Lab-on-a-chip (LOC) and organ-on-a-chip (OOC) devices are highly versatile platforms that enable miniaturization and advanced controlled laboratory functions (i.e., microfluidics, advanced optical or electrical recordings, high-throughput screening). The manufacturing advancements of LOCs/OOCs for biomedical applications and their current limitations are briefly discussed. Multiple studies have exploited the advantages of mimicking organs or tissues on a chip. Among these, we focused our attention on the brain-on-a-chip, blood–brain barrier (BBB)-on-a-chip, and neurovascular unit (NVU)-on-a-chip applications.
- lab-on-a-chip
- organ-on-a-chip
- microfluidic platforms
- blood brain barrier
- neurovascular unit
- drug screening
- neurodegenerative disorders
Note: The following contents are extract from your paper. The entry will be online only after author check and submit it.
1. Introduction
2. LOC Materials and Manufacturing Advancements for Biomedical Research
| Material/Property | Silicon/Glass | Elastomers | Thermosets | Thermoplastics | Hydrogel | Paper | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| optical transparency | no/high | high | high | medium to high | low to medium | low | ||
| hydrophobicity | hydrophilic | hydrophobic | hydrophobic | hydrophobic | hydrophilic | amphiphilic | ||
| thermostability | very high | medium | high | medium to high | low | medium | ||
| resistance to oxidizer | excellent | moderate | good | moderate to good | low | low | ||
| solvent compatibility | very high | low | high | medium to high | low | medium | ||
| permeability to oxygen (Barrer | a | ) | <0.01 | ≈500 | 0.03–1 | 0.05–5 | >1 | >1 |
| surface charge | very stable | not stable | stable | stable | N/A | N/A | ||
| common technique for microfabrication/features | photolithography, laser-assisted etching | casting | casting, photopolymerization | thermo-molding | casting, photopolymerization, 3D bioprinting | photolithography, printing | ||
| smallest channel dimension | <100 nm | <1 μm | <100 nm | ≈100 nm | ≈10 μm | ≈200 μm | ||
| channel profile | limited 3D/3D | 3D | arbitrary 3D | 3D | 3D | 2D | ||
| multilayer channels | hard/easy | easy | easy | easy | Medium | easy | ||
| throughput | medium to high | high | high | high | low to medium | high |
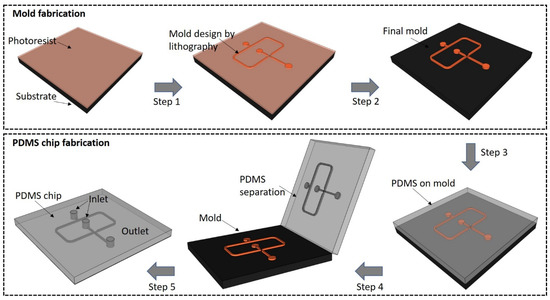
2.1. PDMS LOCs
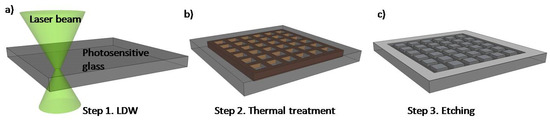
2.2. Glass LOCs
2.3. Biomedical Applications of LOCs
| Organ/Tissue Type | Chip Material | Membrane Material | Application | Reference |
|---|
| Model | Chip Material | Membrane Material | Culture Type | Cells | Application | Reference | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BBB | PDMS and glass | Polycarbonate | Co-culture | Endothelial cells (b.End3) and astrocytes (C8D1A) | BBB permeability | [100] | [99] |
| BBB | PDMS | Polyethylene terephthalate | Co-culture | Endothelial cells (BMEC from hiPCS) and astrocytes (from IMR90-4 iPSCs) | BBB permeability due to TNF-α in liver failure/melanoma | [101] | [100] |
| [ | |||||||
| 66 | |||||||
| ] | |||||||
| [ | |||||||
| 65 | |||||||
| ] | |||||||
| Skin-on-a-chip | PDMS | Polyester | Mimicking edema and inflammation of the skin and testing dexamethasone effects | [67] | [66] |
| Organ/Tissue Type | Type of Cells | Application | Reference | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Alveolus-on-a-chip | PDMS | PDMS | Interface alveolar epithelium/endothelium for the study of inflammation-induced thrombosis | ||||||||
| Brain organoid-on-a-chip | 3D brain organoids derived from human-induced pluripotent stem cells (hiPSCs) | [ | Modeling the neurodevelopmental disorders under environmental exposure (e.g., nicotine) | 60] | [77 | [59] | |||||
| ] | [ | 76 | ] | Bone marrow-on-a-chip | PDMS | PDMS | |||||
| 3D brain-on-a-chip | Analysis of the cellular response to drugs and radiation | Neurospheroids obtained from prenatal E16 rat cortical neurons | [ | In vitro brain model for neurodegenerative disease (e.g., Alzheimers’ disease) and high-throughput drug screening | [42] | [41] | 61] | [60] | |||
| Gut-on-a-chip | PDMS | Polyester | Development of a platform for drug screening and substance toxicity testing | [62] | [61] | ||||||
| Brain-on-a-chip | Neurospheroids obtained from human neural progenitor and human iPSC-derived neural progenitor cells | Investigating the development of Alzheimer’s disease and testing drugs against this neuropathology | [78] | [77] | Heart-on-a-chip | PDMS | No membrane | Testing the inotropic effect of isoproterenol on cardiac contractility | [63] | [62] | |
| BBB | OrganoPlate | No membrane | Neurospheroid network-on-a-chip | Neurospheroids obtained from primary culture obtained from the cerebral cortex of Wistar rats | Studying neural transplantation therapy for treating severe degenerative brain disease | [ | PMMA and PDMS | No membrane | Evaluation of cardiovascular toxicity of some pharmaceutical products | [64] | [63] |
| 79 | ] | [ | Intestine–liver–brain–kidney-on-a-chip | PDMS | PDMS | Production and testing of an autologous iPSC derived four-organ-on-a-chip in long-term cocultivation conditions (i.e., 14 days) | [69] | [68] | |||
| 78 | ] | ||||||||||
| 3D brain-on-a-chip | Neurospheroids obtained from prenatal rat (E18) cortical neurons | Modulation of cell–ECM interactions at the neuronal level by analyzing neurospheroids and their study in pathological conditions | [80] | [79] | Kidney-on-a-chip | PDMS | Polyester | Analysis in conditions close to the physiological ones of renal tubule cells | [70] | [69] | |
| Lung-on-a-chip | PDMS | PDMS | Mimicking and analyzing the long alveolar barrier | [65] | [64] | ||||||
| Lung–liver–heart-on-a-chip | PMMA and PDMS | Polyester | Assessment of the importance of interactions between organs in response to drugs | [68] | [67] | ||||||
| Pancreas-on-a-chip | PDMS | Polyester | Investigating the role of CFTR (Cystic Fibrosis Transmembrane Conductance Regulator) in insulin production |
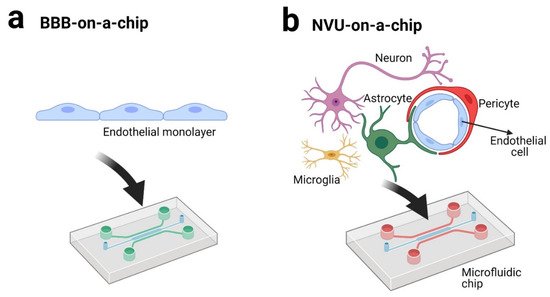
3. BBB andNVU on a Chip
| Type of Analysis | Comparison | Type of Cells | References | |||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TEER ZO1 immunostaining |
Slightly higher resistance values upon 7 days in culture for BBB-on-a-chip compared to the transwell system Similar ZO1 immunostaining |
human endothelial cells hCMEC/D3 | [97] | [96] | ||||||||||
| TEER ZO1 immunostaining |
Astrocyte conditioned medium improves the resistance values of BBB-on-a-chip BBB-on-a-chip has higher resistance values than the transwell model |
Rat brain endothelial cells (RBEC) isolated from neonatal rats neonatal rat astrocytes |
[ | |||||||||||
| 105 | ||||||||||||||
| ] | ||||||||||||||
| 113 | ] | [ | 112] | Tri-culture | ||||||||||
| TEER | μBBB had significantly higher (10-fold) resistance values than the transwell model for co-cultures | b.End3 endothelial cells, with and without co-cultured C8-D1A astrocytes | Endothelial cells (TY10), astrocytes (hAst) and pericytes (hBPCT) | [100 | BBB permeability for different types of molecules (antibodies) | ] | [99] | [98] | [97] | |||||
| BBB | Objet Vero Clear, silicone, and PDMS | Polycarbonate | ||||||||||||
| Barrier permeability and cytokine release profile | Co-culture | Similar permeability of the human 3D BBB-on-a-chip compared to the non-human cells BBB models or to the inflammatory stimulated models (depending on the presence of astrocytes or pericytes) Significantly higher permeability of the human 3D BBB-on-a-chip compared to co-cultures in static transwell plates |
Co-culture of human brain microvascular endothelial cells, human brain pericytes, human astrocytes (from cortex) | [ | Endothelial cells (BMEC from iPSC) and astrocytes (Rat primary culture) | 95] | [BBB permeability for drugs | 94] | [102] | [101] | ||||
| BBB | PDMS | Polycarbonate | Co-culture | Primary mouse brain microvascular endothelial cells and primary mouse astrocytes | Cellular interactions in the BBB under physiological or shear stress conditions | Human iPS cell line IMR90-4 | [103] | [102] | ||||||
| [ | BBB | |||||||||||||
| P-glycoprotein (P-gp) permeability | BBB-on-a-chip model, but not the transwell model, enable the study of P-gp efflux pump permeability and its pharmacological blockade (e.g., verapamil) | 23 | ] | [22]BBB | PDMS | Polyester and polytetrafluoroethylene | Co-culture | Endothelial cells (b.End3) and astrocytes (C8D1A) | Analysis of cell cultures on porous membranes | [104] | [103] | |||
| BBB | PMMA | Polyester | Monoculture | Endothelial cells (b.End3) | Transport of nanoparticles across the BBB | [105] | [104] | |||||||
| BBB | PDMS and polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) | Polyvinylidene fluoride (PVDF) | Co-culture | Human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (hCMEC/D3) and normal human astrocytes | Reproducible platform for the BBB study under static or continuous flow conditions | [106] | [ | PDMS | Polycarbonate | Tri-culture | Human cerebral microvascular endothelial cells (HBMEC), pericytes, and astrocytes | BBB model for the investigation of neuroinflammation | [107] | [106] |
| BBB | PDMS | No membrane | Multi-Culture | Endothelial cells (HBMEC and HUVEC), pericytes (HhPC-PL), astrocytes (NHA), and primary normal human lung fibroblasts (LF) | In vitro reproduction of angiogenesis in the central nervous system | [108] | [107] | |||||||
| BBB | PDMS, PMMA, and PC | N/A | Co-culture | Endothelial cells (HUVEC) and human astrocytes | Testing the biocompatibility of the APTES-coated PDMS surface, on which different types of coating were applied | [109] | [108] | |||||||
| NVU | PDMS | No membrane | Tri-culture | Human iPSC-derived blood–brain barrier cells Human primary astrocytes Human primary pericytes |
Complex platform for the study of neurological diseases | [110] | [109] | |||||||
| NVU | PDMS | PDMS | Co-culture (×2) | Human teratocarcinoma NTERA-2 cl. D1 (hNT2) cells and human endothelial cells (hBMEC) Human teratocarcinoma NTERA-2 cl. D1 (hNT2) cells and Human fetal neural progenitor cells (hNPCs) |
Differentiation of cells on the chip and analysis of the importance of cell interactions in neurodevelopment | [111] | [110] | |||||||
| NVU | PDMS | No membrane | Multi-Culture | Endothelial cells (HUVEC and hCMEC/D3), neurons (primary culture), and astrocytes (primary culture) | Neurovascular unit development | [17] | [16] | |||||||
| NVU | PDMS andpolycarbonate | Polyethylene terephthalate andpolycarbonate | Multi-Culture | Human hippocampal neural stem cells HIP-009 cells, cortical human brain microvascular endothelial cells (hBMVECs), human astrocytes, and human brain pericytes of cortical origin | Effect of intravascular administration of methamphetamine | [18] | [17] |
References
- Whitesides, G.M. The origins and the future of microfluidics. Nature 2006, 442, 368–373.
- Gupta, S.; Ramesh, K.; Ahmed, S.; Kakkar, V. Lab-on-chip technology: Are view on design trends and future scope in biomedical applications. Int. J. Bio-Sci. Bio-Technol. 2016, 8, 311–322.
- Gardeniers, J.; Van den Berg, A. Lab-on-a-chip systems for biomedical and environmental monitoring. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2004, 378, 1700–1703.
- Azizipour, N.; Avazpour, R.; Rosenzweig, D.H.; Sawan, M.; Ajji, A. Evolution of biochip technology: Are view fromlab-on-a-chip to organ-on-a-chip. Micromachines 2020, 11, 599.
- Polini, A.; Prodanov, L.; Bhise, N.S.; Manoharan, V.; Dokmeci, M.R.; Khademhosseini, A. Organs-on-a-chip: A new tool fordrug discovery. Expert Opin. Drug Discov. 2014, 9, 335–352.
- Ghallab, Y.H.; Badawy, W. Lab-on-a-Chip: Techniques, Circuits, and Biomedical Applications; ArtechHouse: Norwood, MA, USA, 2010.
- Hou, X.; Zhang, Y.S.; Trujillo-de Santiago, G.; Alvarez, M.M.; Ribas, J.; Jonas, S.J.; Weiss, P.S.; Andrews, A.M.; Aizenberg, J.; Khademhosseini, A. Interplay between materials and microfluidics. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2017, 2, 1–15.
- Dong, R.; Liu, Y.; Mou, L.; Deng, J.; Jiang, X. Microfluidics-based biomaterials and biodevices. Adv. Mater. 2019, 31, 1805033.
- Jiang, L.; Li, S.; Zheng, J.; Li, Y.; Huang, H. Recent progress in microfluidic models of the blood-brain barrier. Micromachines 2019, 10, 375.
- Nielsen, J.B.; Hanson, R.L.; Almughamsi, H.M.; Pang, C.; Fish, T.R.; Woolley, A.T. Microfluidics: Innovations in materials and their fabrication and functionalization. Anal. Chem. 2019, 92, 150–168.
- Ren, K.; Zhou, J.; Wu, H. Materials for microfluidic chip fabrication. Acc. Chem. Res. 2013, 46, 2396–2406.
- Harrison, D.J.; Fluri, K.; Seiler, K.; Fan, Z.; Effenhauser, C.S.; Manz, A. Micromachining a miniaturized capillary electrophoresis-based chemical analysis system on a chip. Science 1993, 261, 895–897.
- Gale, B.K.; Jafek, A.R.; Lambert, C.J.; Goenner, B.L.; Moghimifam, H.; Nze, U.C.; Kamarapu, S.K. A review of current methods in microfluidic device fabrication and future commercialization prospects. Inventions 2018, 3, 60.
- Whitesides, G.M.; Ostuni, E.; Takayama, S.; Jiang, X.; Ingber, D.E. Soft lithography in biology and biochemistry. Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 2001, 3, 335–373.
- Mata, A.; Fleischman, A.J.; Roy, S. Characterization of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) properties for biomedical micro/nanosystems. Biomed. Microdevices 2005, 7, 281–293.
- Adriani, G.; Ma, D.; Pavesi, A.; Kamm, R.D.; Goh, E.L. A 3D neurovascular microfluidic model consisting of neurons, astrocytes and cerebral endothelial cells as a blood–brain barrier. Lab Chip 2017, 17, 448–459.
- Maoz, B.M.; Herland, A.; FitzGerald, E.A.; Grevesse, T.; Vidoudez, C.; Pacheco, A.R.; Sheehy, S.P.; Park, T.-E.; Dauth, S.; Mannix, R. A linked organ-on-chip model of the human neurovascular unit reveals the metabolic coupling of endothelial and neuronal cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2018, 36, 865–874.
- Ning, R.; Zhuang, Q.; Lin, J.-M. Biomaterial-based microfluidics for cell culture and analysis. In Cell Analysis on Microfluidics; Springer: Singapore, 2018; pp. 181–224.
- Zilberzwige-Tal, S.; Gazit, E. Go with the flow—Microfluidics approaches for amyloid research. Chem. Asian J. 2018, 13, 3437–3447.
- Liu, X.; Zheng, W.; Jiang, X. Cell-based assays on microfluidics for drug screening. ACS Sens. 2019, 4, 1465–1475.
- Oddo, A.; Peng, B.; Tong, Z.; Wei, Y.; Tong, W.Y.; Thissen, H.; Voelcker, N.H. Advances in microfluidicblood–brain barrier (BBB) models. Trends Biotechnol. 2019, 37, 1295–1314.
- Park, T.-E.; Mustafaoglu, N.; Herland, A.; Hasselkus, R.; Mannix, R.; FitzGerald, E.A.; Prantil-Baun, R.; Watters, A.; Henry, O.; Benz, M. Hypoxia-enhanced blood-brain barrier chip recapitulates human barrier function and shuttling of drugs and antibodies. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–12.
- Eddington, D.T.; Puccinelli, J.P.; Beebe, D.J. Thermal aging and reduced hydrophobic recovery of polydimethylsiloxane. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2006, 114, 170–172.
- Bodas, D.; Khan-Malek, C. Formation of more stable hydrophilic surfaces of PDMS by plasma and chemical treatments. Microelectron. Eng. 2006, 83, 1277–1279.
- Hong, S.M.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.H.; Hwang, H.I. Hydrophilic surface modification of PDMS using atmospheric RF plasma. In Proceedings of the Journal of Physics: Conference Series; IOP Publishing: Bristol, UK, 2006; p. 108.
- Tan, S.H.; Nguyen, N.-T.; Chua, Y.C.; Kang, T.G. Oxygen plasma treatment for reducing hydrophobicity of a sealed polydimethylsiloxane microchannel. Biomicrofluidics 2010, 4, 032204.
- Hillborg, H.; Sandelin, M.; Gedde, U.W. Hydrophobic recovery of polydimethylsiloxane after exposure to partial discharges as a function of crosslink density. Polymer 2001, 42, 7349–7362.
- Hoek, I.; Tho, F.; Arnold, W.M. Sodium hydroxide treatment of PDMS based microfluidic devices. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 2283–2285.
- De Menezes Atayde, C.; Doi, I. Highly stable hydrophilic surfaces of PDMS thin layer obtained by UV radiation and oxygen plasma treatments. Phys. Status Solidi C 2010, 7, 189–192.
- Lee, D.; Yang, S. Surface modification of PDMS by atmospheric-pressure plasma-enhanced chemical vapor deposition and analysis of long-lasting surface hydrophilicity. Sens. Actuators B Chem. 2012, 162, 425–434.
- Hemmilä, S.; Cauich-Rodríguez, J.V.; Kreutzer, J.; Kallio, P. Rapid, simple, and cost-effective treatments to achieve long-term hydrophilic PDMS surfaces. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2012, 258, 9864–9875.
- Gaš, B.; Zuska, J.; Coufal, P.; van de Goor, T. Optimization of the high-frequency contactless conductivity detector for capillary electrophoresis. Electrophoresis 2002, 23, 3520–3527.
- Jahangiri, F.; Hakala, T.; Jokinen, V. Long-term hydrophilization of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) for capillary filling microfluidic chips. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2020, 24, 1–11.
- Zhang, B.; Korolj, A.; Lai, B.F.L.; Radisic, M. Advancesinorgan-on-a-chipengineering. Nat. Rev. Mater. 2018, 3, 257–278.
- Morarka, A.; Agrawal, S.; Kale, S.; Kale, A.; Ogale, S.; Paknikar, K.; Bodas, D. Quantum dot based immunosensor using 3D circular microchannels fabricated in PDMS. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2011, 26, 3050–3053.
- Chan, H.N.; Chen, Y.; Shu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Tian, Q.; Wu, H. Direct, one-step molding of 3D-printed structures for convenient fabrication of truly 3D PDMS microfluidic chips. Microfluid. Nanofluidics 2015, 19, 9–18.
- Sugioka, K.; Cheng, Y. Ultra fast lasers—Reliable tools for advanced materials processing. Light Sci. Appl. 2014, 3, e149.
- Takano, A.; Ogawa, T.; Tanaka, M.; Futai, N. On-chip incubation system for long-term microfluidic cell culture. In Proceedings of the 2011 Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society, Boston, MA, USA, 30 August–3 September 2011; pp. 8404–8407.
- Jo, B.-H.; VanLerberghe, L.M.; Motsegood, K.M.; Beebe, D.J. Three-dimensional micro-channel fabrication in polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) elastomer. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2000, 9, 76–81.
- Fleger, M.; Neyer, A. PDMS microfluidic chip with integrated wave guides for optical detection. Microelectron. Eng. 2006, 83, 1291–1293.
- Park, J.; Lee, B.K.; Jeong, G.S.; Hyun, J.K.; Lee, C.J.; Lee, S.-H. Three-dimensional brain-on-a-chip with an interstitial level of flow and its application as an in vitro model of Alzheimer’s disease. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 141–150.
- Hwang, J.; Cho, Y.H.; Park, M.S.; Kim, B.H. Microchannel fabrication on glass materials for microfluidic devices. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 2019, 20, 479–495.
- Matsuo, S.; Sumi, H.; Kiyama, S.; Tomita, T.; Hashimoto, S. Femtosecond laser-assisted etching of Pyrex glass with aqueoussolution of KOH. Appl. Surf. Sci. 2009, 255, 9758–9760.
- Chang, T.-L.; Chen, Z.-C.; Lee, Y.-W.; Li, Y.-H.; Wang, C.-P. Ultrafast laser ablation of soda-lime glass for fabricating microfluidic pillar array channels. Microelectron. Eng. 2016, 158, 95–101.
- Bhattacharya, S.; Datta, A.; Berg, J.M.; Gangopadhyay, S. Studies on surface wettability of poly (dimethyl) siloxane (PDMS) and glass under oxygen-plasma treatment and correlation with bond strength. J. Microelectromech. Syst. 2005, 14, 590–597.
- Plecis, A.; Chen, Y. Fabrication of microfluidic devices based on glass—PDMS—Glass technology. Microelectron. Eng. 2007, 84, 1265–1269.
- Haubert, K.; Drier, T.; Beebe, D. PDMS bonding by means of a portable, low-cost corona system. Lab Chip 2006, 6, 1548–1549.
- Aran, K.; Sasso, L.A.; Kamdar, N.; Zahn, J.D. Irreversible, direct bonding of nanoporous polymer membranes to PDMS or glass microdevices. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 548–552.
- Sima, F.; Xu, J.; Wu, D.; Sugioka, K. Ultrafast laser fabrication of functional biochips: New avenues for exploring 3D micro-and nano-environments. Micromachines 2017, 8, 40.
- Sugioka, K.; Cheng, Y. Femtosecond laser processing for optofluidic fabrication. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 3576–3589.
- Jipa, F.; Iosub, S.; Calin, B.; Axente, E.; Sima, F.; Sugioka, K. High repetition rate UV versus VIS picosecond laser fabricationof 3D microfluidic channels embedded in photosensitive glass. Nanomaterials 2018, 8, 583.
- Hanada, Y.; Sugioka, K.; Shihira-Ishikawa, I.; Kawano, H.; Miyawaki, A.; Midorikawa, K. 3D microfluidic chips with integrated functional microelements fabricated by a femtosecond laser for studying the gliding mechanism of cyanobacteria. Lab Chip 2011, 11, 2109–2115.
- Sima, F.; Sugioka, K.; Vázquez, R.M.; Osellame, R.; Kelemen, L.; Ormos, P. Three-dimensional femtosecond laser processing for lab-on-a-chip applications. Nanophotonics 2018, 7, 613–634.
- Jipa, F.; Orobeti, S.; Butnaru, C.; Zamfirescu, M.; Axente, E.; Sima, F.; Sugioka, K. Picosecond Laser Processing of Photosensitive Glass for Generation of Biologically Relevant Microenvironments. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 8947.
- Sima, F.; Kawano, H.; Hirano, M.; Miyawaki, A.; Obata, K.; Serien, D.; Sugioka, K. Mimicking intravasation–extravasation with a3D glass nanofluidic model for the chemotaxis-free migration of cancer cells in confined spaces. Adv. Mater. Technol. 2020, 5, 2000484.
- Sima, F.; Kawano, H.; Miyawaki, A.; Kelemen, L.; Ormos, P.; Wu, D.; Xu, J.; Midorikawa, K.; Sugioka, K. 3D biomimetic chips for cancer cell migration in nanometer-sized spaces using “Ship-in-a-Bottle” femtosecond laser processing. ACS Appl. Biomater. 2018, 1, 1667–1676.
- Wu, D.; Wu, S.Z.; Xu, J.; Niu, L.G.; Midorikawa, K.; Sugioka, K. Hybrid femtosecond laser microfabrication to achieve true 3D glass/polymer composite biochips with multiscale features and high performance: The concept of ship-in-a-bottle biochip. Laser Photonics Rev. 2014, 8, 458–467.
- Ramadan, Q.; Zourob, M. Organ-on-a-chip engineering: Toward bridging the gap between lab and industry. Biomicrofluidics 2020, 14, 041501.
- Jain, A.; Barrile, R.; van der Meer, A.D.; Mammoto, A.; Mammoto, T.; DeCeunynck, K.; Aisiku, O.; Otieno, M.A.; Louden, C.S.; Hamilton, G.A. Primary human lung alveolus-on-a-chip model of intravascular thrombosis for assessment of therapeutics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 103, 332–340.
- Torisawa, Y.-S.; Spina, C.S.; Mammoto, T.; Mammoto, A.; Weaver, J.C.; Tat, T.; Collins, J.J.; Ingber, D.E. Bone marrow–on–a–chip replicates hematopoietic niche physiology in vitro. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 663–669.
- Kimura, H.; Yamamoto, T.; Sakai, H.; Sakai, Y.; Fujii, T. An integrated microfluidic system for long-term perfusion culture and on-line monitoring of intestinal tissue models. Lab Chip 2008, 8, 741–746.
- Agarwal, A.; Goss, J.A.; Cho, A.; McCain, M.L.; Parker, K.K. Microfluidic heart on a chip for higher throughput pharmacological studies. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 3599–3608.
- Zhang, Y.S.; Arneri, A.; Bersini, S.; Shin, S.-R.; Zhu, K.; Goli-Malekabadi, Z.; Aleman, J.; Colosi, C.; Busignani, F.; Dell’Erba, V. Bioprinting 3D microfibrous scaffolds for engineering endothelialized myocardium and heart-on-a-chip. Biomaterials 2016, 110, 45–59.
- Stucki, A.O.; Stucki, J.D.; Hall, S.R.; Felder, M.; Mermoud, Y.; Schmid, R.A.; Geiser, T.; Guenat, O.T. A lung-on-a-chip array with an integrated bio-inspired respiration mechanism. Lab Chip 2015, 15, 1302–1310.
- Mun, K.S.; Arora, K.; Huang, Y.; Yang, F.; Yarlagadda, S.; Ramananda, Y.; Abu-El-Haija, M.; Palermo, J.J.; Appakalai, B.N.; Nathan, J.D. Patient-derived pancreas-on-a-chip to model cystic fibrosis-related disorders. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 1–12.
- Wufuer, M.; Lee, G.; Hur, W.; Jeon, B.; Kim, B.J.; Choi, T.H.; Lee, S. Skin-on-a-chip model simulating inflammation, edema and drug-based treatment. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12.
- Skardal, A.; Murphy, S.V.; Devarasetty, M.; Mead, I.; Kang, H.-W.; Seol, Y.-J.; Zhang, Y.S.; Shin, S.-R.; Zhao, L.; Aleman, J. Multi-tissue interactions in an integrated three-tissue organ-on-a-chip platform. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–16.
- Ramme, A.P.; Koenig, L.; Hasenberg, T.; Schwenk, C.; Magauer, C.; Faust, D.; Lorenz, A.K.; Krebs, A.-C.; Drewell, C.; Schirrmann, K. Autologous induced pluripotent stem cell-derived four-organ-chip. Future Sci. OA 2019, 5, FSO413.
- Jang, K.-J.; Suh, K.-Y. A multi-layer microfluidic device for efficient culture and analysis of renal tubular cells. Lab Chip 2010, 10, 36–42.
- Maschmeyer, I.; Lorenz, A.; Ramme, A.; Hasenberg, T.; Schimek, K.; Hübner, J.; Lauster, R.; Marx, U. A microfluidic four-organ-chip for interconnected long-termco-culture of human intestine, liver, skin and kidney equivalents. Toxicol. Lett. 2015, 2, S176.
- Junaid, A.; Mashaghi, A.; Hankemeier, T.; Vulto, P. An end-user perspective on Organ-on-a-Chip: Assays and usability aspects. Curr. Opin. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 1, 15–22.
- Miccoli, B.; Braeken, D.; Li, Y.-C.E. Brain-on-a-chip devices for drug screening and disease modeling applications. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2018, 24, 5419–5436.
- Jahromi, M.A.M.; Abdoli, A.; Rahmanian, M.; Bardania, H.; Bayandori, M.; Basri, S.M.M.; Kalbasi, A.; Aref, A.R.; Karimi, M.; Hamblin, M.R. Microfluidic brain-on-a-chip: Perspectives for mimicking neural system disorders. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 8489–8512.
- Ndyabawe, K.; Kisaalita, W.S. Engineering Microsystems to recapitulate brain physiology on a chip. Drug Discov. Today 2019, 24, 1725–1730.
- Zhao, Y.; Demirci, U.; Chen, Y.; Chen, P. Multi scale brain research on a microfluidic chip. Lab Chip 2020, 20, 1531–1543.
- Wang, Y.; Wang, L.; Zhu, Y.; Qin, J. Human brain organoid-on-a-chip to model prenatal nicotine exposure. Lab Chip 2018, 18, 851–860.
- Jorfi, M.; D’Avanzo, C.; Tanzi, R.E.; Kim, D.Y.; Irimia, D. Human neurospheroid arrays for in vitro studies of Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–13.
- Kato-Negishi, M.; Tsuda, Y.; Onoe, H.; Takeuchi, S. A neurospheroid network-stamping method for neural transplantation to the brain. Biomaterials 2010, 31, 8939–8945.
- Lee, G.; Lim, J.; Park, J.; Lee, W.; Yoon, D.S.; Kim, S.H.; Kim, M.-K.; Lee, S.-H.; Kim, D.-H. Construction of neurospheroids via surface modified concave microwells. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 2018, 62, 341–351.
- Iadecola, C. The neurovascular unit coming of age: A journey through neurovascular coupling in health and disease. Neuron 2017, 96, 17–42.
- Jamieson, J.J.; Gerecht, S. Chipping away at blood-brain-barrier modeling. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 831–832.
- Van der Helm, M.; vanderMeer, A.; Eijkel, J.; vandenBerg, A.; Segerink, L. Microfluidic organ-on-chip technology for blood-brain barrier research. Tissue Barriers 2016, 4, e1142493.
- Hawkins, B.T.; Davis, T.P. The blood-brain barrier/neurovascular unit in health and disease. Pharmacol. Rev. 2005, 57, 173–185.
- Bertini, G.; Bramanti, P.; Constantin, G.; Pellitteri, M.; Radu, B.M.; Radu, M.; Fabene, P.F. New players in the neurovascular unit: Insights from experimental and clinical epilepsy. Neurochem. Int. 2013, 63, 652–659.
- Muoio, V.; Persson, P.; Sendeski, M. The neurovascular unit—Concept review. Acta Physiol. 2014, 210, 790–798.
- Abbott, N.J. Astrocyte–endothelial interactions and blood–brain barrier permeability. J. Anat. 2002, 200, 523–534.
- Bélanger, M.; Allaman, I.; Magistretti, P.J. Brain energy metabolism: Focus on astrocyte-neuronmetabolic cooperation. Cell Metab. 2011, 14, 724–738.
- Savtchouk, I.; Volterra, A. Gliotransmission: Beyond black-and-white. J. Neurosci. 2018, 38, 14–25.
- Kettenmann, H.; Kirchhoff, F.; Verkhratsky, A. Microglia: New roles for the synaptic stripper. Neuron 2013, 77, 10–18.
- BioRender Home Page. Available online: (accessed on 18 May 2021).
- DeFelice, F.G.; Munoz, D.P. Opportunities and challenges in developing relevant animal models for Alzheimer’s disease. Ageing Res. Rev. 2016, 26, 112–114.
- Khandaker, G.M.; Cousins, L.; Deakin, J.; Lennox, B.R.; Yolken, R.; Jones, P.B. Inflammation and immunity in schizophrenia: Implications for pathophysiology and treatment. Lancet Psychiatry 2015, 2, 258–270.
- Brown, J.A.; Codreanu, S.G.; Shi, M.; Sherrod, S.D.; Markov, D.A.; Neely, M.D.; Britt, C.M.; Hoilett, O.S.; Reiserer, R.S.; Samson, P.C. Metabolic consequences of inflammatory disruption of the blood-brain barrier in an organ-on-chip model of the human neurovascular unit. J. Neuroinflamm. 2016, 13, 1–17.
- Herland, A.; van derMeer, A.D.; FitzGerald, E.A.; Park, T.-E.; Sleeboom, J.J.; Ingber, D.E. Distinct contributions of astrocytes and pericytes to neuroinflammation identified in a 3D human blood-brain barrier on a chip. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150360.
- Wang, J.D.; Khafagy, E.-S.; Khanafer, K.; Takayama, S.; ElSayed, M.E. Organization of endothelialcells, pericytes, and astrocytes into a 3D microfluidic in vitro model of the blood–brain barrier. Mol. Pharm. 2016, 13, 895–906.
- Griep, L.M.; Wolbers, F.; de Wagenaar, B.; ter Braak, P.M.; Weksler, B.; Romero, I.A.; Couraud, P.O.; Vermes, I.; van der Meer, A.D.; van den Berg, A. BBB on chip: Microfluidic platform to mechanically and biochemically modulate blood-brain barrier function. Biomed. Microdevices 2013, 15, 145–150.
- Wevers, N.R.; Kasi, D.G.; Gray, T.; Wilschut, K.J.; Smith, B.; VanVught, R.; Shimizu, F.; Sano, Y.; Kanda, T.; Marsh, G. A perfused human blood–brain barrier on-a-chip for high-throughput assessment of barrier function and antibody transport. Fluids Barriers CNS 2018, 15, 1–12.
- Xu, H.; Li, Z.; Yu, Y.; Sizdahkhani, S.; Ho, W.S.; Yin, F.; Wang, L.; Zhu, G.; Zhang, M.; Jiang, L. A dynamic in vivo-like organotypic blood-brain barrier model to probe metastatic brain tumors. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 1–12.
- Booth, R.; Kim, H. Characterization of a microfluidic in vitro model of the blood-brain barrier (μBBB). Lab Chip 2012, 12, 1784–1792.
- Motallebnejad, P.; Thomas, A.; Swisher, S.L.; Azarin, S.M. An isogenic hiPSC-derived BBB-on-a-chip. Biomicrofluidics 2019, 13, 064119.
- Wang, Y.I.; Abaci, H.E.; Shuler, M.L. Microfluidicblood–brain barrier model provides in vivo-like barrier properties for drug permeability screening. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 184–194.
- Jeong, S.; Kim, S.; Buonocore, J.; Park, J.; Welsh, C.J.; Li, J.; Han, A. A three-dimensional arrayed microfluidic blood–brain barrier model with integrated electrical sensor array. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2017, 65, 431–439.
- Sellgren, K.L.; Hawkins, B.T.; Grego, S. An optically transparent membrane supports shear stress studies in a three-dimensional microfluidic neurovascular unit model. Biomicrofluidics 2015, 9, 061102.
- Falanga, A.P.; Pitingolo, G.; Celentano, M.; Cosentino, A.; Melone, P.; Vecchione, R.; Guarnieri, D.; Netti, P.A. Shuttle-mediated nanoparticle transport across an in vitro brain endothelium under flow conditions. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2017, 114, 1087–1095.
- Moya, M.L.; Triplett, M.; Simon, M.; Alvarado, J.; Booth, R.; Osburn, J.; Soscia, D.; Qian, F.; Fischer, N.O.; Kulp, K. A reconfigurable in vitro model for studying the blood–brain barrier. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2020, 48, 780–793.
- Ahn, S.I.; Sei, Y.J.; Park, H.-J.; Kim, J.; Ryu, Y.; Choi, J.J.; Sung, H.-J.; MacDonald, T.J.; Levey, A.I.; Kim, Y. Microengineered human blood–brain barrier platform for understanding nanoparticle transport mechanisms. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–12.
- Lee, S.; Chung, M.; Lee, S.R.; Jeon, N.L. 3D brain angiogenesis model to reconstitute functional human blood–brain barrier in vitro. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 2020, 117, 748–762.
- Nguyen, P.Q.H.; Duong, D.D.; Kwun, J.D.; Lee, N.Y. Hybrid elastomer–plastic microfluidic device as a convenient model for mimicking the blood–brain barrier in vitro. Biomed. Microdevices 2019, 21, 1–11.
- Vatine, G.D.; Barrile, R.; Workman, M.J.; Sances, S.; Barriga, B.K.; Rahnama, M.; Barthakur, S.; Kasendra, M.; Lucchesi, C.; Kerns, J. Human iPSC-derived blood-brain barrier chips enable disease modeling and personalized medicine applications. Cell Stem Cell 2019, 24, 995–1005.e1006.
- Kilic, O.; Pamies, D.; Lavell, E.; Schiapparelli, P.; Feng, Y.; Hartung, T.; Bal-Price, A.; Hogberg, H.T.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Guerrero-Cazares, H. Brain-on-a-chip model enables analysis of human neuronal differentiation and chemotaxis. Lab Chip 2016, 16, 4152–4162.
- Prabhakarpandian, B.; Shen, M.-C.; Nichols, J.B.; Mills, I.R.; Sidoryk-Wegrzynowicz, M.; Aschner, M.; Pant, K. SyM-BBB: A microfluidic blood brain barrier model. Lab Chip 2013, 13, 1093–1101.
- Deosarkar, S.P.; Prabhakarpandian, B.; Wang, B.; Sheffield, J.B.; Krynska, B.; Kiani, M.F. A novel dynamic neonatal blood-brain barrier on a chip. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0142725.
- Stoica, R.; Rusu, C.M.; Staicu, C.E.; Burlacu, A.E.; Radu, M.; Radu, B.M. Ca2+ homeostasis in brain microvascular endothelial cells. Int. Rev. Cell Mol. Biol. 2021; 362, part A, in press.
- Alcendor, D.J.; Block, F.E., III; Cliffel, D.E.; Daniels, J.S.; Ellacott, K.L.; Goodwin, C.R.; Hofmeister, L.H.; Li, D.; Markov, D.A.; May, J.C. Neurovascular unit on a chip: Implications for translational applications. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2013, 4, 1–5.
- Huh, D.; Torisawa, Y.-S.; Hamilton, G.A.; Kim, H.J.; Ingber, D.E. Microengineered physiological biomimicry: Organs-on-chips. Lab Chip 2012, 12, 2156–2164.
- Gumbleton, M.; Audus, K.L. Progress and limitations in the use of in vitro cell cultures to serve as a permeability screen for the blood-brain barrier. J. Pharm. Sci. 2001, 90, 1681–1698.
