Inflammation is a crucial and complex process that reestablishes the physiological state after a noxious stimulus. In pathological conditions the inflammatory state may persist, leading to chronic inflammation and causing tissue damage. Sesquiterpene lactones (SLs) are composed of a large and diverse group of highly bioactive plant secondary metabolites, characterized by a 15-carbon backbone structure. In recent years, the interest in SLs has risen due to their vast array of biological activities beneficial for human health. The anti-inflammatory potential of these compounds results from their ability to target and inhibit various key pro-inflammatory molecules enrolled in diverse inflammatory pathways, and prevent or reduce the inflammatory damage on tissues. Research on the anti-inflammatory mechanisms of SLs has thrived over the last years, and numerous compounds from diverse plants have been studied, using in silico, in vitro, and in vivo assays. Besides their anti-inflammatory potential, their cytotoxicity, structure–activity relationships, and pharmacokinetics have been investigated.
- anti-inflammatory
- bioactivity
- sesquiterpene lactone-rich natural extracts
- germacranolides
- guaianolides
- eudesmanolides
- heliangolides
- pseudoguainolides
- inflammatory pathway
- NF-κB
- pro-inflammatory mediators
Note: The following contents are extract from your paper. The entry will be online only after author check and submit it.
1. Sesquiterpene Lactones
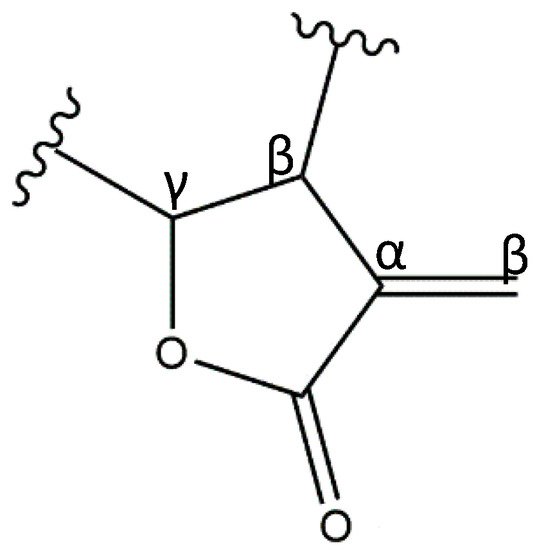
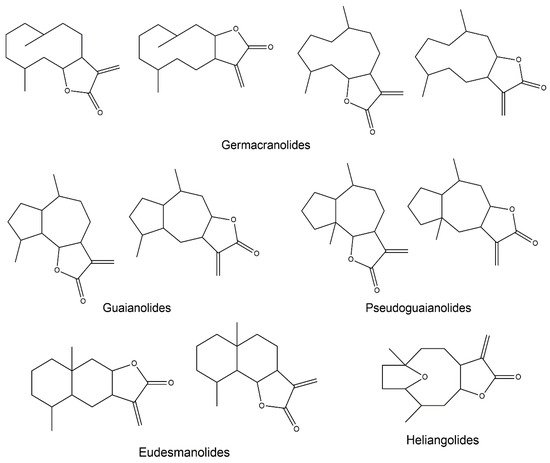
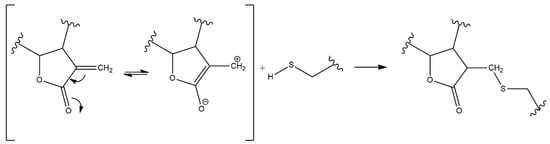
2. Anti-Inflammatory Potential of Sesquiterpene Lactones
2.1. General Notes on Inflammation
2.2. SL-Containing Extracts
| Source | Main SLs | Model | Extract Concentration Range | Inflammatory Pathways | Consequences | References | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cichorium intybus | L. | Dihydrolactucin, lactucin, deoxylactucin, jacquinelin and dihydrolactucopicrin | In vitro | RAW 264.7 murine macrophages + LPS | IC | 50 | (μg/mL): 117 for COX-2; 39 for iNOS; 48 for TNF-α; 22 for IL-1β; 21 for NO | - | ↓ COX-2, iNOS, TNF-α, IL-1β, NO | [17] | |||
| In vivo | Paw edema model: Wistar rats + carrageenan (subcutaneous) | 50–100 mg/kg (oral administration) | - | ↓ paw volume (edema) | |||||||||
| Arthritis model: Wistar rats + collagen (intravenous) | 200 mg/kg (oral administration) | - | |||||||||||
| Artemisia leucodes | L. | Leukomisin and austricin | In vitro | RAW264.7 murine macrophages + LPS | 2–100 μg/mL | - | ↓ COX-2, iNOS, IL-1β, NO | [18] | |||||
| COX-1 and -2 enzymatic assay | 45–225 μg/mL | ↓ COX-2 | |||||||||||
| In vivo | Paw edema model: Wistar rats + carrageenan (subcutaneous) | 50–200 mg/kg (oral administration) | ↓ paw edema | ||||||||||
| Chronic inflammation model: Wistar rats + cotton implant granuloma test | 50 mg/kg (oral administration) | ↓ granuloma and inflammatory cell infiltrate | |||||||||||
| Artemisia khorassanica | L. | Unspecified | In vitro | J774A.1 murine macrophages + LPS | 10–100 μg/mL | ↓ NF-κB | ↓ COX-2, PGE | 2 | , iNOS, NO, TNF-α and IL-1β | [19] | |||
| Artemisia | sps ( | A. kopetdaghensis, A. santolina, A. Sieberi, A. Fragrans, A. Absinthium, A. ciniformis | ) | Saturated, unsaturated and unusual SLs | In vitro | J774A.1 murine macrophages + LPS | 10–100 μg/mL | - | ↓ COX-2, PGE | 2 | , iNOS and NO | [20] | |
| Eupatorium perfoliatum | L. | Diguaiaperfolin (dimeric guaianolide) and Eupafolin (flavonoid) | In vitro | RAW264.7 murine macrophages + LPS | 1–100 μg/mL | - | ↓ NO, CSF-3, IL-6, IL-1α, IL-1β, TNF, Chemokine (C-C motif) ligand (CCL)-2, CCL22 and CXCL10 | [21] | |||||
| Xanthium spinosum | L. | Ziniolide | In vitro | Rat polymorphonuclear leukocytes (PMNLs) + ionophore A23187 and Ca | 2+ | 0–100 μg/mL | ↓ NF-κB and arachidonic acid | ↓ 5-LOX | [22] | ||||
| Human platelets + ionophore A23187 | 25–200 μg/mL | ↓ COX-1 and 12-LOX; ↑ 15(S)-HETE | |||||||||||
| HeLa cells + Phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) | 12.5–100 μg/mL | ↓ NF-κB activation | |||||||||||
| Arnica montana | L. | Helenalin and dihydrohelenalin ester derivatives | In vitro | Jurkat T cells + TNF-α or PMA | 0.5–10 μL/mL | ↓ NF-κB and NFAT | ↓ NF-κB and NFAT DNA-binding | [23] | |||||
| Human PBMCs from healthy donors + LPS | 0.001–10 μL/mL | ↓ TNF-α and IL-1β | |||||||||||
| Centaurea | L. species ( | C. aphrodisea, C. athoa, C. hyalolepis, C. iberica, C. polyclada | ) | SL fraction (athoin, 14-O-acetylathoin and methyl-14-O-acetylathoin-12-oate in C. | athoa | ) | In vitro | SW1353 human chondrosarcoma cells + PMA | 0–100 μg/mL | ↓ NF-κB | ↓ NF-κB activity | [24][25] | [24,25] |
| RAW264.7 murine macrophages + LPS | ↓ NO | ||||||||||||
| In vivo | Paw edema model: Wistar rats + carrageenan (subcutaneous) | 6.75–50 mg/kg (oral administration) | ↓ edema | ||||||||||
| Inula helenium | L | Alantolactone and isoalantolactone | In vitro | bEnd.3 mouse endothelial cells + TNF-α | 0.6–2.4 μg/mL | ↓ NF-κB and MAPKs | ↓NF-κB inhibitor (IκB)-α, NF-κB p65, p38 and c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) phosphorylation | [26] | |||||
| RAW264.7 murine macrophages + LPS | ↓ IL-1, IL-6 and iNOS | ||||||||||||
| Primary synovial fibroblasts from rheumatoid arthritis patients + TNF-α | ↓ IL-1, MCP-1 and MMP-3 | ||||||||||||
| In vivo | Adjuvant-induced mice arthritis model | 12.5–50 mg/kg (oral administration) | ↓ paw swelling | ||||||||||
| Collagen-induced mice arthritis model | |||||||||||||
| Arctium lappa | L. | Onopordopicrin | In vivo | Colitis model: Wistar rats + Trinitrobenzene Sulfonic Acid (TNBS) (enteral instillation) | 25–50 mg/kg (oral administration) | - | ↓ TNF-α and COX-2; ↓ histological damage; ↓ mucin layer loss; ↓ neutrophil infiltration | [27] | |||||
| Vernonia scorpioides | L. | Diacethylpiptocarphol and related hirsutinolides |
In vivo | Acute ear edema model: Swiss mice + 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol acetate (TPA) (topical) | 0.003–1 mg (topical) | ↓ NF-κB | ↓ neutrophil infiltration, edema and epidermal proliferation | [28] | [29] | ||||
| Chronic ear edema model: Swiss mice + arachidonic acid (topical) or croton oil (topical) | 1 mg (topical) | ||||||||||||
2.3. Germacranolides
2.3.1. Parthenolide
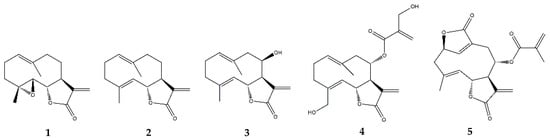
2.3.2. Costunolide
2.3.3. Other Germacranolides
2.4. Guaianolides
2.5. Eudesmanolides
2.6. Heliangolides
2.7. Pseudoguaianolides
2.8. Other SL Subclasses
| SL Subclass |
Compound Name (ID Number) |
Model | Compound Concentration Ranges Tested | Inflammatory Pathways | Consequences | References | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Germacranolides | Parthenolide (1) |
In vitro | Rat aortic smooth muscle cells + LPS/IFN-γ | 3–30 μM | ↓ NF-κB | ↓ iNOS and NO release | [31] | |||
| In vitro | BV2 mouse microglia + LPS | 5 μM | ↓ NF-κB | ↓ IL-6 and TNF-α | [32] | |||||
| In vitro | Rat primary neural-glial cells + LPS | 403 μM | ↓ NF-κB, NF-IL6, Nrf-1 and PGC1α | ↓ IL-6 and TNF-α | [33] | |||||
| In vivo | Wistar rats + LPS (intraperitoneal injection) | 1 mg/kg (intraperitoneal injection) | ↓ IL-6 and TNF-α in plasma; ↓ COX-2, NF-IL6, SOCS3, IκBα and Tribbles pseudokinase 1 (Trib1) in hypothalamus; ↓ fever | |||||||
| In vitro | Jurkat T cells and primary peripheral human T cells + PMA/ionomycin or anti-CD3/CD28 | 1.25–5 μM | ↓ NF-κB and AP-1 | ↓ IL-4, IL-2 and IFN-γ | [34] | |||||
| Primary peripheral human T cells + PMA/ionomycin or anti-CD3/CD28 | ||||||||||
| In vitro | Blood from healthy donors + PMA/ionomycin | 10–500 μM | - | ↓ IL-2; ↓ T-lymphocyte activation | [35] | |||||
| In vitro | Human THP-1 monocytes + LPS | 0.75–12 μM | ↓ NF-κB and MAPKs | ↓ IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β, IL-8, IL-18 and NO; ↓ iNOS, TLR4 and TRAF6 | [36] | |||||
| Human primary monocytes + LPS | ||||||||||
| In vivo | Hindpaw edema model: Holtzman rats + carrageenan (subcutaneous injection) | 5–20 mg/kg (intraperitoneal injection) | - | ↓ Hyperalgesia and edema | [37] | |||||
| In vitro | HepG2 human hepatocytes + IL-6, oncostatin M or leukemia inhibitory factor | 5 μM | ↓ STAT3 and JAKs | ↓ STAT3 phosphorylation, dimerization and activity | [39] | |||||
| Costunolide (2) |
In vitro | Human THP-1 monocytes + IL-6 | 6–25 μM | ↓ IL-6/STAT3 and JAKs | ↓ MCP-1, CXCL10, ICAM-1; ↓ STAT3 phosphorylation and DNA-binding activity; ↓ Intracellular GSH | [40] | ||||
| In vitro | RAW264.7 murine macrophages + LPS | 0.1–1 μM | ↑ Nrf-2; ↓ NF-κB | ↑ HO-1; ↓ IL-6 and TNF-α | [38] | |||||
| In vitro | Human keratinocytes from healthy donors + IL-22, IFN-γ or TNF-α | 12.5 μM | ↓ STAT3 and STAT1 | ↓ Intracellular GSH; ↓ CCL2, CXCL10, ICAM-1 and SOCS3; ↑ Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and Erk1/2 | [41] | |||||
| In vitro | RAW264.7 murine macrophages + LPS | 0.1–3 μM | ↓ AP-1 and MAPKs | ↓ IL-1β | [42] | |||||
| In vitro | Primary rat chondrocytes + IL-1β | 2–6 μM | ↓ NF-κB and Wnt/β-catenin; ↑ SOX-9 | ↓ MMP-3, MMP-9, MMP-13, iNOS, COX-2 and IL-6; ↑ collagen II | [43] | |||||
| In vivo | Sprague-Dawley rats (surgically induced osteoarthritis model) | 6 μM (intra-articular injection) | attenuation of cartilage degeneration | |||||||
| In vivo | Angiogenesis model: Swiss albino mice + polyester-polyurethane sponge implants | 5–20 mg/kg (cannula) | - | ↓ Angiogenesis, macrophage and neutrophil accumulation, and collagen deposition; ↓ IL-1β, IL-6, IL-17, TNF-α, TGF-β; ↑ IL-10 | [44] | |||||
| Eupatolide (3) | In vitro | RAW264.7 murine macrophages + LPS | 0.1–10 μM | ↓ NF-κB, AP-1, MAPKs, Akt | ↓ COX-2, PGE | 2 | , iNOS, NO and TRAF6 | [45] | ||
| Human embryonic kidney (HEK)-293 cells + LPS | ↑ proteossomal degradation of TRAF6 | |||||||||
| Onopordopicrin (4) | In vitro | NIH-3T3 cell line + TNF-α | IC | 50 | (μM): 8.6 for NF-κB; 15.3 for STAT3; EC | 50 | (μM): 2.2 for Nrf-2 | ↓ NF-κB and STAT3; ↑ Nrf-2 | ↓ NF-κB activity | [46] |
| HeLa cell line + IFN-γ | ↓ STAT3 activity | |||||||||
| HaCaT keratinocytes | ↑ Nrf-2 activity | |||||||||
| Deoxyelephantopin (5) | In vitro | RAW264.7 murine macrophages + LPS | 2.5–10 μM | - | ↓ high mobility group box (HMGB) 1, pyruvate kinase M2 (PKM2), glucose transporter 1 (GLUT1), lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA) and phosphoinositide-dependent kinase 1 (PDK1) and IL-1β | [47] | ||||
| In vivo | C57BL/6J mice + LPS (intraperitoneal injection) | 10 mg/kg (intraperitoneal injection) | - | ↓ endotoxic shock and sepsis | ||||||
| Guaianolides | Dehydrocostuslactone (6) | In vitro | THP-1 human cells + IL-6 | 6–25 μM | ↓ IL-6/STAT3 and JAKs | ↓ MCP-1, CXCL10, ICAM-1; ↓ STAT3 phosphorylation and DNA-binding activity; ↓ Intracellular GSH | [40] | |||
| In vitro | Human keratinocytes from healthy donors + IL-22, IFN-γ or TNF-α | 12.5 μM | ↓ STAT3 and STAT1 | ↓ Intracellular GSH; ↓ CCL2, CXCL10, ICAM-1 and SOCS3; ↑ EGFR and Erk1/2 | [41] | |||||
| In vivo | Colitis model: BALB/c mice + Dextran sulfate sodium (DSS) (oral administration) | 10–20 mg/kg | ↓ IL-6/STAT3 | ↓ TNF-α, IL-1β, MPO, SOD, IL-6, IL-17, IL-23, COX-2, iNOS | [50] | |||||
| In vitro | RAW 264.7 macrophages + LPS | 10–20 μM | ↓ MyD88/TRIF; ↓ NF-κB; ↓ IRF-3 | ↓ COX-2, INF-β, IP-10 | [51] | |||||
| Micheliolide (7) | In vitro | BV2 microglia cells + LPS | 1–10 μM | ↓ NF-κB; ↓ PI3K/Akt ↓ MAPKs |
↓ TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, COX-2, iNOS | [52] | ||||
| In vitro | RAW 264.7 macrophages + LPS | 1–10 μM | ↓ NF-κB | ↓ IL-6, TNF-α, IL-1β | [53] | |||||
| In vitro | RAW264.7 macrophages + LPS | 0–10 μM | ↓ NF-κB; ↓ PI3K/Akt | ↓ IL-6, TNF-α, MCP-1, INF-β and IL-1β | [54] | |||||
| Human dendritic cells and monocytes + LPS | ↓ IL-6, TNF-α, MCP-1, INF-β | |||||||||
| In vivo | Arthritis model: DBA/1 mice + collagen (intradermal injection) | 30 mg/kg (intraperitoneal injection) | - | ↓ TIMP-1, M-CSF, ICAM-1, INF-γ | [55] | |||||
| Cynaropicrin (8) | In vitro | RAW 264.7 macrophages + LPS | 0–35 μM | - | ↓ TNF-α and NO | [56] | ||||
| Human macrophages U937 + LPS | ||||||||||
| Primary splenocytes from mice + concanavalin A, phytohemagglutinin and LPS | ↓ lymphocyte proliferation | |||||||||
| Arglabin (9) | In vitro | Peritoneal macrophages from ApoE | 2 | .Ki mice + LPS and cholesterol crystals | 50 nM | ↓ NF-κB; ↓ NLRP3 |
↓ IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-18 | [57] | ||
| 11β,13-dihydrolactucin (10) | In vitro | Yeast | S. cerevisiae | + MnCl | 2 | 0.36–18 μM | ↓ Calcineurin-Crz1 (NFAT) | ↓ NFAT nuclear translocation and transcriptional activity | [58] | |
| 8-deoxylactucin (11) | In vitro | Human colon-cancer cells HT29 + TNF-α | 115 μM | ↓ NF-κB | ↓ PGE | 2 | [59] | |||
| Eudesmanolides | Alantolactone (12) | In vitro | bEnd.3 mouse endothelial cells + TNF-α | 2.6–10.3 μM | ↓ NF-κB and MAPKs | ↓ IκBα, NF-κB p65, p38 and JNK phosphorylation | [26] | |||
| RAW264.7 murine macrophages + LPS; | ↓ IL-1, IL-6 and iNOS | |||||||||
| Primary synovial fibroblasts from rheumatoid arthritis patients + TNF-α | ↓ IL-1, MCP-1 and MMP-3 | |||||||||
| In vitro | RAW 264.7 macrophages + LPS | 1.25–10 μM | ↓ NF-κB; ↓ MyD88 |
↓ iNOS, COX-2, TNF-α | [60] | |||||
| In vivo | Colitis model: C57BL/6 mice + DSS (oral administration) | 50 mg/kg (oral administration) | ↓ NF-κB; ↑ hPXR |
↓ iNOS, ICAM-1, COX-2, TNF-α, IFN-γ, IL-6 | [61] | |||||
| Isoalantolactone (13) | In vitro | bEnd.3 mouse endothelial cells + TNF-α | 2.6–10.3 μM | ↓ NF-κB and MAPKs | ↓ IκBα, NF-κB p65, p38 and JNK phosphorylation | [26] | ||||
| RAW264.7 murine macrophages + LPS | ↓ IL-1, IL-6 and iNOS | |||||||||
| Primary synovial fibroblasts from rheumatoid arthritis patients + TNF-α | ↓ IL-1, MCP-1 and MMP-3 | |||||||||
| In vitro | 293T cells + TNF-α | 2.5–10 μM | ↓ NF-κB and MAPKs | ↓ UbcH5 | [62] | |||||
| In vivo | Hepatitis model: BALB/c mice + TNF-α and D-galactosamine (D-GalN) (intraperitoneal injection) | 10 mg/kg (intraperitoneal injection) | ↓ serum alanine aminotransferase (ALT); ↓ hepatocyte damage; ↓ IL-6, MCP-1, ICAM-1 and VCAM-1 | |||||||
| JEUD-38 (14) | In vitro | RAW 264.7 macrophages + LPS | 2.5–10 μM | ↓ NF-κB and MAPKs | ↓ iNOS | [63] | ||||
| 7-hydroxyfrullanolide (16) | In vitro | THP-1 cell + LPS | 0.3–100 μM | ↓ NF-κB | ↓ NF-κB activation and nuclear translocation | [64] | ||||
| HUVECs + LPS | ↓ ICAM-1, VCAM-1, E-selectin ↓ Monocyte adhesion |
|||||||||
| PBMCs + LPS | ↓ NF-κB-related gene expression | |||||||||
| In vitro | PBMCs + LPS | 0.3–100 μM | - | ↓ IL-6 and TNF-α | [65] | |||||
| Primary human synovial tissue cells | ||||||||||
| In vivo | Colitis model: BALB/c mice + DSS (oral administration) | 75 mg/kg (oral administration) | - | ↓ TNF-α and IL-6; ↓ Colonic edema; ↓ Shortening of the colon; ↓ hemoglobin and rectal bleeding; ↓ neutrophil infiltration |
||||||
| Paw edema model: Wistar rats + carrageenan (subcutaneous injection) | 100 mg/kg | - | ↓ paw edema | |||||||
| Arthritis model: DBA/1J mice + collagen (intradermal injection) | 25–75 mg/kg (oral administration) | - | ↓ joint deformities and bone destruction | |||||||
| Santamarin (17) | In vitro | RAW264.7 macrophages + LPS | 5–40 μM | ↓ NF-κB; ↑ Nfr2 |
↓ COX-2 and iNOS; ↓ TNF-α, IL-1β ↑ HO-1 |
[66] | ||||
| Murine peritoneal macrophages + LPS | ↓ COX-2 and iNOS; ↓ TNF-α, IL-1β | |||||||||
| Heliangolides | Lychnopholide (18) | In vitro | J774A.1 macrophages + INF-γ and LPS | 0.0125–0.2 μM | - | ↑ IL-10; ↓ NO |
[67] | |||
| Eremantholide (19) | J774A.1 macrophages + INF-γ and LPS | 0.625–10 μM | - | ↑ IL-10; ↓ TNF-α |
||||||
| Budlein A (20) | In vitro | RAW264.7 + TNF-α or IL-1β | 2.7 × 10 | 4 | –26.7 μM | ↓ NF-κB | ↓ NF-κB activity | [68] | ||
| In vivo | Arthritis model: C57BL/6 mice + methylated bovine serum albumin (intra-articular injection) | 1–10 mg/kg (oral administration) | ↓ edema; ↓ neutrophil and leukocyte infiltration; ↓ proteoglycan degradation; ↓ IL-33, TNF-α, IL-1β, COX-2 | |||||||
| In vivo | Paw edema model: Swiss mice + carrageenan (subcutaneous injection) | 1–10 mg/kg | - | ↓ TNF-α, IL-1β; ↓ edema, and neutrophil infiltration; ↓ mechanical hypernocecipetion | [69] | |||||
| In vivo | Gout arthritis model: Swiss mice + monosodium urate crystals (intra-articular injection) | 1–10 mg/kg (oral administration) | ↓ NF-κB; ↓ NLRP3 inflammasome |
↓ TNF-α and IL-1β; ↓ neutrophil recruitment; ↓ edema and mechanical hypersensitivity |
[70] | |||||
| In vitro | Bone marrow derived macrophages (BMDMs) + LPS and monosodium urate crystals | 2.7–26.7 mM | ↓ TNF-α and IL-1β | |||||||
| Diacethylpiptocarphol (21) | In vivo | Colitis model: BALB/c mice + DSS (oral administration) | 5 mg/kg (oral administration) | - | ↓ TNF-α; ↑ TGF-β; ↓ immune cell infiltration and tissue damage |
[71] | ||||
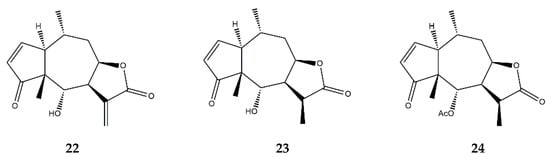
| Pseudoguaianolides | Helenalin (22) | In vitro | Jurkat T cells + TNF-α | 5–200 μM | ↓ NF-κB | ↓ NF-κB DNA-binding | [72] | |||
| In vitro | Jurkat T cells + TNF-α | 10 μM | ↓ NF-κB | ↓ NF-κB DNA-binding and nuclear translocation | [73] | |||||
| In vitro | Jurkat CD4 | + | T-cells | 0.5–5 μM | ↓ NFAT ↓ NF-κB |
↓ IL-2 ↓ proliferation of CD4 | + | cells | [23][74] | [23,74] |
| In vitro | THP-1 cells + LPS | 0.52–1.08 μM | ↓ NF-κB | ↓ IL-1α, IL-19, MCP-3, GM-CSF | [75] | |||||
| In vitro | A2780 human ovarian cancer cell line | 0.5–2 μM | ↓ NF-κB | ↓ NF-κB p65 expression | [76] | |||||
| 11α,13-dihydrohelenalin (23) | In vitro | PBMCs + LPS | 2–20 μM | ↓ NF-κB and NFAT | ↓ IL-2, IL-6, GM-CSF, TNF-α, INF-γ, iNOS | [77] | ||||
| Jurkat T-cells + LPS | ↓ NF-κB and NFAT levels | |||||||||
| 11α,13-dihydrohelenalin–acetate (24) | In vitro | PBMCs + LPS | 2–20 μM | ↓ NF-κB and NFAT | ↓ IL-2, IL-6, GM-CSF, TNF-α, INF-γ, iNOS | |||||
| Jurkat T-cells + LPS | ↓ NF-κB and NFAT levels | |||||||||
| In vitro | Human granulocytes + Ionophore A23187 | 1–600 μM | ↓ Arachidonic Acid | ↓ Leukotriene C | 4 | synthase; ↓ 5-lipooxygenase |
[78] | |||
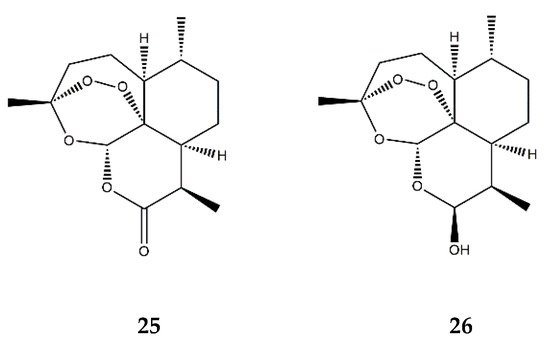
| Endoperoxide SL | Artemisinin (25) | In vitro | HUVECs + TNF-α | 50–200 μM | ↓ NF-κB; ↓ MAPKs | ↓ ICAM-1, VCAM-1; ↓ adhesion of monocytes | [80] | |||
| Dihydroartemisinin (26) | In vitro | RAW 264.7 macrophages + PMA | 5–25 μM | ↓ NF-κB, AP-1 and MAPKs | ↓ COX-2 | [81] | ||||
