The use of food supplements or functional food has significantly increased in the past decades, especially to compensate both the modern lifestyle and the food shortages of the industrialized countries. Despite food supplements are habitually intended to correct nutritional deficiencies or to support specific physiological functions, they are often combined with common drug therapies to improve the patient’s health and/or mitigate the symptoms of many chronic diseases such as cardiovascular diseases, cystic fibrosis, cancer, liver and gastrointestinal diseases. In recent years, increased attentions are given to the patient’s diet, and the use of food supplements and functional food rich in vitamins and antioxidants plays a very important role in the treatment and prevention of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s disease (PD). Natural compounds, phytochemicals, vitamins, and minerals can prevent, delay, or alleviate the clinical symptoms of PD in contrast to some of the main physiopathological mechanisms involved in the development of the disease, like oxidative stress, free radical formation, and neuroinflammation.
- Parkinson’s disease
- food supplements
- functional food
- antioxidants
- anti-inflammatory
- neuroprotection
- natural compounds
1. Introduction
2. Natural Compounds Useful in the Prevention and Management of PD
Scientific evidences have shown that numerous molecules and natural compounds are able to mitigate the symptoms of PD by counteracting the physiopathological mechanisms which dominate the disease, such as oxidative stress and neuroinflammation. Furthermore, some molecules have shown to possess neuroprotective and neuro-modulatory properties. Table 1 displays the analyzed molecules, describing for each compound the beneficial effects demonstrated experimentally and the performed mechanism that support a positive incidence in the treatment of PD.| Molecule | Beneficial Effects | Mechanism | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| oenzyme Q10 | Antioxidant Neuroprotection |
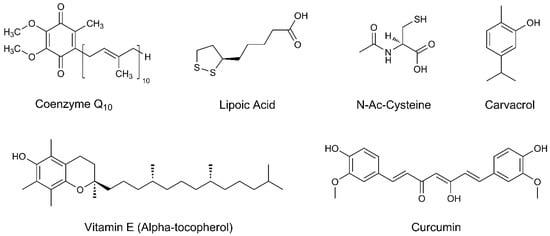
Coenzyme Q10, due to its 1,4-benzoquinone structure, is a powerful antioxidant acting as a free radical scavenger. Since it is also a redox component of the electron transport chain of mitochondria, it may exert neuroprotection through the modulation of mitochondrial activity in neuronal cells. | [44,45,46,47,48,49,50][10][11][12][13][14][15][16] |
| Lipoic acid | Antioxidant Anti-inflammatory Neuroprotection |
The dithiolane ring, with its oxidized and reduced forms, makes lipoic acid a potent antioxidant. As an anti-inflammatory agent, it inhibits NF-kappaB and inflammatory cytokines like TNF-α. Neuroprotection is given by enhancing the intracellular levels of cysteine, thus increasing the glutathione levels. | [51,52,53,54][17][18][19][20] |
| N-acetyl-cysteine | Antioxidant Neuroprotection |
The thiol group of N-acetyl-cysteine can act both as a direct antioxidant and as a glutathione precursor. It increases the mitochondrial complex I and IV activities and prevents reactive species of oxygen (ROS) accumulation in neuronal cells. | [55,56,57,58,59,60][21][22][23][24][25][26] |
| Vitamin E | Antioxidant | Vitamin E acts as a scavenger of several ROS by donating a hydrogen atom to free radicals, thus reducing their reactivity and toxicity. | [61,62,63,64,65,66][27][28][29][30][31][32] |
| Carvacrol | Antioxidant Anti-inflammatory Neuromodulation |
Carvacrol induces the production of antioxidative enzymes and modulates oxidative stress. The anti-inflammatory effect is exerted by reducing the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. Carvacrol is also able to inhibit the acetylcholinesterase activity, with positive effects on memory and cognitive performance in PD. | [67,68,69][33][34][35] |
| Curcumin | Antioxidant Anti-inflammatory Neuroprotection |
Curcumin is an excellent free radical scavenger thanks to the phenolic rings and diketone groups. It protects mitochondrial complex I from enzyme nitration and subsequent inhibition, reducing mitochondrial disfunction. Anti-inflammatory and neuroprotective actions are exerted by modulation of chemokines which mediate the inflammatory cascade. | [70,71,72,73,74,75,76,77,78][36][37][38][39][40][41][42][43][44] |
| Omega−3 fatty acids |
Antioxidant Anti-inflammatory |
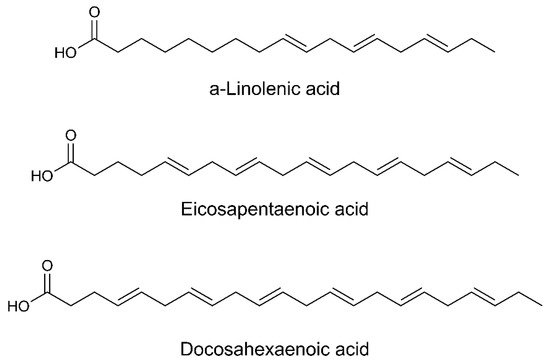
Omega-3 fatty acids reduce ROS formation acting as free radical scavengers. They also decrease chemotaxis of neutrophils and monocytes, as well as the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines. | [79,80][45][46] |
| Whey protein | Antioxidant | Since whey protein is an excellent source of cysteine, it can increase the production of glutathione, thus reducing oxidative stress. | [81,82][47][48] |
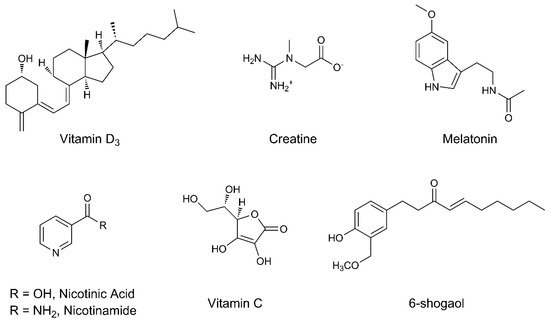
| Vitamin D3 | Antioxidant Neuroprotection | Vitamin D3 inhibits oxidative stress, reduces free radical formation, and decreases neurotoxicity by enhancing autophagy signaling pathways. Neuroprotection is exerted by reducing the endothelial dysfunction observed in patients with PD. | [83,[84,85,4986,87]][50][51][52][53] |
| Creatine | Antioxidant Neuroprotection |
Creatine is able to contrast free radicals and ROS acting as antioxidant. Moreover, it can stimulate mitochondrial activity through the production of phosphocreatine, thus modulating the production of ATP and the energy homeostasis in the brain. | [88,89,90,91][54][55][56][57] |
| Melatonin | Antioxidant | Melatonin has interesting antioxidant properties, probably related to the indole group. The antioxidant activity is also performed by preventing the antioxidative catalysts lowering in neuronal cells. | [92,93,94,95,96][58][59][60][61][62] |
| Niacin (Vitamin B3) |
Antioxidant Neuroprotection |
Niacin and its active form nicotinamide reduce oxidative stress. Neuroprotection is reached since they are involved in the biosynthesis of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD), an essential cofactor for the ATP production at the mitochondrial complex I level. | [97,98,99,100,101,102][63][64][65][66][67][68] |
| Vitamin C | Antioxidant | Vitamin C is an excellent antioxidant, suitable in reducing ROS levels, lipid peroxidation, and oxidative stress. It is also useful in regenerating other antioxidants. | [103,104,105,106][69][70][71][72] |
| 6-shogaol | Antioxidant Anti-inflammatory Neuroprotection |
The α,β-unsaturated ketone moiety makes 6-shogsol a good free radical scavenger. It possesses anti-inflammatory properties by reducing the production of prostaglandin E and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α and interleukin-1β. Neuroprotection is assessed by inhibiting microglial activation. | [107,108,109][73][74][75] |
| β-carotene | Antioxidant | β-carotene is an excellent free radical scavenger. The high number of conjugated double bonds in its structure confers to this compound’s peculiar antioxidant properties. | [110,111,112,113][76][77][78][79] |
| Lycopene | Antioxidant | Lycopene is an excellent free radical scavenger. The high number of conjugated double bonds in its structure confers to this compound’s peculiar antioxidant properties. | [114,115,116,117,[81][82118][80]][83][84] |
| Flavonoids Quercetin Epigallocatechin-3-gallate Ginkgo Biloba extract |
Antioxidant Anti-inflammatory Neuroprotection Neuromodulation |
The antioxidant activity of flavonoids depends upon the arrangement of functional groups on the 15-carbon skeleton. Beside the free radical scavenger capacity, they regulate the overproduction of inflammatory cytokines, reducing pro-inflammatory mediators and conferring to neuroprotection. This last property is exerted also through the increment of striatal dopamine and the modulation of cell survival/cell cycle genes, which increase neuronal survivability. | [119,120,121,122,86][87][88]125,[126,127,89][128,90][134,91][135,136][85][92][93][94][95] |
2.1. Coenzyme Q10
2.2. Lipoic Acid
2.3. N-Acetyl-Cysteine
2.4. Vitamin E
2.5. Carvacrol
2.6. Curcumin
2.7. Omega-3 Fatty Acids
2.8. Whey Protein
2.9. Vitamin D3
2.10. Creatine
2.11. Melatonin
References
- Grand View Research Dietary Supplements Market. Available online: (accessed on 21 April 2019).
- EFSA Food Supplements. Available online: (accessed on 3 March 2019).
- Binns, C.W.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, A.H. Problems and prospects: Public health regulation of dietary supplements. Annu. Rev. Public Health 2018, 39, 403–420.
- Pravst, I. Dietary supplement labelling and health claims. In Dietary Supplements; Berginc, K., Kreft, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 3–24.
- Stratton, R.J. Summary of a systematic review on oral nutritional supplement use in the community. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2000, 59, 469–476.
- Webb, G.P. Dietary Supplements and Functional Foods, 1st ed.; Blackwell Publishing Ltd.: Oxford, UK, 2007.
- Mostafavi, S.-A.; Hosseini, S. Foods and Dietary Supplements in the Prevention and Treatment of Neurodegenerative Diseases in Older Adults. In Foods and Dietary Supplements in the Prevention and Treatment of Disease in Older Adults; Watson, R., Ed.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 63–67.
- Evatt, M.L. Nutritional therapies in Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Treat. Options Neurol. 2007, 9, 198–204.
- Olasehinde, T.; Oyeleye, S.I.; Ogunsuyi, O.B.; Ogunruku, O. Functional Foods in the Management of Neurodegenerative Diseases. In Functional Foods: Unlocking the Medicine in Foods; Oboh, G., Ed.; Graceland Prints: Memphis, TN, USA, 2017; pp. 72–81.
- Beal, M.F.; Matthews, R.T.; Tieleman, A.; Shults, C.W. Coenzyme Q10 attenuates the 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) induced loss of striatal dopamine and dopaminergic axons in aged mice. Brain Res. 1998, 783, 109–114.
- Shults, C.W. Therapeutic role of coenzyme Q10 in Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2005, 107, 120–130.
- Garrido-Maraver, J.; Cordero, M.D.; Oropesa-Ávila, M.; Fernández Vega, A.; de la Mata, M.; Delgado Pavón, A.; de Miguel, M.; Pérez Calero, C.; Villanueva Paz, M.; Cotán, D.; et al. Coenzyme Q10 Therapy. Mol. Syndromol. 2014, 5, 187–197.
- Shults, C.W. Effects of Coenzyme Q10 in Early Parkinson Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 1541.
- Müller, T.; Büttner, T.; Gholipour, A.; Kuhn, W. Coenzyme Q10 supplementation provides mild symptomatic benefit in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci. Lett. 2003, 341, 201–204.
- Storch, A. Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial on Symptomatic Effects of Coenzyme Q10 in Parkinson Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2007, 64, 938.
- Zhu, Z.; Sun, M.; Zhang, W.-L.; Wang, W.-W.; Jin, Y.-M.; Xie, C.-L. The efficacy and safety of coenzyme Q10 in Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Neurol. Sci. 2017, 38, 215–224.
- Shay, K.P.; Moreau, R.F.; Smith, E.J.; Smith, A.R.; Hagen, T.M. Alpha-lipoic acid as a dietary supplement: Molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2009, 1790, 1149–1160.
- Zhang, S.; Xie, C.; Lin, J.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Liu, Z. Lipoic acid alleviates L-DOPA-induced dyskinesia in 6-OHDA parkinsonian rats via anti-oxidative stress. Mol. Med. Rep. 2017, 17, 1118–1124.
- Jalali-Nadoushan, M.; Roghani, M. Alpha-lipoic acid protects against 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity in a rat model of hemi-parkinsonism. Brain Res. 2013, 1505, 68–74.
- Li, Y.-H.; He, Q.; Yu, J.; Liu, C.; Feng, L.; Chai, Z.; Wang, Q.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, G.-X.; Xiao, B.; et al. Lipoic acid protects dopaminergic neurons in LPS-induced Parkinson’s disease model. Metab. Brain Dis. 2015, 30, 1217–1226.
- Aldini, G.; Altomare, A.; Baron, G.; Vistoli, G.; Carini, M.; Borsani, L.; Sergio, F. N-Acetylcysteine as an antioxidant and disulphide breaking agent: The reasons why. Free Radic. Res. 2018, 52, 751–762.
- Pinnen, F.; Cacciatore, I.; Cornacchia, C.; Sozio, P.; Cerasa, L.S.; Iannitelli, A.; Nasuti, C.; Cantalamessa, F.; Sekar, D.; Gabbianelli, R.; et al. Codrugs Linking L-Dopa and Sulfur-Containing Antioxidants: New Pharmacological Tools against Parkinson’s Disease. J. Med. Chem. 2009, 52, 559–563.
- Di Stefano, A.; Marinelli, L.; Eusepi, P.; Ciulla, M.; Fulle, S.; Sara, E.; Di Filippo, E.S.; Magliulo, L.; Di Biase, G.; Cacciatore, I. Synthesis and Biological Evaluation of Novel Selenyl and Sulfur-l-Dopa Derivatives as Potential Anti-Parkinson’s Disease Agents. Biomolecules 2019, 9, 239.
- Banaclocha, M.M. Therapeutic potential of N-acetylcysteine in age-related mitochondrial neurodegenerative diseases. Med. Hypotheses 2001, 56, 472–477.
- Holmay, M.J.; Terpstra, M.; Coles, L.D.; Mishra, U.; Ahlskog, M.; Öz, G.; Cloyd, J.C.; Tuite, P.J. N-acetylcysteine Boosts Brain and Blood Glutathione in Gaucher and Parkinson Diseases. Clin. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 36, 103–106.
- Monti, D.A.; Zabrecky, G.; Kremens, D.; Liang, T.; Wintering, N.A.; Cai, J.; Wei, X.; Bazzan, A.J.; Zhong, L.; Bowen, B.; et al. N-Acetyl Cysteine May Support Dopamine Neurons in Parkinson’s Disease: Preliminary Clinical and Cell Line Data. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0157602.
- Engin, K.N. Alpha-tocopherol: Looking beyond an antioxidant. Mol. Vis. 2009, 15, 855–860.
- Filograna, R.; Beltramini, M.; Bubacco, L.; Bisaglia, M. Anti-Oxidants in Parkinson’s Disease Therapy: A Critical Point of View. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2016, 14, 260–271.
- Fahn, S. A pilot trial of high-dose alpha-tocopherol and ascorbate in early Parkinson’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 1992, 32, S128–S132.
- Zhang, S.M.; Hernan, M.A.; Chen, H.; Spiegelman, D.; Willett, W.C.; Ascherio, A. Intakes of vitamins E and C, carotenoids, vitamin supplements, and PD risk. Neurology 2002, 59, 1161–1169.
- Scheider, W.L.; Hershey, L.A.; Vena, J.E.; Holmlund, T.; Marshall, J.R.; Freudenheim, J.L. Dietary antioxidants and other dietary factors in the etiology of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 1997, 12, 190–196.
- DATATOP: A Multicenter Controlled Clinical Trial in Early Parkinson’s Disease. Arch. Neurol. 1989, 46, 1052.
- Can Baser, K. Biological and Pharmacological Activities of Carvacrol and Carvacrol Bearing Essential Oils. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2008, 14, 3106–3119.
- Marinelli, L.; Di Stefano, A.; Cacciatore, I. Carvacrol and its derivatives as antibacterial agents. Phytochem. Rev. 2018, 17, 903–921.
- Haddadi, H.; Rajaei, Z.; Alaei, H.; Shahidani, S. Chronic treatment with carvacrol improves passive avoidance memory in a rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Arq. Neuropsiquiatr. 2018, 76, 71–77.
- Mythri, R.B.; Bharath, M.M.S. Curcumin: A potential neuroprotective agent in Parkinson’s disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2012, 18, 91–99.
- Wang, X.S.; Zhang, Z.R.; Zhang, M.M.; Sun, M.X.; Wang, W.W.; Xie, C.L. Neuroprotective properties of curcumin in toxin-base animal models of Parkinson’s disease: A systematic experiment literatures review. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 2017, 17, 1–10.
- Pan, J.; Ding, J.-Q.; Chen, S.-D. The protection of curcumin in nigral dopaminergic neuronal injury of mice model of Parkinson disease. Chin. J. Contemp. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2007, 7, 421–426.
- Peng, F. Neuroprotection effect of curcumin on 6-OHDA lesioned Parkinson’s disease in rats model. J. Hebei North Univ. 2010, 27, 21–23.
- Yu, S.; Wang, Y.; Wang, X. Curcumin prevents dopaminergic neuronal death in experimental Parkinson’s disease research. J. China Med. Univ. 2012, 41, 569–570.
- Guo, Y.X.; Yang, B.; Shi, L.; Gu, J.; Chen, H. Anti-inflammation mechanism of curcumin in mice with lipopolysaccharide-induced Parkinson’s disease. J. Med. Postgrad. 2012, 25, 582–587.
- Tripanichkul, W.; Jaroensuppaperch, E.O. Ameliorating effects of curcumin on 6-OHDA-induced dopaminergic denervation, glial response, and SOD1 reduction in the striatum of hemiparkinsonian mice. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2013, 17, 1360–1368.
- Rajeswari, A.; Sabesan, M. Inhibition of monoamine oxidase-B by the polyphenolic compound, curcumin and its metabolite tetrahydrocurcumin, in a model of Parkinson’s disease induced by MPTP neurodegeneration in mice. Inflammopharmacology 2008, 16, 96–99.
- Mansouri, Z.; Sabetkasaei, M.; Moradi, F.; Masoudnia, F.; Ataie, A. Curcumin has neuroprotection effect on homocysteine rat model of Parkinson. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2012, 47, 234–242.
- Zanetti, M.; Grillo, A.; Losurdo, P.; Panizon, E.; Mearelli, F.; Cattin, L.; Barazzoni, R.; Carretta, R. Omega-3 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids: Structural and Functional Effects on the Vascular Wall. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–14.
- Taghizadeh, M.; Tamtaji, O.R.; Dadgostar, E.; Daneshvar Kakhaki, R.; Bahmani, F.; Abolhassani, J.; Aarabi, M.H.; Kouchaki, E.; Memarzadeh, M.R.; Asemi, Z. The effects of omega-3 fatty acids and vitamin E co-supplementation on clinical and metabolic status in patients with Parkinson’s disease: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Neurochem. Int. 2017, 108, 183–189.
- Micke, P.; Beeh, K.M.; Schlaak, J.F.; Buhl, R. Oral supplementation with whey proteins increases plasma glutathione levels of HIV-infected patients. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2001, 31, 171–178.
- Tosukhowong, P.; Boonla, C.; Dissayabutra, T.; Kaewwilai, L.; Muensri, S.; Chotipanich, C.; Joutsa, J.; Rinne, J.; Bhidayasiri, R. Biochemical and clinical effects of Whey protein supplementation in Parkinson’s disease: A pilot study. J. Neurol. Sci. 2016, 367, 162–170.
- Zhao, X.; Zhang, M.; Li, C.; Jiang, X.; Su, Y.; Zhang, Y. Benefits of Vitamins in the Treatment of Parkinson’s Disease. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 1–14.
- Wang, J.-Y.; Wu, J.-N.; Cherng, T.-L.; Hoffer, B.J.; Chen, H.-H.; Borlongan, C.V.; Wang, Y. Vitamin D3 attenuates 6-hydroxydopamine-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Brain Res. 2001, 904, 67–75.
- Jang, W.; Kim, H.J.; Li, H.; Jo, K.D.; Lee, M.K.; Song, S.H.; Yang, H.O. 1,25-Dyhydroxyvitamin D3 attenuates rotenone-induced neurotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells through induction of autophagy. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 451, 142–147.
- Evatt, M.L.; DeLong, M.R.; Khazai, N.; Rosen, A.; Triche, S.; Tangpricha, V. Prevalence of Vitamin D Insufficiency in Patients with Parkinson Disease and Alzheimer Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2008, 65, 1348–1352.
- Knekt, P.; Kilkkinen, A.; Rissanen, H.; Marniemi, J.; Sääksjärvi, K.; Heliövaara, M. Serum Vitamin D and the Risk of Parkinson Disease. Arch. Neurol. 2010, 67, 808–811.
- Lawler, J.M.; Barnes, W.S.; Wu, G.; Song, W.; Demaree, S. Direct antioxidant properties of creatine. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 290, 47–52.
- Matthews, R.T.; Ferrante, R.J.; Klivenyi, P.; Yang, L.; Klein, A.M.; Mueller, G.; Kaddurah-Daouk, R.; Beal, M.F. Creatine and Cyclocreatine Attenuate MPTP Neurotoxicity. Exp. Neurol. 1999, 157, 142–149.
- Yang, L.; Calingasan, N.Y.; Wille, E.J.; Cormier, K.; Smith, K.; Ferrante, R.J.; Flint Beal, M. Combination therapy with Coenzyme Q 10 and creatine produces additive neuroprotective effects in models of Parkinson’s and Huntington’s Diseases. J. Neurochem. 2009, 109, 1427–1439.
- Bender, A.; Koch, W.; Elstner, M.; Schombacher, Y.; Bender, J.; Moeschl, M.; Gekeler, F.; Muller-Myhsok, B.; Gasser, T.; Tatsch, K.; et al. Creatine supplementation in Parkinson disease: A placebo-controlled randomized pilot trial. Neurology 2006, 67, 1262–1264.
- Reiter, R.J. Oxidative damage in the central nervous system: Protection by melatonin. Prog. Neurobiol. 1998, 56, 359–384.
- Antolín, I.; Mayo, J.C.; Sainz, R.M.; del Brío, M.D.L.A.; Herrera, F.; Martín, V.; Rodríguez, C. Protective effect of melatonin in a chronic experimental model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain Res. 2002, 943, 163–173.
- Dabbeni-Sala, F.; Di Santo, S.; Franceschini, D.; Skaper, S.D.; Giusti, P. Melatonin protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity in rats: A role for mitochondrial complex I activity. FASEB J. 2001, 15, 164–170.
- Morgan, W.W.; Nelson, J.F. Chronic administration of pharmacological levels of melatonin does not ameliorate the MPTP-induced degeneration of the nigrostriatal pathway. Brain Res. 2001, 921, 115–121.
- Van der Schyf, C.J.; Castagnoli, K.; Palmer, S.; Hazelwood, L.; Castagnoli, N. Melatonin fails to protect against long-term MPTP-induced dopamine depletion in mouse striatum. Neurotox. Res. 2000, 1, 261–269.
- Shen, L. Associations between B vitamins and Parkinson’s disease. Nutrients 2015, 7, 7197–7208.
- Jia, H.; Li, X.; Gao, H.; Feng, Z.; Li, X.; Zhao, L.; Jia, X.; Zhang, H.; Liu, J. High doses of nicotinamide prevent oxidative mitochondrial dysfunction in a cellular model and improve motor deficit in a Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurosci. Res. 2008, 86, 2083–2090.
- Anderson, D.W.; Bradbury, K.A.; Schneider, J.S. Broad neuroprotective profile of nicotinamide in different mouse models of MPTP-induced parkinsonism. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 610–617.
- Hellenbrand, W.; Boeing, H.; Robra, B.P.; Seidler, A.; Vieregge, P.; Nischan, P.; Joerg, J.; Oertel, W.H.; Schneider, E.; Ulm, G. Diet and Parkinson’s disease. II: A possible role for the past intake of specific nutrients. Results from a self-administered food-frequency questionnaire in a case-control study. Neurology 1996, 47, 644–650.
- Alisky, J.M. Niacin improved rigidity and bradykinesia in a Parkinson’s disease patient but also caused unacceptable nightmares and skin rash—A case report. Nutr. Neurosci. 2005, 8, 327–329.
- Johnson, C.C.; Gorell, J.M.; Rybicki, B.A.; Sanders, K.; Peterson, E.L. Adult nutrient intake as a risk factor for Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Epidemiol. 1999, 28, 1102–1109.
- Chan, A.C. Partners in defense, vitamin E and vitamin C. Can. J. Physiol. Pharmacol. 1993, 71, 725–731.
- Sershen, H.; Reith, M.E.; Hashim, A.; Lajtha, A. Protection against 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine neurotoxicity by the antioxidant ascorbic acid. Neuropharmacology 1985, 24, 1257–1259.
- Seitz, G.; Gebhardt, S.; Beck, J.F.; Böhm, W.; Lode, H.N.; Niethammer, D.; Bruchelt, G. Ascorbic acid stimulates DOPA synthesis and tyrosine hydroxylase gene expression in the human neuroblastoma cell line SK-N-SH. Neurosci. Lett. 1998, 244, 33–36.
- Hughes, K.C.; Gao, X.; Kim, I.Y.; Rimm, E.B.; Wang, M.; Weisskopf, M.G.; Schwarzschild, M.A.; Ascherio, A. Intake of antioxidant vitamins and risk of Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2016, 31, 1909–1914.
- Dugasani, S.; Pichika, M.R.; Nadarajah, V.D.; Balijepalli, M.K.; Tandra, S.; Korlakunta, J.N. Comparative antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects of [6]-gingerol, [8]-gingerol, [10]-gingerol and [6]-shogaol. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 127, 515–520.
- Park, G.; Kim, H.G.; Ju, M.S.; Ha, S.K.; Park, Y.; Kim, S.Y.; Oh, M.S. 6-Shogaol, an active compound of ginger, protects dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease models via anti-neuroinflammation. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2013, 34, 1131–1139.
- Ha, S.K.; Moon, E.; Ju, M.S.; Kim, D.H.; Ryu, J.H.; Oh, M.S.; Kim, S.Y. 6-Shogaol, a ginger product, modulates neuroinflammation: A new approach to neuroprotection. Neuropharmacology 2012, 63, 211–223.
- Mueller, L.; Boehm, V. Antioxidant activity of β-carotene compounds in different in vitro assays. Molecules 2011, 16, 1055–1069.
- Yang, F.; Wolk, A.; Håkansson, N.; Pedersen, N.L.; Wirdefeldt, K. Dietary antioxidants and risk of Parkinson’s disease in two population-based cohorts. Mov. Disord. 2017, 32, 1631–1636.
- Ono, K.; Yamada, M. Vitamin A potently destabilizes preformed α-synuclein fibrils in vitro: Implications for Lewy body diseases. Neurobiol. Dis. 2007, 25, 446–454.
- Etminan, M.; Gill, S.S.; Samii, A. Intake of vitamin E, vitamin C, and carotenoids and the risk of Parkinson’s disease: A meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2005, 4, 362–365.
- Conn, P.F.; Schalch, W.; Truscott, T.G. The singlet oxygen and carotenoid interaction. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B Biol. 1991, 11, 41–47.
- Di Mascio, P.; Kaiser, S.; Sies, H. Lycopene as the most efficient biological carotenoid singlet oxygen quencher. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1989, 274, 532–538.
- Kaur, H.; Chauhan, S.; Sandhir, R. Protective Effect of Lycopene on Oxidative Stress and Cognitive Decline in Rotenone Induced Model of Parkinson’s Disease. Neurochem. Res. 2011, 36, 1435–1443.
- Prema, A.; Janakiraman, U.; Manivasagam, T.; Justin Thenmozhi, A. Neuroprotective effect of lycopene against MPTP induced experimental Parkinson’s disease in mice. Neurosci. Lett. 2015, 599, 12–19.
- Sandhir, R.; Mehrotra, A.; Kamboj, S.S. Lycopene prevents 3-nitropropionic acid-induced mitochondrial oxidative stress and dysfunctions in nervous system. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 57, 579–587.
- Kostić, A.Ž.; Milinčić, D.D.; Gašić, U.M.; Nedić, N.; Stanojević, S.P.; Tešić, Ž.L.; Pešić, M.B. Polyphenolic profile and antioxidant properties of bee-collected pollen from sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) plant. LWT 2019, 112.
- De-Melo, A.A.M.; Estevinho, L.M.; Moreira, M.M.; Delerue-Matos, C.; de Freitas, A.D.S.; Barth, O.M.; de Almeida-Muradian, L.B. Phenolic profile by HPLC-MS, biological potential, and nutritional value of a promising food: Monofloral bee pollen. J. Food Biochem. 2018, 42, 1–21.
- Yao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Shi, J.; Thomas-Barberan, F. Flavonoids in food and their health benefits. Plant Food Hum. Nutr. 2004, 59, 113–122.
- Jung, U.J.; Kim, S.R. Beneficial Effects of Flavonoids Against Parkinson’s Disease. J. Med. Food 2018, 21, 421–432.
- Kumar, A.; Sehgal, N.; Kumar, P.; Padi, S.S.V.; Naidu, P.S. Protective effect of quercetin against ICV colchicine-induced cognitive dysfunctions and oxidative damage in rats. Phyther. Res. 2008, 22, 1563–1569.
- Sriraksa, N.; Wattanathorn, J.; Muchimapura, S.; Tiamkao, S.; Brown, K.; Chaisiwamongkol, K. Cognitive-Enhancing Effect of Quercetin in a Rat Model of Parkinson’s Disease Induced by 6-Hydroxydopamine. Evid. Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 2012, 823206.
- Xing, L.; Zhang, H.; Qi, R.; Tsao, R.; Mine, Y. Recent Advances in the Understanding of the Health Benefits and Molecular Mechanisms Associated with Green Tea Polyphenols. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 1029–1043.
- Farzaei, M.H.; Bahramsoltani, R.; Abbasabadi, Z.; Braidy, N.; Nabavi, S.M. Role of green tea catechins in prevention of age-related cognitive decline: Pharmacological targets and clinical perspective. J. Cell. Physiol. 2019, 234, 2447–2459.
- Tanaka, K.; S.-Galduroz, R.; Gobbi, L.; Galduroz, J. Ginkgo Biloba Extract in an Animal Model of Parkinson’s Disease: A Systematic Review. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2013, 11, 430–435.
- Wu, W.R.; Zhu, X.Z. Involvement of monoamine oxidase inhibition in neuroprotective and neurorestorative effects of Ginkgo biloba extract against MPTP-induced nigrostriatal dopaminergic toxicity in C57 mice. Life Sci. 1999, 65, 157–164.
- Rojas, P.; Serrano-García, N.; Mares-Sámano, J.J.; Medina-Campos, O.N.; Pedraza-Chaverri, J.; Ögren, S.O. EGb761 protects against nigrostriatal dopaminergic neurotoxicity in 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3, 6-tetrahydropyridine-induced Parkinsonism in mice: Role of oxidative stress. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2008, 28, 41–50.
