G. Structural Insight into the Core of CAD. Structure 2017, 25, 819–820.
- Lipscomb, W.N.; Kantrowitz, E.R. Structure and Mechanisms of Escherichia coli Aspartate Transcarbamoylase. Accounts Chem. Res. 2011, 45, 444–453.
- Grande-García, A.; Lallous, N.; Díaz-Tejada, C.; Ramón-Maiques, S. Structure, Functional Characterization, and Evolution of the Dihydroorotase Domain of Human CAD. Structure 2014, 22, 185–198.
- Lee, M.; Chan, C.W.; Graham, S.C.; Christopherson, R.I.; Guss, J.M.; Maher, M.J. Structures of Ligand-free and Inhibitor Complexes of Dihydroorotase from Escherichia coli: Implications for Loop Movement in Inhibitor Design. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 370, 812–825.
- Löffler, M.; Carrey, E.A.; Knecht, W. The pathway to pyrimidines: The essential focus on dihydroorotate dehydrogenase, the mitochondrial enzyme coupled to the respiratory chain. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2020, 39, 1281–1305.
- Okesli, A.; Khosla, C.; Bassik, M.C. Human pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis as a target for antiviral chemotherapy. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol. 2017, 48, 127–134.
- Wittmann, J.G.; Heinrich, D.; Gasow, K.; Frey, A.; Diederichsen, U.; Rudolph, M.G. Structures of the Human Orotidine-5′-Monophosphate Decarboxylase Support a Covalent Mechanism and Provide a Framework for Drug Design. Structure 2008, 16, 82–92.
- Deans, R.M.; Morgens, D.W.; Ökesli, A.; Pillay, S.; Horlbeck, M.A.; Kampmann, M.; Gilbert, L.; Li, A.; Mateo, R.; Smith, M.; et al. Parallel shRNA and CRISPR-Cas9 screens enable antiviral drug target identification. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2016, 12, 361–366.
- Ladner, J.E.; Kitchell, J.P.; Honzatko, R.B.; Ke, H.M.; Volz, K.W.; Kalb, A.J.; Ladner, R.C.; Lipscomb, W.N. Gross quaternary changes in aspartate carbamoyltransferase are induced by the binding of N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate: A 3.5-A resolution study. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1982, 79, 3125–3128.
- Thoden, J.B.; Holden, H.M.; Wesenberg, G.; Raushel, F.M.; Rayment, I. Structure of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase: A journey of 96 A from substrate to product. Biochemistry 1997, 36, 6305–6316.
- Thoden, J.B.; Phillips, G.N.; Neal, T.M.; Raushel, F.M.; Holden, H.M. Molecular Structure of Dihydroorotase: A Paradigm for Catalysis through the Use of a Binuclear Metal Center. Biochemistry 2001, 40, 6989–6997.
- Ruiz-Ramos, A.; Velazquez-Campoy, A.; Grande-García, A.; Moreno-Morcillo, M.; Ramón-Maiques, S. Structure and Functional Characterization of Human Aspartate Transcarbamoylase, the Target of the Anti-tumoral Drug PALA. Structure 2016, 24, 1081–1094.
- Serre, V.; Penverne, B.; Souciet, J.L.; Potier, S.; Guy, H.; Evans, D.; Vicart, P.; Herve, G. Integrated allosteric regulation in the S. cerevisiae carbamylphosphate synthetase—Aspartate transcarbamylase multifunctional protein. BMC Biochem. 2004, 5, 6.
- Carrey, E.A. Phosphorylation, allosteric effectors and inter-domain contacts in CAD; their role in regulation of early steps of pyrimidine biosynthesis. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 1993, 21, 191–195.
- Coxam, B.; Neyt, C.; Grassini, D.R.; Le Guen, L.; Smith, K.A.; Schulte-Merker, S.; Hogan, B.M. carbamoyl-phosphate synthetase 2, aspartate transcarbamylase, and dihydroorotase (cad) regulates Notch signaling and vascular development in zebrafish. Dev. Dyn. 2015, 244, 1–9.
- Cammer, W.; Downing, M. Localization of the multifunctional protein CAD in astrocytes of rodent brain. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 1991, 39, 695–700.
- Cotruvo, J.A.; Stubbe, J. Class I Ribonucleotide Reductases: Metallocofactor Assembly and Repair In Vitro and In Vivo. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2011, 80, 733–767.
- Martin, E.; Palmic, N.; Sanquer, S.; Lenoir, C.; Hauck, F.; Mongellaz, C.; Fabrega, S.; Nitschké, P.; Degli Esposti, M.; Schwartzentruber, J.; et al. CTP synthase 1 deficiency in humans reveals its central role in lymphocyte proliferation. Nature 2014, 510, 288–292.
- Mollick, T.; Laín, S. Modulating pyrimidine ribonucleotide levels for the treatment of cancer. Cancer Metab. 2020, 8, 1–11.
- Carreras, C.W.; Santi, D.V. The catalytic mechanism and structure of thymidylate synthase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995, 64, 721–762.
- Rd, S.G. Pyrimidine biosynthesis. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 1979, 32, 1290.
- Huang, M.; Graves, L.M. De novo synthesis of pyrimidine nucleotides; emerging interfaces with signal transduction pathways. Experientia 2003, 60, 321–336.
- Teoh, S.T.; Ogrodzinski, M.P.; Lunt, S.Y. UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase knockout impairs migration and decreases in vivo metastatic ability of breast cancer cells. Cancer Lett. 2020, 492, 21–30.
- Wolfe, A.L.; Zhou, Q.; Toska, E.; Galeas, J.; Ku, A.A.; Koche, R.P.; Bandyopadhyay, S.; Scaltriti, M.; Lebrilla, C.B.; McCormick, F.; et al. UDP-glucose pyrophosphorylase 2, a regulator of glycogen synthesis and glycosylation, is critical for pancreatic cancer growth. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2103592118.
- Ng, B.G.; Wolfe, L.A.; Ichikawa, M.; Markello, T.; He, M.; Tifft, C.J.; Gahl, W.A.; Freeze, H.H. Biallelic mutations in CAD, impair de novo pyrimidine biosynthesis and decrease glycosylation precursors. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2015, 24, 3050–3057.
- Zhu, A.; Hopkins, K.M.; Friedman, R.A.; Bernstock, J.D.; Broustas, C.G.; Lieberman, H.B. DNMT1 and DNMT3B regulate tumorigenicity of human prostate cancer cells by controlling RAD9 expression through targeted methylation. Carcinogenesis 2020, 42, 220–231.
- Panigrahi, S.K.; Broustas, C.G.; Cuiper, P.Q.; Virk, R.K.; Lieberman, H.B. FOXP1 and NDRG1 act differentially as downstream effectors of RAD9-mediated prostate cancer cell functions. Cell. Signal. 2021, 86, 110091.
- Chen, K.-Y.; Chen, C.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Chang, M.-C. Resveratrol induced premature senescence and inhibited epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cancer cells via induction of tumor suppressor Rad9. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0219317.
- Lindsey-Boltz, L.A.; Wauson, E.M.; Graves, L.M.; Sancar, A. The human Rad9 checkpoint protein stimulates the carbamoyl phosphate synthetase activity of the multifunctional protein CAD. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, 4524–4530.
- Nakashima, A.; Kawanishi, I.; Eguchi, S.; Yu, E.H.; Eguchi, S.; Oshiro, N.; Yoshino, K.-I.; Kikkawa, U.; Yonezawa, K. Association of CAD, a multifunctional protein involved in pyrimidine synthesis, with mLST8, a component of the mTOR complexes. J. Biomed. Sci. 2013, 20, 24.
- Sato, T.; Akasu, H.; Shimono, W.; Matsu, C.; Fujiwara, Y.; Shibagaki, Y.; Heard, J.J.; Tamanoi, F.; Hattori, S. Rheb Protein Binds CAD (Carbamoyl-phosphate Synthetase 2, Aspartate Transcarbamoylase, and Dihydroorotase) Protein in a GTP- and Effector Domain-dependent Manner and Influences Its Cellular Localization and Carbamoyl-phosphate Synthetase (CPSase) Activity. J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 290, 1096–1105.
- Ben-Sahra, I.; Howell, J.J.; Asara, J.M.; Manning, B.D. Stimulation of de Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis by Growth Signaling Through mTOR and S6K1. Science 2013, 339, 1323–1328.
- Guo, X.; Chen, S.; Yu, W.; Chi, Z.; Wang, Z.; Xu, T.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, D.; Guo, Y.; Fang, H.; et al. AKT controls NLRP3 inflammasome activation by inducing DDX3X phosphorylation. FEBS Lett. 2021. online ahead of print.
- Hu, X.; Wang, D.; Sun, L.; Gao, Y.; Zhou, D.; Tong, X.; Li, J.; Lin, H.; Qing, Y.; Du, S.; et al. Disturbed mitochondrial acetylation in accordance with the availability of acetyl groups in hepatocellular carcinoma. Mitochondrion 2021, 60, 150–159.
- Gama, R.R.; Arantes, L.M.R.B.; Sorroche, B.P.; De Marchi, P.; Melendez, M.E.; Carvalho, R.S.; de Lima, M.A.; Vettore, A.L.; Carvalho, A.L. Evaluation of acetylation and methylation in oral rinse of patients with head and neck cancer history exposed to valproic acid. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 16415.
- Chen, Y.T.; Xiang, D.; Zhao, X.Y.; Chu, X.Y. Upregulation of lncRNA NIFK-AS1 in hepatocellular carcinoma by m6A methylation promotes disease progression and sorafenib resistance. Hum. Cell 2021, 1–12.
- Cho, H.J.; Ryu, K.-J.; Baek, K.E.; Lim, J.; Kim, T.; Song, C.Y.; Yoo, J.; Lee, J.Y.A.H.G. Cullin 3/KCTD5 Promotes the Ubiqutination of Rho Guanine Nucleotide Dissociation Inhibitor 1 and Regulates Its Stability. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2020, 30, 1488–1494.
- Chen, H.; Venkat, S.; McGuire, P.; Gan, Q.; Fan, C. Recent Development of Genetic Code Expansion for Posttranslational Modification Studies. Molecules 2018, 23, 1662.
- Van Damme, P.; Lasa, M.; Polevoda, B.; Gazquez, C.; Elosegui-Artola, A.; Kim, D.S.; De-Juan-Pardo, E.; Demeyer, K.; Hole, K.; Larrea, E.; et al. N-terminal acetylome analyses and functional insights of the N-terminal acetyltransferase NatB. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 12449–12454.
- Choudhary, C.; Kumar, C.; Gnad, F.; Nielsen, M.L.; Rehman, M.; Walther, T.C.; Olsen, J.V.; Mann, M. Lysine Acetylation Targets Protein Complexes and Co-Regulates Major Cellular Functions. Science 2009, 325, 834–840.
- Bruserud, O.; Stapnes, C.; Tronstad, K.J.; Ryningen, A.; Ånensen, N.; Gjertsen, B.T. Protein lysine acetylation in normal and leukaemic haematopoiesis: HDACs as possible therapeutic targets in adult AML. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2006, 10, 51–68.
- Liu, Z.; Ning, F.; Cai, Y.; Sheng, H.; Zheng, R.; Yin, X.; Lu, Z.; Su, L.; Chen, X.; Zeng, C.; et al. The EGFR-P38 MAPK axis up-regulates PD-L1 through miR-675-5p and down-regulates HLA-ABC via hexokinase-2 in hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Cancer Commun. 2021, 41, 62–78.
- Brown, K.M.; Xu, M.; Sargen, M.; Jang, H.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, T.; Zhu, B.; Jones, K.; Kim, J.; Mendoza, L.; et al. Novel MAPK/AKT-impairing germline NRAS variant identified in a melanoma-prone family. Fam. Cancer 2021, 1–9.
- Sigoillot, F.D.; Kotsis, D.H.; Serre, V.; Sigoillot, S.M.; Evans, D.R.; Guy, H.I. Nuclear localization and mitogen-activated protein kinase phosphorylation of the multifunctional protein CAD. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 25611–25620.
- Cobb, M.H.; Goldsmith, E.J. How MAP kinases are regulated. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 14843–14846.
- Graves, L.M.; Guy, H.I.; Kozlowski, P.; Huang, M.; Lazarowski, E.; Pope, R.M.; Collins, M.A.; Dahlstrand, E.N.; Earp, H.S., 3rd; Evans, D.R. Regulation of carbamoyl phosphate synthetase by MAP kinase. Nature 2000, 403, 328–332.
- Evans, D.R.; Guy, H.I. Mammalian Pyrimidine Biosynthesis: Fresh Insights into an Ancient Pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 2004, 279, 33035–33038.
- Carrey, E.A.; Campbell, D.G.; Hardie, D.G. Phosphorylation and activation of hamster carbamyl phosphate synthetase II by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. A novel mechanism for regulation of pyrimidine nucleotide biosynthesis. EMBO J. 1985, 4, 3735–3742.
- Kolch, W.; Heidecker, G.; Kochs, G.; Hummel, R.; Vahidi, H.; Mischak, H.; Finkenzeller, G.; Marme, D.; Rapp, U.R. Protein kinase C alpha activates RAF-1 by direct phosphorylation. Nature 1993, 364, 249–252.
- Kotsis, D.H.; Masko, E.M.; Sigoillot, F.D.; Di Gregorio, R.; Guy-Evans, H.I.; Evans, D.R. Protein kinase A phosphorylation of the multifunctional protein CAD antagonizes activation by the MAP kinase cascade. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 2007, 301, 69–81.
- Saxton, R.A.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth, Metabolism, and Disease. Cell 2017, 168, 960–976.
- Linke, M.; Fritsch, S.D.; Sukhbaatar, N.; Hengstschläger, M.; Weichhart, T. mTORC1 and mTORC2 as regulators of cell metabolism in immunity. FEBS Lett. 2017, 591, 3089–3103.
- Ardestani, A.; Lupse, B.; Kido, Y.; Leibowitz, G.; Maedler, K. mTORC1 Signaling: A Double-Edged Sword in Diabetic β Cells. Cell Metab. 2018, 27, 314–331.
- Li, Y.; Li, J.; Zhou, Q.; Liu, Y.; Chen, W.; Xu, H. mTORC1 signaling is essential for neurofibromatosis type I gene modulated osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. J. Cell. Biochem. 2018, 120, 2886–2896.
- Laplante, M.; Sabatini, D.M. mTOR Signaling in Growth Control and Disease. Cell 2012, 149, 274–293.
- Wullschleger, S.; Loewith, R.; Hall, M.N. TOR Signaling in Growth and Metabolism. Cell 2006, 124, 471–484.
- Avruch, J.; Hara, K.; Lin, Y.; Liu, M.; Long, X.; Ortizvega, S.; Yonezawa, K. Insulin and amino-acid regulation of mTOR signaling and kinase activity through the Rheb GTPase. Oncogene 2006, 25, 6361–6372.
- Vetter, I.R.; Wittinghofer, A. The guanine nucleotide-binding switch in three dimensions. Science 2001, 294, 1299–1304.
- Wyant, G.A.; Abu-Remaileh, M.; Wolfson, R.L.; Chen, W.; Freinkman, E.; Danai, L.V.; Heiden, M.G.V.; Sabatini, D.M. mTORC1 Activator SLC38A9 Is Required to Efflux Essential Amino Acids from Lysosomes and Use Protein as a Nutrient. Cell 2017, 171, 642–654.e12.
- Robitaille, A.M.; Christen, S.; Shimobayashi, M.; Cornu, M.; Fava, L.L.; Moes, S.; Prescianotto-Baschong, C.; Sauer, U.; Jenoe, P.; Hall, M.N. Quantitative Phosphoproteomics Reveal mTORC1 Activates de Novo Pyrimidine Synthesis. Science 2013, 339, 1320–1323.
- Wang, X.; Yang, K.; Wu, Q.; Kim, L.J.Y.; Morton, A.R.; Gimple, R.C.; Prager, B.C.; Shi, Y.; Zhou, W.; Bhargava, S.; et al. Targeting pyrimidine synthesis accentuates molecular therapy response in glioblastoma stem cells. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaau4972.
- Zoncu, R.; Bar-Peled, L.; Efeyan, A.; Wang, S.; Sancak, Y.; Sabatini, D.M. mTORC1 Senses Lysosomal Amino Acids Through an Inside-Out Mechanism That Requires the Vacuolar H+-ATPase. Science 2011, 334, 678–683.
- Chernova, O.B.; Chernov, M.V.; Ishizaka, Y.; Agarwal, M.L.; Stark, G.R. MYC abrogates p53-mediated cell cycle arrest in N-(phosphonacetyl)-L-aspartate-treated cells, permitting CAD gene amplification. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 536–545.
- Abadjian, M.-C.Z.; Edwards, W.B.; Anderson, C.J. Imaging the Tumor Microenvironment. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2017, 1036, 229–257.
- Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Xu, L.; Zhang, J.; Cao, H. High expression levels of pyrimidine metabolic rate–limiting enzymes are adverse prognostic factors in lung adenocarcinoma: A study based on The Cancer Genome Atlas and Gene Expression Omnibus datasets. Purinergic Signal. 2020, 16, 347–366.
- Ridder, D.A.; Schindeldecker, M.; Weinmann, A.; Berndt, K.; Urbansky, L.; Witzel, H.R.; Heinrich, S.; Roth, W.; Straub, B.K. Key Enzymes in Pyrimidine Synthesis, CAD and CPS1, Predict Prognosis in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 744.
- Rabinovich, S.; Adler, L.; Yizhak, K.; Sarver, A.; Silberman, A.; Agron, S.; Stettner, N.; Sun, Q.; Brandis, A.; Helbling, D.; et al. Diversion of aspartate in ASS1-deficient tumours fosters de novo pyrimidine synthesis. Nature 2015, 527, 379–383.
